





































The following pages outline the content from Biology Plus which provides the answers to the State Examination Commission’s Higher Level Sample Paper 2 and Ordinary Level Sample Paper 2 for Leaving Certificate Biology (2025).

This handout breaks down each question by section, outlining exactly where the answers can be found in the textbook.






































Educational Company of Ireland

















Leaving Certificate Examination – Sample 2 Biology – Higher Level
Question 1 (50 marks)


Question Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus

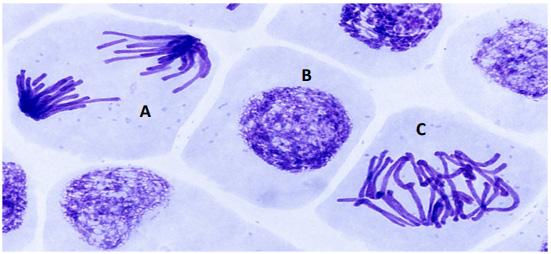
(a) The light microscope image below is of cells in a garlic root tip at different stages in the cell cycle. Mitosis is one part of the cell cycle and is followed by cell division. Analyse the image and answer the questions that follow.


Chapter 16

(i) Identify both stages of mitosis that each of the cells labelled A and C are undergoing.
(ii) Identify the stage of the cell cycle that the cell labelled B is undergoing.



(iii) On the image above, write the letter X on the location of a cell membrane.
(iv) Uncontrolled cell division can lead to cancer. Name two environmental risk factors that increase the chance of cancer development.













Question







(b) The following experiment was carried out to investigate the effectiveness of a vaccine. Read the article and answer the questions that follow.
An international, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial was carried out to see if the vaccine was effective. A total of 43 448 people received injections: 21 720 with the vaccine and 21 728 with the placebo. Randomly assigned persons aged 16 years or older received two doses, 21 days apart, of either the placebo or the vaccine. Two doses of the vaccine gave 95% protection against the pathogen in persons 16 years of age or older.
Adapted from Polack et al., 2020.








Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus




(i) Why was it important that the vaccine was tested in people from all around the world?
(ii) What does “placebo-controlled” mean in the context of this experiment?
(iii) A total of 43 448 people aged 16 years or older took part in this experiment.

Chapter 2
Comment on the sample size used in relation to the reliability of the data.
(iv) Would it be correct to conclude that this vaccine works in children under the age of 16 years? Justify your answer.











(c) The simplified diagram shown below is of the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane, proposed by Singer and Nicolson in 1972.

(i) Identify the part of the membrane labelled C.
(ii) Identify molecule A, which can be involved in cell signalling, such as in the immune system.
(iii) The discovery of molecule B, which spans the membrane, allowed Singer and Nicolson, and others to relate this molecule to an essential function of all membranes. State this essential function.
(iv) State one technological development in microscopy, such as the one shown in the image that allowed for the development of the detailed structure of the cell membrane.

(d) The image below is of a plant stem as seen under a light microscope. Some of the cells in tissue X are involved in the movement of sucrose from the leaves towards the roots in plants. Labels Y and Z also represent tissues.

Chapter 7
Chapter 30
Question Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
(i) Name the types of tissue labelled X, Y and Z.
(ii) State a function of tissue Y.
(iii) State one adaptation of tissue Y, from the image or from your studies of plant structure, that allows the tissue to carry out its function.
(e) Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow.
Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) are a family of neurodegenerative disorders of the central nervous system (CNS) that include scrapie in sheep, bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) in cattle and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) and variant CJD (vCJD) in humans (World Health Organisation, WHO, 2002). TSEs result from the misfolding of a particular protein called a prion, which is normally found on the nerve cell membranes in the brain. Adapted from fsai.ie
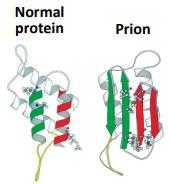
(i) Explain why prions can be classified as pathogens.
(ii) BSE in cattle was first identified in the United Kingdom (UK) in the 1980s and the first cases of vCJD were reported in 1996. Suggest a way in which this prion might have been transmitted from cattle to humans to cause disease.
(iii) Prions are an example of a misfolded protein. Explain the importance of folding in proteins.
(iv) Name another non-cellular pathogen.
Chapter 30
Chapter 8 and 22
Answer any five questions from the following questions 2 to 7. Each question carries 50 marks.
Question 2 (50 marks)
Question
(a) The National Biodiversity Data Centre, as part of their Citizen Science programme, collects and records data on wild species received from members of the public. This helps to monitor the species diversity index in any given area. The data collected from County Cork (JanMay 2024) on six different species of plants is shown in the table below.
Data from records.biodiversityireland.ie
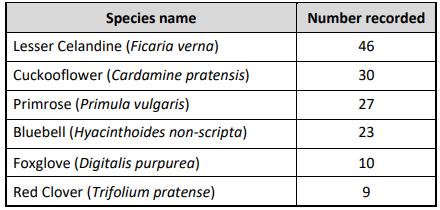
(i) What is meant by the term species?

(ii) What is meant by the term species diversity index?
(iii) Using the data and formula, calculate the species diversity index for County Cork.
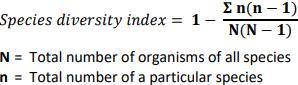
(iv) Explain the significance of the diversity index number you calculated in part (iii).
(v) A student stated that “the number of each species recorded in the table from January to May 2024 in County Cork will not be the same if calculated over a year”. Do you agree or disagree with this statement? Justify your answer.
Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
Chapter 6 and 31
Question Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
(b) Read the passage below and answer the questions that follow.
Red clover is a plant that contains nodules on its roots. These nodules contain bacteria that live in a symbiotic relationship with the clover and which play an essential role in the process of nitrogen fixation during the nitrogen cycle.
Farmers are encouraged to sow clovers with their grass as it helps towards environmental sustainability. Adapted from teagasc.ie

(i) Name the specific type of symbiotic relationship between red clover and the bacteria in the root nodules.
(ii) Name one other type of symbiotic relationship.
(iii) What is the significance of symbiotic relationships in nature?
(iv) Outline the importance of nutrient cycles such as the nitrogen cycle.
(v) Describe the process of nitrogen fixation during the nitrogen cycle.
(vi) Predict what you think may happen to the diversity of plants in a habitat if more clover was grown. Explain your answer.
(vii) Suggest why sowing clover plants helps farmers move towards or improve environmental sustainability.
Chapter 32 and 34
Question
(c) Read the passage below and answer the questions that follow.
Systemic insecticides can be used in agriculture to target insects that damage commercial crops. These chemicals are often applied to the soil. They are water-soluble and can be absorbed and distributed throughout all plant tissues.

One group of insecticides called neonicotinoids are suspected of poisoning honeybees, bumblebees, and other beneficial insects. It has been shown that they interfere with insect nervous systems. These chemicals are found in the pollen and nectar that the bees collect.
Adapted from Fairbrother et al., 2014
(i) Name two plant organs that facilitate the absorption and transfer of insecticides from the soil water to the plant flowers.
(ii) State two processes that allow for the uptake and transfer of watersoluble insecticides in plants.
(iii) In the box below, draw a labelled diagram of the internal structure of a flower that would be visited by a bumblebee.
Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
Chapter 24 and 30
Question 3 (50 marks)
Question
(a) The diagram below shows three stages in a technique used in molecular genetics called polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
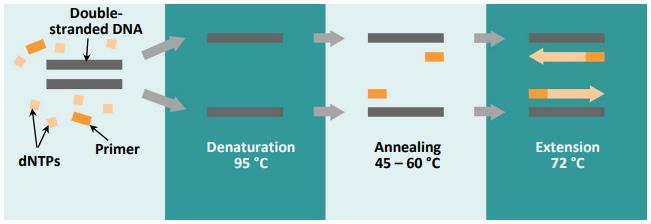
(i) Analyse the diagram and explain what is happening to the doublestranded DNA template during the denaturation or first stage of polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Some components of PCR shown in the diagram include: a DNA template (double-stranded DNA), nucleotides (dNTPs), and primers (short, singlestranded sections of DNA that bind to the template DNA either side of the DNA sequence of interest).
Where
Chapter 35
Question
Some components not shown in the diagram include: Taq polymerase (a type of DNA polymerase), pH buffer, magnesium chloride and a thermocycler machine.
(ii) On the diagram above, draw a circle around the temperature at which you think Taq polymerase works optimally.
(iii) A student states that: “a pH buffer is not a necessary component for PCR”.
Do you agree or disagree with this statement? Justify your answer.
(b) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique used to amplify small amounts of a DNA sequence of interest, into larger more detectable quantities. The DNA must first be extracted from a sample before PCR can be carried out and the results analysed. The main stages of this process are shown in the diagram below.
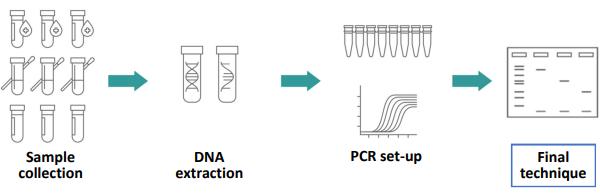
(i) Name the final technique shown in the diagram above that is used to separate DNA fragments.
(ii) Describe how the technique you have named at (i) above is used to separate DNA fragments.
(iii) During the sample collection stage, it is important to follow good laboratory practices, which always includes wearing laboratory gloves. Suggest why the wearing of laboratory gloves is mandatory given the two steps that follow sample collection.
Chapter 35
Chapter 35
Question
(c) Taq DNA polymerase was originally isolated from the bacterium Thermus aquaticus which was first discovered in a hot spring in Yellowstone National Park in North America in the 1960s. This enzyme can resist the high temperatures necessary in PCR.
The chart below is of a phylogenetic tree showing the evolutionary relationship between the different types of DNA polymerase from various bacterial species when compared to Taq DNA polymerase.

(i) Name a bacterial species that is most closely related to Thermus aquaticus, in terms of the structure of its DNA polymerase. Explain your answer.
Note: Thermus aquaticus is highlighted in the chart.
(ii) Suggest two ways by which the gene that codes for DNA polymerase might have evolved in the genus, Thermus.
(iii) State two sources of evidence, other than phylogeny, that support evolution by natural selection.
(d) Genome databases can be used to obtain information on genetic diseases.
The table shows an extract of information from a genome database.

(i) Explain the term inheritance.
(ii) What does ‘X-linked’ mean?
(iii) What chromosome number is the sickle cell disease allele present on?
Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
Chapter 6 and 12
Chapter 11 and 35
Question
(iv) Name a sector of society that could make use of the genetic data access that genome databases provide and suggest how access to this data is of use to this sector of society.
(v) Discuss one possible ethical issue in relation to advancements in genetic technologies.
Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
Chapter 11 and 35
Question 4 (50 marks)
Question
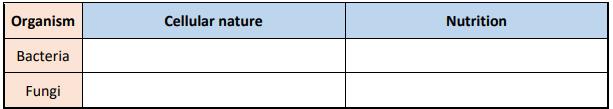
(a) Image A shows the interaction between the bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens and the button mushroom Agaricus bisporus. The bacterium causes blotches on the mushrooms. Image B shows unaffected button mushrooms.

(i) On the image above, draw an arrow from the letter X to the location of the bacteria growing on the button mushroom in image A.
(ii) Draw a labelled diagram of a bacterial cell in the box below.
(iii) Distinguish briefly between bacteria and fungi in terms of cellular nature and nutrition.
Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
Chapter 33
(b) The graph below shows a growth curve for one species of bacteria grown in a bioreactor. The majority of bacteria follow this growth curve, but some species can enter a fifth phase, not shown on the graph.
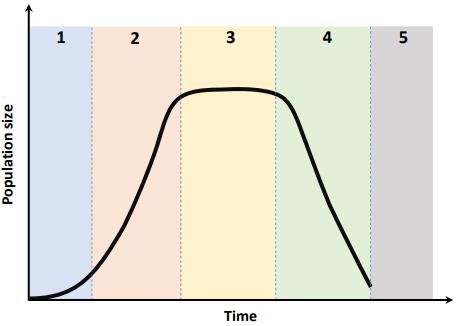
(i) Identify the four phases (1, 2, 3 and 4) of the bacterial growth curve shown on the graph above.
(ii) By drawing on the growth curve above, complete the line showing the fifth phase that some species of bacteria can enter.
(iii) State the name given to this fifth phase of the growth curve.
(iv) What structure forms in bacteria that allows them to enter the fifth phase of the growth curve?
(c) The image below is of a bioreactor that can be used in bioprocessing with microorganisms in the pharmaceutical industry.

33
Chapter 33
(i) There are sensor probes in the bioreactor that detect and measure factors that influence the growth of microorganisms. State any two factors that influence the growth of microorganisms.
(ii) Explain how one of the factors you have given at (i) above affects the growth of microorganisms.
(iii) Other than the pharmaceutical industry, identify two industries where microorganisms are used to produce substances of use to humans.
(d) Describe an activity you carried out in the laboratory to investigate one factor that affects the growth of microorganisms. You may use a labelled diagram if you wish.
Chapter 33
Chapter 33
Question
(a) The diagram shows the internal structure of the human heart.
(i) Identify the blood vessels labelled A and B.
(ii) What happens to the valve labelled in the diagram when the ventricles contract?
(iii) On the diagram, draw an X where the pacemaker is located.
(iv) Describe how the carbon dioxide concentration in blood plasma varies between blood vessels A and B.

(v) In the space below, model one structural difference between an artery and a vein, by describing the difference and/or drawing a labelled diagram.
(b) The transport of materials within humans is carried out using a twocircuit circulatory system.
(i) Identify both circuits.
(ii) Describe the pathway of blood circulation in one of these circuits.
(iii) Describe what may happen to the heart when a coronary artery becomes completely blocked.
(iv) Explain the term blood pressure.
Chapter 29
Chapter 29
(c) The graph below shows the change in arterial blood pressure of an athlete over two consecutive heartbeats. Analyse the graph and answer the questions that follow.
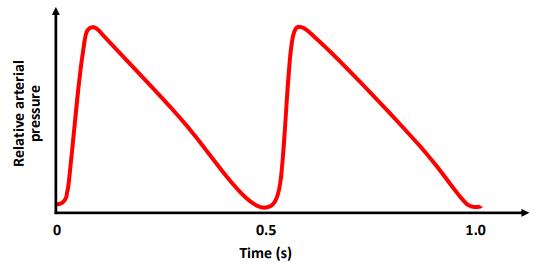
(i) On the graph above, write the letter X to indicate a point in time during which the left ventricle is contracting.
(ii) Using the information given on the graph above, calculate the heart rate in beats per minute (bpm) of the athlete.
(iii) Does the graph shown above represent an athlete at rest? Justify your answer.
(d) (i) Explain why cardiac muscle cells have large numbers of mitochondria.
(ii) In the space below, model how an antagonistic muscle pair functions in the movement of a synovial joint by providing a description and/or drawing a labelled diagram.
Chapter 29
Chapter 18 and 29
Question Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
(a) Read the passage below and answer the questions that follow.
The Venus flytrap (Dionaea muscipula) is a plant that catches and digests insects. It is native to North and South Carolina in America, where it is common in damp mossy and boggy areas.
Venus flytraps do not rely on digesting insects for energy, but rather use the nitrogen-rich animal proteins to enable their survival in poor soil conditions.

The plant’s leaves have spiny ‘teeth’ along their edges and can fold together and enclose an insect landing inside. This action is triggered by pressure on sensitive hairs in each leaf. Glands on the leaf surface then secrete a red sap that digests the insect’s body.
Adapted from National Wildlife Federation, nwf.org
(i) Suggest a reason why the Venus flytrap must consume insects.
(ii) Why do you think Venus flytraps do not rely on insects for energy?
(iii) Identify a structural adaptation that allows the Venus flytrap to survive in its habitat.
(iv) State a biotic factor that can influence the population size of the Venus flytrap.
(v) Do you think that climate warming will endanger this plant population? Justify your answer.
(vi) Bogs, where the Venus flytrap can be found, are one example of a carbon sink.
List two other examples of carbon sinks.
(vii) Draw a labelled diagram of the carbon cycle.
Chapter 32 and 34
Question
(b) Light intensity is one factor that can affect the rate of photosynthesis. The table below shows the results from a student’s investigation into the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis of an aquatic plant. The light intensity was varied by placing a desk lamp at various distances away from the plant.
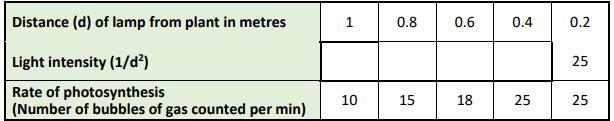
(i) Complete the table of results to show all the light intensities.
(ii) In the space below, draw a line graph of the student’s results.
(iii) Analyse the data and state a conclusion for the investigation.
(iv) Identify one variable that would need to be controlled in this investigation to increase the reliability of the data.
(c) Describe the non-cyclic pathway of the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
You may use a labelled diagram if you wish.
Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
Chapter 14
Chapter 14
Question
(a) Three types of biomolecule include lipids, carbohydrates and proteins.
(i) Complete the table below, by writing Lipid or Carbohydrate or Protein into each box to match the molecular formula to its corresponding biomolecule.

(ii) State a reason to support your answers in (i) above.
(iii) Identify two nutritional sources of lipids.
(iv) Proteins are used by cells to carry out certain metabolic reactions. State two examples of proteins that have roles in metabolic reactions.
(b) A fizzy drink (red lemonade) containing 2 % (2 g/100 cm3) glucose solution was used to prepare different concentrations of glucose solutions as shown in the table below.

Students were given these solutions in unmarked cups and asked to use glucose test strips to quantitatively investigate the level of glucose in the unknown samples. The colour chart for glucose on the test strip bottle used by the students is shown in the table below. Analyse the data and answer the questions that follow.

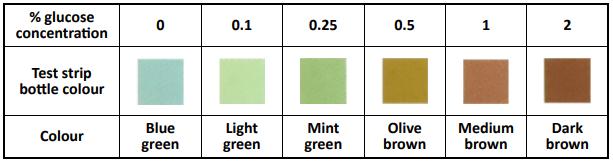
(i) How would a student know if a sample they tested contained 1 % glucose solution?
(ii) Would a student be able to accurately identify a 0.375 % glucose solution using this technique? Justify your answer.
Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
Chapter 8
Chapter 8






(c) Draw a labelled diagram of the human digestive system.
(d) The human body uses enzymes to chemically digest food. The diagram below illustrates a model of how enzymes function.


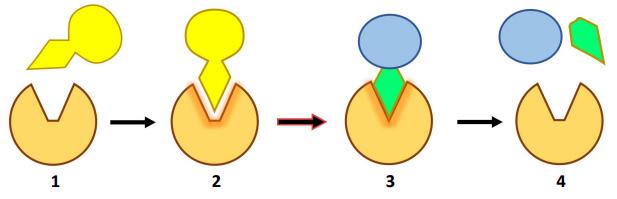
(i) Enzymes can be referred to as ‘selective catalysts’. Explain this term based on your knowledge of enzymes.

(ii) Using the diagram above, explain how enzymes function in catalysing biochemical reactions. In your answer refer to the events that take place at each numbered stage in the diagram above.






























Question
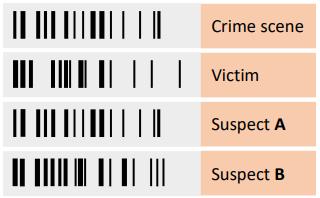
(a) DNA is often found at the scene of a crime. A forensic scientist gathers information including biological samples from victims and any suspects to provide DNA for analysis.





Question 1 (50 marks)


(i) The images below show samples that may be collected at the crime scene. Identify the two samples that could be used to provide DNA by placing a tick () in the correct boxes.










Chapter 35
(ii) These DNA profiles were produced from one of the samples above. Analyse the DNA profiles and identify which suspect left their DNA at the crime scene.
Justify your answer.









Question Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
(b) The process of photosynthesis in plants is represented below by the balanced chemical equation.
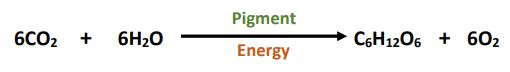
(i) State the source of the energy necessary for photosynthesis to occur.
(ii) What is the name of the pigment needed for photosynthesis?
(iii) Choose whether the reaction above is catabolic or anabolic. Put a tick () in the correct box.
(iv) Photosynthesis plays a role in the carbon cycle. The diagram shows part of the carbon cycle. By writing in the boxes below, complete the diagram naming the two processes 1 and 2 which release CO2 into the atmosphere.
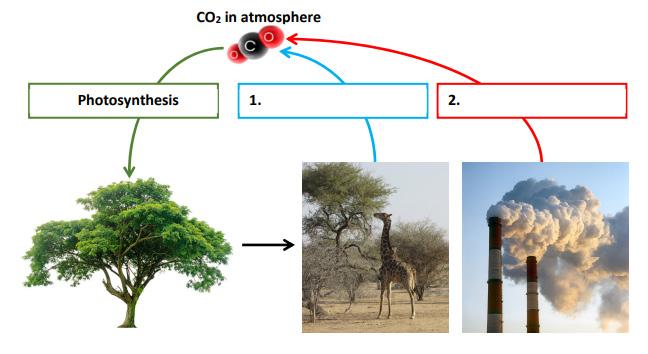
Chapter 14 and 34
Question
(c) Read the article and answer the questions that follow.
The natterjack toad (Epidalea calamita) is Ireland’s only native toad and is unique to coastal ponds and sand dunes in Co. Kerry.


In order to protect this endangered species 9500 toadlets have been released into ponds created by local farmers in Co. Kerry, as part of a joint project between the National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS), Dingle Oceanworld and Fota Wildlife Park.
Adapted from Hundreds of natterjack toads to be released into Kerry dunes, Irish Examiner 22nd July 2024
(i) Using the article above, identify the genus and species of the natterjack toad by placing a tick () in the correct boxes.
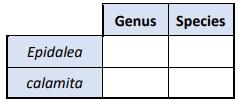
(ii) To which kingdom of life does the natterjack toad belong?
(iii) Identify a suitable habitat of the natterjack toad.
(iv) Different scientific groups often work together on a project. Name one group that has been involved in this project.
(v) Suggest one reason why so many (more than 9500) toadlets have been released in recent years.
Chapter 6 and 31
Question Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
(d) The diagram opposite shows the life cycle of the dandelion, a type of flowering plant. Complete the sentences below in relation to the flowering plant using words from the following list.
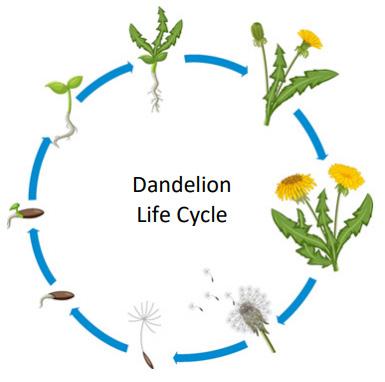
(i) The sexual reproductive structure in plants is the ……….
(ii) The anther produces ……….
(iii) The transfer of pollen grains from an anther to a stigma is called ……….
(iv) The seed has a protective outer layer called the ……….
(v) The seeds are dispersed and then grow into a new plant in a process called ……….
(e) Sexual reproduction in humans involves fertilisation (fusing) of a male gamete (sperm) and a female gamete (egg) to produce a fertilised egg called a zygote.
The diagram below represents the male reproductive system.

(i) On the diagram above, draw an arrow from label X to the tube that carries both urine and semen.
(ii) Name the parts labelled A and B of the male reproductive system.
Chapter 24
Chapter 23
Question Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
(iii) What hormone is produced by the part labelled B?
(iv) Contraception is a method where fertilisation is prevented or the fertilised egg is not allowed to develop. The condom is one method of contraception. Name one other method of contraception.

(v) Outline one health benefit of using a condom when engaging in sexual activity.
Chapter 23
Answer any five questions from the following questions 2 to 7. Each question carries 50 marks.
Question 2 (50 marks)
Question Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
(a) Cells are the building blocks of all organisms. A student wanted to examine the structures and organelles of plant cells using a light microscope, such as the one shown in the image. Describe how the student prepared and mounted these plant cells. You may use a labelled diagram.

(b) A student took the photograph below of the plant cells at a magnification of x100. Analyse the photograph and answer the questions that follow.

(i) Name the part of the cell labelled X in the photograph above.
Chapter 7
Chapter 1, 5 and 7
Question
(ii) Living organisms can be classified as unicellular or multicellular. Identify if the cells shown in the photograph above belong to a unicellular or a multicellular organism by placing a tick () in the correct box.

(iii) State the function of the cell wall.
(iv) How should the student refer to these results in the report? Place a tick () in the correct box.

(c) The image below is a micrograph of an animal cell.
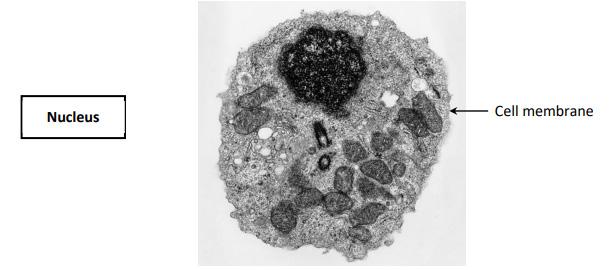
(i) The nucleus controls the activities of the cell. Identify the nucleus on the above image, by drawing an arrow from the word Nucleus to its correct location on the image.
(ii) Identify if the cell in the image above is a prokaryotic cell or a eukaryotic cell by placing a tick () in the correct box. Justify your answer.
(iii) Name a type of microscope other than a light microscope.
(iv) Suggest one reason why a biologist may need to use the microscope you named at part (iii) above when examining cells.
Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
Chapter 1, 5 and 7
Chapter 6 and 7
Question Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
(d) Images A and B below are micrographs of two different cell organelles.
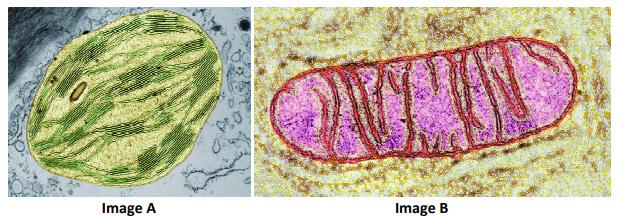
(i) Identify which image (A or B) is the mitochondrion.
(ii) Both organelles are involved in metabolism. Explain the term metabolism.
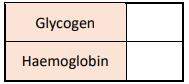
(iii) Photosynthesis and respiration are two processes that occur in cells. Complete the table below to match the organelles with their cellular processes by placing a tick () in the correct boxes.
(iv) What is the role of respiration in organisms?
Chapter 7 and 15
Question
(a) All living cells have a semi-permeable membrane. Molecules can move across membranes by passive transport (diffusion) and active transport.
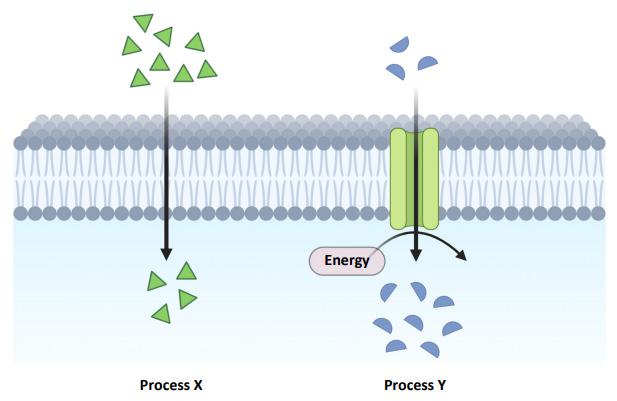
(i) The diagram above illustrates part of a cell membrane showing both active and passive transport of materials across it. Identify which process (X or Y) is active transport.
(ii) Justify your answer to part (i) above.
(iii) During breathing, oxygen passes into the blood in the lungs by diffusion. Name one other gas that moves by diffusion during breathing.
Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
Chapter 25 and 28
(b) The images and table below show how a student prepared an activity to investigate the effect of surface area on the rate of osmosis.
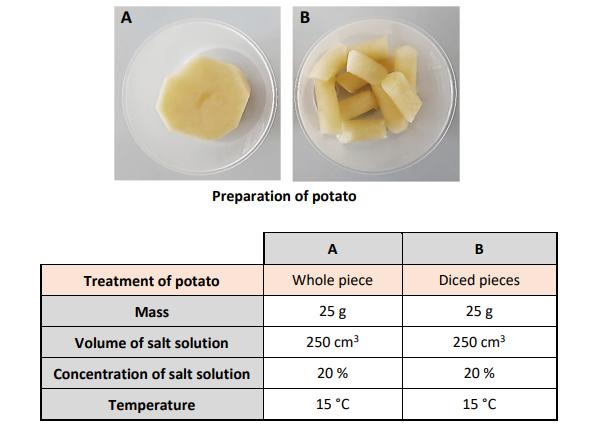
(i) Analyse the information above and pose a hypothesis for this investigation.
(ii) State one way in which the student ensured the investigation was fair.
(iii) Identify the dependent and independent variables in this investigation.
(iv) The student measured the rate of osmosis by measuring the loss in mass of the potatoes every 10 minutes for 60 minutes. The results of the investigation were presented in the table below. The student plotted the results for the whole piece of potato, as shown in the graph below.

Chapter 2 and 25
Question Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
1. Using the graph plotted below (blue dashed line), how long did it take for the whole piece of potato to lose 2 g of water?
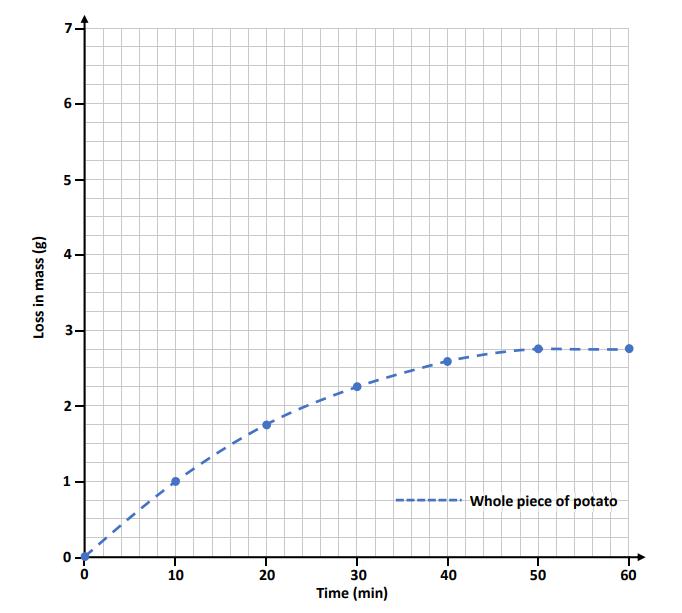
2. Plot a line graph of the results for the diced pieces of potato.
3. Sketch another line graph to predict the result if 25 g of potatoes were diced even smaller than those originally used.
(v) Analyse the data and state a conclusion for the student’s investigation.
Chapter 2 and 25
Question
(c) The photograph shows a potato plant.
(i) On the photograph, draw an arrow from label R to identify the potato roots.

(ii) One function of roots in plants is to absorb water and minerals from the soil. State one other function of roots.
(iii) The roots have root hairs. How do root hairs improve the rate of water absorption?
(iv) Water and minerals are transported in specialised plant vascular tissue.
Name this transport tissue in plants.
Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
Chapter 30
Question 4 (50 marks)
Question
(a) Chromosomes are found in cells and are composed of two substances. One of the substances is DNA.

(i) Identify the second substance that makes up chromosomes. Put a tick () in the correct box.

Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
Chapter 10 and 12
Question
(ii) What name is used to describe the shape of a DNA molecule?
(iii) DNA is made up of many nucleotides joined together (polynucleotide).
The diagram below shows the structure of a DNA nucleotide. Match parts Y and Z to their correct names from the following list.

(iv) The base sequence of one part of a DNA strand is written in the table below. Complete the table to show the sequence on the complementary strand.

(v) A change in the base sequence of DNA is known as a mutation and results in variation within species. Identify one other cause of variation.
(b) Genetics is the study of inheritance, the passing on of DNA (genes) from parent to offspring. Some cats have patches of white fur known as white spotting. White spotting is inherited by a dominant allele.
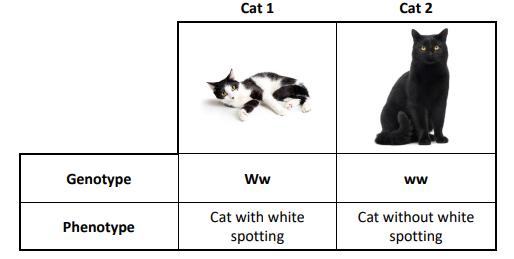
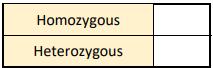
(i) Is cat 2 described as homozygous or heterozygous? Place a tick () in the correct box.
Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
Chapter 10 and 12
Chapter 11
Question
(ii) Explain your answer to part (i) above.
(iii) Cat 1 has the genotype Ww. Which other genotype will result in a white spotted cat?
(iv) A Punnett square is one way of modelling genetic inheritance. Using the method below, or another method, show the pattern of inheritance in across between cat 1 and cat 2.
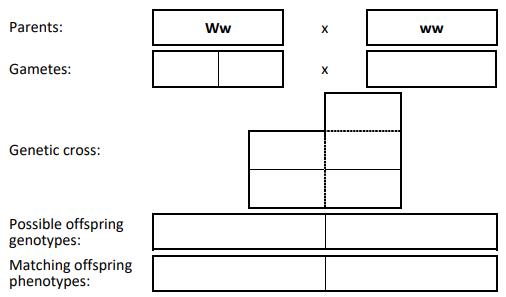
(v) What is the percentage chance of an offspring having white spotting?
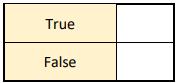
(vi) Epigenetics is the study of how non-genetic factors such as diet and environment can influence gene expression. Place a tick () in the correct box to indicate if this statement is true or false.
Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
11
Question Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
(c) Evolution refers to genetic changes in a species over time in response to changes in their environment. A phylogenetic tree, as shown below, can be used to represent evolutionary relationships between organisms.

(i) Name one organism listed above which does not have hair.
(ii) Identify the term scientists use to describe species X. Put a tick () in the correct box.
Chapter 6 and 12
(iii) Which organism above is most closely related phylogenetically to the elephant?
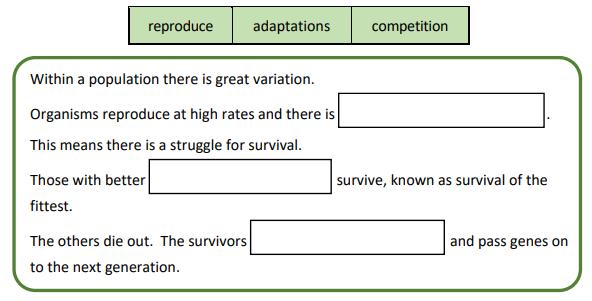
(iv) Evolution by natural selection is a commonly accepted theory among scientists. Using the words from the list below, complete the paragraph to explain natural selection.
Question
(a) The image below shows foods with a range of nutrients. A balanced diet involves eating the correct amount of each type of nutrient.

(i) Identify a food from the image, or otherwise, that is rich in protein and a food that is rich in carbohydrate.
(ii) State one factor that influences how much of each food type an individual needs.
(iii) Digestion involves breaking large food molecules such as protein, lipids and starch into smaller food molecules. Explain why we need to digest large food molecules, such as starch.
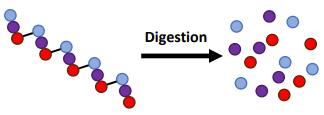
(b) (i) The first table below shows a list of small food molecules.
Using the list of small food molecules, complete the table below by matching each large food molecule with its corresponding small food molecule from the list.
Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
Chapter 8 and 27
Chapter 8 and 27
Question
Saliva is a liquid produced by salivary glands in the mouth. It consists of mostly water with some digestive enzymes. The diagram shows food in the mouth being mixed with a digestive enzyme in saliva.
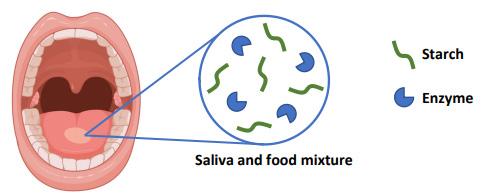
(ii) Name the enzyme in saliva that breaks down starch in the mouth.
(iii) Teeth are also visible in the diagram. Describe the role of teeth in digestion.
(c) (i) The diagram shows some of the organs involved in the human digestive system. Match the letters D, E and F on the diagram with the organs listed in the table below.

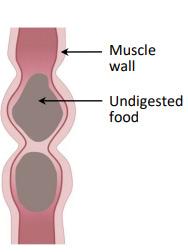
(ii) Undigested food ends up in the large intestine and is eliminated from the body as faeces. The diagram on the right shows the movement of undigested food through the large intestine. Briefly describe how undigested food is moved through the large intestine.

(iii) Which term describes the removal of faeces from the body?
Place a tick () in the correct box.

Chapter 8 and 27
Chapter 27
Question
(d) Describe how you investigated the presence of a named food biomolecule. Include a description of a control in your answer. You may use a labelled diagram.
Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
Chapter 8
Question 6 (50 marks)
Question
(a) The circulatory system uses blood, blood vessels and the heart to deliver substances around the body. The image shows a unit (470 cm3) of blood donated in a blood donation clinic.
(i) Identify component R.
(ii) Identify the substance which makes up most of component R. Put a tick () in the correct box.

(iii) Two blood cells X and Y are shown in the image on the right. Name X and Y.
(iv) Identify the chemical in cell X that carries oxygen. Put a tick () in the correct box.
(v) What is the function of cell Y?
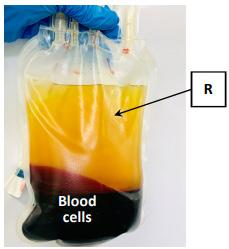

(vi) If a person is to receive a blood donation, their blood group (type) must be compatible with the blood they are to receive. Name one blood grouping system.
Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
29
(b) The diagrams show three types of blood vessels, not drawn to scale.
(i) Identify each type of blood vessel using the names from the following list:
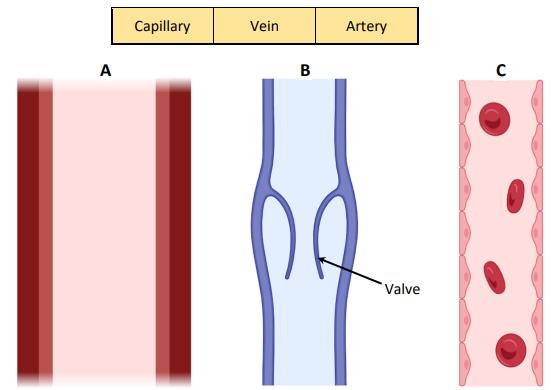
(ii) On diagram B above, draw an arrow to show the direction of blood flow.
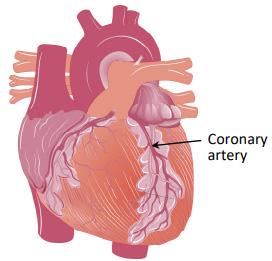
The diagram below shows the structure of the heart and shows the coronary artery delivering blood to the cardiac muscle.
(iii) Suggest what might happen if this artery was blocked.
(iv) Suggest a lifestyle choice that makes it less likely that this artery will get blocked. Chapter 29
Question
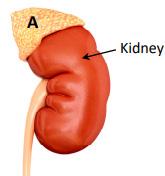
(c) Adrenaline is an important hormone in the body.
(i) Name the gland A that produces adrenaline. A scientist investigated the effect of exercise on blood adrenaline concentration. Their data is shown in the table below.
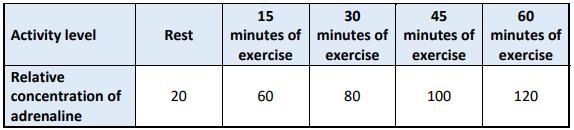
(ii) Using the data, draw a suitable graph in the space below.
(iii) What is the relationship between exercise levels and the amount of adrenaline in the blood?
(iv) What do you think would happen to the concentration of adrenaline once the exercise had stopped?
Chapter 8 and 20
Question
(v) The chemical structure for the hormone adrenaline is shown below. It is made up of the elements carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O) and nitrogen (N).
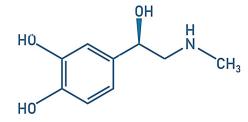
Identify the type of food biomolecule that is made up of these same four elements and is used to make hormones such as adrenaline in the body.
Put a tick () in the correct box.
(vi) State one use of hormonal manipulation in sport.
Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
Chapter 8 and 20
Question Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
(a) Bacteria and Fungi are two kingdoms of living things.

(i) The table below contains statements about bacteria and fungi. Identify which organism is being described by each statement. Put a tick () in the correct boxes.

(ii) The diagram below shows Rhizopus, a fungus that grows on bread. Use the list below to label A, B and C on the diagram.
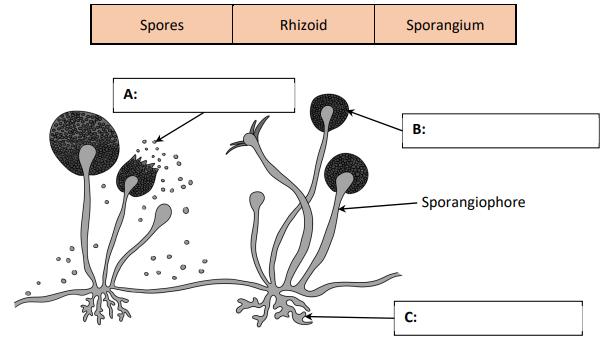
Chapter 33
Question Where you'll find the answer in Biology Plus
(b) Some bacteria and fungi can cause disease.
(i) Identify the name which describes organisms or agents that cause disease by placing a tick () in the correct box.
(ii) Identify one other agent or organism that can cause disease.
(iii) Draw a labelled diagram of a bacterial cell in the space provided below.
(c) Antibiotics are chemicals that affect bacteria.
(i) What is meant by antibiotic resistance?
The image shows bacterial growth in a petri dish with nutrient agar (food for the bacteria). Antibiotic discs (A, B, C, D, E and F) were placed on the agar and the bacteria were allowed to grow.

(ii) Identify an antibiotic disc that was not effective against the bacteria.
(iii) Identify an antibiotic disc that was most effective against the bacteria.
(iv) Explain how you decided this antibiotic disc was the most effective.
Chapter 22 and 33
Chapter 12
(d) Microorganisms have many roles in nature, including in the nitrogen cycle. The diagram below shows part of the nitrogen cycle. X and Y represent two processes of the cycle.

(i) Identify processes X and Y.
(ii) Name one process (other than X and Y) in the nitrogen cycle that promotes a healthy soil microbiome.
(iii) Describe how climate warming affects the soil microbiome.
(iv) Soil is one example of a microbiome. State one location of a microbiome in or on the human body.
Chapter 33 and 34


























