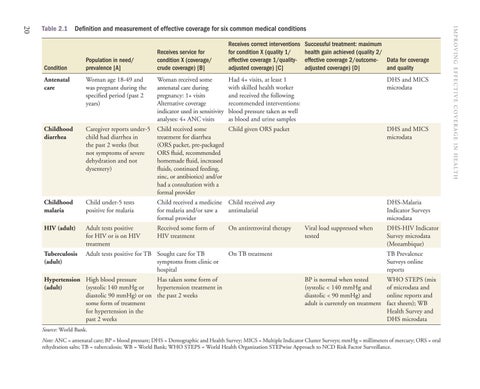
Definition and measurement of effective coverage for six common medical conditions
Condition
Population in need/ prevalence [A]
Receives service for condition X (coverage/ crude coverage) [B]
Receives correct interventions for condition X (quality 1/ effective coverage 1/qualityadjusted coverage) [C]
Successful treatment: maximum health gain achieved (quality 2/ effective coverage 2/outcome- Data for coverage adjusted coverage) [D] and quality
Had 4+ visits, at least 1 with skilled health worker and received the following recommended interventions: blood pressure taken as well as blood and urine samples
DHS and MICS microdata
Antenatal care
Woman age 18-49 and was pregnant during the specified period (past 2 years)
Woman received some antenatal care during pregnancy: 1+ visits Alternative coverage indicator used in sensitivity analyses: 4+ ANC visits
Childhood diarrhea
Caregiver reports under-5 child had diarrhea in the past 2 weeks (but not symptoms of severe dehydration and not dysentery)
Child given ORS packet Child received some treatment for diarrhea (ORS packet, pre-packaged ORS fluid, recommended homemade fluid, increased fluids, continued feeding, zinc, or antibiotics) and/or had a consultation with a formal provider
DHS and MICS microdata
Childhood malaria
Child under-5 tests positive for malaria
Child received a medicine Child received any for malaria and/or saw a antimalarial formal provider
DHS-Malaria Indicator Surveys microdata
HIV (adult)
Adult tests positive for HIV or is on HIV treatment
Received some form of HIV treatment
Tuberculosis (adult)
Adult tests positive for TB Sought care for TB symptoms from clinic or hospital
Has taken some form of Hypertension High blood pressure hypertension treatment in (adult) (systolic 140 mmHg or diastolic 90 mmHg) or on the past 2 weeks some form of treatment for hypertension in the past 2 weeks
On antiretroviral therapy
Viral load suppressed when tested
On TB treatment
DHS-HIV Indicator Survey microdata (Mozambique) TB Prevalence Surveys online reports
BP is normal when tested (systolic < 140 mmHg and diastolic < 90 mmHg) and adult is currently on treatment
WHO STEPS (mix of microdata and online reports and fact sheets); WB Health Survey and DHS microdata
Source: World Bank. Note: ANC = antenatal care; BP = blood pressure; DHS = Demographic and Health Survey; MICS = Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys; mmHg = millimeters of mercury; ORS = oral rehydration salts; TB = tuberculosis; WB = World Bank; WHO STEPS = World Health Organization STEPwise Approach to NCD Risk Factor Surveillance.
IMPROVING EFFECTIVE COVERAGE IN HEALTH
20
Table 2.1