MIDDLE EAST AND NORTH AFRICA REGION ECONOMIC UPDATE OCTOBER 2021
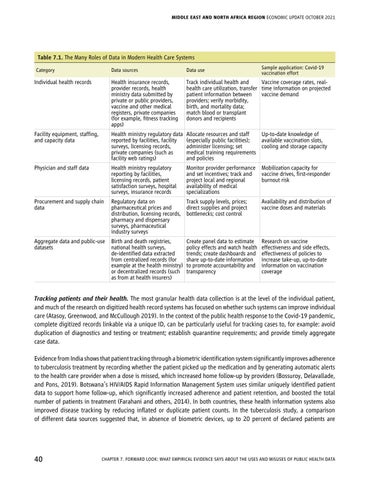
Table 7.1. The Many Roles of Data in Modern Health Care Systems Category
Sample application: Covid-19 vaccination effort
Data sources
Data use
Individual health records
Health insurance records, provider records, health ministry data submitted by private or public providers, vaccine and other medical registers, private companies (for example, fitness tracking apps)
Track individual health and Vaccine coverage rates, realhealth care utilization, transfer time information on projected patient information between vaccine demand providers; verify morbidity, birth, and mortality data; match blood or transplant donors and recipients
Facility equipment, staffing, and capacity data
Health ministry regulatory data reported by facilities, facility surveys, licensing records, private companies (such as facility web ratings)
Allocate resources and staff Up-to-date knowledge of (especially public facilities); available vaccination slots, administer licensing; set cooling and storage capacity medical training requirements and policies
Physician and staff data
Health ministry regulatory reporting by facilities, licensing records, patient satisfaction surveys, hospital surveys, insurance records
Monitor provider performance and set incentives; track and project local and regional availability of medical specializations
Procurement and supply chain data
Regulatory data on Track supply levels, prices; pharmaceutical prices and direct supplies and project distribution, licensing records, bottlenecks; cost control pharmacy and dispensary surveys, pharmaceutical industry surveys
Availability and distribution of vaccine doses and materials
Aggregate data and public-use datasets
Birth and death registries, national health surveys, de-identified data extracted from centralized records (for example at the health ministry) or decentralized records (such as from at health insurers)
Research on vaccine effectiveness and side effects, effectiveness of policies to increase take-up, up-to-date information on vaccination coverage
Create panel data to estimate policy effects and watch health trends; create dashboards and share up-to-date information to promote accountability and transparency
Mobilization capacity for vaccine drives, first-responder burnout risk
Tracking patients and their health. The most granular health data collection is at the level of the individual patient, and much of the research on digitized health record systems has focused on whether such systems can improve individual care (Atasoy, Greenwood, and McCullough 2019). In the context of the public health response to the Covid-19 pandemic, complete digitized records linkable via a unique ID, can be particularly useful for tracking cases to, for example: avoid duplication of diagnostics and testing or treatment; establish quarantine requirements; and provide timely aggregate case data. Evidence from India shows that patient tracking through a biometric identification system significantly improves adherence to tuberculosis treatment by recording whether the patient picked up the medication and by generating automatic alerts to the health care provider when a dose is missed, which increased home follow-up by providers (Bossuroy, Delavallade, and Pons, 2019). Botswana’s HIV/AIDS Rapid Information Management System uses similar uniquely identified patient data to support home follow-up, which significantly increased adherence and patient retention, and boosted the total number of patients in treatment (Farahani and others, 2014). In both countries, these health information systems also improved disease tracking by reducing inflated or duplicate patient counts. In the tuberculosis study, a comparison of different data sources suggested that, in absence of biometric devices, up to 20 percent of declared patients are
40
CHAPTER 7. FORWARD LOOK: WHAT EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE SAYS ABOUT THE USES AND MISUSES OF PUBLIC HEALTH DATA