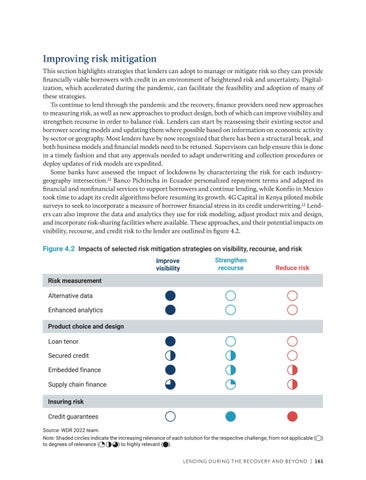
Improving risk mitigation This section highlights strategies that lenders can adopt to manage or mitigate risk so they can provide financially viable borrowers with credit in an environment of heightened risk and uncertainty. Digital ization, which accelerated during the pandemic, can facilitate the feasibility and adoption of many of these strategies. To continue to lend through the pandemic and the recovery, finance providers need new approaches to measuring risk, as well as new approaches to product design, both of which can improve visibility and strengthen recourse in order to balance risk. Lenders can start by reassessing their existing sector and borrower scoring models and updating them where possible based on information on economic activity by sector or geography. Most lenders have by now recognized that there has been a structural break, and both business models and financial models need to be retuned. Supervisors can help ensure this is done in a timely fashion and that any approvals needed to adapt underwriting and collection procedures or deploy updates of risk models are expedited. Some banks have assessed the impact of lockdowns by characterizing the risk for each industrygeography intersection.12 Banco Pichincha in Ecuador personalized repayment terms and adapted its financial and nonfinancial services to support borrowers and continue lending, while Konfío in Mexico took time to adapt its credit algorithms before resuming its growth. 4G Capital in Kenya piloted mobile surveys to seek to incorporate a measure of borrower financial stress in its credit underwriting.13 Lenders can also improve the data and analytics they use for risk modeling, adjust product mix and design, and incorporate risk-sharing facilities where available. These approaches, and their potential impacts on visibility, recourse, and credit risk to the lender are outlined in figure 4.2.
Figure 4.2 Impacts of selected risk mitigation strategies on visibility, recourse, and risk Improve visibility
Strengthen recourse
Reduce risk
Risk measurement Alternative data Enhanced analytics Product choice and design Loan tenor Secured credit Embedded finance Supply chain finance Insuring risk Credit guarantees Source: WDR 2022 team. Note: Shaded circles indicate the increasing relevance of each solution for the respective challenge, from not applicable ( to degrees of relevance ( ) to highly relevant ( ).
)
LENDING DURING THE RECOVERY AND BE YOND | 161