WHITNEY LYNN
USD 10 Billion M&A specialist joins XRP Healthcare
ISANSYS LIFECARE
Pioneering patient data solutions for better clinical decisions
EHLERS-DANLOS SOCIETY
CEO & Professor Lara Bloom on her relentless pursuit for change on a global scale

SSUE 3 | 2024 NOT FOR SALE
LIVE LONGER!
Extending lifespan & enhancing life quality through science
INTELEOS
Transforming maternal and foetal healthcare in Africa
TOP 10 HOSPITALS IN AFRICA
Discover Africa’s leading healthcare providers
Dr. Peter Waiswa
MEET GLOBAL HEALTH POLICY INFLUENCER SERVING AS AN ADVISOR TO UNICEF, WHO, GATES FOUNDATION & LATEST ADDITION TO THE XRP HEALTHCARE TEAM







2 | www.xrphealthcare.com
Celebrating XRP Healthcare’s remarkable progress!
Dear Readers,
In only three months, XRP Healthcare has reached impressive goals that show how dedicated they are to changing healthcare in Africa. Right from the start, they’ve stayed focused on making healthcare better and easier to access. Their latest achievements prove how committed they are to this goal.
From its inception, XRP Healthcare has set out to redefine healthcare standards in Africa. With a clear vision and a team of passionate professionals, the company has laid the groundwork for transformative change. Its commitment to excellence has been evident at every step, from strategic planning to operational execution.
One of the most notable achievements in the past three months has been XRP Healthcare’s expansion into Uganda. By successfully trademarking its name in the country and establishing XRP Healthcare Africa, the company has demonstrated its readiness to take on new challenges and opportunities. This strategic move not only strengthens XRP Healthcare’s presence in Africa but also paves the way for greater impact and innovation in healthcare delivery.
XRP Healthcare understands the importance of collaboration in driving meaningful change. Over the past three months, the company has forged strategic partnerships with key stakeholders across the healthcare ecosystem. These partnerships have enabled XRP Healthcare to leverage expertise, resources, and networks to accelerate its mission of transforming healthcare in Africa.
At the heart of XRP Healthcare’s mission is a commitment to innovation and accessibility. The company has launched initiatives aimed at harnessing technology to improve healthcare delivery. From the development of the XRPH App to becoming a validator on the XRP Ledger (XRPL), XRP Healthcare is at the forefront of

Special thanks to; EXECUTIVE TEAM Board/Team Members
FOUNDER
Kain Roomes
CO-FOUNDER
Laban Roomes
leveraging innovation to expand access to quality healthcare services.
Behind every milestone achieved by XRP Healthcare is a dedicated team of professionals committed to making a difference. From the CEO and Founder Kain Roomes to Laban Roomes – the business development officer, healthcare experts, and support staff, each member of the XRP Healthcare team plays a vital role in driving the company’s success. Their passion, dedication, and expertise are the driving forces behind XRP Healthcare’s transformative impact in Africa.
As we celebrate XRP Healthcare’s milestones over the past three months, we also look forward to the future with optimism and excitement. With a solid foundation, strategic partnerships, and a commitment to innovation, XRP Healthcare is well-positioned to continue making a positive impact on healthcare in Africa. Together, we can build a healthier, more prosperous future for all.
We applaud XRP Healthcare’s extraordinary journey over the past three months, let us embrace the optimism and promise it brings for the future of healthcare in Africa. With each milestone achieved, we move closer to a healthier, more vibrant continent where quality healthcare is accessible to all.
We invite you, our valued readers, to explore the interesting articles in this magazine. We’ve put together a collection of topics about modern healthcare that we think you’ll enjoy. We hope you find them informative and inspiring as we learn more about how healthcare is changing. Happy reading, and here’s to a healthier future for Africa.
Best regards,
Editor,Benjamin Opuko, XRP Healthcare Magazine.
EDITOR Benjamin Opuko
JOURNALIST
Hellen Mucheru
GRAPHIC DESIGNER
Cynthia Achieng’
PUBLISHED BY; XRP HEALTHCARE
LOCATION; The Mayden Hotel, Nad Al Sheba Dubai, UAE
EMAIL; Press.xrph2023@gmail.com
WEBSITE; www.xrphealthcare.com
3 | www.xrphealthcare.com
Editorial
70. CONSUMER HEALTH
Ai-Driven health assistants and chatbots provide personalised health information

Transforming lives through care, access, research, and education

From humble origins to global health policy influencer

45. SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY-
Bringing acute care beyond hospital walls with the Patient Status Engine Technology
4 | www.xrphealthcare.com
CONTENTS
6. EHLERS - DANLOS SOCIETY
17. EXECUTIVE INTERVIEW - DR. PETER WAISWA
ISANSYS LIFECARE


Crafting a new healthcare paradigm in Africa through masterful mergers and acquisitions

37. HEALTHCARE DELIVERY - INTELEOS 26. BUSINESS AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP WHITNEY LYNN 88. MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY
Discover Africa’s top hospitals ranked by Webometrics
Bridging the ultrasound specialists gap in Sub-Saharan Africa through POCUS training, certifications, and improved referral systems

Explore the impact of digital health platforms and ecosystems on healthcare access and outcomes
5 | www.xrphealthcare.com
70. TOP 10 HOSPITALS IN AFRICA

HUMANITY AND PHILANTHROPY
PROFESSOR LARA BLOOM - PRESIDENT AND CEO OF EHLERS-DANLOS SOCIETY
From stripes to strength:
How the Ehlers-Danlos Society transforms lives through advocacy, research, and community support
BY BENJAMIN OPUKO

In the medical world, few symbols are as fitting as the zebra. Each zebra’s stripe pattern, as unique as human fingerprints are, is a perfect emblem for the Ehlers-Danlos Society. Just as no two zebras have the same pattern, no two individuals with EhlersDanlos Syndrome (EDS) experience the condition in the same way. This rare group of connective tissue disorders is marked by a striking diversity in symptoms and severity, creating a spectrum of challenges that are as unique as the individuals themselves. Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS) presents with hallmark symptoms like joint hypermobility, where joints extend beyond normal limits, often
leading to instability, recurrent dislocations, and chronic pain, notably in the fingers, elbows, shoulders, knees, and hips. Skin hyperextensibility is another key feature, characterised by stretchy skin prone to tearing, bruising, and atrophic scarring, commonly seen in the neck, elbows, knees, and wrists. It also affects connective tissues beyond joints and skin, resulting in fragile blood vessels, increasing susceptibility to bruising and bleeding, and compromising soft tissues like muscles, tendons, and ligaments, heightening the risk of injury and chronic pain. Additional symptoms vary depending on EDS type and severity, encompassing gastrointestinal,
HUMANITY AND PHILANTHROPY

cardiovascular, dental, and neurological issues. Severe complications, particularly in vascular EDS, include life-threatening vascular events. Early diagnosis and multidisciplinary management are crucial for mitigating symptoms and reducing risks associated with EDS.
Enter the Ehlers-Danlos Society, an organisation dedicated to supporting those living with EDS and advancing research for better diagnosis and treatment. Guiding this mission is CEO Professor Lara Bloom, whose personal journey with EDS has deeply informed her advocacy efforts. Diagnosed after a gruelling 13-year odyssey, Professor Bloom’s own experience with the condition transformed her aspirations, redirecting her from a career in photography to one of impactful advocacy. For close to two decades, she has been a steadfast voice, tirelessly raising awareness and championing support for individuals grappling with Hypermobility spectrum disorders (HSD) and various forms of EDS.
Resilience and relentless pursuit of answers
“I was diagnosed with EDS when I was 24, after a 13-yearlong diagnostic odyssey,” Professor Lara Bloom reveals. For over a decade, she navigated the complexities of her condition, seeking clarity and understanding.
Before her diagnosis, Professor Bloom was a photographer, capturing the world through her lens. However, EDS made it impossible for her to continue in that career. “I was unable to continue with that career,” she shares, reflecting on a significant turning point in her life.
Refusing to be deterred, Professor Bloom embarked on a new path. “I went back to university and studied global politics and international relations and ended up working in this space,” she explains. Today, Professor Bloom stands at the forefront of the Ehlers-Danlos Society, where she channels her experiences and expertise into transformative work. “I love it and feel privileged every day to do what I do,” she says, her words brimming with gratitude and enthusiasm.

The Ehlers-Danlos Society’s reach extends beyond geographical borders, spanning over 50 countries worldwide. At its core is a commitment to the CARE model—Compassion, Access, Research, and Education—a holistic approach to addressing the multifaceted needs of those affected by EDS. Through Professor Bloom’s leadership, the society is a beacon of hope and knowledge, illuminating paths to improved quality of life and understanding for individuals navigating the complexities of EDS and HSD.
Reflecting on the Society’s mission, Professor Lara Bloom underscores the importance of their CARE approach, stating, “We are dedicated to providing a community for healthcare professionals and people living with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and hypermobility spectrum disorders, providing our CARE acronym, which stands for Care, Access, Research, and Education.”
Strong advocacy
Professor Bloom is a strong proponent of healthcare advocacy, working tirelessly to ensure that individuals with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) and hypermobility spectrum disorders (HSD) receive the quality care they deserve. Holding the esteemed position of Professor of Practice in Patient Engagement and Global Collaboration
8 | www.xrphealthcare.com
HUMANITY AND PHILANTHROPY

at Penn State College of Medicine, her dedication to this mission is unwavering. “We advocate for improved access to specialised medical services and treatments, empowering individuals to live their fullest lives,” she affirms.
Yet, Professor Bloom’s dedication extends far beyond words; it manifests in her relentless pursuit of change on a global scale. She traverses continents in a whirlwind of activity, lending her voice to highlevel forums and conferences. “I speak all over the world on various panels and keynotes, and I have the privilege to visit many countries,” she shares with a sense of purpose.
Her schedule speaks volumes about her unwavering commitment to advocacy. “Yesterday, Brussels; the day before, New York. Next up, Italy, then Geneva for the World Health Assembly,” she shares, illustrating the breadth of her global influence. With a different country on her agenda every week, her dedication to meaningful advocacy shines through.
and advocacy groups, we support groundbreaking research initiatives aimed at unravelling the mysteries of these conditions and developing more effective therapies.”
Education lies at the forefront of the Society’s mission, empowering both healthcare professionals and individuals with EDS and HSD with knowledge and understanding. Professor Bloom emphasises this: “Through educational programs, seminars, and informational resources, we seek to raise awareness, dispel myths, and foster a deeper understanding of these complex conditions.”
United in diversity
Diversity prevails within the intricate landscape of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS) and Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders (HSD). With 14 types of EDS and myriad manifestations of HSD, each individual’s journey through diagnosis and life is unique.

A cornerstone of the Society’s work is its dedication to advancing scientific understanding and treatment options for EDS and HSD. Professor Bloom highlights their collaborative research efforts: “Through partnerships with researchers, clinicians,
Emerging amidst this diversity is the zebra symbol, representing the interconnected yet singular experiences of those with EDS and HSD. Professor Bloom explains, “The zebra serves as our emblem because, like each zebra’s stripes, the experiences of those affected are unique yet recognisable.”
9 | www.xrphealthcare.com
HUMANITY AND PHILANTHROPY

The society’s mission extends beyond awarenessraising; it embraces its members’ individual narratives. Professor Bloom emphasises, “It’s crucial to acknowledge that individuals navigate these conditions differently. The spectrum within EDS is vast, and my experience may not mirror that of others. However, a diagnosis should never signify the culmination of one’s journey.”
Her words offer solace to those grappling with diagnosis. “It marks the dawn of a new chapter—a realm teeming with fresh aspirations, fears, and dreams. It’s imperative to recognise that life persists, albeit in a different hue than before,” she elaborates.
In these words, we glimpse the unwavering commitment of the Ehlers-Danlos Society—a journey characterised by hope and purpose, striving towards a world where individuals afflicted with EDS and HSD are met with empathy and effective care. As Professor Bloom affirms, “That’s the horizon we’re journeying towards.”
EDS Impact
The impact of the Society’s work is profound. It extends beyond mere advocacy and education. It offers a lifeline to those who have felt isolated and misunderstood, providing them with a sense of belonging and validation. It’s about transforming lives, instilling hope, and fostering a supportive community where individuals can thrive.

The Ehlers-Danlos Society is a beacon of hope and a driving force of progress. In its quest to better understand and treat Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) and hypermobility spectrum disorders (HSD), society has made remarkable advances in research and advocacy. Professor Lara Bloom passionately shares, “We’ve funded million dollars into research over the past few years, 14 million dollars.”
This significant investment is pushing forward important work, especially in biomarker studies. “We’ve been pioneering biomarker studies to try and find the pathogenic variant behind hypermobile EDS and HSD,” Professor Bloom explains. This research is essential as it aims to uncover the genetic details of these conditions, leading to more accurate diagnoses and targeted treatments.
The Society’s efforts extend beyond identification.
They are paving the way for new therapies. “We’ve been moving towards getting to a point where we could have therapeutics in the area,” says Professor Bloom. This approach promises a future with effective treatments, improving many people’s lives.
Additionally, the Ehlers-Danlos Society is changing how research is funded. “We’ve been providing funding for the research community that was never there before,” Professor Bloom proudly states. This support is crucial for ongoing studies and new investigations that could lead to breakthroughs. The impact of these efforts is profound. By closing gaps in knowledge and resources, the Society is speeding up discovery and bringing real hope to those affected by EDS and HSD.
echoing the sentiments of countless individuals who have found solace and understanding through the Ehlers-Danlos Society.

“People are very grateful to the organisation for giving them a voice and a space to find a community and support, to find education and learn more, and to find answers after they’ve been looking and searching for them for many decades,” Prof. Bloom shares earnestly. Her words resonate deeply,
Indeed, the impact of the Society’s work extends far beyond mere advocacy and education. It’s about providing a lifeline to those who have felt isolated and misunderstood for years, offering them a sense of belonging and validation. For many, the Society serves as a beacon of hope in a world that often feels overwhelming and uncertain. As Prof. Bloom reflects on the organisation’s mission, her passion shines through. “So, we’re very happy to provide a home for people with these conditions.”
Despite the commendable impact, the EhlersDanlos Society faces significant challenges. As Professor Lara Bloom candidly states, “I think for any non-profit, the challenge is funding, you know. Research is very expensive, and it costs a lot of money to run an organisation like ours and to support the staff involved in making these things happen. I would say the biggest challenge is funding.”

HUMANITY AND PHILANTHROPY
Beyond funding, the Society grapples with the weight of historical neglect. “The other huge challenge we have is that until we came along and launched in 2016, there were at least two decades of neglect before that. Therefore, we have spent a long time healing that neglect and trying to build strong foundations so that now we can move forward,” Professor Bloom reflects.
“That attracts the right people and grant givers as well. If we just keep doing the best we can every day, we hope that that will continue to attract funding.” This focus on excellence sustains their current efforts and opens doors to new opportunities and resources.
Vibrant, supportive network
The Ehlers-Danlos Society is a lifeline for those affected by Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) and


Attracting big donors
Aware of the significance of the judicious use of funds, Prof. Lara mentions that the society is dedicated to using its funds wisely. Professor Bloom explains, “We’re just trying to do great work. That attracts big donors. We are also keeping all of our governance in check and making sure that we run things in the best way possible.” This careful approach ensures that every dollar is spent effectively, supporting initiatives that create real change.
hypermobility spectrum disorders (HSD). Their offerings go beyond just medical advice—they create a vibrant, supportive community where individuals can find solace, connection, and purpose. Professor Lara Bloom passionately explains, “People can come in and participate in the research process. by joining our Global Registry. We offer the return for participating as part of the progression towards a better tomorrow. That is the best return you can have. But what we do provide is a lot of support.”
This support is multi-faceted and far-reaching. “We have virtual support groups. We have in-person hybrid events. We have educational resources,” says
12 | www.xrphealthcare.com
HUMANITY AND PHILANTHROPY
Professor Bloom. These resources ensure that no one feels isolated, no matter where they are.
The Society also leverages technology to build a strong, interconnected community. “We have ways for the community to connect with each other on forums and through an app,” Professor Bloom continues. These resources ensure that no one feels alone, no matter where they are. “There are a lot of different ways that we can provide that home, like I said, for people and for them to be part of paving the way towards the future.” The Society fosters an environment where members feel understood and valued through forums, apps, and events.
get to that and then even think about therapies and cures. But, you know, let’s get the basics right, of people getting a diagnosis and access to the care they need.”
This pragmatic yet hopeful outlook underscores the Society’s commitment to laying strong foundations. Their immediate goal is to ensure everyone can obtain a timely diagnosis and access necessary care. Professor Bloom emphasises, “We want to get to a point where our big overarching visions are to get to a point where people are diagnosed when their symptoms begin.”

The Ehlers-Danlos Society is more than an organisation; it’s a community where individuals can contribute to a brighter future. By participating in research, they become active players in the quest for better treatments and understanding of these conditions. This involvement offers a profound sense of purpose and hope, underscoring the Society’s mission to transform lives through connection, support, and collective effort.
Professor Bloom’s words echo a powerful message: “We provide a home for people, and they are part of paving the way towards the future.” This sentiment captures the essence of the Society’s work— building a world where individuals with EDS and HSD are empowered, supported, and united in their journey towards a better tomorrow.
Let’s get the basics right

The Ehlers-Danlos Society is driven by an ambitious vision for the future, one that aims to transform the landscape of diagnosis, treatment, and care for those living with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) and hypermobility spectrum disorders (HSD). As Professor Lara Bloom passionately shares, “We’re still quite a long way off from that. But it would be great to even
Looking beyond immediate needs, the Society envisions a world where the quality of care is not dictated by geography or wealth. “We envision that geography and wealth no longer determine your quality of life and that people can have access to the care that they need, both physically and psychologically, no matter where they live,” Professor Bloom says. This powerful statement reflects a deep commitment to equity and accessibility, highlighting
13 | www.xrphealthcare.com
HUMANITY AND PHILANTHROPY

the Society’s resolve to bridge gaps and eliminate disparities.
The future goals of the Ehlers-Danlos Society are not just aspirations—they are a roadmap to a world where every person with EDS and HSD receives the support they deserve. Their mission is more than just medical care; it’s about ensuring dignity, equity, and a better quality of life for all.
You don’t want to miss this!
The anticipation for the upcoming event in Philadelphia, in partnership with XRP Healthcare, is palpable. Professor Lara Bloom shares her expectations and hopes for what promises to be an enlightening and enriching experience.
“We’re going to be bringing together hundreds of
14 | www.xrphealthcare.com
people living with the condition, alongside some of the world’s leading healthcare experts in the field,” Professor Bloom explains. This gathering will serve as a platform for individuals to connect, learn, and share their experiences, fostering community and understanding.
The event will feature diverse talks, discussions, and workshops, providing attendees with valuable insights and networking opportunities. Professor Bloom emphasises, “They’re going to be presenting talks and discussions and workshops for people to learn and network and meet others just like them.

It’s going to be a fantastic, enriching few days for everyone involved.”
Professor Bloom extends a heartfelt invitation to all participants, encouraging them to approach
the event with open minds and hearts. “I would like to tell people to come with open ears, open hearts, open minds, and get ready to learn a lot,” she shares. While acknowledging the intensity of the experience, Professor Bloom emphasises the profound fulfilment that awaits attendees as they depart equipped with newfound resources to navigate their journey with EDS and HSD.
XRP Healthcare’s support has been instrumental in bringing this event to fruition, and Professor Bloom expresses gratitude for their contribution: “We’re grateful to XRP Healthcare for supporting it to make it possible.” In addition to the event, the collaboration between the Ehlers-Danlos Society and XRP Healthcare extends to practical assistance for individuals managing their conditions.
Through the Prescription Savings Card initiative, individuals can access significant discounts of up to 80% on medications for EDS and HSD, including pain relievers and muscle relaxants. Accepted at over 68,000 pharmacies nationwide, including Walmart, CVS, and Walgreens, this partnership offers tangible relief for those navigating the challenges of managing their conditions.
As the event approaches, anticipation builds for what promises to be a transformative and empowering experience for all involved. The combined efforts of the Ehlers-Danlos Society and XRP Healthcare highlight their steadfast dedication to supporting individuals affected by EDS and HSD, offering hope, resources, and a sense of community to those in need.
Look out for EDS’s robust lineup of impactful initiatives
At the core of the Ehlers-Danlos Society’s mission lies a spirit of collaboration and unity, as Professor Lara Bloom, President and CEO underscored. “I think at the heart of everything we do is collaboration,” she emphasises. “We have broken down the silos and the fragmentation and worked beyond borders to globally collaborate with as many people as we can because I truly believe that together we’re stronger.”
Looking ahead, the Society has a robust lineup of initiatives to foster global cooperation and
15 | www.xrphealthcare.com
HUMANITY AND PHILANTHROPY

knowledge-sharing. Professor Bloom reveals, “We’ve got a lot going on. We have an international scientific symposium next year. We have another global learning conference in February in Australia.” These events serve as vital platforms for experts and individuals affected by Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) and hypermobility spectrum disorders (HSD) to come together, exchange ideas, and drive progress in research and care. In addition to these flagship events, the Society is actively engaging with its community through virtual echo summits. “We have a lot of virtual echo summits going on this year and next year,” Professor Bloom shares. These summits offer accessible avenues for participation and learning, catering to diverse audiences across geographical boundaries.

For those eager to get involved, Professor Bloom extends an invitation to explore the Society’s upcoming events and initiatives. “I would recommend that anyone reading this go to our website and have a look at our upcoming events and all the different ways to take part.” With a myriad of opportunities for engagement, the Ehlers-Danlos Society welcomes individuals from all walks of life to join in their mission of collaboration, education, and advocacy.

16 | www.xrphealthcare.com
HUMANITY AND PHILANTHROPY

EXECUTIVE INTERVIEW
DR. PETER WAISWA
DR. PETER WAISWA
Meet Healthcare Industry Expert Peter Waiswa, XRP Healthcare’s latest appointment
BY BENJAMIN OPUKO

researchers who supported his PhD studies at the Karolinska Institutet in Sweden. He earned a joint PhD (2010) and later a Post-Doctoral fellowship from Makerere University in Uganda and Karolinska Institutet.

Currently, Dr. Waiswa is an Associate Professor at Makerere University School of Public Health and a visiting researcher at Karolinska Institutet since 2013. His career began as a district medical officer with Uganda’s Ministry of Health, which deeply informed his academic pursuits. Holding a Master’s of Science in Public Health, he is widely published in maternal, newborn, and child health, as well as health systems. Dr. Waiswa’s expertise has earned him a seat on the WHO Independent Technical Advisory Board for Maternal, Newborn, Child, and Adolescent Health (STAGE), influencing global health policies.
XRPH: Your journey from a small village primary school in Uganda to becoming an internationally recognised academic and researcher is truly inspiring. Can you share with us some of the pivotal moments or influences in your life that helped shape your career and led to your significant contributions in the fields of Maternal Newborn and Child Health?
Dr. Peter Waiswa is a distinguished scholar whose journey from a modest village in Uganda to global academic prominence epitomises resilience and intellect. Despite financial hardships, his inquisitive nature set him apart, catching the attention of
Dr. Waiswa: I was born in Uganda, in Naigobya village, Bukoma sub county, in Luuka district, in the Busoga region close to Lake Victoria. Despite belonging to the royal Baise Ngobi clan, my family was relatively poor, though slightly better off by village standards since my father worked as a teacher. I grew up and started school in this region with my twin brother, Paul Tenywa. Remarkably, my mother had four sets of twins, but my brother and I were the only pair where both children survived.
18 | www.xrphealthcare.com
EXECUTIVE INTERVIEW

Childhood in our village was challenging, with major killers like malaria, diarrhoea, pneumonia, and measles being prevalent. Despite these hardships, my twin brother and I survived, reflecting the difficult conditions of the time.
I was seen as stubborn, questioning the status quo, and challenging practices like long hours of labour in the garden, which we now recognise as child abuse. Even as a child, I understood the unfairness and stood up against it, questioning teachers and elders.
This trait persisted as I transitioned to Iganga Primary School in primary 5, one of the best then in the country. Initially, having just moved from a village school, I struggled to fit in with students who spoke English fluently and wore shoes, unlike me. However, with determination and support, I caught up and excelled, finishing primary seven as one of the top students in both the school and the district.
and share some examples of how these efforts have made a difference in the lives of those you aim to help?
Dr. Waiswa: I started school at Naigobya Primary School. I’m currently involved in efforts to improve education for the children there, recognising the importance of both education and health. Naigobya Primary School is a rural school with many classes still housed in dusty floor buildings. My family and I, along with others from the village, have been working to improve the school through our initiative, One Village at a Time (OVAAT). This initiative encourages villagers to take an active role in developing our community.
We’re focusing on education first, engaging the school in a participatory process. Instead of simply providing what they need, like books or supplies, we’re working to ensure that the school and community members lead the way while we support them. So far, we’ve established a library, provided books and sports equipment, and through the help of Rotary, we’ve installed a system to bring safe, piped water to the school.
We have provided electricity to the school and started greening the village, beginning with the school. Recently, we supported the school planted over 500 trees, including fruit trees, on the school compound. Our goal is to give back to the school that nurtured us.

Throughout my education, I always asked questions and challenged the status quo. I believe it’s important for every child to ask “why” because it shows a desire to understand. My own children, who often ask me “why,” remind me of the importance of this curiosity, even though it can be challenging at times.
I am currently working on my autobiography, which is in its final stages. Once it is ready for publication, I look forward to sharing more about it.
XRPH: Can you discuss your approach to philanthropy and giving back to the community,
The school has produced several notable individuals, including Professor Charles Waiswa, a veterinary medicine professor at Makerere University, and a paediatrician who is also a lecturer there, among others. We believe that every village has smart people, but opportunities are often the challenge. That’s why we’re focusing on supporting our school.
In the past, education was more universally accessible, but now many children, especially those in villages, struggle to attend school due to financial constraints. This is why we are committed to helping.
Our work in Iganga was done primarily on the premise of making an impact in the community with the skills, time, and numbers we had. As such, we built teams and equipped one another. The most common denominator with all of the health workers in the district was always lack of resources.
19 | www.xrphealthcare.com EXECUTIVE INTERVIEW

Nevertheless, with all this against us, we kept doing what we could do. The availability of a couple of us skilled coupled with a lack of enough resources, enabled us to innovate and find better ways of championing programs in the district. For instance, there was a program by the UNICEF/World Health Organisation run in specific districts called IMCI (Integrated Management of Childhood Illnesses).
IMCI was an important strategy for UNICEF, WHO, and the Ministry of Health of Uganda. The approach that IMCI took was that the health of a child had to be holistic. If a child comes to the clinic with a fever, you just don’t treat the fever. You cater for other things such as immunisation, nutrition, and anaemia.
In other words, the child was to be seen as a whole, not just the symptoms they have come with. Consequently, the approach was to build the capacity of the facility where the children would get all-round medical care, and have a mechanism for follow-up in the community. They wanted to see if that was an effective strategy.
XRPH: Given the financial challenges you faced during your early education, how did these
experiences shape your determination and approach to overcoming obstacles in your academic and professional journey?
Dr. Waiswa: Despite excelling in primary school, I couldn’t attend prestigious secondary schools like Namilyango or Mwiri due to financial constraints. My father, a low-income technical school teacher, couldn’t afford the fees. Instead, I went to Budini Secondary School, a rural and more affordable missionary school in Busoga.
At Budini, I was considered “elite” since many students were from even more remote villages than me. Despite our shared poverty, the Catholic brother who ran the school kept fees very low and encouraged us to believe that anything was possible. This environment was great for me.
However, my questioning nature got me into trouble. At the end of O-Level, the brother told me I was too stubborn and suggested I shouldn’t return. I agreed and moved to Jinja College, a Catholic school in Jinja city, for my A-Level. My questioning continued to cause issues, leading me to switch schools again to finish my A-Level.
20 | www.xrphealthcare.com EXECUTIVE INTERVIEW

Despite these struggles, I went on to Mbarara University to study medicine. Mbarara University of Science and Technology was a relatively new institution, and I studied there for five years. After qualifying as a doctor, I did my internship at Lubaga Hospital, a mission hospital in Kampala, following my Catholic faith.
Dr. Waiswa: I eventually resigned the Uganda Red Cross and returned to my home district to care for my parents and serve my community in Iganga distr35ict. I worked in Iganga for several years, always striving to excel despite the challenging environment. During this time, I caught the attention of professors from Makerere University, Sweden, and the US. They recognised my inquisitive nature and began offering me opportunities. My questioning led to research opportunities because asking questions is fundamental to discovery.
I received a scholarship to study in Israel, where I completed a Master’s in Public Health. My time in Israel coincided with the Iraq War and heightened tensions between Israelis and Palestinians. Despite the challenging security situation, I found the experience enriching. Israel has one of the best education systems in the world, and the Master’s program was intense and compact, lasting just one year.
I excelled in the program and am now considered one of its notable alumni. After completing my Master’s, I returned to Uganda and hoped to join the UN. However, I ended up going back to home town, Iganga, where I continued to contribute to my community.
Professor George Pariyo advised me, “Peter, you belong in academia, not the UN.” At first, I couldn’t believe him, knowing the lifestyle associated with

After completing my internship at Lubaga Hospital, there was a ban on recruitment, so jobs were scarce. Fortunately, I secured a position as an officer in charge of first aid with the Uganda Red Cross, where I was involved in health programs. This job provided a good salary and a mix of office and fieldwork.
XRPH: How did you navigate the transition from your early education, given the financial constraints, to eventually pursuing advanced levels of study, including your PhD and Post-Doctoral fellowship?

21 | www.xrphealthcare.com EXECUTIVE INTERVIEW
EXECUTIVE
UN jobs. However, good mentors are worth listening to, so I heeded his advice.
I later joined a PhD program at the Karolinska Institute, which provided funding to Uganda to enhance scientific research. They understood the importance of homegrown scientists in making a difference. I worked on a collaborative project between Makerere University and Karolinska. Makerere has a strong reputation, and we take pride in being one of the best, although the University of Nairobi is also highly competitive.
Earning a PhD from Karolinska, which awards the Nobel Prize in Medicine, was a significant achievement. My research focused on understanding and preventing newborn deaths, inspired by my childhood experiences of losing family members. I wanted to understand why they died and find solutions.
to become a professor. Recently, someone from Kampala International University staff mentioned that I am one of the top researchers in the country, Africa, and the world, with over 200 publications and currently an H-index of 48 (https://scholar.google. com/citations?user=ylPProwAAAAJ&hl=en). While I appreciate the acknowledgement, I remain modest, echoing Jesus’ words: “It is you who say that, not me”, when asked if he was a son of God.
XRPH: Reflecting on your extensive career, what would you say is your proudest accomplishment to date?
Dr. Waiswa: I have achieved quite a lot, perhaps even more than many professors in academia. Most importantly, I’ve made significant contributions in my village, home region, country, and globally, especially in improving health systems for mothers, newborns, and children.

After completing my PhD, I returned to Makerere Universityand advancedthroughthe academic ranks
I’ve influenced numerous policies and participated in global initiatives that shape the global health

INTERVIEW
agenda. I often serve as a consultant. The demands of my work—long hours of sitting, writing, researching, and working in academia—take a toll on my health. Academia can be isolating and underappreciated, even if you excel. Universities often don’t provide adequate support, and professors remain humble despite their achievements.
In addition to my academic work, I’ve started several charities. One of them is Uganda Development and Health Associates (UDHA), a large NGO in eastern Uganda, which I co-founded with friends. I also helped establish a Busoga Health Forum, an NGO of hundreds of health workers with colleagues, which has become a significant NGO. As the chairman,
theirs. My goal is to inspire others to follow suit and make a positive difference in the world.
XRPH: Can you tell us more about your involvement with international organisations like WHO, UNICEF, and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, especially regarding your roles as an advisor and advocate for maternal and child health initiatives? Dr. Waiswa: I see myself as a voice for Africa, and I’m not afraid to speak out in various forums. Often, Africans are not adequately represented or tend to stay silent. By sharing our expertise and perspectives, we can bring valuable insights to the table. Thanks to my credibility, education, research,


Prof. Peter Waiswa During the hybrid Launch of the Digital Health Payment Initiative and Research in Africa project.
I’ve overseen the construction of new healthcare units and centres, pushing forward many health initiatives. Last year, at the wedding of the King of Busoga, we did a medical camp which attended to over 10,000 people. I have also helped set up numerous neonatal health units all over the country.
In today’s world, the internet offers endless opportunities for learning and growth. However, true success isn’t measured solely by academic achievements or citations. It’s about the impact you make in communities. As an academic, I find fulfilment in engaging with and learning from communities, enriching both my knowledge and
and engagement, I’m invited to provide technical support by various organisations.
I work closely with the World Health Organisation (WHO), Global Fund, Gavi, Gates Foundation, the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), The United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), Save the Children, Africa Centres for Disease Control (Africa CDC), Africa Academy of Sciences, and many others. Some of these collaborations involve formal advisory roles, such as my position on the advisory group to the WHO Director-General on Reproductive
23 | www.xrphealthcare.com EXECUTIVE INTERVIEW
Health, Maternal, and Newborn Child Health, known as STAGE.
I serve on various committees and as a technical advisor with organisations like the Gates Foundation and UNICEF. For example, I’m part of the Steering Committee advising the Gates Foundation on initiatives to save mothers, newborns, and children. With UNICEF, I’m involved in a formal committee focusing on newborn health. Additionally, I collaborate with WHO in several capacities, participating as a technical expert not only from Uganda but globally, providing insights and perspectives from the global South.
My involvement is not merely token representation but based on expertise and merit. Areas like newborn and child health, and health systems in which I specialise, are recognised globally, placing me among the top experts in the field. These groups help shape policies, guidelines, and research agendas, influencing healthcare strategies worldwide.
While I don’t consider myself primarily an advocate, I use evidence to inform decision-making and policy formulation. Advocacy plays a role, but I prioritise evidence-based approaches to drive change.
XRPH: Could you please share about your involvement with XRP Healthcare as a strategic advisor in Uganda?
be solely sourced from abroad. While occasional medical travel may be an option, a robust healthcare system relies on local infrastructure and services. Improving our local healthcare system is crucial. Governments often lack the resources to address all healthcare needs adequately. Therefore, initiatives like those led by the private sector, such as XRP Healthcare, are valuable. They can leverage expertise and resources from international investors to enhance the local healthcare sector through strategic investments.
XRPH: Since you started working with the community, have you noticed any significant reductions in infant mortality rates?

Dr. Waiswa: I’m involved with XRP Healthcare because I admire their commitment to improving the quality and capacity of healthcare in Uganda. Currently, our healthcare system is fragmented, mostly privatised, and often lacks regulation. Despite this, we face complex health challenges. Investing in healthcare in Uganda and Africa holds great promise because the market is growing along with demand. Additionally, it can be a socially impactful business endeavour.
My expertise lies in health systems, and I’m often frustrated by the fragmentation and inadequate capacity and quality within our healthcare system. It’s unsustainable for people to have to travel abroad for medical care, and it hinders local development. Everyone should have access to quality care within their own community.
It’s a misconception to believe that healthcare can
Dr. Waiswa: The mortality rates for mothers, newborns, and children have significantly decreased, particularly for children aged 1 to 5 years, which has been almost miraculous. While improvements for mothers and newborns have been somewhat slower, there has been progress in this area as well.
Regarding community acceptance of our charity work, there have been challenges. Sometimes, individuals face opposition from their own communities due to various reasons.
XRPH: Can you provide insights into your involvement with charitable organisations and initiatives in Uganda, and how they have contributed to addressing key societal challenges in the country?
Dr. Waiswa: I’m involved in several charitable initiatives and organisations. For instance, I lead the Busoga Health Forum, a network of over 1,000 health workers. Additionally, I founded Uganda Development and Health Associates, which focuses on HIV prevention among young people in eastern Uganda.
I serve on the boards of various organisations, including Reproductive Health Uganda and the Uganda Red Cross. I also established a Maternity and Newborn Child Centre of Excellence at Makerere University.
Furthermore, I founded the Maternity and Newborn Child Health Research group in Ghana and am involved in numerous other charities. Through
24 | www.xrphealthcare.com EXECUTIVE INTERVIEW
EXECUTIVE INTERVIEW
these endeavours, we raise funds, engage policymakers, and conduct research aimed at improving healthcare systems. My primary focus is on implementation research, also known as developmental research, which seeks to enhance healthcare systems and practices at the community level.
XRPH: What notable impacts have your community-based initiatives had, and how have they contributed to positive changes within the communities you’ve served?
Dr. Waiswa: The community’s involvement and cooperation have been instrumental in the success of our health initiatives. Through various charitable organisations and projects such as the Busoga Health Forum and Uganda Development and Health Associates, we’ve been able to address issues like HIV among young people in eastern Uganda for nearly two decades. Additionally, I serve on boards of organisations like Reproductive Health Uganda and the Red Cross.
One significant project I initiated is the establishment of a maternity and newborn child centre of excellence at Makerere University, along with the INDEPTH Network, which focuses on demographic survey sites worldwide. I’ve also launched a group in Ghana, the Maternity and Newborn Child Health Research.
Through these efforts, we mobilise funds, engage policymakers, and conduct research aimed at improving healthcare systems. Much of our work revolves around implementation research, which seeks to enhance healthcare practices at the community level.
We prioritise human-centred design and cocreation, involving local experts and community members in the redesign of healthcare approaches. This approach has yielded remarkable results, with high levels of acceptability, impact, and sustainability. Communities, once empowered with evidence-based knowledge, often excel in implementing initiatives tailored to their needs.
Our efforts have particularly impacted maternal and newborn child health, as evidenced by several successful trials. For instance, we recently published
a paper in The Lancet, highlighting the effectiveness of our strategies.
XRPH: Could you elaborate on some of the impactful research projects you’ve been involved in that have significantly influenced policy-making across various regions of the continent?
Dr. Waiswa: We’ve conducted important studies that could improve healthcare, especially in developing countries. We have done many interventional studies which have saved many lives. For instance, the Saving Mothers Giving Life (SMGL) project reduced maternal deaths at community level by over 30%, and the Preterm Birth Initiative (PTBi) saved preterms by over 35% (done in Uganda and in Kenya). PTBi was a big grant from the Gates Foundation in which we partnered with University of California San Francisco (UCSF).
Moreover, with funding from USAID and PEPFAR, we looked into ways to save mothers’ lives in Uganda and Zambia. Our findings showed a potential 40% decrease in maternal mortality at the community level, a milestone not previously seen in Africa. This model has since been adopted in numerous African countries receiving funding from USAID, including Nigeria and Malawi.
XRPH: What are the most significant lessons you have gained from your extensive career as a doctor and researcher?
Dr. Waiswa: Our main lesson from these efforts is the importance of academic credibility, working with both global and local experts, and using evidencebased methods to create meaningful change. We’re committed to continuing this work to improve healthcare outcomes worldwide.


25 | www.xrphealthcare.com

NEW XRP HEALTHCARE CHAIRMAN WHITNEY LYNN ON MERGERS AND ACQUISITIONS
BY HELLEN MUCHERU
Whitney Lynn’s journey is a fascinating blend of personal ambition, family influence, and military discipline. Born in California, Whitney was deeply inspired by his father, an entrepreneur who rose from an orphanage to achieve great success. Whitney reflects, “My dad was a major influence in my life, setting a high bar for success and motivating us to emulate his positive traits. He started several successful companies, and my three siblings and I have found success in different industries.”
In 1957, he started a company called Blast Deflectors Incorporated (BDI), which became the market leader in providing jet blast deflectors. Some of these deflectors are installed and visible at Dubai International Airport. His company celebrated its 60th anniversary in 2017, marking tremendous visibility and success in the industry. Blast Deflectors Incorporated was sold in 2018 and goes by a different name now.
Raised in a family that valued education and hard work, Whitney’s father attended prestigious schools like Harvard, Stanford, and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) on scholarships. This educational foundation instilled a strong entrepreneurial spirit in Whitney and his siblings, driving them to pursue success in various fields.
BUSINESS AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP
EARLY YEARS AND MILITARY INFLUENCE
Whitney’s early years were profoundly shaped by his time at a military prep school. “This background influenced my focus and direction in life. I attended a military prep school, which helped stabilise and guide me,” he recalls. The structured environment provided a stable foundation that would have a lasting impact on his development.
Following prep school, Whitney attended the University of Arizona, where he joined the Reserve Officers’ Training Corps (ROTC) during the Vietnam War. The ROTC program, a leadership training and development initiative, prepares college students for service opportunities in the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, and Space Force. After graduation, Whitney became a commissioned officer, gaining invaluable leadership experience.
In San Francisco, Whitney worked at a large army hospital as an administrative assistant in the Department of Surgery. Here, he dealt with scheduling and administrative tasks, giving him insight into the complexities of military healthcare. “This was a very eye-opening experience,” he notes. Later, he served as a company commander at Fort Hood, Texas, where he refined his leadership skills, learning the importance of leading by example, listening, and effectively communicating with his team.
TRANSFORMING AFRICAN HEALTHCARE: WHITNEY LYNN’S VISION FOR XRP HEALTHCARE
Success of mergers and acquisitions (M&A) hinges on expertise, a solid plan, and a steadfast commitment to excellence. Few understand this better than Whitney Lynn, a former army officer who now serves as the chairman of XRP Healthcare. His mission is ambitious yet crucial: to revolutionise healthcare provision and access standards across Africa through the innovative use of blockchain technology, strategic mergers, and acquisitions.
ESTABLISHING A GLOBAL STANDARD
“I learned a long time ago that acquiring an organisation requires expertise and a solid plan,” Lynn begins, setting the tone for our discussion. “With XRP Healthcare, we aim to establish high standards

and create a globally recognised brand in efficient healthcare.”
The cornerstone of Lynn’s strategy is a precisely developed process for evaluating potential acquisitions. “We need a clear process for evaluating hospitals, doctor’s offices, and other medical facilities we intend to acquire. We use a template to identify what we’re looking for, focusing on companies willing to merge or sell. This requires a skilled team to determine which companies fit our criteria.”
The M&A process, Lynn notes, is fundamentally similar across various industries, whether it involves hardware, software, or healthcare facilities. The key lies in selectivity and strategic alignment. “Our goal is to establish XRP Healthcare as a global standard for healthcare efficiency. To achieve this, we must be selective about the companies we include. Typically, these are companies led by individuals looking to retire, who have run profitable operations.”
LEADERSHIP AND LOCAL EXPERTISE
A pivotal figure in Lynn’s team is Peter Waiswa, a globally recognised healthcare consultant who has collaborated with UNICEF and the Bill and
27 | www.xrphealthcare.com
BUSINESS AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP

Melinda Gates Foundation. Professor Peter Waiswa is working closely with Kain and Laban Roomes to ensure that the due diligence of the process of mergers and acquisitions is done as per the book. “Peter’s leadership is essential in identifying and consolidating top-quality companies. We aim to offer superior quality, accessibility, and high
standards in healthcare, making XRP Healthcare the epitome of excellence.”
This process is far from automatic. It requires discipline, a clear vision, and strong leadership from the top down. “Creating this global standard involves providing affordable, effective, and accessible healthcare of the highest standard. We plan to start this initiative successfully in Uganda and hopefully expand throughout Africa.”
RIGOROUS PROCESS AND SUSTAINABLE GROWTH
Lynn emphasises the need for rigorous processes and firm standards. “Our team exemplifies this commitment. Regardless of the industry—be it hardware, software, or healthcare—the processes of identifying, due diligence, and fair agreements are consistent.”
Challenges abound, especially when dealing with individual hospitals, pharmacies, and doctor’s offices. However, XRP Healthcare’s expertise enables them to qualify these entities quickly and efficiently. “It’s important to proceed methodically, establishing templates for our qualifications and processes without taking shortcuts. Everything must be done thoroughly to ensure we provide the best possible healthcare and make the organisations we acquire stronger for the people they serve.”
VISION FOR THE FUTURE
XRP Healthcare aims to be highly successful by offering accessible, top-tier healthcare while maintaining a profitable business model. According to Lynn, this approach will attract other entities to join them. He adds that sustainability and impactful outcomes are essential, achieved through a quality organisation and process.
For Lynn, M&A is not just a business strategy; it’s a mission to address urgent healthcare needs. “Ultimately, while this is a business, it’s also about providing something urgently needed. Bill and Melinda Gates, WHO, and UNICEF all recognise this. Our vision is to establish XRP as a global brand by
We aim to offer superior quality, accessibility, and high standards in healthcare, making XRP Healthcare the epitome of excellence.”
28 | www.xrphealthcare.com
BUSINESS AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP

truthfully and effectively meeting these needs,” he notes.
Looking ahead, Lynn’s vision for XRP Healthcare remains ambitious. “Yes, it was quite positive,” Lynn says, referring to an article he found online about his recent achievements. “It directly relates to XRP Healthcare. It’s an update mentioning William Miller, who served as the interim CEO until September, when Whitney G. Lynn, also known as expert an of mergers and acquisitions expert of XRP Healthcare, assumed the role of interim president and CEO.”
A TRADEMARK OF EXCELLENCE
A significant milestone in this ambitious journey is the registration of the XRP Healthcare trademark in Uganda. “This is a key point,” Lynn emphasises. “This initiative is not just about a trademark; it’s about establishing XRP as a leading healthcare brand in Africa. The press release, which was excellently written, truly captured our objectives: to create a standard of healthcare excellence for Africa that meets global standards.”
This commitment, Lynn notes, is serious and unprecedented. “Our goal is to create something never before seen in Africa, providing affordable, effective, and accessible healthcare. Starting in Kampala, Uganda, and expanding further, this initiative will significantly benefit the people.”
The current healthcare system in many parts of Africa is highly fragmented, a challenge Lynn is determined to address. “Our mission is to consolidate this system under the XRP brand, ensuring that any facility with the XRP name is recognised as a firstclass, top-quality facility. This will require exceptional quality and execution, as people will quickly recognise whether we meet these standards.”
Lynn’s confidence in the initiative is palpable. “I’m confident—99.999% sure—that we have all the pieces in place to do this right. We have a solid plan, a dedicated team, and the commitment to make this vision a reality.”
FROM MILITARY SERVICE TO HEALTHCARE LEADERSHIP

29 | www.xrphealthcare.com
BUSINESS AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP

Whitney Lynn’s path to leading XRP Healthcare is rooted in a rich history of leadership and discipline, honed during his military service. “I attended a military prep school and then went to the University of Arizona, where I was in ROTC. This was during the Vietnam War, so I graduated as a commissioned officer. My experience was amazing.”
Initially drawn to medicine, Lynn’s entrepreneurial spirit led him down a different path. “I always had an interest in becoming a doctor. A family friend, who was a doctor, encouraged me to pursue medicine, noting my personality and willingness to help me
get into a good school. However, I found myself more drawn to entrepreneurship.”
Lynn’s military career began with immediate leadership responsibilities. “During the Vietnam War, I was put into leadership positions immediately. I was first stationed at a large hospital in San Francisco as the administrative assistant in the surgery department, where I saw many soldiers returning from Vietnam. This was a very eye-opening experience.”
His leadership journey continued as a company commander at Fort Hood, Texas. “I learned a lot
30 | www.xrphealthcare.com
about leadership by example, especially as a young lieutenant working with experienced sergeants. It was crucial to lead by example, listen, and not dictate. This experience taught me a lot about discipline, understanding people, and how to motivate them.”
Lynn’s approach to leadership is deeply influenced by his military experiences. “I’ve always been a natural leader, but I learned that leadership isn’t just about talking the part; it’s about acting the part. Communication and openness are key. I never took a dictatorial approach; instead, I listened to everyone’s opinions. The skills I developed included discipline, understanding people, and striving for quality in every task we were given. This set the foundation for my strong emphasis on quality throughout my career.”
The lessons from his military service are evident in every aspect of Lynn’s leadership at XRP Healthcare. “Everything has to be done perfectly. There are no shortcuts. You don’t get any slack. You do it exactly right. I learned that in the military, and I’ve carried it into every company I’ve run. It had to be tough and held to the highest standards, including quality and people.”
One of the most profound lessons Lynn learned in the military was the importance of motivating people and effective communication. “Motivating people was another key lesson, especially when sending troops to Vietnam. Communication and understanding what they were thinking was crucial. Listening is very important. Too many executives and company commanders don’t listen; they just talk, and that eventually backfires.”
This emphasis on communication and understanding is a hallmark of Lynn’s leadership style. “I’ve always been a communicator. I ask, ‘What do you think? What’s bothering you?’ While the responsibility for a mission or success lies with me, I need the best possible input from my team.”
Lynn’s military service, though brief, was transformative. “I was in the military for only two years, but I learned a lot. Some good, some bad, but the good was really valuable. It grounded me at a young age, giving me confidence and practical
leadership experience. I had 144 men under me and had to be concerned about their health, welfare, and families, ensuring they got paid every week. Back then, it was in cash, unlike today’s digital payments.”
The weight of responsibility Lynn bore in the military shaped his approach to leadership and quality. “The responsibility was significant, but it was a very good experience that shaped my approach to leadership and quality,” Whitney shares.
A DEFINING CHALLENGE: TURNING AROUND A SINKING SHIP
Lynn’s ability to lead through crisis was profoundly tested in the late 1990s when he was brought in to help with an acquisition at a struggling software company. “It involved a public corporation in the late 1990s, which had burned through hundreds of millions of dollars in cash. This software company, founded by a charismatic Frenchman, had lavish facilities, including an expansive campus with topnotch amenities. I was brought in to help with an acquisition, which was my second or third at the time.”
Upon arriving, Lynn discovered the company was bleeding money at an alarming rate—US$12 million a month. “The CEO had just been ousted, and I was asked to step in as the interim CEO. Stepping into the CEO’s opulent office on my first day, I realised the extravagance was part of the problem.” The challenge was to reorient everyone in the company, redirect finances, and implement a feasible plan to turn things around. “I remember a crucial

31 | www.xrphealthcare.com
BUSINESS AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP

conversation with the CFO about our cash reserves, which were dwindling rapidly. Despite the daunting task ahead, I embarked on the journey to restore profitability, which meant making tough decisions like layoffs and refocusing priorities.”
Lynn also vividly recalls his first CEO meeting, a massive all-hands gathering where the employees looked at him with a mixture of hope and scepticism. The core issues, Lynn explains, boiled down to poor communication and disjointed efforts among departments. “Engineering, sales, and marketing were each operating in silos with conflicting agendas. Sales wasn’t aligned with marketing, and engineering was out of sync with both.”
Lynn believes in measuring success by tangible results. “At every company I led, I emphasised goalsetting and execution. It became evident that clear communication, prioritisation, and decisive action were key to success.”
While some team members quickly understood the need for change, others took more time to
adapt. “High stress was inevitable, considering the expectations of the board and shareholders, but it underscored the importance of swift and effective leadership in challenging times.”
Lynn’s task was clear: salvage a sinking ship and restore its buoyancy. “While the initial success was small, it marked the beginning of a larger journey toward revitalisation,” he says.
Defining success for Lynn meant achieving financial objectives while also prioritising employee satisfaction and contribution acknowledgement. “Effective management involved active listening and avoiding dictation. The experience was highstress, demanding rapid problem-solving and immediate action to address issues.”
THE FUNDAMENTALS OF MERGERS AND ACQUISITIONS
“First and foremost, successful mergers and acquisitions require both a willing buyer and a willing seller,” Lynn emphasises, distilling the essence of M&A. “It’s crucial to understand the objectives of the company’s owners or stockholders. While everyone aims for an optimal outcome, realistic expectations are essential as evaluations may not always meet initial hopes.”
Lynn elaborates on the motivations behind companies seeking acquisition. “Typically, companies seek acquisition due to limited resources for marketing and expansion or financial constraints. Identifying potential buyers and understanding valuation are critical aspects of advising companies. It’s common for companies to overestimate their worth, necessitating alignment with current market conditions. Presently, deals often involve more cash upfront with lower deferred payments, reflecting current market trends.”
ALIGNING EXPECTATIONS AND MARKET REALITIES
“I believe it’s a realistic expectation,” Lynn says, highlighting the importance of market alignment. “Essentially, it boils down to having a willing seller, an informed advisor who understands the current market and what potential buyers can offer. These are fundamental aspects to consider when preparing to sell a company.”
Lynn stresses the importance of post-acquisition
32 | www.xrphealthcare.com
BUSINESS AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP

leadership. “Typically, the seller is required to stay on for a transitional period after the sale, often for a year or more. During this time, restructuring occurs to ensure long-term success. In my experience with our family-owned company, which we sold when it was thriving, my younger brother, the CEO, had to remain involved for several years. This is a common scenario in most transitions.”
THE ROLE OF CONTINUITY AND LEADERSHIP
In the context of XRP Healthcare, Lynn underscores the significance of continuity. “Employees face a degree of stress when adapting to new ownership and operational structures. The goal is to facilitate a smooth and profitable transition from one way of doing business to another.”
“Post-acquisition leadership plays a critical role in ensuring the company’s success after the sale,” Lynn continues. “It’s essential to support the new owners in every way possible to achieve this goal. A positive relationship between the old and new owners is vital. While negotiations may be tense, once a deal is reached, the previous owner must step into a mentoring role.”
Lynn finds particular satisfaction in mentorship. “Personally, I find mentorship particularly rewarding. I’ve been involved with an incubator company, which has been an enriching experience.”
ACHIEVEMENTS AND PERSONAL MILESTONES
Reflecting on his professional journey, Lynn points to a significant achievement from the 1980s. “One of my significant achievements dates back to my involvement in the tape backup industry. At that time, there were various incompatible standards among different companies, hindering market growth. Recognising the importance of standards for industry growth, I spearheaded an effort to establish common standards through an industry group.”
This initiative not only consolidated the industry but also paved the way for future mergers and acquisitions. “I often gave talks on the importance of mergers and acquisitions during this period, emphasising their role in driving growth and innovation.”
Lynn takes pride in his foresight and leadership in establishing these standards. “While it was a collaborative effort involving many individuals, I take pride in having the foresight to recognise the need for industry standards and the initiative to drive this change. This experience taught me valuable lessons in launching new products into new markets, a skill that I continue to utilise in my endeavours.”
On a personal note, Lynn cherishes the achievements and milestones shared with his family. “One of my proudest achievements is my daughter, who brings immense happiness and pride into my life. We shared a memorable experience completing an Ironman together, enduring 16 hours and 20 minutes of physical exertion and pain, yet finishing with smiles on our faces. It was an incredibly bonding moment, filled with pride and joy.”
During the Ironman, Lynn witnessed his daughter’s determination and resilience. “She overcame challenges like riding 112 miles on the bike, which she initially disliked. Despite stopping for snacks along the way, we made it through, and I couldn’t be prouder of her accomplishments and the person she has become.”
Engaging in activities like triathlons shares parallels with business. Both require training, perseverance through challenges, and pride in accomplishment. “It’s about doing your best,” Lynn emphasises, echoing the mantra “just do your best.” This
33 | www.xrphealthcare.com
BUSINESS AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP

philosophy applies to various endeavours, from athletics to entrepreneurship.
For aspiring entrepreneurs, passion, teamwork, determination, and continuous learning are paramount. “The entrepreneurial landscape is vast, with numerous startups emerging daily, fuelled by the American ethos of hard work and accomplishment. Education, focus, and measurable results are essential ingredients for success.”
This ethos of hard work and accomplishment resonates with Lynn’s upbringing. “My father instilled the values of the American capitalist system—earning success through dedication and achievement. One key lesson I’ve learned is the significance of determination, listening, continuous growth, and surrounding oneself with the best possible team. This ethos is reflected in our work at XRP, where excellence is not just a goal but a standard upheld by every member—from our CFO to our Uganda team.”
PIONEERING LEADERSHIP AND MENTORSHIP IN HEALTHCARE AND TECHNOLOGY
Whitney Lynn’s journey as a leader and mentor is as compelling as his current role as chairman of XRP Healthcare. His insights into mentorship and leadership offer a window into his methodical approach to fostering innovation and guiding companies through complex mergers and acquisitions.
Lynn’s commitment to mentorship is exemplified by his experience where he taught entrepreneurs
how to craft effective pitch decks to secure funding or acquisition. He interacted with a diverse group of individuals, primarily engineers who were CEOs looking to sell their companies. His approach as a mentor was not to dictate but to guide them towards the right decisions, ensuring they retained ownership of their ideas. “Trust was crucial in this process,” Lynn notes. “They needed to trust my advice, and I needed to listen carefully to their objectives because ultimately, it was their company, not mine.”
Preparing companies for investment involved creating a compelling pitch deck, typically around 15 slides, outlining their product, market size, exit strategy, and other key details. “It was essential to present these aspects believably, demonstrating how they could be achieved.”
“My approach as a mentor was never to dictate what they should do. Instead, I aimed to guide them towards the right decisions, ensuring that they retained ownership of their ideas,” he explains. Trust was a crucial component in this process. “They needed to trust my advice, and I needed to listen carefully to their objectives because ultimately, it was their company, not mine.”
Emphasising the importance of having a strategic vision he notes, “One critical aspect I emphasised in my seminars and webcasts was the importance of having a strategic vision. Starting with a realistic and achievable vision is crucial. Many people have grand visions, but success comes from understanding how to make those visions a reality.”
34 | www.xrphealthcare.com
BUSINESS AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP

“Successful companies often have visionary founders who understand both the vision and how to execute it effectively. The vision should not only be achievable but also add value, addressing future trends and creating something that people will want,” he notes.
Currently, Lynn continues his work part-time as a consultant in the M&A markets, focusing on AI and healthcare. These are two of the most prominent areas with a significant number of new startups. His focus is on staying involved in what’s happening in the M&A markets with various technologies, particularly artificial intelligence and healthcare. He is not just concentrating on startups in these fields but is closely following the most active sectors, which currently include healthcare and AI.Healthcare startups are incredibly prevalent,” Lynn observes, “likely due to the universal recognition of healthcare’s importance globally, from Africa to the United States, each with its unique challenges. The mission of these startups is clear: to drive change in the healthcare sector.”
Future trends in healthcare, according to Lynn, go beyond traditional concerns like security and hacking. They encompass a broad spectrum of innovations. Adapting to constant change is vital, as change is inevitable. Flexibility and the ability to pivot towards new innovations are crucial for success in this dynamic field.
EMBRACING THE CHALLENGE OF IRONMAN AND BEYOND
Whitney Lynn’s journey through seven consecutive Ironman triathlons exemplifies his relentless drive
and passion for overcoming challenges. Known for his strategic acumen in the business world, Lynn’s athletic endeavours reveal another layer of his A-type personality, showcasing his commitment to pushing boundaries and achieving excellence.
“For fifteen years, I participated in the Ironman triathlon, which consists of a 2.4-mile swim, a 112mile bike ride, and a 26.2-mile run,” Lynn shares. Ironman is renowned for its gruelling distances and is considered the pinnacle of triathlons. “So, why did I undertake this challenge repeatedly? Well, I’ve always had a competitive personality and relish in facing challenges head-on.”
The initial spark for Lynn’s Ironman journey struck while he was visiting Hawaii. “The inspiration struck when I witnessed the Ironman event while visiting Hawaii, where I had recently purchased property. The determination to participate was immediate, and over the next 15 years, I completed a total of seven Ironman races.”
Among these races were four Ironman World Championships on the Big Island of Hawaii, a testament to Lynn’s dedication and resilience. “One particularly memorable experience was completing a race alongside my 24-year-old daughter, forging an incredible bond during the gruelling 16-hour endeavour,” he recalls. This shared experience stands out as a pinnacle of his athletic career, highlighting the personal connections forged through intense physical challenges.
BEYOND THE FINISH LINE
Lynn’s Ironman journey also includes a remarkable year where he participated in multiple events in rapid succession. “In a particularly intense year, I managed to squeeze in participating in Ironman Austria, followed by a unique cycling experience in the Pyrenees Mountains during the Tour de France,” he reflects. These experiences underscored his unwavering commitment to pushing his limits and exploring new challenges. Then, in October of that year, he competed in the Ironman World Championship in Kona, Hawaii.
Reflecting on these experiences, Lynn admits, “There’s an inexplicable allure to pushing oneself to accomplish such feats.” This allure mirrors his approach to leadership and mentorship in the business world, where he consistently seeks to inspire and guide others to achieve their best.
35 | www.xrphealthcare.com
BUSINESS AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP

Jumping into business in Dubai? We’ve got
You wouldn’t jump out of a plane without a parachute. Just like you shouldn’t star t a business with just a licence. Take the leap. Enjoy the experience. We’ll handle the rest.
visit virtuzone.com Our work doesn't stop at business setup. From managing your accounting and corporate tax, to opening a corporate bank account, handling your client calls and collecting your mail, our corporate services will streamline your operations, so you can focus on the big picture.
your back
Inteleos: Transforming maternal and foetal healthcare in Africa with unified POCUS implementation
BY BENJAMIN OPUKO
In Sub-Saharan Africa, a transformative initiative is underway to revolutionise maternal healthcare delivery through innovative solutions, with a focus on strengthening the referral system and ensuring timely and appropriate care for expectant mothers. Spearheading this effort are two consultant specialists from Inteleos, alongside Dr. Thapelo Motshudi, a South African radiologist. Together, through their concerted efforts, they are on a mission to transform the narrative of maternal healthcare through the implementation of Pointof-Care Ultrasound (POCUS).
Joseph Williamson, a High-risk obstetric clinical specialist, sonologist and Medical Quality Consultant at Inteleos emerges as our guide. As both an Inteleos program lead and the head of clinical training for South Africa and Sub-Saharan Africa, Joseph introduces us to the organisation’s critical role in healthcare, especially in Africa. Inteleos, a global leader in credentialing in sonography and diagnostic imaging, is playing a pivotal role in this transformative endeavour.

Faith Muigai, a healthcare advisory and quality improvement specialist at Inteleos, steps into the conversation as the Business Development lead for Inteleos in East Africa, and the program lead in Kenya.
At the forefront of their efforts is the integration of point-of-care ultrasound technology into healthcare policies. This ground-breaking innovation aims to empower midwives, clinical officers, and medical officers with enhanced diagnostic capabilities, enabling early detection of complications and facilitating proper referrals to appropriate healthcare facilities. With a particular emphasis on primary care, this initiative holds the potential to significantly improve maternal and foetal health outcomes across the country.
STEPPING UP TO FILL THE GAP OF ULTRASOUND SPECIALISTS
In Sub-Saharan Africa, the shortage of clinicians capable of performing essential tests, particularly ultrasounds, presents a significant
challenge. Joseph, a consultant specialist at Intelios, emphasises, “A past census informed that Kenya has a population of about 43 million people but has only 250 radiologists. Nigeria has one radiologist for every 650,000 people and South Africa has 1.5 radiologists per 100,000 people. This is unsustainable.”
Typically, ultrasounds are performed by radiologists, sonographers and sonologists so the shortage of these specialists highlights a severe lack of human capital, exacerbated by migration and the loss of general professionals. Additionally, even when human capital is available, there is often a lack of skills to perform point-of-care diagnostics.
To address this pressing issue, Intelios proposes training and credentialing clinical officers, midwives, and other healthcare professionals outside of radiology and obstetrics to perform point-of-care ultrasounds. This solution is gaining traction, with governments in Kenya, the Caribbean, Nigeria, and other low- and middle-income countries recognising the urgency of the matter.
Implementing this solution offers numerous benefits. Point-of-care ultrasound enables midwives and clinical officers to identify potential complications early, significantly improving maternal-foetal outcomes. In many African regions, such as South Africa, where 70% of public patients never see an obstetric doctor, empowering midwives with ultrasound skills could revolutionise healthcare delivery.
Furthermore, enhancing the skills of midwives and clinical officers not only makes them more effective but also enhances job satisfaction and contributions to maternal health. Cost-effectiveness is another advantage, with POCUS being more affordable compared to traditional ultrasound platforms, thus improving resource efficiency. Joseph highlights, “A POCUS handheld wireless device can cost about US$3,000, whereas a traditional radiology platform costs around US$25,000, highlighting the resource efficiency of POCUS.”
ADDRESSING LOCAL NEEDS

Addressing local needs is paramount. The World Health Organisation advocates for every woman to have access to at least one ultrasound. However, with the current shortage of radiologists, sonologists and obstetricians in Africa, meeting this standard is challenging. POCUS emerges as a viable solution, ensuring women in rural areas receive the ultrasounds they need, thereby enhancing accessibility and enabling rapid decisionmaking.
Inteleos plays a crucial role in this initiative, providing international certification to validate the skills of midwives and clinical officers globally. This validation builds confidence and ensures healthcare providers can diagnose with
38 | www.xrphealthcare.com
HEALTH CARE DELIVERY
Left: Dr. Thapelo Motshudi, Right: Joseph Williamson.

Faith
Muigai, a healthcare advisory and quality improvement specialist at IFC,
certainty based on their training and certification.
POCUS offers a promising solution to enhance maternal and foetal health outcomes in Africa by improving accessibility, enabling rapid decisionmaking, and providing global certification for healthcare providers. This initiative, actively pursued by Intelios, holds the potential to transform healthcare delivery in Kenya and beyond.
In an effort to drive improvements in maternal and neonatal care, healthcare professionals are turning to innovative solutions such as point-ofcare diagnostics. According to Faith, a prominent figure in the field, early detection facilitated by these technologies enables timely interventions, ultimately reducing the risk of severe complications associated with pregnancy-related conditions like preeclampsia and gestational diabetes.
“Providing midwives with the tools and training to perform point-of-care ultrasounds would allow them to create a referral pathway to obstetricians and
other specialists when necessary, thus improving outcomes,” Joseph says.
BENEFITS OF TRAINING MIDWIVES IN ULTRASOUND IMAGING
Dr. Motshudi, a renowned radiologist in Johannesburg South Africa, advocates for equipping midwives with ultrasound training to enhance their diagnostic capabilities. According to Dr. Motshudi, from an imaging perspective, training midwives to perform ultrasounds is highly beneficial.
This training enables them to efficiently utilise ultrasound devices to assess critical factors, such as identifying whether there is one baby or two. He emphasises that these crucial assessments are often missed, even by skilled midwives, without access to such technology. Identifying these issues early, he asserts, is vital as it allows for timely referrals to obstetricians or higher-level facilities for necessary interventions, such as caesarean sections or specialised deliveries.
Dr. Motshudi believes that this low-cost intervention has the potential to be implemented globally and could save countless lives by ensuring timely and appropriate referrals.
“Prosper Healthcare focuses on training midwives, doctors, and other healthcare workers, including ambulance technicians, in point-of-care ultrasound. While our initial focus is on obstetrics, we aim to expand into other imaging areas. We collaborate with a group of sonographers, some of whom are employed by us, to conduct both theoretical and practical training,” he says.
According to Faith, early detection facilitated by imaging technologies enables timely interventions, ultimately reducing the risk of severe complications associated with pregnancy-related conditions like preeclampsia and gestational diabetes.
Access to quality care remains a pressing concern, particularly in rural areas where advanced healthcare facilities are scarce. Faith stresses the importance of training midwives in point-of-care diagnostics to ensure that women in underserved regions receive high-quality prenatal care, ultimately reducing maternal and neonatal mortality rates.
39 | www.xrphealthcare.com

“Our primary focus is on areas with alarmingly high maternal mortality rates, such as Garissa and Mandera counties,” Faith asserts. “These regions require urgent attention to address the pressing healthcare needs of expectant mothers.”
In collaboration with Dr. Edward Serem, head of Maternal and Reproductive Health, Faith outlines a strategic plan to deploy point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) devices to empower midwives in these high-priority counties. “The goal is to empower midwives with POCUS devices to make timely and informed decisions, ultimately reducing maternal mortality,” Faith emphasises.
The initiative will commence with a phased approach, beginning with targeted implementation in high-priority counties. “We’ll start small, testing and validating our approach before scaling up,” Faith explains. This cautious approach ensures the efficacy of the program before broader implementation.
Faith reveals that comprehensive policies, curriculum development, and training materials are currently under development, slated for government endorsement by June 30th. “These
foundational elements will pave the way for national implementation across Kenya, starting with the identified high-priority counties,” she affirms.
While point-of-care ultrasound doesn’t replace comprehensive ultrasounds, it significantly enhances bedside monitoring throughout the care continuum. Well-trained midwives can provide continuous and comprehensive care during pregnancy, labour, and postpartum, ultimately improving outcomes for both mothers and babies. Professional development plays a pivotal role in empowering midwives with advanced skills. Faith notes, “Point-of-care training increases their confidence and competence in managing obstetric emergencies, leading to better job satisfaction and retention in the healthcare sector.”
DRIVING IMPROVEMENTS IN MATERNAL AND NEONATAL CARE
Early detection and access to quality healthcare are paramount in maternal and neonatal care. Three healthcare professionals—Joseph, Faith, and Dr. Motshudi—offer valuable insights into driving improvements in this critical area.
“Early detection enables timely interventions, reducing the risk of severe complications,” explains
40 | www.xrphealthcare.com
Joseph. “Improved monitoring of maternal and foetal health can lead to better management of pregnancy-related conditions, such as preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and intrauterine growth restriction.”
Faith adds, “Access to quality care is a crucial issue, particularly in rural and remote areas. Many rural areas in Kenya lack advanced healthcare facilities. Training midwives in point-of-care diagnostics ensures that even women in these areas receive high-quality prenatal care, vital for reducing maternal and neonatal mortality.”
Point-of-care ultrasound, as Faith asserts, “does not replace comprehensive ultrasounds but enhances bedside monitoring throughout the continuum of care. Well-trained midwives can provide continuous and comprehensive care during pregnancy, labour,

and postpartum, improving outcomes for mothers and babies.”
Dr. Motshudi emphasises the importance of professional development. “Point-of-care training empowers midwives with advanced skills, increasing their confidence and competence in managing obstetric emergencies. Skilled midwives can make more informed decisions on the spot, reducing delays in treatment and improving overall care efficiency.”
Furthermore, Joseph contends that integrating point-of-care ultrasound technologies into the health system strengthens health infrastructure. “Medical equipment manufacturers in Africa are developing affordable solutions for frontline healthcare providers. Integrating these technologies can lead to standardised protocols and practices, ensuring consistent and high-quality care across regions.”
Resistance to change is a common hurdle, notes Dr. Motshudi, but he challenges the notion that midwives create unnecessary competition with other trained professionals in ultrasound technology. “It’s human nature to initially resist new interventions in our professional fields, often out of a desire to protect our established roles,” he explains. “However, this protectionist logic is flawed, and in fact, the opposite is true.”
“In reality, specialists will be busier because midwives will refer more patients to them,” he asserts. “As health professionals, our primary concern is improving patient outcomes.” Collaborative approaches in healthcare, involving midwives, doctors, and specialists, not only boost confidence but also benefit patients
. “Competent, skilled professionals attract more patients, improving their practice and generating more revenue,” Dr. Motshudi highlights. Thus, there’s value in training for everyone involved.
UNITING STAKEHOLDERS FOR IMPACTFUL CHANGE
In the quest to enhance maternal and neonatal care, stakeholders are coming together in unprecedented ways, driven by a shared commitment to leveraging innovative technologies. Faith and Joseph highlight recent shifts towards a more unified approach, emphasising the need for standardised skills across all healthcare providers.
Faith underscores the importance of standardising curricula rather than devices, ensuring healthcare professionals can make accurate assessments regardless of the equipment they use. This approach has garnered support from Kenya’s Ministry of Health, recognising the need to integrate these skills into the national healthcare system.
Faith believes that data collected through point-of-
41 | www.xrphealthcare.com
HEALTH CARE DELIVERY
care diagnostics can inform public health strategies, impacting policy changes. Institutions like Kenyatta University, AMREF International University, and Aga Khan University are already contributing to research aimed at reducing maternal and neonatal mortality rates.
Collaboration extends beyond academic institutions to regulatory bodies such as the Nursing Council of Kenya (NCK), Kenya Medical Practitioners and Dentists Council (KMPDC), Clinical Officers Council (COC), Society of Radiography in Kenya (SORK), and Kenya Association of Radiologists (KAR). The goal is to expand skills safely and within a defined scope of practice, enabling informed decision-making and appropriate referrals.
Joseph, speaking from experience in South Africa, highlights the efficiency of private healthcare in driving change. Private institutions are embracing point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) training independently, focusing on accreditation and demonstrating its impact on maternal mortality rates through research.
Research efforts extend to patient safety and the creation of better care pathways in Sub-Saharan Africa. There are private clinics which are actively involved in breast and obstetric POCUS research, contributing valuable insights into clinical pathways and healthcare provision. While South Africa pursues a private route, Kenya is engaging the government for public sector involvement in POCUS implementation.
“As consultants, we assess each country’s landscape, considering factors like cultural significance and patient demographics, to determine the best approach—whether to start with the public, private, or a combination of both.
For example, in Kenya, prioritising policy laid the groundwork for successful implementation, a strategy we’re now adapting in South Africa, albeit with some delay. Ultimately, it’s about navigating the route that leads us to the desired destination of improved healthcare outcomes,” Joseph says.
ROOTING FOR QUALITY IN THE CARE CONTINUUM

Joseph points out the imperative for a global standardisation of POCUS practices. “The global push for POCUS reflects a crucial need to address disparities in medical practice,” Joseph states. “Historically, there’s been a stark contrast between healthcare in remote areas and urban centres, leading to unequal standards of care.”
Inteleos is at the forefront of changing this narrative, aiming to rectify the imbalance by advocating for consistent POCUS standards worldwide. “Whether in Mombasa or Kigali, the quality of POCUS should remain uniform,” Joseph insists.
Central to this endeavour is the role of policy in setting benchmarks for training, competency, and technical performance evaluation. “Similar to assessing a surgeon’s qualifications, it’s essential to ensure that practitioners are proficient in POCUS techniques and adhere to established protocols,” he emphasises.
Furthermore, Joseph highlights the importance
42 | www.xrphealthcare.com
HEALTH CARE DELIVERY

of clinical accuracy, patient care impact, and documentation practices as critical components of quality assurance in POCUS. “As someone deeply invested in healthcare quality, I emphasise the importance of integrating quality control measures into POCUS implementation,” Joseph says. “By upholding rigorous standards, we can not only enhance patient care but also advocate for the widespread adoption of POCUS as a reliable diagnostic tool.”
In stressing the paramount importance of safety in healthcare provision, Joseph highlights global efforts to align with standards set by organisations like the World Health Organisation (WHO). “Ministries of health worldwide aim to align with global standards,” he says. Government regulation ensures that practitioners work within their scope of practice and adhere to defined standards, preventing unqualified individuals from providing medical services.
Furthermore, Joseph underscores the role of regulations in establishing parameters for healthcare professionals. “For example, while a midwife can use POCUS as part of their assessment toolkit, it doesn’t make them a fully qualified sonographer,” he explains.
Joseph argues that POCUS equips midwives with the tools needed to make informed decisions about patient care and to determine when specialist intervention is necessary. This highlights the critical role of policy, which defines who can use POCUS, how it should be implemented, and why it is essential— all aimed at ensuring safety and maintaining high standards of care.
A VERSATILE TECHNOLOGY
According to Joseph, the landscape of POCUS technology is evolving rapidly. “While the focus of
POCUS is currently on obstetrics, it’s rapidly expanding into other areas such as cardiac, vascular, and emergency medicine,” he explains. The versatility of POCUS allows it to address various patient needs, depending on demographics and geographic location.
Regarding its clinical applications, Joseph emphasises the immense potential of POCUS. “It can address a wide range of conditions, including HIV, tuberculosis, and more,” he elaborates. “The clinical aspects of POCUS are vast and could warrant a separate discussion.”
“In South Africa, we’re delving into various aspects beyond obstetrics, exploring how POCUS can impact areas like nephrology, HIV, and tuberculosis. We’re leveraging private institutions for implementation and research.
“Tanzania, on the other hand, is a focus for nephrology, particularly dialysis and kidney POCUS. In the Caribbean island of Barbados, we are assessing how POCUS could benefit cardiac patients. In Nigeria, we are focusing on inserting POCUS within the nursing schools’ curriculum. This illustrates that POCUS extends beyond obstetrics and beyond specific countries—it’s transformative across various medical specialities.”
However, Joseph acknowledges that they’re merely scratching the surface of POCUS’s potential. “Another critical area we’re delving into is patient safety—identifying any potential adverse effects associated with its utilisation,” he notes.
Aspirations in collaborative healthcare innovation “There’s an aspirational aspect to our collaborations and what’s currently happening,” says Motshudi, reflecting on the strategic partnerships that are shaping the future of healthcare. One of the standout collaborations is with Inteleos and U-Image, a South African equipment manufacturer that has developed a small, portable ultrasound device roughly the size of an iPhone.
“This wireless device connects to a viewing screen like an iPad,” Dr Thapelo explains. “While we aren’t exclusive with this company, we prefer supporting
43 | www.xrphealthcare.com
a fellow African enterprise over sourcing equipment from Europe, America, or China, though these regions remain significant players in the equipment market.”
Dr. Motshudi shares that they are also exploring partnerships with rural doctors in South Africa and local universities for research purposes. The aim is to obtain scientific validation for their work, providing crucial data to decision-makers and policymakers to encourage investment in this innovative area of healthcare. “These discussions are advanced, and we hope to start a project soon,” he reveals.
An essential aspect of these collaborations involves insurance companies. “If insurance companies support midwifery and point-of-care ultrasound, it would significantly reduce costs,” Dr. Motshudi notes. “Patients without complications could have normal deliveries with midwives rather than more expensive hospital deliveries with obstetricians. This approach benefits insurers by lowering overall expenses.”
Although some of these relationships are not yet finalised, the conversations are active. Dr. Motshudi reveals that his team is also engaging with a South African certification body to develop its own POCUS standards program, aiming to assure that those practising POCUS meet the minimum requirements for medical quality of care.
“Another exciting area we’re experimenting with is artificial intelligence,” Dr. Motshudi adds, highlighting ongoing discussions with partners in Estonia. “We are developing artificial intelligence (AI) tools, not specifically for point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) as it is not well-suited for AI at the moment, but for other areas of training we are exploring. Our vision extends beyond POCUS to include various areas of imaging and healthcare that might benefit from AI.”
EYE FOR QUALITY: ELEVATING HEALTHCARE STANDARDS
Dr. Motshudi envisions a healthcare system where quality is paramount, not just for midwives but across the entire healthcare environment. “Our major focus is on introducing quality systems into any healthcare setting,” he asserts. This commitment to quality involves implementing world-class systems and processes, aligned with the best facilities globally.
“Quality means following the right protocols and guidelines and having policies in place for various scenarios, such as how to handle an injury within your facility,” Dr. Motshudi explains. These elements are part of a comprehensive quality management system, often overlooked when starting health facilities.
He emphasises the importance of quality and certification, asserting that accreditation by a reliable institution validates practices against global standards. “This ensures your methods are consistent with the best practices in the profession, rather than relying on personal claims of excellence,” he adds.
Beyond clinical protocols, Dr. Motshudi highlights the importance of robust business processes, including HR management. “It’s crucial to ensure employees are fully trained and continuously updated with the latest protocols,” he notes.
Continuous professional development, ethics policies, and patient satisfaction surveys are all vital components of a high-quality healthcare system. “Patient satisfaction surveys help gather feedback and improve the patient experience, addressing issues like long wait times and lack of communication,” he says. “These require intentional systems and processes to manage effectively.”
Joseph further elaborates on the importance of clinical governance in enhancing healthcare quality. “Consider how a hospital is run and who oversees quality assurance and medical documentation,” he points out. The technology used in hospitals must be appropriate for the specific clinical practice. “For instance, an obstetric practice should have the right technology for its needs, rather than purchasing equipment arbitrarily,” he adds. In a tech-laden industry like healthcare, ensuring that technology aligns with clinical needs is crucial.
Both Dr. Motshudi and Joseph stress that alongside Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS), their dedication extends to enhancing overall quality and governance in healthcare facilities. “We aim to challenge the perception that healthcare facilities in Africa provide subpar service compared to those in the US or Europe,” Dr Motshudi says. By focusing on quality systems, certification, and patient satisfaction, they are setting a new standard for healthcare excellence in the region
44 | www.xrphealthcare.com
HEALTH CARE DELIVERY
The digital health evangelist bringing acute care beyond hospital walls with the Patient Status Engine Technology
 KEITH ERREY - XRP HEALTHCARE’S CHIEF TECHNOLOGY OFFICER
KEITH ERREY - XRP HEALTHCARE’S CHIEF TECHNOLOGY OFFICER
Keith Errey’s journey from Australia to the heart of Europe is nothing short of inspiring. With a foundation in physics, his path led him to the prestigious halls of Oxford University, where he immersed himself in cutting-edge technology and innovation. His initial role in a university spin-out provided a global platform, allowing him to work on pioneering projects that spanned continents. This period of his career was not only about professional growth but also about fostering a deep-seated passion for technological advancements.
Keith’s innovation journey didn’t stop there. His exploration into consultancy introduced him to a professor from Imperial College London, leading to the creation of a company focused on changing semiconductor technology. Though the company is no longer around, its impact, especially in healthcare, is significant, thanks to its work on lowpower silicon chip technology. “After leaving that the Oxford spin-out, I wanted to try something new, so I started a small consultancy. It was around the year 2000 while running the consultancy that I met a professor from Imperial College in London,” Keith recalls.
“Together, we set out to build a company with a fresh approach to semiconductor technology, especially for healthcare. While the company is no longer active, our goal was to pioneer lowpower silicon chip technology for healthcare,” he explains. “By 2004-2005, our collaboration led to a breakthrough—a single-chip solution for wearable technology, a big step forward in our exploration of wearable tech,” Keith fondly remembers.
TACKLING POOR DATA TO IMPROVE MEDICAL DECISIONS
Reflecting on his journey, Keith recounts that together with his co-founder, Rebecca Weir, they embarked on a new venture. They aimed to leverage the economies of scale from the semiconductor and consumer electronics industries to create affordable medical devices for widespread use. This goal led to the founding of Isansys Lifecare. “Our mission with Isansys was to develop new systems
45 | www.xrphealthcare.com
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
for monitoring patients and collecting patient data, and to use this data to build tools for improving clinical decision support, without making them prohibitively expensive. This journey began in 2010, and it has been a long but rewarding path since then,” he notes.
“I have been involved in the field of wearable technologies for healthcare for over 20 years,” he narrates. “My interest in healthcare was sparked by the realisation that many medical decisions are often based on poor data.” He explains that while good doctors can use their intuition to make sense of this data, not all healthcare professionals have the same level of training and understanding.
Keith elaborates on the key issue, stating that it was the lack of high-quality data on people living their everyday lives which meant that the essential baseline of “what is normal” was missing. He notes that most data at the time came from patients in hospitals, who were by definition now well and connected to large machines and not living normally. “This was long before the advent of devices like Fitbits and the Apple Watch.”
He recalls that his initial company began developing smart patches and testing them in hospitals. Around 2009, in a London hospital, they introduced what they called the digital plaster, a type of smart
patch technology. However, he and Rebecca Weir decided to leave the company in 2010 because they recognised that the technology, despite being good, was heading towards a dead end and couldn’t evolve further without very significant investment..
Keith’s innovative spirit and dedication have positioned Isansys Lifecare as a leader in healthcare technology. By focusing on creating accessible, data-driven medical devices, Keith and his team continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in healthcare, ensuring better outcomes for patients around the world.
PSE TECHNOLOGY BRINGS HIGH-LEVEL ACUTE CARE BEYOND HOSPITAL WALLS
“More interestingly,” Keith remarks, “the Patient Status Engine (PSE) technology is enabling the provision of high-level acute care outside hospitals.” The Patient Status Engine pioneers as the world’s premier medically certified, intelligent end-to-end clinical data infrastructure and ground-breaking patient monitoring platform, facilitating acute care delivery throughout the entire patient journey, whether at home, in a hospital, or anywhere in between.
He explains that acute care can now be provided at home with a well-organised workforce, offering a different and effective way to deliver healthcare. This development holds significant implications

SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
for healthcare discussions in Africa, where such innovations can provide high-quality care outside traditional hospital settings. “These advancements demonstrate that technology can unlock limitless possibilities in healthcare,” Keith says.
“Our work with the NHS has been significant, though not our greatest achievement,” acknowledges Keith Errey, reflecting on Isansys’ collaboration with the National Health Service. Despite several innovative studies within the NHS, the vast organisation has yet to fully adopt Isansys’ technology. “The NHS, being a large entity, tends to move at a slower pace,” Keith explains. “Their hesitation stems not from a preference for alternative solutions, but rather from a lack of recognition of the benefits of integrating and implementing our technology.” Despite this, Keith remains optimistic about changing their perspective in the future.
adoption in the future.
“In contrast, several European countries, particularly in Scandinavia, have shown more interest in and have started to adopt our technology,” Keith points out. Collaborations with various Scandinavian hospitals have integrated Isansys’ technology into standard care protocols. These hospitals utilise their data to enhance patient care, streamline documentation tasks for nurses, and optimise patient outcomes.
Keith’s interest in global healthcare doesn’t stop at Europe. “In India, we have been working independently of the Spiritus system,” Keith reports.

One of Isansys’ early projects involved working with children at Birmingham Children’s Hospital. Keith highlights their ground-breaking work in working in a team developing one of the first machine learning or artificial intelligence models for predicting patient deterioration in young patients around 2016-2017. However, the NHS has yet to advance this initiative, although Keith remains hopeful about its potential

“I have been personally interested in the Indian market for a long time, spending considerable time travelling and meeting people there.” This dedication has led to the establishment of Isansys India, a joint venture with local entrepreneurs and investors, which now has contracts with all the major hospital groups in India.
Keith mentions, “These include large hospitals such as the Apollo Group, Manipal Group, Max, Astor, Fortis, and others.” These major hospital groups are embracing Isansys’ technology as it enables them to undergo digital transformation in their wards. Additionally, this technology allows them to increase the number of patients they can serve by providing services outside the hospital as well.
COMBINING SENSORS, CONNECTIVITY AND AI INTO ONE MEDICAL PLATFORM
The Patient Status Engine (PSE) technology is making waves in the world of healthcare. It’s a smart system that brings together sensors, connections, and artificial intelligence (AI) into one single platform-as-a-medical-device to collect and analyse information about patients’ health. Keith, the person behind this innovation, talks about how AI, which is all about understanding big sets of data and finding patterns, is becoming more and more important in healthcare. “Our PSE platform is wellsuited for working with AI and machine learning in healthcare. This will be a major change in the future of healthcare,” he predicts.
According to Keith, this combination of technology is a big deal. It means that doctors and healthcare workers will have new tools to understand patients’ health better and make decisions about their care.
47 | www.xrphealthcare.com
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY

The PSE is a sign of how technology is transforming healthcare, opening up new possibilities for how we take care of people.
Keith continues to elaborate on the potential for AI systems to revolutionise healthcare globally, particularly by enabling a more holistic approach. “AI systems, as they become smarter and more widespread, will enable a better and more holistic approach to healthcare everywhere. Currently, much of healthcare is based on European practices, which might not always be suitable in different contexts like Africa. We need to personalise care not only at the individual level, but also appropriately for different groups of people,” he says.
By integrating data from traditional healthcare systems with allopathic healthcare, Keith envisions a more dynamic and personalised approach to improving patient outcomes. “By gathering data and recognising the benefits of traditional healthcare systems alongside allopathic healthcare, we can create a more dynamic, personalised approach to helping people get better and stay well. This is an exciting future that I can see beginning to take shape,” he concludes, highlighting the transformative potential of these advancements.
be dynamic, constantly improving in functionality and usefulness over time. We see the future of healthcare as being very dynamic, centred around connectivity and data, rather than static objects,” he explains, providing a glimpse into the innovative future Isansys envisions.
Isansys Lifecare recognised with prestigious awards In the field of healthcare innovation, Isansys Lifecare has garnered a remarkable array of accolades and awards, showcasing the company’s pioneering contributions to the industry.
Among its notable achievements, Isansys Lifecare has been recognised by esteemed organisations such as OBN, the Thames Valley Chamber of Commerce, and Business Cloud, securing prestigious titles like Best Public and Private Healthcare Collaboration, Best New Medtech, and Best Established Medtech.
Reflecting on these accomplishments, Keith also highlights the significance of government recognition and grant funding in propelling their mission forward. “The awards that are most pleasing to me are those where we receive recognition from the government and grant funding to pursue new projects,” he notes. Notably, Isansys Lifecare secured a million-pound grant from the UK government to develop their second-generation Patient Status Engine, a milestone that fuelled significant advancements in their technology.

Looking ahead, Keith discusses the Patient Status Engine (PSE), a pioneering medical device platform that Isansys has developed. “It’s built to
Furthermore, Isansys Lifecare’s participation in the European Union’s Horizon program underscores its commitment to collaborative innovation on a global scale. As a key contributor to the TARGET program, focused on atrial fibrillation-related stroke, Isansys Lifecare is at the forefront of groundbreaking research aimed at revolutionising disease management. “Through this collaboration, we believe that by using data from our Patient Status Engine, we can help doctors control the disease better and possibly predict and prevent atrial fibrillation events,” Keith explains, highlighting the transformative potential of their initiatives for patients worldwide.
Central to Isansys Lifecare’s innovative approach is the concept of digital twins, a cutting-edge technique that leverages computer modelling to monitor patient health in real-time. Keith elaborates,
48 | www.xrphealthcare.com
“A digital twin is a computer model of a patient that monitors their health in real-time.” This technology enables personalised, data-driven healthcare solutions, empowering healthcare providers to simulate treatments and optimise patient care strategies.
Looking ahead, Keith envisions a future where digital twin technology becomes widely accessible, ushering in a new era of personalised healthcare. “While this may sound futuristic, it’s becoming a reality now,” he remarks, emphasising the potential for this approach to revolutionise treatment modalities and enhance patient outcomes. “The concept of a digital twin allows for innovative treatments and a better understanding of why certain treatments work,” Keith concludes, underscoring the profound impact of personalised healthcare on the future of medicine.
Advancing XRP Healthcare’s mission of making healthcare more affordable and accessible
Commenting on his new role, Keith Errey expressed enthusiasm about joining XRP Healthcare, stating, “I am excited to be part of the XRP Healthcare team and contribute to their mission of transforming the healthcare landscape in Africa. The potential for innovation and positive impact is immense, and I look forward to leveraging my experience to drive strategic initiatives and contribute to the company’s success.”


Expressing his excitement about collaborating with XRP Healthcare, Keith states, “Working with XRP Healthcare and their vision to deliver healthcare in new ways is very exciting.” He elaborates, “One of the areas where I can contribute is my experience in raising money through public markets, such as flotation or reverse mergers, which they are currently exploring in Dubai. This experience can help raise initial finance and ongoing working capital for the business.”
“XRP Healthcare is a relatively new company,” Keith explains, highlighting the genesis of his involvement with the organisation. “I met Laban in London, and we had an extensive conversation one afternoon. Since then, we’ve been in regular contact, developing a mutual respect and understanding for each other’s goals in healthcare.”
Keith further reveals, “Laban and Kain offered me the opportunity to become an advisor to their company, and more recently, the position of Chief Technology Officer – CTO for healthcare products and devices. For me, this is a fantastic opportunity to continue my journey in making healthcare more affordable and accessible .”
According to Keith, addressing the issue of healthcare affordability is paramount. He emphasises, “Healthcare is often too expensive, and it needs to be approached from a different business perspective to make it affordable for more people.” He adds, “Healthcare is a basic right, but it does cost money. It’s important for those of us who can influence this to make it as affordable as possible.” Regarding the recent achievements of XRP Healthcare, Keith highlights, “XRP Healthcare has made significant strides recently, becoming a registered trademark in Uganda and preparing for an IPO.” He further notes, “The team’s hard work behind the scenes is making these achievements possible. Our goal is to make healthcare truly affordable and accessible whenever people need it.”
SCALING BENEFITS, NOT MONOPOLIES
As Keith explains, XRP Healthcare’s mission extends far beyond profit margins, focusing instead on
49 | www.xrphealthcare.com
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Georgina Horton receiving the “Best Established MedTech” Award in the OBN Awards 2021
leveraging economies of scale to deliver tangible benefits to individuals and communities worldwide. “Our approach at XRP Healthcare is centred on bringing economies of scale that benefit people without monopolising the market,” Keith elucidates. At the heart of their strategy lies a commitment to revolutionising the pharmacy business, with a keen emphasis on ensuring the availability of high-quality products through local pharmacies. By eradicating counterfeit drugs, optimising distribution channels, and ensuring fair pricing, XRP Healthcare aims to foster a healthcare ecosystem where quality care is accessible to all.
While Isansys endeavours span continents, Keith notes that their most significant impact is being felt in regions like India, where hospitals are embracing their technology as a beacon of innovation. “Hospitals in India have warmly embraced our technology,” Keith remarks. “They view our Patient Status Engine (PSE) as the next-generation solution, replacing cumbersome equipment with wearable devices and small tablets for seamless patient monitoring both in hospitals and at home.”
In Africa, where healthcare infrastructure is still developing, Keith sees an opportunity to implement the Isansys PSE platform into XRP Healthcare’s solutions in a way that is tailored to local needs. “There’s no need to replicate Western healthcare models,” Keith asserts. “Instead, we aim to provide low-impact, low-cost connected healthcare solutions that harness the power of technology to improve care outcomes.”
affirms. “This transformation will not only improve health outcomes but also alleviate the burden of unaffordable medical costs, paving the way for a healthier, more equitable future for all.”
Tailoring healthcare solutions for Africa’s diversity Keith emphasises the importance of understanding the local nature of healthcare. He points out that in a small country like Switzerland, the diversity of languages already poses a challenge. This complexity is magnified across Africa, a continent rich with numerous languages and cultures.
“When someone is sick, they want to communicate with a healthcare provider who speaks their language and understands their cultural context,” Keith explains. “Africa is a collection of diverse nations and tribes. Effective healthcare solutions must be tailored to work with local people and their specific needs.”
Although Keith acknowledges his current lack of detailed knowledge about the optimal expansion model for the continent, his interest in learning and adapting is clear. He underscores the importance of patience in the healthcare sector, noting that progress is often slower compared to other fields. “Even a very good idea needs thorough testing and gradual deployment at scale. Persistence is essential. I’ve been in this field for a long time, and it’s important not to give up,” he advises.

Central to Keith’s vision is the notion of scalability without exploitation. “With XRP Healthcare, we share a vision that is profitable but transcends profit as the only motive,” he emphasises. “Our goal is to make healthcare universally accessible and affordable, without compromising on quality or fairness.” By manufacturing locally and bypassing traditional reliance on suppliers, Keith believes XRP Healthcare can contribute to the emergence of high-tech manufacturing hubs across Africa.
Looking ahead, Keith envisions a healthcare revolution driven by accessibility and affordability. “Our immediate focus is on ensuring access to genuine, non-counterfeit medications for all,” he
Keith also reflects on the challenges faced by major healthcare and medical device companies like Philips, GE Healthcare, and Welch Allyn, which have attempted to develop technology similar to the PSE multiple times but eventually abandoned these efforts due to the prolonged timelines. “Their established market positions are challenged by our technology, so they are resistant to change. It’s often up to outsiders to bring innovation,” he says. “I prefer to think of myself as an agitator rather than a disruptor—someone who makes noise on the sidelines and works slowly to bring about change.”
Despite these challenges, Keith remains optimistic about the potential for rapid progress with XRP Healthcare. “I believe that with XRP Healthcare, things might progress more quickly, which is why I am very interested in working with them on this,”
50 | www.xrphealthcare.com
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY

he notes. “The faster, the better. But remember, patience is crucial in this field.”
In a conversation about the potential of deploying Isansys’ Patient Status Engine (PSE) technology in Africa, Keith expresses his strong belief in the logical and beneficial nature of such an endeavour. “Yes, that is the logical step at some point. Very much so,” he affirms.
COLLECTIVE EFFORTS OF A DEDICATED TEAM
Keith expresses deep appreciation forthe recognition his company has received, emphasising that these awards are a testament to the collective effort of his dedicated team. “The first thing I want to say is that it’s very pleasing to be recognised, but this isn’t just an award for me; it’s an award for my team. None of us can work effectively without a strong team of good people around us,” Keith states, highlighting the collaborative nature of their achievements.
He further elaborates on the value of these accolades, noting that while there is no monetary prize, the recognition from peers and the community holds significant importance. “They are the ones who make a difference, and that’s what I find most
gratifying about these awards. It’s rewarding to share this recognition with our team,” he affirms.
Keith prefers to have his colleagues receive the awards onstage, underscoring the importance of their visibility as integral members of the successful team. “When we attend award ceremonies, I prefer to have my colleagues go up to the stage to receive the awards. It’s important for them to be seen as part of the successful team,” he says.
In closing, Keith expresses his optimism for the future, foreseeing a healthcare landscape that is more dynamic, personalised, and focused on improving patient outcomes. “This will make healthcare more dynamic, personalised, and focused on helping people get better and stay well. I see this exciting future starting to take shape now, in ways that we could only imagine a few years ago but didn’t have the means to achieve,” he concludes.
“When we attend award ceremonies, I prefer to have my colleagues go up to the stage to receive the awards. It’s important for them to be seen as part of the successful team,”
51 | www.xrphealthcare.com
Georgina Horton, Isansys Comms and PR Head, and Rebecca Weir, co-founder and Director of Business Development, receiving the “Best Use of Technology” Award at the Thames Valley Chamber of Commerce Business Awards 2018.
XRP Healthcare expands into Uganda with successful trademark registration

XRP Healthcare, a leading force in healthcare innovation, has officially trademarked its name in Uganda, marking a significant step in its dedication to improving healthcare in the region. At the same time, the company has decided to end its partnerships with third parties, emphasising its commitment to moving forward independently.
This trademark registration is crucial for XRP Healthcare to establish its own pharmacies, medical centres, and hospitals in Uganda. The move shows XRP Healthcare’s dedication not only to expansion, but also to improving the quality and availability of healthcare services through its own establishments. By taking this step, XRP Healthcare demonstrates its strong focus on becoming a major player in Uganda’s healthcare sector, aiming to make quality medical services more accessible across the country. Strengthening its trademark rights, the company reaffirms its commitment to building trust, reliability, and excellence in healthcare through its brand.
brand in Uganda through acquisitions.”
Chairman Whitney Lynn added, “Registering our trademark in Uganda isn’t just a formality; it shows our commitment to the communities we serve and marks the beginning of a new era in healthcare innovation. By moving forward independently, we’re staying true to our mission.”
Business Development Officer Laban Roomes commented, “The trademark registration in Uganda is a significant achievement, protecting our brand identity in the market. Now, our acquisitions can proudly display our logo, maintaining the integrity of our brand.”
Renowned healthcare expert Peter Kyobe Waiswa, who recently joined XRP Healthcare, expressed his excitement about transforming Uganda’s private healthcare sector through strategic partnerships and innovative solutions.

Looking ahead, XRP Healthcare plans to transform healthcare in Uganda byacquiring private healthcare facilities. Through partnerships and investments, it aims to raise the standard of healthcare, ensuring everyone has access to comprehensive medical care through its acquisitions or the XRPH App.
CEO and Founder Kain Roomes stated, “We’re already laying the groundwork for these initiatives, ensuring legal and regulatory compliance. With the trademark secured, we’re ready to establish our
This development signals a new direction for XRP Healthcare, as it opts for internal financing rather than relying on external investors for its expansion in Africa. This strategic move positions it for sustained growth in consolidating Africa’s fragmented healthcare sector.
XRP Healthcare remains steadfast in its mission to transform healthcare and improve communities worldwide. With its trademark registered in Uganda, the company is set to redefine healthcare standards, driving innovation and accessibility in the industry.
52 | www.xrphealthcare.com
XRP HEALTHCARE NEWS UPDATES
XRP Healthcare moves forward as one entity for African M&A venture
XRP Healthcare has embarked on addressing the complex healthcare landscape in Africa by establishing XRP Healthcare Africa, a new entity headquartered in Uganda.
This strategic initiative is aimed at transforming healthcare operations throughout the continent, with the primary objective of establishing a sustainable and efficient healthcare system in Africa. XRP Healthcare Africa has been established as an independent entity, compliant with all regulatory requirements in Uganda, ensuring seamless and self-sustained operations.
CEO/Founder Kain Roomes shares the vision: “XRP Healthcare Africa will be a strong, unified entity that meets the needs of people in Africa. By bringing all our local mergers and acquisitions under this new entity, we won’t have to rely on other companies. This makes it easier for us to reach our goals.”
With streamlined acquisitions and a local focus, XRP Healthcare’s Dubai branch will still handle acquisitions across Africa. But having XRP Healthcare Africa means they can manage local deals and operations better.
According to a 2023 report by Bowmans Law, the pharmaceutical, medical, and biotech industries have been exceptionally dynamic in terms of mergers and acquisitions (M&A), particularly within the private equity sector. Notable 2022 transactions included the acquisition of ownership stakes in hospitals, pharmacies, and other healthcare entities.

Laban Roomes, Business Development Officer at XRP Healthcare, explains: “XRP Healthcare Africa lets us deal with the specific challenges and opportunities in African healthcare. Being local means, we can better understand and meet the needs of the communities we serve.”

The health sector is expected to experience increased M&A activity as businesses implement measures to recover from the economic effects of the Covid-19 pandemic. From 2016 to the present, approximately US$4.2 billion has been invested in African healthcare, with pharmaceuticals attracting the most invested capital, and technology leading in terms of deal count.
XRP Healthcare plans to keep everyone updated on their progress in bringing together healthcare in Uganda and across Africa. This shows their commitment to raising money independently and using their streamlined structure to improve healthcare for everyone in Africa.
With a Committed Leadership Team, XRP Healthcare Chairman Whitney Lynn, who has over 45 years of experience in mergers and acquisitions, is excited: “We’re glad to make our local operations smoother with a legal setup that fits Uganda’s system. This is a big step, and I’m eager to share our plans and progress in Uganda. It shows our commitment and sets the stage for big changes in African healthcare.”
53 | www.xrphealthcare.com
XRP HEALTHCARE NEWS UPDATES
XRP Healthcare unveils revolutionary swap facility in open-source XRPH Wallet

XRP Healthcare, a modern healthcare solution utilising web3 technology, has introduced an innovative feature in its XRPH Wallet. This feature enables users to seamlessly swap XRP and USDT for XRPH, the native token of the XRP Healthcare ecosystem. The XRPH Wallet reflects XRP Healthcare’s strong commitment to open-source principles and its drive to encourage innovation within the XRPL community.
Designed with accessibility in mind, the swap process is intuitive and user-friendly. XRP Healthcare
has published a detailed stepby-step tutorial on their YouTube channel, guiding users through the process of downloading the XRPH Wallet from both the App Store and Google Play. This initiative highlights XRP Healthcare’s dedication to empowering users with the necessary tools and knowledge to fully utilise blockchain technology.
In addition to facilitating transactions, the XRPH Wallet features a digital XRP Healthcare prescription savings card. This card offers users discounts of up to 80% on prescriptions and medications at over 68,000 pharmacies across the United States. Furthermore, users earn XRPH rewards each time they use this digital prescription savings card, adding further value to the offering.
The second edition of the XRP Healthcare magazine, available through the XRPH App, provides users with insights into the cutting-edge digital publication, which is also accessible in physical print.

The XRPH Wallet and native token are specifically designed for fast and secure payments, particularly in emerging pharmaceutical markets. As XRP Healthcare expands through mergers and acquisitions within the African healthcare sector, the XRPH token will play a crucial role in shaping the future of healthcare payments and accessibility. To promote autonomy and innovation within the XRPL ecosystem, XRP Healthcare encourages other projects built on the XRPL to leverage its opensource framework.
XRP HEALTHCARE NEWS UPDATES
Renowned industry expert Peter Kyobe Waiswa joins XRP Healthcare to transform private healthcare in Uganda


XRP Healthcare, a healthcare investment and management firm based in the UAE, has welcomed Peter Kyobe Waiswa to its team as a Healthcare Industry Expert. With his extensive experience and advisory roles with organisations like UNICEF, WHO, and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Peter’s expertise is set to enhance XRP Healthcare’s operations in Uganda’s private healthcare sector. In his new role with XRP Healthcare, Peter Kyobe Waiswa will provide insights and guidance as the company conducts due diligence on various targeted acquisitions aimed at upgrading systems and facilities, improving access to medication, and enhancing technical resources.
“I am thrilled to be part of XRP Healthcare and to contribute to transforming Uganda’s private healthcare landscape,” said Peter Kyobe Waiswa. “Through strategic partnerships and innovative solutions, our aim is to improve access to high-quality healthcare services for the people of Uganda.”
Peter Kyobe Waiswa brings a wealth of experience as a Ugandan researcher, medical doctor, and academic administrator. He is an associate professor of Health Policy, Planning, and Management at Makerere University, specialising in health policy and systems, especially in maternal, newborn, and child health in low and middle-income countries.
55 | www.xrphealthcare.com
XRP HEALTHCARE NEWS UPDATES

Peter’s academic journey is remarkable. He earned his Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery from Mbarara University in 1992, followed by a Master’s in Public Health from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem Braun School of Public Health and Community Medicine. He completed his joint PhD in Medicine and post-doctoral fellowship from Makerere University and the Karolinska Institute, Sweden.
Whitney Lynn, Chairman of XRP Healthcare, expressed, “We are honoured to have Peter Kyobe Waiswa join our team. Peter’s background includes pivotal roles with respected health-focused philanthropic and international organisations, where he has influenced key initiatives and policies. His extensive experience will guide our strategic decisions in mergers and acquisitions.”
Peter has played impactful roles throughout his career, from serving as National First Aid Officer of the Uganda Red Cross to working as a doctor and assistant district medical officer for Iganga District.
He has been a key member of Makerere University’s Department of Health Policy, Planning, and Management since 2008. Peter is also a founding member of NGOs such as Uganda Development and Health Associates (UDHA), Busoga Health Forum, and One Village At A Time (OVAAT).
He leads research groups at The INDEPTH Network Maternal, Newborn and Child Health Working Group (MNCH-WG) and The Makerere University Centre of Excellence for Maternal Newborn and Child Health. Peter also serves as a technical advisor for organisations including WHO, UNICEF, The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, International Paediatric Association, and the African Academy of Sciences. He was appointed to the World Health Organisation Strategic and Technical Advisory Group of Experts (STAGE) for Maternal, Newborn, Child, and Adolescent Health and Nutrition in May 2020.
“We are excited to welcome Peter Kyobe Waiswa to XRP Healthcare. His extensive experience in global health leadership will drive our strategic mergers and acquisitions. With his profound understanding of Uganda’s healthcare landscape, Peter is integral to our mission of enhancing accessibility to private healthcare,” said Laban Roomes, Business Development Officer at XRP Healthcare.
With an H-Index of 46 and over 200 peer-reviewed scientific publications, Peter Waiswa’s appointment marks a significant milestone for XRP Healthcare. His dedication to healthcare advancement and wealth of experience make him an invaluable asset as XRP Healthcare continues its mission to transform healthcare in Uganda and Africa through mergers and acquisitions.
“We are delighted to welcome Peter Kyobe Waiswa to the XRP Healthcare family. With a track record of influential roles within globally renowned healthfocused entities, Peter brings invaluable experience to our team. His expertise will shape our strategic moves in mergers and acquisitions,” said Kain Roomes, founder and CEO of XRP Healthcare.

56 | www.xrphealthcare.com
XRP HEALTHCARE NEWS UPDATES

XRP Healthcare Magazine Issue 2 - The official media partner of MEDEXPO Africa Kenya 2024

In Africa, amidst the exciting world of medical innovations, MEDEXPO Africa Kenya 2024 stood out as a symbol of progress in healthcare. This toptier international medical event brought together experts, exhibitors, and delegates for three days of exploration and teamwork to shape the future of healthcare on the continent.
During this important gathering, XRP Healthcare Magazine Issue 2 took the spotlight as the official publication. It shared insights, trends, and stories that reflected the innovative spirit driving MEDEXPO Africa Kenya 2024. An outstanding feature of this edition was an exclusive spotlight on MrBeast, a well-known philanthropist and social media influencer, offering a fresh perspective on the blend of technology and healthcare.
We express our sincere thanks to Expogroup for hosting this remarkable exhibition. It acted as a catalyst for bringing together leaders, innovators, and stakeholders in the healthcare field. Beyond just showcasing products and services, the event created valuable connections and opportunities for potential partnerships that could transform healthcare delivery in Africa and beyond.
XRP Healthcare Magazine Issue 2 dives deep into the latest advancements, challenges, and opportunities in the healthcare sector. Featuring topical issues on medical equipment to insights into digital healthcare solutions, this edition is a goto resource for anyone passionate about making a positive impact in healthcare.
58 | www.xrphealthcare.com
XRP HEALTHCARE NEWS UPDATES




PICTORIAL - 25TH EDITION OF MEDEXPO KENYA



60 | www.xrphealthcare.com PICTORIAL - 25TH EDITION OF MEDEXPO KENYA
Ripple XRP: Transforming global payments

Ripple, a blockchain-based digital payment network, is leading the charge in revolutionising crossborder transactions with its native cryptocurrency, XRP. Ripple Labs, the company behind Ripple, focuses on building global payment systems for financial institutions, aiming to make international transactions faster, cheaper, and more secure.
XRP serves as the digital asset associated with Ripple, powering the XRP Ledger (XRPL), a blockchain network developed by Ripple. While Ripple provides technology for financial institutions, XRP is the digital asset used for various purposes, including payments.

However, Ripple faces a significant challenge
from an ongoing lawsuit by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), alleging that XRP is an unregistered security. This legal battle has created market uncertainty, impacting XRP’s price. Despite this, Ripple continues to focus on its core objectives, serving as a payment settlement asset exchange and remittance system, similar to the SWIFT system used by banks for international money transfers.
XRP’s fast and scalable transactions settle within 3-5 seconds, with remarkably low transaction fees, making it attractive for both individuals and institutions. Moreover, the XRP Ledger, operational since 2012, boasts over 80 million closed ledgers and is significantly more energy-efficient than proof-ofwork blockchains.
61 | www.xrphealthcare.com
XRP HEALTHCARE NEWS UPDATES
XRP applications: From financial institutions to developers
XRP finds applications in various sectors, including financial institutions, individuals seeking alternatives to traditional banking, and developers leveraging its open-source nature for building applications. The XRP Ledger’s open-source foundation allows developers to build powerful applications without harming the environment. The ledger can handle up to 3,400 transactions per second, making it scalable for various use cases. Additionally, Ripple’s technology extends to Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), with central banks using a private version of the XRP Ledger for issuing and managing digital currencies securely.
Looking ahead, XRP’s journey has seen highs and lows, influenced by market dynamics and legal battles. Factors like legal outcomes, real-world utility, and market trends will shape XRP’s future. Despite challenges, Ripple and XRP remain influential in transforming global payments, offering lightningfast transactions, low fees, and sustainability commitments. Whether you’re a financial institution, developer, or individual, exploring XRP and the XRP Ledger can lead to innovative financial solutions.

XRP Healthcare halts swap to preserve token value
XRP Healthcare, a pioneering platform integrating healthcare with blockchain technology via the XRP Ledger (XRPL), has announced its intention to discontinue the XRP to XRPH swap facility by June 7th or once the available supply is depleted. This move is aimed at enhancing the scarcity of XRPH tokens, which have a limited supply of only 100 million.
The decision has sparked significant interest in the global crypto community, driven by unprecedented demand for XRPH. As the native token of XRP Healthcare, XRPH allows users to purchase healthcare products and services on the platform’s decentralised marketplace. However, news of the swap facility’s cessation led to a sharp decline in XRPH’s value.
A CLOSER LOOK
According to a press release, this strategic decision emphasises the importance of maintaining the limited supply of XRPH tokens across exchanges and the XRP Healthcare Prescription Savings Card App, available on Android and iOS. Users can leverage these tokens to buy healthcare-related products and services at over 68,000 pharmacies, including Walmart, CVS, and Walgreens, offering up to 80% savings on prescriptions and medications in return for US$1.00 of XRPH tokens each time the card is used.
With a finite supply of only 100 million tokens, XRPH’s circulating supply stood at 70,708,715 tokens as per CoinMarketCap at the time of writing. This highlights
the growing adoption of the healthcare-based token on the XRP Ledger, indicating that a dry spell in supply could be imminent as the venture gains popularity.
Kain Roomes, CEO and Founder of XRP Healthcare, remarked, “Halting the swap facility is a crucial step in ensuring the long-term integrity and scarcity of XRPH tokens. By blackholing the issuing account, we are aligning with the best practices in the cryptocurrency space to maintain the value of our tokens for our consumers.”
Blackholing involves prohibiting the issuing account from creating more tokens, thereby preserving the finite supply.
Scarcity is a major driver of cryptocurrency prices and plays a fundamental role in the cryptocurrency world. Bitcoin, a prominent example, undergoes a halving event roughly every four years. This event reduces the reward for mining new blocks by half, inherently limiting the supply of new Bitcoins. Another good example is the widely popular meme coin Shiba Inu (SHIB), which burns tokens to increase its price.
EXPANSION INTO AFRICA
XRP Healthcare is actively pursuing expansion plans throughout Africa, with a focus on Uganda. The company has successfully registered its trademark in Uganda, marking a significant step towards branding private healthcare acquisitions, including pharmacies, medical centers, and hospitals, under the XRP Healthcare logo.
62 | www.xrphealthcare.com
XRP HEALTHCARE NEWS UPDATES

CANCER IN SUB-SAHARAN AFRICA: A CALL TO ACTION
BY HELLEN MUCHERU

Cancer is becoming an escalating public health crisis in sub-Saharan Africa, particularly impacting women’s health. The increasing incidence and mortality rates of breast and cervical cancer in this region underscore the urgent need for comprehensive interventions. According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, with low- and middle-income countries, including those in subSaharan Africa, bearing a disproportionately high burden. This article examines the current landscape of cancer in sub-Saharan Africa, the efforts being made to address this crisis, and the critical role of international collaboration in combating these diseases.
Women are the backbone of every community, family, and nation. However, they are disproportionately affected by certain types of cancer, particularly breast and cervical cancer. In sub-Saharan Africa, these two cancers account for over half of the cancer burden among women. For instance, in Kenya, breast and cervical cancers are responsible for almost a third of all annual cancerrelated deaths. Early detection and treatment of these cancers can significantly improve outcomes,
but global health disparities mean that these services are often unavailable or inaccessible in many parts of sub-Saharan Africa.
Cervical cancer, highly detectable and curable, remains one of the most common cancers worldwide and the leading cause of cancer mortality among women in Kenya. Sub-Saharan Africa bears the highest burden of cervical cancer globally, with 19 of the 20 hardest-hit countries located in this region. Early detection and treatment of these cancers can significantly improve outcomes, but global health disparities often render these services unavailable or inaccessible in many parts of sub-Saharan Africa.
A significant challenge in combating breast and cervical cancer in sub-Saharan Africa is the late diagnosis. Between 60-70% of women in African countries are diagnosed at a late stage, drastically reducing their chances of survival. Only one in two women diagnosed with breast cancer in an African country will survive five years, compared to over 90% in high-income countries. This stark disparity underscores the urgent need for improved early detection and treatment services.
63 | www.xrphealthcare.com
DISEASE FOCUS


The role of global alliances and philanthropy Global alliances and philanthropic initiatives are intensifying efforts to tackle the cancer crisis in sub-Saharan Africa. A notable example is the Global Alliance for Women’s Health, an initiative of the World Economic Forum supported by Siemens Healthineers, which has launched the Cervical and Breast Cancer Coalition. This coalition, introduced during the World Health Assembly, aims to accelerate advancements in the detection, treatment, and care of breast and cervical cancer.
It seeks to achieve this through unprecedented collaborations and innovative solutions involving key stakeholders.
Prominent advocate Melinda French Gates emphasises underscores the importance of investing in women’s health. Her philanthropic endeavours, including a US$12.5 billion commitment, target various issues affecting women and families. Melinda emphasises that improving women’s health can uplift entire communities and economies, echoing the growing evidence supporting the multiplier effect of such investments.
Elisabeth Staudinger, President of Siemens Healthineers, also underscores the need for international cooperation and innovation in healthcare. Staudinger points out that addressing the healthcare gap in sub-Saharan Africa requires not only financial investments but also technological advancements and strategic partnerships. Siemens Healthineers’ involvement in the Cervical and Breast Cancer Coalition exemplifies how private sector participation can drive significant progress in public health initiatives.

64 | www.xrphealthcare.com
Elisabeth Staudinger (Left), President of Siemens Healthineers alongside high-profile delegates during past World Economic Forum.
WHO’s Strategic Directions for Cancer Control
The World Health Organisation (WHO) has outlined strategic directions for cancer control that emphasise preventive measures, early detection, treatment, and palliative care. These strategies are specifically tailored to address the unique challenges faced by low- and middle-income countries, aiming to alleviate the burden of cancer through comprehensive and cost-effective interventions. WHO’s initiatives focus on strengthening health systems, improving access to essential medicines and technologies, and fostering multisectoral partnerships.
Central to WHO’s approach is the improvement of screening programs. The organisation advocates for widespread screening programs for breast and cervical cancer, highlighting that early detection through regular screenings can significantly reduce mortality rates by identifying cancers at more treatable stages. In addition, WHO emphasises the importance of vaccination programs, particularly the HPV vaccine, which is highly effective in preventing cervical cancer. Integrating HPV vaccination into national immunisation programs is a key recommendation to protect future generations.
promotes multisectoral partnerships, encouraging collaboration between governments, nongovernmental organisations, the private sector, and international agencies. These partnerships are key to mobilising resources and implementing comprehensive cancer control programs.
The economic impact of investing in women’s health
Investing in women’s health has profound economic implications, underscored by the potential for significant returns on investment. A report by the Global Alliance for Women’s Health, titled “Closing the Women’s Health Gap: A US$1 Trillion Opportunity to Improve Lives and Economies,” illustrates the transformative impact of addressing health conditions that disproportionately affect women. By targeting these conditions, the time women spend in poor health could be reduced by nearly two-thirds, leading to substantial improvements in health outcomes and the quality of life for over 3.9 billion people globally.

Strengthening health systems is another critical strategy. Building resilient health infrastructures that can deliver comprehensive cancer care— from prevention to palliative care—is essential. This includes training healthcare workers, enhancing infrastructure, and ensuring a steady supply of necessary medications. Moreover, WHO underscores the importance of community education and awareness. Raising awareness about early detection and available treatment options is crucial, as community-based education programs can empower women to seek care promptly and reduce the stigma associated with cancer.
Accurate data collection and research are also vital components of WHO’s strategy. Gathering and analysing data on cancer trends through the establishment of cancer registries and research initiatives is essential for planning effective interventions. Furthermore, WHO
The economic benefits are equally striking. The report indicates that such improvements in women’s health could lead to a 1.7% increase in per capita GDP. This statistic reveals the considerable economic growth potential tied to better health outcomes for women. Moreover, the data shows that every $1 invested in women’s health initiatives can unlock US$3 in economic growth. This return on investment makes women’s health one of the most compelling avenues for societal and economic advancement.
The broader implications of these findings emphasise the critical need for sustained investments in women’s health. Improving women’s health not only enhances their individual well-being but also drives economic growth, highlighting the interconnectedness of health and economic prosperity. These investments ripple through societies, enhancing productivity, reducing healthcare costs, and fostering more robust economic systems. In essence, prioritising women’s health is not just a moral imperative but also a strategic economic decision that promises widespread benefits.
65 | www.xrphealthcare.com
HEALTH CARE DELIVERY

LET’S GO GREEN: A PHARMACIES’ PATH TO A MORE SUSTAINABLE
FUTURE

In an era where environmental concerns dominate global discourse, the healthcare industry is not exempt from the imperative to adopt ecofriendly practices. As the world grapples with the consequences of climate change and environmental degradation, industries across the spectrum are striving to become more sustainable. Among these, pharmacies are increasingly turning to sustainable methods to reduce their ecological footprint, underscoring the significance of environmental responsibility in the healthcare sector.
The concept of green pharmacies encompasses a broad spectrum of practices aimed at minimising environmental impact. These practices include reducing waste and energy consumption, adopting sustainable packaging, and promoting eco-friendly products. Pharmacies are pivotal in the healthcare system, and their shift towards sustainability reflects
a growing recognition of their role in protecting the environment.
A critical aspect of this transformation is the reduction of pharmaceutical waste. Medications can lead to significant environmental contamination if not disposed of properly, affecting water systems and wildlife. Green pharmacies implement rigorous waste management protocols, ensuring that unused or expired medications are disposed of safely, thereby preventing environmental pollution.
Sustainable practices in pharmacies
Many pharmacies are taking significant steps to reduce their energy consumption by investing in energy-efficient lighting, heating, and cooling systems. By doing so, they are cutting down on their overall energy use, which contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Walgreens, a major pharmacy chain in the United States, is a prime example of this effort. Walgreens has been investing
66 | www.xrphealthcare.com
PHARMACIES

in energy-efficient lighting and refrigeration systems across its stores. By retrofitting their lighting with LED bulbs, Walgreens has significantly reduced its energy consumption, lowering greenhouse gas emissions. This helps the environment and results in cost savings for the company over time.
Pharmacies generate various types of waste, including packaging materials, expired medications, and single-use items. Implementing robust recycling programs and waste reduction strategies minimises this environmental impact. For example, CVS Health has made significant strides in this area by implementing a comprehensive recycling program across its stores. The company has also introduced initiatives to reduce the amount of plastic used in
packaging. CVS has also switched to paper bags and encourages customers to bring reusable bags. These efforts reduce waste and foster a culture of environmental responsibility among customers.
Reducing water usage is another critical aspect of sustainability. Pharmacies are adopting practices to minimise water waste through efficient fixtures and water-saving technologies. Wallgreens Boots UK, for example, has implemented water-saving measures in its stores, including installing low-flow faucets and toilets. These measures have resulted in substantial reductions in water consumption, contributing to the company’s overall sustainability goals. By conserving water, Boots UK not only helps protect this vital resource but also sets a positive example for other businesses in the industry.
Sustainable packaging
Traditional pharmaceutical packaging often involves a significant amount of plastic and non-recyclable materials. Transitioning to ecofriendly packaging can drastically reduce the environmental impact. Walgreens has partnered with Terracycle to launch a recycling program for difficult-to-recycle items such as beauty product packaging and prescription bottles. Customers can return these items to participating stores, where they are collected and sent to Terracycle for recycling. This initiative helps reduce the amount of waste in landfills and promotes recycling materials that are typically challenging to process.
Some pharmacies are exploring the use of biodegradable and compostable materials for packaging. These materials break down more easily in the environment, reducing long-term waste. Gaia Herbs, a company specialising in herbal supplements, is a leader in this area. Gaia Herbs uses biodegradable and compostable packaging for many of its products. This commitment to sustainable packaging helps minimise the environmental impact of their products from production to disposal, demonstrating that combining high-quality products with ecological responsibility is possible
Encouraging the use of reusable containers is another effective strategy to reduce waste.
67 | www.xrphealthcare.com
Pharmacies can offer incentives for customers who bring their containers for refills. The Refill Shoppe is an excellent example of this approach. This pharmacy allows customers to bring their containers to refill with various products, including over-thecounter medications and personal care items. This approach reduces waste and promotes a culture of reuse and sustainability. By encouraging customers to reuse containers, The Refill Shoppe helps lessen the demand for single-use packaging and fosters more sustainable consumer behaviour.
Environmentally conscious initiatives
Obtaining green certification can demonstrate a pharmacy’s commitment to sustainability. Certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) can guide pharmacies in adopting best practices that significantly reduce their environmental impact. For example, Kaiser Permanente, an American integrated managed care consortium based in Oakland, California, United States, has achieved LEED certification for several pharmacies. These certifications reflect the organisation’s dedication to sustainable building practices, including energy efficiency, waste reduction, and sustainable sourcing. CVS also has the LEED certification.
Pharmacies can also influence sustainability through the products they choose to stock. Prioritising eco-friendly and sustainably sourced products supports a greener supply chain and promotes environmental responsibility. Pharmaca Integrative Pharmacy is a notable example of this approach. Pharmaca focuses on offering sustainably sourced products, including organic and fair-trade items. By selecting suppliers committed to sustainable practices, Pharmaca helps reduce the overall environmental impact of its products. This provides customers with high-quality, eco-friendly options and supports businesses prioritising sustainability, reinforcing a cycle of environmental consciousness and responsibility throughout the supply chain.
Educating customers and the community about sustainability is crucial for fostering widespread environmental consciousness. Pharmacies can play a vital role in this through workshops, informational materials, and community programs. Rite Aid, for
instance, engages in community outreach by organising events focused on sustainability. These events include medication take-back programs, where customers can safely dispose of expired or unused medications, preventing them from ending up in landfills or water supplies. Additionally, Rite Aid conducts educational workshops on eco-friendly living, providing valuable information and resources to help customers make more sustainable choices in their daily lives. These initiatives help raise awareness and encourage sustainable practices among customers, contributing to a broader culture of environmental stewardship.
The impact of green pharmacies
The shift towards green pharmacies has farreaching environmental and public health implications. By adopting sustainable practices, pharmacies can significantly lower their ecological footprint. This includes reducing waste, conserving resources, and promoting sustainable products. For instance, minimising single-use plastics and transitioning to biodegradable packaging reduces the amount of non-biodegradable waste entering landfills and oceans. Implementing energy-efficient systems and water-saving technologies further conserves vital resources, substantially decreasing the pharmacy’s overall environmental impact.
In addition to direct environmental benefits, these efforts contribute to a broader culture of sustainability. By visibly committing to eco-friendly practices, pharmacies set an example for their customers and the wider community. This visibility can encourage customers to adopt eco-friendly choices in their own lives, such as opting for reusable bags and containers, properly disposing of medications, and supporting products and companies that prioritise sustainability. This ripple effect can lead to a more environmentally conscious society where sustainable practices become the norm rather than the exception.
Moreover, green pharmacies can serve as role models for other sectors within the healthcare industry. Their commitment to sustainability can inspire hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare providers to adopt similar practices, amplifying the positive impact on the environment. For instance,
68 | www.xrphealthcare.com
PHARMACIES

hospitals might follow suit by implementing waste reduction programs or investing in renewable energy sources. Clinics might begin sourcing ecofriendly medical supplies and adopting energyefficient technologies. As more healthcare providers embrace sustainability, the collective impact can be substantial, leading to significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, waste generation, and resource consumption across the industry.
Furthermore, the transition to sustainable practices can also have positive economic implications for pharmacies and the healthcare sector. Energyefficient technologies and waste reduction strategies often lead to long-term cost savings. Reduced energy consumption lowers utility bills, and efficient waste management can decrease disposal costs. These savings can be reinvested into further sustainability initiatives or other business areas, creating a positive feedback loop of continuous improvement and environmental stewardship.
In addition, the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible businesses presents an opportunity for pharmacies to differentiate themselves in a competitive market. Pharmacies prioritising sustainability can attract a loyal
customer base that values eco-friendly practices, potentially increasing their market share and fostering customer loyalty
Challenges and future directions
Despite the progress made in adopting sustainable practices, pharmacies face several challenges to the widespread implementation of these ecofriendly initiatives. One of the primary challenges is the initial cost of implementing eco-friendly technologies. Transitioning to energy-efficient systems, sustainable packaging, and other green technologies often requires a significant upfront investment. This can be a barrier for smaller pharmacies with limited budgets, despite the longterm cost savings and environmental benefits these technologies can provide.
Regulatory hurdles also pose a significant challenge. The pharmaceutical industry is highly regulated, and pharmacies must comply with strict guidelines to ensure the safety and efficacy of medications. These regulations sometimes limit the ability to adopt certain sustainable practices, such as using innovative packaging materials or new waste disposal methods. Additionally, the lack of industrywide standards and guidelines for sustainability can make it difficult for pharmacies to know which practices to adopt and how to measure their environmental impact effectively.
However, the future looks promising for green pharmacies. As awareness of environmental issues grows, the demand for sustainable practices in all sectors, including pharmacies, will likely increase. Consumers are becoming more environmentally conscious and seeking businesses prioritising sustainability. This shift in consumer behaviour can drive pharmacies to adopt more eco-friendly practices to meet customer expectations and remain competitive.
Technological advancements and innovative solutions will further support the transition to greener practices. Advances in packaging technology, for example, are leading to the development of more sustainable materials that meet regulatory requirements and have a lower environmental impact. Additionally, improvements in energy-efficient technologies and renewable energy sources can help reduce the initial costs associated with these investments, making them more accessible to a broader range of pharmacies.
69 | www.xrphealthcare.com

TOP 10 HOSPITALS IN AFRICA
Identifying the top hospitals in Africa can depend on various factors, including medical specialities, patient outcomes, facilities, and international rankings. In this case, ranking has been done based on International ranking, based on the Webometrics ranking by the Spanish public research organisation, the Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC). This ranking evaluates hospitals worldwide based on their efficiency. Out of the top 11,780 hospitals globally, only 100 are located in Africa.
Gambro Healthcare in Swaziland is the highestranked African hospital at 598th globally, followed
by As Salam International Hospital in Egypt, ranked 1542nd in the world and second in Africa. South Africa has three hospitals in the top 10 African hospitals, while Morocco has notable rankings with Mohammed VI Hospital in Marrakech, and Hassan Interestingly, some high-quality centres are found in poorer countries, such as the Institut Pasteur in Madagascar (2065th globally) and the Edna Adan Maternity Hospital in Somaliland (4149th globally). However, hospitals from Central and West Africa are notably absent from the list of the world’s top 6,000 institutions.
70 | www.xrphealthcare.com
1. GAMBRO HEALTHCARE
World Ranking -598
Country: Swaziland

Gambro Healthcare Swaziland, recently acquired by Baxter International Inc., is dedicated to advancing therapeutic options for dialysis and intensive care patients worldwide. This hospital is the leading healthcare facility in Africa, ranked 598th globally. It provides exceptional care to thousands of patients both within Swaziland and in neighbouring regions.
2. AS SALAM INTERNATIONAL HOSPITAL
World ranking – 1542
Country: Egypt

supported by a 300-bed JCI-accredited tertiary care facility. The team includes 40 certified physicians across various disciplines, four clinical pharmacists, and seven nurses, all working collaboratively to provide patient-centred care. Services include a 24/7 emergency department, outpatient clinics, an early detection and screening unit, a day-care chemotherapy unit, and an inpatient unit with advanced imaging and intensive care facilities. Specialised in cancer care, As-Salam International Hospital offers a wide range of services such as medical and surgical oncology, radiation oncology, pain management, physiotherapy, clinical nutrition, psycho-oncology, interventional radiology, and nuclear medicine. The hospital is committed to patient safety, environmental, facility, and food safety, ensuring a secure and patient-focused environment.

As-Salam International Hospital, part of the Alameda Healthcare group, is one of Egypt’s largest tertiary care hospitals. Established in 1982, it spans 5,200 square meters and houses 300 beds. The hospital adheres to international standards, particularly for high-risk oncology patients, and is equipped with the latest technology and skilled professionals. It has been accredited by the Joint Commission International (JCI) since 2015.
The hospital’s oncology department, founded in 1984, has evolved into a comprehensive center
3. NETCARE GROUP
World ranking: 1546
Country: South Africa
Netcare Group provides innovative and high-quality healthcare solutions in South Africa. Managing a network of hospitals across both South Africa and the United Kingdom, Netcare has garnered a reputation for its exceptional patient care and is widely regarded as a reputable employer. Notably, it holds the distinction of being the largest private training institution for essential medical personnel and healthcare workers in South Africa. With a commitment to offering a comprehensive range of medical services tailored to individual health and care needs. Leveraging advanced digital systems, the group aims to integrate care seamlessly and enhance the overall patient experience across its operations. Netcare’s services extend beyond acute private hospital care to

71 | www.xrphealthcare.com HOSPITALS
include specialised offerings such as radiosurgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and robotic-assisted surgery through Netcare Cancer Care, primary healthcare services through Medicross, emergency medical services via Netcare 911, and mental health services through Akeso.
Furthermore, Netcare is actively engaged in providing innovative solutions to improve access to quality and affordable private healthcare through NetcarePlus, along with renal dialysis services through National Renal Care (NRC). Notably, Netcare is a leading private trainer of emergency medical and nursing personnel in the country, further contributing to the advancement of healthcare services. As a result of its comprehensive offerings and commitment to excellence, Netcare ranks as the third-best hospital in Africa
4. LIFE HEALTHCARE HOSPITAL GROUP
World ranking: 1563
Country: South Africa
November 2016, purchasing Alliance Medical for approximately 10.4 billion rand.(U$ 0.6 Billion)
With its extensive network of hospitals and strategic acquisitions, Life Healthcare has solidified its position as the largest hospital group in South Africa and ranks among the top hospitals in Africa, holding the fourth position.
5. INSTITUT PASTEUR DE MADAGASCAR

Life Healthcare Group, formerly known as Afrox Healthcare, holds the distinction of being the second largest private hospital operator in South Africa, boasting a substantial capacity of 6,500 beds. Additionally, it stands out as the largest blackowned hospital operator in the country. Specialising in acute hospital care, Life Healthcare is a frontrunner

in the private healthcare sector of South Africa, operating hospitals in major metropolitan areas across seven provinces and employing a workforce of 15,890 individuals.
Previously listed on the JSE Securities Exchange, Afrox Healthcare underwent a significant transformation when it was acquired by Business Venture Investments Limited (Bidco), a black empowerment group, in 2005. Under its new ownership, Life Healthcare made a significant acquisition in
World ranking: 2065
Country: Madagascar
The Institut Pasteur de Madagascar, overseen by the Ministry of Health and Family Planning, operates as a recognised charity by the Madagascar government. Since its inception in 1898, it has been a vital member of the Pasteur Network, working towards disease prevention, treatment, and economic development through research, public

health initiatives, and training programs. Governed by an agreement between the Institut Pasteur in Paris and the Malagasy government, it employs around 500 staff, mostly Malagasy.
With 9 research units and 10 laboratories or reference centres, it plays a significant role in addressing infectious diseases such as plague, tuberculosis, malaria, and more. Despite being a private institute, it hosts three branches of the Ministry of Public Health and offers services to the public, including a medical testing laboratory, a food hygiene and environmental laboratory, and an international vaccination centre.
The Institut Pasteur de Madagascar actively engages in training activities, collaborating with universities and offering research internships. This commitment to healthcare and research excellence has established it as a key player in public health in Madagascar. This state-of-the-art hospital provides
72 | www.xrphealthcare.com
HOSPITALS
quality medical services at affordable costs, making it the fifth-best hospital in Africa.
6. NEUROPSYCHIATRIC HOSPITAL ARO ABEOKUTA
World ranking: 2091
Country: Nigeria
The Neuropsychiatric Hospital Aro, Abeokuta, is a Federal Institution in Nigeria with a rich historical legacy dating back to its establishment as the country’s first purpose-built psychiatric hospital in 1944. With a capacity of 735 beds, it is renowned for its innovative Aro Village System of mental healthcare. The hospital operates with a tripartite mandate: clinical service delivery, training of mental health professionals, and research, guided by a vision to become a national centre of excellence in mental health.

It has consistently ranked as the top hospital in Nigeria by the International Webometric Ranking of World Hospitals since 2013. Additionally, it has implemented a ground-breaking program to integrate mental healthcare into primary healthcare across all 20 Local Government Areas of Ogun State. The hospital has also worked to reduce stigma by opening up its services to the community, including establishing a General Medical Practice and Antenatal Care Clinic. It has participated in global initiatives like the World Health Organisation’s field trial of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11) Diagnostic Manual, showcasing its commitment to service delivery, training, and research in mental health. Established in 1944, the hospital continues to
evolve and innovate in its mission to provide quality mental healthcare services.
7. GANZOURI SPECIALISED HOSPITAL
World ranking: 2244
Egypt
Ganzouri Specialised Hospital (GSH), a private general hospital founded by Dr Mostafa El-Ganzouri in 1971, has been serving the Cairo community for nearly 50 years. Situated in the heart of Cairo, GSH boasts 8 fully equipped operating rooms, a 180-bed facility, a 13-bed Neonatal & Pediatric ICU, 30 highly equipped ICUs, 7 NICU beds, and 85 ward beds. With a team of over 145 doctors and consultants across various specialities and sub-specialities,

GSH prioritises customer-oriented care and invests in human resource development through a specialised training centre.
Emphasising specific sub-specialities, GSH provides a comprehensive range of services to a diverse patient base, including over 200 dedicated corporate customers such as petroleum companies, banks, and national organisations. The hospital serves patients not only from Cairo but also from across the Arab world and African countries. Recognised as one of the top ten hospitals in the Arab world and the seventh in North Africa, GSH continually strives to deliver exceptional healthcare services to its community and beyond.
8. DIANI BEACH HOSPITAL KENYA
World ranking: 2499
Country: Kenya
Diani Beach Hospital, a premier private healthcare facility established in 1997 by Dr. K. S. Rekhi, is located on the picturesque south coast of Kenya, near the Leisure Lodge Golf Course. It is recognised as the
73 | www.xrphealthcare.com
HOSPITALS
most skilled health facility in Kenya and one of the best in Africa, known for its high-quality medical care and efficient staff. The hospital initially featured

two private rooms, a laboratory, a pharmacy, and a radiology department. It later expanded to include six more private rooms, as well as male and female general wards.
9. CENTRE HOSPITALIER MOHAMMED VI MARRAKECH
World ranking: 3133
Country: Morocco
Established in 2001, Mohammed VI University Hospital is dedicated to providing tertiary-level care, offering specialised medical and surgical services for both emergency and scheduled activities. Collaborating with the Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy and the Institute for Training in Health Careers, the hospital contributes to clinical

university education and postgraduate medical and pharmaceutical training, as well as practical nursing staff training. Additionally, Mohammed VI University Hospital conducts scientific research following public policies, collaborating with research establishments and providing expertise in biomedical and technical forensic fields. As a leader in healthcare innovation, the hospital serves as a reference for clinical research, while also participating in public health initiatives, including
health promotion, prevention, and health security actions. Moreover, the hospital prioritises patient safety through education and guarantees, and actively participates in organising and regulating pre-hospital and hospital emergencies.
10. CHILDREN’S HOSPITAL TRUST
World ranking: 3665
Country: South Africa
Established in 1994, the Children’s Hospital Trust is a non-profit organisation dedicated to raising funds for the Red Cross War Memorial Children’s Hospital in Cape Town, South Africa—the largest dedicated children’s hospital in sub-Saharan Africa. Over the years, the Trust has invested over R1 billion (US$ 52.86 million) to improve infrastructure, train specialists, and support child healthcare projects.
Working in partnership with various organisations, including the Western Cape Department of Health and the UCT Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, the Trust focuses on improving public health infrastructure and training specialist paediatric health workers. 100% of donations received by the Trust go directly to the hospital, prioritising paediatric healthcare needs without any administration costs.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the Trust secured funding to provide support to vulnerable families and assist the hospital’s COVID-19 response plan. Donations play a crucial role in fulfilling the Trust’s mission of advancing paediatric care and saving children’s lives across Africa. The hospital serves approximately 250,000 patients annually, with a significant portion coming from impoverished and marginalised communities, including a third who are younger than a year old.

74 | www.xrphealthcare.com
HOSPITALS

THE PLACE OF
AI-POWERED HEALTH
ASSISTANTS:

INNOVATING SOLUTIONS TO CHALLENGES IN MODERN HEALTHCARE
BY BENJAMIN OPUKO
Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into healthcare is no longer just a futuristic concept—it’s a revolutionary reality transforming patient care today. Advancements in AI technology are reshaping the healthcare landscape with unprecedented diagnostic accuracy and seamless administrative efficiency. According to Precedence Research, the global artificial intelligence (AI) market in healthcare was estimated at US$15.1 billion in 2022 and is expected to surpass US$187.95 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 37% during the forecast period from 2022 to 2030.
The growing adoption of digital technologies in the healthcare sector, driven by the need to reduce healthcare costs and enhance patient care, significantly boosts the healthcare market’s global artificial intelligence (AI) market. The increasing
prevalence of chronic diseases and the ageing population are expanding the patient pool in hospitals, leading to a substantial volume of health data that requires effective storage and management. This situation underscores the rising demand for personalised medicines and the necessity of maintaining digital health records, fuelling AI in the healthcare market.
Innovative technologies such as AI and machine learning are being integrated into healthcare systems, enabling health professionals to identify diseases early and improve patient care. Data analytics, deep learning technology, natural language processing (NLP), predictive analytics, and content analytics are aiding healthcare professionals in early diagnosis and enhanced care services. AI health assistants are game-changers for both pa-
75 | www.xrphealthcare.com
CONSUMER HEALTH

tients and healthcare professionals. These technologies create a more dynamic and responsive healthcare system by automating routine tasks and reducing the burden on providers. Professionals can now focus on complex patient care, feeling less overwhelmed and more capable of addressing patient needs. This infusion of AI into healthcare elevates the patient experience and revitalises the medical profession.
THE RISE OF CHATBOTS IN HEALTHCARE
Chatbots are one of the most prominent examples of AI health assistants, offering a range of advantages that significantly enhance the patient care experience. Unlike traditional healthcare providers, chatbots are available around the clock, providing patients with immediate responses to their queries. This 24/7 availability ensures that patients can access healthcare support at any time, whether it’s the middle of the night or during a holiday, reassuring them about the continuous support they can receive.
In addition to their constant availability, chatbots are adept at checking symptoms. By assessing symptoms through user input, they can provide initial guidance on whether a doctor’s visit is necessary. This function is particularly valuable as it can aid in the early detection of conditions, helping patients
identify potential health issues before they become severe. It improves patient outcomes and reduces unnecessary hospital visits, alleviating the burden on healthcare facilities.
A prime example is Babylon Health’s chatbot, which conducts symptom assessments and offers medical advice based on a vast database of medical knowledge. It is popular in the United Kingdom for its ability to triage patients effectively. Another example is the Mayo Clinic’s Chatbot, developed to provide COVID-19 guidance, helping users assess their symptoms and find testing locations.
The AI chatbots are also making significant strides in mental health support. Platforms like Woebot and Wysa offer mental health assistance by providing cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) techniques, mood tracking, and coping strategies. These tools offer a confidential and accessible way for individuals to manage their mental health, providing support that might otherwise be inaccessible due to stigma or lack of resources. Woebot, for instance, engages users in therapeutic conversations and helps them develop coping mechanisms for anxiety and depression. Similarly, Wysa offers a safe space for users to discuss their feelings
76 | www.xrphealthcare.com CONSUMER HEALTH
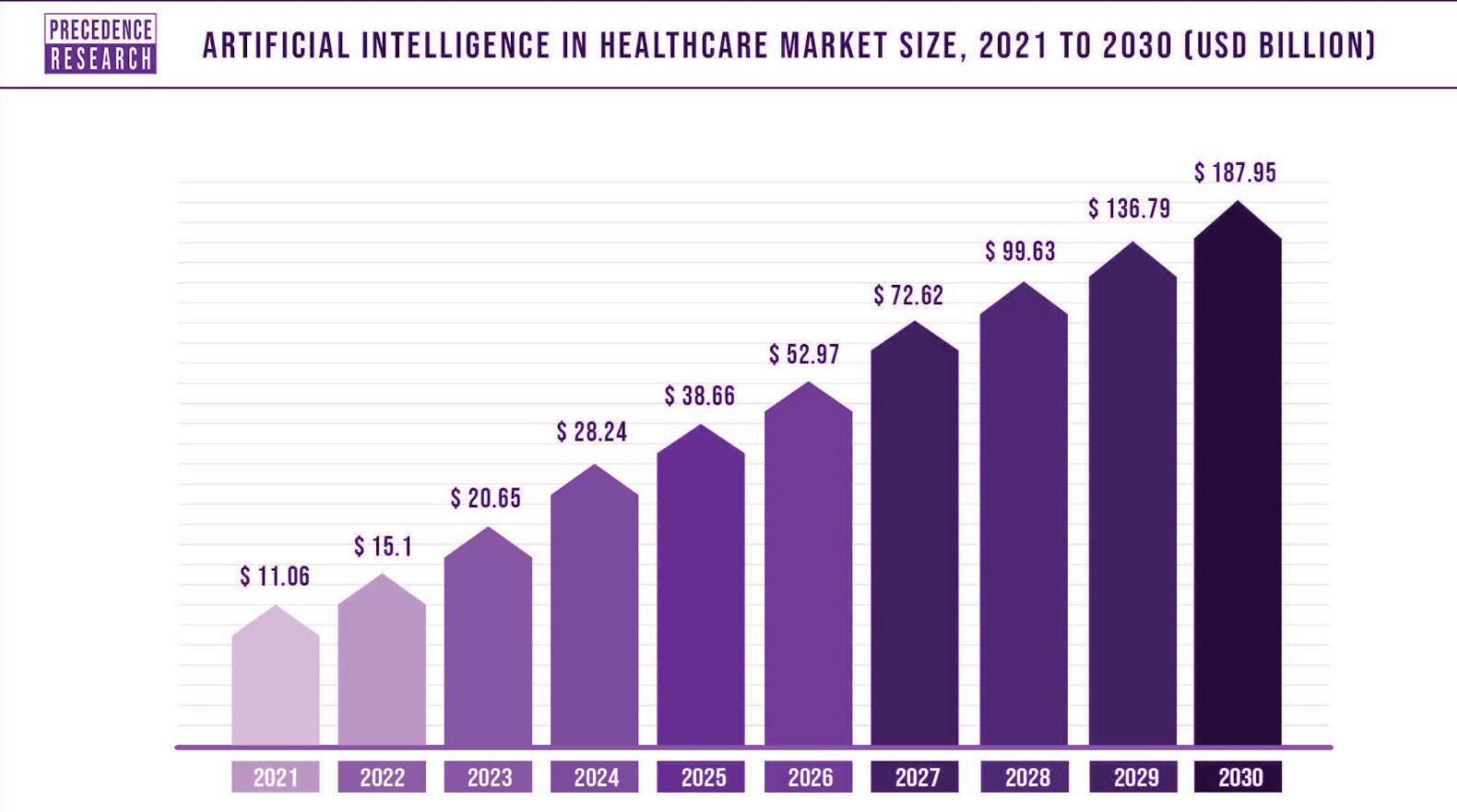
and access mindfulness exercises.
Furthermore, chatbots excel in medication management, a crucial aspect of patient care often overlooked. These tools can remind patients to take their medications at the correct times, significantly reducing the risk of missed doses. This function is particularly beneficial for individuals with chronic conditions who must adhere to complex medication schedules. By ensuring patients take their medications as prescribed, chatbots help improve adherence to treatment plans, leading to better health outcomes. Medisafe’s chatbot is a notable example, offering personalised medication reminders and health tracking to ensure patients stay on top of their medication regimens.
VIRTUAL HEALTH ASSISTANTS
signs, and provide insights into health data collected from wearable devices.
For instance, when integrated with the Apple Health app, Apple’s Siri can help users monitor their daily activity levels, track workouts, and even measure vital signs like heart rate and blood pressure using data from Apple Watch. Similarly, Google Assistant can work with various fitness trackers to provide detailed reports on sleep patterns, physical activity, and other health metrics. By compiling and analysing this data, virtual assistants offer users valuable insights into their health trends, encouraging healthier lifestyle choices and more informed decision-making.

Beyond chatbots, virtual health assistants like Apple’s Siri, Amazon’s Alexa, and Google Assistant increasingly integrate with health apps and services, enhancing functionality and providing a more comprehensive healthcare experience. These virtual assistants can track physical activity, monitor vital
In addition to health tracking, virtual health assistants are adept at managing administrative tasks such as appointment scheduling. They can help users schedule appointments, manage calendars, and even interface with electronic health records (EHRs) to ensure seamless care coordination. For example, Amazon’s Alexa allows patients to book doctor’s appointments, remind users of upcoming medical appointments, and even sync with health-
77 | www.xrphealthcare.com CONSUMER HEALTH
care providers’ systems to provide a more integrated healthcare experience. This capability simplifies managing healthcare appointments and helps ensure patients do not miss important check-ups or treatments, improving adherence to healthcare plans.
ceive medical guidance without needing physical travel.
In August 2023, Bayer and Ada Health partnered to empower individuals to take charge of their health through advanced digital tools. Users can directly access personalised health information and recommendations by integrating Ada’s AI-based health assessment platform with Bayer’s product websites such as Aspirin, Aleve, Midol, Canesten, and Iberogast. This collaboration aims to shift healthcare from reactive to proactive, providing users with credible, science-based insights to manage their health effectively.

Health education is another critical function of virtual health assistants. These assistants provide personalised health education, answering questions about diseases, treatments, and preventive care based on reliable sources. For instance, Google Assistant can respond to queries about common health conditions, symptoms, and treatments by drawing on information from reputable health organisations like the Mayo Clinic and WebMD. Similarly, Siri can provide users with health tips, explain medical terms, and offer guidance on managing various health issues. By delivering accurate and personalised health information, virtual assistants empower users to take charge of their health and make informed decisions, underlining their role in managing their health.
ENHANCING ACCESS AND EFFICIENCY
One of the foremost advantages of AI-powered health assistants is their ability to provide healthcare information and support anytime and anywhere, effectively breaking down geographical and temporal barriers to access. Accessing healthcare services can be challenging for underserved populations in remote or rural areas and individuals with limited mobility or transportation options. The AI health assistants bridge this gap by offering remote consultations, symptom assessments, and health advice via mobile devices or computers. For example, in regions where healthcare facilities are scarce, AI chatbots like Ada Health and Babylon Health provide virtual consultations, enabling individuals to re-
Ada Health’s platform, which has conducted over 25 million personal health assessments since 2016, utilises an advanced algorithm to generate tailored care options based on individual symptoms and risk factors. Bayer’s chief scientific officer, David Evendon-Challis, and Chief Marketing and Digital Officer, Patricia Corsi, emphasise that this partnership is about making reliable health information accessible and encouraging individuals to take more ownership of their health. This integration enhances health outcomes and builds trust in digital health solutions worldwide. Such partnerships are a testament to these AI tools’ potential to reshape healthcare globally.
Additionally, AI-powered health assistants integrated into hospital websites and mobile apps handle common queries, provide service information, and assist with pre-registration, reducing staff workload and improving patient experience. Moreover, these AI tools optimise resource allocation by analysing patient data to predict service demand, resulting in shorter wait times, reduced administrative burdens, and improved patient outcomes.
CHALLENGES AND FUTURE DIRECTIONS
While AI-powered health assistants offer promising benefits, they also encounter significant challenges that need addressing to ensure their successful integration into healthcare systems. For example, health data security and privacy are paramount when implementing AI-powered health assistants. Developers must adhere to strict regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Account-
78 | www.xrphealthcare.com
These systems must undergo rigorous testing and validation to provide accurate, evidence-based health information. Developers must train AI algorithms on high-quality, diverse datasets and continuously update them with new medical knowledge and best practices. Additionally, developers should implement error detection and correction mechanisms to minimise the risk of misdiagnosis or incorrect advice. By prioritising accuracy and reliability, developers can instil confidence in AI-powered health assistants and ensure they deliver trustworthy and clinically sound guidance to users.
Building and maintaining user trust is essential for the widespread adoption and acceptance of AI-powered health assistants. Transparent communication about how AI works, its limitations, and the measures taken to protect user privacy is crucial for building user trust. Developers should provide clear information about the capabilities and limitations of AI systems and the roles and responsibilities of healthcare providers in the decision-making process. Moreover, soliciting user feedback and incorporating their input into the development process can help ensure that AI-powered health assistants meet the needs and expectations of their intended users. By prioritising transparency and user engagement, developers can foster trust and confidence in AI-powered health assistants, facilitating successful integration into healthcare practice.

ability Act (HIPAA) to safeguard sensitive user information. It includes implementing robust encryption protocols, limiting access to data, and regularly auditing systems for compliance. By prioritising data privacy, developers can foster trust among users and mitigate the risk of unauthorised access or data breaches.
The accuracy and reliability of AI systems are also critical for ensuring patient safety and well-being.
Despite these challenges, the future of AI-powered health assistants is bright, with ongoing advancements in AI technology promising even more sophisticated and effective tools. As these technologies continue to evolve, they hold the potential to fundamentally transform healthcare, making it more accessible, efficient, and personalised than ever before. By addressing the challenges of data privacy, accuracy, reliability, and user trust, developers can unlock the full potential of AI-powered health assistants and revolutionise the delivery of healthcare services for patients worldwide.
79 | www.xrphealthcare.com
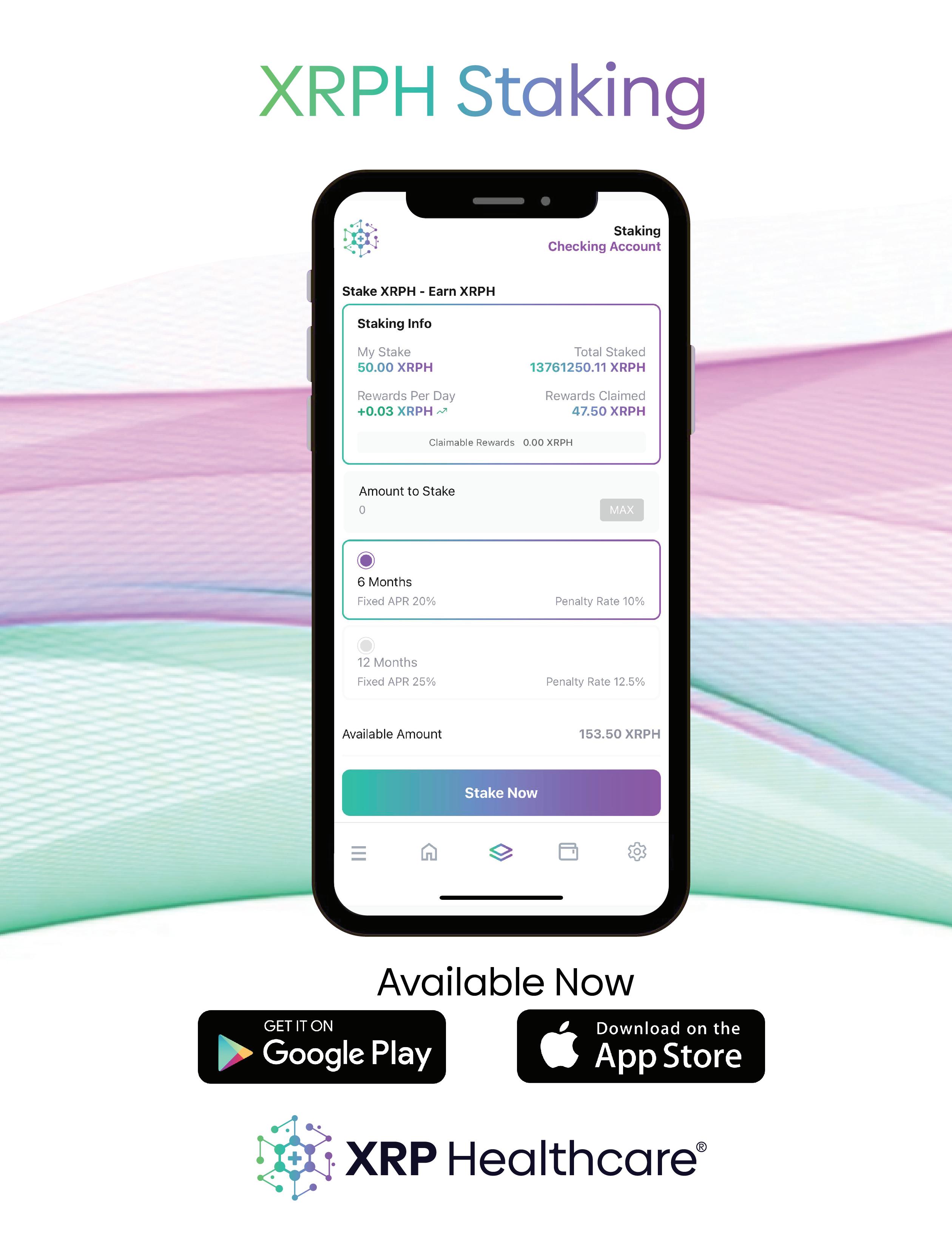
Medical devices
Advances in implantable medical devices enhancepatient outcomes and quality of life
BY BENJAMIN OPUKO
Implantable medical devices are small devices or structures that are placed inside the body to support or improve bodily functions. These devices are used to help treat a variety of medical conditions and can range from pacemakers, which help regulate heartbeats, to artificial joints that replace damaged parts of the body.
The general purpose of implantable medical devices in modern medicine is to either support the body in doing what it should naturally do or to replace a part of the body that no longer functions properly. For example, a pacemaker helps a heartbeat regularly, while a hip implant can replace a damaged hip joint to restore mobility.
The significance of these devices in healthcare cannot be overstated. They play a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and enhancing
quality of life. By providing necessary support to vital bodily functions, these devices help patients live longer, healthier, and more active lives. For instance, a person with a pacemaker can lead a normal life without worrying about irregular heartbeats, and someone with a joint implant can move around freely without pain.
81 | www.xrphealthcare.com
MEDICAL DEVICES
HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT
Early innovations
The journey of implantable medical devices began with some groundbreaking early innovations. One of the first significant examples is the pacemaker. In 1958, the first implantable pacemaker was successfully used to regulate the heartbeat of a patient.
This device was a remarkable breakthrough because it provided a solution for people with heart rhythm problems, allowing them to live longer and healthier lives.
Another early example is the hip replacement. The first successful hip replacement surgery was performed in the 1960s. This procedure involved replacing a damaged hip joint with an artificial one, significantly reducing pain and improving mobility for patients with severe arthritis or hip injuries. These early devices laid the foundation for the wide range of implantable medical devices we have today.
Evolution over time
example, modern pacemakers can now be checked and tweaked by doctors using a wireless connection, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits.
TYPES OF IMPLANTABLE MEDICAL DEVICES
Cardiovascular devices
Cardiovascular devices are some of the most common and life-saving implants. Pacemakers, for example, are small devices placed in the chest to help control abnormal heart rhythms. They send electrical pulses to the heart to ensure it beats regularly. Defibrillators are another type of cardiovascular implant. These devices monitor the heart’s rhythm and can deliver a shock if they detect a life-threatening irregular heartbeat, preventing sudden cardiac arrest. Stents are small tubes inserted into blood vessels to keep them open, ensuring proper blood flow, especially after a heart attack or in cases of severe artery blockages.
Orthopaedic implants


Since those early days, implantable medical devices have evolved dramatically, thanks to major milestones and technological advancements. In the 1970s, the development of more sophisticated materials, such as titanium and special plastics, made implants more durable and biocompatible, meaning they were better accepted by the human body.
The 1980s and 1990s saw the introduction of more advanced electronic implants, such as cochlear implants, which help restore hearing to people with severe hearing loss. These devices convert sound into electrical signals that directly stimulate the auditory nerve, enabling users to hear again.
In the 2000s, the miniaturisation of electronic components allowed for the creation of smaller, more efficient devices. This period also saw the rise of implantable defibrillators, which can detect and correct life-threatening heart rhythms automatically.
More recently, advances in wireless technology have enabled the development of smart implants that can be monitored and adjusted remotely. For
Orthopaedic implants help people regain mobility and reduce pain in their joints and bones. Joint replacements, such as hip and knee replacements, involve replacing damaged joints with artificial ones made of metal, plastic, or ceramic. These implants can last for many years and significantly improve the quality of life for patients with severe arthritis or injuries. Spinal implants are used to stabilise the spine, often in cases of spinal fractures or scoliosis. Bone grafts, either synthetic or harvested from the patient’s body, are used to repair or replace damaged bones and support new bone growth.
Neurological devices
Neurological devices are designed to help patients with conditions affecting the brain and nervous system. Deep brain stimulators, for instance, are implanted in the brain to help manage symptoms of Parkinson’s disease and other movement disorders. They send electrical impulses to specific parts of the brain, improving muscle control and reducing tremors. Cochlear implants are another type of neurological device. These implants bypass damaged parts of the ear and directly stimulate the auditory nerve, allowing people with severe hearing loss to hear. Spinal cord stimulators are used to manage chronic pain by sending electrical
82 | www.xrphealthcare.com
MEDICAL DEVICES
signals to the spinal cord, blocking pain signals from reaching the brain.
Drug delivery systems
Drug delivery systems are designed to provide long-term medication administration. Implantable pumps can deliver precise doses of medication directly to specific parts of the body. For example, insulin pumps are used to manage diabetes by continuously delivering insulin to the body, helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Reservoirs are implanted under the skin and can store medication that is released slowly over time, reducing the need for frequent injections and ensuring consistent drug delivery.
Other specialised implants

In addition to the more common types of implants, there are many specialised devices designed for specific medical conditions. Insulin pumps, as mentioned earlier, are crucial for diabetes management, allowing patients to maintain better control over their blood sugar levels. Emerging technologies, such as bioelectronic medicine, are opening new frontiers in treatment. These devices use electrical signals to modulate nerve activity, potentially treating a range of conditions from chronic pain to inflammation and even some psychiatric disorders.
TECHNOLOGICAL ADVANCEMENTS
Materials Science
Advancements in materials science have greatly improved the safety and longevity of implantable medical devices. Biocompatible materials, such as titanium and certain plastics, are now commonly used to ensure that implants are well-tolerated by the body and do not cause adverse reactions. For example, modern hip replacements use highquality ceramic and plastic components that are durable and reduce the risk of wear and tear. These advancements mean that implants can last longer and perform better, reducing the need for additional surgeries and improving patient outcomes.
Miniaturisation
The miniaturisation of medical devices has made them less invasive and more effective. Smaller, more compact devices can be implanted with minimal disruption to the body, leading to quicker
83 | www.xrphealthcare.com
MEDICAL DEVICES
recovery times and less discomfort for patients. For instance, modern pacemakers are much smaller than their earlier counterparts, making the implantation process simpler and reducing the risk of complications. Smaller devices also mean that they can be implanted in more delicate parts of the body, expanding their potential uses.
Wireless technology
Wireless technology has revolutionised the way implantable devices are monitored and managed. Many modern implants, such as pacemakers and defibrillators, now come with wireless capabilities that allow healthcare providers to remotely monitor a patient’s condition. This means that doctors can check on the device’s performance and the patient’s health without requiring frequent in-person visits. For example, some pacemakers can send data to a secure online portal that doctors can access, ensuring that any issues are detected and addressed promptly.
Battery life and energy harvesting
for faster production times and more accessible options for patients requiring unique or complex implants.
Clinical applications and benefits
Implantable medical devices have made significant strides in improving patient outcomes across various medical conditions. For example, pacemakers have been instrumental in improving survival rates for patients with heart arrhythmias. According to studies, pacemakers can reduce the risk of death from heart conditions by nearly 34%, highlighting their critical role in modern cardiology. Similarly, defibrillators, which can correct life-threatening heart rhythms, have been shown to decrease mortality rates by up to 40% in patients at high risk of sudden cardiac death.


Improvements in battery technology have extended the life of implantable devices, making them more reliable and convenient. Newer batteries last longer, which means that patients need fewer replacements and can rely on their devices for longer periods. Additionally, researchers are exploring methods of energy harvesting to power these devices. For example, some experimental implants can generate power from the body’s natural movements or heat, potentially eliminating the need for batteries altogether. This would make implants even more sustainable and less dependent on periodic maintenance.
3D printing and customisation
The 3D printing technology has had a significant impact on the creation of patient-specific implants. With 3D printing, custom implants can be designed to perfectly fit the unique anatomy of an individual patient. This ensures better functionality and comfort, as the implants are tailored to the patient’s specific needs. For example, in orthopaedic surgery, 3D-printed joint replacements can be created to match the exact contours of a patient’s bone, leading to better integration and a more natural feel. Customisation through 3D printing also allows
Orthopaedic implants, such as hip and knee replacements, have dramatically improved mobility and overall health for millions of patients. These devices allow individuals with severe joint pain and mobility issues to regain movement and function, significantly enhancing their quality of life. Statistics
show that over 90% of patients who undergo hip replacement surgery experience significant pain relief and improved joint function, enabling them to return to their daily activities with greater ease and comfort.
Neurological devices, including deep brain stimulators and cochlear implants, have transformed the lives of patients with conditions such as Parkinson’s disease and profound hearing loss. Deep brain stimulators can reduce the symptoms of Parkinson’s by up to 70%, allowing patients to
84 | www.xrphealthcare.com
MEDICAL DEVICES
regain control over their movements and lead more active lives. Cochlear implants have enabled many individuals with severe hearing loss to hear again, greatly improving their communication abilities and social interactions.
Implantable drug delivery systems, such as insulin pumps for diabetes management, provide precise and consistent medication administration, leading to better disease control and fewer complications. Insulin pumps have been shown to improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of diabetesrelated complications by maintaining more stable glucose levels compared to traditional injection methods.
The quality of life enhancements brought about by these devices are profound. Patients with cardiovascular implants can engage in physical activities with reduced fear of heart-related incidents. Those with orthopaedic implants can enjoy pain-free movement and participate in activities they once thought impossible. Individuals with neurological implants can reclaim their independence, and those using drug delivery systems can manage chronic conditions more effectively, reducing the burden of daily medication routines.
Challenges and considerations

While implantable medical devices offer significant benefits, they also come with challenges that need careful consideration. One of the primary concerns is biocompatibility and the risk of rejection. Even with advancements in materials science, ensuring that implants are well-tolerated by the body remains a significant challenge. When an implant is not biocompatible, the body’s immune system may react negatively, causing inflammation or even rejection of the device. For instance, some patients may develop allergies or sensitivities to the materials used in implants, leading to complications. To address this, researchers continually work on developing new materials and coatings that are more biocompatible and less likely to provoke an immune response.
Surgical risks and complications are another critical consideration. Any surgical procedure carries inherent risks, and implant surgeries

85 | www.xrphealthcare.com
MEDICAL DEVICES
are no exception. Complications can include infections, bleeding, and adverse reactions to anaesthesia. For example, in orthopaedic surgeries like hip replacements, there is a risk of blood clots forming, which can be dangerous if not managed properly. Surgeons and medical teams take several measures to mitigate these risks, such as using sterile techniques to prevent infections and closely monitoring patients during and after surgery to manage any complications that arise. Additionally, advancements in surgical techniques and technology, such as minimally invasive procedures, have helped reduce these risks, leading to quicker recovery times and fewer complications.
Another challenge is the long-term durability and functionality of implants. Over time, wear and tear can affect the performance of the device, sometimes necessitating additional surgeries to repair or replace the implant. For instance, while modern hip replacements are designed to last many years, they may eventually wear out and require revision surgery. Continuous monitoring and maintenance are essential to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of these devices.
improving patient outcomes. Biodegradable devices represent another innovative direction. These implants are designed to dissolve safely in the body after they have served their purpose, eliminating the need for additional surgeries to remove them. This technology could be particularly beneficial for temporary implants used in healing or supporting tissues during recovery.
Advanced bioelectronics also paves the way for more sophisticated implants that interact seamlessly with the body’s systems. These devices can stimulate nerves, muscles, or organs to restore function or alleviate symptoms of chronic conditions. For example, bioelectronic medicine is exploring ways to treat diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease by targeting the body’s nervous system.

Moreover, there are economic considerations to take into account. The cost of implantable devices and the associated surgical procedures can be high, making them inaccessible to some patients. Efforts are being made to reduce costs through technological advancements and more efficient production methods. For example, 3D printing technology has the potential to lower the cost of custom implants by reducing the time and materials needed for production.
Future directions
Emerging technologies are set to revolutionise the field of implantable medical devices. One exciting area of research is smart implants, which can monitor and adjust their functions in real time. These devices use advanced sensors and wireless technology to provide continuous feedback to healthcare providers and patients. For example, smart cardiac implants can detect arrhythmias and automatically administer the necessary therapy,
Personalised medicine is becoming increasingly important in the field of implantable devices. The trend is moving towards creating implants tailored to the individual needs and genetic profiles of patients. This approach ensures that devices are more effective and less likely to cause adverse reactions. For instance, 3D printing technology allows for the creation of custom-fit joint replacements that match the unique anatomy of each patient, leading
86 | www.xrphealthcare.com MEDICAL DEVICES

to better outcomes and greater comfort.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are also being integrated into implantable devices to enhance their functionality and monitoring capabilities. Artificial intelligence can analyse data from implants to predict potential issues before they become serious problems. For example, AI algorithms can detect patterns in heart rate data from pacemakers, alerting doctors to early signs of heart disease. Machine learning can also help personalise treatment plans based on the data collected from implants, providing more targeted and effective care.

“
Improvements in battery technology have extended the life of implantable devices, making them more reliable and convenient. Newer batteries last longer, which means that patients need fewer replacements and can rely on their devices for longer periods.
87 | www.xrphealthcare.com
MEDICAL DEVICES
DIGITAL HEALTH
How digital health platforms and ecosystems drive access and outcomes
 BY BENJAMIN OPUKO
BY BENJAMIN OPUKO

In an era of rapid technological advancement, virtually every facet of our lives is undergoing transformation, and healthcare is no exception. Digital health platforms stand at the forefront of this revolution, offering a gateway to a more efficient, accessible, and patient-centred healthcare experience.
Digital health platforms encompass eclectic technological tools and solutions designed to enhance various aspects of healthcare delivery, from managing patient records to facilitating remote consultations. At their core, these platforms leverage the power of technology to improve patient care, streamline administrative processes, and ultimately, enhance healthcare outcomes.
Imagine a world where medical records are easily accessible at the touch of a button, where patients can connect with their healthcare providers from the comfort of their homes, and where datadriven insights help clinicians make more informed decisions. This is the promise of digital health platforms.
These platforms enable seamless communication and collaboration among healthcare providers by digitising and centralising medical information, leading to more coordinated and personalised care. Moreover, they empower patients to take a more active role in managing their health, fostering greater engagement and adherence to treatment plans.
88 | www.xrphealthcare.com
MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY
From telemedicine platforms that enable virtual consultations to electronic health records (EHR) systems that digitise patient information, digital health platforms are transforming the way healthcare is delivered and experienced.
Types of Digital Health Platforms
Among the diverse array of digital health platforms, telemedicine shines as a symbol of accessibility and convenience. Telemedicine platforms facilitate remote consultations between patients and healthcare providers, transcending geographical barriers and ensuring that healthcare remains within reach, regardless of location. For instance, platforms like DoctorOnCall in Malaysia, Practo in India, and Kry in Sweden offer patients the opportunity to consult with healthcare professionals from the comfort of their homes.
Complementing telemedicine, Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems play a pivotal role in digitising and centralising patient information. Platforms like Epic and Cerner digitise medical records, enabling seamless access and updates across different healthcare settings. This consolidation fosters better coordination of care and reduces the likelihood of errors, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes. Examples of EHR systems implemented in Europe include Lorenzo in the UK and MyClinic in Germany.

across systems, promoting care coordination and efficiency. Real-time data access empowers healthcare providers with up-to-date information, facilitating timely decision-making and interventions. Personalised care delivery, supported by data analytics and decision support tools, tailors treatment plans to individual patient needs, improving effectiveness and efficiency. Moreover, improved patient engagement, facilitated by access to health information and communication tools, empowers patients to take an active role in their care, leading to better adherence and outcomes.
Navigating challenges in implementing and adopting digital health platforms
Remote Patient Monitoring solutions represent another facet of digital health platforms, providing continuous monitoring of patients’ health outside traditional clinical settings. Through wearable sensors and mobile apps, platforms like Philips’ HealthSuite and Biofourmis’ Biovitals® enable healthcare providers to monitor vital signs and symptoms in real time. This proactive approach allows for early intervention, particularly beneficial for patients managing chronic conditions such as heart failure or diabetes. In Africa, examples such as Babyl in Rwanda and the Vula Mobile app in South Africa are making strides in remote patient monitoring.
At the heart of digital health platforms lie key features and benefits that drive their effectiveness. Interoperability ensures seamless data exchange
While digital health platforms offer immense potential to transform healthcare, their implementation and adoption are not without challenges. One of the foremost concerns is data privacy and security. As digital health platforms collect and store sensitive patient information, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of this data is paramount. Instances of data breaches and cyberattacks pose significant risks to patient privacy and trust in these platforms.
Regulatory compliance is another hurdle that healthcare organisations must navigate when implementing digital health platforms. Regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe impose stringent requirements for the protection and management of patient data. Ensuring compliance with these regulations adds complexity and cost to the implementation process.
Interoperability issues present further challenges,
89 | www.xrphealthcare.com
MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY
as healthcare systems often operate with disparate platforms that struggle to communicate and exchange data seamlessly. This lack of interoperability hampers care coordination and limits the potential benefits of digital health platforms. Healthcare providers also face resistance to adopting new technologies, whether due to concerns about workflow disruptions, lack of training, or scepticism about the effectiveness of digital solutions.
Moreover,there are disparities in accesstotechnology, particularly in underserved communities and developing countries. Limited internet connectivity, lack of infrastructure, and socioeconomic factors can impede access to digital health platforms, exacerbating healthcare inequalities. Despite these challenges, efforts are underway to address them and promote the widespread adoption of digital health platforms.
The vital role of integration and interoperability in digital health platforms
Integration and interoperability among different digital health platforms are essential for realising their full potential. Seamless communication and data exchange between systems enable
healthcare providers to access comprehensive patient information and deliver coordinated care. Initiatives such as Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) and Health Level Seven International (HL7) are driving standards and protocols to promote interoperability. In particular, FHIR offers a modern, web-based approach to exchanging healthcare information, making it easier for different systems to connect and share data. The HL7 standards provide a framework for the exchange, integration, sharing, and retrieval of electronic health information.
By adhering to these standards and promoting interoperability, digital health platforms can overcome silos and facilitate collaboration among healthcare providers. This interoperability enables smoother transitions of care, reduces duplication of tests and procedures, and enhances the overall efficiency and quality of healthcare delivery.
Examples of successful integration initiatives include regional health information exchanges (HIEs) that facilitate the sharing of electronic health records among healthcare organisations. For instance, the European Union’s Connecting Europe Facility (CEF) program supports projects aimed at promoting interoperability and cross-border exchange of

MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY
healthcare data among member states. Role of artificial intelligence and machine learning Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionising healthcare by enhancing the capabilities of digital health platforms. These technologies enable platforms to analyse vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and derive actionable insights to improve decision-making, automate tasks, and personalise patient care.
Predictive analytics is one area where AI and ML are making significant strides. By analysing historical patient data, these algorithms can forecast future health outcomes and identify patients at risk of developing certain conditions. For example, AIpowered predictive models can help healthcare providers anticipate complications in patients with chronic diseases, enabling early interventions to prevent adverse events.
Natural language processing (NLP) is another application of AI that facilitates the extraction and analysis of unstructured data from clinical notes, medical records, and other textual sources. The NLP algorithms can parse and interpret human language, enabling digital health platforms to extract relevant information, generate summaries, and assist in clinical decision-making. For instance, NLP-powered chatbots can interact with patients to gather information about their symptoms,
provide basic medical advice, and triage them to appropriate care pathways.
Image recognition is yet another area where AI and ML are transforming healthcare. These technologies enable digital health platforms to analyse medical images, such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, to assist radiologists and other healthcare providers in diagnosing conditions and detecting abnormalities. For example, AI algorithms can detect early signs of diabetic retinopathy in retinal images, enabling timely interventions to prevent vision loss.
Patient empowerment and engagement
Digital health platforms play a crucial role in empowering patients to take control of their health and actively participate in their care. Patient portals, mobile health apps, and wearable devices are among the key features that promote selfmonitoring and adherence to treatment plans.


Patient portals provide patients with secure online access to their health information, including lab results, medication lists, and appointment schedules. These portals enable patients to review their medical records, communicate with their healthcare providers, and actively engage in shared decision-making. For example, platforms like MyChart and Epic’s patient portal empower patients to schedule appointments, request prescription refills, and access educational resources from the comfort of their homes.
Mobile health apps offer another avenue for patient engagement, providing tools and resources for selfmanagement and monitoring of health conditions. From medication reminders to symptom trackers, these apps help patients track their progress, adhere to treatment plans, and make informed decisions about their health. For instance, apps like MyFitnessPal and mySugr empower patients with diabetes to monitor their diet, exercise, and blood glucose levels, leading to better self-management and improved outcomes.
Wearable devices, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, are increasingly integrated into digital health platforms to monitor vital signs, track activity levels, and detect changes in health status. These devices provide real-time feedback
MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY
and personalised insights, motivating patients to adopt healthier lifestyles and adhere to treatment plans. For example, wearable devices like Fitbit and Apple Watch monitor heart rate, sleep patterns, and physical activity, empowering users to make informed decisions about their health and wellbeing.
Navigating integration challenges of adopting digital health platforms
Overcoming resistance from healthcare providers and seamlessly integrating digital health platforms into existing workflows are crucial for realising the benefits of these technologies. One key strategy
these technologies effectively through handson workshops, online tutorials, and continuing education opportunities. Additionally, continuous support and feedback mechanisms are vital for addressing challenges and refining digital health platforms over time. Dedicated support teams, help desks, and user forums create avenues for providers to seek assistance, troubleshoot issues, and share best practices.
By prioritising user experience and providing adequate training and support, healthcare organisations can successfully overcome resistance and seamlessly integrate digital health platforms


to facilitate adoption is ensuring user-friendly interfaces. Digital health platforms should boast intuitive designs that align with the workflows and preferences of healthcare providers. Features such as streamlined navigation, clear instructions, and customisable settings enhance usability and encourage adoption.
Comprehensive training programs are another essential aspect. These programs familiarise healthcare providers with the functionalities and benefits of digital health platforms. Providers can gain confidence and competence in using
into their workflows. Regarding regulatory landscape and compliance, digital health platforms must navigate a complex regulatory environment to safeguard patient privacy, ensure data security, and promote safety and effectiveness. Key regulations include the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), which sets standards for protecting and handling patients’ protected health information (PHI). Compliance with HIPAA regulations is essential to safeguard patient privacy and prevent unauthorised access or disclosure of sensitive data.
92 | www.xrphealthcare.com
MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY

Additionally, digital health platforms that qualify as medical devices are subject to FDA regulations to ensure safety and effectiveness. The FDA evaluates these platforms based on their intended use, risk classification, and potential impact on patient health. For instance, mobile health apps and software as a medical device (SaMD) may require FDA clearance or approval before being marketed and used in clinical practice.
Compliance with these regulations significantly impacts the development and deployment of digital health solutions. It influences design considerations, data security measures, and regulatory submissions. Healthcare organisations must navigate these regulations effectively to ensure legal compliance and mitigate regulatory risks.
Future trends and opportunities
Looking ahead, the field of digital health platforms holds immense promise, with several future trends and opportunities on the horizon. One significant trend is the proliferation of remote care models, driven by advancements in telemedicine and remote patient monitoring technologies. Remote care enables healthcare providers to deliver highquality care to patients in the comfort of their homes, reducing the need for in-person visits and improving access to healthcare services. This trend is particularly relevant in light of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has accelerated the adoption of telemedicine and highlighted the importance of remote care models in ensuring continuity of care.
Virtual care delivery is also on the rise, fuelled by innovations in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies. These immersive
technologies have the potential to transform medical education, patient engagement, and surgical training. For example, VR simulations can provide healthcare professionals with realistic training scenarios, allowing them to practice procedures and improve clinical skills in a safe and controlled environment. Similarly, AR applications can enhance patient education and rehabilitation by overlaying digital information onto the real world, making complex medical concepts more accessible and understandable.
Advancements in wearables and sensors are driving another wave of innovation in digital health. Wearable devices, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and biosensors, enable continuous monitoring of vital signs, activity levels, and other health metrics. These devices provide valuable insights into patients’ health status, enabling early detection of health issues and personalised interventions. The global wearable medical devices market is projected to reach billions of dollars in the coming years, driven by increasing consumer demand for health and wellness monitoring devices.
Furthermore, emerging technologies like blockchain hold the potential to revolutionise healthcare by enhancing data security, interoperability, and patient privacy. Blockchain technology enables secure and tamper-proof storage and sharing of healthcare data, facilitating secure data exchange among different stakeholders. For example, blockchain-based platforms can streamline the sharing of electronic health records (EHRs) among healthcare providers while ensuring patient consent and data integrity.

93 | www.xrphealthcare.com
THE LONGEVITY REVOLUTION
Advancements in science towards lifelong health and longevity
BY BENJAMIN OPUKO
As humanity continues to strive for longer, healthier lives, the field of ageing and longevity research stands at the forefront of scientific inquiry. A journey through ageing research begins with a glance back in time, where early scholars pondered the mysteries of ageing. From Aristotle’s musings on the “four humours” to the groundbreaking work of Gerontology pioneers like Elie Metchnikoff and Leonard Hayflick, each era has contributed to humanity’s evolving comprehension of the ageing process. Milestones
such as the discovery of telomeres by Elizabeth Blackburn and Carol Greider have transformed our understanding of cellular ageing, laying the foundation for modern research endeavours. But the story of cellular ageing is far from linear. Recent advances in the field have revealed a complex web of interconnected pathways and molecules that govern the ageing process. Telomere shortening, DNA damage, mitochondrial dysfunction, and epigenetic alterations are just a few of the additional
94 | www.xrphealthcare.com
MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY MEDICAL RESEARCH
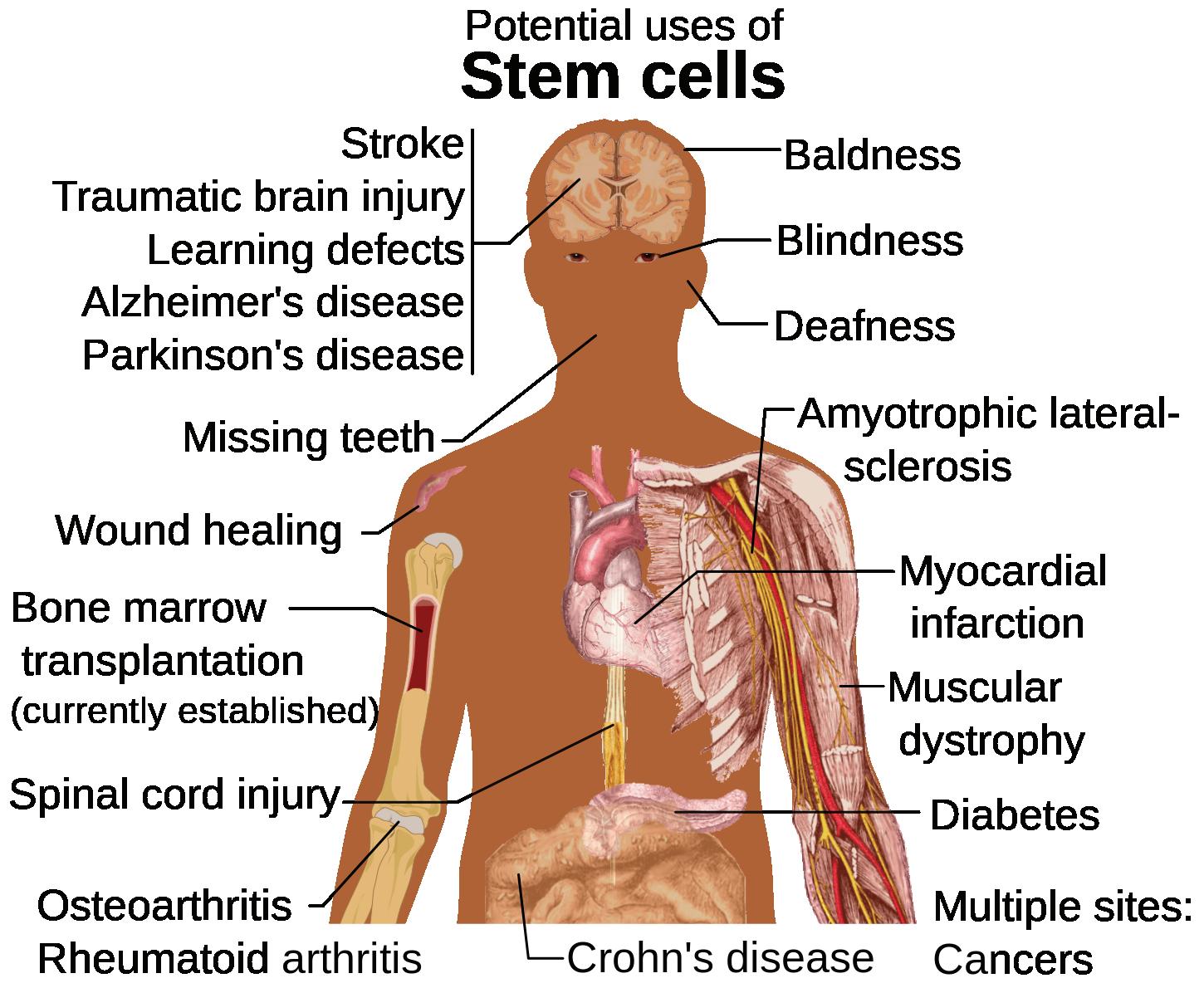
factors under scrutiny, each playing a unique role in shaping cellular senescence and age-related decline.
Biological mechanisms of ageing and emerging therapies
At the cellular level, ageing unfolds through complex biological mechanisms, including cellular senescence, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Understanding these processes is key to developing targeted interventions that combat age-related degeneration and prolong healthspan –the period of life free from age-related diseases and disability. Senolytics, compounds that selectively eliminate senescent cells, show remarkable potential in rejuvenating ageing tissues.
In addition to senolytics, researchers are exploring a diverse array of innovative interventions aimed at promoting healthy ageing and extending lifespan. Calorie restriction mimetics, compounds that mimic the effects of calorie restriction without requiring a drastic reduction in food intake, have garnered attention for their potential to delay ageing and age-related diseases. These compounds work by activating cellular pathways associated with longevity and stress resistance, offering a promising approach to enhancing longevity and resilience in ageing populations.
Furthermore, regenerative medicine approaches hold tremendous potential for rejuvenating ageing tissues and organs, restoring their structure and function. Stem cell therapies, which harness the regenerative capacity of stem cells to repair damaged tissues and promote tissue regeneration, offer hope for treating age-related degenerative conditions such as osteoarthritis and neurodegenerative diseases. Similarly, tissue engineering techniques, which involve the creation of functional tissues and organs using a combination of cells, biomaterials, and growth factors, hold promise for replacing damaged or diseased tissues and restoring function in ageing individuals.
In addition to these novel therapies, researchers are exploring the potential of interventions targeting other hallmarks of ageing, such as mitochondrial dysfunction, epigenetic alterations, and inflammation. By addressing these underlying mechanisms of ageing, emerging therapies aim to not only extend lifespan but also improve healthspan, enabling individuals to live longer, healthier lives free from the burden of age-related diseases. As research in this field continues to advance, the development of safe and effective interventions for promoting healthy
95 | www.xrphealthcare.com
MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY MEDICAL RESEARCH
ageing remains a key priority, offering hope for a future where ageing is no longer synonymous with decline, but rather with vitality and resilience.
Current trends in ageing research
Ever wondered why some people seem to defy ageing while others face age-related challenges? The world of ageing and longevity research holds the answers. Today, ageing research is experiencing a revival, driven by progress in genetics, biotechnology, and data analysis. Scientists have been diligently exploring how genes influence the ageing process, uncovering specific genes and pathways associated with prolonged health and vitality. While we can’t change our genes, understanding them better empowers us to make choices that support healthy ageing. Concurrently, simple lifestyle changes, like eating healthier and exercising more, are proving to be powerful ways to stay healthy as people age and reduce the risk of age-related illnesses. Studies consistently show that individuals who adopt these behaviours tend to enjoy longer, healthier lives with fewer health issues.
Inside our bodies, tiny cells play a pivotal role in ageing. Scientists are unravelling the details of cellular ageing mechanisms, such as oxidative stress and inflammation, to find ways to maintain cell health and slow down ageing. Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species and the body’s antioxidant defences, leads to cellular damage and accelerates ageing. Similarly, chronic inflammation, driven by a dysregulated immune response, can wreak havoc on cellular function and contribute to age-related diseases. Exciting developments in ageing research are paving the way for innovative therapies, including drugs that target ageing cells and regenerative medicine techniques, offering promising prospects for extended health and vitality in the future.
Recognising that everyone ages differently, personalised approaches to ageing are gaining traction. By considering factors like genetics and lifestyle habits, doctors can tailor treatments and interventions to meet individual needs, ensuring the most effective outcomes. Moreover, social connections, access to healthcare, and environmental conditions significantly influence
ageing outcomes. By addressing these factors, we can create communities that support healthy ageing for all.
In today’s digital age, technology plays a pivotal role in ageing research, offering tools like fitness trackers and telemedicine apps to help us monitor our health and make informed choices as we age. These advancements make it easier than ever to stay healthy and active well into our later years. Ageing may be a natural part of life, but it doesn’t have to mean slowing down or losing vitality. By staying informed and making simple lifestyle changes, we can all enjoy longer, healthier lives. So why wait? Start making healthier choices today and unlock the secrets of ageing for yourself!
Impact of cellular ageing research on human health Cellular ageing research has played a pivotal role in advancing human health, particularly in the treatment of cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. By investigating the complex cellular mechanisms underlying these conditions, researchers have developed targeted therapies tailored to inhibit cancer cell growth while sparing healthy cells, thereby minimising treatment side effects. Furthermore, insights from cellular ageing research have facilitated the identification of novel biomarkers for early cancer detection, leading to more timely interventions and improved patient outcomes. Additionally, investigations into cellular senescence—a state of irreversible growth arrest— have offered promising avenues for eliminating
96 | www.xrphealthcare.com
MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY MEDICAL RESEARCH
senescent cancer cells, thereby hindering tumour recurrence.
In diabetes management, cellular ageing research has illuminated the role of oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction in disease pathogenesis. This understanding has fuelled the development of medications targeting these cellular processes, resulting in improved insulin sensitivity, better regulation of blood sugar levels, and prevention of diabetic complications. Moreover, research into cellular senescence within pancreatic beta cells—the insulin-producing cells—holds potential for regenerative medicine approaches aimed at restoring beta cell function in individuals with diabetes.
Insights derived from cellular ageing research have also contributed to the development of therapies for cardiovascular diseases by targeting key cellular processes involved in disease progression. Medications designed to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation have demonstrated efficacy in improving endothelial function, reducing arterial plaque build-up, and decreasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Furthermore, investigations into the role of cellular senescence in promoting vascular ageing and atherosclerosis have spurred the exploration of senolytic drugs—compounds capable of selectively eliminating senescent cells— to mitigate cardiovascular disease progression and enhance vascular health.
Furthermore, cellular ageing research has emerged as a cornerstone in the understanding and management of Alzheimer’s disease and cognitive decline. Researchers have explored the complex cellular processes involved in Alzheimer’s disease and cognitive decline, revealing important mechanisms like the build-up of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in Alzheimer’s disease, and oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction in cognitive decline. These insights have paved the way for targeted therapies aimed at preventing or reducing the build-up of abnormal proteins, as well as identifying biomarkers for early detection and intervention. Brain cells, including neurons, microglia, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and endothelial cells, undergo cell senescence, leading to various neurodegenerative diseases. Studies on
cellular senescence have highlighted the role of senescent cells in promoting neurodegeneration, offering promising strategies for preventing or delaying cognitive decline in ageing populations. Through ongoing research, cellular ageing holds the potential to revolutionise the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of Alzheimer’s disease and cognitive impairment, ultimately improving outcomes and quality of life for affected individuals.
Technological advancements such as single-cell sequencing, CRISPR gene editing, and artificial intelligence are poised to revolutionise ageing research, providing valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms of ageing and opening doors to innovative treatment approaches. Additionally, personalised therapies tailored to individual genetic profiles and disease susceptibilities hold promise for optimising treatment outcomes and enhancing the quality of life for older adults.
Lifestyle factors wield significant influence over the ageing process
In addition to genetic factors, lifestyle choices play a pivotal role in shaping the ageing process and influencing overall health and well-being. Nutrition, in particular, emerges as a critical determinant of longevity, with studies highlighting the importance of a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in promoting cellular health and reducing the risk of age-related diseases. Furthermore, emerging research suggests that specific dietary patterns, such as the Mediterranean diet or the Okinawan diet, may confer additional benefits for healthy ageing, owing to their emphasis on nutrient-dense foods and anti-inflammatory properties.
Physical activity represents another key pillar of healthy ageing, with regular exercise exerting profound effects on both physical and cognitive function. Engaging in aerobic activities, strength training, balance exercises, and flexibility exercises can help preserve muscle mass, improve cardiovascular health, enhance mobility, and mitigate age-related declines in cognitive function. Moreover, emerging evidence suggests that exercise may exert beneficial effects on cellular ageing processes, such as telomere length and mitochondrial function, further underscoring the
97 | www.xrphealthcare.com
MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY MEDICAL RESEARCH
importance of staying physically active as we age.
Quality sleep is essential for overall health and well-being, with insufficient sleep linked to an array of adverse health outcomes, including cognitive decline, metabolic disturbances, and immune dysfunction. Establishing healthy sleep habits, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimising sleep environment, can promote restorative sleep and support healthy ageing. Effective stress management is also integral to healthy ageing, as chronic stress can accelerate cellular ageing processes and increase the risk of age-related diseases. Adopting stress-reducing techniques, such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, and social support networks, can help mitigate the negative effects of stress on health and promote resilience in the face of life’s challenges. By incorporating evidence-based lifestyle modifications into daily routines, individuals can optimise their health and well-being as they age.
Navigating the ethical crossroads of ageing research
As science inches closer to unlocking the secrets of ageing, ethical considerations loom large. Questions surrounding the accessibility and affordability of emerging therapies weigh heavily on the ethical landscape of ageing research. The potential for emerging treatments to exacerbate existing health disparities and widen the gap between socioeconomically advantaged and disadvantaged populations necessitates careful consideration and proactive measures to ensure equitable access to healthcare resources. Moreover, the societal implications of extending human lifespan raise profound ethical dilemmas regarding resource allocation, environmental sustainability, and intergenerational equity. As the pursuit of scientific progress intersects with ethical imperatives, it is essential to strike a delicate balance between advancing scientific knowledge and safeguarding the welfare and dignity of all individuals. Collaborative efforts between scientists, policymakers, ethicists, and community stakeholders are crucial for navigating these complex ethical dilemmas and ensuring that advancements in ageing research serve the collective interests of humanity.
The future of ageing and longevity researchW
Looking ahead, the horizon of ageing and longevity research is ripe with potential for groundbreaking discoveries and transformative advancements. One promising avenue of exploration lies in harnessing the power of artificial intelligence (AI) to transform how we understand and address the complexities of ageing. The AI-driven algorithms can analyse vast datasets, uncover hidden patterns, and predict outcomes with unprecedented accuracy, offering invaluable insights into the mechanisms of ageing and the development of personalised interventions. In addition to AI, researchers are increasingly turning their attention to deciphering the epigenetic signatures of ageing, which refer to changes in gene expression that occur as a result of external factors such as diet, lifestyle, and environmental exposures. By elucidating the epigenetic mechanisms underlying ageing, scientists aim to develop novel strategies for modulating gene expression and promoting healthy ageing.
Furthermore, interdisciplinary collaboration emerges as a cornerstone of future advancements in ageing research, as researchers from different fields come together to pool their expertise and tackle complex challenges from multiple angles. By bridging disciplines such as genetics, biology, psychology, sociology, and public health, interdisciplinary research endeavours hold the potential to generate holistic insights into the multidimensional nature of ageing and inform the development of comprehensive interventions that address the diverse needs of ageing populations. Ethical stewardship remains paramount as scientists navigate the uncharted territories of ageing research, ensuring that scientific advancements are pursued with integrity, transparency, and respect for human dignity. By upholding ethical principles and prioritising the well-being of individuals and communities, science can mitigate potential risks and maximise the benefits of ageing research for society as a whole.
Ultimately, the future of ageing research holds the promise of not only prolonging life but also enriching it with vitality and meaning.
98 | www.xrphealthcare.com
MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY MEDICAL RESEARCH






99 | www.xrphealthcare.com www.xrphealthcare.com | 119www.goldgenie.com/gold-plating-kits London: +44 208 804 6200 Dubai: +971 4 248 5180 Make More Than USD $500 Per Day In Your Own Portable Plating Business From Home. Simple, Turn-Key Business. Before After Price from USD $1,600

































































 KEITH ERREY - XRP HEALTHCARE’S CHIEF TECHNOLOGY OFFICER
KEITH ERREY - XRP HEALTHCARE’S CHIEF TECHNOLOGY OFFICER




















































 BY BENJAMIN OPUKO
BY BENJAMIN OPUKO