The project is being implemented with the support of UNICEF Ukraine and with financial support from the Government of Norway.
Implemented by: Partner:





The project is being implemented with the support of UNICEF Ukraine and with financial support from the Government of Norway.
Implemented by: Partner:





Therapist of Neuro and Psychomotor Skills of Developmental Age (TNPEE)
Paola Luttazi
U.O.C. Day Hospital Neurorehabilitation and Adapted Sports Activities
Referent Dott.ssa Della Bella Gessica
OPBG Palidoro
• Main factors influencing psychomotor development
• Factors related to the individual child
• Environmental Adaptation
• New synapses and experiential stimuli
• Neuronal plasticity
• Evaluation of neuropsychomotor development
• Functional ability evaluation
• Video recording procedure
• Adaptive fuctions
• FAMILY CENTERED APPROACH TO INTERVENTATION
Factors related to the individual child
Genetically Predetermined Abilities Musculoskeletal
Physique
Temperament Environmental Adaptation





´The newborn must adapt quickly to new environmental conditions and to autonomously manage neonatal functionsª
He undergoes:
Regulation of the autonomic nervous system
Adaptation to sensory perceptions coming from inside and outside his body
Less contained and confined postural-motor system
Autonomous regulation of behavioral states of sleep-wakefulness
Attachment process
There are "sensitive - vulnerable" periods during development


Ability to reorganize and restructure synapses as a function of changing environmental conditions;

Mechanisms that come into play following brain damage and are the basis of functional recovery;
It represents the basis of learning processes;
It is expressed more in developmental age


´Motor learning is defined as an adaptive modification of motor behavior that leads to the stable acquisition of skills, implemented through a complex perceptual-motor-cognitive process, in the search for a solution to a task that emerges in the interaction between the individual and the environmentª
1995
´Contact with the outside world, living immersed in the surrounding world, from which he receives and to which he is forced to give, is one of the essential conditions for his growthª
G., 1995
´Adapting to the new environment is in fact the first form of learning that the child has to face after birthª
Bottos, 2003
Clinical Objectivity

Instrumental Investigations
Evaluation of Functional Abilities

Evaluation of Adaptive Functions


Systematic observation of the patient


Classification systems
Rating scales



Questionnaires

It is an essential methodological tool for documenting over time the evolution of the child's adaptive functions and his development potential, guiding the definition of enabling/rehabilitative training.
Method widely used both in clinical practice and in scientific research
Allows a longitudinal evaluation of individual paths
Il offers the possibility of grasping and generalising typifying forms of behavior on the basis of wich one can extraxt guidin criteria for a prognostic judgemnt

However, it involves a preliminary subjective judgmetn
Few and non-homogeneous protocols used
Method not always available
It allows for greater discussion with the parentabout the patient’s stregths
Video recording General Movements 0-3 months
Video recording postural motor skills and Alberta Scale compilation
Video recording and evaluation of visual fuctions (orthoptist)
Video recording adaptive fuctions (some facilitated tests GPCI protocol)
Video recording mother-child interaction-relationship (psychologist)


Video recording General Movements 0-3 months
Spontaneous motility
Video perspective Camera n Setting Timing Activity
Full Body View 1 (horizontal plane) Patient positioned on the mat alone, with supervision and safely using nearby cuschions
2 minutes of video recording Spontaneous motility

VIDEO RECORDING PROCEDURE OF POSTURAL MOTOR SKILLS AND FUNCTIONS


18 MONTHS




Day Hospital di Neuroriabilitazione ed Attivit‡ Sportiva Adattata OPBG



Prone, supine and sitting position
Full Body View
(frontal plane)
2 (sagittal plane)
3 (horizontal plane)
Patient positioned on the mat, with supervision and/or interaction from the therapist
Variable activation times based on the patient’s adaptation and spontaneous activation
Posture aimed at motor approach to the object and/or visual auditory attention to a target


Posture supported by visual /auditory attention to a target Supported standing
2 (sagittal plane)
3 (horizontal plane)
Patient kept in an upright posizion by the therapist
Variable activation times based on the patient’s adaptation and spontaneous activation








Origin and year of publication: Canada 1990
Age target: 0-18 months
Test elements: Gross motor skills
Objective: identify delays in gross motor development, assess changes in motor skills over time following the child's maturation or an intervention, provide useful information for the drafting of the rehabilitation program


Administration method: conducted by a specialist

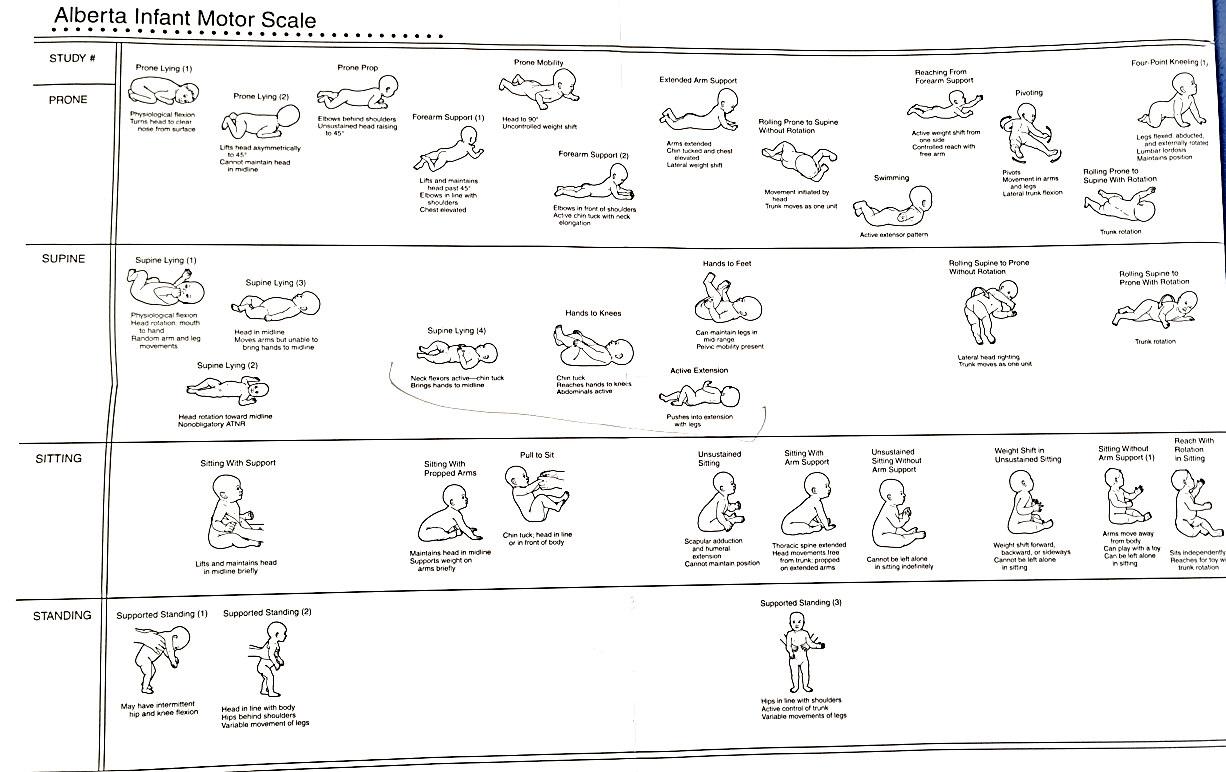


Below are some of the most well-known scales on specific fuctional skills with respect to motor development:
AIMS (Alberta Infant Motor Scale) HINT (The Harris Infant Neuromotor Assessment) EMQ (The Early Motor Questionnaire)
PDMS-II (The Peabody Developmental Motor Scales) GMFM (Gross Motor Function Measure) GMFCS - Gross Motor Function Classification System



OPBG uses parental consent to video and photos, promotes respect for the privacy of the patient and his family


INFANT 6 MONTHS
Right unilateral chianal atresia
Neuropsychiatric consulation in ENT
Total P. ALBERTA ; 5 percentile


INFANT 6 MONTHS
Right unilateral chianal atresia
Neuropsychiatric consulation in ENT
Total P. ALBERTA ; 5 percentile

Infant 11 months
Delayed acquisition of motor stages
Sent by the pediatrician
Total p. ALBERTA: inferiori to 5 percentile


Infatn 9 months
Dealyed acquisition of motor stages
Neuropsychiatric consultation
Total p. ALBERTA: inferior to 5 percentile


Video recording postural motor skills and ALBERTA SCALE compilation
Infant 2 and 15 days
Delay in postural –motor acquisitions
Sent by the pediatrician
Total p. ALBERTA: 5 percentile


Video recording and evaluation of visual fuctions (orthoptist)
Observe and recognize the signs of risk of visual disorders in newborns and infants
DIRECT

- Localization of light source
- visuoal attachment with a cotË gaze
-head movements towards a visual target
- stimulus tracking
-movement of the limbs towards the visual target
-the ´avoidingª or avoidance reaction;
-postural reactions;
- Facial expressions
-blinking of the eyelids



Video recording and evaluation of visual fuctions (orthoptist)
Infant 2 and 15 days
Delay in postural –motor acquisitions
Sent by the pediatrician
Total p. ALBERTA: 5 percentile
Video recording and evaluation of visual fuctions (orthoptist)
Infant 2 and 15 days
Delay in postural –motor acquisitions
Sent by the pediatrician
P. totale ALBERTA: 5 percentile
Video recording and evaluation of visual fuctions (orthoptist)
Vision- Test Lea Gratings
Infant 11 months
Delayed acquisition of motor stages
Sent by the pediatrician
Contrast Sensitivity- Test Hiding Heidi


Video recording adaptive fuctions (some facilitated tests GPCI protocol)

Adaptive functions






Video recording adaptive fuctions (some facilitated tests GPCI protocol)
projection setting required skills
3/4 in front
zoom on the eyes
A: cot or carpet
B: suspended ball with transparent string and stick (length 30 cm, diameter 2 cm)
C: supine
D: stationary object placed on the median line and to the side; then three-dimensional cross movement with slow and fast movements, the bath must be placed first in a vertical position (perpendicular to the pinnacle) then horizontal to the child.
Reaching of the object on the space sectors
Mode of adaptation of the upper limb to the characteristics of the object
Hand eye coordination
Infant 4 months
Dealayed acquisition of motor stages
Sent by pediatrician
Total p. ALBERTA: 5 percentile
3/4 in front
A: On the carpet (near the mother)
B:Interesting gift for the child
C: supine
D:Initially without the object, then move or operate the object placed to the side or above, attracting the child's interest to evoke or facilitate a pivoting, rolling, crawling and possible transition to a sitting posture.
Postural adaptation
Characteristics of motor activity (variability or stereotype, prevalence distribution pattern)
Initiation, finalization and persistence in voluntary activity
Compensatory strategies with possible exploitation of pathologies
Monitoring mode
visual range
projection setting
3/4 in front
3/4 from above (height 1.5 m) distance approximately 1 m zoom on the eyes
A: carpet or floor
B: interesting object
C: sitting
D: place the object to the side, at a distance incompatible with the possibility of catching it while standing still, invite the child to take it to induce movements in the environment ("shuffling", switching to prone and/or all-over positions)
A: chair with non-slip surface; with or without armrests, of a height such that the feet are on the ground; with or without a table spreader at elbow height, possibly with a recess
B: interesting objects related to the child's skills: rattle, doll, telephone, cup with spoon, container with cubes, bottle with screw cap, beads to string, interlocking barrels or matryoshkas, interlocking board, marker with cap and blank sheets of paper, cardboard book, etc.
C: sitting posture that allows the greatest possible freedom in the use of the upper limbs, with a stable trunk and flexion of the hips
D: propose to the child the choice of the sequence of play and spontaneous use of objects; if necessary facilitate the activity with verbal suggestion or imitation of a model of a still object placed on the median line and to the side; subsequently three-dimensional cross movement with first slow then fast movement; the object must be placed first in a vertical position (parallel to the sagittal plane) and then horizontally with respect to the child
required skills
Characteristics of motor activity (variability or stereotypy, prevalence and pattern distribution)
Initiative, finalization and persistence in voluntary activity
Compensatory strategies with possible exploitation of the pathology
Approach method, grasping and releasing
Adaptation (proximal and distal) of the upper limb to the characteristics of the object
Manual preference
Hand-eye coordination
Bimanual coordination Initiative, finalization and persistence of the manager
Practical organization
Problem solving strategies (ability to search for alternatives, to exploit the pathology, etc.)
Verbal and gestural comprehension and communication, contextual
Visual tracking
Video recording adaptive fuctions (some facilitated tests GPCI protocol)
Infant 9 months
Delayed acquisition of motor stages
Sent by pediatrician
Total p. ALBERTA: 5 percentile







Video recording mother-child interaction-relationship

Infant 9 months
Delayed acquisition of motor stages
Sent by pediatrician
Total p. ALBERTA: 5 percentile

Adaptive behavior is a distict but related construct to developmental quotient (DQ)


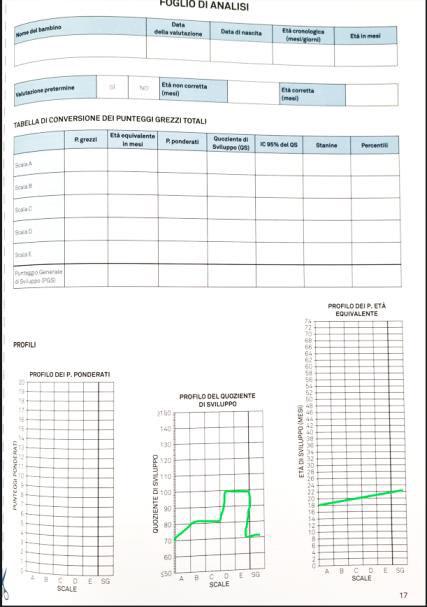


Le Griffiths’ scales of child development third edition (Griffiths III)
Scale A - Learning Basics: aims to explore the basics of learning by analyzing the level of understanding achieved by the child in exploring objects. It also evaluates working memory and executive functions.
Scale B - Language and communication: evaluates language development.
Scale C - Hand-eye coordination: evaluates visual-motor, fine-motor, speedmovement, strength and grip skills.
Scale D - (Personal-social-emotional): development of the self, interaction, autonomy.
Scale E - Gross motor: evaluates postural, gross motor, resistance, balance and rhythm skills.
EMOTIONAL DEVELOPMENT
MOTOR DEVELOPMENT
Parent Support and Enriched Environment
SENSORY DEVELOPMENT
NEUROPSYCHOMOT OR DEVELOPMENT
COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT
SOCIALRELATIONAL DEVELOPMENT

Developmental Disability: Families and Functioning in Child and Adolescence.
•Rosenbaum P.
Frontiers in rehabilitation sciences volume 2, 2021


We believe it is really important to provide educational information material and an exchange of videos/photos provided by the families themselves on moments of daily life.









Il presente documento Ë stato elaborato in n.xx slide da Ospedale Pediatrico Bambino Ges˘ il xxxxxx.
I contenuti sono strettamente riservati; Ë vietata la riproduzione e la divulgazione, anche solo parziale, senza il benestare scritto di Ospedale Pediatrico Bambino Ges˘.