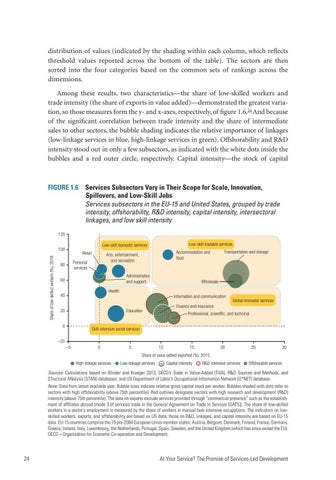
distribution of values (indicated by the shading within each column, which reflects threshold values reported across the bottom of the table). The sectors are then sorted into the four categories based on the common sets of rankings across the dimensions. Among these results, two characteristics—the share of low-skilled workers and trade intensity (the share of exports in value added)—demonstrated the greatest variation, so those measures form the y- and x-axes, respectively, of figure 1.6.24 And because of the significant correlation between trade intensity and the share of intermediate sales to other sectors, the bubble shading indicates the relative importance of linkages (low-linkage services in blue, high-linkage services in green). Offshorability and R&D intensity stood out in only a few subsectors, as indicated with the white dots inside the bubbles and a red outer circle, respectively. Capital intensity—the stock of capital
FIGURE 1.6 Services Subsectors Vary in Their Scope for Scale, Innovation, Spillovers, and Low-Skill Jobs Services subsectors in the EU-15 and United States, grouped by trade intensity, offshorability, R&D intensity, capital intensity, intersectoral linkages, and low skill intensity 120
Share of low-skilled workers (%), 2018
Low-skill tradable services
Low-skill domestic services
100
Retail
Arts, entertainment, and recreation
Personal services
80
Accommodation and food
Administrative and support
60
Transportation and storage
Wholesale
Health
40
Information and communication
20
Education
0
Global innovator services
Finance and insurance Professional, scientific, and technical
Skill-intensive social services
–20 –5
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
Share of value added exported (%), 2015 High-linkage services
Low-linkage services
Capital intensity
R&D-intensive services
Offshorable services
Sources: Calculations based on Blinder and Krueger 2013; OECD’s Trade in Value-Added (TiVA), R&D Sources and Methods, and STructural ANalysis (STAN) databases; and US Department of Labor’s Occupational Information Network (O*NET) database. Note: Data from latest available year. Bubble sizes indicate relative gross capital stock per worker. Bubbles shaded with dots refer to sectors with high offshorability (above 75th percentile). Red outlines designate sectors with high research and development (R&D) intensity (above 75th percentile). The data on exports exclude services provided through “commercial presence” such as the establishment of affiliates abroad (mode 3 of services trade in the General Agreement on Trade in Services [GATS]). The share of low-skilled workers in a sector’s employment is measured by the share of workers in manual-task-intensive occupations. The indicators on lowskilled workers, exports, and offshorability are based on US data; those on R&D, linkages, and capital intensity are based on EU-15 data. EU-15 countries comprise the 15 pre-2004 European Union member states: Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, and the United Kingdom (which has since exited the EU). OECD = Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
24
At Your Service? The Promise of Services-Led Development