IMPROVING EFFECTIVE COVERAGE IN HEALTH
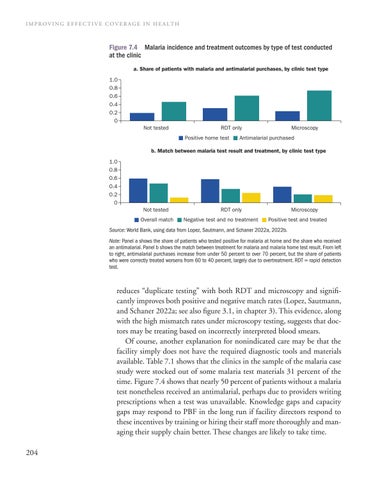
Figure 7.4 Malaria incidence and treatment outcomes by type of test conducted at the clinic a. Share of patients with malaria and antimalarial purchases, by clinic test type 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 Not tested
RDT only Positive home test
Microscopy
Antimalarial purchased
b. Match between malaria test result and treatment, by clinic test type 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 Not tested Overall match
RDT only Negative test and no treatment
Microscopy Positive test and treated
Source: World Bank, using data from Lopez, Sautmann, and Schaner 2022a, 2022b. Note: Panel a shows the share of patients who tested positive for malaria at home and the share who received an antimalarial. Panel b shows the match between treatment for malaria and malaria home test result. From left to right, antimalarial purchases increase from under 50 percent to over 70 percent, but the share of patients who were correctly treated worsens from 60 to 40 percent, largely due to overtreatment. RDT = rapid detection test.
reduces “duplicate testing” with both RDT and microscopy and significantly improves both positive and negative match rates (Lopez, Sautmann, and Schaner 2022a; see also figure 3.1, in chapter 3). This evidence, along with the high mismatch rates under microscopy testing, suggests that doctors may be treating based on incorrectly interpreted blood smears. Of course, another explanation for nonindicated care may be that the facility simply does not have the required diagnostic tools and materials available. Table 7.1 shows that the clinics in the sample of the malaria case study were stocked out of some malaria test materials 31 percent of the time. Figure 7.4 shows that nearly 50 percent of patients without a malaria test nonetheless received an antimalarial, perhaps due to providers writing prescriptions when a test was unavailable. Knowledge gaps and capacity gaps may respond to PBF in the long run if facility directors respond to these incentives by training or hiring their staff more thoroughly and managing their supply chain better. These changes are likely to take time. 204