FALL 2024


FIRE Semester 1
Role of Alternative Fuel Vehicles in Mitigating Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Listening to Indigenous Communities. Climate Action as an Image Event. Music & Environmental Activism. Mass Media & Responsibility in Coverage of Climate Change. Climate Change Local to Age. Pop Culture & Climate Change Action. Fanning the Flames: Human Impacts
Infographic Competition

o h d ildfi G i ll E i d
Centering Climate Change
This Fall 2024, FIRE Semester 1 students engaged in an exploration of a range of research topics central to better understanding one of the Grand Challenges of our time: Climate Change.
FIRE Semester 1 students identified one of eighteen topics to investigate over the course of the semester. Topics spanned a range of research fields and disciplines, including social sciences, natural sciences, physical sciences, and humanities. These topics showcased the diverse ways researchers approach climate change, highlighting the multifaceted nature of this critical issue.
Throughout the semester, teams read and reviewed literature, compiled Annotated Bibliographies, developed and refined research questions, delivered research pitches, and designed infographics to synthesize and share their findings.
Teams were invited to enter their Infographics into an infographic competition. FIRE Faculty Leaders, FIRE Admin, and Academic Peer Mentors selected the top infographics developed by FIRE Semester 1 Teams. Selected infographics are presented in the following pages.
AgeandAttitude: Climatechange divide

Age and Attitude: Climate Change Divide Title
ClimateChangeisthechangeinenvironmentalconditions,suchas temperature,rainfall,airquality,andsoon,overaperiodoftime
“younger generations whatisthetopicandmainpoint?
Ourtopic,ClimateChangetoAge,isabouthow differentgenerationsthinkaboutclimatechange, howtheyarebeingimpactedbyit,andwhat they’redoingaboutthisissue Themainargument aboutthistopicisthatoldergenerationsare greedyanddonotcareaboutourclimate However,afterreadingmanyarticles,thisisnot true Theperceptionsofbothyoungerandolder generationsaremoresimilarthenyoumaythink
Comparingthedifferent generationsofage
GenerationZ(1997-2012)andGeneration Alpha(2010+)
“older
generations
BabyBoomers(1946-1964)andGeneration X(1965-1980) Attitude
Creators
Micah Hoover, Shu Leong, Owen Serra, & Bethel Teklu
Description from Creators
YoungerGenerationsareoftenmoreaware ofclimatechangeanditsimpacts,asitis morewidelyreportedinthemedia They tendtohavehigherlevelsofnegative emotionsassociatedwithclimatechange, likeanxietyorworryaboutthefuture
Actions Attitude
YoungerGenerationsaremorelikelyto participateinmovements,make sustainableLifeChoices,andsupport positiveenvironmentalpolicies3
Others
Socialmedia,popculture,andsocialcircles greatlyimpactyoungergenerationsandtheir perspectivesonclimatechange Although theytendtochangesomeoftheiractions, theystillsupportcelebritieswhohave significantcarbonfootprints(Ex Taylor SwiftandKimKardashian)5
There'samuchmoresignificant variationbetweentheinformedand theuninformedinolderGenerations Whileyoungergenerationsaremore skepticalaboutpolicymakers,older Generationsaremoreskepticalabout thewholeconceptofclimatechange
Others 3 Actions
SimilartoyoungerGenerations,older Generationsdoparticipatein sustainableLifeChoices,Community involvement,andsupporting environmentalpolicies
OlderGenerationsaremoresusceptible toadversehealthoutcomesbecauseof climatechange1Additionallythereisa historicalcontextonhowtheir perspectiveshavebeenshaped
Collaborativesolutionsacrossgenerations
Promoteintergenerationaldialogue CommunityInitiatives
intergenerationalharmony hosteducationalprograms hostintergenerationalpanels shareresources utilizesocialmedia respect
hostlocalclean-ups sustainabletransportation energyefficiency communicateopenly reduce,reuse,recycle advocateforchange
“The main message of our infographic is that younger and older generations view climate change more similarly than most people believe. We discussed the attitudes and actions of each generation, as well as other factors that could impact their views. We also want to address some ways to promote intergenerational dialogue and protect our Earth.”
GenerationforChange
Title
Antibiotic Resistance and Climate Change
Creators
Anna Leight, Keara Ragasa, Anushka Sharma, & Sophia Villar
Description from Creators
“The purpose of the infographic is to educate the general public and raise awareness surrounding the issue of rising antibiotic resistance observed in microbial communities as a result of climate change. Research on this issue is relatively new and emerging, but it poses great risks to human and environmental health, making it imperative for measures to be taken to address climate change and/or antibiotic resistance.”
ANTIBIOTICRESISTANCE AND CLIMATECHANGE

WHAT
Long-termshiftsintemperatureandweather patterscausedbybothnaturalcyclesand humanactivities
Examplesinclude:Burningfossilfuels&the albedoeffectonicecaps
EFFECTS

Risingglobaltemperaturescreatefavorable environmentsformicrobialorganisms,leading toariseinantibioticresistanceincommon pathogens Antibioticresistancecontinuesto riseasantibioticsareusedmorefrequentlyto combatthesepathogens
IMPACT
IncreasedInfectionRates: Asbacteriabeginstoevolve whichmakesinfectionsharder totreat
AgriculturalContributionto Resistance:Overuseof antibioticscancauseresistant bacteriatotransfertohumans throughfoodconsumption
EnvironmentalSpreadof ResistanceGenes:Resistant bacteriaandtheirgenes spreadthroughwatersystems whichincreasetheriskof cross-speciesinfection
SOLUTIONS
ClimateChange&Disease
Spread:Risingtemperaturesand extremeweathereventscan increasetherangeofdisease carryinginsectswhichincrease thespreadofdiseaseslike malaria
FoodSecurityThreats:Climate changeaffectscropyieldsand reducesfoodavailability,while antibiotic-resistantbacteria threatenanimalgroupsthatare essentialforfoodproduction
Biodiversity:Bothclimate changeandantibioticresistance threatenbiodiversity,whichcan destabilizecriticalecosystems
GETVACCINATED
Vaccinationshelppreventdiseasesthatrequireantibiotics BEENVIRONMENTALLYFRIENDLY
Toreducetheimpactofclimatechangeonantibiotic resistance,practicingenergyefficiencyandsustainable practicescancontributetoaslowerrateofglobalwarming
SPREADTHEWORD
Educateothersaboutclimatechangeandantibioticresistance andencouragechange
M Savage V &Yeh P (2020) CompoundngEffectsofCimateWarmngand AntibotcResstance iScience 23(4) 101024 https://doiorg101016/ isc 2020101024
2MacFadden,D R,McGough S F,Fisman D Santilana M,&Brownsten J S (2018) Antibioticresstanceincreaseswithloca temperature NatureClimateChange 8(6) 510–514 https:/doiorg/101038/s41558-018-0161-6
3Santos-Lopez A Marshal C W Haas A L Turner C Rasero J &Cooper V S (2021) Therolesofhstory chance andnatura selection intheevolutionofantibioticresstance eLife 10 e70676 https:/doiorg/107554/eLife70676
4Chavez J (2023 February7) Climatechange scontributingtotheriseofsuperbugs newUNreportsays CNN https//wwwcnncom/20230207heathsuperbugs-clmate-change-scnindexhtml
Theintendedaudienceofthisinfographicisthegeneralpublic,specificallyurban communities Bothdiseaseandvectorsfordiseaseareeasilyspreadinurbanenvironments Furthermore,urbanenvironmentstendtohavesignificantgreenhousegasemissions,andare impactedheavilybyclimatechange Thesefactorsmakeitimperativeforcommunity memberstobeawareoftheongoingresearchandpotentialdangersoftheriseof antibioticresistancethathascomeasaresultofclimatechange

Title
Biodiversity and Ecology Conservation
Creators
Emily Fisher, Eleanora Watson, Advait Anilal, & Nick McGonigle
Description from Creators
“The main message we were trying to convey was how to solve the problems surrounding biodiversity and ecology conservation, specifically concerning plants and animals. We used a specific example to tie in our main ideas and give the reader a real-world example of why this is such an issue and how it contributes to the growing climate change problem.”
Title
The Impact of Responsible Coverage
Creators
Kousalya Potti, Gwen Baker, Onkar Bajwa, & Sithil Meegoda
Description from Creators
“Our infographic aims to help FIRE students recognize the bias in media coverage of climate change. We highlight how media often frames climate change through political and economic lenses, which can influence public attitudes. We encourage FIRE students to seek diverse and reliable sources to avoid being misled on this crucial issue.”

TheImpactof Responsible Coverage
PublicPerceptionMatters
Mediacoverageinfluenceshowthepublic understandstheclimatecrisis
Evidencebasedreportingisessentialfor understandingthedegreeofthecrisis
Only48%ofAmericansbelieveinhumancausedclimatechangewhile20%saythat thereisnosolidevidenceforthis




GatewayBeliefModel



FlawintheU.SMedia Coverage
Atheorythatexplainshowpeople’s attitudesshiftbasedontheir perceptionofthescientific community’sstanceonanissue
80%ofpeopleexposedtoscientific consensusreportingaremorelikelyto believeinclimatechange
Only7%ofAmericansarewillingto trustthemediatolearnaboutclimate change

USmediaoftenframesclimatechangethrough politicalandeconomiclenses
Leadstopolarizationanddoubt Incontrast,Frenchmediafocuseson environmentalandmoralresponsibility
Createspublicsupportforclimateaction
WhyMediaResponsibilityMatters

Sources:

Presentingclimatedenialasequalto scienceconfusesaudiences
Misleadingorbiasedcoverageweakens publicsupportforclimatesolutions U.Smediamustdoabetterjobofpresenting evidencebasedinformationthatbuilds publictrust
Ensuresthataudiencesfeelinformed andconfidentaboutthefacts

BarkemeyerR,Figge,F,Hoepner,A,HoltD,Kraak,JM&Yu,P-S(2017)Mediacoverageof climatechange:AninternationalcomparisonEnvironmentandPlanningC:Politicsand Space,35(6),1029–1054https://doiorg/101177/0263774x16680818 Boykoff,MT,&Boykoff,JM(2007)Climatechangeandjournalisticnorms:Acase-study ofUSmass-mediacoverageGeoforum,38(6),1190–1204 https://doiorg/101016/jgeoforum200701008
BrüggemannM&EngesserS(2016December30)Beyondfalsebalance:How interpretivejournalismshapesmediacoverageofclimatechangeGlobalEnvironmental Changehttps://wwwsciencedirectcom/science/article/pii/S0959378016305209 Funk,C(2016,October4)1publicviewsonclimatechangeandclimatescientistsPew ResearchCenterhttps://wwwpewresearchorg/internet/2016/10/04/public-views-onclimate-change-and-climate-scientists/ Young,N&Dugas,E(2012)ComparingClimateChangeCoverageinCanadianEnglishandFrench-LanguagePrintMedia:EnvironmentalValuesMediaCultures,andtheNarration ofGlobalWarmingTheCanadianJournalofSociology/CahiersCanadiensdeSociologie, 37(1),25–54http://wwwjstororg/stable/canajsocicahican37125
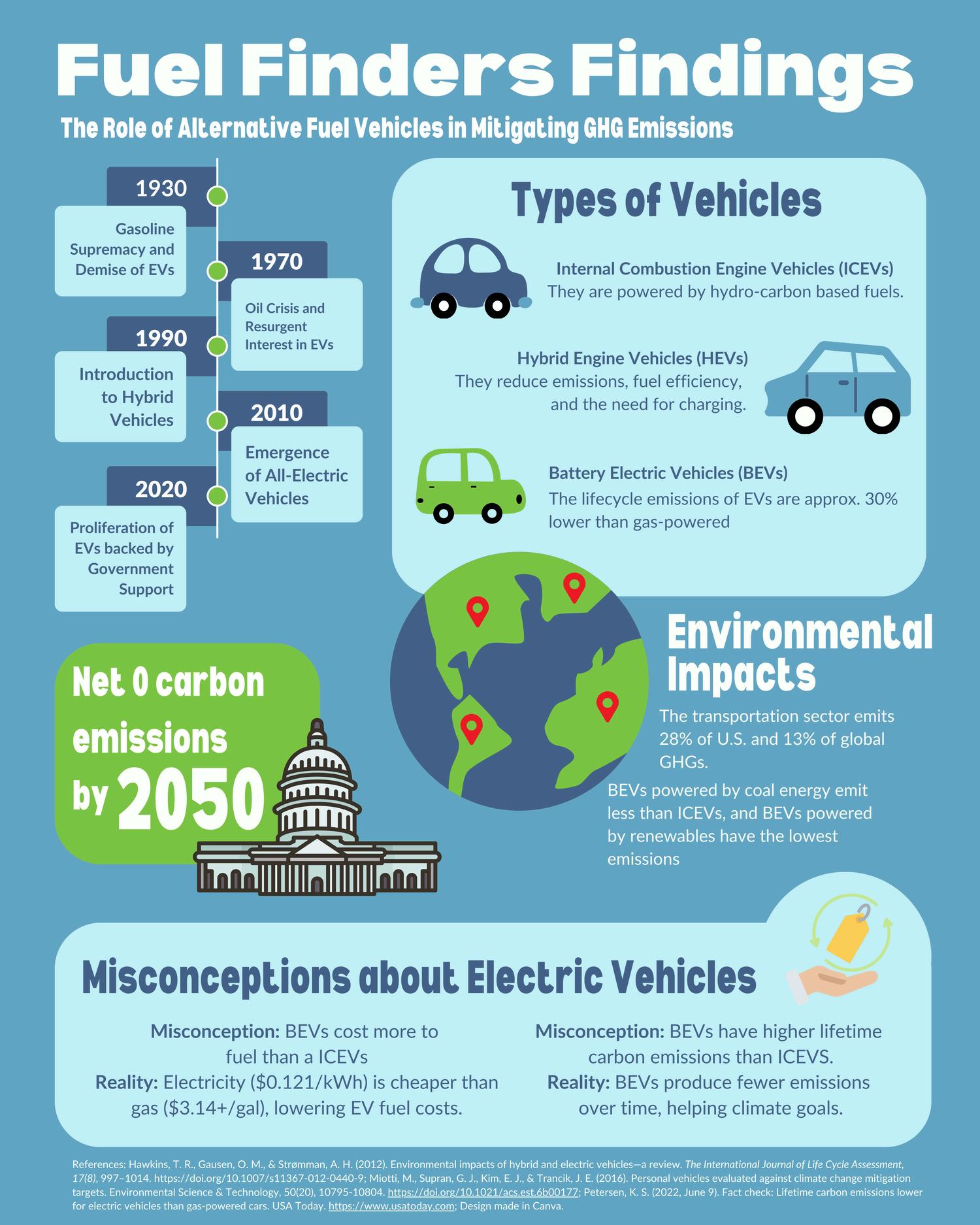
Fuel Finder
Findings Title
Creators
Zoey Katz, Bhavesh Mantrabuddi, Eric Li, & Kaushal Gorla
Description from Creators
“The infographic explains the history of electric vehicles and also goes over the environmental impacts of different types of vehicles. The infographic also covers some consumer misconceptions about electric vehicles that some people may have.”