ANTONIO OLEA
ARCHITECTURE PORTFOLIO REVISION 02.2023
LANDSCAPE
EDUCATION
CALFORNIA STATE POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY, POMONA
Master of Landscape Architecture
• Graduation pending May 2024
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, FRESNO
Bachelor of Science, City and Regional Planning
• Certificate, Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
• Certificate, Environmental Planning
FRESNO CITY COLLEGE, FRESNO 2019
A.S Business Administration
SKILLS
DESIGN:
Pro Landscape
Visual Plan Making
ArcGIS

Morpholio Trace (iPad)
AutoCAD
RHINO
Twinmotion
Adobe (Indesign,Photoshop, Illustrator)
Blender
COMPUTER APPLICATIONS:
Microsoft Suite, Quickbooks, Google Earth Pro
AFFILIATIONS
Member, Escondido Democratic Club
Member, San Diego Botanic Garden
Member, California Garden & Landscape History
Society
Student Member, American Society of Landscape Architects
WORK EXPERIENCE
DULEY’S LANDSCAPE, INC (FRESNO, CA) August 2017- July 2021
PROJECT ADMINISTRATOR/ PROJECT ESTIMATOR
• Developed necessary paperwork for bid creation and project execution—including, Material Submittals, As-builts, Bid Sheets, and Project Bidding Documents
• Integrated computer programs to effectively calculate material and visual designs for estimating potential projects
• Collaboration with owner in bid creation for commercial jobs ranging from 50K to 500K throughout the Central Valley
• Analyzing and evaluating landscape and irrigation architectural plans to assist project managers and laborers
GREEN PERSPECTIVES, INC. ( San Diego/ Orange County) September 2015– August 2017
OFFICE MANAGER
Manage Office operations for landscape company initiating with 20 employees and growing to over sixty.
All aspects of growth including:
• Payroll issues and resolutions along with new employee onboarding Workers’ compensation management including:
• Injury reporting, insurance liaison, policy updating, and implementation of new procedures
• Managing automobile, general liability, and umbrella insurance
Accounts payable / accounts receivable including:
• Estimation creation, invoicing (partial bills, retention, collection of W-9, and other IRS Documentation)
• Employee record keeping in accordance with state of CA laws
STARBUCKS COFFEE CORPORATION, (San Diego/Fresno) February 2015 – October 2020
BARISTA, TRAINER
• New barista training: development of new barista by providing on-going coaching and performance feedback
• Assist in role planning, risk management, and meeting customer sales goals
ACCOMPLISHMENTS
SCHOLARSHIP RECIPIENT | California Planning Association
Central Chapter (August 2020)
TONY OLEA PHOTOGRAPHY | San Diego, CA 2013-2018
• Established successful photography business
• Create visual videography and photography shoots for special events
TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS
PROJECT HIGHLIGHTS
01- POLLUTION PAST BORDERS - Transborder Landscapes Workshop
Summary: Transborder Landscapes examines the Tijuana River juxtaposed between US and Mexico. San Diego and Tijuana face contrasting economies, cultures, and policies, despite the shared landscape. This dual governance led to the demise of the river landscape because of largely opposing agendas between the two nations.
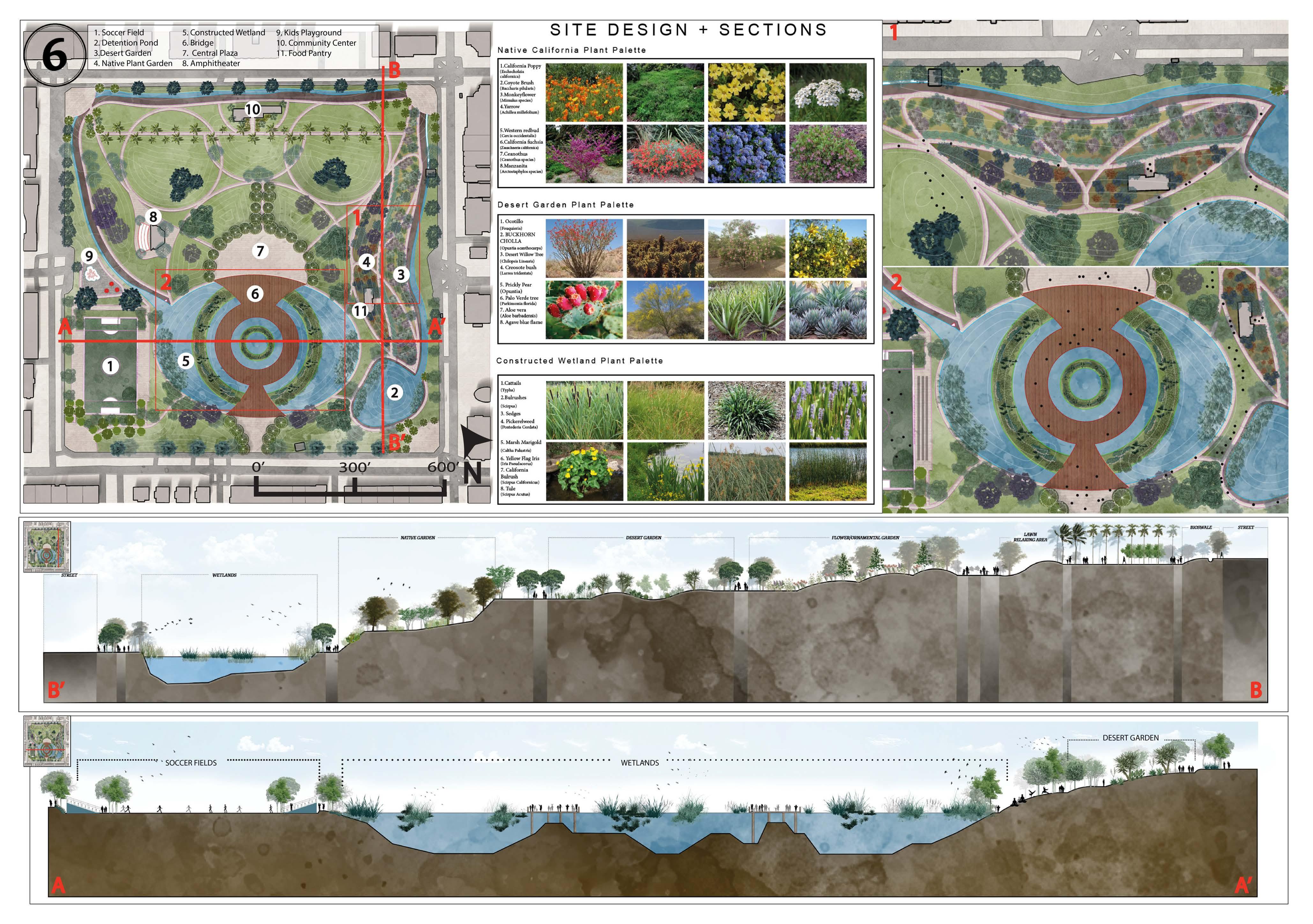
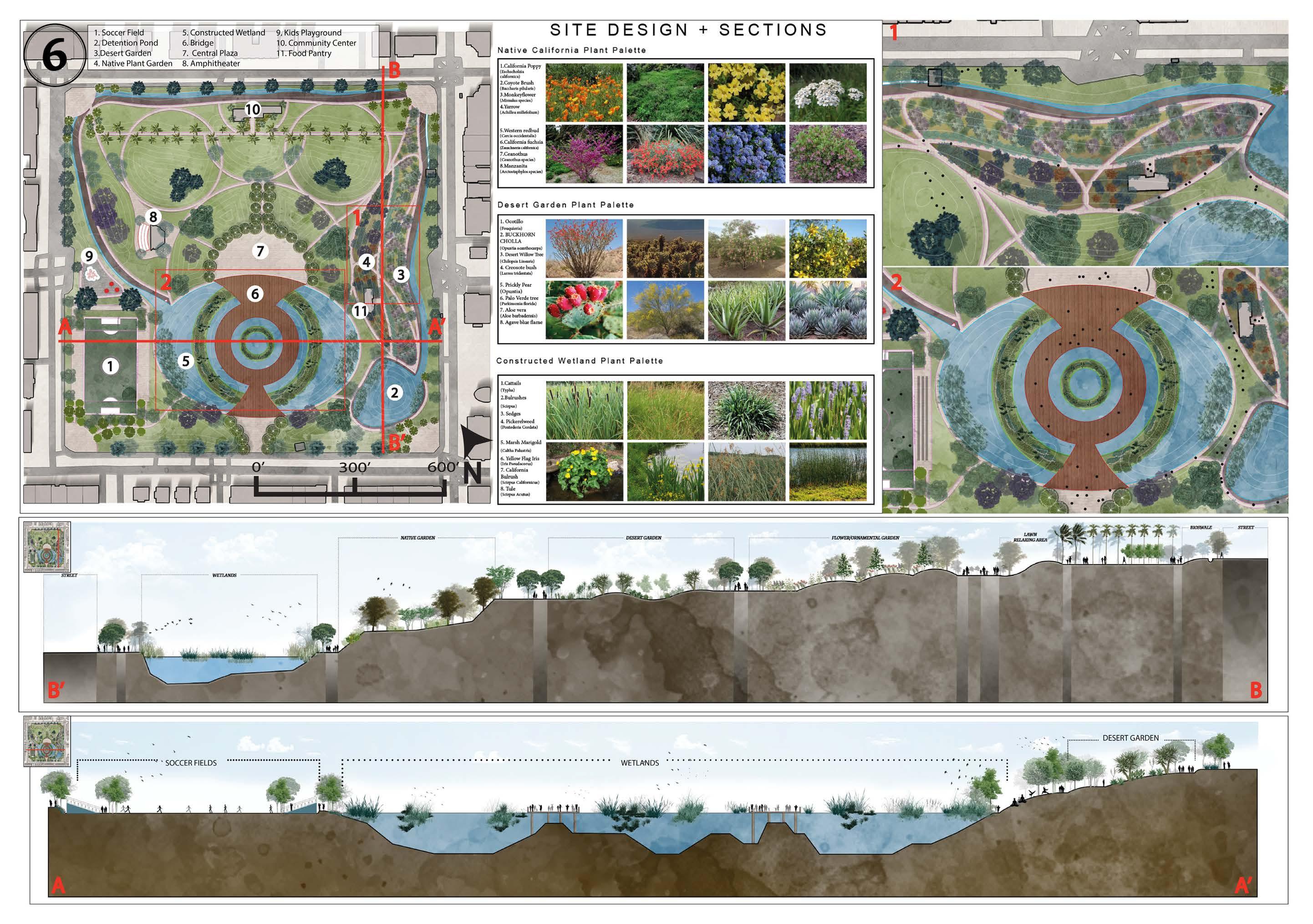
02- PARQUE DE REFUGIO
Summary: Fall 2022 Studio project focused on redesigning Macarthur Park in Los Angeles County that focused on ecological planning and community.
03 - RESIDENTIAL MODELLING
Summary: Project focused on rendering a 2D plan into 3D space through multiple graphic design programs.
04 - GIS WORK
Summary: Project spread showcases GIS capability and strategies used to further improve design through data representation through mapmaking and visualization of natural systems at a state and local level.
TRANSBORDER LANDSCAPES WORKSHOP (SAN DIEGO, CA)
POLLUTION PAST POLLUTION PAST BORDERS BORDERS
- Water Sensitive Areas



POLLUTION PAST POLLUTION PAST BORDERS BORDERS
PROJECT AGENDA



Workshop Directors: Jimmy Ta, Raul Bielsa
Location: San Diego, CA
Attended: May 2022
Project Partner: Andy Sett

- Ecological Significance
SAN DIEGOx TIJUANA SAN DIEGOx TIJUANA
Transborder Landscapes Programme is a 3-year long-term research on the US/MX

POLLUTION PAST POLLUTION PAST
- Endangered Species Waster
Workshop Agenda
Transborder Landscapes Programme is a 3-year long-term research on the US/MX Transborder Landscapes, addressing complex socio-political, climate and territorial questions.
Transborder Landscapes examines the Tijuana River juxtaposed between US and Mexico. San Diego and Tijuana face contrasting economies, cultures, and policies, despite the shared landscape. This dual governance led to the demise of the river landscape because of largely opposing agendas between the two nations.

Home Sewage Waste


Plastics and Metals
Industrail Byproduct




DISTINCT ENVIRONMENTS


In response to the socio-economic impact the landscape poses, Transborder Landscapes looks at the Tijuana River, an interface between San Diego and Tijuana, to inform policy through design interventions, cartography, and agency through the local communities. The course will look at the geomorphological process of the region and the methods in which each country manages the river. The stark differences between the two countries will be examined at the local level and the impacts it poses through its landscape.
San Diego’s natural environment of the river consists of a natural landscape from the border to imperial beach of riparian scrub and coastal sage scrub.

Visiting the site we ivestigated the importance continually testing the bodies of water and determining proper handling of sensitive areas that are prone to impact of existing wildlife. We visited the Tijuana Estuary visitor center, located on the north side of the river, then made our way to the southern part of the river, where the border lies on on a beach where Mexico and the United States meet.
PROJECT GOALS
The city of Tijuana has seen exponential growth in domestic and foreign businees entering the country for cheap labor. Understand the economics of both countries, we can determine that if the economy is growing and the need of production is increasing, the city of Tijuana can expect maquiladoras, fabricas and manifacturas being established. Determining from our map, we conclude that industrial zones will be impacted, which can then contribute to the overall pollution and health of Rio Tijuana, which can be detrimental to the ecological sensitive areas of the river on the San Diego side.
Overall, there are no simple solutions that both countries can agree with, but through our efforts of map design and GIS data we are able to make an impact on the decision-makers of our government representatives to create eco-friendly policy.
PROJECT GOALS
San Diego and Tijuana have created a convergence of cultures and economic prosperity over the last century. Both nations have created a new wave of socio-political and environmental issues that have impacted the unique landscape of the Tijuana and San Diego River. This project focuses on the diverse landscape on both regions of the border and its established conditions that have been obstructed by polluters caused by manufacturing and other sectors of production. The goal of the project is to locate and determine the critical locations in Tijuana that have a high probability of contamination of the Rio Tijuana.
E E EE E
We located all major maquiladoras, fabricas, and manifacturas that have established business in sensitive areas that have continually impacted the health and safety of Rio Tijuana. These industrial sectors are represented as ‘+’ symbols on the map, and the different colors on the Tijuana region represent residential, commercial, and industrial areas that also dwell in within sensitive areas of the Rio Tijuana. In comparison on the San Diego region, we focused on the environmental conditions of the unique landscape that Rio Tijuana has created as the river flows out of Imperial Beach in San Diego. We used GIS data to demonstrate environmentally sensitive areas, which consists of areas where endangered species, wildlife, and incorporate areas of biological significance that is established on the clean water act. The different shades of blue display the range of historical habitats. The wide range of ecological diversity within the Rio Tijuana are examples of the urgency to continually support healthy practice to protect the life that the river brings.
the San Diego region, we focused on the environmental conditions of the unique landscape that Rio Tijuana has created as the river flows out of Imperial Beach in San Diego. We used GIS data to demonstrate environmentally sensitive areas, which consists of areas where endangered species, wildlife, and incorporate areas of biological significance that is established on the clean water act. The different shades of blue display the range of historical habitats. The wide range of ecological diversity within the Rio Tijuana are examples of the urgency to continually support healthy practice to protect the life that the river brings.
will be impacted, which can then contribute to the overall pollution and health of Rio Tijuana, which can be detrimental to the ecological sensitive areas of the river on the San Diego side.
- Water Sensitive Areas - Ecological Significance - Endangered Species Waster Water, Industrial Byproduct, Trash DISTINCT ENVIRONMENTS Home Sewage Waste Plastics and Metals Industrail Byproduct San Diego’s natural environment of the river consists of a natural landscape from the border to imperial beach of riparian scrub and coastal sage scrub. Visiting the site we ivestigated the importance continually testing the bodies of water and determining proper handling of sensitive areas that are prone to impact of existing wildlife. We visited the Tijuana Estuary visitor center, located on the north side of the river, then made our way to the southern part of the river, where the border lies on on a beach where Mexico and the United States meet. The city of Tijuana has seen exponential growth in domestic and foreign businees entering the country for cheap labor. Understand the economics of both countries, we can determine that if the economy is growing and the need of production is increasing, the city of Tijuana can expect maquiladoras, fabricas and manifacturas being established. Determining from our map, we conclude that industrial zones
Historical Habitats Alkali meadow complex High marsh transition zone Beach Dune Grassland Coastal sage scrub Mudflat/Sandflat Perennial freshwater wetland Pond River channel River wash Riparian scrub Salt flat Open water Salt marsh Subtidal water Vernal pool
Transborder Landscapes, addressing complex socio-political, climate and territorial questions. Transborder Landscapes examines the Tijuana River juxtaposed between US and Mexico. San Diego and Tijuana face contrasting economies, cultures, and policies, despite the shared landscape. This dual governance led to the demise of the river landscape because of largely opposing agendas between the two nations. In response to the socio-economic impact the landscape poses, Transborder Landscapes looks at the Tijuana River, an interface between San Diego and Tijuana, to inform policy through design interventions, cartography, and agency through the local communities. The course will look at the geomorphological process of the region and the methods in which each country manages the river. The stark differences between the two countries will be examined at the local level and the impacts it poses through its landscape.
Environmentally Sensitive Areas Flowlines
- AA Visiting School
San Diego and Tijuana have created a convergence of cultures and economic prosperity over the last century. Both nations have created a new wave of socio-political and environmental issues that have impacted the unique landscape of the Tijuana and San Diego River. This project focuses on the diverse landscape on both regions of the border and its established conditions that have been obstructed by polluters caused by manufacturing and other sectors of production. The goal of the project is to locate and determine the critical locations in Tijuana that have a high probability of contamination of the Rio Tijuana. We located all major maquiladoras, fabricas, and manifacturas that have established business in sensitive areas that have continually impacted the health and safety of Rio Tijuana. These industrial sectors are represented as ‘+’ symbols on the map, and the different colors on the Tijuana region represent residential, commercial, and industrial areas that also dwell in within sensitive areas of the Rio Tijuana. In comparison on
Water, Industrial Byproduct, Trash
0 0.8 1.6 2.4 3.2 0.4 Miles Tijuana Maquiladoras E Tijuana Manifacturas E Tijuana Fabricas E Legend Dispersed Residential residential Commercial
TRANSBORDER LANDSCAPES
Transborder Landscapes Programme is a 3-year long-term research on the US/MX Transborder Landscapes, addressing complex socio-political, climate and territorial questions. Transborder Landscapes examines the Tijuana River juxtaposed between US and Mexico. San Diego and Tijuana face contrasting economies, cultures, and policies, despite the shared landscape. This dual governance led to the demise of the river landscape because of largely opposing agendas between the two nations. In response to the socio-economic impact the landscape poses, Transborder Landscapes looks at the Tijuana River, an interface between San Diego and Tijuana, to inform policy through design interventions, cartography, and agency through the local communities. The course will look at the geomorphological process of the region and the methods in which each country manages the river. The stark differences between the two countries will be examined at the local level and the impacts it poses through its landscape. - AA Visiting School Tijuana Residential Tijuana Commercial Tijuana Industrial E E EE E Industrial
PROJECT AGENDA
N V SAN DIEGO TIJUANA
PROJECT AGENDA


Transborder Landscapes Programme is a 3-year long-term research on the US/MX Transborder
POLLUTION PAST POLLUTION PAST BORDERS BORDERS
TRANSBORDER LANDSCAPES SAN DIEGO x TIJUANA
DISTINCT ENVIRONMENTS
San Diego’s natural environment of the river consists of a natural landscape from the border to imperial beach of riparian scrub and coastal sage scrub. Visiting the site we investigated the importance continually testing the bodies of water and determining proper handling of sensitive areas that are prone to impact of existing wildlife. We visited the Tijuana Estuary visitor center, located on the north side of the river, then made our way to the southern part of the river, where the border lies on on a beach where Mexico and the United States meet.
The city of Tijuana has seen exponential growth in domestic and foreign business entering the country for cheap labor. Understanding the economics of both countries, we can determine that if the economy is growing and the need of production is increasing, the city of Tijuana can expect maquiladoras, fabricas and manifacturas being established. Determining from our map, we conclude that industrial zones will be impacted, which can then contribute to the overall pollution and health of Rio Tijuana, which can be detrimental to the ecological sensitive areas of the river on the San Diego side.
Overall, there are no simple solutions that both countries can agree with, but through our efforts of map design and GIS data we are able to make an impact on the decision-makers of our government representatives to create eco-friendly policy.
PROJECT PROCESS


SITE INVENTORY ANALYSIS



Byproduct San Diego’s natural environment of the river consists of a natural landscape from the border to imperial beach of riparian scrub and coastal sage scrub.
DISTINCT ENVIRONMENTS
Visiting the site we ivestigated the importance continually testing the bodies of water and determining proper handling of sensitive areas that are prone to impact of existing wildlife. We visited the Tijuana Estuary visitor center, located on the north side of the river, then made our way to the southern part of the river, where the border lies on on a beach where Mexico and the United States meet.
The city of Tijuana has seen exponential growth in domestic and foreign businees entering the country for cheap labor. Understand the economics of both countries, we can determine that if the economy is growing and the need of production is increasing, the city of Tijuana can expect maquiladoras, fabricas and manifacturas being established. Determining from our map, we conclude that industrial zones will be impacted, which can then contribute to the overall pollution and health of Rio Tijuana, which can be detrimental to the ecological sensitive areas of the river on the San Diego side.
Overall, there are no simple solutions that both countries can agree with, but through our efforts of map design and GIS data we are able to make an impact on the decision-makers of our government representatives to create eco-friendly policy.
PROJECT GOALS
San Diego and Tijuana have created a convergence of cultures and economic prosperity over the last century. Both nations have created new wave of socio-political and environmental issues that have impacted the unique landscape of the Tijuana and San Diego River. This project focuses on the diverse landscape on both regions of the border and its established conditions that have been obstructed by polluters caused by manufacturing and other sectors of production. The goal of the project is to locate and determine the critical locations in Tijuana that have a high probability of contamination of the Rio Tijuana.
We located all major maquiladoras, fabricas, and manifacturas that have established business in sensitive areas that have continually impacted the health and safety of Rio Tijuana. These industrial sectors are represented as ‘+’ symbols on the map, and the different colors on the Tijuana region represent residential, commercial, and industrial areas that also dwell in within sensitive areas of the Rio Tijuana. In comparison on the San Diego region, we focused on the environmental conditions of the unique landscape that Rio Tijuana has created as the river flows out of Imperial Beach in San Diego. We used GIS data to demonstrate environmentally sensitive areas, which consists of areas where endangered species, wildlife, and incorporate areas of biological significance that is established on the clean water act. The different shades of blue display the range of historical habitats. The wide range of ecological diversity within the Rio Tijuana are examples of the urgency to continually support healthy practice to protect the life that the river brings.
ENVIRONMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS
POLLUTANT HAZARDS/CONTRIBUTERS

REMEDIATION SITES

- Ecological Significance - Endangered Species Waster Water, Industrial Byproduct, Trash
- Water Sensitive Areas
Plastics
Industrail
Home Sewage Waste
and Metals
0 0.8 1.6 2.4 3.2 0.4 Miles Tijuana Maquiladoras E Tijuana Manifacturas E Tijuana Fabricas E Legend Historical Habitats Alkali meadow complex High marsh transition zone Beach Dune Grassland Coastal sage scrub Mudflat/Sandflat Perennial freshwater wetland Pond River channel River wash Riparian scrub Salt flat Open water Salt marsh Subtidal water Vernal pool Dispersed Residential residential Commercial
Landscapes, addressing complex socio-political, climate and territorial questions. Transborder Landscapes examines the Tijuana River juxtaposed between US and Mexico. San Diego and Tijuana face contrasting economies, cultures, and policies, despite the shared landscape. This dual governance led to the demise of the river landscape because of largely opposing agendas between the two nations. In response to the socio-economic impact the landscape poses, Transborder Landscapes looks at the Tijuana River, an interface between San Diego and Tijuana, to inform policy through design interventions, cartography, and agency through the local communities. The course will look at the geomorphological process of the region and the methods in which each country manages the river. The stark differences between the two countries will be examined at the local level and the impacts it poses through its landscape. - AA Visiting School Tijuana Residential Tijuana Commercial Tijuana Industrial Antonio Olea, Andy Sett May 2022 E E EE E Environmentally Sensitive Areas Flowlines Industrial
PARQUE REFUGIO PARQUE REFUGIO
Park Design Inspiration



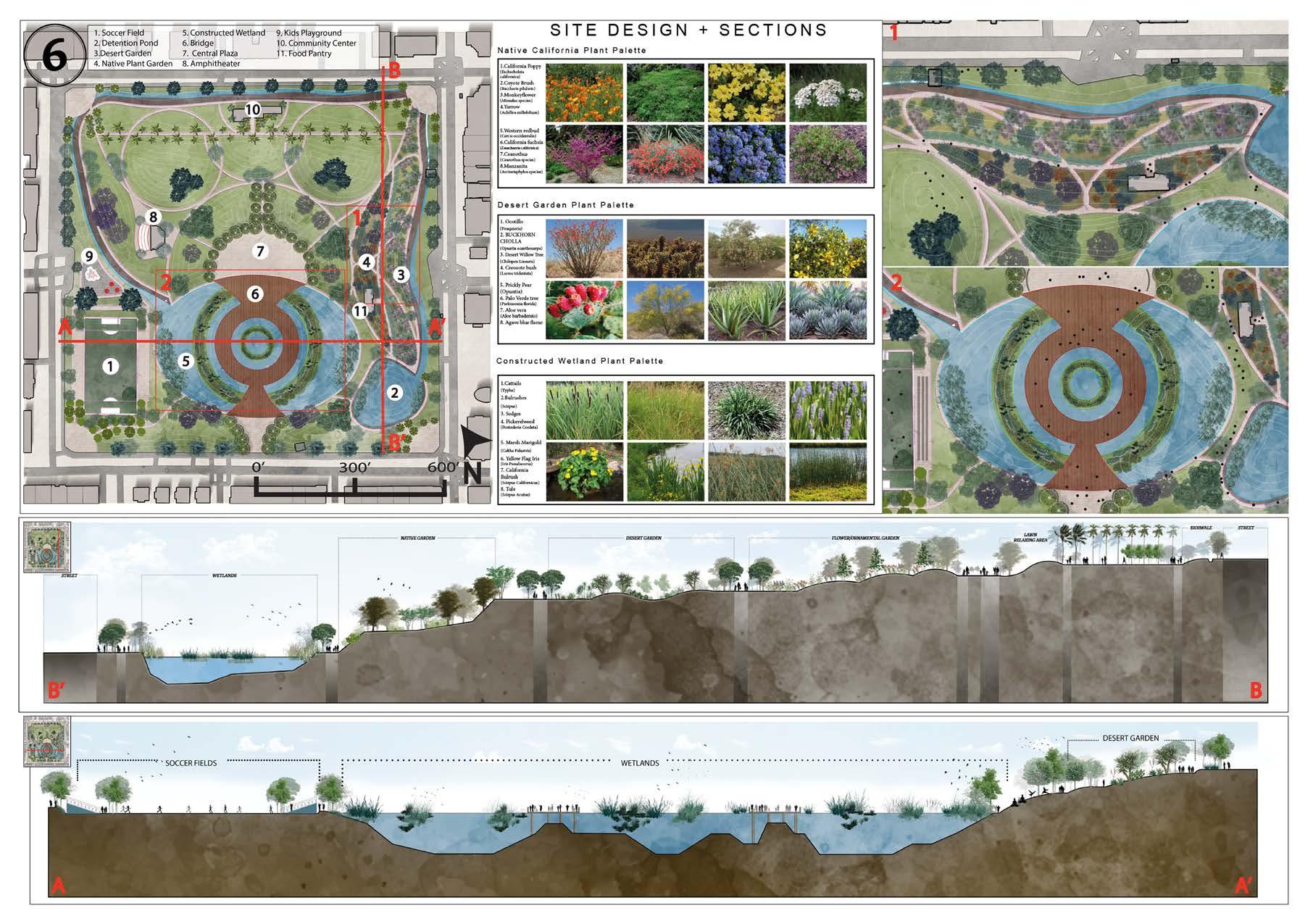
Reforming Macarthur Park to the serve Indigenous communities of Los Angeles

Fall 2023 Studio
day.
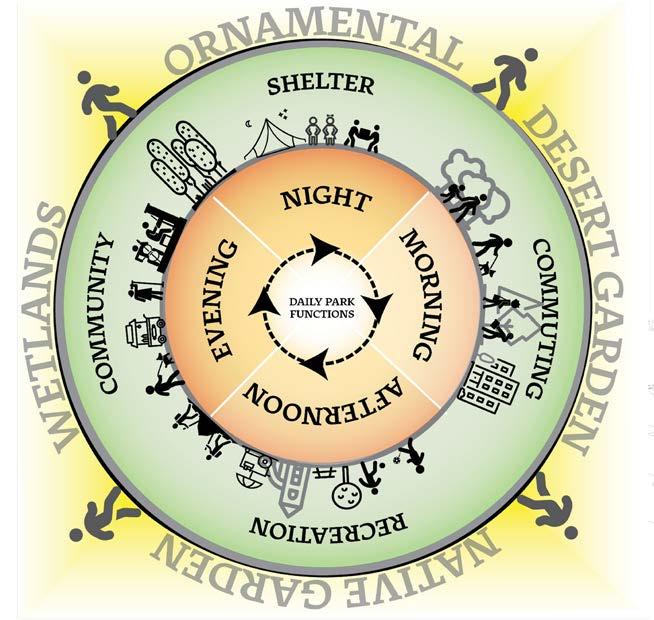
Phasing Diagram
Diagram displaying the use of the park throughout the
Utilizing Oaxacan Textile for Park Design


3D MODELING 3D MODELING
COURSE: ADVANCE COMMUNICATION
PROGRAMS USED: RHINO, TWINMOTION
SEMESTER: FALL 2022
PROFESSOR: KEVIN FINCH
PROJECT:
HANDDRAWN PLAN TO 3D RENDER IN TWINMOTION
In this course we began to understand the basic 3D model and 3D render from a handrawn plan. The goal was to digitize and render into a 3D model as the final product.
(STEP 1) IMAGE 1: REFERENCE BACKYARD CONCEPT DRAWING
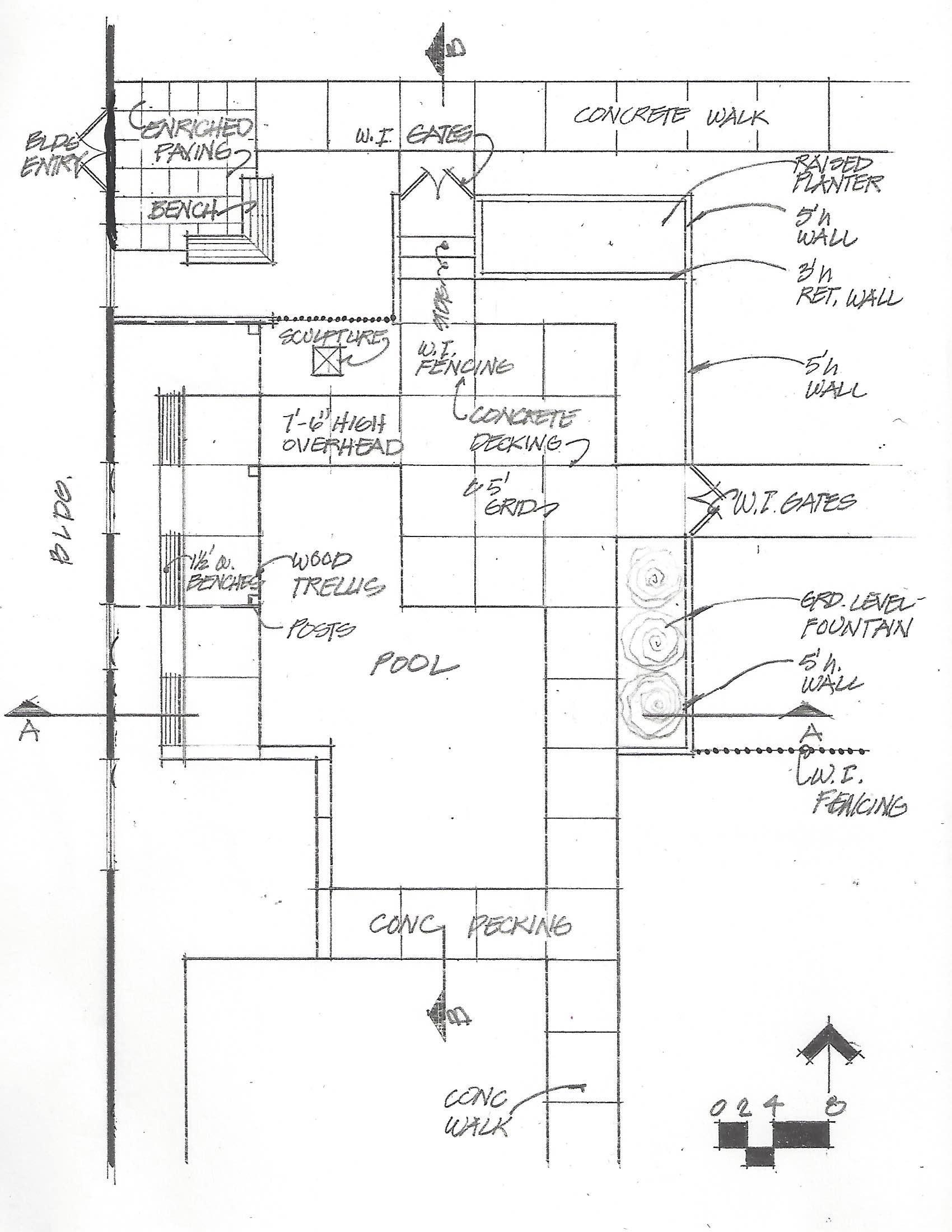
(STEP 2) IMAGE 2: REDRAWN LINEWORK IN RHINO
(STEP 3) IMAGE 3: 3D RENDER FROM LINEWORK
(STEP 4) IMAGE 4: 3D MATERIAL RENDER IN TWINMOTION
IMAGE 1: BACKYARD CONCEPT DRAWING
REFERENCE
IMAGE 2: REDRAWN LINEWORK IN RHINO
IMAGE 3: 3D RENDER FROM LINEWORK
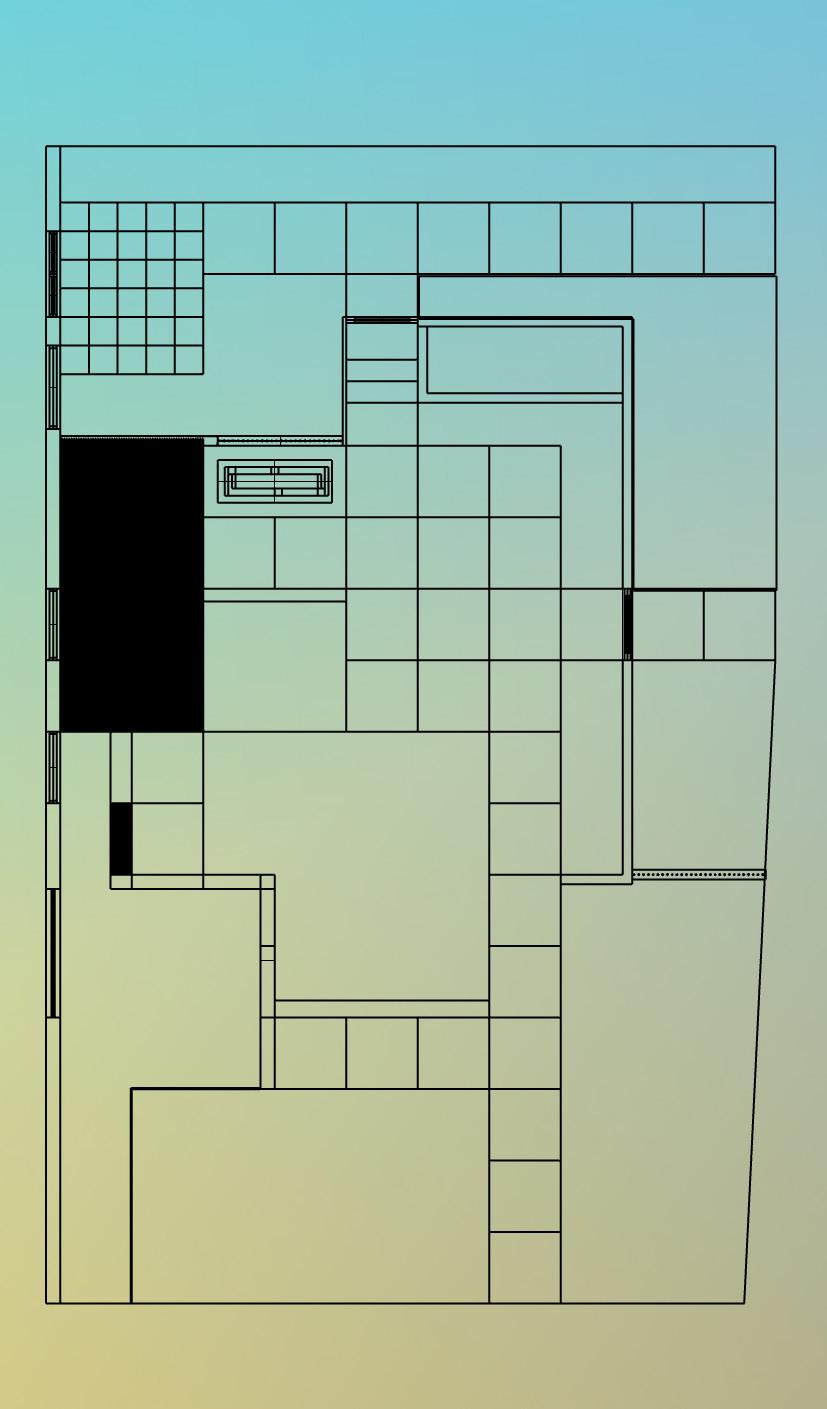

IMAGE 4: 3D MATERIAL RENDER IN TWINMOTION

POOL SOD PLANTING AREA PLANTING AREA PLANTING AREA WATER FEATURE SOD PLANTING AREA PLANTING AREA
GIS WORK GIS WORK
Through my knowledge of Geographic Informations Systems (GIS), I was able to apply Data to maps to make informed decisions regarding project sites. GIS maps shown here utilize both GIS and Indesign, to not only extract geographic data, but also visually design a map that models the data through different symboligies within GIS and Indesign.
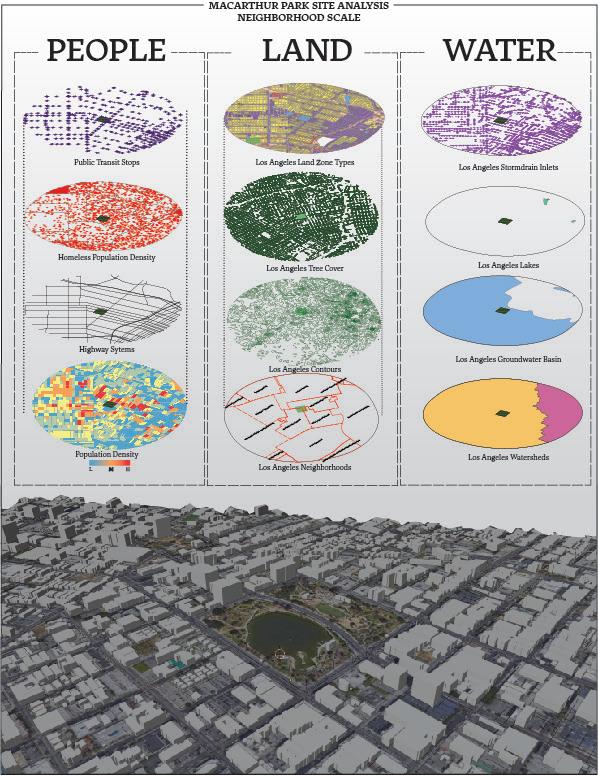
Programs Used: GIS, Indesign, Photoshop, Blender
MAP 1: Macarthur Park Site Inventory Analysis
Data from different state agencies are displayed to further understand Westlake Neighborhood in Los Angeles. Data that were used to investigate the project site of Macarthur Park included information such as:
- Public Transit Stops
- Los Angeles Watersheds
- Los Angeles Tree Cover
- Los Angeles Population Density
MAP 2: California Hydrology
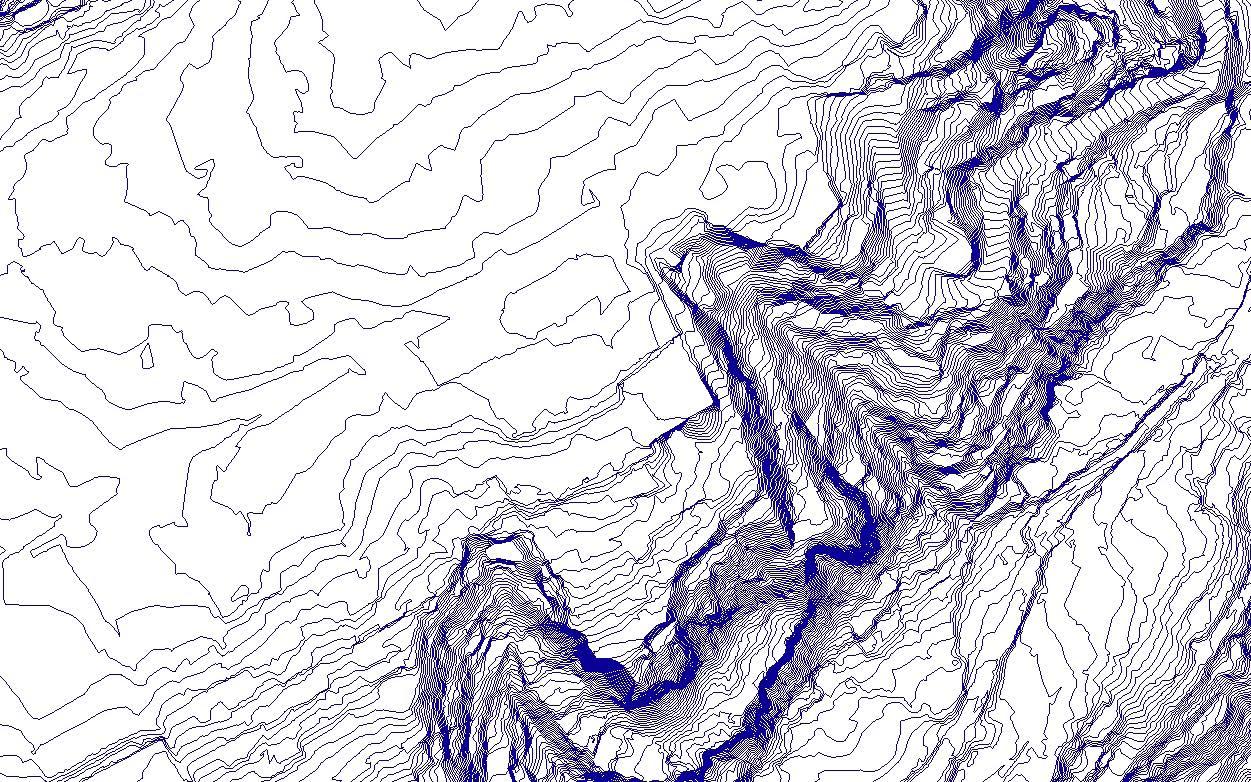
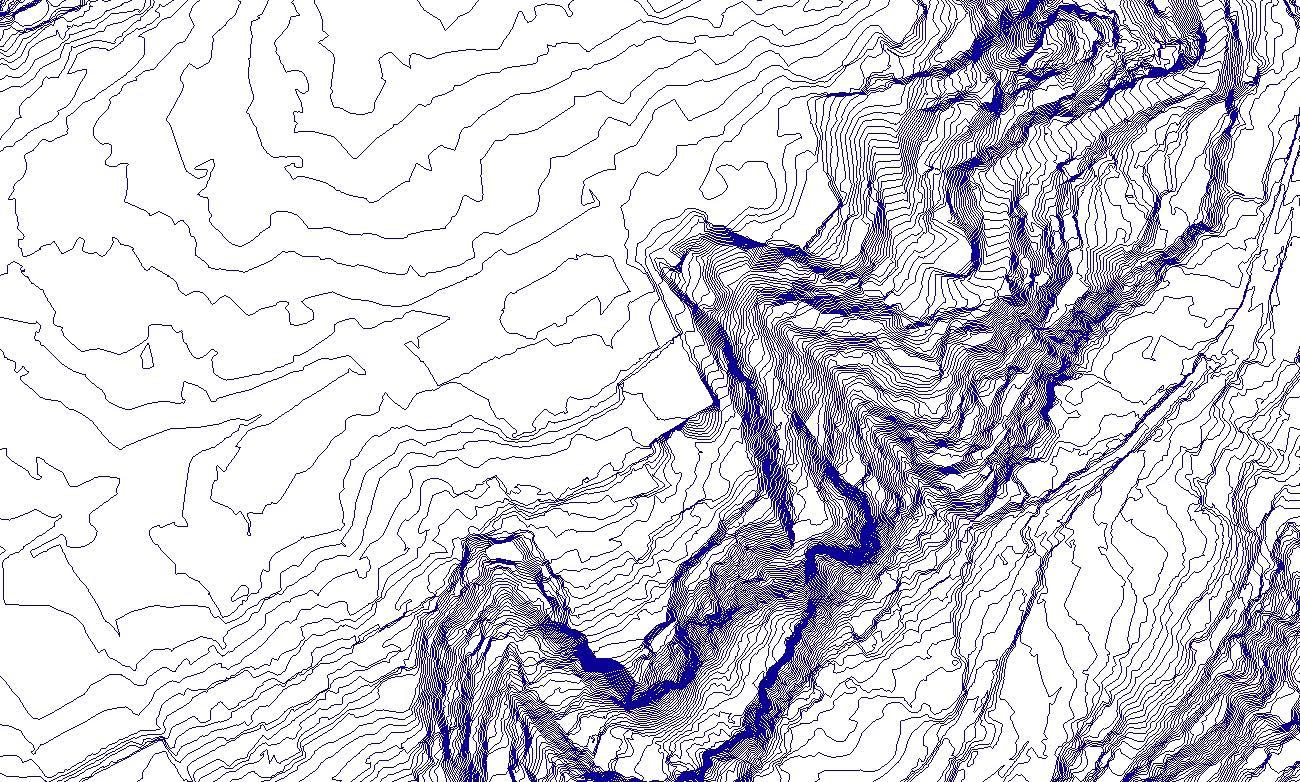
Our initial phase of our studio project for Fall 2022 included an indepth study of water in the state of California. Using GIS, locating important aspects of rivers, groundwater basins and topography of California gave us great insight of where California is extracting this natural resource.
MAP
3:
Los Angeles Municipal Water Resources
Second phase of the studio project, included the study of water at a regional scale. Our project was located in the county of Los Angeles, which became of a manageable scale to determine where the county allocates its water resouces to accomade the population. Data used for this map included:
- Active Wells, Water Treatment Centers, Water Storage Facilities, and Streams and Rivers.
MAP 1: Macarthur Park Site Inventory Analysis
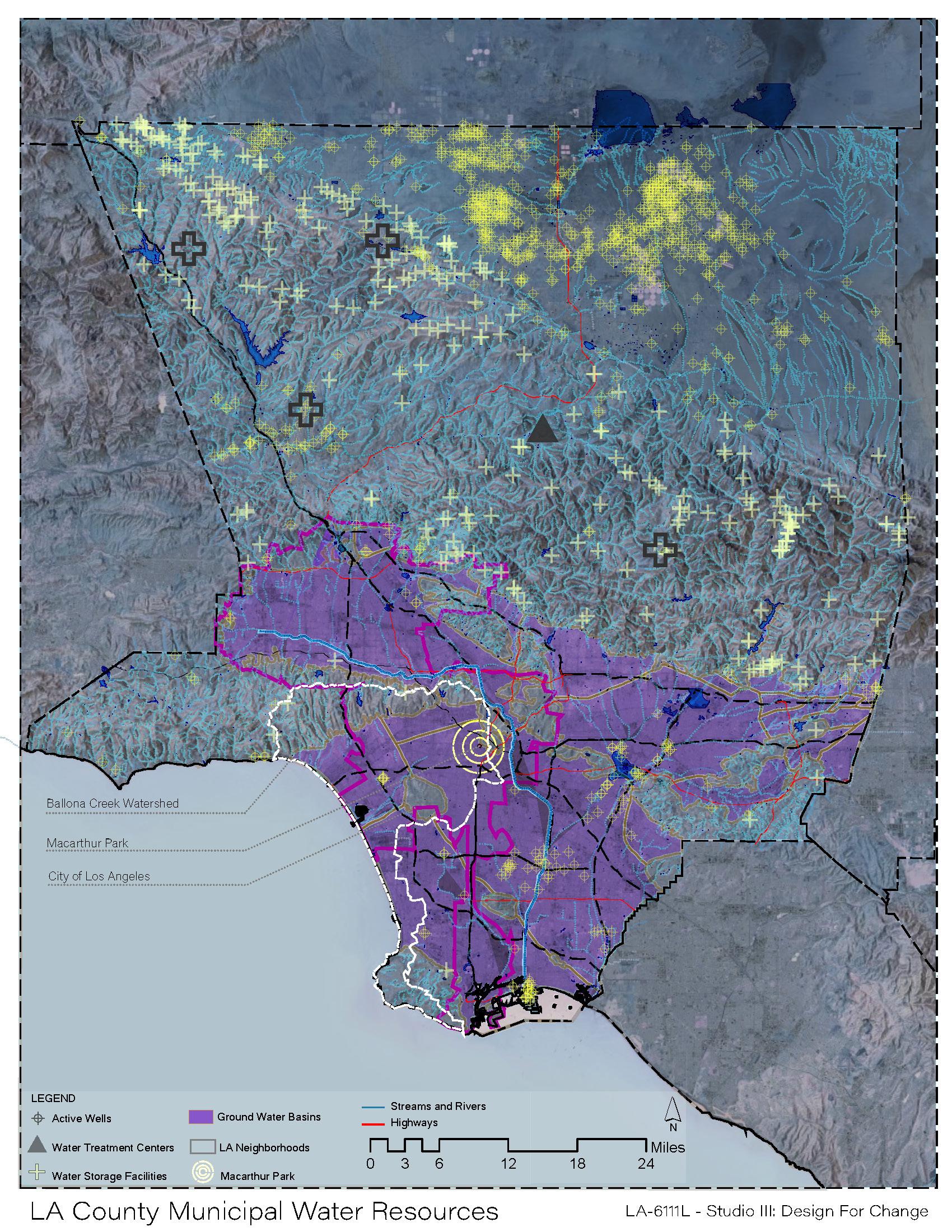
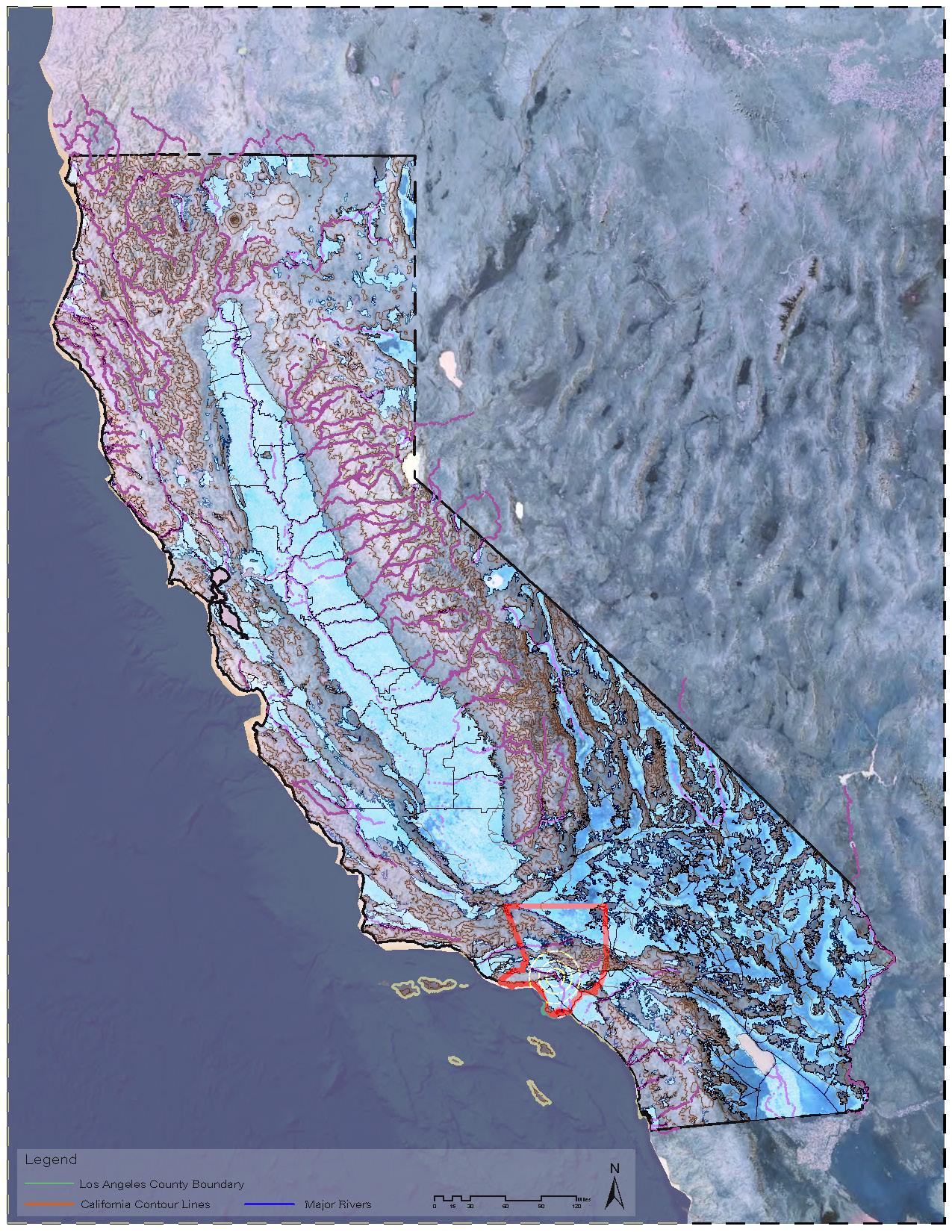
MAP 2: California Hydrology MAP 3: Los Angeles County Municipal Water Resources























