180 | Noncommunicable Diseases in Saudi Arabia
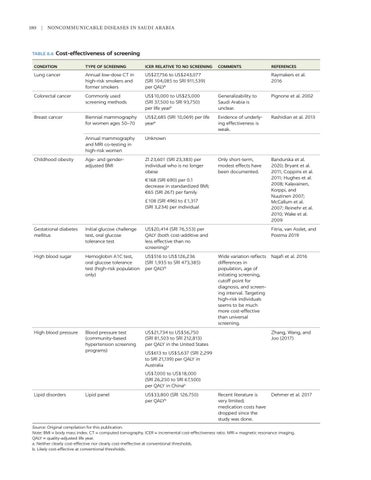
TABLE 8.6 Cost-effectiveness
of screening
CONDITION
TYPE OF SCREENING
ICER RELATIVE TO NO SCREENING
Lung cancer
Annual low-dose CT in high-risk smokers and former smokers
US$27,756 to US$243,077 (SRl 104,085 to SRl 911,539) per QALYa
Colorectal cancer
Commonly used screening methods
US$10,000 to US$25,000 (SRl 37,500 to SRl 93,750) per life yearb
Generalizability to Saudi Arabia is unclear.
Pignone et al. 2002
Breast cancer
Biennial mammography for women ages 50–70
US$2,685 (SRl 10,069) per life yearb
Evidence of underlying effectiveness is weak.
Rashidian et al. 2013
Annual mammography and MRI co-testing in high-risk women
Unknown
Age- and gender- adjusted BMI
Zl 23,601 (SRl 23,383) per individual who is no longer obese
Only short-term, modest effects have been documented.
Bandurska et al. 2020; Bryant et al. 2011; Coppins et al. 2011; Hughes et al. 2008; Kalavainen, Korppi, and Nuutinen 2007; McCallum et al. 2007; Reinehr et al. 2010; Wake et al. 2009
Childhood obesity
COMMENTS
€168 (SRl 690) per 0.1 decrease in standardized BMI; €65 (SRl 267) per family £108 (SRl 496) to £1,317 (SRl 3,234) per individual
Gestational diabetes mellitus
Initial glucose challenge test, oral glucose tolerance test
US$20,414 (SRl 76,553) per QALY (both cost-additive and less effective than no screening)a
High blood sugar
Hemoglobin A1C test, oral glucose tolerance test (high-risk population only)
US$516 to US$126,236 (SRl 1,935 to SRl 473,385) per QALYb
High blood pressure
Blood pressure test (community-based hypertension screening programs)
US$21,734 to US$56,750 (SRl 81,503 to SRl 212,813) per QALY in the United States
REFERENCES
Raymakers et al. 2016
Fitria, van Asslet, and Postma 2019
Wide variation reflects differences in population, age of initiating screening, cutoff point for diagnosis, and screening interval. Targeting high-risk individuals seems to be much more cost-effective than universal screening.
Najafi et al. 2016
Zhang, Wang, and Joo (2017)
US$613 to US$5,637 (SRl 2,299 to SRl 21,139) per QALY in Australia US$7,000 to US$18,000 (SRl 26,250 to SRl 67,500) per QALY in Chinab
Lipid disorders
Lipid panel
US$33,800 (SRl 126,750) per QALYb
Recent literature is very limited; medication costs have dropped since the study was done.
Dehmer et al. 2017
Source: Original compilation for this publication. Note: BMI = body mass index. CT = computed tomography. ICER = incremental cost-effectiveness ratio. MRI = magnetic resonance imaging. QALY = quality-adjusted life year. a. Neither clearly cost-effective nor clearly cost-ineffective at conventional thresholds. b. Likely cost-effective at conventional thresholds.