
“Aspects of ‘Constructing and

“Aspects of ‘Constructing and
presenting
data’ can be addressed
in other foundation subjects, where the data handling cycle can be applied in a relevant context, such as in science or geography.”
NCETM Curriculum Prioritisation
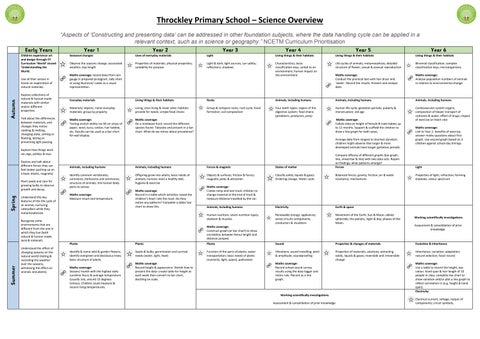
Early Years Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4
Children experience art and design through EY Curriculum ‘World’ strand: ‘Understanding the World
Use all their senses in hands-on exploration of natural materials.
Explore collections of natural & human-made materials with similar and/or different properties.
Talk about the differences between materials, and changes they notice: cooking & melting changing state, sinking or floating, letting or preventing light passing.
Explore how things work via cogs, pulleys & toys.
Explore and talk about different forces they can feel (water pushing up on a boat, elastic, magnets).
Plant seeds and care for growing bulbs to observe growth and decay.
Understand the key features of the life cycle of an animal, nurturing caterpillars while they metamorphosise.
Recognise some environments that are different from the one in which they live (both natural & human made, local & national).
Understand the effect of changing seasons on the natural world (noting & recording the weather over the seasons, witnessing the effect on animals and plants).
Seasonal changes


Observe the seasons change; associated weather; day length
Maths coverage: record data from rain gauge in prepared pictogram, tally chart or using Numicon/ cubes as a visual representation.
Everyday materials

Materials/ objects; name everyday materials; group by property

Maths coverage:
Testing stretch ability via 30 cm strips of paper, wool, lycra, cotton, hair bobble, etc. Results can be used as a bar chart for wall display.

Properties of materials; physical properties; suitability for purpose

Light & dark; light sources; sun safety; reflections; shadows

Living things & their habitats
Characteristics; basic classification keys; suited to an environment; human impact on the environment



Living things & their habitats
Living, once living & never alive; habitats provide for needs; simple food chains

Maths coverage:
On a minibeast hunt, record the different species found. Tabulate and present in a bar chart. What do we notice about prevalence?

Group & compare rocks; rock cycle; fossil formation; soil composition

Animals, including humans
Four teeth types; organs of the digestive system; food chains (predators, producers, prey)


5 Year 6
Living things & their habitats
Life cycles of animals metamorphosis; detailed structure of flower; sexual & asexual reproduction
Maths coverage:
Conduct the practical test with hair dryer and ‘seeds’. Record the results. Present and analyse data.
Animals, including humans
Human life cycle; gestation periods; puberty & menstruation; old age
Maths coverage:
Collate data on height of female & male babies up to 12 months. Support & scaffold the children to draw a line graph for both sexes.
Arrange data from longest to shortest duration; children might observe that larger & more developed animals have longer gestation periods.
Compare efficacy of different graphs (bar graph, line, mixed bar & line) with two data sets. Report on findings; what patterns emerge?


Animals, including humans
Identify common vertebrates; carnivores, herbivores and omnivores; structure of animals; link human body parts to senses
Maths coverage:
Measure result and temperature.


Animals, including humans
Offspring grow into adults; basic needs of animals humans need a healthy diet, hygiene & exercise
Maths coverage:
Record in a table which activities raised the children’s heart rate the most. Do they notice any patterns? Complete a table/ bar chart to show this.


Forces & magnets
Objects & surfaces; friction & forces; magnetic poles & attraction
Maths coverage:
Create ramp and test track: children to change material at the end of track & measure distance travelled by the car:
Animals, including humans

Human nutrition; seven nutrition types; skeleton & muscles
Maths coverage:

Construct graph (or bar chart) to show correlation between femur length and distance jumped.

Plants
Identify & name wild & garden flowers; identify evergreen and deciduous trees; basic structure of plants
Maths coverage:

Season/ month with the highest daily sunshine hours & average temperature (usually July, around 19 degrees Celsius). Children could measure & record rising temperatures.


Plants
Seeds & bulbs; germination and survival needs (water, light, heat)
Maths coverage:
Record height & appearance. Decide how to present the data: create table for height at each week then convert to bar chart, deciding on scale.

Plants
Function of the parts of plants; water transportation; basic needs of plants (nutrients, light, space); pollination

States of matter
Classify solids, liquids & gases. Ordering change. Water cycle.

Forces
Balanced forces; gravity; friction; air & water resistance; mechanisms


Living things & their habitats

Binomial classification complex classification keys microorganisms
Maths coverage: Analyse population numbers of animals in relation to environmental change.

Animals, including humans
Cardiovascular system organs; composition of blood; transport of nutrients & water; effect of drugs; impact of exercise on heart rate
Maths coverage:

Link to Year 2- benefits of exercise; answer maths questions about first graph. Use second graph based on 3 children against school day timings.

Light
Properties of light; refraction; forming shadows; colour spectrum

Electricity
Renewable energy; appliances; series circuits components; conductors & insulators

Earth & space
Movement of the Earth, Sun & Moon; oblate spheroids; the planets; night & day; phases of the Moon


Sound
Vibrations; sound travelling; pitch & amplitude; soundproofing
Maths coverage:
Record school sound survey results using the data logger and metre rule. Record as a line graph.

Properties & changes of materials
Properties of materials; solutions; extracting solids, liquids & gases; reversible and irreversible change


Working scientifically investigations
Assessment & consolidation of prior knowledge.
Evolution & nheritance
Inheritance; variation; adaptation; natural selection; fossil record
Maths coverage:
Use a table to record the height, eye colour, hand span & hair length of 10 people in class; complete bar chart to show variation and/or plot a line graph to reflect correlation in (e.g. height & hand span).
Electricity
Working scientifically investigations
Assessment & consolidation of prior knowledge.

Electrical current; voltage; output of components; circuit symbols;