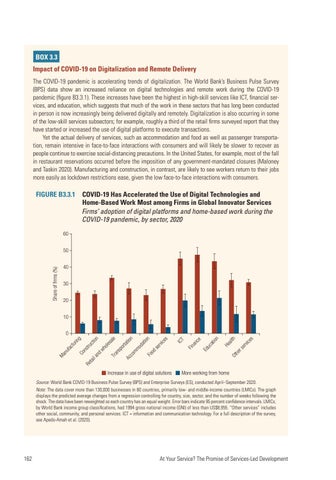
BOX 3.3 Impact of COVID-19 on Digitalization and Remote Delivery The COVID-19 pandemic is accelerating trends of digitalization. The World Bank’s Business Pulse Survey (BPS) data show an increased reliance on digital technologies and remote work during the COVID-19 pandemic (figure B3.3.1). These increases have been the highest in high-skill services like ICT, financial services, and e ducation, which suggests that much of the work in these sectors that has long been conducted in person is now increasingly being delivered digitally and remotely. Digitalization is also occurring in some of the low-skill services subsectors; for example, roughly a third of the retail firms surveyed report that they have started or increased the use of digital platforms to execute transactions. Yet the actual delivery of services, such as accommodation and food as well as passenger transportation, remain intensive in face-to-face interactions with consumers and will likely be slower to recover as people continue to exercise social-distancing precautions. In the United States, for example, most of the fall in restaurant reservations occurred before the imposition of any government-mandated closures (Maloney and Taskin 2020). Manufacturing and construction, in contrast, are likely to see workers return to their jobs more easily as lockdown restrictions ease, given the low face-to-face interactions with consumers.
FIGURE B3.3.1 COVID-19 Has Accelerated the Use of Digital Technologies and Home-Based Work Most among Firms in Global Innovator Services Firms’ adoption of digital platforms and home-based work during the COVID-19 pandemic, by sector, 2020 60
Share of firms (%)
50 40 30 20 10
es
h
vic
alt
rs
er
He Ot
he
ce
uc ati on Ed
an
ICT
Fin
od
ati on Fo od se rvi ce s
ion
mm
Ac co
or
tat
le sa
an sp
nd la tai
Re
Tr
wh
ole
cti tru
ns Co
Ma
nu
fac
tur
ing
on
0
Increase in use of digital solutions
More working from home
Source: World Bank COVID-19 Business Pulse Survey (BPS) and Enterprise Surveys (ES), conducted April–September 2020. Note: The data cover more than 130,000 businesses in 60 countries, primarily low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). The graph displays the predicted average changes from a regression controlling for country, size, sector, and the number of weeks following the shock. The data have been reweighted so each country has an equal weight. Error bars indicate 95 percent confidence intervals. LMICs, by World Bank income group classifications, had 1994 gross national income (GNI) of less than US$8,955. “Other services” includes other social, community, and personal services. ICT = information and communication technology. For a full description of the survey, see Apedo-Amah et al. (2020).
162
At Your Service? The Promise of Services-Led Development