INTERNET OF THINGS HANDBOOK
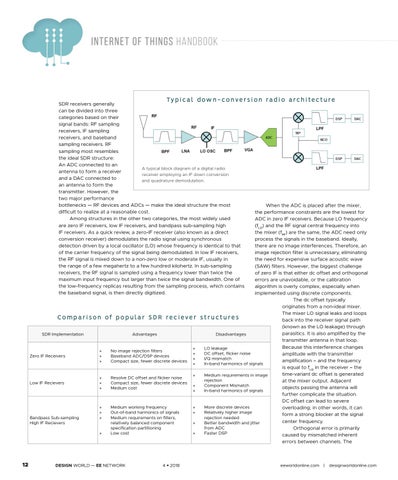
Ty p i c a l d ow n - c o n ve r s i o n r ad i o a r c h i t e c t u r e
SDR receivers generally can be divided into three categories based on their signal bands: RF sampling receivers, IF sampling receivers, and baseband sampling receivers. RF sampling most resembles the ideal SDR structure: An ADC connected to an A typical block diagram of a digital radio antenna to form a receiver receiver employing an IF down conversion and a DAC connected to and quadrature demodulation. an antenna to form the transmitter. However, the two major performance bottlenecks — RF devices and ADCs — make the ideal structure the most difficult to realize at a reasonable cost. Among structures in the other two categories, the most widely used are zero IF receivers, low IF receivers, and bandpass sub-sampling high IF receivers. As a quick review, a zero-IF receiver (also known as a direct conversion receiver) demodulates the radio signal using synchronous detection driven by a local oscillator (LO) whose frequency is identical to that of the carrier frequency of the signal being demodulated. In low IF receivers, the RF signal is mixed down to a non-zero low or moderate IF, usually in the range of a few megahertz to a few hundred kilohertz. In sub-sampling receivers, the RF signal is sampled using a frequency lower than twice the maximum input frequency but larger than twice the signal bandwidth. One of the low-frequency replicas resulting from the sampling process, which contains the baseband signal, is then directly digitized.
Co m p a r i s o n o f p o p u l a r S D R r e c i eve r SDR Implementation
Advantages
Zero IF Receivers
»» »» »»
No image rejection filters Baseband ADC/DSP devices Compact size, fewer discrete devices
Low IF Recievers
»» »» »»
Resolve DC offset and flicker noise Compact size, fewer discrete devices Medium cost
»» »» »»
Medium working frequency Out-of-band harmonics of signals Medium requirements on filters, relatively balanced component specification partitioning Low cost
Bandpass Sub-sampling High IF Recievers
»»
12
DESIGN WORLD — EE NETWORK
Microchip article — IoT HB 04-18 V3 FINAL.indd 12
4 • 2018
»» »» »» »» »» »» »»
»» »» »» »»
When the ADC is placed after the mixer, the performance constraints are the lowest for ADC in zero IF receivers. Because LO frequency (fLO) and the RF signal central frequency into the mixer (fRF) are the same, the ADC need only process the signals in the baseband. Ideally, there are no image interferences. Therefore, an image rejection filter is unnecessary, eliminating the need for expensive surface acoustic wave (SAW) filters. However, the biggest challenge of zero IF is that either dc offset and orthogonal errors are unavoidable, or the calibration algorithm is overly complex, especially when implemented using discrete components. The dc offset typically originates from a non-ideal mixer. The mixer LO signal leaks and loops s t ruc tu res back into the receiver signal path (known as the LO leakage) through parasitics. It is also amplified by the Disadvantages transmitter antenna in that loop. Because this interference changes LO leakage DC offset, flicker noise amplitude with the transmitter I/Q mismatch amplification – and the frequency In-band harmonics of signals is equal to fLO in the receiver – the time-variant dc offset is generated Medium requirements in image rejection at the mixer output. Adjacent Component Mismatch objects passing the antenna will In-band harmonics of signals further complicate the situation. DC offset can lead to severe More discrete devices overloading; in other words, it can Relatively higher image form a strong blocker at the signal rejection needed center frequency. Better bandwidth and jitter from ADC Orthogonal error is primarily Faster DSP caused by mismatched inherent errors between channels. The
eeworldonline.com | designworldonline.com
4/17/18 2:31 PM