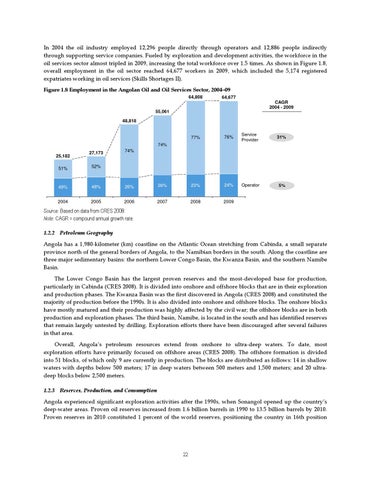
In 2004 the oil industry employed 12,296 people directly through operators and 12,886 people indirectly through supporting service companies. Fueled by exploration and development activities, the workforce in the oil services sector almost tripled in 2009, increasing the total workforce over 1.5 times. As shown in Figure 1.8, overall employment in the oil sector reached 64,677 workers in 2009, which included the 5,174 registered expatriates working in oil services (Skills Shortages II). Figure 1.8 Employment in the Angolan Oil and Oil Services Sector, 2004–09 64,808
64,677 CAGR 2004 - 2009
55,061 48,818
77%
76%
Service Provider
31%
Operator
5%
74% 25,182
27,173
74%
51%
52%
49%
48%
26%
26%
23%
24%
2004
2005
2006
2007
2008
2009
Source: Based on data from CRES 2008. Note: CAGR = compound annual growth rate. 1.2.2 Petroleum Geography
Angola has a 1,980-kilometer (km) coastline on the Atlantic Ocean stretching from Cabinda, a small separate province north of the general borders of Angola, to the Namibian borders in the south. Along the coastline are three major sedimentary basins: the northern Lower Congo Basin, the Kwanza Basin, and the southern Namibe Basin. The Lower Congo Basin has the largest proven reserves and the most-developed base for production, particularly in Cabinda (CRES 2008). It is divided into onshore and offshore blocks that are in their exploration and production phases. The Kwanza Basin was the first discovered in Angola (CRES 2008) and constituted the majority of production before the 1990s. It is also divided into onshore and offshore blocks. The onshore blocks have mostly matured and their production was highly affected by the civil war; the offshore blocks are in both production and exploration phases. The third basin, Namibe, is located in the south and has identified reserves that remain largely untested by drilling. Exploration efforts there have been discouraged after several failures in that area. Overall, Angola’s petroleum resources extend from onshore to ultra-deep waters. To date, most exploration efforts have primarily focused on offshore areas (CRES 2008). The offshore formation is divided into 51 blocks, of which only 9 are currently in production. The blocks are distributed as follows: 14 in shallow waters with depths below 500 meters; 17 in deep waters between 500 meters and 1,500 meters; and 20 ultradeep blocks below 2,500 meters. 1.2.3 Reserves, Production, and Consumption
Angola experienced significant exploration activities after the 1990s, when Sonangol opened up the country’s deep-water areas. Proven oil reserves increased from 1.6 billion barrels in 1990 to 13.5 billion barrels by 2010. Proven reserves in 2010 constituted 1 percent of the world reserves, positioning the country in 16th position
22