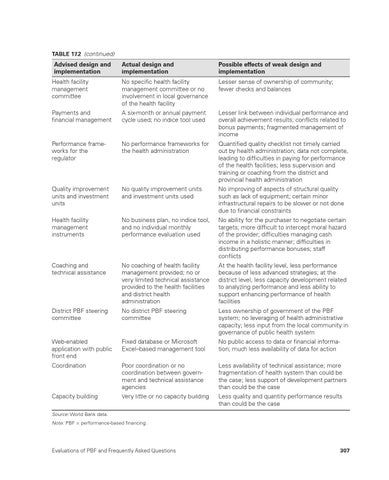
TABLE 17.2 (continued)
Advised design and implementation
Actual design and implementation
Possible effects of weak design and implementation
Health facility management committee
No specific health facility management committee or no involvement in local governance of the health facility
Lesser sense of ownership of community; fewer checks and balances
Payments and financial management
A six-month or annual payment cycle used; no indice tool used
Lesser link between individual performance and overall achievement results; conflicts related to bonus payments; fragmented management of income
Performance frameworks for the regulator
No performance frameworks for the health administration
Quantified quality checklist not timely carried out by health administration; data not complete, leading to difficulties in paying for performance of the health facilities; less supervision and training or coaching from the district and provincial health administration
Quality improvement units and investment units
No quality improvement units and investment units used
No improving of aspects of structural quality such as lack of equipment; certain minor infrastructural repairs to be slower or not done due to financial constraints
Health facility management instruments
No business plan, no indice tool, and no individual monthly performance evaluation used
No ability for the purchaser to negotiate certain targets; more difficult to intercept moral hazard of the provider; difficulties managing cash income in a holistic manner; difficulties in distributing performance bonuses; staff conflicts
Coaching and technical assistance
No coaching of health facility management provided; no or very limited technical assistance provided to the health facilities and district health administration
At the health facility level, less performance because of less advanced strategies; at the district level, less capacity development related to analyzing performance and less ability to support enhancing performance of health facilities
District PBF steering committee
No district PBF steering committee
Less ownership of government of the PBF system; no leveraging of health administrative capacity; less input from the local community in governance of public health system
Web-enabled application with public front end
Fixed database or Microsoft Excel–based management tool
No public access to data or financial information; much less availability of data for action
Coordination
Poor coordination or no coordination between government and technical assistance agencies
Less availability of technical assistance; more fragmentation of health system than could be the case; less support of development partners than could be the case
Capacity building
Very little or no capacity building
Less quality and quantity performance results than could be the case
Source:: World Bank data. Note:: PBF = performance-based financing.
Evaluations of PBF and Frequently Asked Questions
307