



NEWS Volume 51 No. 6 December, 2023 Overview of Ozone Applications Overview of Ozone Applications Municipal Commercial Mineral Processing Horticulture Human Health Las Vegas Palms Casino Resort Europe, Africa, Asia, Australasia Group 2024 International Conference (EA3G2024) AUG. 26–29 2024 Volume 52 / No. 2 • March 2024 International Ozone Association-Pan American Group (IOA-PAG) 2024 Conference Porto Portugal World of Wine Venue NOV. 27–29 2024

OZONE NEWS
Volume 52 / No. 2 • March 2024
Editor-in-Chief: Dr. Saad Jasim
Ozone News (ISSN 1065-5905) is a bimonthly publication of the International Ozone Association (IOA). Annual subscription rate: $150.00. For editorial and advertising information, please contact: International Ozone Association/Editorial Office
Attn: Dr. Saad Jasim, P.Eng.
4483 Cherry Hill Road
Windsor, ON N9G 2W3 Canada
Tel: +1-226-280-3522
Email: saadjasim@ioa-pag.org and sjenvcons@gmail.com
Membership and Publication Information:
The International Ozone Association is a nonprofit educational and scientific organization dedicated to the collection and dissemination of information on, and to promote research in, any and all aspects of ozone and related oxygen species technologies. Membership is open to any individual, corporation, or organization having interest in the latest developments and advancements in ozone technology.
As a member of the IOA, you’ll receive bimonthly issues of Ozone News, bimonthly issues of the technical journal Ozone: Science & Engineering (OS&E), and IOA’s Publication Catalog, which includes worldwide conference proceedings, monographs, and special reprints. In addition, members receive discounts on IOA worldwide publications and meetings.
Website: www.ioa-pag.org
For membership and publication information, please contact the IOA office nearest you:
Pan American Group (PAG)
International Ozone Association, Pan American Group
Attn: Megan Corcoran
c/o AAMSI
1521 I Street
Sacramento, CA 95814
Tel: (1) 916-441-0629
Email: support@ioa-pag.org • Web: www.ioa-pag.org
European-African-Asian-Australasian Group (EA3G)
Ms. Beatrice Bernard, Secretariat
IOA-EA3G Secretaruat
7 rue Marcel Doré - Bât. B16
86000 Poitiers France
Tel: 33 (0) 5 49 45 44 54
Fax: 33 (0) 5 49 45 40 60
Email: ioa@esip.univ-poitiers.fr • Web: www.ioa-ea3g.org
Nippon Islands Group (NIG)
Mr.. Tetsuya Tamura
Japan Ozone Association
Intelligent Flats 301, 10-10 Nihonbashi Tomizawa-cho
Chuko- Tokyo 103-0006, Japan
Tel: (81) 3 6661 1622
Fax: (81) 3 6661 1623
Email: tamura@j-ozone.org • Web: www.j-ozone.org
WELCOME
4 Mark Your Calendars
Index of Advertisers
List of Sponsors
EDITOR’S NOTE
5 A Team Effort
INDUSTRY NEWS

6 New Chair of IOA Publications Committee: Dr. Keisuke Ikehata
7 1st Reuse Impact Award
8 World Water Day 2024
9 Advancing Commercial Ozone Cleaning with Stabilized Aqueous Ozone
10 City of Fayetteville Installs BlueInGreen’s HyDOZ® Solution
11 How to Destroy Pathogens and Micropollutants with Ozone
13 Part 2: Ozone in Medicine; Ozone as Redox Bioregulator
15 Studies Make Strong Case for Ozone Sidestream Injection
20 Welcome, New Members

2024 CONFERENCES
20 Iberoamerican Conference on Advanced Oxidation Technologies
20 12th Annual Meeting of The American This Academy of Ozonotherapy
21 IOA—International Ozone Association EA3G2024 Europe, Africa, Asia, Australasia Group International Conference
22 International Ozone Association-Pan American Group (IOA-PAG) 2024 Conference
OZONE NEWS 2024 6 22 VOLUME 52, NO. 2 IOA OZONE NEWS 3
IOA
INDEX OF ADVERTISERS
Page 2 Air Physics Co., Ltd.
Page 5 ANSEROS Klaus Nonnenmacher GmbH
Page 5 Statiflo
Page 6 BMT
Page 7 BMT
Page 8 Mazzei
Page 9 Tersano
Page 10 Plasma Technics, Inc.
Page 11 Teledyne API
Page 24 AirSep
Mark Your Calendar
April 11–15, 2024 — Global Water Summit 2024, Sofitel London, Heathrow. www.watermeetsmoney.com
June 10–13, 2024 — AWWA Annual Conference and Exposition, (ACE24), Anaheim Convention Center, Anaheim, CA. www.awwa.org
June 13–14, 2024 — Japan Ozone Association Annual Conference on Ozone Science & Technology, Ryukoku University, Fukakusa Campas in Kyoto City, Japan
August 11–15, 2024 — IWA World Water Congress and Exposition, Metro Toronto Convention Center, Toronto. www.worldwatercongress.org
August 25–29, 2024 — IOA-PAG Annual Conference, Palms Resort & Casino, Las Vegas, NV. www.ioapag.org
August/September 2025 — IOA World Congress, Atlanta, GA. www.ioa-pag.org
November 27–29, 2024 — Europe, Africa, Asia, Australasia Group 2024 International Conference (EA3G2024), Porto, Portugal. www.ioa-ea3g.org








WELCOME
Association. All rights reserved.
part of this publication may be reproduced, stored, transmitted, or disseminated in
form or by any means without prior written permission from the
Association. The publisher assumes
responsibility for any statements of fact or opinion expressed in the published papers. 4 IOA OZONE NEWS VOLUME 52, NO. 2 GOLD SPONSOR SILVER SPONSORS
Copyright ©2024 International Ozone
No
any
International Ozone
no
THANKS TO OUR SPONSORS
EDITOR’S NOTE
A Team Effort
I want to extend my heartfelt appreciation for the invaluable assistance in launching the first issue of Ozone News in 2024, which was my first as the new Editor-in-Chief.

Thanks to all the IOA members for their article contributions. The attention to detail, insightful suggestions and meticulous approach have significantly improved the quality and clarity of the piece. Your continued support is a key to our success.
I’m truly grateful for the effort by our new publisher, Active Media Publishing, dedicated to meticulously helping me in design and organization. Also, many thanks to Oregon Web Press for providing a high-quality finished product delivered on time to our members.
Dr. Saad Y. Jasim, P.Eng. Ozone News Editor-in-Chief International Ozone Association

Contact us to find out more: www.statiflo.com enquiries@statiflogroup.com
Statiflo supply a range of custom designed Ozone contacting systems which continually meet and exceed our guaranteed 95% mass transfer efficiency.

The Statiflo Gas Dispersion System (GDS) is often used by our customers to replace other high-maintenance and low-efficiency technologies, reducing overall costs and reducing your environmental impact.
Key benefits include:
• Highly efficient mixing
• Continuous performance over a wide flow range
• Smaller sidestreams than competitive solutions resulting in significant energy savings
• Very low pressure loss
• Uniformly distributes ozone
• No deterioration in performance after prolonged use
• Easy to install
• Available in all sizes
• Available in both pipe and duct designs
• Suitable for new and retrofit installations
• Custom designed for each application
INLINE STATIC MIXERS AND GAS DISPERSION SYSTEMS STATIFLO_A5_AD.indd 1 28/06/2022 13:20
VOLUME 52, NO. 2 IOA OZONE NEWS 5
Dr. Saad Jasim, P.Eng.
New Chair of IOA Publications Committee: Dr. Keisuke Ikehata
The International Ozone Association (IOA) is pleased to announce that Dr. Keisuke Ikehata is the new Chair of the Publications Committee of the IOA. The International Ozone Association, Board of Directors and members want to express great appreciation to Mr. Angelo Mazzei who decided to step down after many years of successful and hard work as the Chair of the Publication Committee of the IOA.
Dr. Ikehata is an Assistant Professor in the Ingram School of Engineering, Texas State University, San Marcos, TX. He joined Texas State as one of four founding members of the new Civil Engineering Program in July 2019. Dr. Ikehata received his PhD in Civil and Environmental Engineering from the University of Alberta in 2003. He has 20 years of experience in water quality and treatment research and engineering, including eight-plus years in the industry as a consulting

engineer in Southern California. Dr. Ikehata has been a member of the International Ozone AssociationPan American Group (IOA-PAG) and Japan Ozone Association (JOA) since 2006 and 2014, respectively, and served as an editorial board member for Ozone: Science & Engineering and IOA-PAG board member since 2017. His current research centers around the use of alternative water resources, including brackish water, reclaimed water, and stormwater for potable applications using advanced treatment (including ozone and advanced oxidation processes) and monitoring technologies, as well as the taste, odor, and appearance of drinking water, including purified wastewater for direct potable reuse.

w
w
w
listed, CE, RoHS
wInternal ozone generator for automatically testing the utility scrubber every 24 h or on command
wTwo
(utility & reserve), automatically switched on scrubber failure
w
wCabinet version: IP65 (splash proof)
m
m
m

INDUSTRY NEWS 6 IOA OZONE NEWS VOLUME 52, NO. 2
features:
Diagnostics software
Sniffer Mode
Dr. Keisuke Ikehata
Unique
m
m
Scrubber test on demand
Dimensions selectable: 3 ppm & µg/m v
Firmware updates in the Field
m
Three EMO circuits, User configurable
Three year warranty on all parts & labor
Five year warranty on the long-life UV lamp
w
w
Traceable to NIST
Pressure & temperature compensated
19" rack or cabinet versions
w
Compliance: cTUVus
scrubbers
1 l/min,
controlled
Sample gas flow
internal pump auto
by an electronic flow meter
Monitoring the ambient ozone concentration is trace analysis! Only 100 parts per billion usually have to be measured. UV photometry is the only method which meets the precision and reliability demands of this delicate ozone measurement task. Occupational Safety Demands a Reliable Ambient Ozone Monitor! OZONE MONITOR BMT 932 BMT MESSTECHNIK GMBH - Hamburger Str. 19 - D-14532 Stahnsdorf, Germany - Phone +49-3329-69677-0 - www.bmt-berlin.de OSTI Inc. (Ozone Systems & Technology Int'l) - P.O. Box 63928 - Colorado Springs, CO 80962 - Phone +1-831-649 1141 - www.osti-inc.com
1st Reuse Impact Award
Congratulations, Dr. Keisuke Ikehata, for receiving the 1st Reuse Impact Award.
Dr. Keisuke Ikehata, assistant professor at Texas State University, received the 1st Reuse Impact Award from WateReuse Texas during the 2023 WateReuse Texas Conference in Frisco, Texas.
The Reuse Impact Award is a new award for 2023 that recognizes individuals, projects, facilities, or organizations that have made significant contributions to increase water reuse in Texas. Award recipients exhibit leadership in advancing education, advocacy, technology, and/or management of water resources, showcasing innovative approaches that others can follow to build resilient communities through water recycling. Awardees in this category will include exemplary water reuse projects, systems, and/or facilities that demonstrate the value of water reuse to the community they serve


wThree year warranty, on all parts & labor
wFive year warranty on the long-life UV lamp
wContaining over thirty years of experience in designing highest quality UV photometers
wBackward compatibility with BMT 964 series of analyzers
wPanel mount, portable, and wall mount models (IP65)

or that have advanced water reuse practices in Texas by developing novel approaches to reuse. This can be awarded to a project, facility, organization, etc., that has had a significant impact on reuse in Texas over the last three years. Dr. Ikehata is a member of the International Ozone Association (IOA), and the new Chair of the Publications Committee for the IOA.

wState-of-the-art design, highest quality materials
wUnprecedented accuracy, stability, and reliability through design competence
wProven by thousands of installations around the world
wThe companion to your PC or PLC
wUSB port for field updates, log downloads and PC communication (Diagnostics)
wCalibration error less than 0.5% of range 3
wRanges from 0 - 2 to 0 - 800 g/Nm 3
wSelectable dimensions: g/Nm, %wt/wt, ppmv
wFull internal diagnostics
wLife long logging of Event & Error Log and concentration with date and time stamp
wWindows software for easy control included
wPower supply: 85 - 264 VAC or 12 - 36 VDC
wCabinet with enhanced sample gas filtering
wCabinet certified to NRTL / cTUVus and for ship operations (USCG)
wModbus RTU or TCP available
VOLUME 52, NO. 2 IOA OZONE NEWS 7 INDUSTRY NEWS
Andrea Tom of CDM Smith presents Dr. Keisuke Ikehata with the award.
If you are Tired of Battling Service Related Issues OZONE ANALYZER BMT
BMT MESSTECHNIK GMBH - Hamburger Str. 19 - D-14532 Stahnsdorf, Germany - Phone +49-3329-69677-0 - www.bmtberlin.de OSTI Inc. (Ozone Systems & Technology Int'l) - P.O. Box 63928 - Colorado Springs, CO 80962 - Phone +1-831-649 1141www.osti-inc.com
965
World Water Day 2024
The campaign for World Water Day, March 22, 2024, is now live. This year’s theme is ‘Water for Peace’, which focuses on the critical role water plays in the stability and prosperity of the world.
When water is scarce or polluted, or when people have unequal or no access, tensions can rise between communities and countries.
More than three billion people worldwide depend on water that crosses national borders. Yet, out of 153 countries that share rivers, lakes and aquifers with their neighbours, only 24 countries report having cooperation agreements for all their shared water.
As climate change impacts increase, and the global population grows, we must unite around protecting and conserving our most precious resource.
By working together to balance everyone’s human rights and needs, water can be a stabilizing force and a catalyst for sustainable development.
World Water Day is a United Nations (UN) observance coordinated by UN-Water. Every year, it raises awareness
March 22, 2024

of a major water-related issue and inspires action to tackle the water and sanitation crisis.
This year’s Task Force of UN-Water Members and Partners is coordinated by the UN Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) and UN Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
Be part of the global campaign on ‘Water for Peace’. We need everyone — from individuals and families to companies and governments — to do what they can to cooperate on water and pave the way for a more harmonious society.
Source: UN-Water

8 IOA OZONE NEWS VOLUME 52, NO. 2
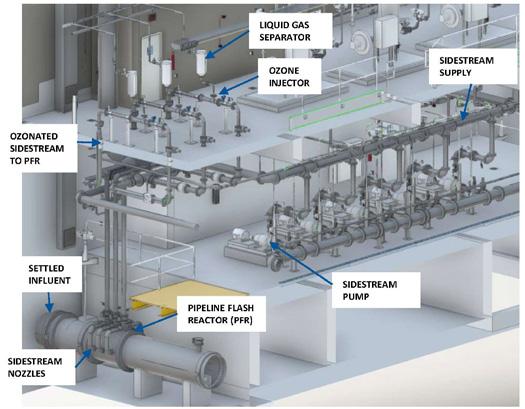
INDUSTRY NEWS Sidestream Injection & Pipeline Flash Reactor (PFR)... • uniformly distributes ozone • minimizes size & cost of ozone contacting system
Advancing Commercial Ozone Cleaning with Stabilized Aqueous Ozone
Tersano, Inc. remains a pioneer in the ozone industry for its innovation of Stabilized Aqueous Ozone (SAO®). This revolutionary advancement has facilitated aqueous ozone’s commercial adaptation and given rise to a paradigm shift in how the world views cleaning.
Aqueous ozone has an industrial history dating back to the early 20th century, led by its application in water treatment processes. However, its rapid degradation to water and oxygen has limited its use in commercial cleaning applications.
In recognition of this limitation, Tersano patented a cartridge filtration system that dramatically extends aqueous ozone’s shelf life while enhancing cleaning. The resulting product, Stabilized Aqueous Ozone (SAO®), passes ASTM D4488-A5 tests as a cleaner for up to seven days and meets various standards, including AOAC 960.09 and EN13697, as a disinfectant for up to 24 hours.
SAO has been commercially adopted across healthcare,
food service, transportation, education and hospitality sectors, simplifying processes while creating safer, more sustainable building environments.
A complete solution, SAO simplifies cleaning for staff and reduces need to purchase, transport, distribute, store and restock multiple cleaning products. Produced on site and on demand, SAO minimizes product waste while circumventing supply chain interruptions. Non-corrosive and safe for various surfaces, SAO minimizes the risks of application error while preserving the lifetime value of cleaning equipment and building surfaces.
In addition to simplified processes, SAO provides a safer, more sustainable environment for building occupants. With 0-0-0 SDS, SAO has no health or environmental hazard classifications. SAO is fragrancefree, safe for human contact, and dermatologically tested for sensitive skin. With no harsh chemical residues, SAO reduces slip-and-fall coefficients. SAO’s on-site generation and Tersano’s cartridge recycling program reduces waste and keeps single-use plastic bottles and containers from landfills, creating a closed-loop system.
Source: Tersano Inc.

VOLUME 52, NO. 2 IOA OZONE NEWS 9 INDUSTRY NEWS
City of Fayetteville Installs BlueInGreen’s HyDOZ® Solution

Plant officials at a 12 MGD wastewater plant in Arkansas began evaluating disinfection alternatives to upgrade their current system as well as address the removal of contaminants of emerging concern (CEC). The facility, which included primary clarification, activated sludge, secondary clarification and sand filtration, elected to use dissolved ozone to replace its current ultraviolet (UV) system. After researching different ozone systems, plant officials chose to install BlueInGreen’s HyDOZ® technology in order to more efficiently meet current permit requirements, as well as prepare for future legislation.
Source: ChartWater BlueInGreen

INDUSTRY NEWS
10 IOA OZONE NEWS VOLUME 52, NO. 2
How to Destroy Pathogens & Micropollutants with Ozone
Utilities continually face new challenges. Where treatment facilities were once expected to simply disinfect the water, they must now avoid creating disinfection byproducts during the process. New and more stringent regulations require removal of additional micropollutants and emerging contaminants. Finding the best technology to accomplish these goals can be difficult.
De Nora Water Technologies is a global company with over 50 years of experience providing reliable, effective, and innovative products for the water industry. Water Online spoke with Alex Bettinardi of De Nora to find out how ozonation can combat micropollutants and aid disinfection.
How does the ozonation process work?
Ozone is a pale blue gas composed of three oxygen

atoms (O3). Ozonation is a water treatment method where ozone is generated on-site and introduced into water to eliminate a wide range of organic compounds and microorganisms. The transformation of oxygen into ozone, a very powerful oxidant, occurs with the use of energy. Inside the ozone generator vessel, ozone is produced from oxygen present in the feed gas by means of a silent electric discharge (non-thermal plasma). Ozone is dissolved into the water. It produces a direct oxidation reaction on the pollutants/molecules.
What are some of the applications for ozonation at water treatment plants?
Ozone is used as a stand-alone technology in some cases. It can also be combined with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), ultraviolet light, or active chlorine to perform an advanced oxidation process (AOP). This AOP produces highly reactive hydroxyl radicals (·OH). These reactive species are the strongest oxidants that can be applied in water. They are used to address contaminants with high chemical oxygen demand (COD) or non-biodegradable molecules.








TELEDYNE API EverywhereyoulookTM www.teledyne-api.com • Water Treatment • Semiconductor • Medical, Pharmaceutical • Food & Beverage OZONE measuring technology for every application, from the ozone EXPERTS Teledyne API provides solutions for all your ozone monitoring and process control needs. Whether your requirement is for high concentration, off-gas, vent gas, ambient gas or residual gas in water, we have the right solution for you. Providing a wide range of options Generator Output 465H Off-Gas 465M Vent/Ambient Gas 465L FINAL_2023 OZONE_1_7.0x4.75DATED1_27_23CROPPED.indd 1 1/27/2023 9:52:54 AM INDUSTRY NEWS VOLUME 52, NO. 2 IOA OZONE NEWS 11

They also improve the overall quality of the water.
Ozonation can be used to complement chlorine disinfection of drinking water. By using ozone, utilities can limit or avoid the use of chlorine if there’s a concern about dangerous byproduct formation. Ozone also treats groundwater that has been polluted by metals, like iron and manganese, and inorganics, such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S), that are easily oxidated by O3.
Why is ozonation a good solution for micropollutants in wastewater? How does it work to eliminate them in particular?
Ozone is among the most powerful known oxidizing agents and has one of the highest redox potentials. The formation of byproducts is very low and sometimes absent. Stand-alone ozone effectively treats nonbiodegradable products, including micropollutants substantially untreated through the conventional activated sludge process.
What other solutions are available for combating micropollutants? Why might ozonation be a better option?
There are several technologies available to remove micropollutants, including reverse osmosis membranes. However, granular activated carbon (GAC) is the most convenient and simple technology for this application. GAC is typically used in combination with ozone because GAC alone is not always enough. The advantage of ozonation is related to the direct oxidation of micropollutants. Ozonation transforms micropollutants into more biodegradable compounds that are easily adsorbed and decomposed on the downstream filter, commonly called the biological activated filter.
What do you know about the threat posed by micropollutants? Do many treatment operations consider them to be a concern?
Endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) are chemicals that, at certain doses, can interfere with endocrine systems. These disruptions can cause cancerous tumors, birth defects, and other developmental disorders. Drugs and pharmaceutical residuals are not effectively treated with the traditional wastewater treatment plants. Switzerland is the first country that has enacted a specific law, but many countries are conscious about this serious concern. Some countries, like Germany and France, are addressing the micropollutant issue even faster than Switzerland, despite a lack of regulation. Would you say that ozonation is the best technology for combating micropollutants?
In most cases, GAC alone is not enough to protect the population from EDCs’ risks. Ozonation is surely one of most effective and convenient treatment options available when used in combination with other technologies. Technologies often paired with ozonation include GAC and biological filtration, which uses a different filter media.
What can you tell me about De Nora Ozone (DNO) disinfection solutions? How long has that been part of De Nora’s portfolio? What does that offer in terms of ozone solutions?
Founded in 1970, Italian-based Ozono Elettronica Internazionale (OEI) offered ozonation disinfection solutions to municipal drinking and wastewater treatment markets, the pharmaceutical and food industries, and agribusiness. The technology was acquired by De Nora in May 2015 to complement De Nora’s existing line of products. DNO now has a special focus on developing and extending its reach into the water and agrifood sectors.
With more than 1,200 worldwide installations, DNO technologies range from 40 g/hour to 100 Kg/hour ozone production. Stand-alone modular units or customized systems are available for the entire process: gas feed preparation, ozone generation, contact systems, ozone destroyers, instrumentation and controls, and packaged or containerized units
Source: Water Online
INDUSTRY NEWS 12 IOA OZONE NEWS VOLUME 52, NO. 2
Part 2: Ozone in Medicine; Ozone as Redox Bioregulator
II. Overall mechanism of action in chronic inflammatory diseases. The anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects.
Renate Viebahn-Haensler and Olga Sonia León Fernández
Key words: Biological medicine, redox medicine, chronic inflammations, prevention.

Abstract: At low concentrations and doses, and as a complement to basic medication, medical ozone will help to restore glutathione balance, and as final objective, cell protection against ROS (reactive oxygen species) in chronic inflammatory diseases. GSH (glutathione reduced form) in the liver increases, detoxification increases and side effects of medications are diminished. It starts with the oxidation of GSH by “ozone peroxides”, and after a considerable number of regulatory processes and mechanisms, leads to the regulation of glutathione balance GSH ⇋ GSSG (glutathione reduced ⇋ oxidized form‚) itself, briefly illustrated here in rheumatoid arthritis.
Chronic inflammatory diseases as main indication of systemic ozone application.
balance and improving the detoxification capacity of the liver. This can be demonstrated using very meaningful biomarkers from the group of oxidative stress parameters and suitable antioxidants as protective markers in order to show the improvement of the redox balance. Immune dysbalance is another characteristic of RA. Proinflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-1, interleukin-6) IL-1, IL6, TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-α) are elevated in RA and can be taken as typical parameters for monitoring the progress of treatment: as a rule, they decrease with ozone administration. Here too, ozone at low concentrations and doses intervenes thanks to its regulatory effect.

Ozone as redox bioregulator and its biochemical mechanism.
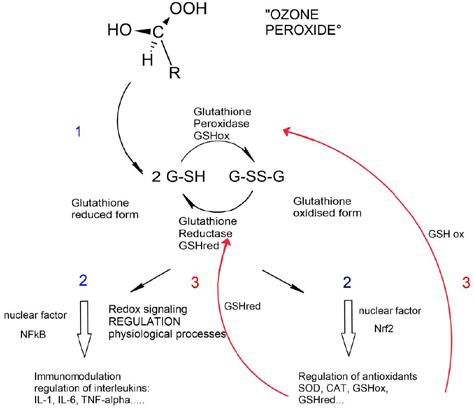
In blood or tissue, ozone reacts with the isolated double bonds of fatty acids in the cell membrane forming “ozone peroxides” RCH(OH)-OOH (hydroxy hydro peroxides) as intermediates. Less active than ozone itself, they are immediately reduced by glutathione GSH via ionic reaction mechanisms, whereas GSH is oxidized to its inactive form GSSG, see Figure 1.
Today, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is considered to be the prime example of a chronic inflammatory disease ideal for a complementary application of the low-dose ozone concept (procedure discussed in part I in Ozone News 2024 describing the use of concentrations from 10 up to 40µg /mL and doses from 500-2,000 µg per treatment in 50 mL of blood, or 2,000 to 8,000 g in the form of rectal insufflation as standard).
RA, an autoimmune disease, is widespread worldwide and generally requires long-term treatment, e.g. with Methotrexate (MTX), Ibuprofen, folic acid, such as described in the clinical trials here mentioned. Unfortunately MTX treatment is limited in time due to liver toxicity.
Typically, RA. in the same way as with other chronic inflammatory processes, is accompanied by high oxidative stress and reduced antioxidative capacity: the biochemical redox system is out of balance and the biological regulation -the repair mechanism- is blocked. Here we can intervene with medical ozone in two ways in addition to basic MTX therapy: regulating the redox

The glutathione system is one of the most important antioxidants in biology protecting cell metabolism from oxidative stress. In a healthy biological system the balance is far over on its left side, in red blood (RBC) and liver cells 2 GSH ⇋ GSSG: 90% to 10%, high enough to protect Fe2+ in the RBC´s from being oxidized to Fe3+ making it lose its ability to transport oxygen. Liver cells need a huge amount of GSH for an effective detoxification process.
In chronic inflammatory diseases, such as RA involving high oxidative stress, the GSH/GSSG system is out of balance, and a deficit of GSH is measured.
The reaction between “ozone peroxides” with GSH sends information to the cell nucleus starting redox bioregulation: At low doses, in addition to the basic medication, ozone will help to restore the glutathione
INDUSTRY NEWS VOLUME 52, NO. 2 IOA OZONE NEWS 13
Renate ViebahnHaensler
Olga Sonia León Fernández
Figure 1. The “ozone peroxide” is immediately reduced by GSH, the active form of glutathione, forming the oxidized product GSSG, the inactive form of glutathione.
FIGURE 1


in (μMol)
malondialdehyde
as anti-CCP (anti-cyclic citrullinate peptides). This completely
aspect of an immune memory resulting from the low-dose ozone concept will be further pursued and should be consolidated by including other autoimmune diseases. See references for further details.
balance so that, finally, the cells are protected against ROS (reactive oxygen species) to a far better extent. GSH in the liver increases, detoxification increases and side effects e.g. of MTX are diminished. The corresponding antioxidative enzymes are upregulated through redox bioregulation. GSH reductase (GSHred) and oxidase (GSHox) are needed to recover the GSH/GSSG balance as shown in Figure 2.
Result: Restoration of GSH balance in a clinical study with RA patients.
The GSH/GSSG balance is improved after a first cycle and, in a much more pronounced way after a second cycle (not shown here) of systemic ozone treatment, measured as GSH (Figure 3a) and anti CCP as a measure for the decrease in auto antibodies (Figure 3b).
Conclusion
In chronic inflammatory diseases such as RA, complementary ozone treatment leads to an extensive restoration of glutathione balance and improves protection of the cells against oxidative stress -a characteristic of these diseases that are often autoimmune in origin. It starts with the oxidation of GSH by “ozone peroxides”, and -through a considerable number of regulatory processes and mechanisms- finally leads to the regulation of the glutathione balance GSH ⇋ GSSG itself.
References
Takon, O.G., Viebahn-Haensler, R., López, C.G., Serrano, E.I., Tamargo, S.B., Polo, V.J.C., Sánchez, S.S., León, F.O.S., 2017. “Medical Ozone Reduces the Risk of GGT and Alkaline Phosphatase Abnormalities and Oxidative Stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients treated with Methotrexate”. SMJ. Arthritis Res. 1: 1004 doi:10.36876/smjar.1004
Togi, S., Togo, M., Nagashima, S., Kitai, Y., Muromoto, R., Kashiwakura, J., Miura, T., Matsuda, T. 2021. “Implication of NFkB Activation of Ozone-Induced HO-1 Activation”.
BRP Reports 4: 59-63
Viebahn-Haensler, Renate, Olga Sonia León Fernández 2021
Ozone in Medicine. The Low-Dose Ozone Concept and Its Basic Biochemical Mechanisms of Action In Chronic Inflammatory Diseases” Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22157890
Viebahn-Haensler, R.: and León Fernández, O. “Ozone as Redox Bioregulator in Preventive Medicine: The Molecular and Pharmacological Basis of the Low-Dose Ozone
Concept—A Review” Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ ijms242115747
Viebahn-Haensler, R., O. León Fernández, 2024. “Ozone in Medicine. The Low-Dose Ozone Concept and its Redox-Bioregulatory Effect as Prominent Biochemical Mechanism Underlying all Indications of Systemically Administered Ozone” Ozone: Sci. Eng. 46: xxx. Online: December 26, 2023. https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/24/21/15747
INDUSTRY NEWS 14 IOA OZONE NEWS VOLUME 52, NO. 2
Figure 3a: Restoration of GSH/GSSG balance in a clinical trial involving rheumatoid arthritis RA (n = 60) following 20 rectal ozone insufflations, using the following ozone concentrations and doses: 25–40 μg/mL and 5000–8000 μg per treatment during 4 weeks. MTX-group (n = 30): basic therapy MTX+Ibuprophen+Folic acid. MTX+ozone-group (n = 30): basics as MTX-group plus ozone rectally. GSH: reduced glutathione
increases; whereby -at the same time- the oxidative stress marker MDA
(μMol) decreases. Figure 3b: After a second treatment cycle, following an interval of 3 months, even the auto antibodies show a remarkable decrease corresponding to the improvement in clinical parameters, measured
new
FIGURE 2
FIGURE 3a
FIGURE 3b
Studies Make Strong Case for Ozone Sidestream Injection
Jim Lauria*1, Angelo Mazzei1
1 Mazzei Injector Company, 500 Rooster Drive, Bakersfield, CA 93307 USA * Corresponding author: jlauria@mazzei.net
Key words: Sidestream injection; transfer efficiency; venturi
Summary: Mazzei Injector Company executives conducted an in-depth analysis of the International Ozone Association (IOA) installation database, water media reports, presentations at IOA conferences, and the company’s own files on customer and competitor installations, to assess trends in ozone dissolution in North American drinking water and wastewater ozone facilities over the last 30 years. Driven by improvements in transfer efficiency, reduced energy demand, environmental footprint, maintenance costs, worker safety, and other factors, much of the industry shifted from fine bubble diffusers (FBD) to sidestream injection (SSI) for ozone transfer. Using data from case studies presented at the August 2022 IOA-Pan American Group Conference, as well as computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling to validate system designs and compare in-field performance, this presentation will explore the factors that have led to the increased adoption of sidestream injection.
Introduction
Small Sidestream

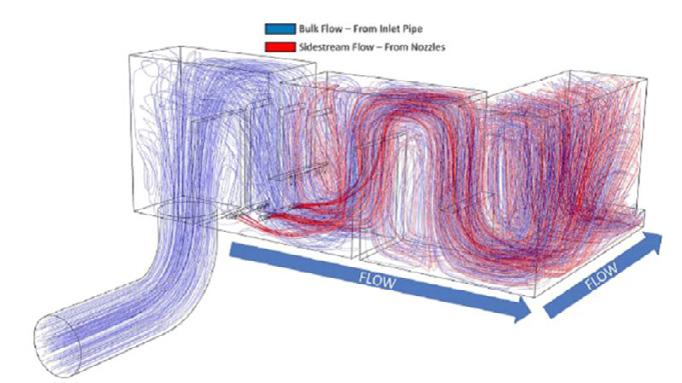
In sidestream injection systems, a percentage of the total flow—typically less than 10%—is diverted through venturi injectors that create a vacuum that draws in ozone and mixes it thoroughly with the sidestream (Figure 2). The ozonated fluid is then returned to the main flow through a Pipeline Flash Reactor (PFR) that features an array of specially designed and placed mixing nozzles to thoroughly mix the sidestream two-stage flow into the bulk flow in just a few meters of pipeline, or a Basin Nozzle Manifold that mixes the sidestream into an over/under or horizontal serpentine contact basin that can be much shallower and smaller than those required for passive diffusion.

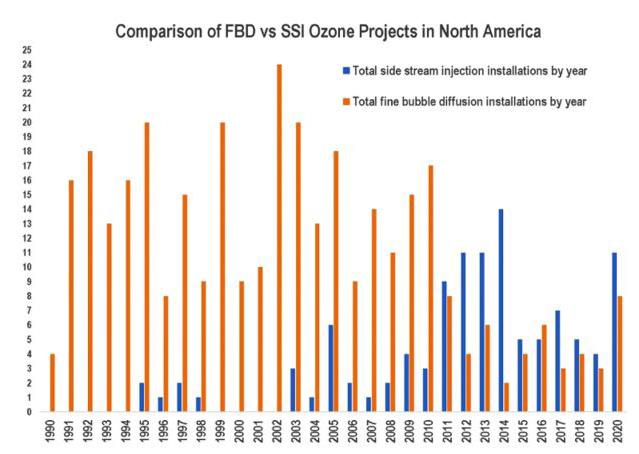
A deep dive into Mazzei Injector Company application engineering files, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) models, and the International Ozone Association (IOA) installation database—a resource available to IOA members—provided Mazzei with insight on the significant shift over the past 30 years from fine bubble diffusion (FBD) ozonation systems to sidestream injection (SSI) ozone delivery. The trend was particularly pronounced over the past decade (Figure 1).
Presentations by a range of ozone users at the August 2022 International Ozone Association-Pan American Group Conference provided an excellent range of examples to illustrate the diverse motivations behind the trend toward sidestream injection ozone systems. Sharing this information with the industry will help optimize ozone transfer, creating new opportunities for ozone in a wide range of applications.
A pivotal technology that tipped the balance in favor of sidestream injection was the advent of liquid oxygen (LOX) ozone generators that could produce ozone gas in concentrations in excess of 10%. Some of today’s systems can create ozone concentrations of 20% or more. Higher concentrations of ozone opened the door for more efficient mixing systems, including SSI. In addition, the development of Pipeline Flash Reactors delivered mixing performance as close to plug flow as realistically possible. Finally, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling became a powerful tool for the precise design, sizing, and siting of mixing nozzles to create mass transfer efficiencies well in excess of 90% (Figure 3). Such high mass transfer efficiencies and low waste of ozone make SSI ideal for high-rate applications such as water reuse systems, hydrogen sulfide removal, and treating emerging contaminants.
Energy and Mass Transfer Efficiency
Sidestream injection requires relatively low pump energy to create a flow that is compressed, then allowed to expand, in the venturi injector, creating a vacuum that draws and mixes ozone into the stream. Venturi SSI systems can achieve mass transfer efficiency in excess of 95% with low coefficient variation—in fact, one of the case studies below measured 5 to 10% coefficient of variation (COV) in sidestream injection systems vs. 20 to 45% with fine bubble diffusers (Steinke et al. 2022).
The energy expended for pumping is often more than offset by reductions in energy needs for ozone generation
INDUSTRY NEWS
VOLUME 52, NO. 2 IOA OZONE NEWS 15
Jim Lauria
Angelo Mazzei
due to greater efficiency in SSI systems or the reduced need to pump against the head pressure of deep mixing basins. Pumping energy also provides other benefits, including thorough, nearly instant mixing for greater mass transfer with minimal contact time, which reduces bromate formation in the presence of bromine (Wert et al. 2016).
Compared to the large, deep contact basins required for passive diffusion, the physical and environmental footprint of SSI systems is extremely low. Minimum floor coverage for a FBD system is 4 ft2 (0.37 m2) per diffuser, and Cryptosporidium inactivation with fine bubble diffuser systems requires 10 or more contact chambers (USEPA 2005).
Because of their high transfer efficiency, oxygen consumption is reduced in SSI systems. Transfer takes place in durable venturi injectors and through mixing nozzles that have no moving parts, so maintenance costs are minimal—the only significant maintenance need is on the sidestream pump. According to a 2017 analysis by the American Water Works Association, SSI systems required 125 fewer days of downtime than FBD systems over
their 25-year service life (AWWA 2017). Worker safety is also improved, as any needed maintenance or adjustment in SSI is in the open, unlike the confined spaces where diffuser stones and gaskets must be checked, cleaned, or replaced annually.
The 2022 IOA-Pan American Group conference included several presentations that highlight the versatility of ozone in terms of flow rates, application, water source, and engineering configuration (Figure 4).
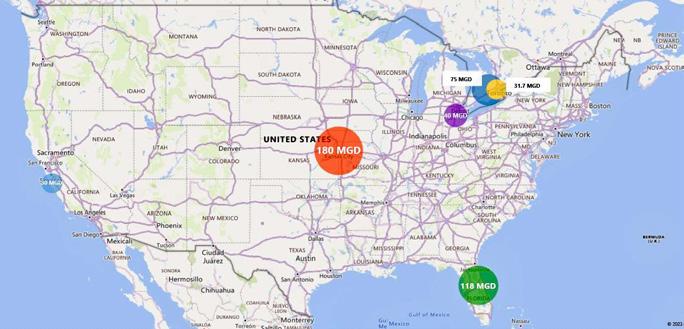
Massive O&M Savings
In 2021/2022, managers of the 75 MGD Mannheim Water Treatment Plant in Kitchener, Ontario, Canada, replaced their FBD system with SSI. The Mannheim plant removes taste and odor (T&O) compounds and color from river water. Following ozone treatment, the water is directed to granular activated carbon (GAC) filtration, UV disinfection, and chlorine treatment. The FBD system was not only inefficient, it was disruptive—excessive off-gassing of ozone had triggered alarms in the Mannheim plant, forcing employees to evacuate the facility.
Among Mannheim management’s key motivations were reducing maintenance time and cost. An internal study calculated that replacing its FBD system with SSI would save the plant 43% in O&M costs—just $190,000 for

INDUSTRY NEWS 16 IOA OZONE NEWS VOLUME 52, NO. 2
Figure 1. Though the first ozone water treatment system in North America was installed in 1940, venturi sidestream injection systems started coming online in the 1990s, when ozone generators were introduced that could produce ozone concentrations of 10% or more.
SSI compared to $332,500 for FBD (Snider 2021).
Managers also observed lower off-gas concentrations, 14-19% improvements in downstream filter performance compared to the plant’s 2018-2021 average, and reduced chlorine consumption of 14% with SSI compared to their previous FBD system. In all, switching to SSI resulted in applied ozone dose increases of 60%, a projected reduction in LOX by 7,000 kg per year, and a projected savings of 40,000 kWh of energy due to reduced waste of ozone.
Less LOX
In Florida, USA, the Orlando Utilities Commission (OUC) chose SSI to deal with high turndown rates resulting from fluctuating demand from more than 240,000 ratepayers in central Florida. The Lower Floridian Aquifer, which OUC taps with 31 wells, is high in hydrogen sulfide (H2S). The utility treats H2S with ozone and sought precise dosing and process control in plants whose design capacities total 118 MGD.
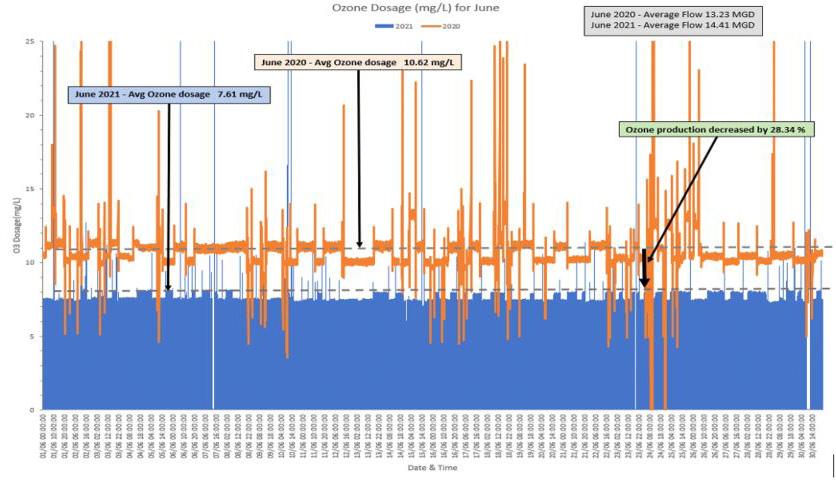
In the summer of 2021, OUC’s plants— where SSI permitted an average decrease of 28.23% in ozone dosage and 29.43% decrease in LOX consumption compared to the previous five-year average of Orlando’s FBD system (Figure 5)—passed a remarkable test. A wave of COVID cases caused a dramatic shortage of LOX in local hospitals, prompting a diversion of liquid oxygen away from water treatment and toward intensive-care units. OUC managed to meet demand for treated water, and the sudden disruption in LOX supply reinforced the benefits of SSI.
The dramatic reduction in LOX consumption highlights another benefit of SSI. The energy required for pumping the small sidestream for ozonation and mixing is more than offset by the savings in energy from the reduced generation of ozone. The switch to the more reliable SSI system also allowed OUC managers to use an ORP system to control ozonation and fine-tune operations even further.
Another safety benefit of replacing FBD with SSI reported by OUC managers is eliminating the need for workers to spend days in confined spaces checking, cleaning, and maintaining diffusers. As noted above, venturi injectors are flushed by the constant flow of water and the sidestream injection system has no moving parts except for its pumps, so there are nearly no maintenance demands on SSI systems, and any checks or pump repairs can be conducted in the open.
Huge Results with a Small Footprint
In Toledo, Ohio, USA, the Collins Park Water Treatment Plant received a 40 MGD capacity expansion to bring its plant peak capacity to 120 MGD. The plant’s staff is under tremendous pressure to protect the Toledo community from microcystin and the T&O compounds geosmin and 2-MIB produced by dramatic harmful algal blooms (HABs) in Lake Erie. Ozone is extremely effective at controlling all three contaminants, removing 99.7%. By adopting a multi-barrier approach of powdered activated carbon (PAC), ozone, granular media filters, and chlorine, Toledo helps keep more than 500,000 ratepayers safe. In a crowded city like Toledo, footprint is a key factor
INDUSTRY NEWS VOLUME 52, NO. 2 IOA OZONE NEWS 17
Figure 3. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling allows engineers to optimize the design and placement of nozzles in basin nozzle manifold systems to enhance mass transfer and reduce energy demand.
Figure 4. Case studies presented at the IOA-Pan American Group 2022 conference illustrated the versatility of ozonation through SSI at plants with a wide range of capacities, applications, and source water.
in system design. The new treatment system had to fit between an existing recarbonation basin and a bank of filters. The 18-to-20-foot (6-meter) deep contact basins required for FBD would not have fit the space and would have cost $300 per square foot to construct. Instead, the City of Toledo and Black & Veatch sited the SSI system in a three-story-tall stack that delivers 95% mass transfer efficiency through a Pipeline Flash Reactor (Figure 6).
Minimizing Bromate Formation
The Regional Municipality of Halton, Ontario, Canada, uses SSI in two of its three water treatment plants, creating an outstanding opportunity to compare SSI and FBD systems side-by-side to treat water from Lake Ontario.
The raw source water contains bromide at levels between 30 and 40 µ/L in water whose temperature fluctuated between 2 and 23 degrees C and averaged less than 5 degrees C. An analysis of 2008-to-2011 data from the Burlington Water Purification Plant (FBD with 35.7-minute detention time) and the Oakville Water Purification Plant (SSI with 20-minute detention), followed by laboratory bench comparisons to study factors in bromate formation, was published by the Water Research Foundation.
Researchers found that while treated water at the BWPP often contained bromate at or above the detection limit— and occasionally over 10 µ/L (Wert et al. 2016). In contrast,
treated water at the OWPP was often below detection limits for bromates, sometimes at the detection level, and never over 10 µ/L.
After extensive data analysis and laboratory studies evaluating differences in source water, applied ozone dose, initial ozone residual, ozone contacting time, and even upstream coagulants, the authors wrote, “the only reason that appears to be the cause or reason for bromate formation at the BWPP and not at the OWPP is the ozone dissolution system.”
Diverse Sources, Outstanding Results
The 30 MGD Pure Water Monterey water recycling plant in Monterey, California, USA, treats a wide range of source water over the year for injection into the local aquifer, where it replenishes drinking water supplies and resists saltwater intrusion. In the winter, most of the plant’s source water is stormwater; in spring and summer, runoff from agricultural fields and municipal wastewater from the area’s tourist industry dominate; and in the fall,
INDUSTRY NEWS 18 IOA OZONE NEWS VOLUME 52, NO. 2
Figure 5. A comparison of ozone dosage between Orlando Utilities Commission’s FBD system in June 2020 (orange) and the SSI system that replaced it (blue; June 2021) illustrates the dramatic difference in ozone demand between the systems.
Figure 6. Sidestream injection systems are efficient in space as well as energy. The Collins Park WTP in Toledo, Ohio, USA was upgraded with an SSI and PFR system stacked on three stories of an existing building, eliminating the cost and space that would have been necessary to build contact basins for an FBD system.
effluent from vegetable processing plants is treated for color and organic matter.
Pure Water Monterey’s multi-barrier treatment system places an SSI ozone system ahead of membrane filtration, reverse osmosis, and a UV/hydrogen peroxide AOP system. Managers report that the SSI ozone system contributes to higher performance of the downstream membrane filtration system, reduces backflush water and chemical consumption, and lengthens cycles between cleaning.
12:1 Turndown Ratio
The 180 peak MGD WaterOne treatment plant in Johnson County, Kansas, USA, draws source water from both the Missouri and Kansas Rivers, using ozone to control taste and odor compounds. WaterOne serves more than 480,000 customers, whose dramatic fluctuations in daily and seasonal demand create a 1:12 turndown ratio. Sidestream injection allows plant managers to adapt to the massive changes in flow through the plant.
To optimize ozonation in step with changing flows, WaterOne uses SSI to treat a small fraction of the total flow, then mixes it back into the main supply through either or both of two Pipeline Flash Reactors—one 54 inches (1.37 meters) and another 84 inches (2.13 meters) in diameter.
Despite the variation in source water and flow, WaterOne’s treated water was recognized by the National Rural Water Association as the winner of the 22nd annual Great American Water Taste Test—the nation’s besttasting water.
Conclusion
The versatility and efficacy of ozone make it an ideal tool for the fast, effective treatment of a wide range of contaminants in water. Optimizing contact, mixing, maintenance, footprint, and safety with sidestream injection (SSI) systems can widen the opportunities for ozone adoption. The benefits of SSI are reflected in several case studies presented at the IOA-PAG 2022 conference, and in the significant trend toward SSI over FBD in recent decades.
References
AWWA Standard F120-18 Ozone Systems for Water.
Cashman, S., Gaglione, A., Mosley, J., Weiss, L., Hawkins, T. R., Ashbolt, N. J., and Arden, S. (2014). Environmental and cost life cycle assessment of disinfection options for municipal drinking water treatment. US Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA.
Computational Fluid Dynamics: Applications in Water, Wastewater, and Stormwater Treatment (2019), Eds. Liu, X and Zhang, J. https://ascelibrary. org/doi/book/10.1061/9780784415313
Special Collection on Emerging Applications of Computational Fluid Dynamics in Water Treatment, ASCE Journal of Environmental Engineering.
International Ozone Association – Pan American Group (https://ioa-pag. org/guidance).
IOA Pan American Group. (2018). A Review of Ozone Systems Costs for Municipal Applications.
Ozone Science & Engineering. 40. pp 266-214.
International Ozone Association – World Congress 2021; https://ioa-pag. org/2021-IOA-World-Congress.
International Ozone Association – Pan American Group 2022 Conference; https://ioa-pag.org/2022-Conference-Proceedings.
Knatz, C., and Pathapati, S. (2021). Application of Computational Fluid Dynamics to Improve Mixing and Disinfection for Ozone Contactors. ASCE Technical Webinar.
Lauria, J. (2021, March 11). Deep Dive Into Data Reveals Powerful Ozone Story. Retrieved from Water Online: https://www.wateronline.com/doc/ deep-dive-into-data-reveals-powerful-ozone-story-0001.
Loeb, B. L., Thompson, C. M., Drago, J., Takahara, H., & Baig, S. (2012). Worldwide Ozone Capacity for Treatment of Drinking Water and Wastewater: A Review. Ozone: Science & Engineering(34), 64 - 77.
Noibi, M., Hooper, J., Bell, K., & Funk, D. (2020). Direct potable reuse using full advanced treatment versus ozone biofiltration: A cost comparison. AWWA Water Science, 2(6), e1210.
Rakness, K. L. (2005). Ozone in Drinking Water Treatment: Process Design, Operation, and Optimization. Denver: American Water Works Association. Schulz, C., Bellamy, W., (2000) The Role of Mixing in Ozone Dissolution Systems.
Smith, F., Walton, T., and Snider, R. (2017). Performance Improvement Through Capital Upgrades. AWWA ACE17.
Snider, R. (2021) 30 Years of Ozone at the Mannheim Water Treatment Plant: Lessons Learned and Next Steps. Ontario Water Works Association Webinar.
Steinke, T., Pathapati, S., Schulz, C., Healy, J., Jewell, B., Jones, E., Sumpter, R., and Newell, Q., (2021). Evaluation of Mixing, Mass Transfer, O&M, Energy, and Material Requirements for H2S Oxidation at the Orlando Utilities Commission (OUC) Water Treatment Plants. AWWA Florida Section 2021 Conference.
USEPA (2005). Surface Water Treatment Rule, USEPA Long Term 2 Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule.
Versteeg, H. K., and Malalasekera, W. (2007). An introduction to computational fluid dynamics: the finite volume method. Pearson Education.
Wert, E., Rakness, K., Mundy, B., and Rosario-Ortiz, F. (2012). Bromate Formation Differences between Ozone Side-Stream-with-Degas and Diffuser Transfer Systems. International Ozone Association – Pan American Group 2012 Conference.
Wert, E., Lew, J., and Rakness, L. (2016). Effect of Ozone Dissolution Systems on Ozone Exposure and Bromate Formation. Water Research Foundation Project 4588.
Wicklein, Ed & Batstone, Damien & Ducoste, Joel & Laurent, Julien & Griborio, Alonso & Wicks, Jim & Saunders, Stephen & Samstag, Randal & Potier, Olivier & Nopens, Ingmar. (2015). Good modeling practice in applying computational fluid dynamics for WWTP modeling. Water Science and Technology. 73. wst2015565. 10.2166/wst.2015.565.
Zhang, J. (2007). An integrated design approach for improving drinking water ozone disinfection treatment based on computational fluid dynamics.
Zhang, J. (2014). Numerical Simulation of Flow in Ozonation Process.
NEWS VOLUME 52, NO. 2 IOA OZONE NEWS 19
INDUSTRY
Welcome, New Members
IOA-EA3G
CROATIA
Dr. Masa HRELEC PATRLJ
Hermana Buzana 6
10000 ZAGREB
GERMANY
Mr. Uwe HUEBNER
Xylem Services GmbH
Mr. Pieter FEENSTRA
Nedap N.V.
Parallelweg 2
NL-7141 DC GROENLO
Mr. Tonnie TELGENHOF
OUDE KOEHORST
Nedap N.V.
Parallelweg 2
NL-7141 DC GROENLO
IOA-PAG
USA
Joseph Jordan
Xylem Water Solutions 14125 South Bridge Circle
Charlotte, NC 28273
Steven Watson
USC San Diego 9500 Gilman Dr La Jolla, CA 92093
MEXICO
Robert de Alba
Kiritu Soluciones
Ignacio Carrillo 1273
Guadalajara, Jalisco 44510
LEBANON
Ziad AD
Imam Ouzai College of Islamic Studies
Beirut CANADA
Andre Bilek
Nebula Group - Climate Controls Systems
20 IOA OZONE NEWS VOLUME 52, NO. 2 MAY 9–11 2024


Iberoamerican Conference on Advanced Oxidation Technologies 12th Annual Meeting of The American Academy of Ozonotherapy ORLANDO, FLORIDA, USA JW MARRIOTT GRANDE LAKES FLORIANOPOLIS, BRAZIL OCEANIA CONVENTION CENTER OCT. 7–11 2024 INDUSTRY NEWS
NEW MEMBERS JAN.–FEB. 2024
Boschstrasse 4-14 32051 HERFORD NEW MEMBERS JAN.–FEB. 2024
THE NETHERLANDS
408 Mersea Road 3 Leamington, Ontario N8H3V5
IOA—International Ozone Association EA3G2024 – Europe, Africa, Asia, Australasia Group International Conference
VILA NOVA DE GAIA (PORTO) PORTUGAL, PORTUGAL • WORLD OF WINE
Ozone and Advanced Oxidation Science, technologies and applications for a better world.
EA3G2024 renews with a long series of successful conferences which were organised to provide an international forum for all concerned including fundamental, engineering and applied aspects of oxidation techniques involving ozone and advanced oxidation systems.

SCOPE & OBJECTIVES: Population growth associated with increases in urbanization, in consumption, in industrialization, in pollution emissions already lead to shortages of water, food, raw materials and globally to climate change. However, climate and earth-resilient development is still possible by devoting greater efforts to certain key sectors: reduction of emissions to air, better resources management and preservation of the natural ecosystems. This involves particularly the implementation of advanced technologies. EA3G2024 event thus aims to present an overview of the current state of knowledge and the latest advances regarding the use of Ozone and Advanced Oxidation to provide solutions face to these challenges.
Topics of interest relevant to the Conference theme include but are not limited to the combinations of:
• Reaction mechanisms, kinetics, by-products
• Ozonation
• Advanced oxidation
• Disinfection
• Ozonolysis
• Hydraulics, hydrodynamics, mass transfer, contactors
• Modelling, validation, system design
• Analytical methods
• Agri-Food production, safety and quality
• Waste, Air and Soil treatment
• Wash water, process water
• Wastewater treatment, recycling and reuse
• Ecosystem preservation
• Industrial applications
• In-field full scale applications
• Product / Process R&D
• Hybrid ozone processes
• Innovative applications
• Regulations
REGISTRATION
• Registration will be available early July 2024.
• The registration fee will cover scientific and technical sessions, book of abstracts, electronic proceedings, lunches, coffee breaks, exhibition and technical tour.
LANGUAGE AND CONFERENCE VENUE
• The official language will be English.
WINTER SCHOOL
PROGRAMME:
• Scientific and technical sessions with oral and poster presentations, discussions
• Networking opportunities and Exhibition of ozone related products and services
• Technical visit of ozone plant(s)
• Conference dinner for delegates and their guests
CALL FOR PAPERS — PUBLICATIONS:
• Researchers, scientists, and professionals are invited to propose oral or poster presentations related to the theme topics.
• Authors should submit an extended abstract in English of two pages (with tables and figures) (dates to be announced soon).
• The Programme Committee will notify authors about the acceptance of their papers for oral or poster presentation (dates to be announced soon).
• During the conference, the Programme Committee will select and award a prize to the best paper presented by a PhD student. All accepted papers will be printed in the conference proceedings and handed out to participants at registration. After the conference, the editors of the IOA journal “Ozone: Science & Engineering” will make a final selection for a potential publication as peer-reviewed article.
ASK EXHIBITION AND SPONSORING OPTIONS:
• The exclusiveness of the conference theme allows exhibitors and sponsors an ideal opportunity to meet a unique and targeted audience.
• For detailed information on sponsoring options, please contact the IOA-EA3G secretariat to make the most of this event.
• A Winter School on “Contaminants of Emerging Concern and Disinfection By Products: Occurrence, Impact and Elimination,” will be held in the World of Wine, from 25 to 26th November, just before the EA3G2024.
• Winter School participants will have a reduced fee in EA3G2024 conference, equivalent to IOA members.
• The Winter School will be organized by the Faculty of Engineering of the University of Porto, University of Coimbra, and Sociedade Portuguesa de Inovação (SPI), under the scope of the projects BlueWWater (INTERREG-POCTEP) and H2OforAll (Horizonte Europe), with the support of IOA.
• The Winter School program will include: i) Floor to PhD Students: section specifically devoted to PhD students where they will have the chance to introduce themselves and their work, through a short oral presentation and/or a poster communication, as well as to meet experts from the School; ii) Lectures on complementary skills: European legislation on drinking water, urban wastewater treatment, and wastewater reuse; Advanced analytical methods for CECs and DBPs, microplastics, ARB, ARGs; Risk assessment; Advanced treatment technologies (Ozonation, Advanced Oxidation Processes, Adsorption, Membrane Filtration); Life Cycle Assessment; Life Cycle Costing; Simulation; iii) Workshop on Wastewater Treatment and Reuse; iv) Workshop on Disinfection by Products (DBPs).
• PhD students are invited to submit an extended abstract in English of two pages (with tables and figures) (dates to be announced soon).
• The Programme Committee will notify authors about the acceptance of their papers for short-oral or poster presentation (dates to be announced soon).
NOV. 27–29 2024
International Ozone AssociationPan American Group (IOA-PAG) 2024 Conference
AUG.
26–29 2024
Palms Casino Resort, Las Vegas, Nevada

Benefits of Attending Include:
• Two days of technical presentations by Ozone experts
• Round-table discussion session hosted by industry leaders
• Workshop for those who are new to Ozone technology
• Exhibit hall with leading manufacturers of Ozone equipment
• Networking opportunities to learn more about Ozone applications
• Technical tour to learn more about other Ozone installations
Technical Program
The Technical Program will feature two days of technical presentations on subjects, such as drinking water treatment, water reuse, industrial applications, etc. Presenting authors may have their work considered for publication in Ozone Science & Engineering (OS&E), the official journal of the International Ozone Association. All conference attendees will receive a complimentary copy of the conference proceedings.
The IOA-PAG Conference will showcase leadingedge technologies for municipal water, municipal wastewater and industrial process applications with special attention to both Ozone and AOP technologies.

Registration
Information for participants, exhibitors, and sponsors will be made available in the coming months! For questions, contact support@ioa-pag.org or (916) 441-0629.
The Call for Abstracts
To submit your abstract, click here. Submissions must be received by March 8, 2024 to be considered for the IOA-PAG Conference program.
2 0 2 4
IOA-PAG Conference

CALL FOR ABSTRACTS
The International Ozone Association - Pan American Group (IOA-PAG) wants you to share your exciting Ozone and AOP technological advancements and experiences in this unique forum showcasing the world's premier advanced treatment technologies! This Conference will provide current technical, process, and operational information to engineers, scientists, and end users of Ozone and Advanced Oxidation technologies with focus on municipal & industrial water, wastewater, water reuse and emerging contaminants in North and South America.

Submit your Abstract by March 8, 2024 online at ioa-pag.org/event-5491046
Topics May Include:
Advanced Oxidation
Aquaculture
Biofiltration
Bromate Formation and Control
Chemical and Biochemical Reactions
Disinfection
DBPs Formation and Control
Drinking Water Treatment
Emerging Contaminants
Marine Mammal Aquarium
Operations and Maintenance
Ozone Systems Design
Ozone Mass Transfer
Ozone Measurement
Pools and Water Features
Regulatory Perspectives
Wastewater Treatment & Water Reuse
Questions?
Accepted Speakers:
Speakers whose abstracts are selected will receive a discount of $100 off of the Early Bird Conference registration fee!
Attention Students:
When submitting your abstract, inform support@ioa-pag.org if you’d like to be considered for a Memorial Scholarship Award to receive a complimentary Conference registration!
Roundtable Discussions:
Roundtable discussions will be featured in the Technical Program If you would like to lead/moderate a discussion using this format, please submit your idea through the Call for Abstracts link
For questions regarding the IOA-PAG Conference or Abstract submissions, please contact the IOA-PAG at support@ioa-pag.com or (916) 441-0629.

A U G U S T 2 6 - 2 9 | L A S V E G A S , N V



















Trust Time -p r PSA an d Syste foo@air sep.com p.com OMPANY ed, oven VPSA ms eneration Today! foor Ozone G 1.800.874 .0202 ■ in www.airsep A CAIRE INC. C Contact Us International Ozone Association c/o AAMSI 1521 I Street Sacramento, CA 95814 Widest selection of systems and options High efficiency and cost effective Eliminate oxegen deliveries Lowest Sound Levels Ease of use, service, and support Trust Time -p r PSA an d Syste foo@air sep.com p.com OMPANY ed, oven VPSA ms eneration Today! foor Ozone G 1.800.874 .0202 ■ in www.airsep A CAIRE INC. C Contact Us International Ozone Association c/o AAMSI 1521 I Street Sacramento, CA 95814 Widest selection of systems and options High efficiency and cost effective Eliminate oxegen deliveries
Sound Levels Ease of use, service, and support ■ Widest selection of systems and options ■ High effeciency and cost effective
Eliminate oxygen deliveries
Lowest sound levels ■ Ease of use, service, and support 1.800.874.0202 ■ info@airsep.com www.airsep.com A CAIRE INC. COMPANY Trusted, Time-proven PSA and VPSA Systems for Ozone Generation Contact Us Today!
Lowest
■
■










































































