Trade Therapy: Deepening Cooperation to Strengthen Pandemic Defenses
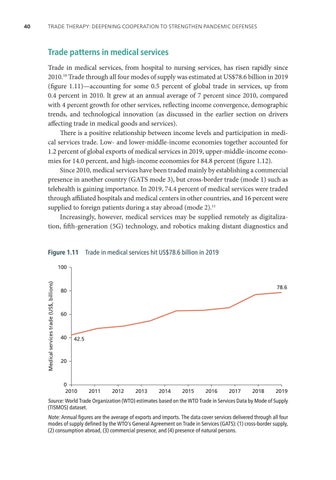
Trade patterns in medical services Trade in medical services, from hospital to nursing services, has risen rapidly since 2010.10 Trade through all four modes of supply was estimated at US$78.6 billion in 2019 (figure 1.11)—accounting for some 0.5 percent of global trade in services, up from 0.4 percent in 2010. It grew at an annual average of 7 percent since 2010, compared with 4 percent growth for other services, reflecting income convergence, demographic trends, and technological innovation (as discussed in the earlier section on drivers affecting trade in medical goods and services). There is a positive relationship between income levels and participation in medical services trade. Low- and lower-middle-income economies together accounted for 1.2 percent of global exports of medical services in 2019, upper-middle-income economies for 14.0 percent, and high-income economies for 84.8 percent (figure 1.12). Since 2010, medical services have been traded mainly by establishing a commercial presence in another country (GATS mode 3), but cross-border trade (mode 1) such as telehealth is gaining importance. In 2019, 74.4 percent of medical services were traded through affiliated hospitals and medical centers in other countries, and 16 percent were supplied to foreign patients during a stay abroad (mode 2).11 Increasingly, however, medical services may be supplied remotely as digitalization, fifth-generation (5G) technology, and robotics making distant diagnostics and Figure 1.11
Trade in medical services hit US$78.6 billion in 2019
100 Medical services trade (US$, billions)
40
78.6
80
60
40
42.5
20
0 2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
2019
Source: World Trade Organization (WTO) estimates based on the WTO Trade in Services Data by Mode of Supply (TISMOS) dataset. Note: Annual figures are the average of exports and imports. The data cover services delivered through all four modes of supply defined by the WTO’s General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS): (1) cross-border supply, (2) consumption abroad, (3) commercial presence, and (4) presence of natural persons.