PORT FOLIO

UCL The Bartlett
Programme: MArch Architectural Design
Application number: 23198119
WAN LUOCHENG


UCL The Bartlett
Programme: MArch Architectural Design
Application number: 23198119
WAN LUOCHENG
An architecture that combines meditation space, living and ruins tours.

A museum designed to display forma urbis and its fragments.
An institutions for persons with physical and mental disabilities.

It can be robotically built according to environmental and operational requirements.


Other works during my undergraduate architecture studies.

An architecture that combines meditation space, living and ruins tours.
The Site Retreat is a powerful place to increase and stimulate the senses, to feel the weight and depth of the sheer cliffs, the immensity of the water and the openness of the horizon; it is a space for contemplation and a landmark within the landscape.The Cabo da Roca, located about 40 km northwest of Lisbon, is the most western point of continental Europe. It is described by the great Portuguese poet Luís de Camões as the place ‘Where the land ends and the sea begins’, in ‘Os Lusíadas’. Architectural Design | Individual Work | Cabo da Roca, Portugal | November 2022 | Teacher: Hua Xing

When generating a vision for an intervention located within such a remarkable place, it is essential that the design proposal emphasises, respects and celebrates the site, while provide a unique and memorable experience.


On the cliff stood a plain stone tablet inscribed with numbers: the longitude and latitude of the numbers showed that this was the westernmost point of the European continent.

The steep and massive cliffs rising one hundred meters above the ocean provide extensive and stunning panoramic views.
The lighthouse, dating from 1772, has a light range of around 48 kilometers and is still today a reference guide for boats and sailors traveling along the coast.
Entrance
Provide a space of transition between the natural landscape and the ‘Site Retreat’.

Skylight
Provide natural light to the interior of the building and provides a unique view of the sky.
Key Element
Skylight
Roof
Look-out point
Provide a look-out point for visitors to rest and engage with the cliffs, the sky and the sea, offering visitors a unique experience within the immensity of the place.
Provide a way for visitors to explore the natural scenery and see the architecture.
Key Element
Light Well
First Floor

Key Element
Meditation Room
Ground Floor



 SECTION A-A
SECTION B-B
SECTION A-A
SECTION B-B
Daylight enters the architecture
Meeting concrete and wood floors
Passing through light well to reach the ground
Light well corresponds to skylight to provide light to the interior of the architecture, and the ruins can be seen from the interior.It increases the internal and external connectivity of the building and responds to the landscape.

Steady concrete and long rectangular windows

The narrow meditation rooms are set against a wide double-height space Sunlight streamed through the windows on the light spiral staircase

 Spiral stair connects the viewing room with the meditation rooms on the first floor, forming a doubleheight space.The claustrophobia of the meditation rooms contrast with the double-height space, shaping the rich interior space.
Spiral stair connects the viewing room with the meditation rooms on the first floor, forming a doubleheight space.The claustrophobia of the meditation rooms contrast with the double-height space, shaping the rich interior space.

A museum designed to display forma urbis and its fragments.

The Forma Urbis is one of the most extraordinary documents from imperial Rome and is a major source for the history of the city. The museum is located in Rome, Italy, next to the ruins of the Roman Forum. A series of flat columns are used to create the rhythmic and geometric beauty of the facade. Combined with the hillside topography, the museum uses a combination of double-height space and small space to display the forma urbis and its fragments. The split-level space and atrium exhibition hall are used to create a rich indoor space experience for visitors.

The Forma Urbis Romae or Forma Urbis Severiana was a very large map of the imperial city of Rome (18 m long by 13 m high) carved on 151 marble slabs arranged in 11 rows, made under the reign of Emperor Septimius Severus, (between 203 and 211 CE). The 235 sqm map hung on a wall of an aula of the Templum Pacis (Forum della Pace). The same wall was later transformed into an exterior wall of the church of SS. Cosmas and Damian.


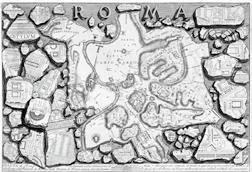

151 marble slabs are mounted onto a wall of a large room (aula) inside the Templum Pacis in Rome. Onto this wall of slabs is carved a detailed map of the imperial city of Rome. The incised lines are filled with red paint so as to stand out against the white background.

The Templum Pacis, together with the aula of the Marble Plan, is abandoned and gradually deteriorates. Many of the marble slabs are robbed for reuse as building material or for the production of lime. The rest gradually fall from the wall and are with time buried at its foot.
Many of the marble fragments are discovered in what by now has become a garden behind the Church of Saints Cosmas and Damian. The pieces pass into the hands of the Farnese family and are moved to the Farnese palace. The discovery unleashes a storm of antiquarian interest in the Plan whose existence, until then, was unknown.
1562
The ownership of the Marble Plan is transferred to the people of Rome and the fragments are moved to the Capitoline Museum. Here, a major project to assemble and exhibit the fragments is undertaken by museum curator Pietro Forrier with the help of Giovanni Battista Nolli, soon to be famous for his own map of Rome.
1741-1742
Computer scientists and archaeologists at the University of Stanford are working in collaboration with the Soprintendenza of the Comune di Roma on the “Forma Urbis Romae Project”, employing digital technologies to try and reconstruct the map through computer-aided reconstruction algorithms able to place each fragment at the right place.

1990




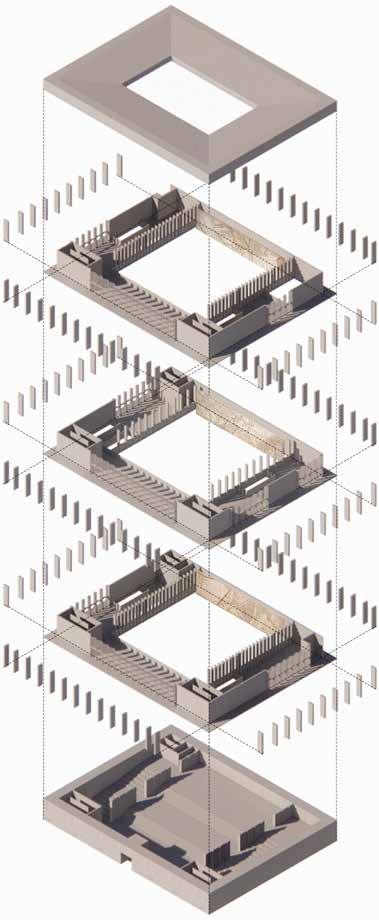
The first floor uses a stepped exhibition hall to adapt to the hillside topography.The second to fourth floors use double-height Spaces to display the map, while each floor also has split-level Spaces and small display Spaces to display the map fragments.The roof is provided with skylights to bring in light.


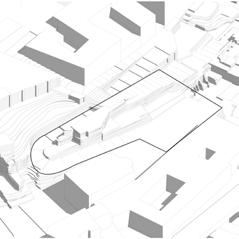
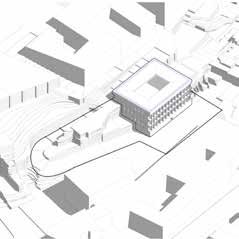
 The site is a hillside with many historic buildings around it.
The thrust of the volume in the middle of the cube forms the roof and base.
Facade design Flat columns column elevation brings rhythmic beauty and shading effect.
A cube rises from the site as the overall form of the building.
Cantilevered slabs are added to each floor to divide the facade, and skylights are inserted into the roof.
The site is a hillside with many historic buildings around it.
The thrust of the volume in the middle of the cube forms the roof and base.
Facade design Flat columns column elevation brings rhythmic beauty and shading effect.
A cube rises from the site as the overall form of the building.
Cantilevered slabs are added to each floor to divide the facade, and skylights are inserted into the roof.
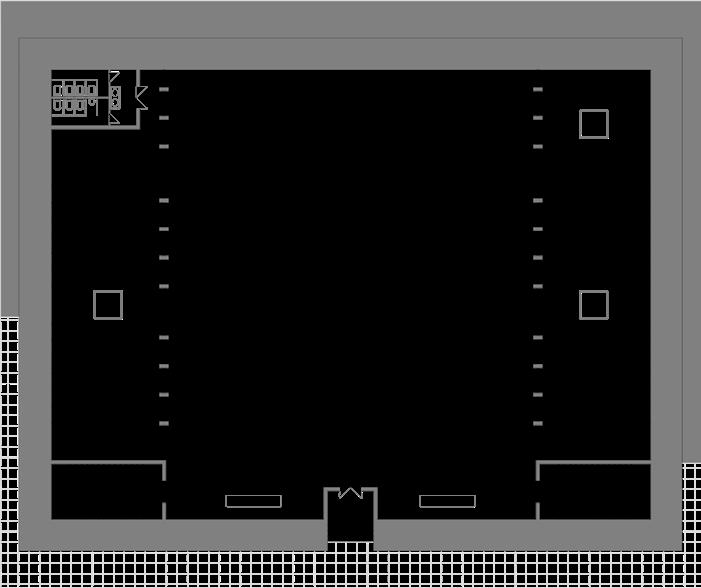

Looking through the columns
Daylight enters the architecture

Meeting concrete and wood floors

A regular array of flat columns


Light passing through the columns leaves regular shadows
Create the beauty of rhythm for the interior space
Skylights bring in sunlight to light the small exhibition halls on each floor. The double height space allows the different levels to relate to each other.Let people have a dialogue with the architectural light and shadow. Flat concrete columns are arranged in rows, separating the small exhibition hall from the full-height exhibition hall. Visitors enter a world of rhythm and light.An institutions for persons with physical and mental disabilities.
From the patient's feelings and needs, it is life and treatment. At present, institutions for the mentally and physically disabled at home and abroad are usually classified according to specific diseases, age groups or the degree of influence of patients on social order, and there is a lack of centralized and comprehensive institutions for dealing with patients.The building is designed as a conceptual design. The aim is to design a centre that accommodates people with multiple physical and mental disabilities simultaneously and provides targeted treatment and organic comfort.

Proportion of healthy people
Proportion of people with physical and psychological disorders
Constructed in the mid-20th century by the CIAM team ten, the mat building is a revision of the earlier modernist attitude of ignoring relationships and everyday life and emphasizing independent objects. Horizontal extension and texture characterize mat biulding.
Ancient Greek physicians believed that psychological abnormalities were caused by the flow of bad bodily fluids through the brain.

Psychological abnormalities and physical disabilities were considered demonic possession.
The so-called pagans, most of whom were actually mentally ill.
The causes of psychosis are attributed to psychological and social stress and, to a lesser extent, genetic and physical damage.
People believe that disability is a pathology, and disabled people are sick people.
Medical scientists believe that mental illness is mainly due to physiological disorders of the brain.
Disabled people are not useless "waste people", nor are they "patients" who are always in a sick state.
Linear-Person-toperson interactions. Spinal-Individual-toindividual, group-toindividual interaction.
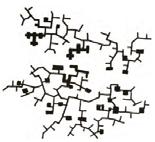
Serial progressionHuman behavior is from centralized to decentralized.
Centric-The distance between people is vaguely widened.
The structural relationship between society and life
It is flexible enough to accept changes in future use.
The overall complete network system Growth and change

From cell to cluster, from cluster to stem and from stem to mat. Master
Order and Organic
The plane presents an organic grid state, and this organic nature is divided by the connection of three layers and an ordered path system. All paths are based on the modulus of the time function, defined by 65.63M thus forming the order element grid.
According to the public buildings of different levels and attributes, the grid space still constitutes a public center and sub-center in different dimensions, so as to realize the spatial division of individuals and groups.




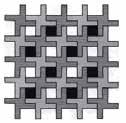

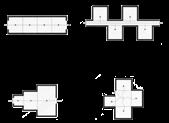


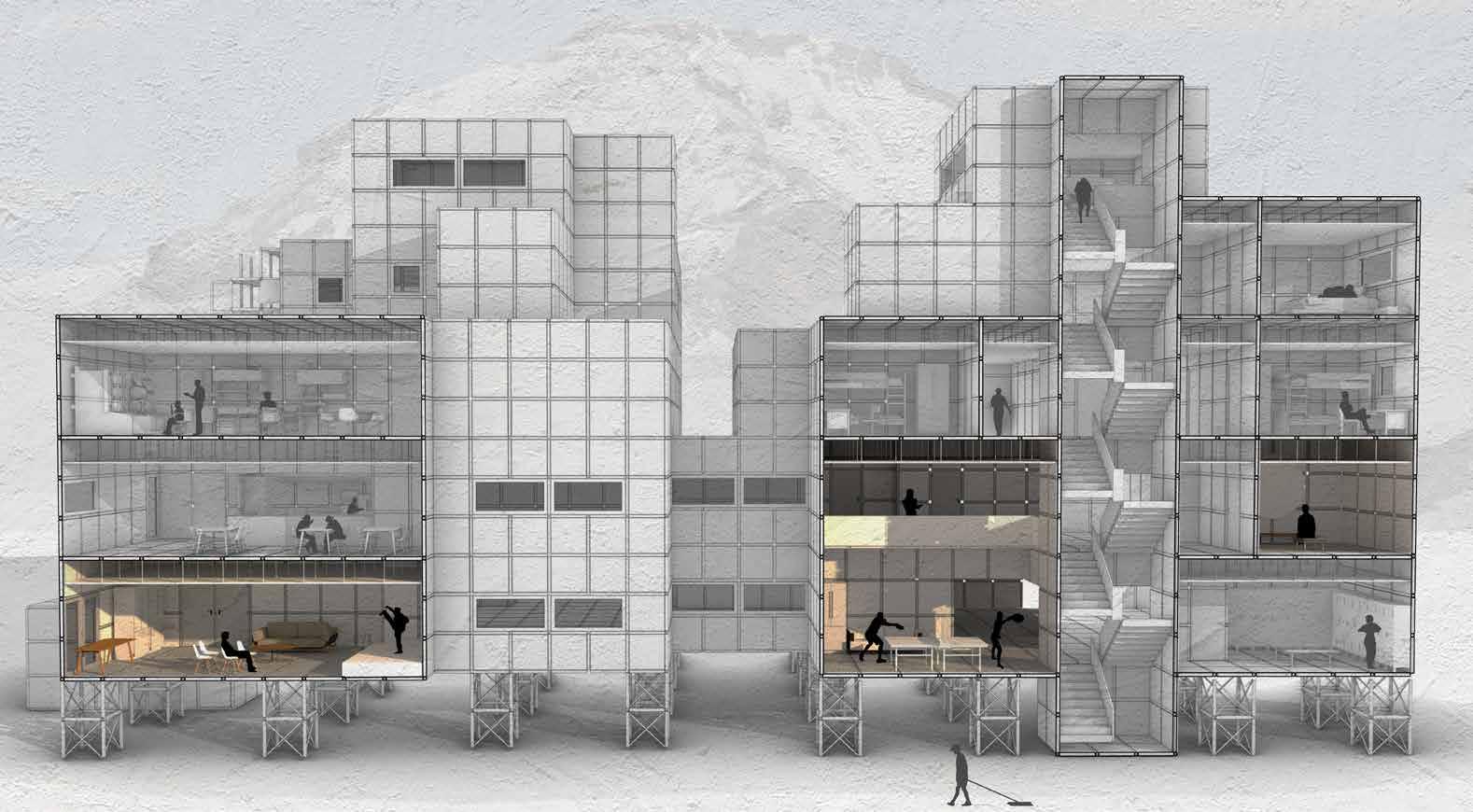
The first floor is a public service area, divided into four areas: treatment, education, business and kitchen.The second floor is a sheltered workshop and a sheltered farm.The third floor is the first residential area, which spreads outward through the central service area and opens up the space.The fourth floor has independent units, and the second floor of the compound units, connected by corridors.




The module of nurse station is arranged on both sides of the atrium on the first floor, in which there are nurse station, nurse rest room, toilet, utility room and building elevator.



The large unit adds more functional space, which can not only meet the basic life of the disabled, but also provide them with more complete space for diagnosis and treatment.
The function of small unit is simpler, provideing a concise, basic living space for the people with physical and mental handicap.
In the medium-sized unit, the number of rooms is increased to accommodate multiple patients at the same time.
Direct view of the roof garden
Standardized small recuperation space

Small, delicate and functional
Large areas of warm light
Provideing resting, visiting and recuperation functions
A large unit integrating various recuperation and leisure functions
The small unit has a variety of layout forms, but the overall plan and area remain the same. It can provide more intimate and comfortable private space and treatment space for people with physical and mental disabilities.


The large unit has an independent sunshine room for recuperators, and also has a relatively open reception space, which can provide rich social space and perfect recuperation function for the physically and mentally disabled.

Spatial renderings of recuperation residential areas The



The central area retracts the horizontal and vertical functional streamlines Rotary ramps provide convenience for people with disabilities Form a central
 The residential areas have flexible space and strong interactivity The layout of greening and public space improves the well-being of sanitarium.
Revolving ramps are arranged in the central traffic core. Four stairwells and some service spaces and auxiliary spaces are arranged in the four corners.
roof garden creates a comfortable natural environment for the building
The residential areas have flexible space and strong interactivity The layout of greening and public space improves the well-being of sanitarium.
Revolving ramps are arranged in the central traffic core. Four stairwells and some service spaces and auxiliary spaces are arranged in the four corners.
roof garden creates a comfortable natural environment for the building
It can be robotically built according to environmental and operational requirements.
Antarctic expedition cabins built on the last continent explored by man remind us of the significant physical and mental challenges endured by early explorers in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The project aims to build a modular research station in Antarctica that can be built using robots. The advantage of using robot automatic construction technology is that it can quickly build or dismantle the building function space according to the changeable extreme weather conditions in Antarctica, and reduce the loss of human and material resources in the construction of extreme weather.



The Antarctic Expedition Lodge, built on the last continent explored by humans, reminds us of the major physical and mental challenges that early explorers endured in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.


EXISITING PROBLEMS
FUNCTIONAL REQUIREMENTS

DIFFERENT SITUATIONS
More common spaces,
rooms are needed.
Extreme climates
The number of people living in the research station has been reduced to a minimum.



Holidays
More meeting space and consider the stage.


 The Antarctic continent has a harsh climate, heavy storms and snow, dry air and scarce precipitation.
Human activity Garbage Construction waste
Basic mode
relaxation
Climate Construction Waste Immutability Equipment Manpower
Bedroom Conference Room Restaurant Laboratory Gym
The Antarctic continent has a harsh climate, heavy storms and snow, dry air and scarce precipitation.
Human activity Garbage Construction waste
Basic mode
relaxation
Climate Construction Waste Immutability Equipment Manpower
Bedroom Conference Room Restaurant Laboratory Gym
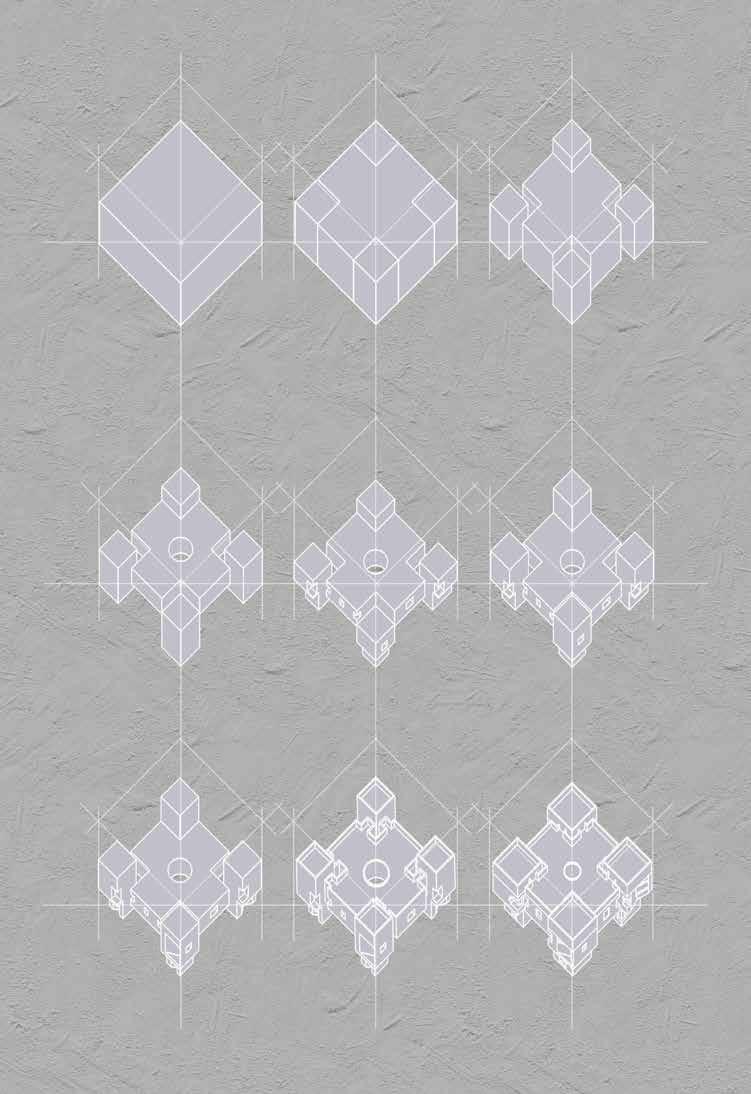
We choose a 20cm*20cm*20cm cube as the prototype of robot.













BASE MODULE


The standard mode can carry up to 30 people for many kinds of use with small clinic and plant growing room.


MODULE PLATE











MODULE SHIPPING
VERTICAL CHANNELS

HORIZONTAL CHANNELS




The polar night mode has artificial light rooms, and mainly focuses on the basic survival needs of personnel and simplifies the office space.


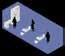












BEDROOM RECREATION ROOM
Alphabets
The severe weather mode lowers the height of the building to withstand wind and snow, reduces some nonessential functional space.
The festival mode increases the recreational space for people to socialize and relax, and it has both experimental and living functions.

KITCHEN
nodes and components assembly into parts


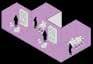


LABORATORY
Words
LIVING ROOM OFFICE
Sentences
composition into spaces and rooms buildings and blocks
Paragraphs

With theater and entertainment space
Promote personnel exchanges and cooperation
It has both scientific research and entertainment functions
Take the lab as the core
Provide complete scientific research facilities and corresponding space
It is the basic mode of scientific research station
The festival mode can provide researchers with more relaxing entertainment activities during their research life in Antarctica, as well as communication and cooperation with other research stations around.
It has the basic experimental and living space of an Antarctic research station, and is equipped with some indoor greenhouses. It can meet most of the daily research needs of researchers.


Centralized dormitory and survival warehouse as the core Functional spaces are reduced and integrated The interior layout is more compact and efficient


It has artificially lit rooms
Focus on the psychological condition of personnel under polar night conditions
It disassembled the redundant auxiliary functional space, leaving only the most basic essential functional space to cope with the extreme Antarctic weather.
The artificial light room and psychological counseling room can relieve the psychological pressure of the staff under the condition of extreme night for a long time. Polar night model has both basic life and experimental work conditions.
Other works during my undergraduate architecture studies.



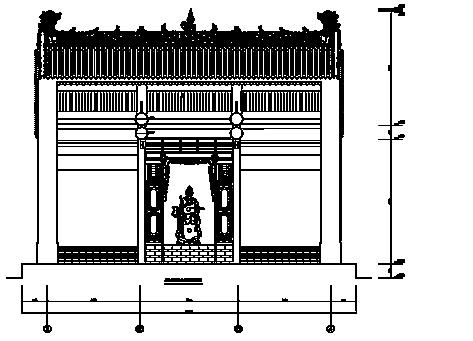
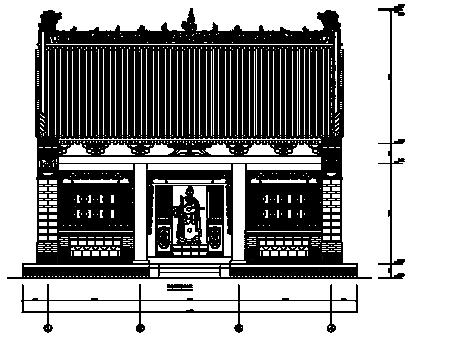
SURVEYING AND MAPPING OF ANCIENT BUILDINGS