Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
Financial instruments The derivative-based financial instruments serve to hedge energy sector exposures and exchange rate risks. These are treated as anticipatory hedges and offset underlying operational business in the future.
84
The derivative financial instruments of the companies concerned (WIEN ENERGIE GmbH, WIEN ENERGIE Vertrieb GmbH & Co KG and ENERGIEALLIANZ) are comprised as follows as at the balance sheet date (adjusted for intra-Group relationships).
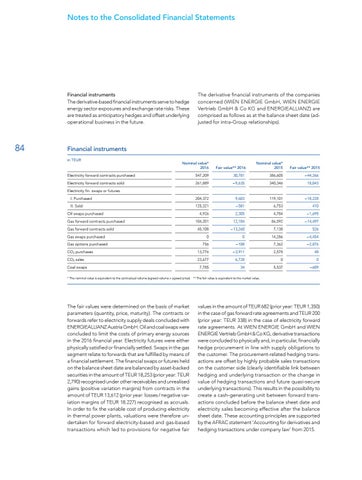
Financial instruments in TEUR
Nominal value* 2016
Fair value** 2016
Nominal value* 2015
Fair value** 2015
Electricity forward contracts purchased
547,209
30,781
386,605
– 44,266
Electricity forward contracts sold
261,889
– 9,635
340,346
18,043
I. Purchased
204,372
9,603
119,101
– 18,228
II. Sold
125,321
– 581
6,753
410
4,926
2,305
4,784
– 1,695
104,201
12,104
86,592
– 14,497
45,108
– 13,260
7,138
526
Electricity fin. swaps or futures
Oil swaps purchased Gas forward contracts purchased Gas forward contracts sold Gas swaps purchased
0
0
14,286
– 4,454
756
– 108
7,362
– 2,876
CO2 purchases
13,776
– 3,911
2,578
48
CO2 sales
23,677
6,728
0
0
7,785
34
5,537
– 609
Gas options purchased
Coal swaps
* The nominal value is equivalent to the contractual volume (agreed volume x agreed price). ** The fair value is equivalent to the market value.
The fair values were determined on the basis of market parameters (quantity, price, maturity). The contracts or forwards refer to electricity supply deals concluded with ENERGIEALLIANZ Austria GmbH. Oil and coal swaps were concluded to limit the costs of primary energy sources in the 2016 financial year. Electricity futures were either physically satisfied or financially settled. Swaps in the gas segment relate to forwards that are fulfilled by means of a financial settlement. The financial swaps or futures held on the balance sheet date are balanced by asset-backed securities in the amount of TEUR 18,253 (prior year: TEUR 2,790) recognised under other receivables and unrealised gains (positive variation margins) from contracts in the amount of TEUR 13,612 (prior year: losses / negative variation margins of TEUR 18.227) recognised as accruals. In order to fix the variable cost of producing electricity in thermal power plants, valuations were therefore undertaken for forward electricity-based and gas-based transactions which led to provisions for negative fair
values in the amount of TEUR 682 (prior year: TEUR 1,350) in the case of gas forward rate agreements and TEUR 200 (prior year: TEUR 338) in the case of electricity forward rate agreements. At WIEN ENERGIE GmbH and WIEN ENERGIE Vertrieb GmbH & Co KG, derivative transactions were concluded to physically and, in particular, financially hedge procurement in line with supply obligations to the customer. The procurement-related hedging transactions are offset by highly probable sales transactions on the customer side (clearly identifiable link between hedging and underlying transaction or the change in value of hedging transactions and future quasi-secure underlying transactions). This results in the possibility to create a cash-generating unit between forward transactions concluded before the balance sheet date and electricity sales becoming effective after the balance sheet date. These accounting principles are supported by the AFRAC statement ‘Accounting for derivatives and hedging transactions under company law’ from 2015.