LeanConsultantsarefacingincreasingpressuretoincreaseproduction while reducing costs. Despite efforts to streamline operations, they continue to struggle with inefficiencies and bottlenecks in the productionprocess.
Manyplantmanagerstodayaredealingwiththesameissuesthatwere prevalentyearsback:
• Inefficient use of space: A poorly designed layout can lead to wastedspace,whichcanincreasecostsandreduceproductivity.
• Difficultyinmonitoringandcontrollingtheproductionprocess:A cluttered and disorganised layout can make it difficult for management to monitor and control the production process, leadingtoerrorsanddelays.
• Longleadtimesandbottlenecks:Alackofflowintheproduction process can lead to long lead times and bottlenecks, which can slowdownproductionandincreasecosts.
• Difficultyinadaptingtochangesindemand:Arigidandinflexible layout can make it difficult for a factory to adapt to changes in demand,leadingtoproductionproblemsandlostsales.
• Difficultyinmaintainingequipment:Apoorlydesignedlayoutcan make it difficult to access and maintain equipment, leading to costlydowntimeandrepairs.
By implementing lean layout, manufacturers can eliminate waste, optimiseflow,andimproveoverallefficiency,ultimatelysolvingthese problemsandresultinginincreasedproductivity,reducedleadtimes, andlowercosts.
If you are new to the lean concept here we have discussed the lean whichisbrokenintothreeparts,youcanjumptoanysectionbyclicking onit.
What is a Lean Plant Layout?
Difference between Traditional & Lean Plant layout ?
What is a good Lean Plant Layout?
Advantages of using a lean plant layout?
Aleanplantlayoutisadesignstrategythataimstooptimizetheuseof spaceandresourcesinamanufacturingfacility.Thegoalistominimize waste and increase efficiency by eliminating unnecessary steps and movement in the production process. This can be achieved by using techniquessuchasjust-in-timeproduction,cellularmanufacturing,and creating a visual workplace. Lean plant layouts can also include features such as flexible manufacturing cells, multipurpose workstations, and the use of ergonomic design principles to improve worker safety and comfort. The overall goal is to create a manufacturing environment that is efficient, safe, and responsive to changingcustomerneeds.
Traditional plant layout:
• Typicallyinvolvesalargeamountoffixedequipment,suchas machineryandconveyors.
• Oftenusesbatchandqueueproductionmethods,whereitems areproducedinlargebatchesandthenstoredininventoryuntil theyareneeded.
• Canresultinlongleadtimesandlargeamountsofinventory
• Oftenincludesalotofspecialisedequipmentanddedicated productionlines
• Canbeinflexibleanddifficulttoadapttochangesindemandor productmix.
Lean plant layout:
• Emphasises flexibility and adaptability, using multi-purpose equipmentandflexibleproductionlines
• Uses just-in-time (JIT) production methods, where items are producedonlyastheyareneeded
• Minimisesinventoryandleadtimes
• Focusesoncontinuousimprovementandwaste
• reduction Can be more responsive to changes in demand and productmix.
In summary, the traditional plant layout focuses on individual departments and functional areas while the lean plant layout focuses onoptimizingtheflowofmaterialsandeliminatingwaste.Regenerate
InLeanPlantLayoutingweworkforeliminationofWaste.Thereare8 types of Wastes of MUDA (Muda is a Japanese word meaning wastefulnessanditisakeyconceptinleanprocessthinkingworkon theconceptofToyotaProductionSystem)inLeanManufacturingthat canbememorisedthroughtheacronym TIMWOODS.
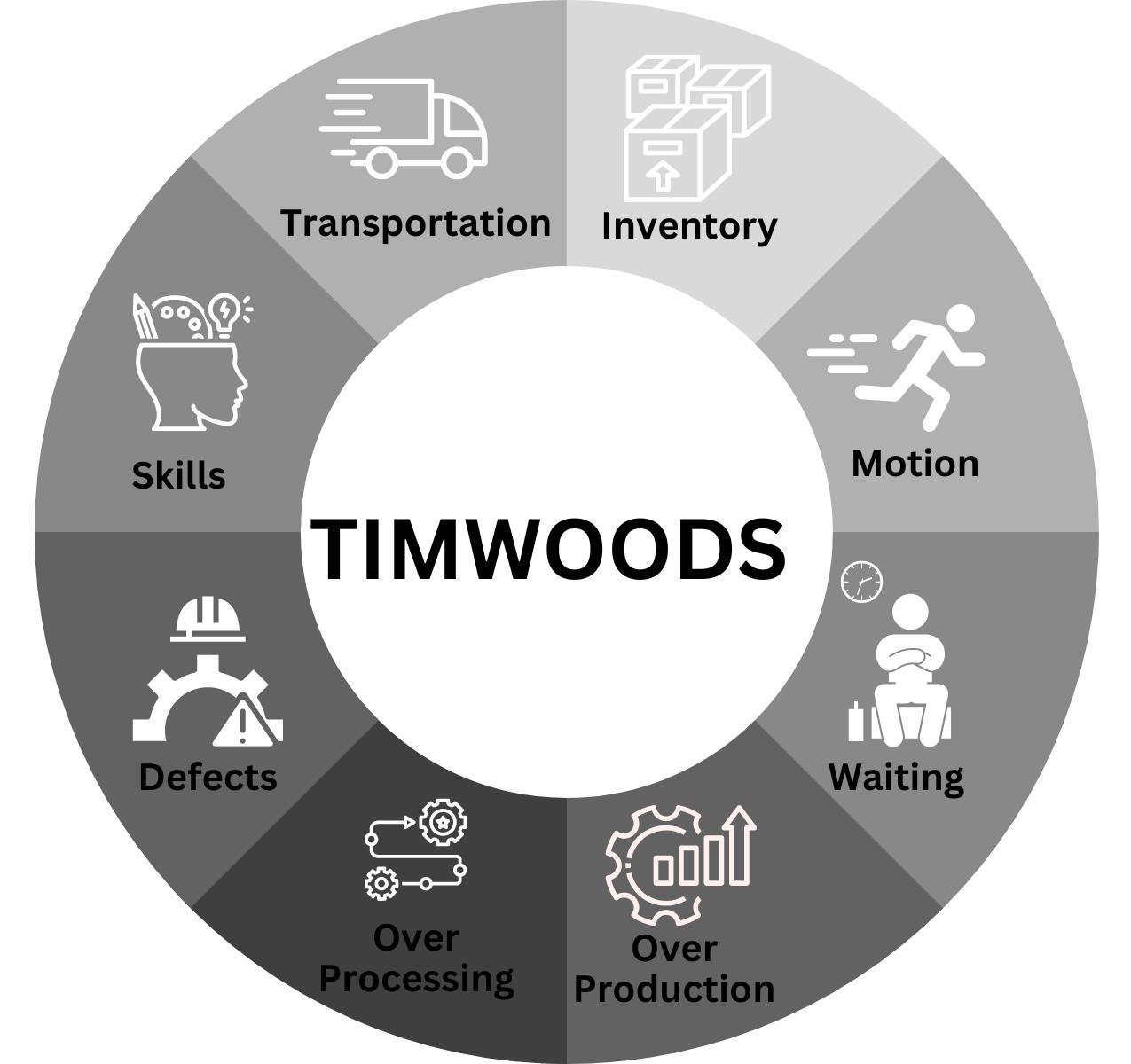
It stands for- Transportation, Inventory, Motion, Waiting, Overproduction,Overprocessing,DefectsandSkills.
Transportation
Transportation ismoving materialand products fromone position to another. In Transportation there is unnecessary movement which doesn't add value to the product, the reason behind is poor route planning, unnecessarily complex flows of material, disorganised workplaces. In Lean Layouting we make a proper workflow for minimisingunnecessarymovements.
Inventory
There are three types of Inventory- Raw material, Work-in-progress inventory and finished products. This includes the waste of storage, wasteofcapitaltiedupinunprocessedinventory,wasteofcontainers used to hold inventory and the lighting of the storage space. In Lean Layoutingweunderstandtheneedofrawmaterialandmakeaproper planforstoragetominimisematerialhandlingcost.
Motion
Motion is an excess movement of People (Walking) which causes additionaldelaysinproduction.InLeanLayoutingweanalyseworkers and their operations to minimise the excess motion to reduce productiontimeanddeliveryfailure.
Waiting
Thistypereferstothewasteoftimeinwaitingforthepreviousprocess to be done. In Lean Layouting we understand the bottleneck of the processandtrytomakeaplanforacontinuousprocess.
Overproduction
Overproduction occurs when we produce more than we need. It is extremelycostlyforamanufacturingcompanyasitdisruptstheflowof materials and affects the quality of the item and overall decreases productivity.InLeanLayoutingweunderstandtheneedofmaterialand trytodecreaseoverproduction.
Over Processing
Over Processing is an unnecessary process and steps that do not add value to the product and adding attributes to a product that are not necessary. In Lean Layouting we make a proper plan for all the productionprocesstoreduceWIPtimeandincreaseProductivity
Defects
Defects refer to a product deviating from the standard design and customer’s expectation. Defective products must be replaced but we haveaheavylossofmanpowerandmaterialthatweusetomakeit.In LeanLayoutingweworktominimisethedefects.
Skills
Thewasteofhumanpotentialcomesunderskillwaste.Inorganisation we do not understand the expertise of an employee and only give orderstofollow.
InLeanLayoutingweunderstandtheexpertiseofemployeesandgive work according to their skills and also we provide some training to increasetheirskillsifneeded.
In lean Layouting, waste is anything that adds costs or delays in productionwithoutaddingvaluetotheproduct.InLeanLayoutingwe identifythesewastesandtakecorrectiveactionstoeliminatethem.
Lean layout results in comforts, convenience, appearance, safety, and profits and a poor layout result in congestion, waste, frustration and inefficiency.FollowingaresomeadvantagesofusingLean
In Manufacturing Cost Reduction
• ReducedconsumptionofpowerbyMinimisedowntime
• Minimisationofscrapanddefects
• Costreductionbymaterialhandling
• Costreductionbymaintenance
• TimesavingwithSMED&increasesavailabilityofmachinesfor theproduction
• Effectiveutilisationofmaterialsbyusingfutureforecasting
• Fullyutilisationofmachinery
• EffectiveutilisationofCubicspace
In Labour Cost Reduction
• Lesslabourrequiredformaterialhandling
• Reducebottleneckandtheover-burdens
• ReductioninwaitingtimeoftheWIP
• Byrightutilisationofskills
In Production Control
• IncreaseproductivitybyreduceWIPtime
• ReducestheWIPspacebySinglePieceFlow
• Designbetterstoragepoints
• Increasedproductionratebyeliminatewaste
• Improvedforecastingstrategy
• Increasedproductionratebyeliminatebottleneck
• Reductionindeliveryfailure
• Suitablespacesareallocatingtoproductioncentres
• Flexibilitytomeetfuturetechnologychangeandproduction requirements
In For Supervision
• Betterflowforsupervisionbymakinggangways
• Reductionintimeofrechecking
• Reductionsupervisionbyeliminatewaste
For Workers
• Makematerialhandlingeasyforworkers
• Reductionofmanpowereffortsbyusingmachinery
• Bettersafetyandlesschanceofaccidents
• Improvedproductivityleadingtohigherwages
• Workingconditionsarebetter,saferandimproved
Nowwehavediscussedtheobjective,Types,factorsaffectingaplant layout.Let'sunderstandhowtetrahedronapproachesaProjectwitha LeanLayoutmethodologywhileconsideringthetopicdiscussed above.
