Information Catalog












Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects millions of women. Sometimes it’s called Stein-Leventhal syndrome.
All bodies need both “male” and “female” hormones to work right, but a woman with PCOS has too much of the male kind, testosterone. This creates problems with the ovaries, which could also include these symptoms:
• Irregular periods or no periods
• Cysts in a “string of pearls” pattern
• Infertility or difficulty falling pregnant
• Weight gain, especially around the waist, which is difficult to lose
• Grow extra hair or have thinning hair
• Acne or dark patches of skin
• Pelvic pain
• Depression
• High cholesterol, which may lead to heart disease, including high blood pressure and heart attack

• Insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes
• Obesity
• Sleep apnea
• Mood disorders, like depression and bipolar disorder
• Endometrial cancer, especially when you’re older

Developing Egg
The ingredients and dosage within FertipilPlus® PCOS have been extensively researched and clinically formulated to provide optimal results. FertipilPlus® PCOS contains both Myo-inositol and D-Chiro- Inositol as well as Alpha Lipoic Acid and Folic Acid. Fertipil Plus PCOS is the latest addition to South Africa’s leading fertility supplement range – Fertipil Plus for Men and Women.
Data from studies suggest that the combination of Myo-Inositol, D-chiro-inositol and other ingredients are beneficial for improving metabolic, hormonal, and reproductive spheres of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) (Kamenov & Gateva, 2020).

Myo-inositol and D-Chiro-Inositol have shown to aid in oocyte maturation, fertilization, post-implantation, insulin signalling and hormonal synthesis within the ovaries (Kamenov & Gateva, 2020).
The combination of MI and DCI as a treatment option for patients with PCOS can help improve metabolic, ovulatory, and hyper androgenic factors of PCOS (Kalra, Kalra, & Sharma, 2016). MI assists in correcting insulin resistance that presents in patients with PCOS (Kalra, Kalra, & Sharma, 2016) while DCI assist in creating a healthy intra-ovarian environment which will correct hyperandrogenism, regulate menstrual cycle, and promote ovulation as well as fertility (Kalra, Kalra, & Sharma, 2016).
Our combination and quantity of MI and DCI are based on a 40:1 ratio. According to a clinical trial conducted by Nordio (the most relied upon study up to date), the ratio of 40:1 MI/DCI was more favourable than the other ratios tested for PCOS (Nordio, Bascaiani, & Camajani, 2019). Within this study, the 40:1 ratio had the best recovery rate for PCOS compared to other ratios as well as restoring ovulation within patients (Nordio, Bascaiani, & Camajani, 2019).
MI has been found to improve the number of good quality oocytes, clinical pregnancies, and delivery rates in obese women with PCOS (Kalra, Kalra, & Sharma, 2016). Furthermore, MI has been proven to play an essential role in oocyte maturation as well as having an insulin-sensitizing effect- all of which assist patients diagnosed with PCOS (Ciotta, et al., 2011). MI also assists in correcting insulin
resistance that presents in these patients (Kalra, Kalra, & Sharma, 2016).
Papaleo found that myoinositol can restore normal ovarian activity and fertility in most patients with PCOS (Papaleo, et al., 2007). In the trial they conducted, 2g of MI combined with folic acid were administered as a soluble powder twice daily (this is an essential focus point) for 6 months to twenty-five women that had PCOS- 22 (88%) experienced a first menstrual cycle after an average 35 days.

Of these 22 women, 18 continued to have regular menstruation and documented spontaneous ovulation. The length of successive cycles improved to 31.7 ± 3.2 days, and there was a significant decrease in androgen levels) (Papaleo, et al., 2007). Nine clinical pregnancies were also recorded (Papaleo, et al., 2007). MI can, thus, be used as a safe means of induction of ovulation in women with PCOS.
In a study of fifty women with PCOS; MI was found to reduce the risk of ovarian hyper stimulation syndrome, insulin sensitivity improved, and menstrual cycles were restored (Artini, et al., 2013). Furthermore, higher pregnancy rates were also observed due to higher quality oocytes as a result of MI treatment (Artini, et al., 2013).
Various studies have been conducted on the effect of DCI on endocrine, metabolic, and reproductive parameters in PCOS patients (Kalra, Kalra, & Sharma, 2016).
In a study to determine the effects of DCI in lean women with PCOS; DCI was administered every day for 6 – 8 weeks (Iuorno, et al., 2002). The results indicated reduced levels of insulin resistance and free testosterone levels (reminding those high levels of androgens
have been associated with PCOS), whilst also decreasing systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and serum triglycerides (Iuorno, et al., 2002).
A similar study was conducted on obese PCOS women where the DCI was found to improve endocrine parameters such as serum testosterone, serum androstenedione, and gonadotropin-releasing hormone-induced LH response (Kalra, Kalra, & Sharma, 2016). The study also found that it reduced BMI, improved hormonal patterns and improved insulin sensitivity markers in PCOS patients with diabetic relatives, who exhibit a greater response as compared to those with no family history of diabetes (Genazzani, et al., 2014).
Looking at the effects of DCI on menstrual cycle regularity, a study showed that menstrual cycles increased with the increase of DCI treatment (La Marca, Grisendi, Dondi, Sighinolfi, & Cianci, 2015). In the same retrospective study, improvement of insulin resistance was noted with the bettering of menstrual cycle regularity (La Marca, Grisendi, Dondi, Sighinolfi, & Cianci, 2015).
DCI has also shown to improve ovulatory function due to the increased action of insulin in patients with PCOS and furthermore reduce androgen concentrations, blood pressure as well as plasma triglyceride concentrations (Nestler, Jakubowicz, Reamer, Gunn, & Allan, 1999).
Therefore, D-chiro-inositol has shown to drastically reduce insulin resistance and male hormones (both being core causes of PCOS) and further improve menstrual cycles and the quality of oocytes.
ALA has been researched to have a positive effect on features of PCOS (Masharani, Gjerde, Evans, Youngren, & Goldfine, 2010). Studies have indicated that PCOS treatment that combines ALA and inositol’s (MI and DCI) can have positive effects on menstrual cycle regularity, ovulation, and hyperinsulinemia (having more insulin in your blood than normal) (Lei, Gao, Liu, & Chen, 2020).
In a study of which 40 women with PCOS were observed before and after a six-month treatment of Myo-inositol and Alpha Lipoic Acid, an increase of the number of menstrual cycles were detected as well as an improvement of the hormonal environment within the patients (De Cicco, et al., 2017).
Several studies reported that insulin resistance is common (and is most likely the cause of) PCOS in patients, regardless of the body mass index (BMI) (Masharani, Gjerde, Evans, Youngren, & Goldfine, 2010). Insulin resistance has been recorded to be more prevalent in obese PCOS patientsstatistics show that hyperinsulinemia caused by insulin resistance occurs in about 80% of women with PCOS and central obesity as well as 15-30% of lean women with PCOS (Masharani, Gjerde, Evans, Youngren, & Goldfine, 2010). Obesity has been seen to exacerbate insulin resistance and it is often a material reason why some women fail to ovulate and have higher than normal androgen levels (Masharani, Gjerde, Evans, Youngren, & Goldfine, 2010).
Both inositols and ALA were reported to be effective in reducing insulin resistance in PCOS patients. While inositols are involved in the structure of the post receptor transduction of the signal induced by the linkage of insulin on its receptor, ALA has been demonstrated in the animal model to increase glucose utilization (De Cicco, et al., 2017). ALA also serves as a powerful antioxidant and reduces oxidative stress in the reproductive system and in general.
Studies have shown that a combination of Inositol and Folic acid substantially reduces the size of ovarian cysts and increases egg quality as well as reduces the risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome in women undergoing ovulation induction as part of an IVF cycle (Regidor, Schindler, Lesoine, & Druckman, 2018).
FertipilPlus® PCOS contains both Inositol and Folic acid in dosages best suited for women who are trying to conceive. According to the study of Regidor, 2000 mg myo-inositol twice daily in combination with 200 µg folic acid twice daily were shown to have the best results- better fertilization rates and better embryo quality (Regidor, Schindler, Lesoine, & Druckman, 2018).

The combination of Myo-inositol and folic acid has been seen to improve the quality of oocytes as well as improve symptoms associated with PCOS and infertility (Regidor, Schindler, Lesoine, & Druckman, 2018).
Studies have shown that patients with PCOS that are treated with Myoinositol and folic acid show reduce germinal vesicles and better oocyte quality (Papaleo, et al., 2007).
This is essential to consider when Fertipil Plus PCOS is compared to other so called “convenient one a day dosage” products. The studies indicate that for best results the dosage of a MI and Folic Acid combination must be split into 2 doses daily in order to effectively regulate insulin levels.
In a study of overweight women with PCOS that were given inositol and folic acid during IVF, 32% of women had a successful pregnancy within the 12-month study period, compared to just 12% of women who only took a straight folic acid supplement without the inositol. These positive results have been repeated by other researchers that used a similar supplement regime to treat women undergoing intrauterine insemination (IUI) rather than IVF. In a recent study of IUI patients with PCOS, pregnancy rates were improved by approximately 50% (regardless of whether they had insulin resistance) after taking myo-inositol for just 3 months beforehand. (Regidor, Schindler, Lesoine, & Druckman, 2018)
Folic acid (also known as folate or vitamin B9) is a vitamin which is crucial to take before and during conception; it has shown to improve fertility rates and lowers the risk of birth defects. Folic acid can help grow and protect cells in the body as well as assist in the development of DNA. This is critical during pregnancy, when cells the body are growing and dividing very quickly for the uterus to expand, the placenta to develop, blood circulation to increase, and the foetus to grow (Laanpere, et al., 2010). However, Folic Acid deficiency at the time of conception has also shown to reduce the rate of full term pregnancies.
It is a commonly known fact that the use of Folic Acid (which is part of the B vitamin group) before pregnancy prevents neural tube defects. Therefore, public health authorities all over Europe recommend an intake of 400 - 500 µg folic acid per day for women of reproductive age and the CDC recommends that folic acid is consumed every day, for at least a month before patients intend to become pregnant, and daily during pregnancy (National Center for Environmental Health (U.S). Division of Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, 1992). Despite several public health campaigns and recommendations for over two decades, the compliance with folic acid supplementation is low in many countries. Results of previous studies have shown that less than 50% of women planning a pregnancy use periconceptional folic acid supplementation.
A study involving participants that took supplements containing folic acid have a much lower chance of neural tube defects than those who did not take supplements containing folic acid (Milunsky, et al., 1989). Folic Acid and birth defects
FertipilPlus® PCOS is the only product on the South African market that has a split daily dosage in its standard pack size of 60 sachets. This formulation and dosage relies on the most widely accredited study on these ingredients by Regidor Et al and Ciotta et al.

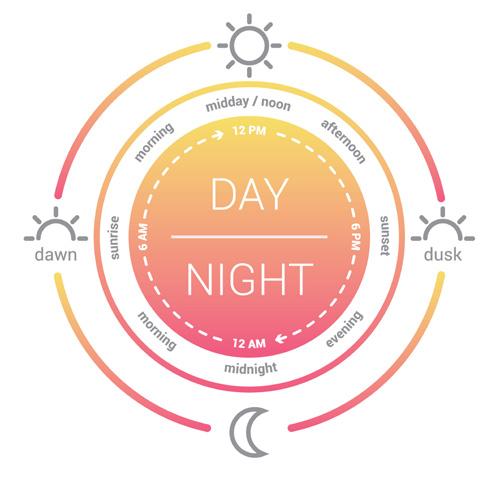
Evidence suggests that insulin resistance, hyper-androgenism and chronic anovulation are core features of PCOS (Dinicola, Chiu, Unfer, Carlomagno, & Bizzarri, 2014). Due to the level of insulin resistance, insulin levels should be maintained and managed during the day and our research shows that for best results, dosages should be split and takes twice daily for effective management of insulin levels. Furthermore, evidence suggest that by administering DCI at higher dosages that the dosage contained in Fertipil Plus PCOS might affect oocyte quality negatively (Dinicola, Chiu, Unfer, Carlomagno, & Bizzarri, 2014), hence another reason for the split dosage.
Most studies that had the best results per reference to insulin resistance, fertility rates, ovulation improvement as well as menstrual regularity- had dosages that were administered twice
Other birth defects (other than neural tube defects) can also be fatal or have lifelong effects on your baby- these are heart and limb defects, urinary tract anomalies, oral facial clefts, spina bifida and anencephalous. Studies suggested that folic acid lowers the risk of birth defects by around 70% (Green, 2002). Folic acid supplementation has also been shown to reduce both reoccurrence and occurrence of birth defects (Laanpere, et al., 2010).
Based on easily accessible pharmacy retail outlets and average price across these platforms. The below chart is based on private market research during March 2022.
FEATURES
Dosage Split (month supply in cluded)

Availability
Myo-Inositol 4000mg total D-Chiro-Inositol 100mg total Folic Acid 500 µg total
Alpha-Lipoic Acid 200mg total
Less than half the dose Less than half the dose
Less than half the dose Half the dose Half the dose
Less than half the dose
Half the dose
Less than half the dose
Artini, P., Di Berardino, O., Papini, F., Genazzani, A., Simi, G., Ruggiero, M., & Cela, V. (2013). Endocrine and clinical effects of myo-inositol administration in polycystic ovary syndrome. A randomized study. Gynecological Endocrinology, 29(4), 375-379. doi:10.3109/09513590.2012.743020
Ciotta, L., Stracquadanio, M., Pagano, I., Carbonaro, A., Palumbo, M., & Gulino, F. (2011). Effects of myo-inositol supplementation on oocyte’s quality in PCOS patients: a double blind trial. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 15(5), 509-514. De Cicco, S., Immediata, V., Romualdi, D., Policola, C., Tropea, A., Di Florio, C., . . Apa, R. (2017). Myoinositol combined with alphalipoic acid may improve the clinical and endocrine features of polycystic ovary syndrome through an insulin-independent action. Gynecology Endocrinology, 33(9), 698-701. doi:10.1080/ 09513590.2017.1313972.
Dinicola, S., Chiu, T., Unfer, V., Carlomagno, G., & Bizzarri, M. (2014). The rationale of the myo-inositol and D-chiro-inositol combined treatment for polycystic ovary syndrome. The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 52(10), 1079-1092.
Genazzani, A., Santagni, S., Rattighieri, E., Chierchia, E. D., Marini, G., & Simoncini, T. (2014). Modulatory role of D-chiro-inositol (DCI) on LH and insulin secretion in obese PCOS patients. Gynecological Endocrinology, 30(6), 438-443. doi:10.3109/0951 3590.2014.897321
Green, N. (2002). Folic Acid Supplementation and Prevention of Birth Defects. The Journal of Nutrition, 132(8), 2356S-2360S. doi:10.1093/jn/132.8.2356S
Iuorno, M., Jakubowicz, D., Baillargean, J., Dillon, P., Gunn, R., Allan, G., & Nestler, J. (2002). Effects of D-Chiro-Inositol in
Lean Women with the Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Endocrine Practice, 8(6), 417-423. doi:10.4158/EP.8.6.417
Kalra, B., Kalra, S., & Sharma, J. (2016). The inositols and polycystic ovary syndrome. Indian Journal of endocrinology and Metabolism, 20(5), 720-724.
Kamenov, Z., & Gateva, A. (2020). Inositols in PCOS. Molecules, 25(23), 5566. doi:10.3390/molecules25235566
La Marca, A., Grisendi, V., Dondi, G., Sighinolfi, G., & Cianci, A. (2015). The menstrual cycle regularization following d-chiroinositol treatment in PCOS women: a retrospective study. Gynecological Endocrinology, 31(1), 52-56. doi:10.3109/095135 90.2014.964201
Laanpere, M., Altmae, S., Stavreus-Evers, A., Nilsson, T., Yngve, A., & Salumets, A. (2010). Folate-mediated one-carbon metabolism and its effect on female fertility and pregnancy viability. Nutrition Reviews, 68(2), 99-113. doi:10.1111/j.17534887.2009.00266.x
Lei, W., Gao, Y., Liu, D., & Chen, Q. (2020). Effects of inositol and alpha lipoic acid combination for polycystic ovary syndrome. Medicine (Baltimore), 99(30), 20696. doi:10.1097/ MD.0000000000020696
Masharani, U., Gjerde, C., Evans, J., Youngren, J., & Goldfine, I. (2010). Effects of Controlled-Release Alpha Lipoic Acid In Lean, Nondiabetic Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology, 4(2), 359-364. doi:10.1177/193229681000400218
Milunsky, A., Jick, H., Jick, S., Bruell, C., Maclaughlin, D., Rothman, K., & Willett, W. (1989). Multivitamin/Folic Acid Supplementation in Early Pregnancy Reduces the Prevalence
of Neural Tube Defects. JAMA, 262(20), 2847-2852. doi:10.1001/ jama.1989.03430200091032
National Center for Environmental Health (U.S). Division of Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities. (1992). Recommendations for the Use of Folic Acid to Reduce the Number of Cases of Spina Bifida and Other Neural Tube Defects. MMWR. Recommendations and reports : Morbidity and mortality weekly report. Recommendations and reports / Centers for Disease Control, 41(14), 1-7.
Nestler, J., Jakubowicz, D., Reamer, P., Gunn, R., & Allan, G. (1999). Ovulatory and Metabolic Effects of d-Chiro-Inositol in the Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. The New England Journal of Medicine, 340, 1314-1320. doi:10.1056/NEJM199904293401703
Nordio, M., Bascaiani, S., & Camajani, E. (2019). The 40:1 myoinositol/D-chiro-inositol plasma ratio is able to restore ovulation in PCOS patients: comparison with other ratios. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 23, 5512-5521. Papaleo, E., Unfer, V., Baillargeon, J., De Santis, L., Fusi, F., Brigante, C., . . Ferrari, A. (2007). Myo-inositol in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome: A novel method for ovulation induction. Gynecological Endocrinology, 23(12), 700-703. doi:10.1080/09513590701672405
Regidor, P., Schindler, A., Lesoine, B., & Druckman, R. (2018). Management of women with PCOS using myo-inositol and folic acid. New clinical data and review of the literature. Hormone Molecular Biological Clinical Ivestigation, 34(2). doi:10.1515/ hmbci-2017-0067
DB Pharmaceuticals is a registered, Grade A certified pharmacy under the South African Pharmacy Council (SAPC) – with registration number Y60310.

We are fully compliant with the current South African Health Products Regulatory Authority (SAHPRA) and the Medicines and Related Substances Control Amendment Act, No. 19 of 1976 requirements for Category D – Complementary Medicines.
The manufacturing facility is licensed with the South African Health Products Regulatory Authority (SAHPRA) which is only granted after a positive GMP inspection by the regulator.
The manufacturing plant is further accredited by the South African Pharmacy Council as a pharmacy owner, grading certificate Grade A, and recording of a pharmacy.

DB Pharmaceuticals welcomes SAHPRA’s approach to regulate the manufacture and sale of Complementary Medicines and Health Supplements which we believe will result in a safer, more efficient experience for patients who seek quality natural health products.
Certification of the manufacturing plant also includes a Department of Health Manufacturing Pharmacy certificate and a Certificate of Acceptability for Food Premises and is registered with the South African National Department of Health.
All our products old and new have been developed by our two inhouse responsible pharmacists who have 37 years of experience between them.
Once products and formulations have been researched and developed the formulation is sent to our team of specialist formulary pharmacists at the manufacturing site who review and test formulations against recent research to ensure safety, quality, and efficacy.

36 Sovereign Drive, Route 21 Corporate Park, Irene, Centurion, Gauteng, South Africa 0062 info@fertipilpcos.co.za www.fertipilpcos.co.za Helpline: 012 111 8313 Like