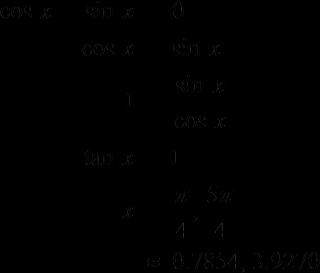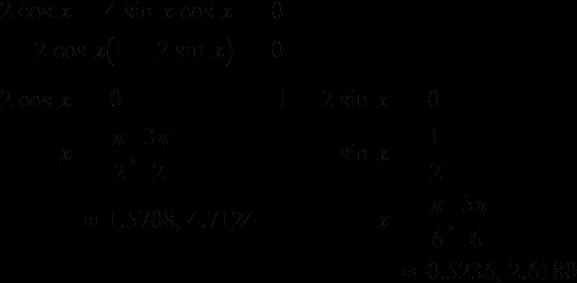Algebra and Trigonometry 10th Edition Larson
1337271179 9781337271172
Full download at: Solution Manual: https://testbankpack.com/p/solution-manual-for-algebra-and-trigonometry10th-edition-larson-1337271179-9781337271172/
C H A P T E R 7
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Section7.1 UsingFundamentalIdentities 584 Section7.2 VerifyingTrigonometricIdentities....................................................591 Section7.3 SolvingTrigonometricEquations......................................................597 Section7.4 Sumand DifferenceFormulas 612 Section7.5 Multiple-Angleand Product-to-SumFormulas................................628 Review Exercises........................................................................................................640 ProblemSolving 651 PracticeTest 658
Analytic Trigonometry
C H A P T E R 7 Analytic Trigonometry Section 7.1 Using Fundamental Identities
584 © 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 2 4 = = − 2 5 3 = − = =
1. tan u 2. csc u 9. sin θ 3 = − , cosθ 4 > 0 θ is in Quadrant IV 3 9 7 3. cot u cosθ = 1 = 3 1 = 16 4 4. csc u tan θ = sin θ = 4 = 3 3 7 5. 1 cosθ 7 7 7 4 6. sin u secθ 1 1 4 = = = = 4 7 7. sec x 5 , tan x < 0 x is in Quadrant II cosθ 7 7 7 4 2 cot θ 1 1 7 = = = cos x = 1 = 1 = 2 tan θ 3 3 7 sec x 5 5 2 cscθ 1 1 4 = = = sin x = 1 2 = 1 4 = 21 25 5 sin θ 3 3 4 2 tan x = sin x 21 = 5 = 21 10. cos θ = , sin θ 3 < 0 θ is in Quadrant IV 2 cos x 2 2 sinθ = 1 2 = 1 4 = 5 5 csc x = 1 = 5 = 5 21 9 3 5 sin x 21 21 tanθ = sinθ = 2 = 5 cot x = 1 = 2 = 2 21 cosθ 2 2 3 tan x 21 21 1 1 3 8. csc x 7 , tan x > 0 x is in Quadrant III. secθ = cosθ = 2 = 2 3 6 cotθ = 1 = 1 = 2 2 5 sin x = 1 = 1 = 6 tanθ 5 5 5 csc x 7 7 6 cscθ 2 = 1 = 1 = 3 3 5
584 © 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 2 7 cos x = 1 6 6 = 1 36 = 13 49 7 sinθ 5 5 5 3 tan x = sin x cos x = 7 = 6 = 13 13 6 13 13 7 sec x = 1 = 1 = 7 = 7 13 cos x 13 13 13 7 cot x = 1 = 1 = 13 tan x 6 6 13
Section 7.1 Using Fundamental Identities 585
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 2 2 2 csc x = 1 + 7 = = cos x
11. tan x = 2 , cos x > 0 x is in Quadrant I. 15. cos x(1 + tan2 x) = cos x(sec2 x) 3 1 cot x = 1 = 1 = 3 = cos x cos2 x tan x 2 2 3 2 4 13 = 1 cos x = sec x sec x = 1 + = 3 3 1 + = 9 3 9 13 Matches (f). cos x 1 1 csc x = 1 + = 1 + = 16. cot x sec x = = = csc x 2 4 2 sin x cos x sin x sin x = 1 = 1 = 2 = 2 13 Matches (a). csc x 13 13 13 sec2 x 1 tan2 x sin2 x 1 2 17. = = = sec2 x cos x = 1 = 1 = 3 = 3 13 sin2 x sin2 x cos2 x sin2 x sec x 13 13 13 3 Matches (e). cos2 (π 2) x sin2 x sin x cot x = 1 = 1 = 3 18. cos x = cos x = sin x = tan x sin x cos x tan x 2 2 3 Matches (d). 12. cot x = 7 , sin x < 0 x is in Quadrant III. 4 19. tanθ cotθ 1 tanθ = tanθ tan x = 1 = 1 = 4 secθ 1 cot x 7 7 4 4 16 65 cosθ = 1 1 sec x = 1 + = 7 2 = 1 + = 49 7 1 + 49 = 65 π cosθ = cosθ 4 16 4 20. cos x sec x = sin x sec x sin x = 1 = 1 = 4 4 65 2 1 csc x 65 65 65 4 = sin x cos x cos x = 1 = 1 = 7 7 65 = tan x sec x 65 65 65 7 21. tan2 x tan2 x sin2 x = tan2 x(1 sin2 x) = tan2 x cos2 x 2 13. sec x cos x = 1 cos x = sin x ⋅ cos 2 x cos 2 x = 1 Matches (c). 22.
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 2 = s i n 2 x sin2 x sec2 x sin2 x = sin2 x(sec2 x 1) 14. cot2 x csc 2 x = (csc 2 x 1) csc 2 x = 1 = sin2 x tan2 x Matches (b). 23. sec x 1 = (sec x + 1)(sec x 1) sec x 1 sec x 1 = sec x + 1 24. cos x 2 = cos x 2 cos2 x 4 (cos x + 2)(cos x 2) = 1 cos x + 2
31. cot2 x + csc x 1 = (csc 2 x 1) + csc x 1
1 sin x
(csc x 1)(csc x + 2) csc x 1 cot x
csc2 x + csc x 2
cos x 32. sin2 x + 3 cos x + 3 = (1 cos2 x) + 3 cos x + 3
cos2 x + 3 cos x + 4
(cos2
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. = 2 586 Chapter 7 Analytic Trigonometry 25. 1 2 cos x + cos x = (1 cos x) 26. sec 4 x tan4 x = (sec 2 x + tan2 x)(sec 2 x tan2 x) 2 4 2 2 ( 2 2 )() = (sin2 x) = sec x + tan x 1 27. 28. = sin4 x cot3 x + cot2 x + cot x + 1 = cot2 x(cot x + 1) + (cot x + 1) = (cot x + 1)(cot2 x + 1) = (cot x + 1)csc 2 x sec3 x sec2 x sec x + 1 = sec2 x(sec x 1) (sec x 1) = (sec2 x 1)(sec x 1) = tan2 x(sec x 1) = sec2 x + tan2 x 29. 3 sin2 x 5 sin x 2 = (3 sin x + 1)(sin x 2) 38. cot u sin u + tan u cos u = cos u(sin u)+ sin u (cos u) 30. 6 cos 2 x + 5 cos x 6 = (3 cos x 2)(2 cos x + 3) sin u = cos u + sin u cos u 2 2 2
39.
=
2
2
=
2
2 2 2 =
=
=
2
=
=
x 3 cos x 4) = (cos x + 1)(cos x 4) 40. cos2 y 1 sin y 1 sin2 y = 1 sin y = (1 + sin y)(1 sin y) 1 sin y = 1 + sin y 33. tanθ cscθ = sinθ ⋅ 1 = 1 = secθ 41. (sin x + cos x)2 = sin2 x + 2 sin x cos x + cos2 x = (sin2 x + cos2 x) + 2 sin x cos x cos θ sinθ cosθ = 1 + 2 sin x cos x 34. tan( x) cos x = tan x cos x sin x cos x cos x = sin x 42. (2 csc x + 2)(2 csc x 2) = 4 csc 2 x 4 = 4(csc2 x 1) = 4 cot2 x 35. sin φ(cscφ sinφ) = (sin φ) 1 sin2 φ 43. 1 + 1 = 1 cos x + 1 + cos x sinφ 1 + cos x 1 cos x (1 + cos x)(1 cos x) = 1 sin2 φ = cos2 φ = 2 1 cos2 x 36. cos x(sec x cos x) = cos x 1 cos x = 2 cos x sin2 x = 1 cos2 x = sin2 x 44. = 2 csc2 x 1 1 = sec x 1 (sec x + 1)
cos x = cos
x tan
x
(cos
x) sin x
sin
x
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 37. sin β tan β + cos β = (sin β) sin β + cos β cos β sec x + 1 sec x 1 (sec x + 1)(sec x 1) = sec x 1 sec x 1 sin2 β = + cos β cos2 β cos β sec2 x 1 = 2 sin2 β + cos2 β = cos β tan2 x 1 = 2 2 = 1 tan x cos β = sec β = 2 cot2 x
Section 7.1 Using Fundamental Identities 587
45. cos x cos x = cos x(1 sin x) cos x(1 + sin x) 1 + sin x 1 sin x (1 + sin x)(1 sin x) = cos x sin x cos x cos x sin x cos x (1 + sin x)(1 sin x) = 2sin x cos x 1 sin2 x = 2sin x cos x cos 2 x = 2sin x cos x = 2 tan x
sin x 1 + cos x sin x + = 1 cos x sin x(1 cos x) + sin x(1 + cos x) (1 + cos x)(1 cos x) sin x sin x cos x + sin x + sin x cos x = (1 + cos x)(1 cos x) 2 sin x = 1 cos 2 x
sin x = sin
x
cos x + 1 + sin x = cos x + (1 + sin x)
1 + sin x cos x cos x(1 + sin x)
(
x tan x)
51. y = tan x + 1 1 sec x + csc x sin x + 1 cos x = 2 + 2 sin x cos x(1 + sin x)
cos2 x + 1 + 2 sin x + sin2 x = cos x(1 + sin x)
= 1 + 1 cos x sin x sin x + cos x = cos x(1 + sin x)
2(1+ sin x)
= cos x sin x + cos x = 2 cos x = 2 sec x
sin x cos x sin x + cos x sin x cos x = cos x sin x + cos x
= sin x 2 (1 + cos y)(1 cos y) = 1 cos y = 1 + cos y
©
Cengage Learning. All
not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
2018
Rights Reserved. May
2
2
2
47.
2
2
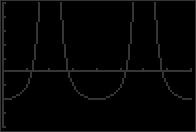
50.
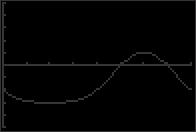
tan
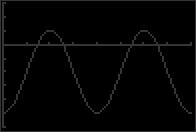
tan x 2 2 tan
+
2
2
5
) = 1 = 5
46.
= sin x = 2 csc x
sec2 x tan x = tan
x sec
x
5 ⋅ tan x sec x = 5(tan x sec x)
x tan x = 1 = cot x
x
sec x tan x sec x tan
x sec
x
(tan x sec x
sec
48.
49. sin2 y 1 cos y 1 cos2 y = 1 cos y 2π 2π 2
588 Chapter 7 Analytic Trigonometry
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
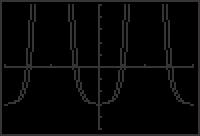
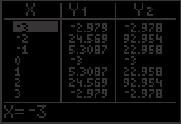
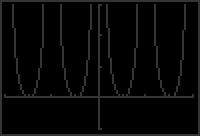
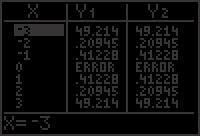
52. y1 = 1 1 cos x = tan x sin x cos x 5 1 1 1 cos x cos x = sin x cos x sin x cos x sin x 2π 2π 1 cos2 x sin2 x sin x = = = = tan x 5 sin x cos x sin x cos x cos x 53. Let x = 3 cos θ 55. Let x = 2 sec θ 9 x2 = = = 9 (3 cosθ)2 9 9 cos2 θ 9(1 cos2 θ) x2 4 = = = (2 secθ)2 4 4(sec2 θ 1) 4 tan2 θ = 9 sin2 θ = 3 sin θ = 2 tan θ 54. Let x = 7 sin θ 56. Let 3x = 5 tan θ 2 2 49 x2 = 49 (7 sin θ)2 9x + 25 = (3x) + 25 = 49 49 sin2 θ = 49(1 sin2 θ) = 49 cos2 θ = (5 tan θ)2 + 25 = 25 tan2 θ + 25 = 25(tan2 θ + 1) = 7 cosθ = 25 sec2 θ 57. Let x = 2 sin θ 4 x2 = 2 4 (2 sin θ)2 = 2 4 4 sin2 θ = 2 = 5 secθ 4(1 sin2 θ) = 2 4 cos2 θ = 2 2 cosθ = 2 cosθ = 2 2 2 sin θ = 1 cos2 θ = 2 2 1 = ± 2 2
Section 7.1 Using Fundamental Identities 589

© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 2
58. x = 10 cosθ tan t 5 3 = 5 3 = 100 x2 100 (10 cosθ)2 63. ln tan t ln(1 cos2 t) = ln 1 cos2 t = ln tan t 5 3 = 5 3 = 100(1 cos2 θ) 100 sin2 θ sin2 t = ln sin t cos t 1 sin2 t 5 3 = 10 sin θ = ln 1 cos t sin t sin θ = 5 3 = 3 10 2 2 = ln sec t csc t cosθ = 1 sin2 θ = 3 1 1 = 64. ln(cos2 t) + ln(1 + tan2 t) = lncos2 t(1 + tan2 t) 2 2 = ln cos2 t sec2 t 59. sin θ = 1 cos2 θ 1 = lncos 2 t ⋅ Let y1 = sin x and y2 = 1 cos2 x, 0 ≤ x ≤ 2π cos t y1 = y2 for 0 ≤ x ≤ π = ln(1) = 0 So, sin θ = 2 1 cos2 θ y2 for 0 ≤ θ ≤ π 65. μW cosθ μ = W sin θ W sin θ = W cosθ = tan θ 0 2π y1 66. sec x tan x sin x = 1 sin x sin x cos x 2 cos x sin x = sin x cos2 x 60. secθ = 1 + tan2 θ sin x sin x cos 2 x Let y = 1 and y = 1 cos x 2 1 + tan2 x, 0 ≤ x ≤ 2π. = cos 2 x sin x(1 cos 2 x) y1 = y for 0 ≤ x < π and 3π 2 2 2 < x ≤ 2π = cos 2 x sin x sin2 x = So, secθ = 1 + tan2 θ for 0 ≤ θ < π 2 and cos2 x = sin x tan2 x 3π < θ 2 < 2π 4 y2 0 2π y1 67. True. tan u = sin u cos u 61. ln sin x + ln cot x 4 = ln sin x cot x = ln sin x ⋅ cos x sin x = ln cos x
False. A cofunction identity can be used to transform a tangent function so that it can be represented by a cotangent function.
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. cot u = cos u sin u s e c u = 1 cos u csc u = 1 sin u 62. ln cos x ln sin x = ln cos x sin x = ln cot x 68.
69. As x → π , tan x → ∞ and cot x → 0. 2
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. = 1 + a 2
Chapter 7 Analytic Trigonometry 70. As x → π + , sin x → 0 and csc x = 1 → ∞ . sin x 72. Let u = a tan θ, then 71. cos( θ) ≠ cosθ cos( θ) = cosθ The correct identity is sin θ = cos( θ) sin θ cosθ a2 + u2 = = = = a 2 + (a tan θ)2 a2 + a2 tan2 θ a2(1 + tan2 θ) a2 sec2 θ = tan θ = a secθ. 73. Because sin2 θ + cos2 θ = 1, then cos 2 θ = 1 sin2 θ cos θ = ± 1 sin θ tan θ = sin θ = sin θ cot θ cos θ ± = cos θ = ± sin θ 1 sin2 θ 1 sin2 θ sin θ sec θ = 1 = 1 csc θ cos θ 1 = sin θ ± 1 sin2 θ 74. To derive sin2 θ + cos2 θ = 1, let sin θ = a and cos θ = b a2 + b2 a2 + b2 2 2 a b a b2 So, sin2 θ + cos2 θ = + = + a2 + b2 a2 + b2 a2 + b2 a 2 + b2 = a2 + b2 a2 + b2 = 1. To derive 1 + tan2 θ = sec2 θ, let tan θ = a and sec θ b a 2 + b2 = b So, 1 + tan2 θ 2 b a 2 = 1 + = b2 b2 + a2 b2 2 2 a2 + b2 a2 + b2 = = b2 b = sec2 θ To derive 1 + cot2 θ = csc2 θ, let cot θ = b and csc θ a a 2 + b2 = . a
590
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. = 1 + b So, 1 + cot2 θ 2 a = 1 + b2 a2 2 a2 + b2 a2 + b2 = = a 2 a 2 2 a2 + b2 = = csc2 θ a Answers will vary.
Section 7.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 1 1 + sin θ
Verifying Trigonometric Identities
75. sec θ(1 + tan θ) sec θ + csc θ cos θ cos θ = 1 + 1 cos θ sin θ cos θ + sin θ = cos2 θ sin θ + cos θ sin θ cos θ = sin θ + cos θ sin θ cos θ cos2 θ sin θ + cos θ = sin θ cos θ
Section 7.2
591
1. identity 2. conditional equation 3. tan u 16. cos (π 2) x sin (π 2) x π sin x = = tan x cos x 1 4. cot u 17. sin t csc 2 t = sin t sec t = sin t cos t 5. sin u sin t = cos t = tan t 6. cot2 u 7. csc u 18. sec2 y cot2 π 2 y = sec2 y tan2 y = 1 8. sec u 19. 1 + 1 = cot x + tan x 9. tan t cot t = sin t cos t cos t = 1 sin t tan x cot x tan x cot x = cot x + tan x 1 10. tan x cot x cos x = 1 = sec x cos x 20. = tan x + cot x 1 1 = csc x sin x 11. (1 + sin α)(1 sin α) = 1 sin2 α = cos2 α sin x csc x sin x csc x csc x sin x = 12. cos2 β sin2 β = cos2 β (1 cos2 β) = 2
2
1 = csc x sin x 13. 14. cos2 β sin2 β sin2 α sin4 α = (1 sin2 β) sin2 β = 1 2 sin2 β = sin2 α(1 sin2 α) = (1 cos2 α)(cos2 α) = cos2 α cos4 α 21. 1 + sin θ cosθ + cosθ = 1 + sin θ = = (1 + sin θ)2 + cos 2 θ cosθ(1 + sin θ) 1 + 2 sin θ + sin2 θ + cos2 θ cosθ(1 + sin θ) 2 + 2 sin θ cosθ(1 + sin θ) 2(1+ sin θ) 15. tan π 2 θ tan θ = cot θ tan θ = cosθ(1 + sin θ)
cos
β 1
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 1 = tan θ tan θ = 1 = 2 cosθ = 2 secθ
cosθ cot θ cosθ cot θ (1 sin θ)
1
1 sin θ
cosθ cosθ sin θ
1
sin θ sin θ
25. 26. 27.
sec y cos y = cos y = 1 cos y cot2 y(sec2 y 1) = cot2 y tan2 y = 1 tan = ( ) = sin θ tan θ 2 θ sin θ cosθ tan θ = sin θ(1 sin θ) secθ 1 cosθ = 1 sin θ sin θ(1 sin θ) = 1 sin θ
=
23. 1 1 + = cos x + 1 cos x 1 =
cos x 1 + cos x + 1 (cos x + 1)(cos x 1)
2 cos x cos2 x 1
28. cot3 t csc t cot t cot2t = csc t cot t(csc2 t 1) = csc t cos t csc2 t 1 sin t
= 1 sin t
= cos t sin t csc2 sin t t 1) = sin2 x = cos t(csc2 t 1)
2 cos x
= 2 csc x cot x cos x cos x = cos x(1 tan x) cos x
1 tan x 1 tan x
= cos x tan x 1 tan x cos x(sin x cos x) cos x = ⋅ 1 (sin x cos x)
sec2 β = tan β
= 2 1 cos x 1 1 + tan2 β sin x sin x 29. tan β + tan β = tan β 24.
=
sin x cos x
1
= secθ 1 ⋅ secθ secθ(secθ 1) = = secθ
t cos
= = =
t
sec x cos x = cos x
cos
©
Cengage
All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
2018
Learning.
( ) (
592 Chapter 7 Analytic Trigonometry
22. 1 sin θ 1 = =
+ sin θ ⋅ 1 sin θ cos2 θ sin θ + sin2 θ
cscθ
2
2
2
1 31.
1
2
32.
x
= sin x cos x cos x sin x sin x cos x
cos x
30. secθ
1 cosθ 1 (1 secθ) secθ secθ 1 cot2 t cos2 t sin
t 1 sin
33.
csc t 1 sin t sin t sin t cos x
x =
sin
cos x + sin x tan x = cos x + sin x
cos x
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. c o s 2 x + s i n 2 x cos x sin2 x = cos x = cos x = sin x sin x = 1 cos x = sec x cos x = sin x tan x
cot x cot y
42. cos x cos y + sin x sin y = (cos x cos y)(cos x + cos y) + (sin x sin y)(sin x + sin y)
sin x + sin y cos x + cos y (sin x + sin y)(cos x + cos y) cos2 x cos2 y + sin2 x sin2 y
sin x + sin y)(cos x + cos y)
cos2 x + sin2 x) (cos2 y + sin2 y)
sin x + sin y)(cos x + cos y)
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
34. cot x tan x = cos x sin x sin x cos x cos2 x sin2 x = sin x cos x 1 sin2 x sin2 x = sin x cos x 1 2 sin2 x = sin x cos x 1 1 2 sin2 x = cos x sin x 1 1 2 sin2 x = cos x sin x sin x = sec x(csc x 2 sin x) cot x cos x sin x cos2 x 1 sin2 x 1 sin2 x 35. = = = = = csc x sin x 36. sec x csc( x) sec( x) 1 cos x 1 sin( x) = 1 cos( x) cos( x) sin x sin x sin x sin x = sin( x) 37. = cos x sin x = cot x sin1 2 x cos x sin5 2 x cos x = sin1 2 x cos x(1 sin2 x) = sin1 2 x cos x cos 2 x = cos 3 x sin x 38. sec 6 x(sec x tan x) sec 4 x(sec x tan x) = sec 4 x(sec x tan x)(sec 2 x 1) = sec 4 x(sec x tan x) tan2 x = sec 5 x tan3 x 39. (1 + sin y) 1 + sin( y) = (1 + sin y)(1 sin y) = 1 sin2 y 41. 1 + sin θ = 1 sin θ 1 + sin θ 1 sin θ 1 + sin θ 1 + sin θ 40. = cos2 y 1 + 1 tan x + tan y = cot x cot y
(1 +
θ)2 = 1 sin2 θ (1 + sin θ)2 = 1 tan
cos 2 θ cot
1 + sin θ = = cot
cot
cosθ
Section 7.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities 593
sin
x tan y 1 1 1 cot x cot y
x cot y
y + cot x
x cot y 1
=
=
43. = 0
(
(
(
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. cot( x) ≠ cot x 44. The first line claims that sec( θ ) = sec θ and The correct substitution is cot( x) = cot x sin( θ) = sin θ The correct substitutions are 1 + cot( x) = cot x cot x = 0 tan x sec( θ) = sec θ and sin( θ) = sin θ

© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. ( )( ) ( 2 2 ) 594
45. (a) 3 2π 2π 1 Identity (b) Identity (c) 1 + cot2 x cos2 x = csc2 x cos2 x = 1 cos2 x = cot2 x sin2 x 3 46. (a) (b) 2π 2π 1 Identity Identity (c) csc x(csc x sin x) + sin x cos x + cot x = csc2 x csc x sin x + 1 cos x + cot x sin x sin x = csc2 x 1 + 1 cot x + cot x = csc2 x 47. (a) 5 y2 y1 2π 2π 1 Not an identity (b) Not an identity (c) 2 + cos2 x 3 cos4 x = (1 cos2 x)(2 + 3 cos2 x) = sin2 x(2 + 3 cos2 x) ≠ sin2 x(3 + 2 cos2 x) 48. (a) π 5 y1 y2 π (b) 5 Not an identity sin4 x sin2 x Not an identity (c) tan4 x + tan2 x 3 = + 3 cos4 x 1 cos2 x sin4 x = cos2 x cos2 x + sin2 x 3 1 sin4 x + sin2 x cos2 x = cos 2 x cos2 x 3 1 sin2 x = sin x + cos x 3 cos2 x cos2 x 1 sin2 x = cos 2 x cos 2 x 1 3
Chapter 7 Analytic Trigonometry
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. = sec2 x tan2 x 3 ≠ sec2 x(4 tan2 x 3)

© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. . cos2 x ( ) Section 7.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities 595 49. (a) 3 50. (a) 3 y1 2π 2π 2 2 y2 3 5 (b) Identity (b) Not an identity (c) Identity 1 + cos x (1 + cos x)(1 cos x) = (c) Not an identity cot α is the reciprocal of cscα + 1 sin x sin x(1 cos x) cscα + 1 cot α 1 cos2 x = sin x(1 cos x) sin2 x = sin x(1 cos x) sin x = 51. They will only be equivalent at isolated points in their respective domains So, not an identity. tan3 x sec2 x tan3 x = tan3 x(sec2 x 1) = tan3 x tan2 x 5 1 cos x = tan x 2 4 52. (tan2 x + tan4 x) sec2 x = sin x sin x 1 + cos 4 x cos 2 x 1 = sin2 x + sin4 x cos4 x cos2 x 1 sin2 x cos2 x + sin4 x = cos4 x cos2 x 1 sin2 x cos 2 x + sin2 x = cos4 x cos2 x 1 sin2 x = 1 = sec4 x tan2 x cos4 x cos2 x 53. (sin2 x sin4 x) cos x = sin2 x(1 sin2 x) cos x = sin2 x cos2 x cos x = sin2 x cos3 x 54. sin4 x + cos4 x = sin2 x sin2 x + cos4 x = (1 cos2 x)(1 cos2 x) + cos4 x = 1 2 cos2 x + cos4 x + cos4 x = 1 2 cos2 x + 2 cos4 x 55. sin2 25° + sin2 65° = sin2 25° + cos2 (90° 65°) = sin2 25° + cos2 25° = 1 56. tan2 63° + cot2 16° sec2 74° csc2 27° = tan2 63° + cot2 16° csc2(90° 74°) sec2(90° 27°) = tan2 63° + cot2 16° csc2 16° sec2 63°
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. = ( t a n 2 6 3 ° s e c 2 6 3 ° ) + ( c o t 2 1 6 ° c s c 2 1 6 ° ) = 1 + ( 1 ) = 2
63. False tan x2 = tan(x ⋅ x) and

2 x = (tan x)(tan x), tan x
64. True. Cosine is an even function,
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 1 596 Chapter 7 Analytic Trigonometry 57. Let θ = sin 1 x sin θ = x = x 60. Let θ = cos 1 x + 1 cosθ = x + 1 1 2 2 1 x 2 4 (x + 1)2 θ 1 x2 θ x + 1 From the diagram, From the diagram, tan(sin 1 x) = tan θ = x . 1 x + 1 4 (x + 1)2 1 x2 tancos 2 = tan θ = x 1 . 58. Let θ = sin 1 x sin θ = x = x + 1 cos x 1 61. cos x csc x cot x = cos x sin x sin x 1 = cos x1 sin2 x x θ 1 x2 = cos x(1 csc 2 x) = cos x(csc2 x 1) = cos x cot2 x From the diagram, cos(sin 1 x) = cosθ 1 x 2 = = 1 1 x2 62. (a) h sin(90° θ) sin θ = h cosθ = h cot θ sin θ 59. Let θ = sin 1 x 1 sin θ = x 1 . (b) 15° 30° 45° 60° 75° 90° s 18.66 8.66 5 2.89 1.34 0 4 4 4 x 1 (c) Maximum:
Minimum:
(d) Noon θ
15°
90°
16 (x 1)2 From the diagram, tansin 1 x 1 = tan θ x 1 = tan
2
≠ tan2 x π π 4 16 (x 1)2 cosθ = cos θ 2 = cos π 2 θ 2 = sin θ
65. False. For the equation to be an identity, it must be true for all values of θ in the domain
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated,
publicly
or posted to a
accessible website, in whole or in part.
Section 7.3 Solving Trigonometric Equations 597
Section 7.3 Solving Trigonometric Equations
The equation is not an identity because it is only true when cos
= 0 or cos θ = 1 So, one angle for which
This equation is not an identity because it is only true
when tan
= 0 So, one angle for which the equation
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 2 b 2 b 2 2 2
66. If sin θ = a , sec θ = c , and 68. tan θ = sec2 θ 1 c b True identity: tan θ = ± sec 2 θ 1 a2 + b2 = c2 a2 c = c2 b2 , then tan θ = sec2 θ 1 is not true for π 2 < θ < π sec2 θ 1 1 = or 3π 2 < θ < 2π So, the equation is not true for sec2 θ c c2 θ 69. = 3π 4. 1 cosθ = sin θ b2 1 = c 2 (1 cosθ) = (sin θ) 2 2 b2 1 2 cosθ + cos θ = sin θ c2 b2 = b2 c2 1 2 cosθ + cos2 θ 2 cos2 θ 2 cosθ = 1 cos2 θ = 0 b2 c 2 b2 b2 = b2 c2 c2 b2 2 cosθ(
= 0
cosθ 1)
the equation
π = c2 a 2 70. = c2 1 + tan θ (1 + tan θ)2 2 = secθ = (secθ)2 a 2 2 = 1 + 2 tan θ + tan θ = sec θ c = sin2 θ 1 + 2 tan θ + tan2 θ 2 tan θ = 1 + tan2 θ = 0 67. Because sin2 θ = 1 cos2 θ, then tan θ = 0 sin θ = ± 1 cos 2 θ; sin θ ≠ 1 cos 2 θ if θ
θ
is not true is
lies in Quadrant III or IV.
θ
θ
π
One such angle is
= 7
4 is not true is π 6
1. isolate 6. sec x 2 = 0 2. general 3. quadratic (a) x = π 3 sec π 2 = 1 2 4. extraneous 5. ta n x
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 3 = 0 3 cos(π 3) = 1 2 = 2 2 = 0 1 2 (a) x = π 3 tan π 3 = 3 3 = 0 (b) x = 5π 3 sec 5π 2 = 1 2 (b) 3 x = 4π 3 3 cos(5π 3) = 1 2 = 2 2 = 0 1 2 tan 4π 3 = 3 3 3 = 0
598 Chapter 7 Analytic Trigonometry
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. = 2 cos 2 2 2 2 cos2 2 2 =
7. 3 tan2 2x 1 = 0 10. csc4 x 4 csc2 x = 0 (a) x = π 12 2 3 tan 2 π 1 = 3 tan2 π 1 (a) x = π 6 csc 4 π 4 csc2 π 1 4 = 12 6 4 2 2 1 3 1 6 6 sin (π 6) 1 4 = sin (π 6) 3 (1 2)4 (1 2)2 (b) = 0 x = 5π 12 2 (b) x = 5π 6 = 16 16 = 0 3tan 2 5π 1 = 3 tan2 5π 1 csc4 5π 4 csc 5π 1 4 12 6 = 4 2 2 1 = 3 1 6 6 sin (5π 6) 1 4 = sin (5π 6) 3 (1 2)4 (1 2)2 = 0 8. 2 cos2 4x 1 = 0 11. 3 csc x 2 = 0 = 16 16 = 0 (a) x = π 16 π π 4 1 = 2 cos 1 3 csc x = 2 csc x = 2 3 16 4 2 x = π + 2nπ 3 = 2 2 1 2 (b) x = 3π 1 = 2 1 = 1 1 = 0 12. tan x + or x = 2π 3 3 = 0 + 2nπ 16 3π 3π 4 1 = 2 cos 1 tan x = 3 x = 2π + nπ 16 4 2 2 = 2 1 3 13. cos x + 1 = cos x 2 2 cos x + 1 = 0 = 1 1 = 0 2 cos x 1 2 x = 2π + 2nπ or x = 4π + 2nπ
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 2 9. 2 sin2 x sin x 1 = 0 3 3 (a) x = π 2 2 sin2 π sin π 1 = 2(1)2 1 1 14. 3 sin x + 1 = sin x 2 sin x + 1 = 0 1 2 2 sin x = = 0 7π (b) x = 7π 6 2 sin2 7π sin 7π 1 2 1 = 2 1 1 x = + 2nπ or 6 x = 11π + 2nπ 6 6 6 2 2 = 1 + 1 1 2 2 = 0
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Solving Trigonometric
15. 3 sec2 x 4 = 0 20. (2 sin2 x 1)(tan2 x 3) = 0 sec2 x = 4 3 2 sin2 x 1 = 0 or tan2 x = 3 sec x = ± 2 3 sin2 x = 1 2 tan x = ± 3 x = π 6 + nπ sin x = ± 1 2 x = π 3 + nπ or x = 5π + nπ sin x = ± 2 x = 2π + nπ 16. 6 3 cot2 x 1 = 0 cot2 x = 1 x = π 4 x = 3π 2 3 + 2nπ + 2nπ 3 cot x = ± 1 3 4 x = 5π 4 x = 7π + 2nπ + 2nπ x = π 3 + nπ 4 or x = 2π 3 + nπ 21. cos3 x cos x = 0 cos x(cos2 x 1) = 0 17. 4 cos2 x 1 = 0 cos x = 0 or cos2 x 1 = 0 cos2 x = 1 4 cos x 1 x = π + nπ 2 cos x = ±1 x = nπ = ± 2 Both of these answers can be represented as x = nπ x = π + nπ or x = 2π 2 + nπ 18. 3 3 2 4 sin2 x = 0 sin2 x = 1 2 22. sec2 x 1 = 0 sec2 x = 1 sec x = ±1 x = nπ sin x = ± 1 2 = ± 2 2 23. 3 tan3 x = tan x 3 x = π + 2nπ 3 tan x tan x = 0 4 x = 3π + 2nπ tan x(3 tan2 x 1) = 0 4 x = 5π 4 x = 7π + 2nπ + 2nπ tan x = 0 x = nπ or 3 tan2 x 1 = 0 tan x = ± x = π 3 3 + nπ, 5π + nπ
Section 7.3
Equations 599
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 4 These answers can be represented as x = π + nπ 24. 6 6 sec x csc x = 2 csc x 19. sin x(sin x + 1) = 0 4 2 sec x csc x 2 csc x = 0 csc x(sec x 2) = 0 sin x = 0 or sin x = 1 csc x = 0 or sec x 2 = 0 x = nπ x = 3π 2 + 2nπ No solution sec x = 2 x = π + 2nπ, 5π + 2nπ 3 3
600 Chapter 7 Analytic Trigonometry
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. =
25. 2 cos2 x + cos x 1 = 0 (2 cos x 1)(cos x + 1) = 0 2 cos x 1 = 0 or cos x + 1 = 0 cos x = 1 cos x = 1 2 x = π + 2nπ, 5π + 2nπ x = π + 2nπ 3 3 26. 2 sin2 x + 3 sin x + 1 = 0 (2 sin x + 1)(sin x + 1) = 0 2 sin x + 1 = 0 or sin x + 1 = 0 sin x 1 2 sin x = 1 x = 3π + 2nπ x = 7π + 2nπ, 11π + 2nπ 2 6 6 27. sec2 x sec x = 2 sec2 x sec x 2 = 0 (sec x 2)(sec x + 1) = 0 sec x 2 = 0 sec x = 2 or sec x + 1 = 0 sec x = 1 x = π + 2nπ, 5π + 2nπ x = π + 2nπ 3 3 28. csc2 x + csc x = 2 csc2 x + csc x 2 = 0 (csc x + 2)(csc x 1) = 0 csc x + 2 = 0 csc x = 2 or csc x 1 = 0 csc x = 1 x = 7π + 2nπ, 11π + 2nπ x = π + 2nπ 6 6 2 29. sin x 2 = cos x 2 sin x = cos x 30. cos x + sin x tan x = 2 cos x + sin x sin x = 2 sin x = 1 cos x cos x cos2 x + sin2 x tan x = 1 x = tan 1 1 x = π , 5π 4 4 cos x = 2 1 = 2 cos x 1 cos x = 2 x = π , 5π 3 3
Section 7.3 Solving Trigonometric Equations 601
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
31. 2 sin2 x = 2 + cos x 2 2 cos2 x = 2 + cos x 2 cos2 x + cos x = 0 36. 3 sec x 4 cos x = 0 3 4 cos x = 0 cos x cos x(2 cos x + 1) = 0 3 4 cos2 x = 0 cos x cos x = 0 or 2 cos x + 1 = 0 3 4 cos2 x = 0 x = π , 3π 2 cos x = 1 3 2 2 1 cos x = 2 cos2 x = 4 3 32. tan2 x = sec x 1 sec2 x 1 = sec x 1 x = 2π , 4π 3 3 37. cos x = ± 2 x = π , 5π , 7π , 11π 6 6 6 6 csc x + cot x = 1 sec2 x sec x = 0 (csc x + cot x)2 = 12 33. sec x(sec x 1) = 0 sec x = 0 or sec x 1 = 0 No Solutions sec x = 1 x = 0 sin2 x = 3 cos2 x csc2 x + 2 csc x cot x + cot2 x = 1 cot2 x + 1 + 2 csc x cot x + cot2 x = 1 2 cot2 x + 2 csc x cot x = 0 2 cot x(cot x + csc x) = 0 2 cot x = 0 or cot x + csc x = 0 x π , 3π cos x 1 sin2 x 3 cos2 x = 0 = = 2 2 sin x sin x sin2 x 3(1 sin2 x) = 0 4 sin2 x = 3 sin x = ± 3 3π 2 is extraneous cos x = 1 x = π (π is extraneous) 2 x = π , 2π , 4π , 5π 3 3 3 3 34. 2 sec2 x + tan2 x 3 = 0 38. x = π 2 is the only solution. sec x + tan x = 1 1 sin x + = 1 cos x cos x 2(tan2 x + 1) + tan2 x 3 = 0 1 + sin x = cos x 3 tan2 x 1 = 0 (1 + sin x)2 = cos2 x tan x = ± 3 3 1 + 2 sin x + sin2 x = cos2 x 1 + 2 sin x + sin2 x = 1 sin2 x x = π , 5π , 7π , 11π 6 6 6 6 2 sin2 x + 2 sin x = 0 35. 2 sin x + csc x = 0 2 sin x + 1 = 0 2 sin x(sin x + 1) = 0 sin x = 0 or sin x + 1 = 0 sin x 2 sin2 x + 1 = 0
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. sin2 x 1 No solution x = 0, π (π is extraneous ) sin x = 1 x = 3π 2 = 2 x = 0 is the only solution. 3π 2 is extraneous
602 Chapter 7 Analytic Trigonometry
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 2 2
39. 2 cos 2x 1 = 0 45. 3 tan x 3 = 0 cos 2x = 1 2 2 tan x = 3 2x = π + 2nπ or 2x = 5π 2 3 + 2nπ 3 3 x = π + nπ x = π + 2nπ x = π + nπ x = 5π + nπ 2 6 3 6 6 x 46. tan + 3 = 0 40. 2 sin 2x + 3 = 0 2 x sin 2x = 3 2 tan 2 x = 3 = 2π + nπ x = 4π + 2nπ 2x = 4π + 2nπ or 2x = 5π + 2nπ 2 3 3 3 3 x = 2π + nπ x = 5π + nπ 47. y = sin π x + 1 3 6 2 π x + = 41. tan 3x 1 = 0 tan 3x = 1 sin 1 0 π x 3x = π + nπ sin = 1 4 x = π + nπ π x 2 = 3π 2 + 2nπ 12 3 42. sec 4x 2 = 0 sec 4x = 2 cos 4x = 1 2 48. x = 3 + 4n For 2 < x < 4, the intercepts are 1 and 3 y = sin π x + cos π x sin π x + cos π x = 0 sin π x = cosπ x 4x = π + 2nπ or 4x = 5π + 2nπ π 3 3 π x = + nπ 4 x = π + nπ x = 5π + nπ 1 12 2 12 2 x = + n 4 43. 2 cos x = 2 = 0 For 1 x 3, the intercepts are 1 , 3 , 7 , 11 2 cos x = 2 < < 4 4 4 4 2 2 49. 5 sin x + 2 = 0 8 x = π + 2nπ or x = 7π + 2nπ 2 4 2 4

© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. x = π + 4nπ x = 7π + 4nπ 0 2π 2 2 44. 2 sin x = 2 3 = 0 5 x ≈ 3.553 and x ≈ 5.872 sin x = 3 50. 2 tan x + 7 = 0 2 2 15 x = 4π + 2nπ or x 5π = + 2nπ 2 3 2 3 x = 8π + 4nπ x = 10π + 4nπ 0 2π 3 3 5 x ≈ 1 849 and x ≈ 4 991

© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Solving
51. sin x 3 cos x = 0 5 55. sec2 x 3 = 0 5 0 2π 0 2π 5 x ≈ 1.249 and x ≈ 4 391 52. sin x + 4 cos x = 0 5 56. 4 x ≈ 0.955, x ≈ 2.186, x ≈ 4.097 and x ≈ 5.328 csc2 x 5 = 0 5 0 2π 0 2π 5 x ≈ 1 816 and x ≈ 4 957 5 x ≈ 0 464, x ≈ 2 678, x = 3 605 and x ≈ 5.820 53. cos x = x 4 57. 2 tan2 x = 15 6 0 2π 0 2π 8 x ≈ 0.739 54. tan x = csc x 18 x ≈ 1.221, x ≈ 1.921, x ≈ 4.362 and x ≈ 5.062 10 58. 6 sin2 x = 5 6 0 2π 0 2π 10 x ≈ 0.905 and x ≈ 5 379 18 x ≈ 1 150, x ≈ 1.991, x ≈ 4 292 and x ≈ 5.133 59. tan2 x + tan x 12 = 0 (tan x + 4)(tan x 3) = 0 tan x + 4 = 0 or tan x 3 = 0 tan x = 4 tan x = 3 x = arctan( 4) + nπ x = arctan 3 + nπ 60. tan2 x tan x 2 = 0 (tan x + 1)(tan x 2) = 0 tan x + 1 = 0 or tan x 2 = 0 tan x = 1 tan x = 2 x = 3π 4 + nπ x = arctan 2 + nπ
Section 7.3
Trigonometric Equations 603
604 Chapter 7 Analytic Trigonometry
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 3 3
tan
1
5 x = π 4 + nπ x = arctan 5 + nπ 62. sec
0 1
0 tan2
0 (tan
0
= 0 tan
1 x
arctan
2
nπ x = arctan(1) + nπ 63. ≈ 1.1071 + nπ 2 sin2 x + 5 cos x = 4 2(1 cos2 x) + 5 cos x 4 = 0 2 cos2 x + 5 cos x 2 = 0 (2 cos x 1)(cos x 2) = 0 = π + nπ 4 2 cos x 1 = 0 or cos x 2 = 0 cos x = 1 2 x = π + 2nπ, 5π + 2nπ cos x = 2 No solution 3 3 64. 2 cos2 x + 7 sin x = 5 2(1 sin2 x) + 7 sin x 5 = 0 2 sin2 x + 7 sin x 3 = 0 (2 sin x 1)(sin x 3) = 0 2 sin x 1 = 0 or sin x 3 = 0 sin x = 1 2 sin x = 3 x = π + 2nπ, 5π + 2nπ No solution 6 6 65. cot2 x 9 = 0 cot2 x = 9 1 = tan2 x 9 ± 1 = tan x 3 x = arctan 1 + nπ, arctan( 1) + nπ
61. sec2 x 6 tan x = 4 1 + tan2 x 6 tan x + 4 = 0 tan2 x 6 tan x + 5 = 0 (tan x 1)(tan x 5) = 0 tan x 1 = 0 tan x 5 = 0
x =
tan x =
2 x + tan x 3 =
+ tan2 x + tan x 3 =
x + tan x 2 =
x + 2)(tan x 1) =
tan x + 2 = 0 tan x 1
x = 2 tan x =
=
(
) +
Section 7.3 Solving Trigonometric Equations 605
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 5 5 =
66. cot2 x 6 cot x + 5 = 0 (cot x 5)(cot x 1) = 0 cot x 5 = 0 or cot x 1 = 0 cot x = 5 cot x = 1 1 = tan x 5 1 = tan x x = arctan 1 + nπ x = π + nπ 5 4 67. sec2 x 4 sec x = 0 sec x(sec x 4) = 0 sec x = 0 sec x 4 = 0 No solution sec x = 4 1 = cos x 4 x = arccos 1 + 2nπ, arccos 1 + 2nπ 4 4 68. sec2 x + 2 sec x 8 = 0 (sec x + 4)(sec x 2) = 0 sec x + 4 = 0 or sec x 2 = 0 sec x = 4 sec x = 2 1 = cos x 1 = cos x 4 2 x = arccos 1 + 2nπ, arccos 1 + 2nπ x = π + 2nπ, 5π + 2nπ 4 4 3 3 69. csc2 x + 3 csc x 4 = 0 (csc x + 4)(csc x 1) = 0 csc x + 4 = 0 or csc x 1 = 0 csc x = 4 csc x = 1 1 = sin x 4 1 = sin x x = arcsin 1 + 2nπ, arcsin 1 + 2nπ x = π + 2nπ 4 4 2 70. csc2 x 5 csc x = 0 csc x(csc x 5) = 0 csc x = 0 or csc x 5 = 0 No solution csc x = 5 1 sin x 5 x = arcsin(1) + 2nπ, arcsin( 1) + 2nπ
606 Chapter 7 Analytic Trigonometry
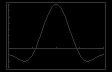


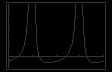
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 3
71. 12 sin2 x 13 sin x + 3 = 0 ( 13) ± ( 13)2 4(12)(3) 30 13 ± 5 sin x = = 2(12) 24 0 2π sin x = 1 or sin x = 3 10 3 4 x ≈ 0 3398, 2 8018 x ≈ 0.8481, 2.2935 The x-intercepts occur at x ≈ 0 3398, x ≈ 0.8481, x ≈ 2 2935, and x ≈ 2 8018. 72. 3 tan2 x + 4 tan x 4 = 0 4 ± 42 4(3)( 4) 4 ± 64 2 tan x = = = 2, tan x = 2 tan x = 2(3) 6 3 2 3 50 x = arctan( 2) + nπ ≈ 1.1071 + nπ x = arctan 2 + nπ ≈ 0.5880 + nπ 0 2 The values of x in [0, 2π) are 0.5880, 3.7296, 2.0344, 5.1760. 10 73. tan2 x + 3 tan x + 1 = 0 3 ± 32 4(1)(1) 3 ± 5 tan x = = 10 2(1) 2 tan x = 3 5 or tan x = 3 + 5 0 2π 2 2 x ≈ 1.9357, 5.0773 x ≈ 2.7767, 5.9183 5 The x-intercepts occur at x ≈ 1.9357, x ≈ 2 7767, x ≈ 5 0773, and x ≈ 5 9183. 74. 4 cos2 x 4 cos x 1 = 0 4 ± ( 4)2 4(4)( 1) 4 ± 32 1 ± 2 cos x = = = cos x = 1 2 2(4) 8 2 cos x = 1 + 2 7 2 2 1 2 x = arccos No solution 2 0 2π ≈ 1 7794 1 + 2 3 > 1 2 1 2 Solutions in [0, 2π) are arccos and 2π arccos 1 2 : 1.7794, 4.5038.
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 2 2
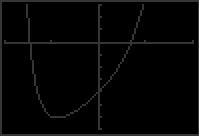
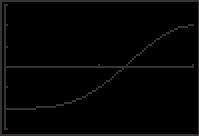
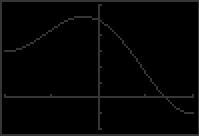



© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Solving Trigonometric Equations
75. 3 tan2 x + 5 tan x 4 = 0, 3 π , π 2 2 77. 4 cos2 x 2 sin x + 1 = 0, 6 π , π 2 2 π π 2 2 p p 2 2 76. 7 x ≈ 1 154, 0 534 cos2 x 2 cos x 1 = 0, [0, π] 3 78. 2 x ≈ 1 110 2 sec2 x + tan x 6 = 0, π , π 2 2 4 0 π 3 x ≈ 1 998 π π 2 2 6 x ≈ 1 035, 0 870 79. (a) f (x) = sin2 x + cos x 2 (b) 0 2π 2 Maximum: (1.0472, 1.25) Maximum: (5 2360,1 25) Minimum: (0,1) Minimum: (3.1416, 1) 80. (a) f (x) = cos 2 x sin x 2 (b) 0 2π 81. (a) 2 Maximum: (3 6652, 1 25)Maximum: (5 7596,1 25)Minimum: (1 5708, 1)Minimum: (4.7124,1) f (x) = sin x + cos x 3 0 2π 3 Maximum: (0.7854,1.4142) Minimum: (3.9270, 1.4142) (b)
Section 7.3
607
608 Chapter 7 Analytic Trigonometry
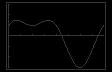
3π is undefined in original function So, it is not 2 a solution. 85.
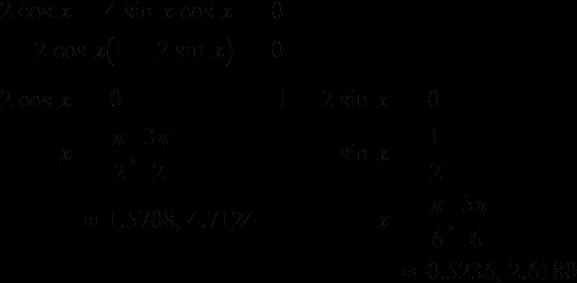
= 3x + 1 appear to have one point of intersection. This implies there is one solution to the 86.
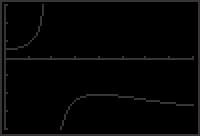
x 1 appear to have three points of intersection. This implies there are three solutions
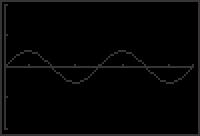
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 2 + =
82. (a) f (x) = 2 sin x + cos 2x 3 (b) 0 2π 3 Maximum: (0.5236,1.5) Maximum: (2 6180,1 5) Minimum: (1 5708,1.0) Minimum: (4.7124, 3.0) 83. (a) f (x) = sin x cos x 2 84. (a) f (x) = sec x + tan x x 6 0 2π 0 2π 2 Maximum: (0.7854, 0 5) Maximum: (3.9270, 0 5) Minimum: (2.3562, 0.5) (b) 8 Maximum: (3.1416, 4.1416) Minimum: (0,1) sec x tan x + sec2 x 1 = 0 Minimum: (5 4978, 0.5) 1 ⋅ sin x + 1 1 = 0 (b) sin2 x + cos2 x = 0 cos x cos x cos x sin2 x + 1 sin2 x = 0 2 sin2 x + 1 = 0 sin x + 1 1 = 0 cos2 x sin x + 1 cos2 x = 0 sin2 x = 1 cos2 x cos2 x 2 sin x + 1 cos2 x 2 = 0 sin x = ± 1 = ± 2 cos x 2 2 sin x + sin2 x = 0 x = π , 3π , 5π , 7π 4 4 4 4 ≈ 0.7854, 2.3562, 3.9270, 5.4978 cos2 x sin x + sin2 x = 0 sin x(1 + sin x) = 0 sin x = 0 or 1 + sin x = 0 x = 0, π ≈ 0, 3.1416 sin x = 1 x = 3π 2
of y1 = 2 sin x and y2 equation 2 sin x = 3x + 1.
of y1 = 2 sin x
y2
2
The graphs
The graphs
and
1
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. + to the equation 2 sin x = 1 x 1. 2
(a) Domain: all real numbers except x = 0.
(b) The graph has y-axis symmetry
(c) As x → 0, f (x) → 1
(d) sin x x = 0 has four solutions in the interval [ 8, 8].
Section 7.3 Solving Trigonometric Equations 609
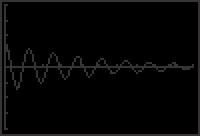
90. y1 = 1.56e 0.22t cos 4.9
Right-most point of intersection: (1.96, 1)
The displacement does not exceed one foot from equilibrium after t = 1 96 seconds.
(a) Domain: all real numbers x except x = 0.
(b) The graph has y-axis symmetry and a horizontal asymptote at y = 1.
(c) As x → 0, f (x) oscillates between 1 and 1
(d) There are infinitely many solutions in the interval 2
Left point of intersection: (1.95, 75)
Right point of intersection: (10 05, 75)
So, sales exceed 7500 in January, November, and December.
(e) The greatest solution appears to occur at
© 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. x 6 1 32 32 Monthly sales (in thousands of dollars)
) = sin x x
87. f (x
t
4
0 10 sin x 1 = 0 sin x = 0 x = 2π, π, π, 2π 88. f (x) = cos 1 4
πt y2 = 75. x
91. Graph y = 58.3 + 32 cos
S 100 75 [ 1,1] They occur at x = (2n + 1)π any integer where n is 50 25 89.
x ≈
6366. y = 1 (cos 8t 3 sin 8t) x 2 4 6 8 10 12 Month (1 ↔ January) 12 92. Range = 300 feet 1 (cos 8t 3 sin 8t) = 0 v0 = 100 feet per second 12 cos 8t = 3 sin 8t r = 1 v0 2 sin 2θ 1 = tan 8t 3 8t ≈ 0.32175 + nπ t ≈ 0.04 + nπ 8 1 (100)2 sin 2θ sin 2θ 2θ θ or = 300 = 0.96 = arcsin(0.96) ≈ 73.74° ≈ 36.9° In the interval 0 ≤ t ≤ 1, t ≈ 0.04, 0.43, and 0.83 2θ = 180° arcsin(0.96) ≈ 106.26° θ ≈ 53.1°
0