




• Insects have two pairs of wings, one of which folds to enable efficient flight, and the second pair protects the first pair of wings.
• They also have antennaeresponsible for touch, taste and smell.
• They also have 3 pairs of legs.
• Insects have compound and simple eyes.
• Their legs and mouthparts can be different, such as prehensile, clinging, swimming and burrowing. As for their mouthparts, they lick, bite, suck, and also pierce and suck.
• They also have an abdomen,which may contain a sting or ovipositor
• Insects have mouthparts that are used to obtain food.
• Insects have a chitinous epidermis that protects the body against damage and water loss.

• Swallowtail butterfly

• Peacock butterfly

• Cabbage moth

• Icarus blue

• Larger crustaceans, including crayfish and crabs, eat numerous invertebrates and small vertebrates
• Crustaceans forming plankton are food for many species of aquatic animals. For example, krill is the basis of food for whales, seals and penguins living in Antarctic waters
• Crustaceans such as barnacles and daphnia, which capture food particles floating in the water, accelerate water purification
• Crustaceans are nutrients for humans, including: crayfish, crayfish, lobsters, crabs and shrimp.
• They are food for aquarium fish.




• Arthropods live primarily on land, from humid equatorial forests to vast areas of ice deserts. We also find them in seas, oceans, rivers and lakes.
• Arthropods are divided into three groups: crustaceans, arachnids and insects. These animals differ in some features of their external structure, including the number of legs and main body parts. for example, the body of insects is divided into a head, thorax and abdomen, while in crustaceans and arachnids there is a cephalothorax and an abdomen.





• The solar systemconsists of the Sun, planets and other smaller celestial bodies, the planets orbit the Sun at different times, and the closer a planet's orbit is to the Sun, the shorter its orbital time. Mercury orbits the Sun in 88 days; It takes Earth just over 365 days while distant Neptune orbits the Sun. in 165 years.


• London is home to the headquarters of important banks, major insurance companies and law firms. The London Stock Exchange is the largest in Europe and the largest news magazines about the business world are published there.


• Paris is an important cultural center in Europe and the world. It has attracted artists for centuries. The city is also famous for museums such as the Louvre. Paris is also called the world capital of fashion, it was there that the first coco Chanel fashion houses were established.
•
• There are climatic zones on Earth: equatorial, tropical, subtropical, temperate and circumpolar. Climatic conditions in each climate zone are determined by latitude, but may be modified by the presence of other geographic factors.


• Earth's rotation is the rotation of the Earth around its axis. It runs from west to east, i.e. counterclockwise. The time of one revolution is 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds - it is said to be a day.
• Ctrl + O – Open document.
• Ctrl + W – Close document.
• Ctrl + B – Makes the text bold.
• Ctrl + I – Italic.
• Ctrl + U – Underline text.
• Ctrl + [ - Decrease the font.
• Ctrl + ] - Increase front size.
• Ctrl + E – Center text.

• The first computer is the Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer, or ENIAC, presented on February 14, 1946. It is consideredthe world's first and largest desktop computer. Work on this machine lasted from 1943 to 1945 at the University of Philadelphia.





• The first website on the Internet was prepared by the CERN centerin Switzerland. You can still visit it today and see what the beginnings of the Internet looked like. The first web page is actually a plain text document in which you can navigate through individual topics using hyperlinks.
• The language used by a user to communicate with a computer. This is a broader concept than the concept of a programming language, because computer languages also include: scripting languages or query languages.It is a language that a computer can understand.There are highlevel and low-level programminglanguages.

• The first webcam was created in 1991 and was mounted next to a coffee machine at the University of Cambridge. This was to allow employees to confirm whether their coffee was ready. Only recently this device was sold at an online auction, reaching a price of PLN 17,000.

• Meet Flocks Wobot - an innovative project created by Dutch designer Christien Meindertsma. The invention is based on the operation of a 3D printer and creates a layered pattern from wool. The robot uses yarn to apply one layer on top of another, making it possible to create even complex patterns on the material without the need to felt the wool or add water.


• Robotic prosthetic limbs are no longer rare. Development in this field is very dynamic, as exemplified by the device created by Brain Robotics. The prosthesis created by this company was called BrainRobotics Bionic Hand. It is equipped with as many as 10 joints and a movable thumb. It allows you to perform 14 different holds. Thanks to its simple design,it can be easily put on and taken off the wrist.

Projection in space:
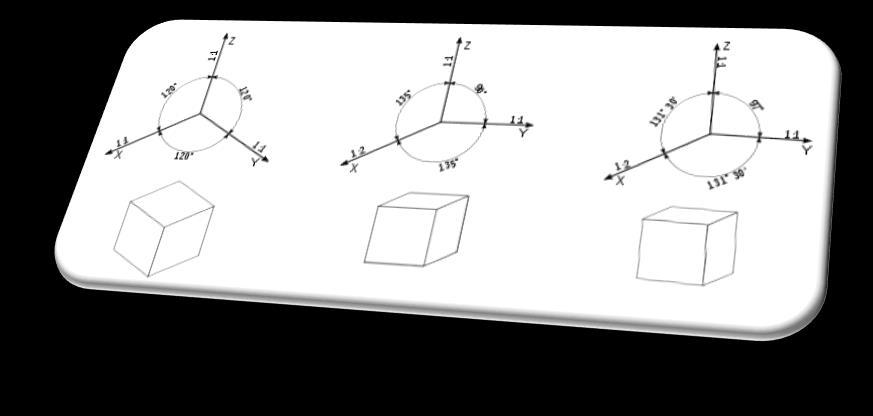
• Axonometricprojections are used to present the shapes of objects in three dimensions. One drawing contains three basic dimensions: height, width and depth. Viewports will then not be created by the three axes: X, Y and Z.
Axonometricprojections include isometric, dimetric oblique and dimetric rectangular projections.All of them can be made both with drawing tools and by hand - in the form of sketches.
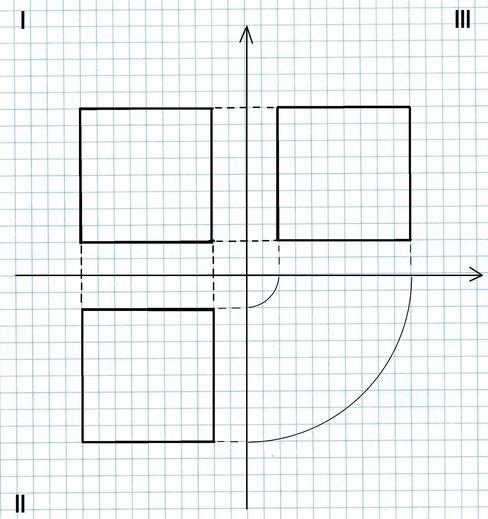
To show the exact shape of a three-dimensional object on a plane, drawings called orthographic projections are made, which show the object from several sides. Most often, they are performed on three planes, called viewports. The first one shows the main view, i.e. the front view. The second view shows the top view and the third view shows the side view.



• Each house is equipped with installations that make life easierfor its inhabitants. Already at the design stage, the arrangement of devices and pipes enabling lighting and heating of the building, water and gas supply and sewage disposal is planned. These installations are installed at the building construction stage.
• Central heating installation
•
• Electrical installation
•
• Water instalation
•
• Sewage installation
•
• Gas installation


• Dry ice is solidified carbon dioxide. So it has nothing to do with water. It is a completely natural substance. There is no smell. It is completely non-flammable and bacteriostatic. It is available in solid form with various appearances. Dry ice is obtained by expanding liquid carbon dioxide. It can be formed by pressing. Under normal conditions, there is no melting, but sublimation, i.e. a transition from a solid state to a gaseous state without a liquid phase. The sublimation temperature is -78.5°C. When you observe dry ice, it appears to be smoking. This vapor is carbon dioxide, which is harmless to the body in small doses.

• Every carbonated drink contains dissolved carbon dioxide. The pressure in the closed vessel(bottle) is higher than atmospheric and this increasedpressure causes carbon dioxide to be dissolved in the liquid. In a champagne bottle, this pressure can be up to six times higher than the pressure outside the vessel. Therefore, a champagne cork can burst at speeds of up to 50 km/h. This is enough to damage the eye.
Opening the bottle reduces the air pressure outside the liquid, which is no longer able to hold the carbon dioxide dissolved in the liquid. It is commonly believed that the entire process begins with forming a vesselcontaining a liquid saturated with carbon dioxide on uneven and slightly dirty surfaces. They are called embryos. The gas bubble absorbs more and more of it, and when it reaches a criticalsize, the buoyant force lifts it up.
• Well, it's not warm at all. After the needle is built, the air temperature inside and outside is the same. So what is cold protection?
Entering an igloo during a winter storm will protect your body from the bitter wind and rapid cooling. That's quite a bit of protection. When the human body is exposed to freezing wind, heat loss is much greaterthan in the absence of wind and frost. We all instinctively blow on hot food to cool it down faster.

• Near the Pole and the Arctic Circle, and sometimes even at our latitude, you can observe the wonderful phenomenon of the Northern Lights. The aurora sometimes reaches enormous sizes. How does the aurora form? The aurora borealis is a characteristic glow of the upper atmosphere in the Arctic and Antarctic regions. The aurora borealis sometimes extends thousands of kilometers around the globe from both poles. However, it is quite thin, only about 100 meters thick. What is the mechanism of its formation? The Earth produces a magnetic field whose lines wrap around the entire globe, becoming much thicker near the south and north poles. This field causes the accelerationof electrons and protons located at altitudes from 3 to 12 thousand kilometers.




• Mendeleev's table contains 118 elements, of which 90 of them can be found in nature on our planet. The rest was created in human laboratories. Is it similar in space? Galaxy Research shows that the Universe contains the most hydrogen and helium atoms of all the elements known to us. If you count one million random atoms "caught" in the Universe, then statistically there will be over 950 thousand atoms of hydrogen (over 95.2%), helium over 47 thousand (over 4.7%) and less than 100 atoms of any other element (that's only 0 .01%).
• An atom is the smallest particle of a chemical element that retains its properties. However, it is not indivisible. it consists of a positively chargedatomic nucleus, containing over 99.9% of the atomic mass, and electrons lcated outside the atomic nucleus. The components of the atomic nucleusprotons and neutrons - are nucleons. The masses of the particles that make up atoms are expressedin atomic mass units u, 1 u = 1.66 * 10 -24 g.



• Air is a homogeneous mixture of gases. It is odorless, colorless, non-toxic and slightly soluble in water. Under normal conditions (0*C, 1013 hPa), 1m3 of air has a mass of approximately 1.28 kg. Air
composition: -78% – nitrogen -
21%– oxygen -0.9% – Argon -
0.1% – other gases – water
vapor, carbon monoxide (IV), hydrogen, ammonia, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons.
• Acids are chemical compounds composed of one or more hydrogen atoms and an acid residue.
We introduce the markings:
• H – Hydrogen Atom (I-Valent)
• R – Acid Residue
• m – Valency of the acid residue (Equal to the number of hydrogen atoms in the molecule of a given acid)
Acids are divided into:
• Oxygen-free – the acid molecule does not contain oxygen atoms,
• Oxygen- the acid molecule is also made up of oxygenatoms.
number of hydrogen atoms
• Oxides are a group of chemical compounds whose oxygencombines with other elements. If a non-metal atom combines with oxygen, it is called a non-metal oxide; if the element is a metal, the oxide is called a metal oxide.
metals non-metals for example MgO, FE2O3 for example SO3, CO2
• Salts are chemical compounds consisting of atoms (more precisely, cations), metals and acid residues (anions of acid residues).
• We will introduce the following symbols:
• M – metal atom (cation).
• n – Valencyof the metal atom (charge of the metal cation)
• R – Acid residue
• m – Valency of the acid residue (anionic charge of the acid residue)
General salt formula: