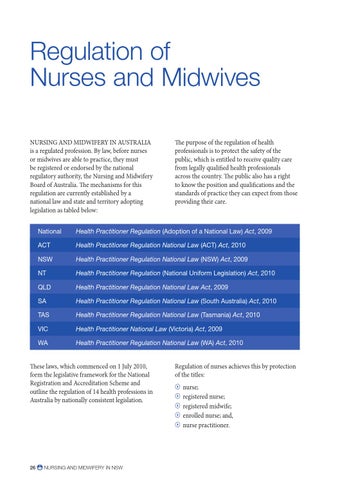
Regulation of Nurses and Midwives Nursing and midwifery in Australia is a regulated profession. By law, before nurses or midwives are able to practice, they must be registered or endorsed by the national regulatory authority, the Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia. The mechanisms for this regulation are currently established by a national law and state and territory adopting legislation as tabled below: National
Health Practitioner Regulation (Adoption of a National Law) Act, 2009
ACT
Health Practitioner Regulation National Law (ACT) Act, 2010
NSW
Health Practitioner Regulation National Law (NSW) Act, 2009
NT
Health Practitioner Regulation (National Uniform Legislation) Act, 2010
QLD
Health Practitioner Regulation National Law Act, 2009
SA
Health Practitioner Regulation National Law (South Australia) Act, 2010
TAS
Health Practitioner Regulation National Law (Tasmania) Act, 2010
VIC
Health Practitioner National Law (Victoria) Act, 2009
WA
Health Practitioner Regulation National Law (WA) Act, 2010
These laws, which commenced on 1 July 2010, form the legislative framework for the National Registration and Accreditation Scheme and outline the regulation of 14 health professions in Australia by nationally consistent legislation.
26
The purpose of the regulation of health professionals is to protect the safety of the public, which is entitled to receive quality care from legally qualified health professionals across the country. The public also has a right to know the position and qualifications and the standards of practice they can expect from those providing their care.
Nursing and Midwifery in NSW
Regulation of nurses achieves this by protection of the titles: c nurse; c registered nurse; c registered midwife; c enrolled nurse; and, c nurse practitioner.