
Rejection of the concept of essence Freedom






The idea of praying for success
Traveling
Career choices
Mortality
Any aspect of self or religious reflection


Promotes individuality

Empowers and motivates individuals

Self improvement
Authenticity is promoted
Values and principles

Name the two key existentialist philosophers mentionned in the presentation.
When did existentialism firstly emerge?
Explain “the absurd” in an existentialist context.
Name the most important branch of the philosophy.

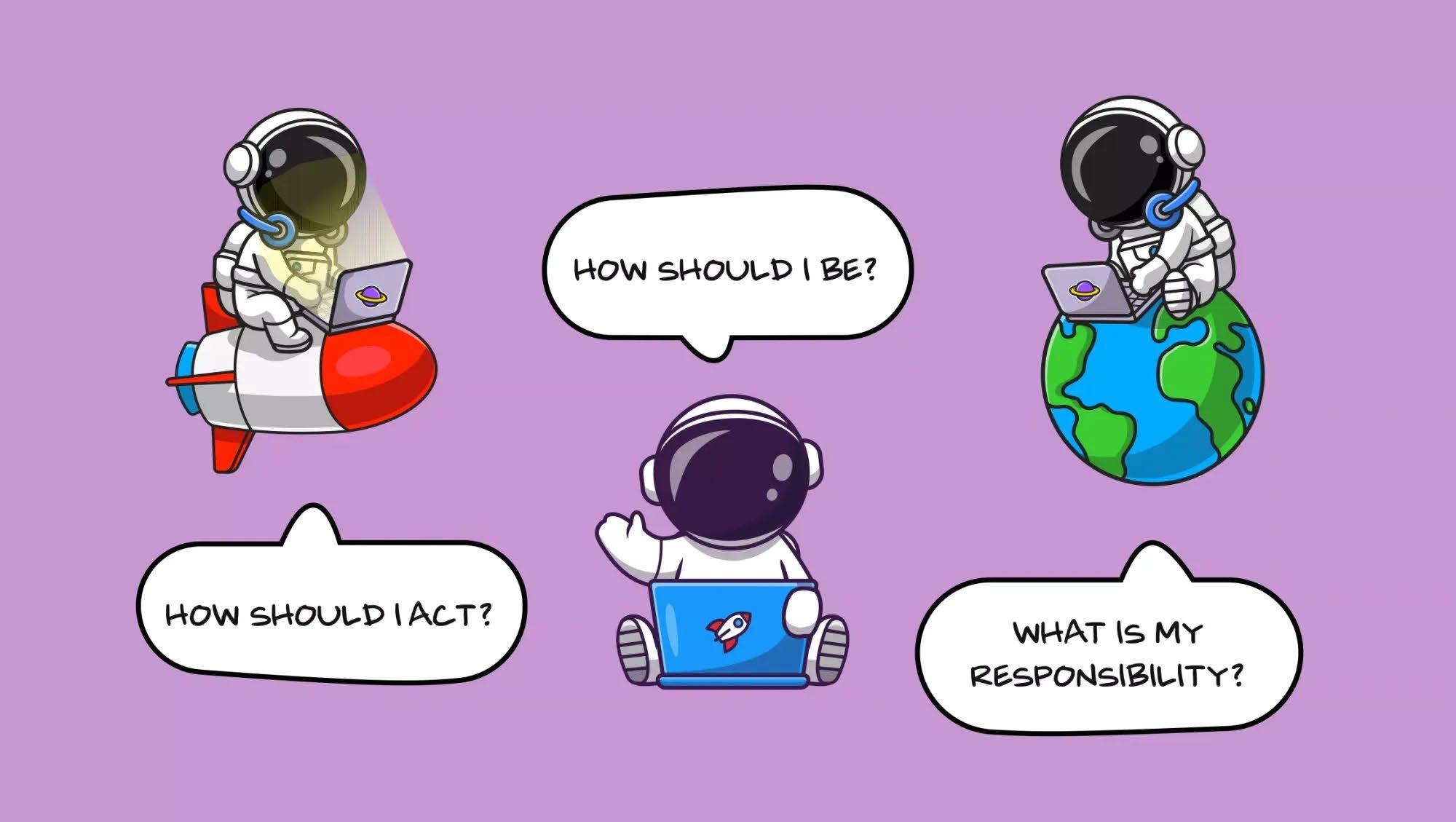
■ Human beings are responsible for themselves


■ Nothing is predetermined
■ “There is no reality except in action”
■ Existence precedes essence
■ Hobbies

■ Freedom of expression

■ Travel and exploration



■ Liberating
■ Empowering
■ Individuality
■ Responsibility
■ Lack of structure
■ Can often be negative
■ Are existentialist principles present throughout our daily lives?
■ What is the meaning of ‘existence precedes essence’?
■ Who said “we are condemned to be free”?
■ What do you think is meant by ‘there is no reality except in action’?
■ https://thomas-oppong.medium.com/jean-paul-sartre-existence-precedes-essenceexperience-life-on-your-own-terms-21f2a09d32f5
■ https://ubyssey.ca/culture/existentialism-for-everyday -life/
■ https://helpfulprofessor.com/existentialism-in-education/
■ https://www.academia.edu/33977495/Strengths_of_Existentialism_Weaknesses_o f_Existentialism_Sartres_Theory_Appealing


• The 3rd approach
•
• Character Based
“The quest to understand and live a life of moral character”
• Acting in accordance with a virtue and being in the correct mental state
• One virtuous action, doesn’t make a person virtuous - Habits leading to choices
•

According to Aristotle, by honing virtuous habits, when faced with difficult decisions, we are likely to make the morally correct one

• Contrasting other approaches – no specific rules
• Answers bigger question –
“What kind of life do I want to live” or “What is a good life” and “How can I be consistent in my moral actions”
When can this be applied?
• Virtue ethics can be applied to basically any decision

• Since it doesn’t have specific rules, it is always relevant
• Some examples are: Loyalty, Courage, Honesty, Respect, Friendliness and many more
• Can be hard to be consistent
• No rules to follow – can lead to inconsistencies
• Works on character development rather than following rules

1. Who was considered the developer of Virtue Ethics
2. True or False – When using a Virtue Ethic approach we choose an extreme
3. According to *the answer to question one* , what does one need to do to become virtuous
• Born on the 28th of June 1712 in Geneva

• He was a philosopher during the enlightenment period
• In 1762, he published his work on social contract theory
• He advocated for popular sovereignty
 Jean-Jacques Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau

• Foundation of Social Order
• Mutual Consent and Obligations
• Philosophical Roots
• Legitimacy of Government
• Legitimacy of taxation

• Government Accountability
• Legitimacy of Public Education


• Political Legitimacy
• Order and Stability
• Assumption of rationality
• Historical Variability
 1. The name of the philosopher
2. Where he was Born
3. One weakness of Social Contract Theory
1. The name of the philosopher
2. Where he was Born
3. One weakness of Social Contract Theory








Achieving maximum pleasure and happiness is the ultimate goal of life
• Branch of Consequentialism

• Distinctions between consequentialism and hedonism
• People naturally seek pleasure and try to avoid pain
• Utilitarianism
Many people go traveling to new places and try new activities seeking adventure and to experience a sense of adrenaline




Some people find happiness through addictions such as drugs, alcohol and smoking. However, this can be argued to do more harm than good in the long term
Relaxation activities such as massages, hobbies, spas, meditation and exercise can be a key source of pleasure for many people.

The idea of seeking individual happiness is strongly encouraged
Flexible
No one way to follow, its adaptable and subjective
Simple and Straightforward Hedonism is easy for people to understand and use for themselves
Positive psychological impact
Helps to improve the individuals mindsets

Disregards other values

Other moral values such as honesty, generosity and justice aren't considered
May promote extreme behaviours

Dangerous, life threatening situations may arise due to extreme beliefs.
Lacks sufficient guidance

Doesn't give a guide on how to handle morally challenging decisions.
Very subjective
Something that may bring pleasure to one person may bring suffering to someone else.



1. What is the main principle of Hedonism?
2. What is the main difference between Hedonism and Consequentialism?
3. How are Hedonism and Utilitarianism connected?
4. What are some disadvantages of Hedonism?