Share of business and professional services in total employment (%)
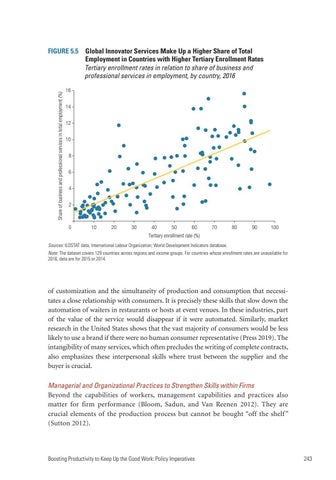
FIGURE 5.5 Global Innovator Services Make Up a Higher Share of Total Employment in Countries with Higher Tertiary Enrollment Rates Tertiary enrollment rates in relation to share of business and professional services in employment, by country, 2016 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Tertiary enrollment rate (%) Sources: ILOSTAT data, International Labour Organization; World Development Indicators database. Note: The dataset covers 129 countries across regions and income groups. For countries whose enrollment rates are unavailable for 2016, data are for 2015 or 2014.
of customization and the simultaneity of production and consumption that necessitates a close relationship with consumers. It is precisely these skills that slow down the automation of waiters in restaurants or hosts at event venues. In these industries, part of the value of the service would disappear if it were automated. Similarly, market research in the United States shows that the vast majority of consumers would be less likely to use a brand if there were no human consumer representative (Press 2019). The intangibility of many services, which often precludes the writing of complete contracts, also emphasizes these interpersonal skills where trust between the supplier and the buyer is crucial. Managerial and Organizational Practices to Strengthen Skills within Firms Beyond the capabilities of workers, management capabilities and practices also matter for firm performance (Bloom, Sadun, and Van Reenen 2012). They are crucial elements of the production process but cannot be bought “off the shelf ” (Sutton 2012).
Boosting Productivity to Keep Up the Good Work: Policy Imperatives
243