Matlab Abdelkhalak El Hami
Visit to download the full and correct content document: https://ebookmass.com/product/optimizations-and-programming-linear-non-linear-dyn amic-stochastic-and-applications-with-matlab-abdelkhalak-el-hami/

More products digital (pdf, epub, mobi) instant download maybe you interests ...

Reliability of High-Power Mechatronic Systems 2: Aerospace and Automotive Applications Issues,Testing and Analysis
Abdelkhalak El Hami (Editor)
https://ebookmass.com/product/reliability-of-high-powermechatronic-systems-2-aerospace-and-automotive-applicationsissuestesting-and-analysis-abdelkhalak-el-hami-editor/

Linear Algebra and Its Applications, Global Edition Lay
https://ebookmass.com/product/linear-algebra-and-itsapplications-global-edition-lay/

Reliability Of High Power Mechatronics Systems 1
Abdelkhalak El Hami (Editor)
https://ebookmass.com/product/reliability-of-high-powermechatronics-systems-1-abdelkhalak-el-hami-editor/

Linear Algebra with Applications, Global Edition 9th Edition, (Ebook PDF)
https://ebookmass.com/product/linear-algebra-with-applicationsglobal-edition-9th-edition-ebook-pdf/

Linear Algebra and Its Applications 5th Edition, (Ebook PDF)
https://ebookmass.com/product/linear-algebra-and-itsapplications-5th-edition-ebook-pdf/




Linear Algebra and Its Applications 4th Edition, (Ebook PDF)
https://ebookmass.com/product/linear-algebra-and-itsapplications-4th-edition-ebook-pdf/
Embedded Mechatronic Systems, Volume 2: Analysis of Failures, Modeling, Simulation and Optimization 2nd Edition
Abdelkhalak El Hami
https://ebookmass.com/product/embedded-mechatronic-systemsvolume-2-analysis-of-failures-modeling-simulation-andoptimization-2nd-edition-abdelkhalak-el-hami/
Embedded Mechatronic Systems, Volume 1: Analysis of Failures, Predictive Reliability 2nd Edition
Abdelkhalak El Hami
https://ebookmass.com/product/embedded-mechatronic-systemsvolume-1-analysis-of-failures-predictive-reliability-2nd-editionabdelkhalak-el-hami/
Dynamic System Modelling and Analysis with MATLAB and Python 1st Edition Jongrae Kim
https://ebookmass.com/product/dynamic-system-modelling-andanalysis-with-matlab-and-python-1st-edition-jongrae-kim/

Optimizations and Programming
Linear, Nonlinear, Dynamic, Stochastic and Applications with Matlab
First published 2021 in Great Britain and the United States by ISTE Ltd and John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Apart from any fair dealing for the purposes of research or private study, or criticism or review, as permitted under the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988, this publication may only be reproduced, stored or transmitted, in any form or by any means, with the prior permission in writing of the publishers, or in the case of reprographic reproduction in accordance with the terms and licenses issued by the CLA. Enquiries concerning reproduction outside these terms should be sent to the publishers at the undermentioned address:
ISTE Ltd
27-37 St George’s Road
John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
111 River Street London SW19 4EU Hoboken, NJ 07030
UK USA
www.iste.co.uk
www.wiley.com
© ISTE Ltd 2021
The rights of Abdelkhalak El Hami and Bouchaib Radi to be identified as the authors of this work have been asserted by them in accordance with the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988.
Library of Congress Control Number: 2020948478
British Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data
A CIP record for this book is available from the British Library
ISBN 978-1-84821-953-3
Chapter1.LinearProgramming ........................3
1.1.Introduction.................................3
1.2.Definitions..................................3
1.3.Geometryofthelinearprogram......................5
1.3.1.Polyhedra.................................5
1.3.2.Extremepointsandvertices......................6
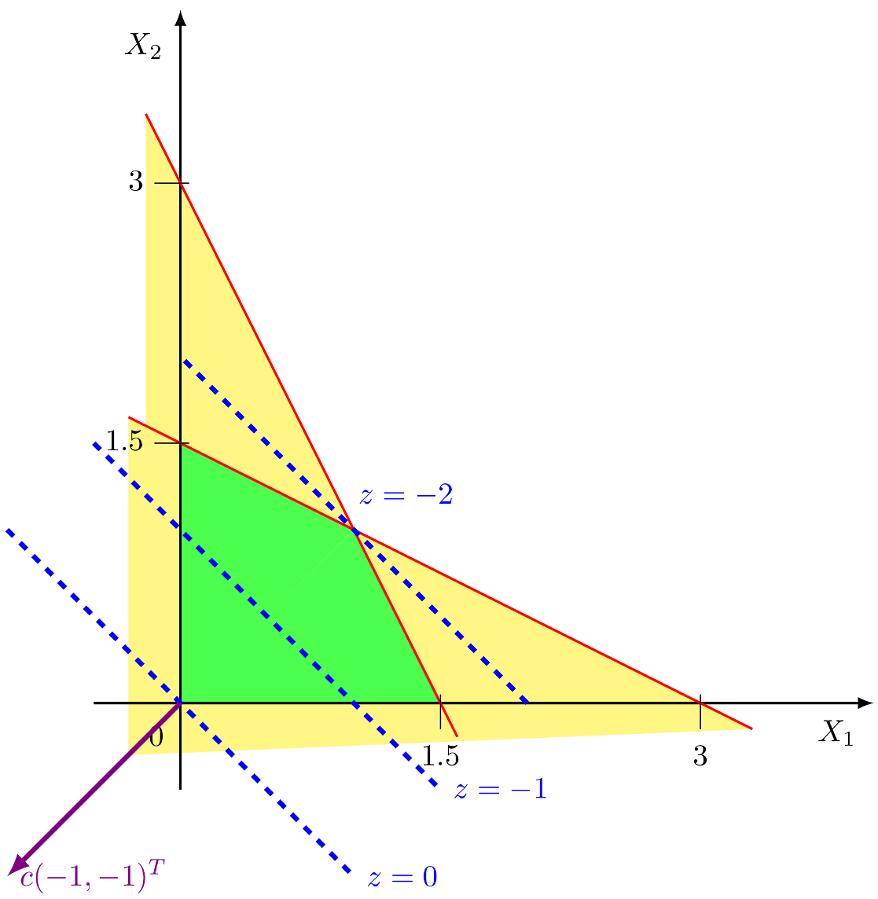
1.4.Graphicalsolvingofalinearprogram...................6
1.5.Simplexalgorithm..............................9
1.5.1.Basicsolutionsandbasicfeasiblesolutions..............9
1.5.2.Simplextableau.............................10
1.5.3.Changeoffeasiblebasis........................11
1.5.4.Existenceanduniquenessofanoptimalsolution...........14
1.6.Initializationofthesimplexalgorithm...................15
1.6.1.Big M method..............................15
1.6.2.AuxiliaryprogramorPhaseI......................17
1.6.3.Degeneracyandcycling.........................20
1.6.4.Geometricstructureofrealizablesolutions..............21
1.7.Interior-pointalgorithm...........................22
1.8.Duality....................................23
1.8.1.Dualitytheorem.............................25 1.9.Relaxation..................................27
1.9.1.Lagrangianrelaxation..........................27
1.10.Postoptimalanalysis............................29
1.10.1.Effectofmodifying
1.10.2.Effectofmodifying
1.11.Applicationtoaninventoryproblem...................34
1.11.1.Optimalsolution............................34
1.11.2.Sensitivitytovariationinstock....................35
1.11.3.Dualproblemofthecompetitor...................36 1.12.UsingMatlab................................36
Chapter2.IntegerProgramming
2.1.Introduction.................................41
2.2.Solvingmethods...............................41
2.2.1.Branch-and-boundmethod.......................42
2.2.2.Thebranch-and-cutmethod......................44
2.3.Binaryprogramming............................49
2.3.1.Knapsackproblem............................49
2.3.2.Investmentproblem...........................50
2.4.Decompositionprinciple..........................57
2.4.1.Bendersdecomposition.........................58 2.5.UsingMatlab.................................62
Chapter3.DynamicProgramming
3.1.Introduction.................................65
3.3.1.Bellman’sequationandtheprincipleofoptimality.........68
3.3.2.Approachofthemethod........................70
3.3.3.AfewexamplesofDP.........................70
3.3.4.SolvinganLP..............................73
3.3.5.Shortestpathproblem..........................74
3.3.6.Knapsackproblem............................79
3.3.7.Stockmanagementproblem......................81
3.4.ContinuousDP................................83
3.4.1.Hamilton–Jacobiequation.......................84
3.4.2.Applicationtoaconsumption-savingsmodel.............84
3.5.StochasticDP................................85
3.5.1.Decision-chanceprocess........................85
3.5.2.Solvingmethod.............................86
3.5.3.Applicationtoacontractproblem...................86
3.5.4.Optimalbinarysearchtree.......................87
3.6.UsingMatlab.................................91
Chapter4.StochasticProgramming
4.1.Introduction.................................93
4.2.Presentationoftheproblem.........................94
4.3.Optimalfeedbackinanopenloop.....................94
4.4.Stochasticlinearprogramming.......................95
4.4.1.Modelswithprobabilitythresholdsontheconstraints........96
4.5.Stochasticlinearprogramswithrecourse.................96
4.5.1.L-shapedmethod............................97
4.5.2.MulticutL-shapedmethod.......................99
4.5.3.Interiorlinearizationmethod......................100
4.6.Nonlinearstochasticprogramming.....................100
4.6.1.Approachestotwo-stepproblemswithrecourse...........100
4.6.2.Regularizeddecompositionmethod..................101
4.6.3.MethodsbasedontheLagrangian...................101
4.6.4.Frank–Wolfemethodforproblemswithsimplerecourse......103
4.6.5.Approximationbysamplingaverage:MonteCarlomethod.....105
4.6.6.Stochasticgradientmethod.......................106
4.7.Stochasticdynamicprogramming.....................107
4.7.1.Markovdecisionprocess........................108
4.7.2.Scenariotree...............................109
4.8.Applicationtothereliabilityofmechanicalsystems...........111
4.8.1.Positionandmodelingofthereliabilityproblem...........113
4.9.UsingMatlab.................................121
5.1.Introduction.................................129
5.2.SymmetricTSP...............................131
5.2.1.Historicaloverview...........................132
5.2.2.Solvingmethods.............................134
5.3.Asymmetrictravelingsalesmanproblem.................140
5.3.1.VariantsoftheATSP..........................140
5.3.2.Mathematicalformulations.......................142
5.3.3.MethodsforsolvingtheATSP.....................144
5.4.Vehicleroutingproblem...........................148
5.4.1.Definition.................................148
5.4.2.Fieldsofapplication...........................149
5.4.3.ParametersoftheVRP.........................150
5.4.4.VariantsoftheVRP...........................151
5.4.5.MathematicalformulationoftheVRP.................153
5.4.6.Algorithmiccomplexity.........................155
5.5.Selectiveroutingproblem..........................156
5.5.1.ProblemssimilartotheVRP......................157
5.5.2.Mathematicalformulation.......................157
5.6.UsingMatlab.................................158
Chapter6.UnconstrainedNonlinearProgramming
6.1.Introduction.................................
6.2.Mathematicalformulation.........................
6.2.1.Existenceanduniquenessresults....................
6.3.Optimalityconditions............................
6.4.Quadraticproblems.............................
6.4.1.Gradientmethodwithoptimalstepsize................
6.4.2.Conjugategradientmethod.......................
6.5.Newton’salgorithm.............................
6.6.Methodsofdescentandlinearsearch...................
6.6.1.Presentationofmethodsofdescent..................
6.6.2.Methodofgreatestslope........................
6.6.3.Acceptablestepsize...........................
6.6.4.Linearsearch...............................
6.6.5.Newton’smethodwithlinearsearch..................
6.7.Quasi-Newtonmethods...........................
6.7.1.DFPandBFGSmethods........................
6.8.Relaxationmethod..............................
6.9.Gradientmethod...............................
6.10.Leastsquaresproblem...........................
6.10.1.Gauss–Newtonmethod........................
6.10.2.Levenberg–Marquardtalgorithm...................
6.12.Applicationtoanidentificationproblem.................
6.13.1.The fminsearch
6.13.2.The fminunc
Chapter7.ConstrainedNonlinearOptimization
7.1.Introduction.................................
7.2.Mathematicalformulation.........................
7.3.Lagrangemultipliers............................
7.4.Optimizationwithinequalityconstraints.................
7.4.1.First-orderconditionsofoptimality..................
7.4.2.Presentationofsaddlepoints......................
7.4.3.Saddlepointandoptimization.....................
7.4.4.Convexcase...............................
7.5.Constrainedminimizationalgorithms...................
7.5.1.Relaxationmethod............................
7.5.2.Projectionmethod............................202
7.5.3.Exteriorpenaltymethod........................204
7.5.4.Uzawa’salgorithm............................205
7.6.Newtonalgorithms:SQPmethod.....................206
7.6.1.Equalityconstraints...........................207
7.6.2.Inequalityconstraints..........................209
7.7.Applicationtostructureoptimization...................210
7.8.UsingMatlab.................................217
7.8.1.The fmincon
7.8.2.The fminbnd
7.8.3.Penaltymethod.............................221
Appendix2.Remindersaboutfunctionsfrom
Appendix3.OptimizationToolbox
Optimizationisthedomainofmathematicsthatstudieshowtominimize(or maximize)acertainobjective,forexample,aneconomicparameterorsometypeof energy.Thisisbothanancienttopic,withtheearliestoptimizationproblemsgoing backtoEuclid,andarelativelynewtopic,withtherecentdevelopmentofnumerical methodssuchaslinearprogramming,whichonlytrulybegantoflourishinthe secondhalfofthe20thcentury.Asanillustration,imaginetheproblemofsearching forapaththatjoinstwopointsonamapintheshortesttime.Someparametersofthe problemmightbeuncertain;forexample,wemightencounteratrafficjamonthe road.Optimizationseekstofindthebestcompromisebetweenthevariouspossible risks.
Inthepresenceofuncertainty,theoptimizer(ordecider)willoftentakeadvantage ofinformationaboutthesystemthatbecomesavailabledynamically,i.e.gradually overtime.Forexample,wewillgraduallydiscoverwhichroadsaremostsusceptible totrafficjamsovertime,aswetrythemout.Thedifficultyofanoptimizationproblem iscloselylinkedtotheamountofinformationneededtomakeanoptimaldecision. Aproblemissaidtobelargeifthisquantityofinformationistoobigforclassical solvingtechniquestobeappliedbybruteforce.
Thisbookisdividedintotwoparts:programming(Part1)andoptimization (Part2).Intheprogrammingpart,wepresentacollectionoftoolsforoperations research,includinglinearprogramming,integerprogramming,binaryprogramming, dynamicprogrammingandstochasticprogramming.Operationsresearchfirstarose intheUnitedKingdomduringtheSecondWorldWar,whenscientificmethodswere usedtostudyvariousaspectsofmilitaryoperations.Sincethen,ithasbecomeakey elementofdecision-makingprocessesinvariouscommercial,industrialand governmentalcontexts,offeringasystematicwaytoapprehendtheeverincreasing complexityofthemanagementproblemsfacedbyboththeprivateandpublicsectors.
FollowingitssuccessinmilitarymattersduringtheSecondWorldWar, operationsresearchwasappliedtooperationalproblemsintheindustryandprivate sectorformanyyears.Inthelastdecadeorso,itsapplicationshavebeenextendedto otherdomains,suchaseconomics,finance,marketingandcorporateplanning.More recently,operationsresearchhasbeenusedtomanagehealthcareandeducation systems,solveenvironmentalproblemsandinotherareasofpublicinterest.Its principalusersaremanufacturing,distributionandretailcompaniesinthemining, energy,transportationandconstructionsectors,aswellasservicecompaniessuchas banks,andvariousgovernmentbodies.Noteworthyexamplesofrecentapplications ofoperationsresearchincludelogisticalstudies,railwaysafety,packagingdesign, strategicworkforceplanning,aerialtransportation,forestryoperations,nuclearfuel optimization,productionplanning,andsoon.
Theoptimizationpartofthisbookisdividedintothreechapters:combinatorial optimization,nonlinearoptimizationwithoutconstraintsandnonlinearoptimization withconstraints.Itisentirelydedicatedtonumericaloptimizationalgorithms,their theoreticalfoundationsandconvergenceproperties,theirimplementationand application,andotherpracticalaspects.Theobjectiveistofamiliarizereaderswith thesenumericalalgorithmsinordertounderstandhowtheybehaveinpractice,how toproperlytakeadvantageof Matlab asatool,howtodesignandadequately implementsuchalgorithmsandhowtocorrectlydiagnoseanydifficultiesthatmight arise.
Eachchapterstartswithafewremindersofkeyresults,butreadersshouldnot hesitatetoconsultthereferenceslistedattheendofthebook.Thisbookisorganized accordingtoastrictlylinearapproach.Asageneralrule,theconceptsareillustrated withexamples.Eachchapterendswithanexamplein Matlab.
Acknowledgments
Wewouldliketothankeveryonewhocontributed,directlyorindirectly,tothe writingofthisbookandespecially,theengineeringandPhDstudentsofINSARouen whomwehavehadthepleasureofsupervisingoverthepastfewyears.