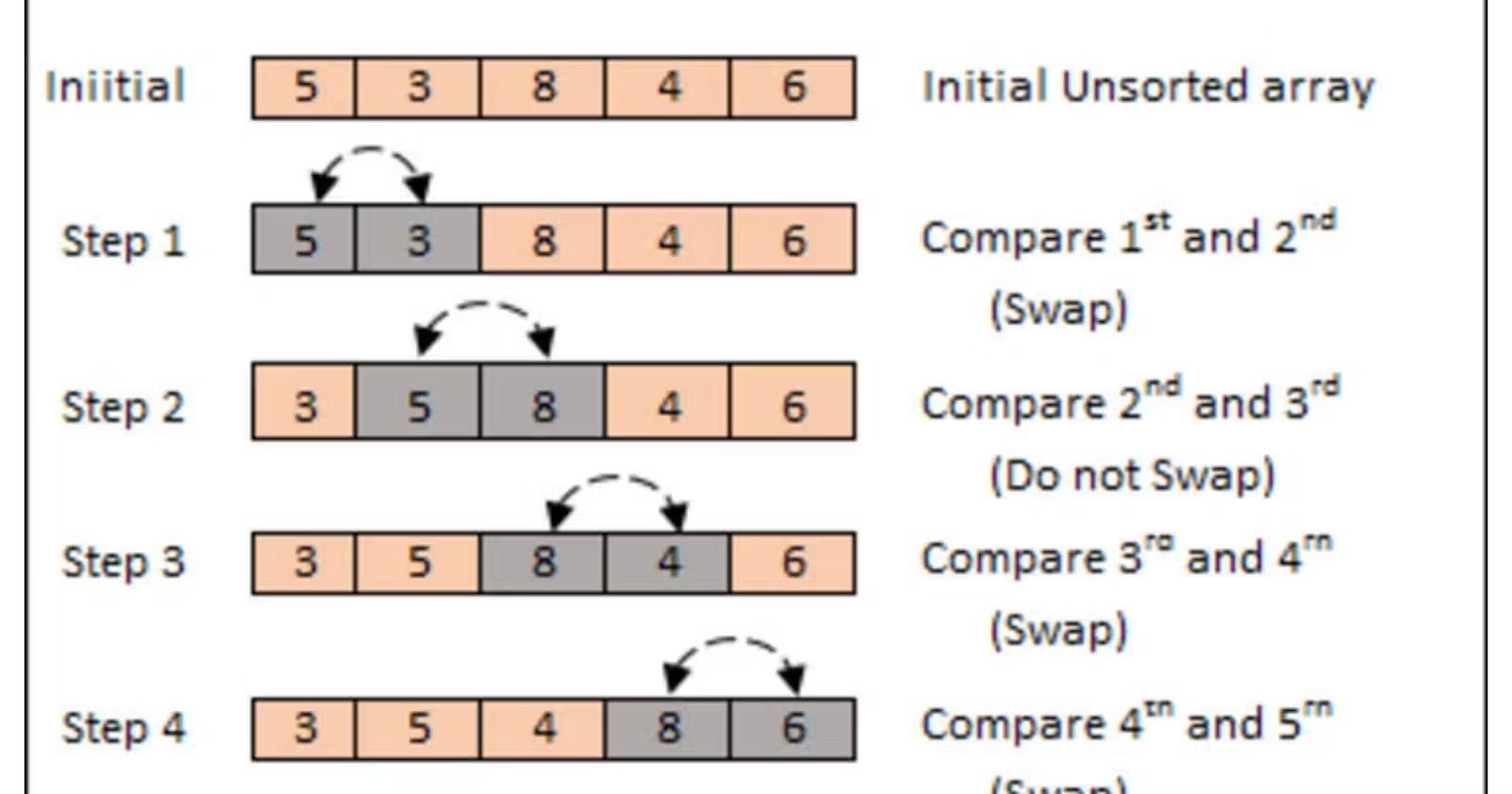
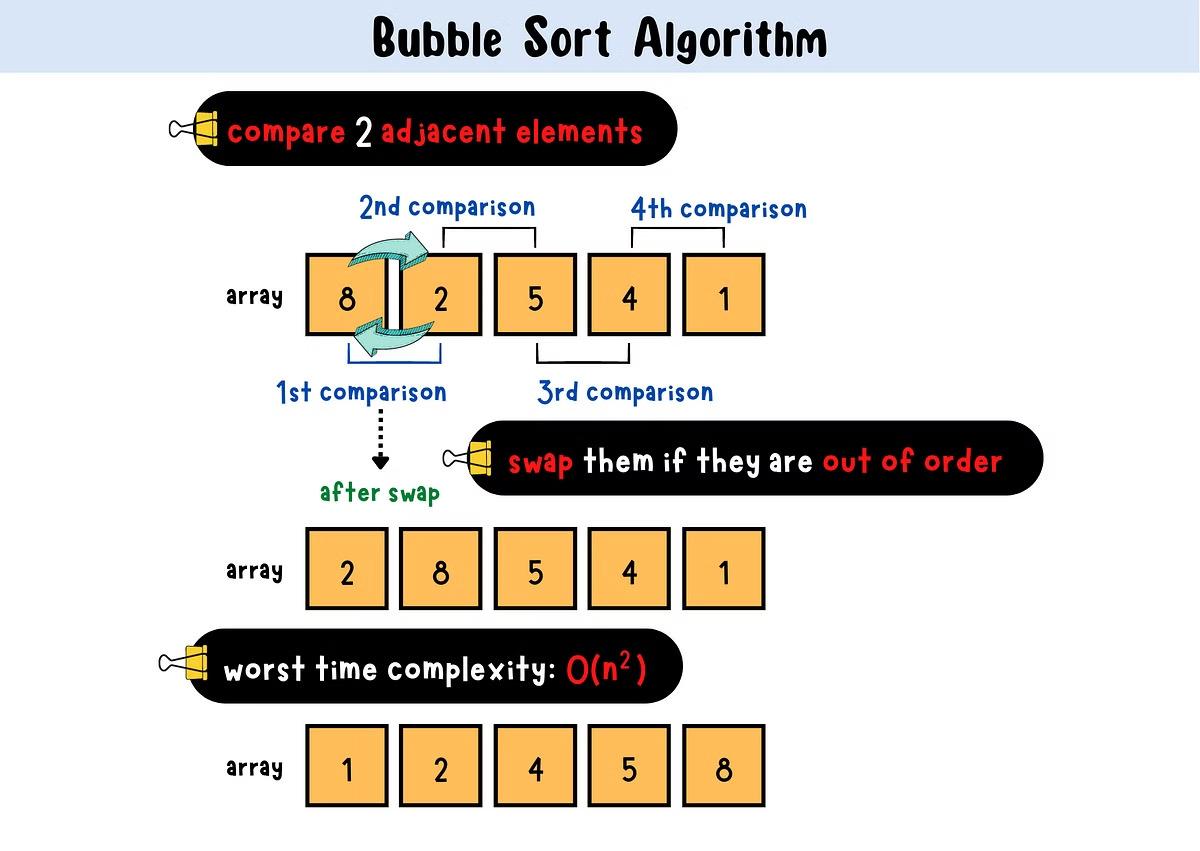
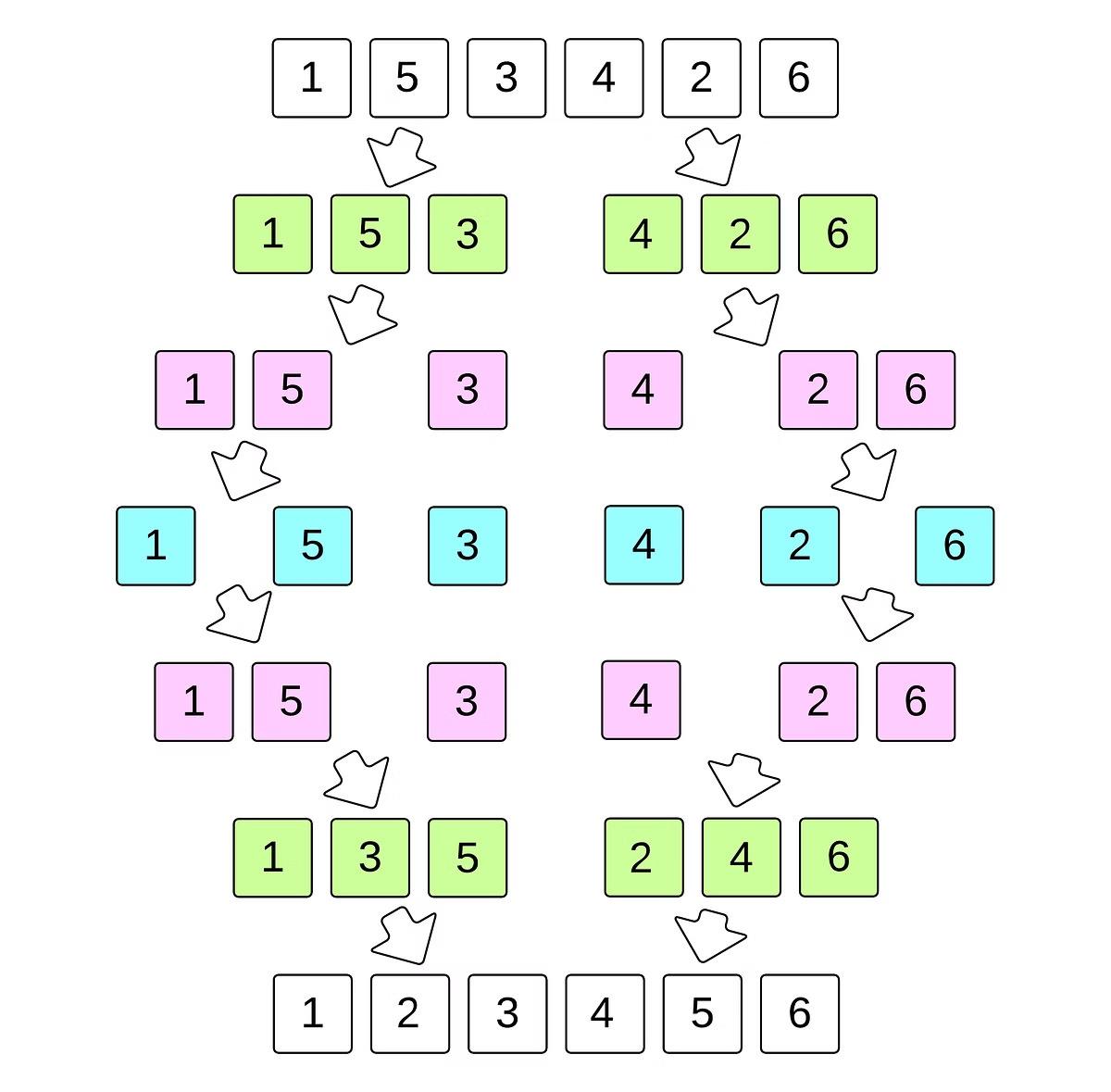
Introduction to Alphabetical Order in Java
Learn how to sort strings in Alphabetical Order in Java with this comprehensive guide. Alphabetical order is a fundamental concept in Java programming. It involves arranging elements, such as strings or arrays, in a specific order based on the Unicode values of the characters. Understanding alphabetical order is crucial for effective data organization and manipulation in Java applications.