

Quantum
Computing: Will there Be A Domino Effect?

Industry involvement increases when quantum computing surpasses classical computers on pertinent tasks. Scaled-up application use will lead to commercialization, pending sufficient funding.
Three product categories are involved in quantum technologies, or those based on the ideas of quantum physics: secure quantum communication systems, highly precise quantum sensing devices, and high-performing quantum computing devices. These products make use of the squeezed states, decoherence, entanglement, and superposition phenomena of quantum physics. They are anticipated to find numerous practical uses in the fields of chemical and biological sciences, cryptography, aviation, logistics, financial services, government, and defense.
The craze for quantum computing has spread beyond academic institutions and research facilities. In the previous three years, investments have grown quickly. Over 100 start-ups have emerged in the field as a result of a boom in financing; more than a third of these have an operating product. Startups that have an operational product and have shown early success have raised over $4 billion.
Exhibit 1
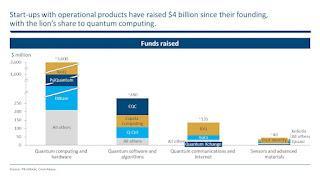
Although quantum computing devices are still small and impractical for commercial use at this point in their development, the field is seeing a surge in start-ups and investor confidence that could lead to quantum computing eventually surpassing classical computing for some applications in the coming years. Quantum computing has the potential to surpass all types of classical computing by the end of this decade in a wide range of applications, such as random-number generation, drug discovery, and chemistry simulation.
Exhibit 2
A number of entities are clearing the way for commercialization as the technology advances (Exhibit 3). Through collaborative research, software businesses and enterprises are investigating quantum algorithms. Full-stack providers put themselves in a position where they may focus on hardware technology while also understanding the needs of end users. By forming alliances or merging with software and algorithm firms that have built relationships with enterprises, hardware-focused companies are moving closer to the end user.
Exhibit 3
Companies are vying to obtain a quantum edge first, but industry consolidation is anticipated. To expedite the creation of a scalable commercial quantum computer, quantum suppliers are developing partnerships with businesses and institutions. Experts and suppliers in the field predict a wave of consolidation to come, addressing the need to co-design next-generation hardware and software for targeted markets, expedite company development and client acquisition, and pool resources for greater economies of scale and top talent. Fernweh has created a maturity index that takes into account a company's current technological condition, the maturity of quantum players, the involvement of major businesses in the ecosystem, and the degree of investor support in order to gauge the progress made toward the mainstream use of quantum computing.
Exhibit 4
There are obstacles in the way of widespread acceptance, though. The most troubling aspect is the limited industry engagement, which is seen in the decreased revenues that a few quantum computing companies have so far experienced (Exhibit 5). Very few Fortune 500 businesses have made financial commitments to work with suppliers of quantum computing. Instead of creating practical applications, companies are more inclined to dedicate internal resources to cooperative research where the main goal is IP creation. Stronger interactions will be required to start a chain reaction of growth and track its consequences.
Exhibit 5
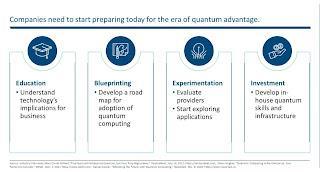
Enterprises and software firms face additional obstacles. Software businesses who choose a hardwareneutral strategy are not focused on creating attractive applications for future hardware platforms that will support quantum-advantage-based applications. The majority of firms will find it difficult to determine which aspects of their operations may profit from quantum technologies. Very few are looking to invest in cultivating internal expertise and quantum talent. In order for quantum computing to expand widely and find commercial use in a wide range of industries, all relevant parties will need to have an impact on how the market is shaped. In order to create appealing applications for realworld use cases, quantum computing providers need to take a more customer-focused approach and embrace a full-stack strategy with increased hardware-software collaboration.
Exhibit 6
View Source:- https://www.ayna.ai/publication/quantum-computing-will-there-be-a-domino-effect
