Lumière Coryphée
Adaptive Facades P6/P9
GODO ZABUR SINGH
What is an Adaptive Façade?
Adaptive façade is a building exterior that can change in response to its surrounding environment to maximize its performance. In this way, the 'skin' of the building is not static, but dynamic and can transform according to requirements.

Location : New Delhi, India


P6/P9 CONTEXTUAL FAÇADE DESIGN ASHLEY GROVER | GODO ZABUR SINGH | HYEONJI SEOL | JUNAID NASIR
Climate Analysis Design strategy needed during a year

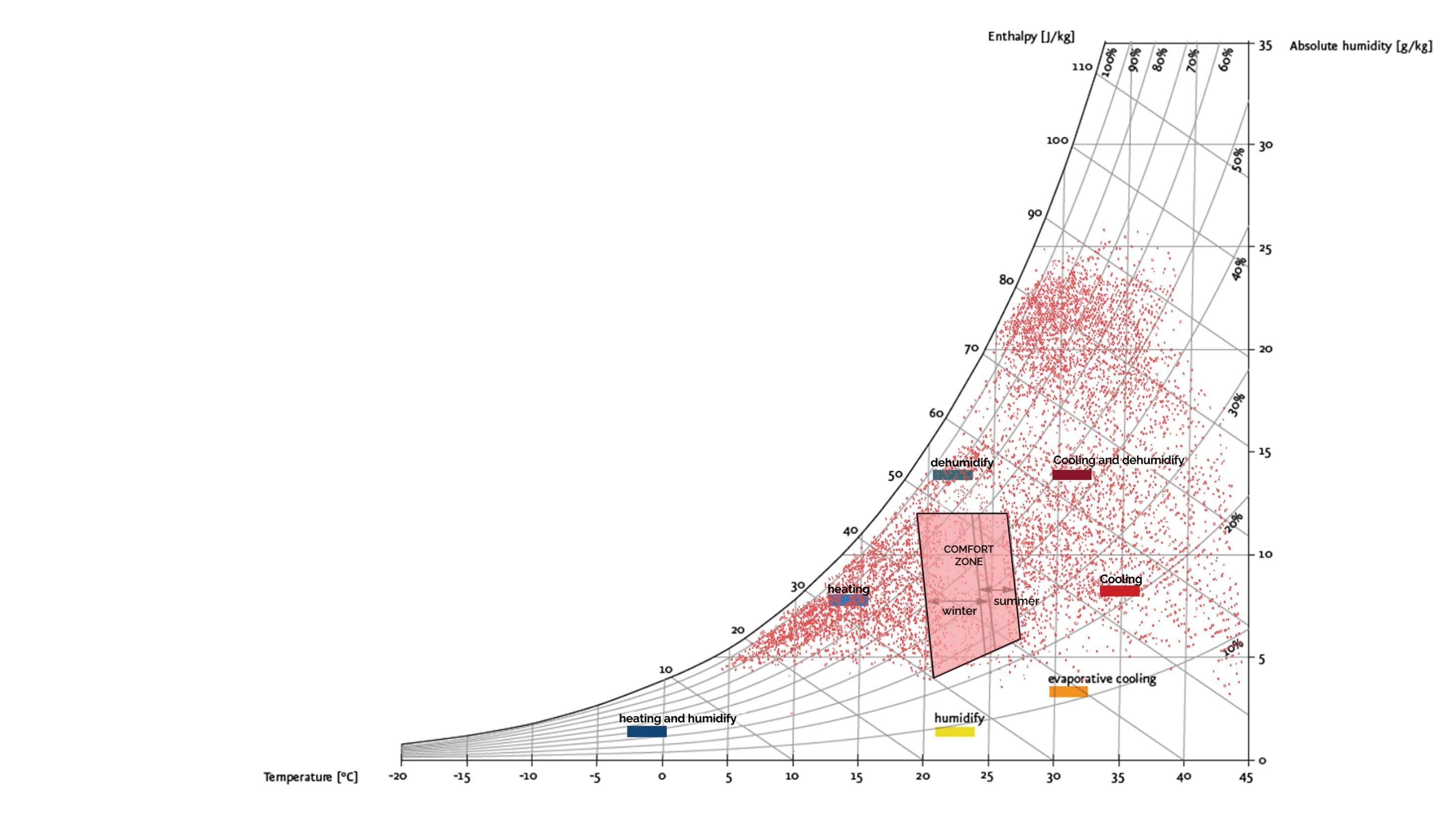
Cooling, add Dehumidification (3552hrs)
Sun Shading of Windows (2299 hrs)
Internal Heat Gain (1625 hrs)
Two-stage Evaporative Cooling (1322 hrs)
Fan-Forced Ventilation Cooling (943 hrs)
Passive Solar Direct Gain High Mass (809 hrs)
Heating, add Humidification (678 hrs)
Dehumidification only (280hrs)
Inference- We need a system which blocks sunlight in interiors during summers and allow it during cold temperature. This will decrease heating and cooling loads giving comfortable interiors.
P6/P9 CONTEXTUAL FAÇADE DESIGN ASHLEY GROVER | GODO ZABUR SINGH | HYEONJI SEOL | JUNAID NASIR
Design inspirations
Dynamic Experiences found in Nature Bio-mimicry
Nyctinasty is the circadian rhythmic nastic movement of higher plants in response to the onset of darkness, or a plant "sleeping" Nyctinastic movements are associated with diurnal light and temperature changes and controlled by the circadian clock




Max Min Kinetic mechanism concept
Development of Origami shading part



Pattern 1
Pattern 2

Pattern 3
Pattern 4
Parameterizing
Origami Pattern
Folding Plan
Simulating the folding pattern


Final pattern - top

Final pattern - bottom

Development of the gear-based inner mechanism
First mechanism concept





Second iteration with improvements







 Inner mechanism with shading attached
Inner mechanism with shading attached
vs
Wax-based system
Electromagnet based system
Mechanism 1 : Based on principle of Autovents for Greenhouses
(Paraffin wax + spring system)
Spring helps bring back the system once the wax is cold again
Autovents for Greenhouses
(Paraffin wax + spring system)
Cool - 5° C
Warm - 35° C
Solid wax
Liquid wax
(Expands)
Metal tube
Metal tube
Metal rod
Metal Rod (Being pushed outside By the wax)

Wax needs a large volume to expand sufficiently
In thicker volumes, the outer layers act as self-insulating and prevents heat from reaching inside
The expansion and phase-change of wax is a slow process



The wax container needs to be expandable as well as sealed, increasing chances of leakage

CONCLUSION
Mechanism 2 : Electromagnet based ( Electromagnet + Heat switch)
the piston move the gears and shading mechanism is engaged
radiation from sun heats the heatswitch above 30 degrees and activates the circuit
power runs through the electromagnet and it pulls the piston towards it
as the circuit completes, current from the power source is drawn




Top Rail
Customized gear+ hands
Metal base (without electricity)
Heat switch (incomplete circuit)

Cool - 5° C
Outer Shell
Top
Customized gear+ hands
Rail
Metal base (Working as an electromagnet)
Heat switch (Completes circuit)
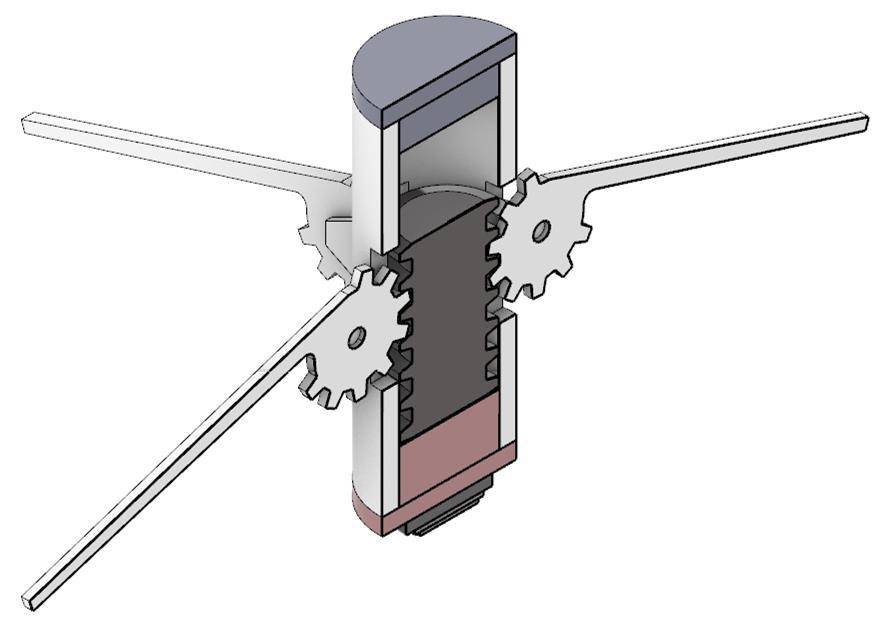
Warm - 35° C
Outer Shell
Prototype Assembly
1. Gear-based inner mechanism
2. Heat switch
3. Battery
4. Piston
5. Screw
6. Electromagnet
7. Cable

1 2 3 4 5 6 7
PROBLEM : The 3d printed model has a very rough surface. Therefore it creates too much friction for the piston to move freely inside the tube.

SOLUTION : This situation was alleviated by sanding all the surfaces that have to come into contact with one another.
PROBLEM : The Electromagnet moves towards the piston as the piston is moving towards the magnet.
SOLUTION : This was corrected by creating a proper housing inside the tube and fixing the magnet in place with adhesive.
PROBLEM : The mechanism is not activated by temperature change.
SOLUTION : Added a heat-switch to complete the circuit.
Final Working Prototype Cluster

Future Prototype Development


arms
grid-attachment
wire-grid
heat-switch
piston
electromagnet


Fabric BIPV
Future Vision
Fabric Solar cells can be used to generate electricity for supporting the mechanism and produce additional energy for the building. Due to its adaptive nature and concave form, it will be an efficient solution for producing energy.




Attachment and Installation Details




A B
Mounting Detail : Cables to standard stick-curtain wall
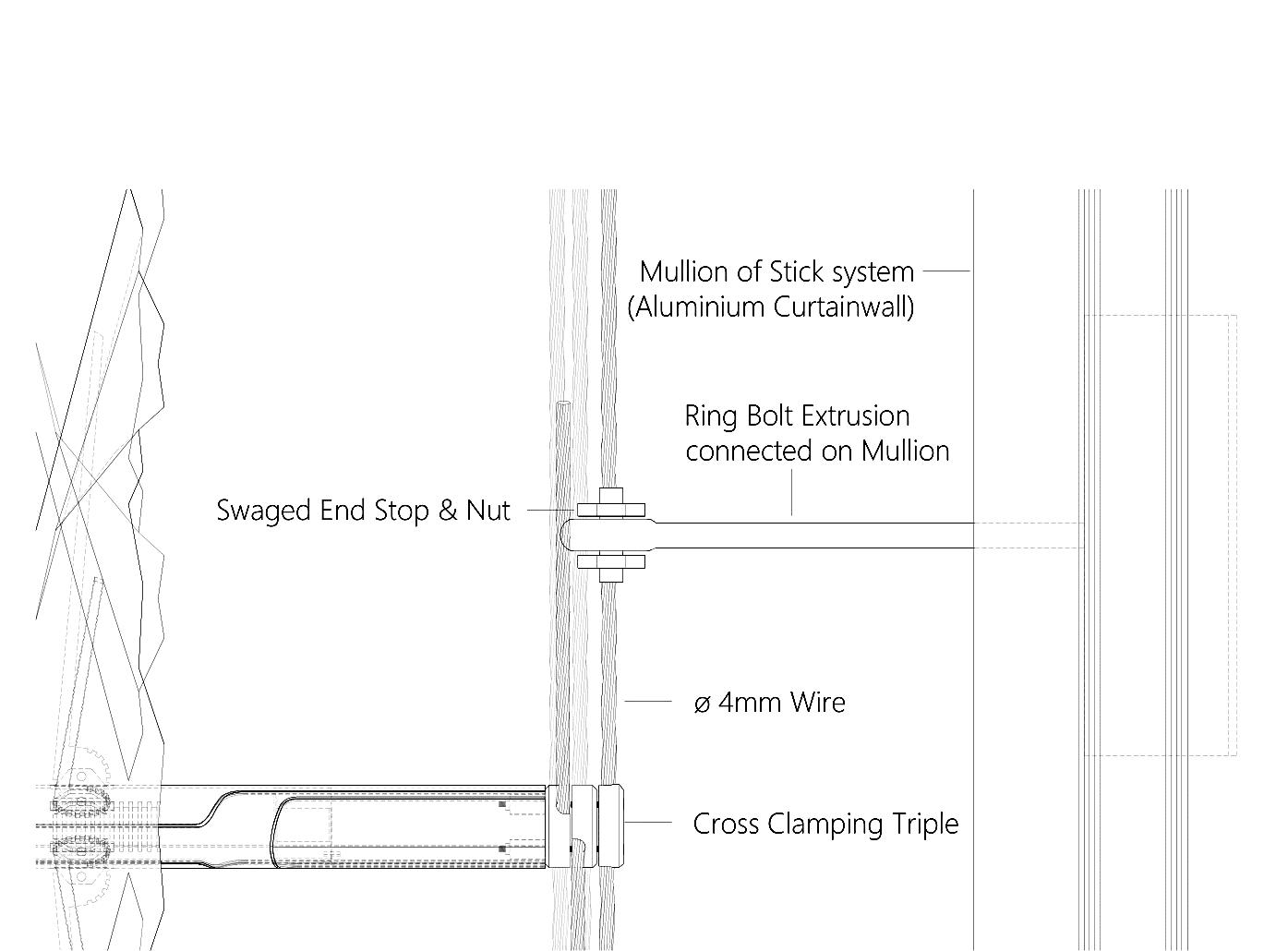
Isometric detail

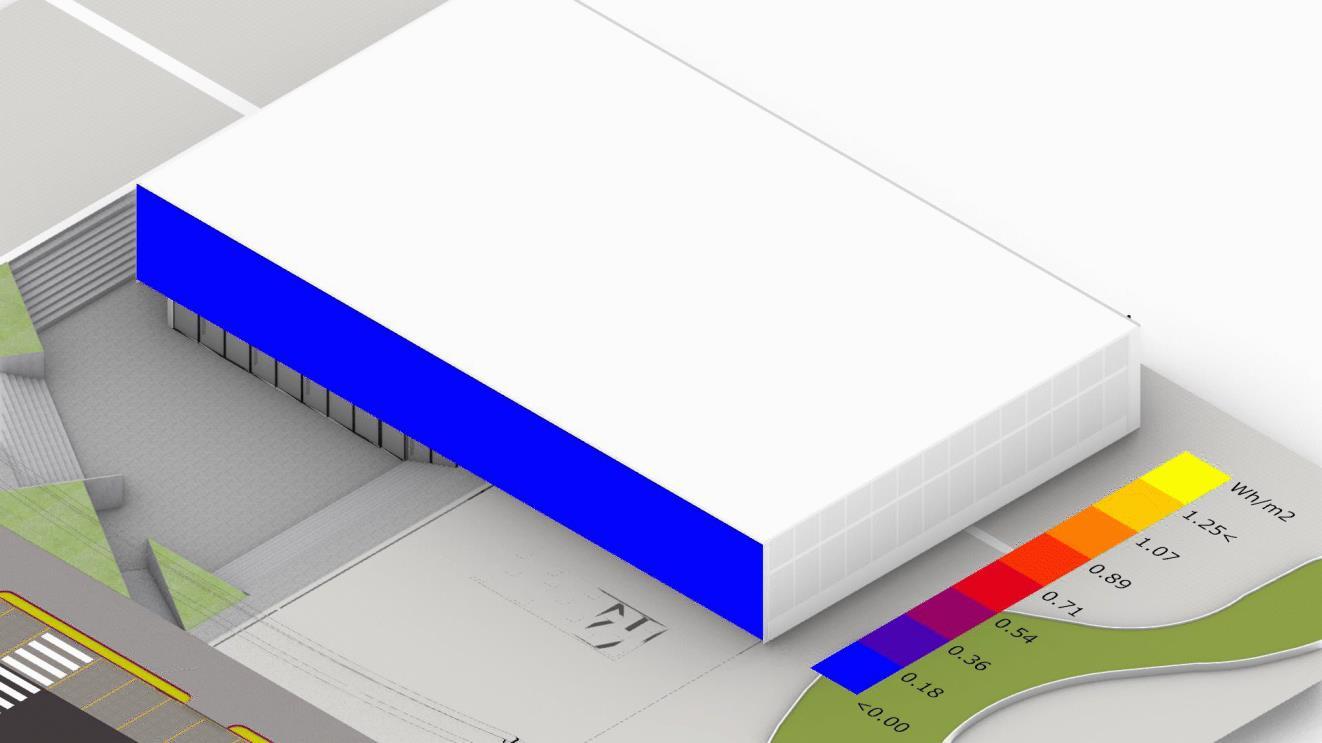
Primary Façade Function
Sun-shading for indoor comfort
Analysis based on average annual radiation from 5 am to 6 pm

Secondary Façade Function Art Installation
Building Scale

































 Inner mechanism with shading attached
Inner mechanism with shading attached