
1 minute read
Design I Process
The site is located in a rich natural environment, so the ground was the first factor in starting the design process. Putting any new mass on the site will affect the ecosystem; after studying variations of manipulating the site, it was concluded that elevating the building off the ground has the least impact on the ecosystem. This idea was introduced in 1920 by Le Corbusier. His iconic Villa Savoye is a paradigmatic example of the use of pilotis that preserves the natural terrain and enables the creation of free space with a greater connection between public spaces and the private sphere of the building(Corbusier, 1998).

Advertisement
Elevating the living space off the ground benefits the design in several ways:
1. It eliminates the need for a concrete slab on the ground floor.
2. It increases the privacy of residents by limiting the view of the houses from the ground level.
3. It has the minimum intervention to the ecosystem and reserves more free space on the ground.
4. The vibration coming from the motorway does not convey to the living space, and followingly it reduces the sound pollution .
The first conceptual 1:1 model was made based on the elevating idea; the model consists of three elements: ground, piles, and the mass representing the living space. In general, it shows the connection between the building and the ground

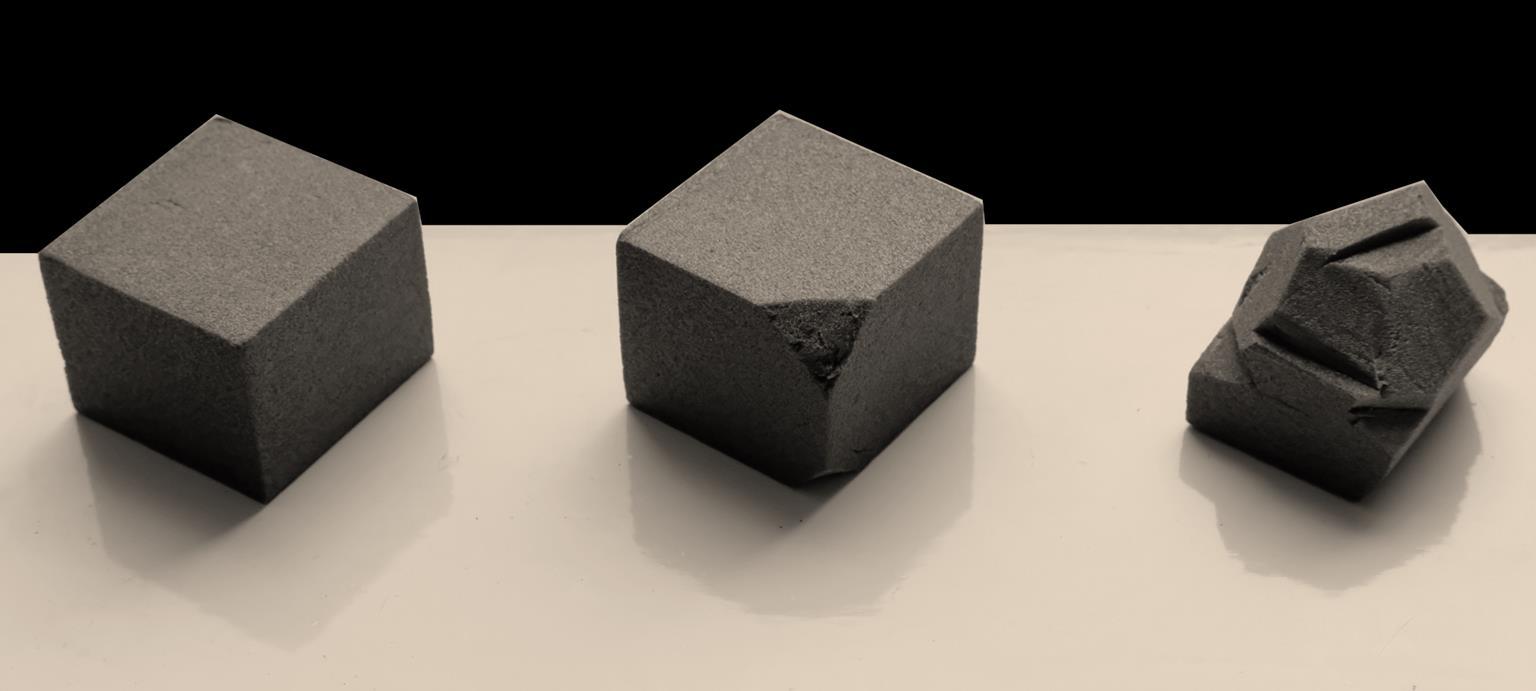



The next step was the formation of the building’s spaces from the mass; according to the fragmentation concept, each space should have its own traits and identity; thus, the house was fragmented into subspaces like the living room and bedrooms, and a pod was allocated to each of them. Then each pod was designed based on its use. For example, the living room’s pod as a gathering space should have a taller height compared to the bedrooms.
As a making technique, carving the initial mass was a method to form the pods. In this way, the scheme can be adapted to various forces like wind and sunlight.










