







Academic Authors: Jatinder Kaur, Ayushi Jain, Chandani Goyal, Kashika Parnami, Anuj Gupta, Simran Singh
Creative Directors: Bhavna Tripathi, Mangal Singh Rana, Satish
Book Production: Rakesh Kumar Singh
Project Lead: Jatinder Kaur
VP, Learning: Abhishek Bhatnagar
All products and brand names used in this book are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
© Uolo EdTech Private Limited First edition 2026
This book is sold subject to the condition that it shall not by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, resold, hired out, or otherwise circulated without the publisher’s prior written consent in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published and without a similar condition including this condition being imposed on the subsequent purchaser and without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the above-mentioned publisher of this book.
Book Title: Tekie.AI ICSE Computer Science 7
ISBN: 978-93-89789-99-7
Published by Uolo EdTech Private Limited
Corporate Office Address:
91Springboard, 3rd Floor
145, Sector 44, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
CIN: U74999DL2017PTC322986
Printed by: Printpro Solutions
Illustrations and images: www.shutterstock.com, www.stock.adobe.com and www.freepik.com
All suggested use of the internet should be under adult supervision.
Standing at the forefront of the digital and AI revolution, the importance of coding, computational thinking, and artificial intelligence has reached unprecedented heights. In today’s professional landscape—be it medicine, space exploration, education, science, or business—AI is transforming every sector.
Recognising this imperative, the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 has strongly recommended the integration of coding, computational thinking, AI awareness, and problem-solving abilities into the curriculum. Moreover, future-ready subjects like Artificial Intelligence, Data Science, and emerging technologies are now at the core of education reforms. It is evident that AI will soon become an integral part of learning even at the elementary level.
Uolo has introduced an innovative 360-degree program for an AI-driven computer science curriculum, known as Tekie.AI, spanning grades 1 to 8. Tekie.AI is a significant stride towards STEM and AI education, empowering learners with skills needed to excel in an intelligent, technology-driven world.
Tekie.AI adopts a captivating and engaging approach to learning, in line with the recommendations of the National Curriculum Framework (NCF) 2023 and NEP 2020. The curriculum is ingeniously woven into the thrilling adventures of Mel and Conji, fictional characters from the enchanting land of Avora. Their journey now explores not only the wonders of coding but also the incredible world of AI—how machines learn and assist humans.
The Tekie.AI series represents a modern way of acquiring AI concepts along with computer science knowledge and honing computational and critical thinking skills. Every chapter features AI Connect, real-world applications, and hands-on activities that make artificial intelligence simple, relatable, and fun. The package comes with digital content, provided free of cost, to ensure a seamless and holistic learning experience for children.
Tekie.AI is a technology-powered curriculum that encompasses the following components:
• Main Content Books: These introduce learners to core computer science concepts, AI fundamentals, and computer tools. Every theory chapter includes an AI Connect section, while each Tools chapter offers hands-on AI activities that make artificial intelligence easy to understand, relatable, and fun.
• Coding Books: Specifically designed to nurture coding skills, these booklets align with experiential and contextual learning, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
• Digital Platform: Tekie.AI offers a digital platform with Computer Science, Coding, and AI assignments that help students practice, explore, and apply concepts in real-world ways.
• Animated Learning Videos: The program is powered with high-quality animation-based videos that deliver learning in an engaging manner.
• Teacher Manual: This valuable resource supports classroom instruction, ensuring that educators effectively deliver the curriculum.
Welcome to the captivating realm of Tekie.AI! We hope you enjoy this educational journey as it equips you with the skills to thrive in an exciting, intelligent, and ever-changing 21st-century world.
Tekie is an interactive, engaging, and experiential computer science program. It enables learners to attain mastery in computer science theory, new-age computer tools and coding. These are delivered through a storytelling-based coursebook and an experiential learningoriented coding book.
The learning experience is augmented by a digital platform that gives learners access to learning videos and experiential activities and projects that are rooted in the curriculum.
Engaging Textbooks
Comic Stories
Teacher Manual
Test Papers
Additional Projects
Test-paper Generator


Student and Teacher Platform
Learning Videos
Interactive Classroom and Homework Assignments
Byte-size Lesson Modules

The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, introduced by the Government of India, represents a transformative shift in the country’s education system. It aims to create a more holistic, dynamic and multidisciplinary approach to education. The NEP highlights the need for early development of computational thinking, coding, and digital literacy as vital skills for students’ holistic growth. UOLO is fully committed to actualising the vision of NEP 2020 by meticulously adhering to its outlined recommendations.











1. Focus on conceptual understanding
2. 21st century skills, values, and dispositions
3. Computational and critical thinking
4. Application in real life
5. Holistic and integrated learning
6. Experiential learning
7. Enjoyable and engaging
8. Artificial intelligence and coding concepts
9. Digital literacy and emerging technologies
10. Factoids on India
Competency-based Education
NEP Pages 12, 17 and 22
Teaching and Learning Pedagogy
NEP Pages 3, 5, 11, 12 and 56
National Pride
NEP Pages 15, 16 and 43
11. Assessment of core concepts and application skills Assessments
NEP Pages 12, 18 and 22
Project-based Learning
Engaging hands-on projects encouraging practical application of computer science and coding
Story-based Approach
Enchanting tales that bring learning themes to life, making education a captivating adventure 5 7
Equipping the students with future-ready skills through exposure to the latest tools and technologies
Engaging chapters to deepen students’ understanding and engagement with AI concepts
Test papers designed to evaluate understanding of core concepts and application of skills 3 4 11
Projects on the digital platform to deepen understanding and develop essential practical skills

Invites learners to discuss in small groups and present different perspectives
Story-style learning videos that deliver concepts to students.
Intellectually stimulating questions designed to encourage deep, analytical, critical, and evaluative thought process
Interactive quizzes that reinforce learning and assess students’ understanding
Think It Through
Probing question related to the concept that arouses curiosity
Tool to create customised assessments that align with the curriculum and help evaluate students’ progress effectively.
Factoids on India
Assessment of core concepts and application skills
The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 outlines essential skills, values, dispositions, and learning approaches necessary for students to thrive in the 21st century. This textbook identifies and incorporates these elements throughout its content, activities, and exercises, ensuring students develop coding skills and essential life skills. Referred to as “NEP Tags”, they are defined as follows:



INTEGRATED



CRITICAL THINKING

Art Integration
Bringing creativity and fun into learning by integrating art with computer science and coding
Sports Integration
Using games and sports in daily life to enrich computer-related activities
Holistic & Integrated Learning
Cross-curricular linkages to make learning-experiences more holistic and joyful and meaningful
HANDS-ON

SDG
Critical Thinking
Coding opportunities to apply higher-order skills like algorithmic and computational thinking and problem-solving
Hands-on Activity
Coding opportunities that enable learners to put theoretical knowledge into practice
Sustainable Development Goals
Coding opportunities related to real-world issues and sustainable development

SEL
Social Emotional Learning
Developing emotional intelligence and collaboration skills through coding exercises

The curriculum is thoughtfully mapped to introduce tools and technologies at each grade level, ensuring a smooth and progressive learning experience for students. Beginning with basic concepts in junior grades, the curriculum gradually incorporates more advanced tools and concepts in higher grades. This structured approach enables students to build on their knowledge each year, equipping them with essential skills in computer science and technology as they progress from grade 1 through grade 8. By the time they reach the higher grades, students are well-equipped to tackle complex projects, think critically, and apply their skills in real-world scenarios. The curriculum not only fosters technical proficiency but also encourages creativity, problem-solving, and a deeper understanding of the digital world.









































1

Theme Page: Lists the chapters covered under a unit
2

Comic Story: To introduce key concepts in a fun way


Did You Know: Interesting facts related to the topic

Discuss: A multi-faceted probing question related to the concept that arouses curiosity




4



Explore More: Short videos to find out more about the topic



3









Do It Yourself: Short exercises between the chapter to pause and assess comprehension

























Drawing an Oval
Follow these steps to draw an oval:
1. Open Paint and click on the Shapes group.
2. Click on the Oval shape.

3. After selecting the shape, go to the drawing area.



4. Hold the left mouse button, drag the mouse, and then release the mouse button. You will see that an oval has been drawn.
Project-based Learning: A project-based learning approach employed to foster an engaging and interactive learning experience Points to Remember: Summary of the chapter
Chapter Checkup: Chapter-end practice exercises aligned to different levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy
Apply your learning: Intellectually stimulating questions designed for higher-order thinking and analysis
Have you ever given a command to the speaker at your home to play a song, and it plays it?
Do you know what these speakers are known as?






These special speakers, which follow your voice commands, are smart speakers Smart speakers can do this because of AI.
What is AI?


Artificial Intelligence: Chapters on Artificial Intelligence to explore the fundamentals of AI, including its principles and applications in various fields
AI stands for Artificial Intelligence It gives machines the ability to learn and do things on their own, just like humans do
• Learning Games: These are educational games that you play on your computer. Some of them use AI to adjust the difficulty level as you play. For example, Quick, Draw!
AI Around Us
Fun with AI: Using Quick, Draw!
1. Visit this link with the help of your teacher: https://quickdraw.withgoogle.com/

AI devices are all around us. There are many types of machines that use Artificial Intelligence (AI) to perform tasks or respond to us. Some examples of such AI devices are:
Fun with AI: Engaging AI activities designed to help students explore and apply AI concepts in practical ways
2. Click on the Let’s Draw! button to start.

• Talking Toys: Some toys use AI to understand your voice and respond with sounds, songs, or even short sentences. These speakers respond to your voice commands. They use AI to understand your voice commands, like when you ask them to play music or tell

• Robot Helpers: daily tasks at home. They can clean floors, cook food, etc. They do work in the same way as a human does.



AI Connect: Linking the topics in theory chapters to real-life applications of Artificial Intelligence
3. The AI will ask you to draw something like a cat, mug,
AI helps teachers and children in many ways at schools:
• Selfie Magic: Some phones use AI to edit your selfies. The AI can adjust lighting, smooth out backgrounds, or add fun filters.

• It listens when you read and helps you say words correctly.
• It checks your spelling and gives better words.
• It plays learning games that change to help you learn better.
• It can look at pictures you draw or write and tell what they are.
AI Activity: Engaging, hands-on activities in every Tools chapter based on an AI-related extension of the topic Magic Sketchpad
Chapter 1 Fun with Computers

a We can talk to our friends using a computer.
b We can smell a flower shown on a computer.
Test Paper 1 (Based on Chapters 1 to 3) A. Fill in the blanks.
c We can learn to dance using a computer.
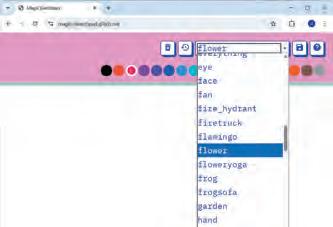
Magic Sketchpad is a website that uses Artificial Intelligence (AI) to help complete your drawings. When you start drawing something, the computer guesses what you are trying to make and adds to it.
Objective: The aim of this activity is to help students understand that AI can learn from drawings and try to guess what we are making. As students draw, they will see how the computer watches their lines, makes a smart guess, and then helps complete the picture.
Test Papers: Designed to evaluate understanding of core concepts and application of skills
1 Open the following website with the help of your teacher: https://magic-sketchpad.glitch.me
Tick () the things for which computers can be used at a school.
2 You will see a blank white area in the centre.
1 Things that are present in nature are called things.
a To teach and learn.
2 Some machines need to work.
b To book tickets.
3 A list of object names appears at the top showing “cat,” “car,” “tree,” etc. options.
3 Computers are used in to keep information of patients.
c To play on the field.
4 At restaurants, computers are used to order and pay for B. Tick () the correct answer.
1 Which of the following is a human-made thing?

a Mountains b Trees
c Cars
2 Which machine helps us






•
•
AI
•
• Number Systems
AI
• Converting Numbers from One System to Another
• Binary Addition
• Binary Subtraction
•
• Virus
• Spread of
• Antiviruses
AI
•
•
AI
•
•
• Creating a
• Entering
• Using Formulas and Functions
•

• Selecting
• Changing
• Copying and Moving Cell
• Deleting Cell Data
• Undo and Redo
• Inserting a Cell, Column, and Row
• Deleting a Cell, Column, and Row
• Applying Autofill
•
• Database Management System (DBMS)
• MySQL
• Data Types in
• Types of SQL Commands
• SQL Queries
•
• Concept of Layers
• Animations
•
• Working with Big Data
• The Future of Big Data
• Fun with AI: Using Impact Filter
• What is Machine Learning?
• How Do the Machines Learn?
• Types of Machine Learning
• Fun with AI: Using Teachable Machine
• Applications of Machine Learning
• Deep Learning

•
• Applications of NLP
• MIT App Inventor

This chapter is not a part of the prescribed ICSE curriculum. It has been added after consideration of the latest trends in the computer science field. Teaching this chapter or including it in the assessment process is entirely at the discretion of the school and the subject teacher.



Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is when computers or machines are designed to think and learn like humans. AI can understand information and make decisions based on what it learns.


A Recommendation System is an AI technology that suggests things you might like.
When you watch a video on YouTube, it shows you more videos that match your interests.
Online shopping sites like Amazon suggest products based on what you searched or bought.
Music apps like Spotify recommend songs that suit your taste.
Job sites like LinkedIn suggest jobs and people you may know based on your profile.

How it Works


AI looks at your past choices (what you clicked, watched or bought).
Then it “recommends” new items that you are most likely to enjoy.
It compares your choices with others who have similar tastes.




John Riedl was a famous computer scientist known for his work on recommendation systems (the technology behind online suggestions).
He co-founded the GroupLens Research group, which created new ways for computers to suggest books, movies, and products.
In 1996, he co-founded Net Perceptions, one of the first companies to use recommendation systems for online shopping and media.
He received big awards like the ACM Software System Award (2010) for his important work in computer science.




AI Recommendation Systems help companies suggest the right products, videos, music, or jobs to people at the right time. They analyze what users watch, buy, or search, and then provide personalized suggestions to improve their experience.
Some well-known companies using recommendation systems are:

Netflix – uses AI to suggest movies and shows based on what you have already watched.
Amazon – recommends products while you shop online, depending on your searches and previous purchases.






YouTube – shows related videos to keep you engaged and watching longer.
Spotify – suggests songs and playlists that match your listening habits and music taste.

LinkedIn – recommends jobs and people you may know by studying your profile and connections.








We all use computers in our everyday lives—to play games, do homework, watch movies, and much more. But have you ever wondered what makes a computer work?
A computer comprises two components: software and hardware. Software and hardware work together to make the computer function properly.
Software is a set of instructions that tells a computer what to do. Software is intangible, which means you cannot touch it. Operating systems (Microsoft Windows, Linux, macOS, etc.), word processing applications (Microsoft Word, Google Docs, OpenOffice Writer, etc.), and web browsers (Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, etc.) are all examples of software.








Hardware refers to the physical components and electronic devices that make up a computer system or any technological device. Hardware is tangible, which means you can touch and physically interact with it.
Software and hardware must be compatible. Before using hardware, software checks whether the hardware meets its requirements. If not, either the hardware or the software may need to be upgraded or replaced. Next, software tells the hardware which tasks to perform and hardware performs these tasks.
The hardware components can be classified into two categories: internal and external hardware.
Just like we have some internal and some external organs in our body that work together to help us perform various activities, a computer also has internal and external parts that team up to make it work. In this chapter, we are going to explore these hardware components and discover how they work together to turn the computer into a powerful machine.
Let us learn more about various hardware in detail.
The external hardware components, also known as peripherals, are attached to a computer outside the central processing unit (CPU) box. External hardware components can be categorised into three kinds:
Input devices: Input devices are used to give instructions to the computer. They convert data from the real world into a form that the computer can understand. Keyboards, mouse, and scanners are examples of input devices.
Output devices: Output devices are used to show the results of the information processed by a computer. They convert data from input and other devices into a form that can be understood by humans. Some common output devices include monitors, printers, speakers, headphones, and projectors.
Storage devices: Storage devices are used to store data and programs so that they can be accessed later. They are used to keep data even when the computer is turned off. Some common storage devices include hard drives, compact discs (CDs), and digital versatile discs (DVDs).
Let us learn more about these external hardware devices in detail:
The mouse is an input device that controls a pointer or a cursor on the computer screen. A mouse has three parts:
1. Left button: This button is used to click, select, drag, or double-click.
2. Right button: The right button is used to display additional information or properties of an item.
3. Scroll wheel: It helps to move a page up or down.
There are two main types of mouse: mechanical mouse and optical mouse.
A mechanical mouse has a metal or rubber ball beneath it that rolls on the surface below when we move the mouse. The movement of the ball is detected by the sensors inside the mouse. This information is used to move the cursor on the screen. A smooth and clean surface, similar to a mat, is critical for smooth functioning of this type of mouse. Nowadays, the mechanical mouse is majorly replaced by optical mouse.
Optical mouse uses a light source, typically a Light-Emitting Diode (LED), and a light detector to detect the movement of the mouse. The light detector measures the amount of light that is reflected from a surface, and this information is used to move the cursor on the screen.
A keyboard is one of the main input devices for computers. A keyboard is made up of buttons which are called keys. These keys can be classified into various groups of keys based on their uses, such as alphabet keys, numeric keys, control key, function keys, and navigation keys.



We can also use a combination of multiple keys to perform an action. These combinations of keys are called shortcut keys.
A printer is an output device that is used to copy digital information (like words or pictures) on a piece of paper or software (as a PDF or .XPS file). A printer is an external hardware device of a computer.
The digital version of the information is called the soft copy, and the printed version of the information on paper is called the hard copy. A computer can work with or without a printer, but a printer can be useful.














There are two main types of printers: impact printers and non-impact printers.
Impact printers: Impact printers create images through a direct contact by striking an ink-soaked strip against paper. They are relatively inexpensive, but they can be noisy and slow. Dot matrix and daisy wheel printers are the most common types of impact printers.
Non-impact printers: Non-impact printers create images without making a direct contact with the paper. They are quieter and faster than impact printers but are more expensive due to their high-quality output. Inkjet and laser printers are examples of non-impact printers.
Some printers, along with paper, can print on cloth, plastic, and leather as well!

A scanner is a device that is used to scan images and documents into a computer. The scanned data is then converted into a digital format and displayed on the screen.
There are various types of scanners available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most common types of scanners include:
Flatbed scanners: Flatbed scanners are the most common type of scanner. They use flat glass surfaces to scan objects, such as documents, photographs, and artwork.
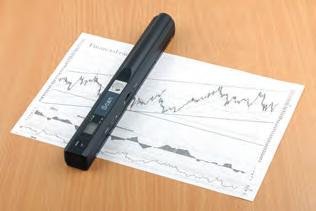

Handheld scanners: Handheld scanners are small, portable scanners that can be held in the hand. They are used to scan objects such as books and magazines that are difficult to scan using a flatbed scanner.
Sheetfed scanners: Sheetfed scanners are used to scan individual sheets of paper. They are typically faster than flatbed scanners, but they can only scan one sheet at a time. The stack of papers is kept on top, and the scanner automatically scans them one by one.


Drum scanners: Drum scanners are the highest-quality type of scanners. They are expensive and are used to scan high-resolution images such as photographs and artwork for magazines and books.
A microphone is an input device that is used to record voice, music, and sound. This device converts sound waves into a digital form that can be stored on a computer. A microphone is used in video conferencing, speech recognition, recordings, and music concerts.

A light pen is a pointing device that is used to interact with a computer screen. This device has a light sensor that detects the position of the pen on the screen. The light pen can be used to select items on the screen, draw lines, or write text. This device has better positional accuracy than a touch screen system.
A webcam is a digital video camera that is connected to a computer. This camera can be used to capture images and videos, and to conduct video calls. Nowadays, web cameras are often used for online chatting and live streaming.


A monitor is the primary output device of a computer which displays images and text on a screen. A monitor is also known as a visual display unit (VDU). The images we see on a monitor are made up of tiny dots called pixels (picture elements). The image clarity depends on the number of pixels on the screen. The display is clearer if the number of pixels is high.
A plotter is a type of a printer that is used to draw graphs and charts. Older plotters used pens, while modern ones use inkjet technology. They are like printers, but are much bigger in size. They are typically used by engineers, architects, and other professionals who need to create high-quality and detailed drawings.


A projector is an output device that projects images on a large screen. This device takes an image as an input from the computer and displays it on a big wide screen. They are often used for presentations, meetings, and in smart classes.

We know that smartphones are also computers. Which input and output devices can you identify in them?
CD stands for a compact disc. These are circular optical discs that are inserted into a CD player (a device designed to play CDs) to read the information that they store. Although these discs are cheap, they offer limited storage capacity (of up to 700 MBs) and can break easily.



DVD stands for a digital versatile disc. It is similar to a CD, but it can store from 4.7 GB to 17 GB of data. However, it is fragile like a CD and comes with limited storage capacity, which may not be enough for large files like 3D computer games and high-resolution movies.
Blu-ray discs are similar to CDs and DVDs, but they offer huge storage capacity. Blu-rays come in various storage capacities, depending on the number of layers of data storage they have. A single-layer Blu-ray disc can hold up to 25 GB, a double-layer disc can hold 50 GB, whereas a triple-layer disc can hold up to 100 GB of data.


A pen drive, also called a USB flash drive, is a small and sturdy portable storage device. It comes in various shapes and sizes. Pen drives are available in capacities up to several terabytes. They are easy to use and are typically rewritable, meaning that you can use them multiple times for storing new files after deleting old files. However, they can be much more expensive than CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs.

Why is it important to get rid of old computers and devices in a way that does not harm the


Modern input devices such as cameras and microphones are not just for taking pictures or recording sound—they also help in artificial intelligence (AI) applications. For example, a camera can capture images that AI software analyses to recognise faces or objects. Similarly, microphones provide sound input that AI systems use for speech recognition, like in virtual assistants (Alexa, Siri, or Google Assistant). This shows how traditional input devices are now being used in smarter ways with AI to make computers more interactive and helpful in daily life.
Choose the correct answer.
1 What does CD stand for in the context of storage devices?
a Compact disc b Computer display c Central device d Circular disc
2 What is the primary function of a printer in a computer system?
a To cool down the CPU when it generates heat.
b To convert digital information into physical copies on paper.
c To scan images and documents in a digital format.
d To connect to the internet.
3 Give one use of each of type of scanner:
a Flatbed scanner:
b Sheetfed scanner:
Internal hardware components are the parts of a computer located inside the CPU box. They include the motherboard, CPU, RAM, ROM, disk drives, and hard disk.
A motherboard is the central component inside a computer that connects all the other components, such as the CPU, RAM, and disk drives. The base of the motherboard consists of a board, which has several copper traces that connect all the other components and allow communication between them.


A motherboard contains:
1. A processor chip (CPU).
2. A basic input/output system (BIOS).
3. Memory chips (RAM and ROM).



The central processing unit (CPU) is like the brain of a computer. It is a small but powerful chip that helps a computer think and process information received from the hardware and software running on the computer.
It has three components:
1. Memory Unit (MU): The memory unit of a computer is like its storage space. It is where the computer keeps all the information, like programs, files, and data.
2. Arithmetic and Logical Unit (ALU): This unit performs arithmetic operations like addition and subtraction, and helps with logical operations like figuring out if something is true or false.
3. Control Unit (CU): It tells a computer what to do and in what order. It also helps move information smoothly among the various components of the computer.
Random access memory (RAM) stores information temporarily. This memory is a computer’s short-term memory that holds the data and programs that the computer is currently using. When you open a program, it goes into RAM so that the computer can work on it quickly. But when you turn off the computer, everything in RAM gets lost.


Read-only Memory (ROM) is a computer’s long-term memory, as it retains information even when the power is off. This memory consists of instructions needed initially when the computer starts. The information stored in this memory cannot be changed, but can only be read.

A disk drive enables users to read, write, delete, and modify data on a storage disk. The disk input/output (I/O) activities are managed by either an internal or external component. There are various kinds of disk drives, including a hard disk drive, and CD and DVD drives. A hard disk drive is the most frequently used disk drive.
A hard disk is a high-capacity disk drive that stores data permanently. At present, hard disks are available in various capacities, 512 GB, 1 TB, 5 TB, and so on. This type of disk has a collection of disks known as platters. Hard disks are made up of one or more platters that are coated with magnetic material. The platters are rotated at high speed, and the data is stored as a series of magnetic charges.

In 1956, the first hard disk was as big as two fridges and as tall as a person, but it could only store 5 megabytes of data!
Switched-mode power supply (SMPS) is the hardware component used to control the power supply. SMPS takes electric power from a source (AC mains) and converts it into low voltage direct current (DC). Its primary function is to always supply well-regulated power to the motherboard and the other parts of the computer. It also has an in-built fan to reduce the heat produced by the computer.
What would happen if SMPSs are not used in a computer?



Modem stands for modulator-demodulator. It is a device that allows a computer to connect to the internet with the help of telephone lines or a wireless medium. Modems convert digital data from a computer to analog signals for transmission over communication channels and analog signals into digital data that the computer can understand.
The process of converting digital data to analog signals is called modulation. The process of converting analog signals back to digital data is called demodulation.
Modems are of two types: internal and external. Internal modems are placed inside a CPU box, and external modems are devices that can be connected to a computer via a USB port.
It is an electronic device designed to spread the heat generated by the CPU.



The heat sink is generally made of aluminium or copper and uses a fan to keep the processor cool. This device helps prevent the CPU and other components from overheating.
A port is a slot on the motherboard that is used to connect hardware devices like keyboard, mouse, monitor, and speaker to the motherboard. The cables of these hardware devices are plugged into these ports so that they are attached to the computer and start functioning.

There are various types of ports on the motherboard.
Let us learn about a few of them:






Serial port
Parallel port

Scan this QR code to take a tour of the parts inside a computer!
Description
A serial port is a port that is used to connect devices such as mouse, keyboards, and printers to computers. This port transfers data 1 bit at a time, which makes it slower than other ports like USB.
Similar to a serial port, a parallel port is used to connect devices such as printers and scanners to computers. This port transfers data 8 bits at a time, which makes it faster than a serial port. USB
A universal serial bus (USB) is a modern port that is used to connect multiple devices to computers, including keyboards, mouse, printers, storage devices, and cameras. This is the most common port on current computers.
Personal System/2 or PS/2 is used to connect keyboards and mouse to computers. Now, USB ports are used in place of PS/2 ports.
FireWire is a high-speed port that is used to connect devices such as external hard drives and digital cameras to computers. This port is being replaced by USB 3.0 and Thunderbolt.
A Video Graphics Array (VGA) port is an older type of video port used to connect a computer to a monitor or projector. Today, VGA is being replaced by newer ports such as HDMI and DisplayPort, which give clearer pictures and can also carry sound.




VGA port used to connect a computer to a monitor or projector. Today, VGA is being replaced by newer ports such as HDMI and DisplayPort, which give clearer pictures and can also carry sound.
HDMI
High-Definition Multimedia Interface, or HDMI is a port that is used to connect a high-definition monitor or TV to a computer. This port can also be used to connect other devices, such as game consoles and HD cameras.
Audio ports are used to connect speakers, headphones, and microphones to computers.
Audio
Ethernet
1 Write T for true and F for false.
An Ethernet is a port that is used to connect a computer to a network. It is the most common way to connect computers to the internet.
a A CPU processes information from both hardware and software.
b ROM retains data even when the computer is turned off.
c A hard disk drive is a type of external hardware component.
d RAM stores data permanently and does not lose data when the computer is turned off.
e A motherboard is responsible for performing arithmetic operations in a computer.
2 Match the type of port with its description.
Port
VGA
USB
Ethernet
Description
Used to connect a computer to a network.
Used to connect projectors to a computer.
Connects a high-definition monitor or TV to a computer.
HDMI A modern port used to connect a wide variety of devices to computers.
A mouse is a pointing device that is used to select and move objects on the screen. 1 2 3 Points
Hardware refers to the physical components and electronic devices that make up a computer system or any technological device.
The computer hardware components can be classified into internal and external hardware.

A keyboard is an input device that is used to enter text and data into the computer.
A monitor is an output device that is used to display the output of the computer.
A printer is an output device that is used to print documents.
CDs can store up to 700 MB of data, DVDs can store from 4.7 GB to 17 GB of data, and Blu-ray discs can store from 25 GB to 100 GB of data.
Internal hardware components are located inside a CPU box, whereas the external hardware components are attached to the computer outside the CPU box.
A motherboard is the central component inside a computer that connects all the other components, such as the CPU, RAM, and disk drives.
The CPU is the brain of the computer which has three components: ALU, CU, and MU.
RAM is the short-term memory of the computer, and it stores the data that is currently being used.
ROM is the long-term memory of the computer, and it stores the data that is needed to start the computer.
The hard disk is the main storage device of the computer; and it stores all the data, including programs, files, and documents.
The SMPS is the power supply unit of the computer, and it converts the AC power into DC power.
The modem is a device that allows a computer to connect to the internet.
The heat sink is a device that helps keep the CPU cool.
The ports are the slots on the motherboard that are used to connect hardware devices.
A. Fill in the blanks.
1 The physical parts of a computer system, such as the CPU, monitor, and keyboard, are called .
2 consists of the ALU, CU, and MU.
3 The CPU, or the central processing unit, is often referred to as the computer’s
4 Random access memory (RAM) stores data .
5 Read-only memory (ROM) is the computer’s memory that retains information even when the power is off.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 Which hardware component connects all the other components of a computer? a CPU b Monitor c Motherboard
RAM
2 Which type of scanner is commonly used for scanning books and magazines?
a Flatbed scanner
c Sheetfed scanner
b Handheld scanner
d Drum scanner
3 Which type of printer creates images through a direct contact by striking an ink-soaked strip against paper?
a Inkjet printer
c Dot matrix printer
4 What is the purpose of a projector?
a To store data
c To project images on a screen
b Laser printer
d Non-impact printer
b To draw high-quality images
d To scan documents
5 Which optical disc format offers the highest storage capacity?
a CD
c Blu-ray disc
C. Who am I?
b DVD
d Pen drive
1 I am a hardware component responsible for converting sound waves into a digital format.
2 I am a part of the CPU that performs arithmetic operations like addition and subtraction, and helps with logical operations.
3 I am a high-capacity disk drive used for permanent data storage.
4 I am a pointing device used to select and move objects on a computer screen.
5 I am an output device commonly used for displaying images and text.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1 An optical mouse uses a light source and a light detector to detect movement.
2 A USB is currently the most common port used to connect various devices to computers.
3 A microphone is an output device used for displaying images on a computer screen.
4 Blu-ray discs have a storage capacity of up to 100 GB.
5 A plotter is typically used by architects and engineers to create high-quality drawings.

E. Answer the following questions.
1 Explain the difference between RAM and ROM.
2 Name two types of impact printers and two types of non-impact printers.
3 What are the advantages of an optical mouse over a mechanical mouse?
4 What are the primary differences between USB, HDMI, and VGA ports?




5 Why can a plotter be preferred over a regular printer for printing a wall-sized world map for a school?
F. Apply your learning.
1 Vivek wants to video call his friend who lives abroad. Which device must he connect to the computer to do this?
2 Suppose Veera is working on a project that requires high-quality images for a digital school magazine. What do you think she should choose: a flatbed scanner or a drum scanner? Justify your choice.
3 Aarav is preparing a presentation for his class. Name the device that he must use to effectively display his slides to the whole class on a large screen.
4 You are in charge of a computer lab and you need to connect various hardware devices such as keyboards, mouses, and monitors to computers. Explain which types of ports you would use and why.
5 Anika wants to store important data from her computer in a storage device that is portable, rewritable, and can store a large amount of data. Name the device she must use.









We have learnt about measuring quantities in Science and Maths. We measure length in centimetres, metres, and kilometres. Similarly, we use grams and kilograms to measure weight.
But what do we use to measure and express these quantities? We use numbers.
But what are numbers made of? They are made of digits—0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. These ten digits together form our Number System.
A Number System is a way of representing and expressing numbers using a set of symbols or digits.
Different number systems can use different symbols and rules to represent a number in that number system.
The base of a number system is the total number of digits the system uses.
The number system that we use is the decimal system, also known as the base-10 system. The numbers are expressed using ten different digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9.

A question arises here: why do we need to learn about different number systems?
The answer is that the different number systems help us understand computers better as computers do not work on the decimal number system. We will later see which other number systems they work on.
Furthermore, learning about different number systems helps us to represent data in different number systems. They also help us to convert data represented in one number system to another number system.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science that makes machines think and learn like humans. To do this, AI must work with numbers, because computers cannot understand words or pictures directly. Everything—whether it is an image, a sound, or a piece of text—is first converted into numbers. For example, when AI processes a photo, it represents the colours and shapes in binary (0s and 1s). Different number systems, such as binary, octal, decimal, and hexadecimal, allow AI to store, calculate, and analyse this information efficiently. Just as we use the decimal system for daily life tasks like counting money or marks, AI uses other number systems to recognise faces, translate languages, and even drive self-driving cars.
There are four number systems commonly used in computing. Computers store and process data in binary; octal and hexadecimal help humans read/write binary more easily, and decimal is used in everyday life. Let us learn more about each of them.
The Decimal Number System is the number system that we use every day. The decimal number system has base 10 that has combinations of the following 10 digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9.
When we deal with a decimal system, we write the base of the number system as the subscript of the number.
For example, if we want to write 70, 128, and 349 in a number system notation, we will write: (70)10, (128)10, and (349)10
The Binary Number System is a base 2 number system that uses only two digits—0 and 1. Each binary digit is called a bit. We express binary numbers as (101)2, (1001)2, (101011)2, and so on.
A bit is the basic unit of information; in practice, storage is measured in bytes (8 bits) and larger units. Different digital devices like calculators, TVs, cell phones, burglar alarms, and watches use this system. But how do these devices represent a bit?
Digits used: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. Base is 10.
Base is 2.
Digits used: 0 and 1.
Imagine a flashlight with a switch that can be on (1) or off (0). The state of an “on” flashlight is 1 and the state of an “off” flashlight is 0.
If we want to store this information:
The flashlight in first case is on and second case is off
It can be depicted as “10”. This is how these digital devices store information using the Binary Number System.
Each number in the decimal number system can be represented in the binary number system as well.
This table shows the decimal numbers 0 through 15 in their binary forms:



Computers store data in binary form using electronic switches that can either be on (representing 1) or off (representing 0). This binary storage is the basis of all digital memory.
Acharya Pingala described binary-like patterns in ancient Sanskrit prosody, and Gottfried Leibniz later formalized the modern binary number system.

The Octal Number System has a base of 8 and has eight digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7. We express numbers in the octal number system as (40)8, (214)8, (376)8, etc.
Base is 8.
The Octal Number System is widely used in computer applications in the aircraft sector. The octal numbers are used in the form of codes.
Just like in the binary number system, all decimal numbers can be represented in the octal number system as well. This table shows the decimal numbers 0 through 15 and their octal forms:
Digits used: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7.
The Hexadecimal Number System has a base of 16 and has digits from 0 to 9 and letters of the alphabet A to F, where A is 10, B is 11, and so on up to F as 15. We express numbers in this system as (CD)16, (129A)16, (A56)16, etc.
Base is 16.
Number System
Digits used: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. Letters used: A, B, C, D, E, and F.
Imagine that you have a special way of counting on your fingers. Instead of just using your regular 10 fingers, you have 16 different symbols to count with. The first 10 symbols are just like your regular fingers, and they are represented by the numbers 0 to 9.
But this is where it gets interesting: after you’ve counted up to 9 on your regular fingers, you don’t stop. Instead, you start using your special symbols, represented by the letters A, B, C, D, E, and F. These symbols represent the numbers 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15, respectively.
So, when you count with your fingers in hexadecimal, it goes like this:
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A (which represents 10), B (which represents 11), C (which represents 12), D (which represents 13), E (which represents 14), F (which represents 15).
The Hexadecimal Number System is commonly used in computer programming and in microprocessors. It is used to describe memory addresses in computers, machine code, and web color codes (for example, #1AC7F0).
This table shows the decimal numbers 0 through 15 and their hexadecimal forms.


Identify the systems that these numbers belong to.
A number in one particular number system can be converted into another with some specific rules. Let us learn how to do it.
Let us learn to convert a decimal number to its binary, octal, and hexadecimal form using the given example.
We will convert (35)10 to its binary form.
Step 1: Divide the number repeatedly by two and note down the remainders. See below:
Step 2: Write the remainders in reverse order.
The final number with only the 0 and 1 digits is the required number. So, (35)10 (100011)2
We can also represent the above method in a different way.
Step 1: Create a table and place the number to be converted in the first row.
Step 2: Write the base of the system, as shown. Here, we want to convert 35 into binary. So, we write 2.
Step 3: Now, divide the number by the base of the target system and write the quotient in the next row. Write the remainder in the cell next to it.
Step 4: Repeat the process till you get a 0 as quotient.
Step 5: Take the remainder from bottom to top. That is the desired binary number. So, we again get (100011)2
We will take the same step-by-step approach. This time, we will use 8 as divisor instead of 2. Let us write (435)10 in its octal form. We follow the same approach. So, (435)10 in octal is (663)8
We will repeat the same process. This time the divisor will be 16, because the base for hexadecimal is 16. We will try to write (846)10 in the hexadecimal form. So, (846)10 in hexadecimal is (34E)16
Convert (442)10 into binary, octal and hexadecimal form.
To convert a number in a given base to a decimal.
Let us use (101011)2 to understand the step-by-step approach.

Step 1: Write the number in a row and note the position of the digits from right to left, as shown:
Step 2: Now make a third row and write the values of base to the power of the position.
Step 3: Make a fourth row and write the products of the digits in each place with the base power number.
Step 4: Find the sum of the numbers found in each place. In this case we get: 32 + 0 + 8 + 0 + 2 + 1 = 43.
So, we get (43)10.
What is the decimal equivalent of (1705)8?
We get, 512 + 448 + 0 + 5 = 965.
So, (1705)8 is (965)10 in decimal.
What is the decimal equivalent of (1AC7)16?
We repeat the same process:
We get, 4096 + 2560 + 192 + 7 = 6855.
So, (1AC7)16 is (6855)10 in decimal.
Convert the following numbers into the decimal form. a (1010)2 b (437)8 c (A9C)16
There is a standard method to convert a binary number into its octal or hexadecimal form.
We will convert (1110101)2 into its octal form.
Step 1: We will group the digits of the binary number. We will form groups of 3, because:
Base of octal = 8.
Base of binary = 2 and 23 = 8.
So, we form groups of 3 starting from the right. If 1 or 2 digits are left, we put them in a new group. See below:
Step 2: Now, treat each group as a separate binary number and convert into the decimal form. So, we get:
Step 3: We join the decimal numbers formed from the grouped digits. The number formed is the desired number.
So, (1110101)2 = (165)8
This time, we form groups of 4 starting from the right.
Think and
Why are we forming groups of 3?
Binary Number (110101011)2 Grouped

Decimal number from grouped digits 110 (= A in hexadecimal)11 (= B in hexadecimal)
We get (1AB)16
So, (110101011)2 = (1AB)16

Convert (1001001001)2 into its octal and hexadecimal form.
The method to convert hexadecimal and octal numbers into their binary form is also very similar. We will also use the concept of groups of digits that we learnt in the previous section.
Let us use the hexadecimal number (1A7)16 to go through the process.
Step 1: We take each digit of the number separately.
Step 2: We then convert each digit into its binary form.
Step 3: Write each derived binary number in groups of 4. Again, we are writing digits in groups of 4 because:
Base of hexadecimal = 16.
Base of binary = 2 and 24 = 16.
So, we get:
Step 4: We now join these different 4-digit binary numbers to get the desired binary number. We get 000110100111.
So, (1A7)16 in the binary form is (000110100111)2 or simply (110100111)2
We follow the same steps while converting an octal number into its binary form. We need to make the group of three instead of four in case of octal numbers.
Convert the following numbers into binary form.
Converting hexadecimal numbers into octal numbers, and vice versa, has to be done via other number systems.
Let us say we want to convert (721)8 into its hexadecimal form.
We first find its decimal form. The decimal form of (721)8 is (465)10.
Now, convert this decimal form into the hexadecimal form. The hexadecimal form of (465)10 is (1D1)16.
So, the hexadecimal form of (721)8 is (1D1)16.
We follow the same steps while converting a hexadecimal number into its octal form.
Alternative Method: Convert octal to binary (3 bits per digit), regroup into 4-bit chunks, then read as hexadecimal (and vice versa).
Convert the following: a (764)8 into its hexadecimal form. b (2B1)16 into its octal form.
Binary addition is similar to the addition of decimal numbers.
When we add (0)2 and (0)2, we get 0. So, (0)2 + (0)2 = (0)2
When we add (0)2 and (1)2, we get (1)2. So, (0)2 + (1)2 = (1)2.
But what happens when we add (1)2 and (1)2? (1)2 is basically 1 in decimal as well. So, (1)2 + (1)2 = (2)10 = (10)2.
So, a new place is created and 1 is carried over.
We can summarise the rules of binary addition as follows:
If we are adding x and y:
So now, we can add bigger binary numbers by this method. For example, let us add (101101)2 and (10110)2.
So, the sum of (101101)2 and (10110)2 is (1000011)2.
Following from the previous section, the rules of binary subtraction are as follows:
In a binary system, only 1 can be carried over. In the decimal system, what numbers can be carried over?


For example, let us subtract (11010)2 and (1100)2
So, the subtraction of (11010)2 and (1100)2 is 01110.
+ (111111)2
– (0001)2 (1110001)2 + (1010101)2 (110011)2 – (01010)2
A Number System is a way of representing and expressing numbers using a set of symbols or digits. Every number can be expressed in different number systems. But the value remains the same.
Base is the number of digits the number system uses. The base of binary is 2, octal is 8, decimal is 10, and hexadecimal is 16.
We use the Decimal Number System in our daily lives.
Binary Number System uses two digits: 0 and 1. Each binary digit is also called a bit.
The Octal Number System is a base-8 number system that uses digits from 0 to 7.
The Hexadecimal Number System has a base of 16. It uses digits from 0 to 9 and letters of the alphabet A to F where A is 10, B is 11, and so on.
We have different rules to convert the number expressed in one number system to another.
A. Fill in the blanks.
The Binary Number System uses two digits: and .
The Binary digit is also known as a
The Decimal Number System is a base number system.
In Octal and Hexadecimal Number Systems, we have bases and respectively.
When converting binary numbers to their octal form, we put digits together in groups of .
B. Tick () the correct option.
Which number system uses only two digits, 0 and 1?
a Decimal b Binary c Octal d Hexadecimal
The Decimal Number System is also known as the system. a Base 2 b Base 8 c Base 10 d Base 16
What does “A” represent in the Hexadecimal Number System? a 7 b 9 c 10 d 12
Which number system is used by digital devices like computers and calculators? a Binary b Decimal c Octal d Hexadecimal
When converting a binary number into a hexadecimal number, we will form groups of how many digits?
C. Who am I?
I only understand two digits, 0 and 1. Computers use me to store and process information.
I am used in counting and doing calculations every day. I have 10 digits, starting from 0 to 9.
I am a number system that uses base 8.
I am unique as I let you use letters of the alphabet as my digits too. Programmers love using me.
I am common to all number systems. My value is also the same in all the number systems.

D. Write T for True and F for False.
The Decimal Number System is based on the digits 0 to 10.
In the Hexadecimal Number System, the letter “D” represents the digit 10.
The Binary Number System is the foundation of how computers understand and process information.
Computers can only perform addition, not subtraction.
(D716240234)16 is an octal number.
E. Answer the following questions.
What is a number system?
What is the base of a number system? Why is it important?
What does the term “hexadecimal” mean in the context of number systems?
Why do we need to convert a decimal number into binary?
F. Apply your learning.
Convert the following decimal numbers into their octal, hexadecimal, and binary forms.
Convert the following binary numbers into their decimal, octal, and hexadecimal forms.
Convert the following numbers into their decimal and binary forms.
Add the following binary numbers. a (101)2 and (110)2 b (10101)2 and (1010)2 c (1110101)2 and (110110)2
Subtract the first binary number from the second binary number. a (11)2 and (110)2 b (1010)2 and (10101)2 c (110110)2 and (1110101)2








The term malware is a composite of malicious and software. Any malicious software or code that is designed to harm, exploit, or compromise computer systems, devices, or networks is called malware. It not only disrupts a computer’s usual operation but also steals vital information.
Computer malware comes in various forms, each with its own set of characteristics and methods of attack. Here are some common forms of computer malware attacks:
1. Virus: A computer virus is a form of malicious software or malware that can infiltrate a computer system.
A virus needs a host file or program and spreads when that host is executed. Computer viruses can spread through infected data via e-mail attachments, USB flash drives, and other sources. The essential resources of a computer, like memory, processing speed, data, and programs are hampered when a virus spreads into the system.
2. Worms: A computer worm is similar to a virus but can spread on its own without human help. A worm can make copies of itself and spread across networks without attaching to host files. This self-replicating activity frequently causes computers and networks to become unresponsive due to excessive memory or bandwidth usage. One famous example is the Blaster Worm, which affected Microsoft’s operating systems.
3. Spyware: Spyware is a harmful software that secretly enters your computer, watches what you do without your knowledge, and shares the gathered information with others who want it. This data can include things like your internet habits, visited websites, passwords, and even credit card numbers. It can also check your files and programs like messaging apps, all while quietly sending this information to someone else. They might sell this data or use it for advertising. Sometimes, spyware can mess up your computer settings, causing slow internet and problems with other programs.
4. Trojan Horse: The term Trojan Horse refers to the wooden horse used by the Greek Army during the Trojan War to enter the city of Troy. A Trojan horse may look like helpful software, but harms your computer once it’s installed. People are tricked into opening it. When Trojans enter your system, they can change your desktop, block programs (especially antivirus ones), and grant unauthorised access to outsiders who can steal your information. Unlike viruses and worms, Trojans don’t spread on their own, you need to open them.
Examples of Trojan Horses include the Beast and Zeus.

5. Sweeper: A sweeper is a malware that pretends to be an antivirus program, fooling users into downloading it unintentionally from malicious websites. Once installed on your computer, it creates fake malware files that start automatically when you log in to Windows. It secretly monitors your online activity, makes changes to your system files, and more, all without your knowledge. When you run it, it pretends to scan your computer and displays fake malware alerts to scare you into thinking your computer is infected.
In this chapter, we will study the computer virus in detail.
1 Write T for true and F for false.
a Malware is a term that specifically refers to software that steals sensitive information from a computer.
b Worms require human intervention to spread from one computer to another.
c Trojan Horses can spread on their own, infecting multiple computers without user interaction.
d Spyware is a harmful software that secretly enters your computer.
2 Fill in the blanks.
a Computer viruses can spread through infected data via , USB flash drives, and other sources.
b Any malicious software or code that is designed to harm, exploit, or compromise computer systems, devices, or networks is called
c Unlike viruses and worms, don’t spread on their own. You need to open them.
d A sweeper is a virus that pretends to be an antivirus program, fooling users into downloading it unintentionally from websites.
Imagine you have a fever caused by a human virus. This virus makes you weaker. In the same way, your computer can get sick too, but not with human viruses. Instead, it is something called a “computer virus”.
A computer virus is like a harmful computer program that sneaks into your computer without your knowledge. Once it is in, it can cause all sorts of problems. It might slow down your computer, mess up your important files and programs, make your computer stop working properly, steal sensitive information, etc.
Just like you need medicine to get better from a real virus, your computer needs special software to get rid of a computer virus. This special software is called antivirus software.

Computer viruses can cause different problems. Here are some common symptoms that may indicate that a computer is infected with a virus:


1. Slow performance: A virus in action can take up a lot of space in a computer’s memory, leading to slower performance. Your computer may take longer to boot up, open applications, or respond to your commands.


2. Pop-up windows: One may start getting too many pop-up windows on their screen which may be virus-affected and can harm the device even more.
3. Self-execution of programs: Malware can run in the background without your knowledge. This could include launching unauthorised programs. This behaviour may indicate a virus or other malware.
4. Account issues: Some viruses are designed to steal login credentials or manipulate your accounts. It could be a sign of a security breach caused by malware.
5. Crashing of the device: In most cases, if the virus spreads in multiple files and programs, there are chances that the entire device may crash and stop working.
A computer virus is a type of harmful software that can sneak into your computer and cause trouble. Let us learn about the harmful effects a computer virus might have.
1. Spread to others: Computer viruses can spread to other computers through various means, such as email attachments, infected files shared over networks, or compromised software installations. This can lead to a widespread outbreak of the virus.
2. Data loss: Some viruses can corrupt or delete your files and data, leading to permanent loss. This loss can be damaging, especially if you haven’t backed up your important information.
3. Stealing information: Certain viruses are designed to steal your personal information, like passwords, credit card numbers, and other sensitive data. This can lead to identity theft and other serious problems.
4. Spreading: Computer viruses often have the capability to replicate and spread to other computers through infected files. They can also take advantage of weaknesses in network connections, which can cause more harm.
5. Privacy breach: Some viruses are designed to collect personal or sensitive information from infected computers, including login credentials, credit card numbers, and more. This information can then be used for identity theft or other malicious purposes.
There are different types of computer viruses:
1. Boot sector virus: This virus category targets the boot sector of a hard drive, which is made up of smaller units called sectors. The initial sector is referred to as the boot sector and contains the master boot record (MBR), responsible for initiating the process of reading and loading the operating system. Boot sector viruses become active during the machine’s boot-up sequence. Examples of such viruses include Disk Killer and Stoned virus.








2. Program file virus: A program file virus, also known as an executable file virus, is a type of computer virus that infects executable program files. These viruses attach themselves to executable files. Executable files usually have file extensions like .exe, .com, .dll, or .sys. When you run an infected program, the virus gets activated and can spread to other executable files on the same system or to other computers.
3. Multipartite viruses: A multipartite virus combines the characteristics of both boot sector and program file viruses. It infiltrates computer systems via contaminated media and subsequently lodges itself in the computer’s memory. Following this, the virus migrates to the hard drive, where it corrupts the boot sector and initiates its propagation throughout the system by infecting executable files. Examples of multipartite viruses include Invader, Flip Tequila, and others.
4. Macro viruses: This virus infects files created with software like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint that support Macros. Macros are sets of instructions that automate tasks. When you open an infected document, the virus enters the memory of your computer. Once active any document you create can get infected too. Examples of such viruses include Melissa, Relax, Bablas, and more.
















5. Polymorphic viruses: The term “polymorphic virus” (poly meaning many, morph indicating changing forms) refers to a virus that manifests in various forms each time it infiltrates a file, altering its binary structure (which is the way a file is organised and stored on a computer’s hard drive) to avoid detection by antivirus software. Some notable examples include Elkern, Marburg, and Satan Bag.
6. Network virus: A network virus can rapidly spread through a LAN (local area network) and sometimes across the internet. It multiplies using shared resources like drives and folders. When it infects a computer, it seeks out more targets, creating a repeating cycle. Examples include Nimda and SQL Slammer.
1 Who am I?


Scan this QR code to know how you can verify whether your computer is infected with a virus or not.
a I am a type of virus that rapidly spreads through shared resources like drives and folders on a network.
b I am a type of virus that alters the binary structure of a file to avoid detection by antivirus software.
c I am a type of virus that corrupts the boot sector of a hard disk and also infects executable program files.
2 Write T for true and F for false.
a Slowing down a computer system is a common symptom of a computer virus infection.
b Computer viruses cannot delete or corrupt files on your computer.
c Viruses have the capability to interfere with computer systems resulting in crashes, data corruption, and loss.
d Pop-up ads are a symptom of a computer virus infection.
A computer virus spreads from one computer to another. It’s like when you have cold and you pass it on to your friends.
Here’s how a computer virus spreads:
1. Removable storage devices: Sharing files using pen drives is common today. If a pen drive has a virus, it can infect the computer it is connected to. If a virus-infected pen drive is inserted into another computer with the AutoRun feature enabled, it can spread the virus automatically. Even if AutoRun is disabled, a virus can still infect a computer when a file on the pen drive is opened.
2. Internet: Computer viruses spread quickly on the internet because they can infect many websites at once. Some websites try to install adware bugs, which flood your screen with pop-up ads. This adware often allows other harmful programs to be installed, filling your computer with unwanted content. Adware, short for “advertising-supported software”, refers to a type of software that displays advertisements on a user’s device, typically without their consent or in an intrusive and disruptive manner.
3. Email attachments: One of the most common ways viruses spread is through email attachments. Cybercriminals send infected files as email attachments, and when you open or download the attachment, the virus infects your computer.





Today, data is as valuable as money or gold, so it’s crucial to protect it from loss or damage.
Computer viruses can be spread through infected data via email, USB flash drives, and other sources. To prevent virus attacks:
1. Use antivirus software and keep it updated.
2. Check if your antivirus detects spyware and install anti-spyware if needed.
3. Install a firewall to control network traffic. Always scan USB flash drives.
4. Avoid downloading pirated software.
5. Scan downloaded files before opening.
6. Regularly scan your hard disk.
7. Back up important files daily.
8. Be cautious with email attachments and only open trusted ones.
Elk Cloner was one of the first microcomputer viruses to spread beyond its original computer or lab.


An antivirus, is a type of computer program or software designed to detect, prevent, and remove malicious software, commonly known as malware, from a computer system. The primary purpose of antivirus software is to protect your computer and data from various types of threats, including viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, spyware, adware, and other forms of malicious software.



Ransomware is a harmful program that locks a person’s files or computer and asks for money in exchange for the key to unlock them.
Here’s an overview of how antivirus software works:
1. Scanning: Antivirus software works primarily by scanning files and programs on your computer or device for known patterns or signatures of malware.
2. Heuristic analysis: This technique looks for suspicious behaviour or code patterns that may indicate the presence of malware, even if no specific signature matches are found. It helps identify new and previously unknown threats.




3. Real-time protection: Many modern antivirus programs offer real-time protection. They monitor the system continuously and scan files as they are accessed, downloaded, or executed.
4. Quarantine: When the antivirus software detects a potentially malicious file or program, it typically quarantines it, isolating it from the rest of the system.
5. Scheduled scans: Users can schedule regular scans of their computer or specific directories to ensure that no malware has evaded real-time protection.
6. Behavioural analysis: Some advanced antivirus solutions use behavioural analysis to monitor the behaviour of programs and processes running on a system to detect viruses.
7. Email and web filtering: Many antivirus programs also offer email and web filtering features to block malicious attachments or websites that may distribute malware.
The Morris worm, from November 2, 1988, was one of the first internet worms and the first to grab widespread media attention.

Using antivirus software is crucial for protecting your computer and data from malware, viruses, and other security threats. Two common tasks when using antivirus software are:
1. Scanning your system.
2. Scanning external media.
1. Install antivirus software: Install antivirus software on your computer. There are many options available, both free and paid. Popular choices include Norton, McAfee, Bitdefender, Avast, and Windows Defender (built into Windows).


2. Update the antivirus database: Ensure that your antivirus software is up-to-date. Most antivirus programs regularly release updates to their virus definitions to detect the latest threats.
3. Open the antivirus program: Launch your antivirus software. You can typically do this by clicking on its icon in the system tray or by searching for it in your computer’s programs.
4. Initiate a full system scan: Most antivirus software provides an option for a full system scan. This scan checks all files and directories on your computer for viruses, malware, and other threats. You will find an option like “Full Scan,” “Complete Scan,” or something similar.
5. Review and take action: After the scan is complete, the software will provide a report. If any threats are detected, the software will provide options for quarantining or deleting infected files.
1. Connect the external media: Plug in the external media device (e.g., USB drive, external hard drive) that you want to scan into an available USB port on your computer.
2. Open the antivirus program: Launch your antivirus software.
3. Select the external media scan option: Look for an option that allows you to scan external media or removable devices. This option is often labelled “USB Scan” or something similar.
4. Choose the external media: Select the external media device you want to scan from the list of available drives.
5. Start the scan: Click the “Scan” or “Start Scan” button to begin scanning the external media, and the software will examine the files and folders to find any threats.
6. Review and take action: Once the scan is complete, the software will provide a report and recommended actions to quarantine or remove any detected threats.
7. Safely eject the external media: After scanning and ensuring that the external media is free from threats, safely eject it from your computer to avoid spreading malware to other devices.

Regular updates are essential for antivirus software for several important reasons:
1. Virus definition updates: Regular updates ensure that your software has the latest virus definitions, enabling it to detect and remove the most recent threats effectively.
2. Protection against new threats: Cybercriminals are always inventing new types of harmful software and ways to attack your computer. If you don’t keep your antivirus program up to date, it might not be ready to protect your computer from these new threats.
3. Security fixing: Antivirus software sometimes needs to be fixed to keep it safe from bad people on the internet. These fixes are like updates that make sure your antivirus software stays strong and does not allow malware to enter.
4. Improved performance: When your antivirus program gets old, it might start to slow down or have trouble working with your computer and other programs. But when you do updates regularly, it can make your antivirus program work better and be more dependable.
5. Improved features: Antivirus companies frequently add new things and tools in their updates to offer users extra protection. Keeping your antivirus up to date ensures that you can use the newest features, which can make your online security even better.

Many computer viruses spread through emails, downloads, and USB drives. Today, artificial intelligence (AI) helps email services like Gmail or Outlook to spot suspicious attachments and links automatically. For example, if a cybercriminal sends an email that pretends to come from a friend, AI can detect unusual patterns and move it to the Spam folder. AI doesn’t just check the sender’s address — it also looks at the style of writing, the type of file attached, and whether the message matches known scam patterns. In this way, AI acts like a smart filter, protecting computers from harmful files and keeping inboxes safer.
1 Number the following steps for scanning your system.
Initiate a Full System Scan
Review and Take Action
Update the Antivirus Database
Install Antivirus Software
Open the Antivirus Program
2 Match the following.
Column A Column B
Boot sector virus
Hides in documents
Macro virus Spreads on its own through networks
Worm Pretends to be useful software
Trojan horse
Targets the startup area of a disk
1 A computer virus is a type of malicious software designed to infect and spread from one computer to another, often with harmful intent.
2 Computer viruses can cause various issues, including slow performance, pop-up windows, self-execution of programs, account issues, and device crashes.
3 There are different types of computer viruses, including boot sector viruses, program file viruses, multipartite viruses, macro viruses, polymorphic viruses, and network viruses.
4 Computer viruses can spread via removable storage devices, the internet, and email attachments.
5 Other forms of malware include virus, worms, spyware, Trojans, and sweepers, each with its own methods of attack and consequences.
6 To prevent virus attacks, use antivirus software, keep it updated, and install anti-spyware and firewalls if necessary.
7 Avoid downloading pirated software, scan downloaded files before opening, and regularly scan your hard disk.
8 Back up important files daily to protect against data loss from virus infections.
9 Antivirus software is designed to detect, prevent, and remove various forms of malware from a computer system.
10 Antivirus software works through scanning, heuristic analysis, real-time protection, quarantine, scheduled scans, behavioural analysis, and email/web filtering.
11 Common antivirus software includes Norton, McAfee, Bitdefender, Avast, and Windows Defender.
12 Regularly update your antivirus software to ensure it can detect and remove the latest threats effectively.
13 Regular updates also provide security fixes, improved performance, new features, etc.
A. Fill in the blanks.
1 A computer virus is a type of designed to infect and spread from one computer to another.
2 One common symptom of a computer virus is a noticeable in computer performance.

3 A virus targets the boot sector of a hard drive.
4 is a virus that pretends to be an antivirus program, fooling users into downloading it unintentionally from malicious websites.
5 viruses attach themselves to executable program files.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 What is a computer virus?
a A type of computer hardware
c A computer ’s operating system
b A type of malicious software
d A network protocol
2 Which of the following is NOT a common symptom of a computer infected with a virus?
a Faster performance
c Unexpected pop-up windows
3 What is the primary motive behind malware attack?
a Improving computer performance
c Stealing sensitive information or causing harm
4 What does the term “heuristic analysis” refer to in antivirus software?
a Real-time scanning of files
c Detecting suspicious behaviour or code patterns
5 What is a “Trojan horse” in the context of computer security?
a A type of antivirus software
c Malicious software that pretends to be helpful
C. Who am I?
1 I am a type of software designed to detect and remove malicious programs from a computer.
2 I replicate myself by modifying other computer programs and can cause a computer to crash if I spread massively.
3 I am a type of malware that secretly enters your computer and steals your personal information.
4 I am a set of instructions that automate tasks.
5 I am a type of malicious software that pretends to be something useful but actually harms your computer when you install me.
b Slow performance
d Unauthorised program execution
b Enhancing data security
d Supporting open-source software
b Scanning of email attachments
d Quarantining infected files
b A self-replicating worm
d A type of firewall
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1 Computer viruses can slow down a computer’s performance.
2 Adware refers to a type of software that displays advertisements on a user’s device, typically without their consent.
3 Many antivirus programs also offer email and web filtering features.
4 The term malware is a composite of malicious and software.
5 Antivirus software can scan and remove viruses from external media devices.
E. Answer the following questions.
1 What is a computer virus?
2 Define any one method through which a computer virus spreads from one system to another.
3 What is the role of antivirus software in protecting a computer?
4 Write any two precautions one can take to prevent a virus infection.
5 How can users safely scan external media like USB flash drives using antivirus software?

F. Apply your learning.
1 Sree notices that his computer has become significantly slower over the past week. He also experiences frequent pop-up windows while browsing the internet. What could be causing Sree’s computer to slow down noticeably, and why?
2 Raj receives an email from an unknown sender with an attachment. The email claims to contain an important document, but he is worried it might be a virus. What precautions should he take?
3 Archi’s computer has been infected with a polymorphic virus. She has antivirus software installed but is struggling to remove the virus. Why is it that she is finding it difficult to remove polymorphic viruses from her system?
4 Raju unknowingly downloaded a program that claimed to be useful but is now experiencing issues with his computer. What type of malware could this be?
5 Tanya’s computer displays a message saying that her files have been locked and she needs to pay to unlock them. What type of malware is likely responsible for this?






Imagine exploring new places, paying bills, shopping for groceries, transferring money, ordering food, or chatting with friends from anywhere without having to leave home—all made possible because of the internet.
The internet is a worldwide network of connected devices for sharing information and communication. Nowadays, the internet has become an essential part of our everyday lives. With its widespread availability, our dependency on the internet has grown significantly. The internet has its advantages, however, it also hosts various dangerous unethical practices if one is not aware of them.
The internet has several advantages:
The internet is a huge library of information on every subject. You can use it to learn about different subjects and also learn different skills, such as using graphic design software, learning coding, improving communication skills, etc.
The internet provides access to news and current events from around the globe, helping us stay informed about what is happening in the world.
We can shop for clothes, books, gadgets, and almost anything online, saving time and letting us choose from a wide range of options.
Through the internet, we can talk to friends and family and even make new friends from around the world, breaking down geographical barriers. Email, messaging apps, and social media platforms enable instant communication, helping us stay in touch with loved ones.
Internet-based services allow us to pay bills, book flights, transfer money, and schedule appointments, all from the comfort of our homes.
The rise of the internet has led to massive growth in businesses. Individuals and companies have embraced online platforms to reach wider audiences, resulting in increased sales, global expansion, and innovative ways of conducting commerce.

The internet enhances media and entertainment experiences. People are drawn to the internet for activities like downloading songs, listening to music, watching movies, playing games, and reading newspapers, comics, and books online.


The internet offers numerous benefits, but it is important to use it carefully because misusing it can create risks. Here are some of the internet’s threats:
Hacking is the process of breaking into a computer system, a website, or an online account without permission. Think of having a box with a lock that only you can open. It is similar to hacking if someone tries to unlock it without your permission. Hackers have advanced knowledge of computers and technology and use their skills to steal important data. Hacking is against the law and can harm people’s privacy and safety.
Hacking can be done for various reasons:
Black hat hackers want to steal information by spreading viruses or creating other problems.
Ethical hackers or White hat hackers work for companies, governments, or cybersecurity firms, engaging in security testing to identify vulnerabilities in computer systems, networks, or applications to prevent malicious hackers from stealing sensitive information from their countries or organisations. This is known as ethical hacking.
Malicious refers to actions done on purpose to cause harm or damage, often intending to create problems, distress, or negative outcomes for others.
When a hacker gets access to digital personal data without your permission, it is called a Cyber Attack
Spam refers to unsolicited, often repetitive messages sent to many people over the internet. These messages can be in the form of emails, texts, or comments on websites. Spam messages can have harmful links or files that might put viruses on your device, leading to unauthorised collection of your personal information.
Spam is unwanted advertising or junk messages in email.
Here are some ways you can recognise spam using the following tips:
• Notice errors in grammar and spelling, as legitimate sources usually have proper writing.
• Attachments or hyperlinks from unknown sources might contain harmful software or inappropriate content.
• Be cautious of messages with generic greetings like Dear Customer instead of your name.
Did You Know?
The very first internet message in 1969 was simply “LO”. Although the intention was to type “LOGIN”, the system crashed after just two letters, which ultimately marked the beginning of the internet.
Plagiarism means taking words, ideas, or images from someone else and presenting them as one’s own work. It is considered an ethical violation and a form of academic or intellectual fraud.
If someone is caught committing plagiarism, there can be various consequences, depending on the situation and the context in which the plagiarism occurred. Some schools and universities use special software to detect plagiarism. This tool checks the work against online sources and databases to find any copied parts. If caught, one could fail the assignment, the course, or even be expelled.

If copyrighted material is used without permission, legal action could be taken by the original creators or copyright holders. This may result in fines or other legal consequences.
Copyright allows creators to own and control their creative stuff, like books, music, videos, or art. It means others can’t use, copy, or share the original work without the permission of the copyright holders.
To avoid plagiarism:
• One can rephrase the material.
• Quote the words of another person by using quotation marks and giving credit to avoid plagiarism.
Cyberbullying is when someone uses the internet to hurt, target, threaten, or harass others. Cyberbullying can happen through various platforms, such as social media, text messages, emails, and online forums. One must be vigilant while using the internet since cyberbullying exists in various forms. It could be in any of the following forms:
Harassment: Sending mean or hurtful messages, repeatedly posting offensive comments, or sharing embarrassing photos or secrets of someone publicly online.

Impersonation: Pretending to be someone else and sending harmful messages or spreading false information using their name.
Cyberstalking: Constantly tracking someone online or sending threatening or intimidating messages to someone, often causing fear and distress.
you wrote a story for class and someone
your
Phishing is an act in which someone tricks you into revealing personal information like passwords, credit card numbers, or other sensitive data by pretending to be a trustworthy person or organisation. This usually comes in the form of messages or emails that seem authentic or from reliable sources like banks or government organisations. Phishing messages often use attachments and urgent language, claiming your account is at risk or you’ll miss something important, pushing you to act quickly.

Phishing focuses on deceiving individuals into revealing sensitive information, often for malicious goals like identity theft or unauthorised access.
Online scams are dishonest schemes occurring on the internet where people try to trick others into giving away money, personal information, or valuable things. Online scams cover a wide range of misleading activities, like fake offers, lottery wins, and investment fraud, where victims are promised something valuable in return to manipulate them into sending money or valuable assets.
Piracy involves the unauthorised copying, distributing, or using of copyrighted materials like software, music, movies, or media without permission from the copyright owners. This causes financial losses for creators. Legal consequences, such as fines or criminal charges, can occur based on copyright laws.







Additionally, pirated content lacks the quality, security, and support of legitimate copies. Pirated software can even carry malware, risking harm to devices and personal data.
Softlifting means unauthorised installing, copying, or sharing software, especially among friends and family. Softlifting is considered to be the most common form of software piracy. This breaks copyright rules and software agreements.
What crime is it if your friend is receiving hurtful messages on his social media that have caused emotional stress for him?
Identity theft is a crime where someone steals personal information like names and credit card details to pretend to be another person. They do this for illegal purposes or to gain money. This stolen information is used to imitate the victim, enabling the thief to secure loans in the victim’s name or acquire prescription drugs, potentially affecting the victim’s medical history.

Identity theft can lead to financial troubles, damaged credit records, and emotional distress. It is a serious crime with significant consequences.
Identity theft can occur in any of the following ways:
Phishing: Sending misleading emails or messages that seem to be from legitimate sources, asking recipients to share sensitive information.
Data Breaches: Hacking into the databases of companies or organisations to steal large amounts of personal data.
Skimming: Illegally capturing credit card information by attaching devices to ATMs, petrol pumps, or other payment terminals. Explore
Write T for true and F for false.

a The internet has had a bad impact on business growth or sales.
b It is hard to talk to a friend who is far away because of the internet.
c Thanks to the internet, money transfer is possible.
State the name of the crime.
a Breaking into computer systems to steal data without permission.
b Using the internet to hurt, threaten, or harass others.
c Copying and distributing software without owner's permission.

The cybercriminals on the FBI’s most-wanted list caused people to lose $100 million.


Safe computing practices are all about protecting ourselves and our devices while using the internet and technology.
Some online safety practices are:
1. Children should always use the internet under the supervision of their parents.
2. Use passwords that are hard to guess and different for each account.
3. Keep your passwords secret and change them periodically.
4. Do not share or disclose your identity with strangers online.
5. Restrict your online profile to being checked by some trusted people only.
6. Keep your computer and phone up-to-date. Updates often fix security holes.
7. Do not click on links in emails or attachments from unknown sources.
8. When shopping or working online, stick to well-known and secure websites.
9. Set a strong password for your home Wi-Fi network to keep outsiders from sneaking in and causing trouble.
10. Do not use public Wi-Fi for online transactions, as it can increase the risk of hacking.
11. Download files from trusted sources only. Unclear downloads can bring unwanted risks to your device.
12. Be cautious when sharing pictures or your location online.
When engaging in online shopping, you may notice that the system remembers information about your prior searches. On platforms like YouTube, Instagram, Facebook, etc., you get suggestions similar to the items you recently searched for or purchased. Your online actions create digital footprints, leaving traces of your online activities.
Digital footprint is the trail of information that you leave behind when you do something online. This data is being saved and can be used for different purposes.
Digital Footprint is created every time you:
• Search for something on the internet
• Shop online
• Post a message
• Click on a link
• Watch a video







There are two types of digital footprints:
1. Active digital footprints: Active digital footprints are the data that are left behind when you knowingly share information online. For example, if you knowingly choose to post something on Instagram, you are aware that other users of the internet can view that information.
2. Passive digital footprints: Passive digital footprints are used when information about a user is gathered from him or her without their knowledge. For instance, when you watch a video online, the website may automatically keep a record of what you watched and then suggest similar videos next time. This is part of your passive digital footprint, because the information is collected in the background without you posting or sharing anything yourself.

What type of digital footprint is created when you search for a recipe online and the website tracks your search history to suggest more recipes?
Let’s learn what creates the traces of our online activities.

1. Browsing history: Every website you visit is recorded in your browser’s history.
2. Social media posts: Anything you post on social media platforms becomes a part of your digital footprint.
3. Searches: Search engines remember your searches and use them to show relevant advertisements.
4. Online purchases: Your online shopping history is stored on e-commerce websites.
5. Emails: Email communication leaves behind a record of your interactions.
It is important to prevent unwanted digital footprints to maintain our privacy online. Here’s how this can be achieved:
1. Privacy settings: Adjust privacy settings on social media platforms to control who can see your posts and personal information.
2. Private browsing: Use private or incognito mode in web browsers to prevent saving your browsing history.
Incognito mode, also known as private browsing or privacy mode, lets you browse the internet without saving your activity on the device.
3. Limited sharing: Be cautious about sharing personal details online. Think before you reveal too much.
4. Regular logout: Log out of your accounts after using them, especially on shared devices.
5. Clearing cache: Periodically clear your browser’s cache, cookies, and browsing history.
6. Avoid Over-sharing: Think twice before posting personal information, location, or sensitive data online.


Every click, search, or video watched online leaves behind a digital footprint. Artificial intelligence (AI) uses this data to learn about people’s interests and suggest content — for example, recommending videos on YouTube or songs on music apps. While this makes online experiences more personalised, it also shows why protecting personal information is important. AI can be helpful, but being aware of your digital footprint ensures that your online activity is safe and responsible.
Computing ethics should be followed to ensure that people use technology and computers in a responsible, respectful manner. Computing ethics keep us safe online, make sure we don’t harm others, and help us make good choices on the internet.
Computing ethics, also known as computer ethics, is a branch of ethics that deals with the moral principles and guidelines governing the responsible and fair use of technology, computers, and digital information. Here are some computing ethics principles that one can follow:
1. Respect the privacy of others and your own by not sharing sensitive information.
2. Always share correct information and do not spread fake stories.
3. Use strong passwords, update your software, and do not do harmful things like hacking.
4. Show respect for copyright by not using or sharing digital content without permission.
5. Make sure that everyone, irrespective of their limited abilities, resources, or location, can use technology easily.
6. Be clear about what you do online, especially when dealing with important tasks or choices that impact on others.
7. Keep learning about the latest in computer ethics and cybersecurity to make smart and ethical choices online.
8. Update your operating systems and other software, like antivirus, frequently.
9. Backup your important data regularly.
10. Be careful while sharing your electronic devices.
11. Buy a licensed copy of the software.
12. Make use of firewalls.
A firewall is a digital security guard for your computer or network. It helps keep out unwanted and potentially harmful data while allowing safe information to pass through.
Match the practice with its description.
Practice Description
Supervising children’s internet usage
Paying online using public Wi-Fi
Data breach consequences
Keeping antivirus updated
Tick () the correct option.
The exposure of user data, such as emails and phone numbers
Computing ethics principles that one must follow
Ensuring that the use of the internet is under parental supervision
It can increase the risk of hacking, resulting in losing all the money in the account
a What is the potential consequence of sharing personal information, location, or sensitive data online?
i Your online presence will become more interesting
ii It will lead to decreased digital footprints
iii Your online security will improve
iv It will threaten your privacy and security
b Which type of digital footprint is created when information is gathered about you without your knowledge?
i Active digital footprint
iii Public digital footprint
c What is one of the goals of computing ethics?
i Spreading fake stories
ii Passive digital footprint
iv Private digital footprint
ii Preventing harm
iii Hacking iv Ignoring privacy
1 The internet lets us book tickets online, shop, talk to friends, and pay bills, no matter where we are.
2 The internet helps businesses grow by reaching more people, doing worldwide transactions, and communicating easily.
3 Hacking is the process of breaking into a computer system, a website, or an online account without permission.
4 Spam refers to unsolicited, often repetitive messages sent to many people over the internet.
5 Plagiarism means taking words, ideas, or images from someone else and presenting them as one’s own work. It is considered a crime or an act of fraud.
6 Cyberbullying is when someone uses the internet to hurt, target, threaten, or harass others.

7 Phishing is when someone tricks you into sharing private information, like passwords or credit card numbers by pretending to be someone you trust.
8 Online scams are tricky schemes on the internet where people try to trick others into giving away money, personal information, or valuable items.
9 Piracy is when people copy or use copyrighted things, like software, music, or movies, without permission from the owners.
10 Identity theft is a crime where someone steals personal information, like names and credit card details, to pretend to be another person.
11 To be safe online, create strong passwords and update them regularly.
12 Avoid clicking on links from unknown sources to stay safe.
13 Digital footprint is the trail of information that you leave behind when you do something online.
14 Incognito mode lets you browse the internet without saving your activity on the device.
15 Computing ethics deals with the moral principles and guidelines governing the responsible and fair use of technology, computers, and digital information.
A. Fill in the blanks.
1 refers to unsolicited, often repetitive messages sent to many people over the internet.
2 An hacker works for governments or cybersecurity firms.
3 Constantly tracking someone online is called
4 lets you browse the internet without saving your activity on the device.
5 A is a digital security guard for your computer or network.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 What is the primary purpose of white hat hackers?
a To spread viruses and malware
c To explore computer systems for fun and learning
2 What is the purpose of online scams?
a To provide free services to users
c To enhance online security measures
b To steal sensitive information
d To keep organisations safe from security risks
b To trick individuals into sharing personal information or money
d To educate people about ethical hacking
3 Which of the following is a good practice to prevent unwanted digital footprints?
a Sharing personal details openly
c Clearing cache and cookies regularly
b Logging into accounts on public computers
d Using the same password for all accounts
4 Which of the following is an example of an ethical computing practice?
a Sharing someone else’s work without permission
c Spreading rumours online
b Creating strong and unique passwords
d Ignoring software updates for security reasons
5 Which of the following is NOT a recommended online safety practice?
a Using strong and unique passwords
c Keeping operating system and antivirus updated
C. Who am I?
b Sharing personal information with strangers
d Using private browsing mode
1 I let you book tickets or pay electricity bills from the comfort of your home.
2 I am a bunch of unwanted and repetitive advertisements in the emails of the users.
3 I am the act of unauthorised installing, copying, or sharing software without permission, usually among friends and family.
4 I am a law that grants creators ownership and control over their creative works.
5 I am the type of digital footprint that remains when you knowingly share information online.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1 The internet restricts us from booking tickets online.
2 The internet enables us to learn about different subjects and acquire new skills.
3 Piracy is the unauthorised copying or distributing of copyrighted materials.
4 Digital footprints do not leave any hints of we do online.
5 Keeping software updated is not necessary for cybersecurity.
E. Answer the following questions.
1 What is the internet?

2 What is softlifting?
3 What are some computing ethics principles?
4 What are digital footprints? Write their types.
5 What are some ways you can recognise spam?
F. Apply your learning.
1 Pranjal visits random and unsafe websites and enters his details on them, and as a consequence, he receives plenty of unwanted emails. What are these unwanted emails called?
2 Priya and Moni created an art project about “Save Wildlife” that won a competition. Unfortunately, someone stole their work and shared it online without permission. What crime did they become victims of?
3 During COVID-19, the avoidance of exchanging physical cash was supported by the internet. How did the internet help in this situation?
4 Ramya was searching for shoes. Later, she received suggestions from various shoe brands in the form of advertisements. Why did these advertisements appear?
5 Arnav sees a funny photo of one of his friends on social media, and he wants to share it on his own social media account. What do you think he should do to ensure he does not violate anyone’s rights and share the content properly?






Imagine that your mother plans to start giving you pocket money of ₹500 to help you learn the value of money. At the end of the month, your mother asks you how you spent the money and how much you have saved. You tell her roughly but do not have an exact record of your expenses and savings.
You can have an exact record of your expenses and savings using a tool called a spreadsheet.
A spreadsheet is a tool for storing data, performing computations, organising information, and analysing data in a tabular format.
There are various spreadsheet tools such as Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, and LibreOffice Calc. Microsoft Excel is a widely used spreadsheet program that usually requires a license for the full desktop version. Google Sheets is a free web-based spreadsheet that supports realtime collaboration. LibreOffice Calc is a free desktop spreadsheet program.
We will be learning Google Sheets to prepare a spreadsheet for your expenses.
Before we start, let us learn about the uses of spreadsheets.
1. Tracking expense and savings: Spreadsheets can be used to track income and expenses, create budgets, and set financial goals.
Did You Know?
The first spreadsheet program was VisiCalc, which was released in 1979.

2. Organising data: Spreadsheets can be used to organise data in many ways, such as creating lists, tables, and charts.
3. Performing calculations: Spreadsheets can be used to perform a variety of calculations, such as adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing numbers. We can even perform complex calculations such as those related to trigonometric functions and statistical analysis.
4. Creating charts and graphs: Spreadsheets can be used to create charts and graphs to visualise data.
Let us create a Google spreadsheet for tracking our monthly expenses.
Steps to create and name a spreadsheet:
1. Open the Chrome browser and then go to https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/.

What are some other things we can do with spreadsheets?


2. Click the plus sign to open a blank spreadsheet.
3. Rename the spreadsheet at the top-left corner by replacing ‘Untitled spreadsheet’ with your project name.

A spreadsheet is made up of rows and columns. These rows and columns form a grid or a table. A Google Sheets window has the following components:
• Cells: Cells are the small boxes in a spreadsheet where you can enter data.
• Rows: Rows are the horizontal lines of cells in a spreadsheet. Rows are numbered 1, 2, 3, and so on.
• Columns: Columns are the vertical lines of cells in a spreadsheet. Columns are labelled with the letters A, B, C, and so on.
• Active cell: An active cell is the cell that is currently selected. During selection, it is highlighted with a blue border.
• Cell address: A cell address is the name of a cell in a spreadsheet. This address is made up of a column letter and a row number, such as A1 or B3.
• Formula bar: The formula bar is located above the spreadsheet. In this bar, you can enter and edit formulas, which are used to calculate values in cells.
• Sheet tab: A sheet tab is a labelled tab located at the bottom of the spreadsheet window. You can have multiple sheets in Google Sheets by adding more sheet tabs. Identify rows and columns for cell B26 and C71.
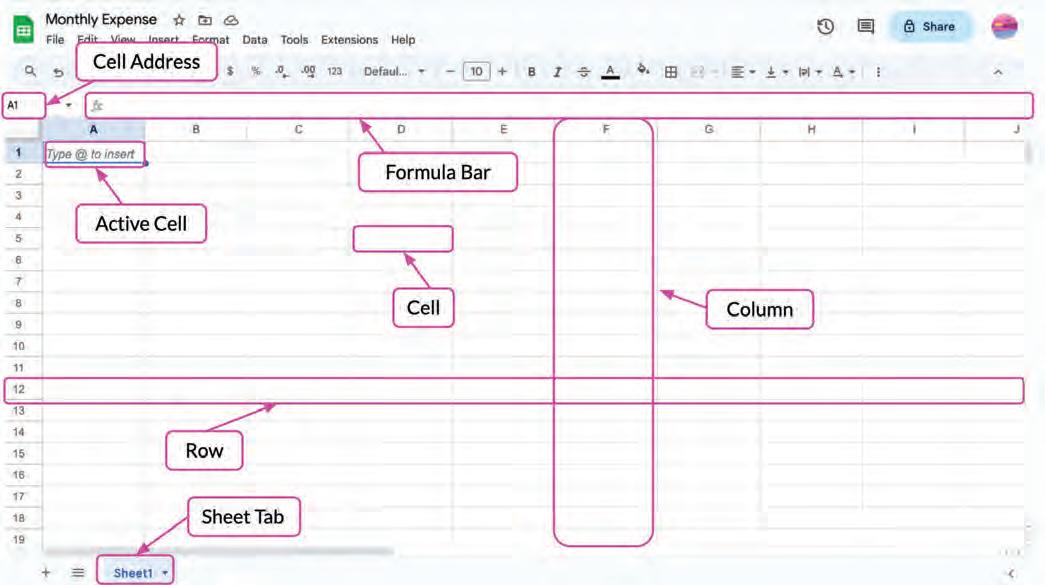
Think and Tell

We can move around in a spreadsheet, using the arrow keys to change an active cell and look at different information. To move left, press the left arrow key. To move right, press the right arrow key. To move up, press the up arrow key; and to move down, press the down arrow key.
1 Do It Yourself 5A
Match the columns.
Column A Column B
Active cell
Formula bar
Cell address
2
Enter and edit formulas
Name of a cell in a spreadsheet that contains a column letter and a row number
A tool for storing data, performing computations, organising information, and analysing data
Spreadsheet The currently selected cell
Answer the following.
a What are cells?
b What is the blue highlighted box known as?
c What is a cell address?
d With what component can we access multiple sheets within Google Sheets?
e How can we change an active cell?

To enter data in a cell, first click the cell to select where you want to type and then start typing.
Now, let us start our project to track our monthly expenses.
Type the given data in a spreadsheet:
We entered the names of the items we bought and their prices. As you can see, the values in a data cell can be of various types. Let us learn about the data types Google Sheets can have.
There are two main data types a cell can have in Google Sheets:
1. Numbers: Numbers can be integers or decimals. They can also be positive or negative.
2. Text: Text is a sequence of characters. These characters can be letters, numbers, or operators. Text can also include date and time.

Identify the type of data if the entered value in a cell is ‘Hello_@’.

Now, we have a record of our monthly expenses on the spreadsheet. To find out how much money we spent in a month, we need to use a formula.
A formula is an expression made up of values, cell addresses, operators, and/or functions that performs a calculation. For example, you can add a formula in a cell to add up the numbers in the entire column or to find the average of a group of numbers.
In a spreadsheet, formulas are made up of numbers, operators, and cell addresses. Let us find out the total amount of money spent in a month by adding a formula in the prices column (B column).
To calculate the total monthly expense:
1. Select the cell where you want the total monthly expense to appear.
2. Type the ‘=’ sign, followed by the cell address you want to add, separated by the ‘+’ operator.
For example: =B2+B3+B4+B5+B6.
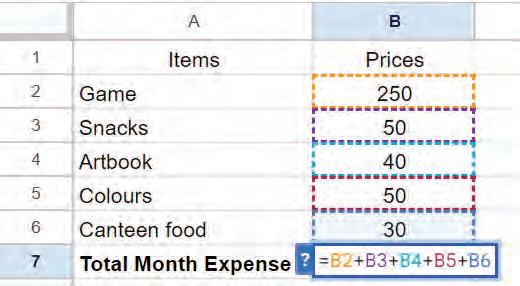
Now, let us find the average price of the items bought in the month. To do this, we will add up the prices of all the items and then divide the sum by the number of items.
To calculate the average price of the items:
1. Select the cell where you want the average price to appear.
2. Type the formula to find the average price.
For example: =(B2+B3+B4+B5+B6)/5.
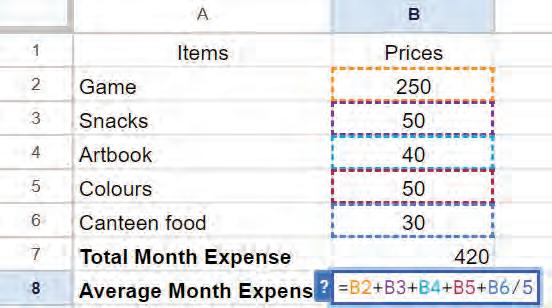
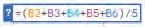
We learnt how to add a formula in a cell to perform calculations in a spreadsheet. However, there is a quicker method for calculations, which is known as a function.

In Google Sheets, we have several built-in functions for various operations.
Functions in Google Sheets are the formulas that are already available. They can analyse data and perform calculations on it.
A function can be applied to a cell range, which is a group of adjacent cells (cells located next to each other).
A cell range is defined by specifying the starting cell and the ending cell. This range includes all the cells that fall between these two cells in a continuous sequence.
Cell ranges are represented using a colon (:) that separates the starting and ending cells.
Refer to the given table to learn about the built-in functions available in Google Sheets. Cell ranges and cell addresses given in the table can be referred to from the monthly expenses project that we have created in Google Sheets.
Function Name
Purpose
SUM Calculates the sum of the values in a cell range.
AVERAGE Calculates the average of the values in a range of cells.
PRODUCT Multiplies the values in the specified range of cells.
MOD Returns the remainder of the division of a number by a divisor.
SQRT Returns the square root of a number.
INT Rounds the number to an integer value.
POWER Returns the result of raising a number to a specified power.
Example
Input =SUM(B2:B6)
Output 420
Input =AVERAGE(B2:B6)
Output 84
Input =PRODUCT(B2:B6)
Output 750000000
Input =MOD(B3,7)
Output 1
Input =SQRT(36)
Output 6
Input =INT(–25.6)
Output –26
Input =POWER(B6,3)
Output 27000
ABS Returns the absolute value of a given number. Input =ABS(–23)
Output 23
COUNT Counts the number of cells in a range that contain numbers.
Input =COUNT(B2:B6)
Output 5
MIN Returns the lowest value in a range of cells. Input =MIN(B2:B6)
Output 30
Function Name
Purpose
Example
MAX Returns the highest value in a range of cells. Input =MAX(B2:B6)
Output 250
IF Verifies if the provided condition is met. This function returns value1 when the condition is true and value2 when the condition is false.
CONCATENATE Combines multiple text strings into one.
LEN Returns the length of the text string.
UPPER Converts the text into capital letters.
LOWER Converts the text into small letters.
TODAY Returns the current date.
NOW Returns the current date and time.
=IF(condition, value_if_true, value_if_ false)
Input =IF(B2<50,"Affordable item" , "Costly item”)
Output Costly item
Input =CONCATENATE (A5,A3)
Output ColoursSnacks
Input =LEN(A1)
Output 5
Input =UPPER(A5)
Output COLOURS
Input =LOWER(A6)
Output canteen food
Input =TODAY ()
Output 10/26/2023
Input =NOW()
Output 10/26/2023 9:41:52
Let us try to calculate the total expenses and the average price using the built-in functions.
The SUM() function is used to calculate the sum of the values in a cell range.
To calculate the total monthly expense using the SUM() function:
1. Click the cell where you want the sum to appear.
2. Type the ‘=’ sign, followed by the function name with round brackets =SUM().
3. Inside the round brackets, add the cell range you want to calculate, i.e., =SUM(B2:B6)
4. To get the total monthly expense, press Enter.
420
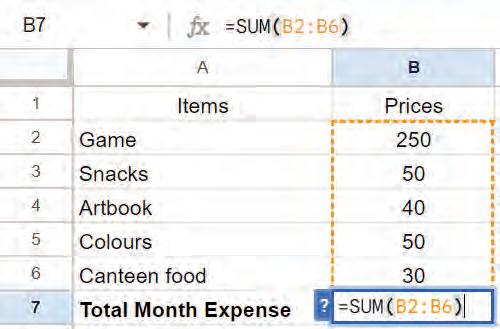
The AVERAGE() function is used to calculate the average of the values in a range of cells.

To calculate the average price of the items using the AVERAGE() function:
1. Click the cell where you want the average to appear.
2. Type the ‘=’ sign, followed by the function name with round brackets =AVERAGE()
3. Inside the round brackets, add the cell range you want to calculate, i.e., =AVERAGE(B2:B6)
4. To get the average price, press Enter

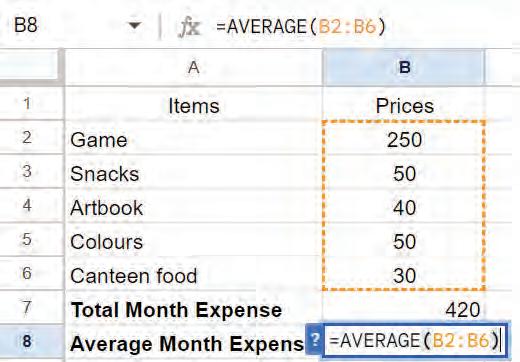



Now, we have a complete and accurate record of what and how much we spent in a month. Whenever we create something on a computer, we need to save it so that we can come back to it later to check or update it, as needed.
However, Google Sheets makes this even easier with its autosave feature that automatically saves your data every time you make a change.
When done, you can close the spreadsheet by clicking Close.
Observe the given table.
Identify and write down the values that the given functions will return.
a =COUNT(B2:B7)
b =AVERAGE(B5:B7)
c =LEN(A6)
d =UPPER(A5)
Which function returns the remainder of the division of a number by a divisor?
a SUM()
c PRODUCT()
b AVERAGE()
d MOD()
1 A spreadsheet is a tool for storing data, performing computations, organising information, and analysing data in a tabular format.
2 An active cell is a cell that is currently selected. When selected, it is highlighted with a blue border.
3 A cell address is the name of a cell in a spreadsheet. It is made up of a column letter and a row number, such as A1 or B3.
4 A sheet tab is a labelled tab located at the bottom of the spreadsheet window. You can have multiple sheets in a Google Sheets by adding more sheet tabs.
5 You can move around in a spreadsheet using the arrow keys to change the active cell and look at various types of information.
6 A cell can have two main data types in a Google Sheets: numbers and text.
7 A formula is an expression made up of values, cell addresses, operators, and/or functions that performs a calculation.
8 Functions in Google Sheets are formulas that are already available. These functions can analyse data and perform calculations.
9 A cell range is defined by specifying the starting cell and the ending cell. This range includes all the cells that fall between these two cells in a continuous sequence.

A. Fill in the blanks.
Hints functions spreadsheet autosave formula bar cell range
1 A is a tool for storing data, performing computations, organising information, and analysing data in a tabular format.
2 The is located above the spreadsheet.
3 The SUM() function is used to calculate the sum of the values in a .
4 are the built-in formulas that analyse data and perform calculations on it.
5 Google Sheets has feature that automatically saves data every time you make a change.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 Which of the following is the correct way to write the SUM() function?
a =SUM(B2-B6)
c =SUM(B2:B6)
b =SUM(B2+B6)
d =SUM(B2 * B6)
2 What is the cell address for the cell in the fifth column and third row?
a C3
c E3
b C5
d F3
3 What is the output of the formula =SQRT(16) in Google Sheets?
a 2
c 8
4 Which symbol is used to begin a formula in Google Sheets?
a = (equals sign)
c – (minus sign)
b 4
d 16
b + (plus sign)
d * (asterisk)
5 Which function is used to combine multiple text strings into one?
a CONCATENATE
c UPPER
C. Who am I?
b LEN
d LOWER
1 I am a function used to multiply the values in the specified range of cells.
2 I am a function used to return the absolute value of a given number.




3 I am a function used to verify whether a provided condition is met.
4 I am a function that converts text into lowercase.
5 I am a function that returns the length of a text string.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1 An active cell is a cell that is currently selected.
2 Rows are the vertical lines of cells in a spreadsheet.
3 MAX returns the lowest value in a range of cells.
4 COUNT returns the number of cells in a range that contain numbers.
5 MOD returns the square root of a number.
E. Answer the following questions.
1 List the common uses of spreadsheets.
2 Which function is used to find the minimum value in a range of cells? Give an example.
3 What are the basic components of the Google Sheets window? Name any three.
4 What is the output of the following formula? =UPPER("hello")
5 What is the output of the following formula? =CONCATENATE("Hello", "world!")
F. Apply your learning.
1 What is the output of the following formula, given that the value of the cell C1 is 50? =IF(C1>10, "Greater than 10", "Less than or equal to 10")

2 Explain the purpose of the IF function in Google Sheets. Use this function to check if the value in cell H1 is greater than 50. If it is, display ‘Yes’; otherwise, display ‘No’. Provide the formula and the result.
3 Create a formula that multiplies the values in cells J1 and J2 and then adds the result to the value in cell J3. Display both the formula and the final result.

4 Observe the given table.
Now, write the formula and the result for the following questions.
a What is the total cost of all the stationery items in the table?
b Which stationery item is the most expensive?
c Which stationery item is the least expensive?
d What is the average price of a stationery item in the table?

Let us Explore Spreadsheets
Activity: Smart Data Cleanup with AI
Objective: Google Sheets uses AI to spot problems like duplicate entries or extra spaces in your data and suggests ways to fix them. Let us try it out.
Follow the given steps:
1 Open Google Sheets and create a new sheet named “Shopping List”.
2 In Column A, type the following item names exactly as shown:
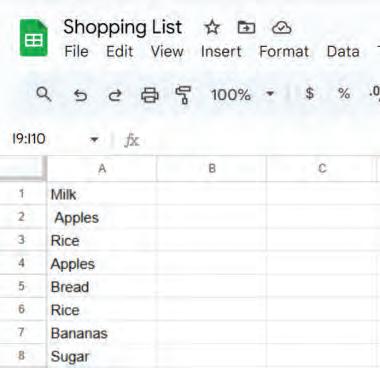
3 Notice that “Apples” has an extra space once, and “Rice” and “Apples” are repeated.
4 Select all the items and go to the Data menu.
5 From the drop-down list, choose Data cleanup > Trim whitespace.
6 The Trim whitespace dialog box appears and the extra space before “Apples” will be removed. Click on OK to close the dialog box.
7 Again, select all the items and go to the Data menu.

8 Choose Data cleanup > Remove duplicates
9 The Remove duplicates dialog box appears. It shows the range of the values you selected.
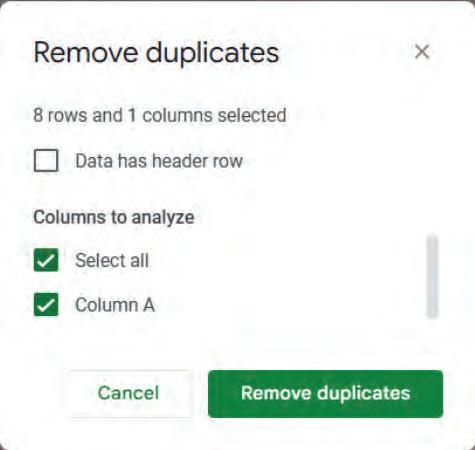
10 Make the selection as required and click the Remove duplicates button.
11 The duplicate rows (or values) will be deleted.
12 Your shopping list is now clean and unique.








In the previous chapter, you learnt how to enter data in a spreadsheet and how to use formulas and functions. Now, we will learn about some advanced features of spreadsheets, such as copying and moving data, inserting and deleting cells, undo, redo, and autofill.
Let us learn to select cells first. We often need to select a group of cells to perform various operations such as copying, moving, inserting, or deleting.
We can select cells in a Google Sheet in various ways:
1. Selecting a cell: Left-click on the cell you want to select.
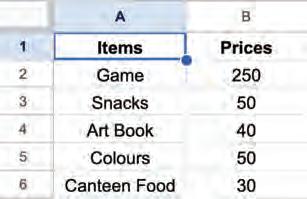
3. Selecting a column: Left-click on the column letter to select all cells in a column.
5. Selecting all data cells: Select a cell holding some data and then press Ctrl + A shortcut key. All the cells containing data will be selected.
2. Selecting a row: Left-click on the row number to select all cells in a row.
4. Selecting multiple cells: Click on the required starting cell and then drag the mouse to the last cell you want to select.
6. Selecting all cells in a sheet: To select all the cells in a sheet, select a blank cell and press Ctrl + A.
If you select a data cell, then press Ctrl + A twice to select all the cells in a sheet.
Changing cell data refers to modifying, replacing, or deleting the data in a cell.
You can follow these steps to change the cell data:
1. Click on the cell you want to edit. A blue border will appear to indicate that it is now the active cell.
2. Start typing to edit or replace the existing data. The new data will appear in the cell as you type.
3. Confirm the changes by changing the active cell using the arrow keys or pressing the Enter key.
Did You Know?
Spreadsheets support real-time collaboration, meaning multiple users can work on the same spreadsheet simultaneously.


Why is it important to know how to select, edit, and format cells in

In Google Sheets, you can copy the data of a cell and paste it in the same sheet or in a different one. You can also move the data and keep it at some other place in the same sheet or a different one. Let us see how to copy and move data from one place to another.
Copying cell data means copying the data from one or more cells and pasting it into another cell or cells in the same spreadsheet or another one. This will keep the data in both places.
You can follow these steps to copy cell data:
1. Select the cell or cells you want to copy.

2. Go to the Edit menu and choose the Copy option to copy the selected cell(s).
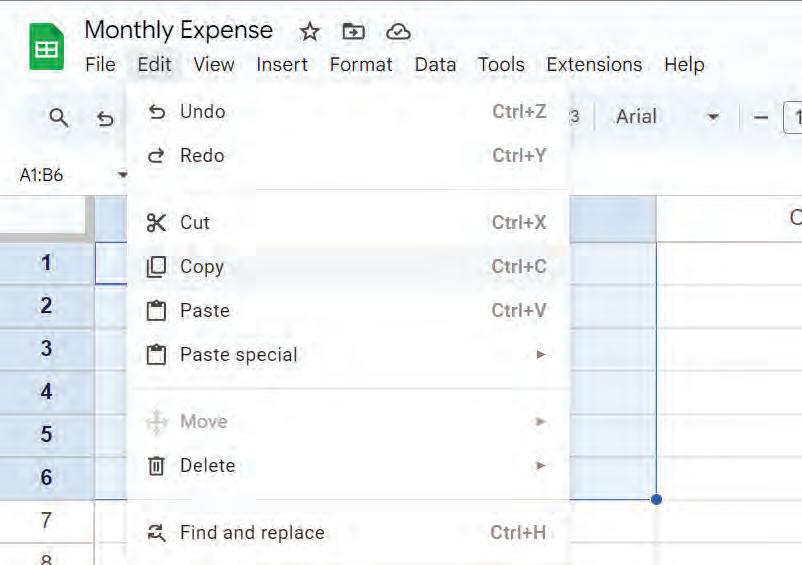
OR
Right-click and choose the Copy option from the pop-up menu to copy the selected cell(s).
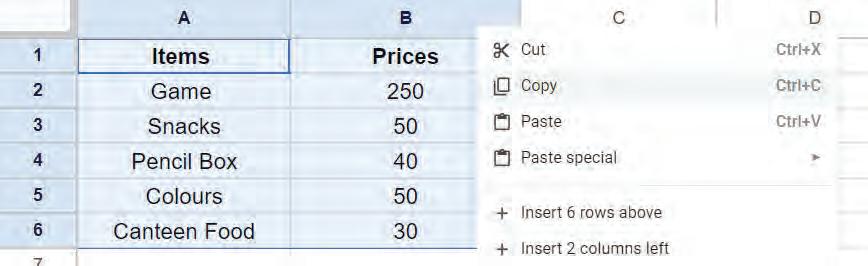
OR Press the Ctrl + C shortcut key on the keyboard to copy the selected cell(s).
The cell data will be copied.
You can follow these steps to paste the copied cell data:
1. Select the cell where you want to paste the copied cell data.
2. Go to the Edit menu and choose the Paste option to paste the copied cell data.

OR Right-click on the cell and choose the Paste option from the pop-up menu to paste the copied cell data.
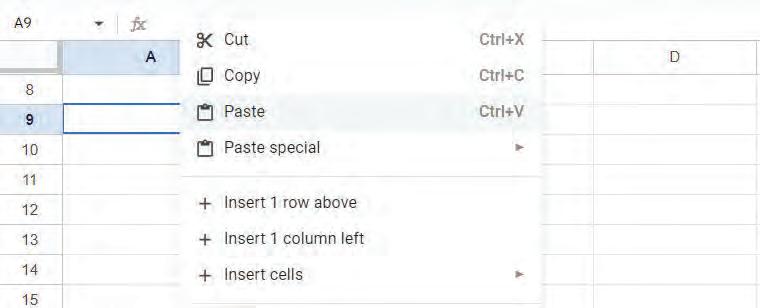
OR Press the Ctrl + V shortcut key on the keyboard to paste the copied cell data. The cell data will be pasted.
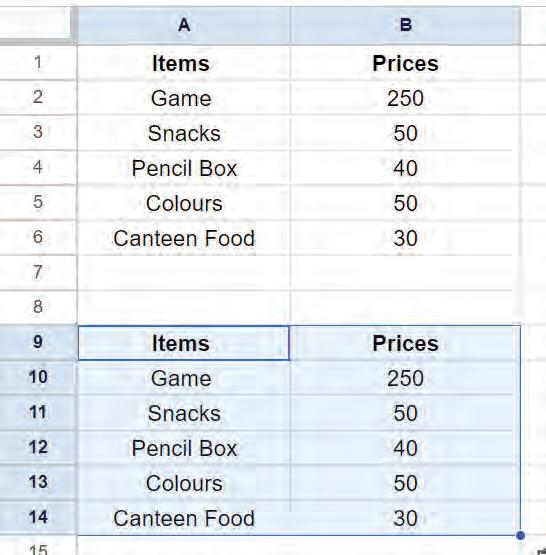
Pasted data

Match the columns. 1
Shortcut key to paste copied cell data

Copy option icon Ctrl + C
Paste option icon

Shortcut key to copy selected cell(s) Ctrl + V
Answer the following.
a How can you change cell data in a Google Sheet?
b What are the ways to copy cell data in a Google Sheet?
Moving cell data means cutting the data from one or more cells and pasting it into another cell or cells in the same spreadsheet or another one. The data will only be in one place after you move it.
You can follow these steps to move cell data:
1. Select the cell data to be moved.
2. Go to the Edit menu and choose the Cut option to cut the selected data.
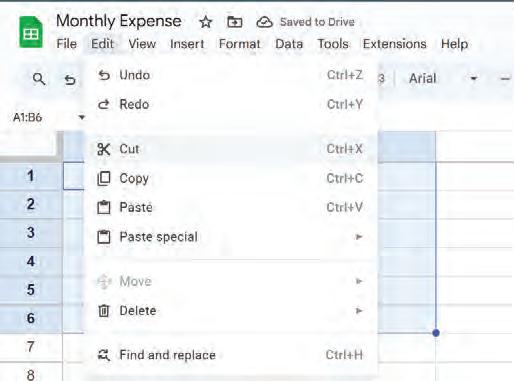
OR
Right-click and choose the Cut option from the pop-up menu to cut the selected data.
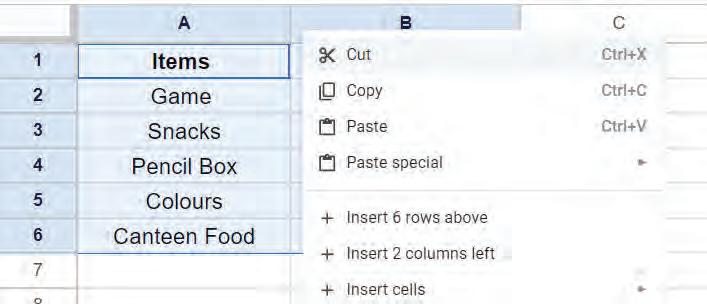
OR Press the Ctrl + X shortcut key on the keyboard to cut the selected data.
A dashed border around the cut data will appear.
3. Select the cell where you want to move the cut cell data.
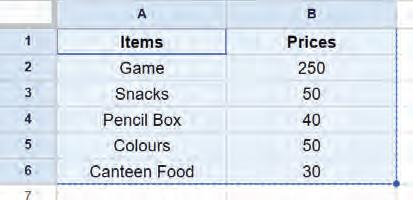
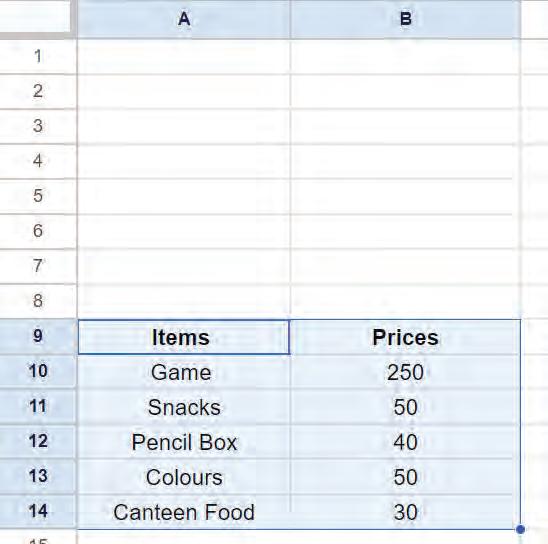
4. Choose any of the three ways to paste the cell data. The data will be moved to the new cells.

Deleting cell data means removing the data from a cell and making it blank.
You can follow these steps to delete cell data:
1. Select the cell(s) from which you want to delete the data.
2. Press the delete key on the keyboard to delete data from the selected cells. The cells will be blank.
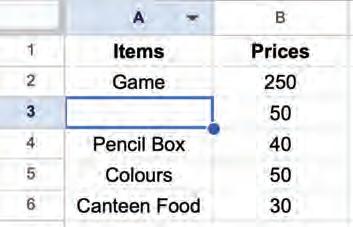
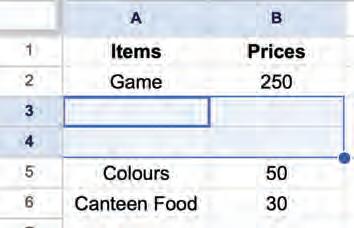
Undo and Redo are two useful features that save our time and help us avoid mistakes such as accidentally removing a row of data, entering the wrong data, or applying the wrong formula.
You can reverse or repeat recent changes made in a spreadsheet using the undo and redo commands.
The Undo feature allows you to undo or revert recent changes made in a spreadsheet.
You can follow these steps to undo changes:
1. Go to the Edit menu and choose the Undo option. Selecting a cell Selecting a group of cells
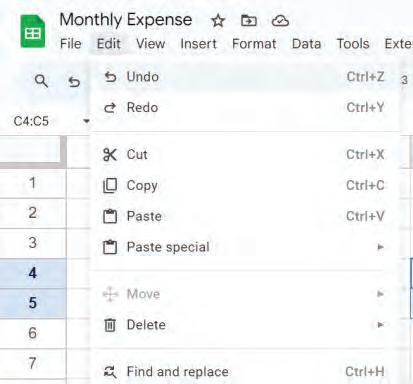
OR Click on the Undo option in the toolbar.
OR
Press the Ctrl + Z shortcut key on the keyboard.
The last change made will be reverted.
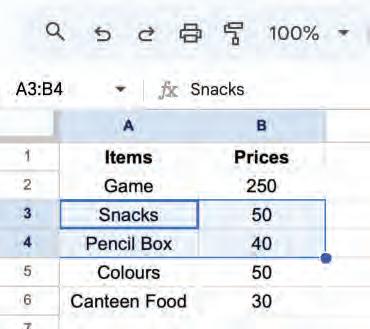
Imagine that you undo some changes you made, but later you realise that you want those changes back. Instead of making the changes again, you can use the redo command.
The redo feature allows you to redo or repeat the recent changes. It will redo the last change that you have undone using the undo command.
You can follow these steps to redo changes:
1. Go to the Edit menu and choose the Redo option.

OR
Click on the Redo option in the toolbar.
OR
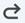
Press the Ctrl + Y shortcut key on the keyboard. The last change undone will be repeated.
When do you think undo and redo can be helpful?

Which keyboard shortcut is used to cut the cells in a spreadsheet?
a Ctrl + C b Ctrl + X c Ctrl + V
Match the following with their meaning.
Column A
Moving cell data
Redo
Undo
It lets you do something again that you did before. 1
Deleting cell data
Column B
It reverses your last spreadsheet action.
This means removing the content from a cell.
The process of relocating information from one location to another within or between spreadsheets.
You can insert a cell, column, and row as you require. Let us see how you can do it.
Inserting a cell means adding a cell within a row or column.
You can follow these steps to insert a cell:
1. Select the cell where you want to insert the new cell.
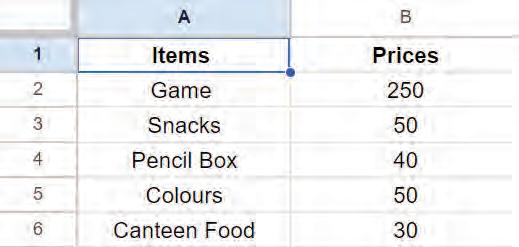
2. Right-click on the cell and choose Insert cells > Insert cells and shift right option from the shortcut menu.
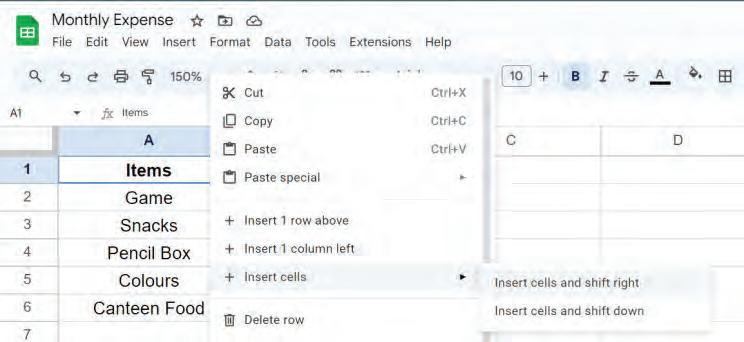
The cell will be inserted, shifting the existing cells to the right.
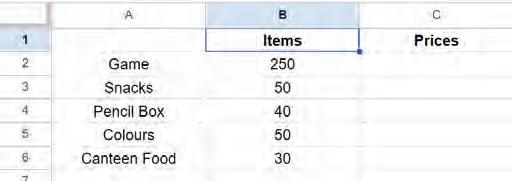
OR
Right-click on the cell and choose Insert cells > Insert cells and shift down
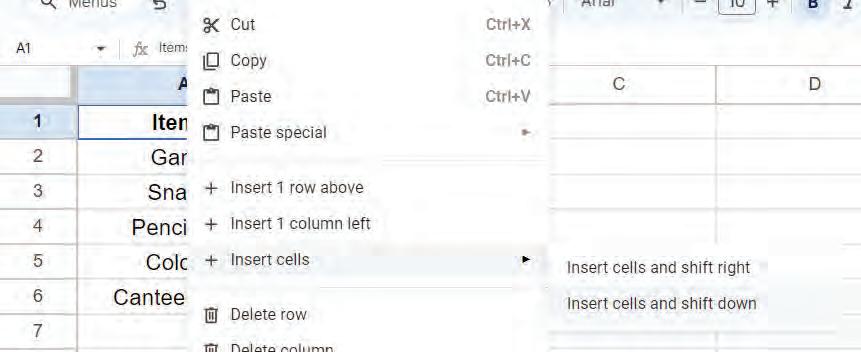
The cell will be inserted, shifting the existing cells downwards.

Inserting a column means adding a new column to a spreadsheet. We can add a column to the left or right of an existing column.
You can follow these steps to insert a column:
1. Choose the column next to where you want to add a new column.
Left-click on the column letter to select the column.
2. Right-click and select the Insert 1 column left option from the pop-up menu.
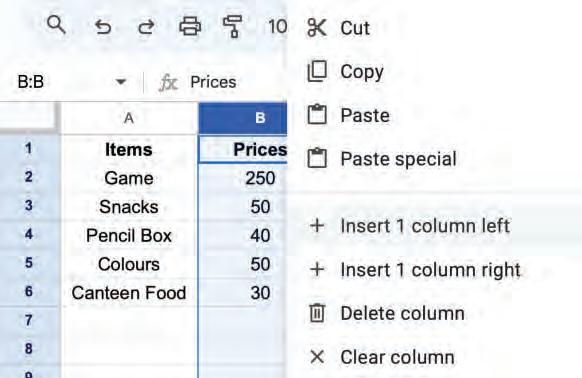
A new column will appear on the left-hand side of the column.
OR
Right-click and select the Insert 1 column right option from the pop-up menu.
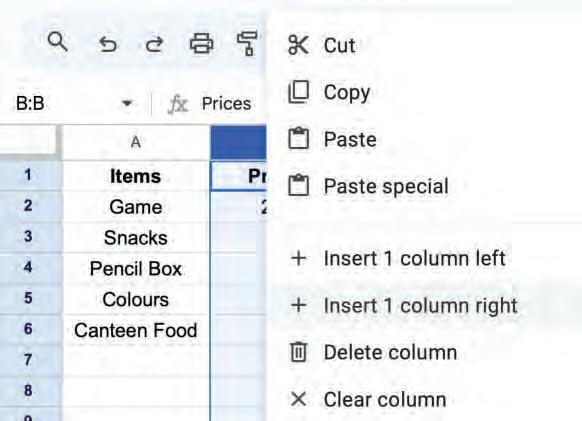
A new column will appear on the right-hand side of the selected column.
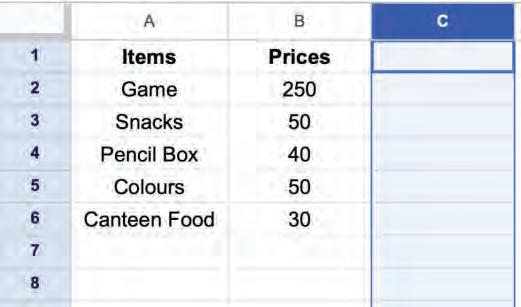
Inserting a row means adding a new row in a spreadsheet. We can add a row above or below an existing row. You can follow these steps to insert a row:
1. Choose the row next to where you want to add a new row.
Left-click on the row number to select the row.
2. Right-click and select the Insert 1 row above option from the pop-up menu.
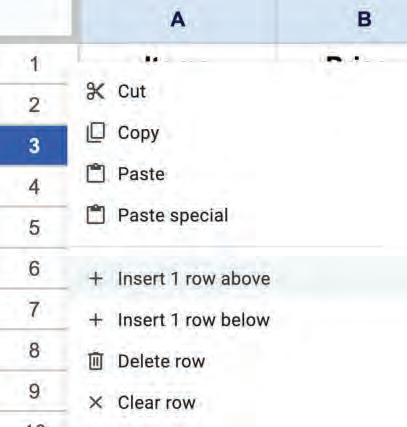
A new row will appear above the row.
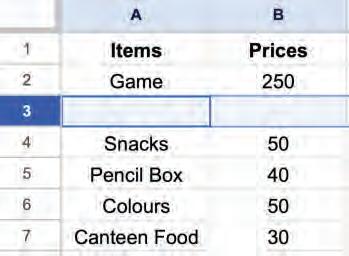

OR
Right-click and select the Insert 1 row below option from the pop-up menu.
A new row will appear below the row.
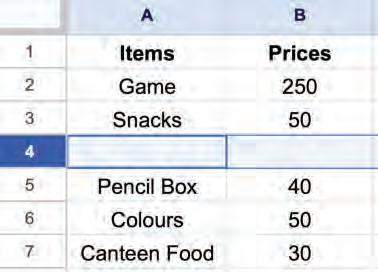
You can delete a cell, column, and row as you require. Let us see how you can do it.
Deleting a cell or cells means removing the selected cells. After deleting the cell(s), the surrounding cells will shift to fill the gap.
You can follow these steps to delete cells:
1. Select a cell or cells you want to delete.
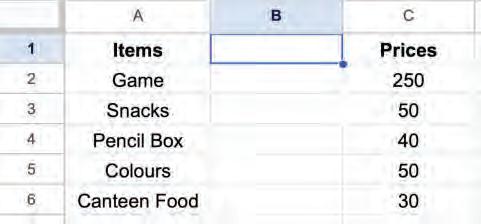
2. Right-click and select the Delete cells > Delete cells and shift left option from the pop-up menu.
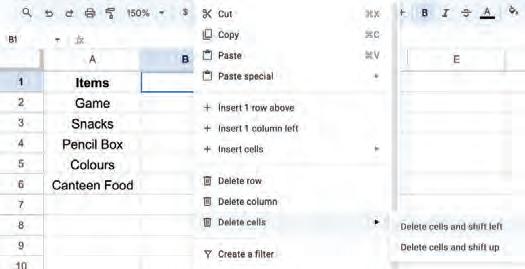
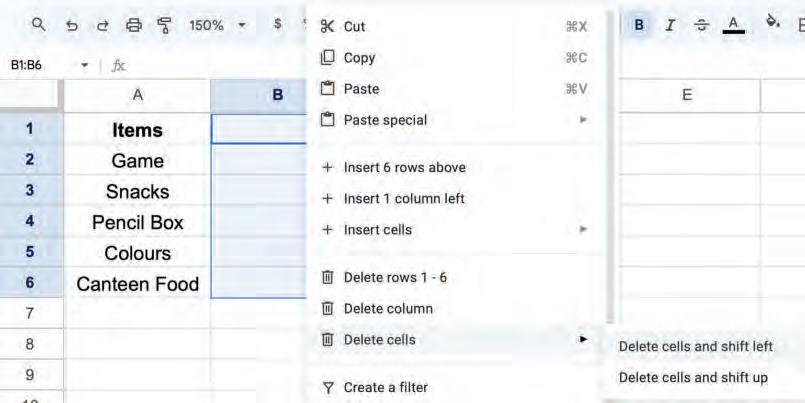
The cell will be deleted and cells next to it will be shifted to the left.
OR
1. Select a cell or cells that you want to delete.
2. Right-click and select the Delete cells > Delete cells and shift up option from the pop-up menu.

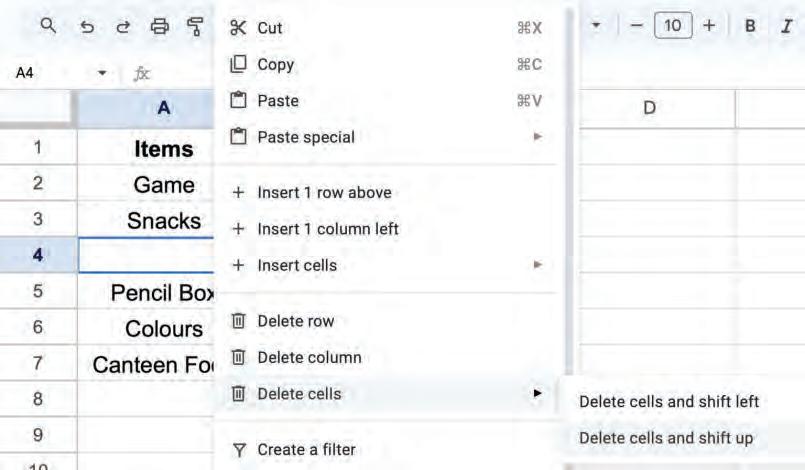

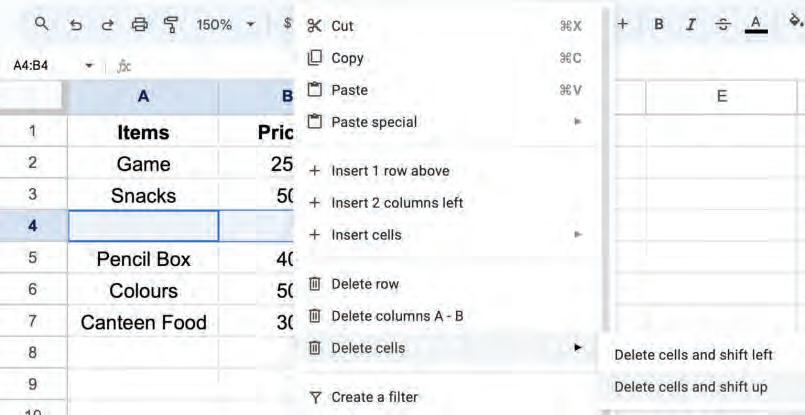
The cell will be deleted, and cells next to it will be shifted upward.
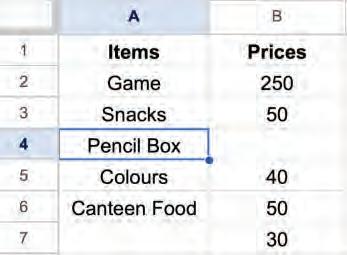
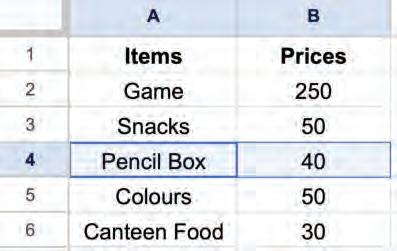
Deleting columns means removing one or more columns. You can follow these steps to delete a column:
1. Left-click on the column letter to select the column you want to delete.
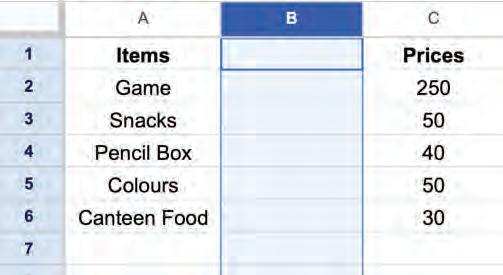
2. Right-click and choose the Delete column option from the pop-up menu to delete the column.
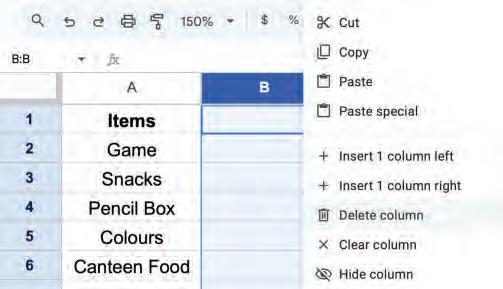
The column will be deleted, and the column on the right will be shifted left.
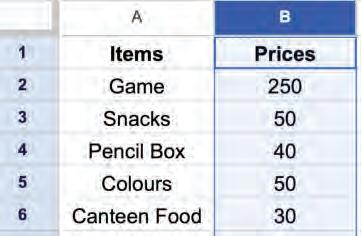
Deleting rows means removing one or more rows. You can follow these steps to delete a row:
1. Left-click on the row number to select the row you want to delete.
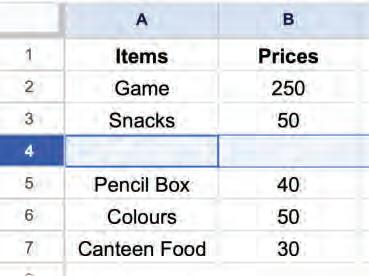
2. Right-click and choose the Delete row option from the pop-up menu to delete the row.
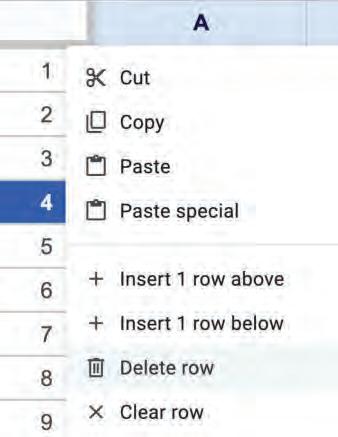
The row will be deleted, and the row below will be shifted up.
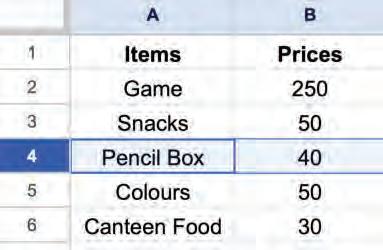

Autofill is a feature that allows you to automatically fill in a series of cells with data based on the pattern of the first few cells.
You can follow these steps to autofill a series of cells:
1. Select the cells for the pattern to be followed to generate new data and fill the series of cells with it.
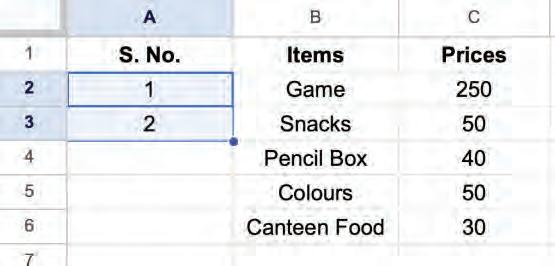
2. Hold the left mouse button and drag the Fill Handle (the small dot that appears at the bottom-right corner of the last cell of the selection) to autofill the cells with new data.
Autofill can be used in different ways. If you type a single value, like 5, and drag, the same value is repeated (5, 5, 5, …). If you type two numbers, like 1 and 2, select them and drag, Autofill continues the series (3, 4, 5, …). Similarly, if you type Monday and Tuesday, select them and drag, Autofill continues the days of the week (Wednesday, Thursday, …). Autofill can be used to generate number series, date series, and text series.
Which of the following is NOT a step to insert a cell in a spreadsheet?
a Select the cell where you want to insert the new cell.
b Left-click on the cell and choose Insert cells, then shift right.
c Right-click on the cell and choose Insert cells, then shift right.
d Right-click on the cell and choose Insert cells, then shift down.
How do you delete a column?
a Left-click the column letter to delete the column.
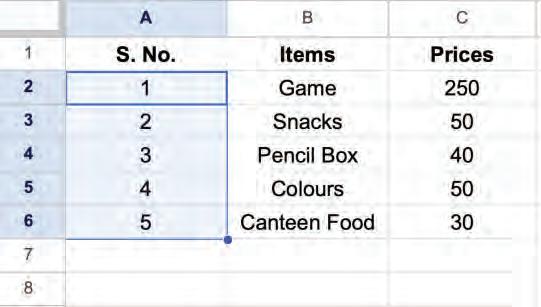
b Left-click the column letter and then right-click to choose the Delete column option.
c Left-click the column letter and press the Delete key.
d Right-click the column letter and press Ctrl + X.
What is the purpose of the fill handle in Autofill?
a To change the font style of selected cells.
b To insert new rows or columns.
c To fill a series of cells based on a pattern of data.
d To perform calculations in the selected cells.
What kind of series can you create using Autofill if you enter "Monday" in one cell and "Tuesday" in the next cell?
a A series of numbers.
b A series of random texts.
c A series of days of the week.
d Autofill cannot be used with text.
1 Cells can be selected in Google Sheets by:
a Clicking on a cell.
b Clicking on a row number to select all cells in a row.
c Clicking on a column letter to select all cells in a column.
d Holding left-click and dragging the mouse over multiple cells.
e Pressing the Ctrl + A shortcut key to select all the cells.
2 Changing cell data means modifying, replacing, or deleting the data in a cell.
3 To replace existing cell data, select the cell and type over it. Press the Enter key or click away from the cell to confirm the change.
4 Copying cell data means to copy the data from one or more cells and paste it into another cell or cells in the same spreadsheet or another one. This will keep the data in both places.
5 Moving cell data means to cut the data from one or more cells and paste it into another cell or cells in the same spreadsheet or another one. The data will only be in one place after you move it.
6 Deleting cell data means removing the data from a cell and making it blank.
7 The undo feature allows you to undo or revert recent changes made in a spreadsheet.
8 The redo feature allows you to redo or repeat the recent changes. It will redo the last change that you have undone.
9 Inserting a cell means adding a cell within a row or column.
10 Inserting a column means adding a new column to a spreadsheet. We can add a column to the left or right of an existing column.
11 Inserting a row means adding a new row in a spreadsheet. We can add a row above or below an existing row.
12 Deleting a cell or cells means removing the selected cells, and the surrounding cells will shift to fill the gap.
13 Deleting rows or columns means removing one or more rows or columns from a Google Sheet.
14 Autofill is a feature that allows you to automatically fill in a series of cells with data based on the pattern of the first few cells.

A. Fill in the blanks.
Hints
1 To copy cell data, you can use the shortcut key.
2 Undo allows you to the most recent change.
3 allows you to reapply actions you have previously undone.
4 To paste cell data, you can use the shortcut key.
5 To select multiple cells, hold the left mouse button and the mouse.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 After selecting a cell, you can replace its data by .
a Clicking
c Typing
2 Which shortcut key combination can be used to paste cell data?
a Ctrl + C
b Deleting
d Formatting
b Ctrl + Z
c Ctrl + V d Ctrl + Y
3 What does the undo feature do?
a Delete the selected cell
b Adds a new row or column
c Apply formatting d Reverses the most recent change
4 What is Autofill used for?
a To automatically fill in a series of cells with data based on the pattern of the first few cells
c To move data from one cell to another
5 How can you delete a cell in Google Sheets?
a Press the Delete key
c Right-click on the cell, select Delete cells and shift up
b To copy and paste data from one cell to another
d To delete data from a cell
b Right-click on the cell, select Delete cells and shift left
d All of these
C. Who am I?
1 I am the process of cutting and pasting cell data.
2 I am a way to select multiple cells with a mouse.
3 I am the small dot that appears at the bottom-right corner of a cell.
4 I am the shortcut key to select all cells in a Google Sheet.
5 I help you automatically fill in a series of cells with data based on a pattern.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1 To select an entire row, you can left-click on the row number.
2 To insert a new row, you can left-click on the row number and select Insert 1 row above or below.
3 To select multiple cells, you can hold down the left mouse button on the first cell in the range and then drag the mouse to the last cell in the range.
4 Deleting a row in a spreadsheet will shift the remaining rows left to fill the gap.
5 You can use autofill to generate number series only.
E. Answer the following questions.
1 What is the difference between copying and moving cell data?
2 How do the undo and redo features work?
3 Write the steps to insert a column.
4 How can you use Autofill in a Google Sheet?
5 What are the different types of series that Autofill can generate?





F. Apply your learning.
1 You are making a spreadsheet to keep track of how many books you read in a year. You want to choose the cells in the row for the month of January so that you can type the number of books you read that month. How can you choose the cells in the row for the month of January?
2 Rahul is making a budget table with different types of expenses and how much he spends on each one. He has missed an entry. How can he add a new row in between for the missed entry in his budget table?
3 You want to create a schedule for your next school project. You create a column with the header "Day" and then fill in Monday and Tuesday in the two cells below. How can you autofill the remaining days?
4 Ananya has a spreadsheet with some information. She needs to delete a group of cells that have wrong information. How can she delete a range of cells from a spreadsheet?
5 Shreya keeps track of the items that she sells in her store. She needs to add a new column to track how many of each item are left. How can she add a new column to track the availability of the items?

Exploring AI-Powered Smart Fill in Google Sheets
Objective: To understand how AI in Google Sheets uses pattern recognition to auto-complete data using the Smart Fill feature.
Activity: Create a Google Sheet containing the names and email ids of the students using the Smart Fill feature of Google Sheets.
Solution: Follow the given steps:
1 Open a new Google Sheet.
2 Create two column headings in Column A and Column B, respectively, as shown.
3 Type the names of the students in Column A.
4 Click on the cell B2 in Column B
5 Type the formula =A2&”gmail.com”
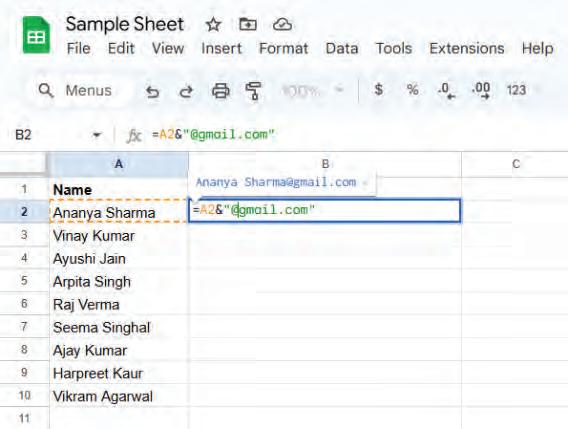
6 Press Enter and observe the pattern suggested by the Smart Fill feature of Google Sheets.

7 The email ID for the first person will be created as “ananya.sharma@gmail.com” and the suggestions for the email id of all the persons in the list will be provided to you as shown here.
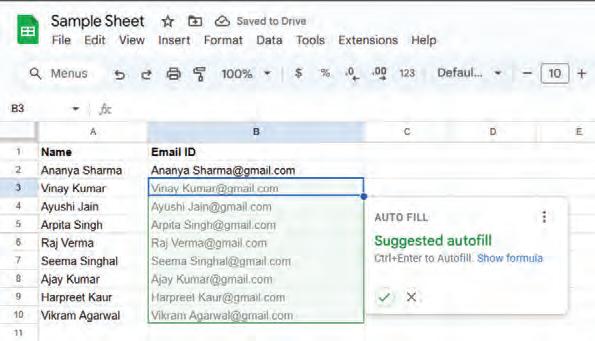
8 Again, press Enter to accept the suggestion or click on the ✓ symbol in the AUTO FILL box.
9 The data will be filled in Column B, without typing individual email IDs.






We are in an age where we are surrounded by a huge amount of data. Data helps us maintain and improve systems. Think about your school. Your school needs to maintain data about all the students, like their names, ages, grades, library card numbers, parent’s names and many other details so that the school can run without any problems. Similarly, data helps shopkeepers to keep track of their sales. Large businesses benefit from data by being able to understand their customers and create products that will be helpful to them. Additionally, it aids scientists in their many scientific endeavours.
However, storing and maintaining this data on the computer becomes a challenge if we do not have a structured system.
It leads to various problems such as having the same information in different places, information not getting updated everywhere, and security and privacy issues.
To resolve these problems, we use databases.
A database is a collection of information or data, stored electronically in a computer system.
Most databases store data in the form of tables. A database can contain multiple tables to store related data.
For example, your school’s database might contain separate tables containing students’ data, teachers’ data, library data, and so on.
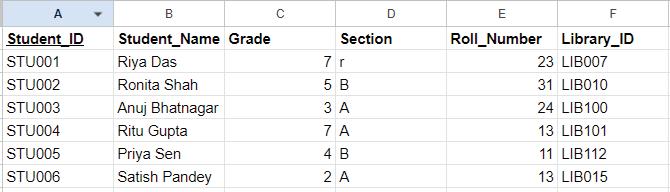
The column headers in the table are known as attributes and the rows are known as records
We use DBMS (Database Management System) to organise and manage the databases. It acts as an interface between the database and user applications.
We will learn more about DBMS later in this chapter.
The first DBMS was developed in the early 1960s by Charles Bachman.

In this digital age, computers are used everywhere to store large amounts of data to keep track of personal and professional needs whether it is a local grocery shop or the stock market. Today, we all rely on some form of database to store information.
Let us learn more about the importance of database:
Organised Information: Databases help to keep information organised and make it easier to find. Most databases store related data using multiple tables. This information is recorded in rows and columns, making it easy to access.
Quick Access: Without a database, you would need to manually search through various files and documents to find data. Databases make it simple to add, delete, or modify data because they store data in rows and columns, allowing quick access to specific information.
Centralisation: Centralising information also structures data and prevents duplication. It saves space and allows you to work better and faster, ultimately increasing your overall productivity.
Large Volumes of Data: Databases can store and organise a huge amount of data easily. That makes it easy to quickly find the specific information as needed.
Data Security: Your data is secure when it is kept in the database. Only authorised persons can access the information which prevents unauthorised access to data.
Ensures Data Integrity: Data integrity ensures that data remains accurate, complete, and consistent throughout its lifecycle.
The database ensures data integrity by providing accurate information, even if multiple users are working in the system at the same time. This means you will always get the right information, even when there are multiple users.
For example, Book Id, Book Name, Genre, Price, and Publisher would be the same throughout, and anyone can access it. Data integrity helps to set rules on how this data can be accessed, used, and modified.













Reduction of Data Redundancy: Data redundancy occurs when we have multiple copies of the same data. Databases help us reduce data redundancy by making sure you do not have copies of the same data spread all over the place. This is important because it can get tricky to update data everywhere it is stored.


Big Data is a huge collection of information. Companies use it to recommend movies and songs you might enjoy. Scan the QR code to know more about it.
A DBMS (Database Management System) is a software that helps us to store, retrieve, and manage data in a database.
To retrieve data means to obtain the data from the database.
DBMS provides an interface between an end-user and a database, which allows users to create, read, update, and delete data in the database. It also provides protection and security to the database. In case of multiple users, it can restrict access to different databases for unauthorised users.
Imagine you have a huge collection of books and need someone to organize them for you. That is exactly what a DBMS does for data in a database.
It helps organise the data, makes it easy to search for specific things, and ensures that everything is safe and secure. So, whenever we want to find something in our database, the DBMS helps us quickly locate the exact information we need.


Database Management System consists of six main components. These are: 1.
6. People
1. Hardware: The hardware of computers consists of physical components such as a keyboard, mouse, monitor, and processor. Hardware is used to capture the data and present the output to the user.
When we try to run any database software like MySQL, we can type any command with the help of our keyboard. Storage devices, such as the hard disk, RAM, and ROM, are also the part of our computer system.
2. Software: Software is a set of programs that help hardware do its job. It is made up of procedures and programs that can understand the language used to talk to databases.
This software then turns those instructions into real commands for the database and makes things happen.
Some examples of DBMS software are MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server, dBase, FileMaker, and Microsoft Access.


Smarthome gadgets, like those controlling lights and music, rely on databases to deliver great experiences.
3. People: The individuals who use and manage the computer system are its most important part. In older computer terminology, they were sometimes called “liveware,” but today we usually call them users or end-users.
These individuals control and manage databases, performing various operations within the Database Management System (DBMS). This group comprises the database administrator, software developer, and end-users.
4. Procedures: A procedure is a form of general instructions or guidelines for using a DBMS. These instructions include how to set up the database, install it, log in and out, manage it, create a backup, and generate reports from the database.
5. Data: These are the actual pieces of information, like numbers or text, that are input into a computer system.
Data refers to the collection of raw facts stored in a database.
Data is the fundamental building block for creating useful information. It is a crucial part of a DBMS. The database contains both the actual data and metadata, which is information about the data.

For example, when you want to store data in a database, you need to identify the attributes to organise that data, such as the data’s size, name, and other related details. These specific pieces of information about the data to be stored are known as metadata.

6. Database Access Language: Database Access Language is a language that allows users to give commands to a database to operate the data stored. You can use this language to ask the database to do many things, such as getting data, modifying it, or removing it.
The most widely used Database Access Language is SQL. SQL stands for Structured Query Language
Match the Columns.
Column A
Database
Data Integrity
Database Management System
Data Redundancy
Column B
Occurrence of duplicate copies of similar data
A special computer program for managing databases
A collection of organised data
A process that makes sure data is accurate, complete, and consistent over the data’s lifecycle
MySQL is a database management system that allows us to create our own databases. It allows us to create, update, and retrieve data using SQL. It is open-source, which means it is free to use. It is popular for its speed, reliability, and scalability.
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a language that lets us access and manipulate databases. It allows us to perform operations on the data stored in the database, such as updating, inserting, deleting, and modifying data, etc.
SQL works on structured data. As a database holds data in a structured way, it is easy to retrieve information from the database using SQL.
SQL is not a database management system, but a query language.

With SQL, we can state our query using commands and ask the database to find specific data, like “Which book has the maximum price?” or “How many books do I have in my collection?”. The database then understands our questions and gives us the right answers.
SQL is simple but a powerful language to deal with databases.
Before we learn more about SQL and create our database, let us learn about keys.
Keys are used to uniquely identify any row of data from the table. We know a database can have multiple tables. Keys are also used to establish and identify relationships between tables.
We will learn about four kinds of keys in this chapter.
1. Primary Key: The primary key is the attribute or set of attributes in a table that uniquely identifies a row in that table. There should be only one primary key in a table. A primary key cannot contain NULL values and must be unique for each row.
Let us observe the Students table. Student_ID is the primary key. Student_ID uniquely identifies each row in the table. In tables, the underlined attribute is the primary key.
Primary Key
STU001Riya Das 7
23 LIB007
STU002Ronita Shah5 B 31 LIB010
STU003Anuj Bhatnagar3 A 24 LIB100
STU004Ritu Gupta7 A 13 LIB101
STU005Priya Sen4 B 11 LIB112
STU006Satish Pandey2 A 13 LIB015
2. Candidate Key: There might be multiple attributes that can uniquely identify a row in a table. In our example, both Student_ID and Library_ID can uniquely identify a row in the table. But we had chosen Student_ID as the primary key.
Candidate key is the attribute that uniquely identifies a row in the table, but is not considered as the primary key. In our example, Library_ID is the candidate key.
3. Composite key: A primary key can consist of more than one attribute. In the Students table, Grade, Section, and Roll_Number when combined together can identify a row uniquely. Hence, it can be a primary key. When a primary key consists of more than one attribute, it is called a composite key.
4. Foreign key: We have previously learnt that a database can have multiple tables. Foreign keys help us to establish a relationship between these tables. Consider the following tables: Students table: Foreign key for Students table
Student_IDStudent_NameGradeSectionRoll_NumberLibrary_IDHouse_ID
STU001Riya Das 7A23
LIB007H001
STU002Ronita Shah5B31 LIB010H001
STU003Anuj Bhatnagar3A24 LIB100H003
STU004Ritu Gupta7A13 LIB101H002
STU005Priya Sen4B11 LIB112H001
STU006Satish Pandey2A13
LIB015H003

House table:
Primary key for House table
House_ID House_name
H001 Red house
H002 Yellow house
H003 Green house
Both the tables have the attribute named House_ID. House_ID is the primary key in the House table but it is not a primary key in Students table. House_ID is considered as a foreign key in the Students table.
Let us learn the basic concepts of SQL and then create queries.
In SQL, data types define the type of data that can be stored in a column of a table. The following are the most common data types of SQL:
Numeric data types are used to store a numeric value in a field. These can be whole numbers (integers) or numbers with decimals.
Common SQL types include:
INTEGER or INT: stores whole numbers (e.g., age INTEGER)
DECIMAL(p, s) or NUMERIC(p, s): stores numbers with a fixed total number of digits (p) and a fixed number of digits after the decimal point (s).
Example: salary DECIMAL(6,3) can store values like 123.456 (6 digits total, 3 after the decimal point).
Text data types are used to store a string value in a field column. It can be a single character or a set of characters.
CHAR: This data type is used to store fixed-length character strings. If the string is shorter than the specified length, it is padded with spaces.
Syntax: CHAR(size) where size represents the maximum (255 Characters) number of characters in a column.
Example: name CHAR(15)
VARCHAR/VARCHAR2: It is used to store variable length alphanumeric data.
Syntax: VARCHAR(size) / VARCHAR2(size) where size represents the maximum (2000 Characters) number of characters in a column.
Example: address VARCHAR2(50)
Date and time data types are used to store date and time values.
DATE: It is used to store date in columns. SQL supports the various date formats other than the standard DD-MON-YY.
Example: dob DATE
TIME: It is used to store time in columns. SQL supports the various time formats other than the standard hh-mm-ss.
Example: joining_time TIME
Did You Know?
Every DATE and TIME can be added, subtracted, or compared as it can be done with other data types.

SQL (Structured Query Language) is used for managing and manipulating databases. SQL commands are broadly categorised into two main types:
• Data Definition Language (DDL)
• Data Manipulation Language (DML)
DDL commands are used to define and modify the structure of database objects, such as tables, indexes, and views. These commands deal with the schema and structure of the database.
The following are the main DDL commands:
1. CREATE: Used to create new database objects like tables, views, and indexes.
2. ALTER: Used to modify the structure of an existing database object.
3. DROP: Used to delete an existing database object.
DML commands are used to manipulate data stored in the database. These commands deal with the actual data in the database.
The following are the main DML Commands:
1. SELECT: Used to retrieve data from the database.
2. INSERT: Used to add new rows of data to a table.
3. UPDATE: Used to modify existing data in a table.
4. DELETE: Used to remove rows from a table.

Let us now learn how to use the SQL queries to create tables and work upon them.
The Create Table command is used for creating tables.
Syntax:
Create Table table_name ( column_name_1 data_type_1, column_name_2 data_type_2, column_name_n data_type_n );
Here is an example of creating a table Students using various data types:
CREATE TABLE Students ( Student_ID VARCHAR(6), Student_Name VARCHAR(50), Grade INT, Section CHAR(1), Roll_Number INT, Library_ID VARCHAR(7), House_ID VARCHAR(4), Enrollment_Date DATE ); This query will create a table with the following structure: Student_ID Student_Name Grade Section Roll_Number Library_ID House_ID Enrollment_Date
The Create Table command is used to create a new table in a database. When defining a table, you can set a primary key to ensure each record is unique.
Syntax:
Create Table table_name ( column_name_1 data_type_1 PRIMARY KEY, column_name_2 data_type_2,
column_name_n data_type_n );
Example:
CREATE TABLE Students ( Student_ID VARCHAR(6) PRIMARY KEY, Student_Name VARCHAR(50), Grade INT, Section CHAR(1), Roll_Number INT, Library_ID VARCHAR(7), House_ID VARCHAR(4), Enrollment_Date DATE );
In the above created Students table, the Student_ID field is the primary key and will contain only the unique values in it.
Now, we have created a table. Let us insert the values in the created table, Students.
Syntax:
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1, value2, ...);
Example:
INSERT INTO Students (Student_ID, Student_Name, Grade, Section, Roll_Number, Library_ID, House_ID, Enrollment_Date) VALUES (‘STU001’, ‘Riya Das’, 7, ‘A’, 23, ‘LIB007’, ‘H001’, ‘24-07-2024’); This command will insert the values in the Students table.
Student_IDStudent_NameGradeSectionRoll_NumberLibrary_IDHouse_IDEnrollment_Date STU001Riya Das7A23LIB007H00124-07-2024

The SELECT statement is used to query the database and retrieve specific data.
Syntax
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
Examples
Let us select all columns for all students from the Students table:
SELECT * FROM Students;
To select specific columns, such as Student_Name and Grade, we use:
SELECT Student_Name, Grade FROM Students;
To filter the results and retrieve only students from Grade 7:
SELECT * FROM Students
WHERE Grade = 7;

There are other Database Management Systems besides MySQL like Microsoft SQL Server and MongoDB. Scan this QR code to know more about them.

To create a table, we use command to define its structure.
To show data from a table, we use command.
Identify and write down the field names with their data types if you have to create a table named Library.
4 Identify the given commands as DDL or DML and write their type in the blank space.
a select
c alter
b update
d insert
5 Look at the structure of the given table. Which field according to you should be a primary key?
Table name: Library_Inventory
Book_ID Title Author Year Publisher ISBN
1 Database is a collection of information stored electronically in a computer system, organised in tables with rows (records) and columns (attributes).
2 DBMS (Database Management System) is a software that helps store, retrieve, and manage data in a database. Examples include MySQL, Oracle, and SQL Server.
3 Primary key is an attribute or set of attributes that uniquely identifies each row in a table. It ensures data integrity by preventing duplicate entries.
4 SQL (Structured Query Language) is a language used to manage and manipulate databases.
5 DDL (Data Definition Language) is a type of SQL commands used to define and modify the structure of database objects. For example, CREATE, ALTER, and DROP.
6 DML (Data Manipulation Language) is a type of SQL commands used to manipulate data stored in the database. For example, SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE.
7 Data types in SQL define the type of data that can be stored in a column. For example, NUMERIC, CHAR, VARCHAR, and DATE.
A. Fill in the blanks.
Hints
A is a collection of information stored electronically in a computer system.
The is the software that helps us store, retrieve, and manage data in a database.
In a table, the column headers are known as
A key uniquely identifies each row in a table.
The SQL command used to insert values in the created table is

B. Tick () the correct option.
Which of the following is a numeric data type in SQL?
a CHAR b VARCHAR
c INT d DATE
What does DML stand for?
a Data Modification Language
c Data Manipulation Language
What is the purpose of the primary key in a table?
a To store text data
c To perform calculations
b Data Management Language
d Data Mining Language
b To uniquely identify each row
d To store date values key help us to establish a relationship between different tables.
a Primary b Composite
c Foreign d Candidate
Which of the following is an example of DBMS software?
a MySQL b Python
C. Who am I?
I am the software that acts as an interface between the database and user applications.
I ensure that the data in a database is correct, whole, and consistent.
I am a language used to manage and manipulate databases.
I am a command used to create a new table in a database.
I am a type of SQL command used to define and modify the structure of database objects.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
Databases are used to keep information organised and make it easier to find.
A primary key can have duplicate values.
SQL stands for Structured Query Language.
The SELECT command is used to insert data into a table.
A DBMS provides
and security to the database.
Answer the following questions.
What is a database, and why is it important?
Explain the role of a Database Management System (DBMS). What are the different components of a DBMS?
Give an example of a SQL query to create a table with a primary
F. Apply your learning. HOTS
Create a table named ‘Teachers’ with columns for Teacher_ID, Teacher_Name, Subject, and Contact_Number. Make Teacher_ID the primary key.
Insert a new row into the “Teachers” table with the following values: Teacher_ID: ‘T001’, Teacher_Name: ‘John Doe’, Subject: ‘Math’, Contact_Number: ‘1234567890’.
Vijay has started his own movie theatre. He wants to keep a record of the movies he plays in his theatre. Write SQL commands to create a database and table for the same.
Rahul is a video game player. He wants to create a leadership board with each player’s name, score, and level achieved. Write the SQL commands to create a leadership board table and add records in it.
Describe a real-world scenario where you would use a composite key in a database table.

Generating SQL Queries with ChatGPT
Objective: To create a database and insert records in the Tekie digital panel, and use ChatGPT to generate SQL queries from plain English questions.
Activity: Create a Movies database, then ask ChatGPT to convert plain English questions into SQL queries and run them on the Tekie platform.
ChatGPT is an AI tool developed by OpenAI. It can understand plain English, provide answers, and even assist with coding. In this activity, we will use it to convert English questions into SQL queries.
Solution: Follow the given steps:
1 Create the database using Tekie digital platform.
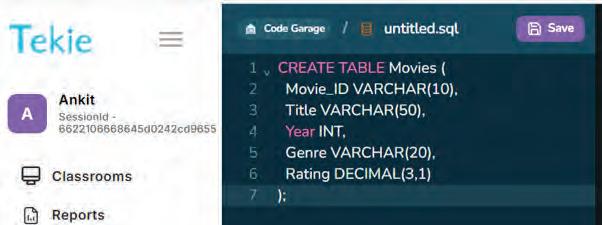
2 Insert records in the database.
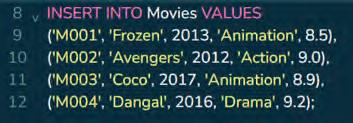
3 Now use AI assistance (ChatGPT):
• Click on the link: https://chat.openai.com/. This will direct you to a web page as shown.
• Click the ‘Try ChatGPT’ button.
• On the web page that appears, type the following question in plain English, click the Enter button and let ChatGPT generate the SQL query for you.
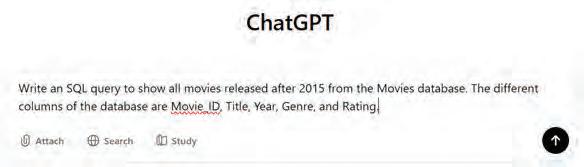
→ ChatGPT SQL Suggestion:

• Similarly, you can ask other questions from ChatGPT:
→ ChatGPT SQL Suggestion:

4 Copy the AI-suggested queries, paste them into your Tekie digital panel, and observe the results in the Output window. Compare the SQL results with your expectations to verify correctness.









Canva is a free online tool for making visual content such as posters, flyers, social posts and presentations. Graphics are images and drawings. When we combine graphics and text, our ideas become easier to understand.
Canva is used for making various types of visuals that can be used in posters, on social media, presentations, flyers, infographics, and many more.
To get started with Canva, follow the steps:
1. Open a web browser.
2. Type www.canva.com in the address bar. The home page of the website opens.

3. Create a new account by clicking on the Sign up button. Or, log in to Canva by using your existing mail address by clicking on the Log in button.
To log in to an existing account To create a new account





After you log in, the first screen will look like the image given here. You can see a variety of design templates and tools that you can choose from.
Let us create a card on the topic, ‘Digital India.’
Follow the given steps to create a card:
1. Click the Create a design button in the top left-hand corner of the screen. The Create a design window will appear.
2. Type ‘card’ in the search bar. The options related to card appear.

3. Select the size of the card that suits your requirement.
4. A new window opens where you can design the card.
To set the background image for your card, follow the steps:
1. Scroll down the left-hand sidebar and then select the Apps option. The Apps panel will appear.
2. Choose the Background option from the list. Various background options will appear. Choose a suitable background from the list.
Elements in Canva are colourful images, stickers, icons, and shapes that you can easily add to your designs to make them interesting.
Let us follow these steps to add some elements on the card:
1. Click the Elements option on the sidebar. A drawer menu appears.
2. Browse the various elements displayed in the menu.
3. You can also type a keyword in the Search elements box and press Enter.
4. The elements related to the keyword will appear.
5. Select an element to add. The selected element appears in the design area.
6. You can select the added element by clicking on it and move it anywhere on the card. You can also rotate the element by clicking on the Rotate button.
Other than elements, you can also add text to your design. Follow the given steps to add text to your project:
1. Click the Text option on the sidebar. A drawer menu appears.
2. Select the Add a text box button.
3. A text box with default settings appears in the design area.
4. You can select the font style and font size from the text options displayed in the options bar above the design area. Now, type the desired text in the text box.

In a similar manner, add more elements and text to your design.

A layer can be considered as a transparent sheet. Suppose you need to create a drawing with various elements. There are multiple transparent sheets with one element drawn on each sheet. Now, put these sheets on top of each other. You can observe a complete drawing with multiple elements.
When you add new elements to Canva, they get placed on top of each other, creating layers of elements.
After all the elements are placed in the design area, you can position them as required. Let us explore the various ways to position an element or a layer.
1. Click on an element.
2. Click on Position in the Options bar.
3. A sidebar opens on the right-hand side, consisting of two tabs, Arrange and Layers.
Let us learn about the various options in the Arrange and Layers tabs.
a. Arrange Tab
In the Arrange tab, the general settings for arranging various elements appear. This panel is further divided into various sections.
Layers Arrangement Section
The first section helps us with the arrangement of layers.
Forward—moves the selected layer a layer above.
To front—moves the selected layer to the top of the stack.
Backward—moves the selected layer a layer below.
To back—moves the selected layer to the bottom of the stack.
This section helps you to align the elements on your page.
For vertical alignment, use the options Top, Middle, and Bottom. For horizontal alignment, use the options Left, Centre, and Right.
Let us align the text ‘Digital India’ to the top of our design:
1. Select the text to be aligned.
2. Then, select the top option, to position the element vertically on the top of the design page.
The Advanced section lets you move, turn, or resize elements in your design, using exact values.
Width refers to how wide an object is, and height refers to how tall an object is.
In Canva, you can type the values to specify the exact object size. You can change the values of width and height by typing the required values in the Width and Height fields. Here, px stands for pixels.
Rotate
The Rotate option in Canva allows you to turn the element around at the required angle. You can use this feature to show elements from various angles.
Follow the given steps to rotate an element:
1. Select the element to be rotated.
2. Change the value of the Rotate field to the required angle.
Alternatively, you can also rotate elements with the help of the Rotate icon.

Hold the Rotate icon and move it to change the angle of the element.
b. Layers Tab
You can use the Layers tab to view the list of the layers in your project. By dragging the layers using a mouse, you can arrange the layers from this tab as well.
Using the All Tab
Go to the Layers tab and select the All tab under it.
Using the Overlapping Tab
Top Layer
Different layers in the design
Bottom Layer
If there are multiple layers in a project, it becomes difficult to select the exact layer on which you want to work. In such a case, the Overlapping tab is helpful.
1. Go to the Layers tab and select the Overlapping tab under it.
2. This tab shows only the layers that overlap with a selected layer. Select the layer you are looking for and make the required changes.
Imagine you are creating graphics in Microsoft Paint. You have added a few shapes and text overlapping each other. Later, you realise that the text is hiding behind the shapes. Is it possible to correct it without re-creating it in Paint? If you create the same project in Canva, how would it be helpful?

Duplicating a layer means creating a copy of it. This can save a lot of time when you want to use the same element multiple times in a project. What if you want to add two mobiles? You will simply duplicate the layers.
Follow the given steps to duplicate a layer:
1. In the Layers tab, right-click the layer that you want to duplicate. A drop-down menu appears.
2. Select the Duplicate option.
3. The selected layer is duplicated.

4. Alternatively, you can select an element and press Ctrl+C and then Ctrl+V to duplicate, or right-click > Duplicate.


Deleting layers that are not needed helps maintain an organised design. To delete an element from your design, delete its corresponding layer.
Follow the given steps to delete a layer:
1. In the Layers tab, right-click the layer you want to delete.
2. Select the Delete option.
3. The selected layer is deleted.

4. Alternatively, select the layer and press Delete or use the right-click > Delete option.

Many leading global companies use Canva because of its ease of use, strong collaboration features, and versatile functionality.
Create a similar design in Canva and guess the alignment of the text ‘Happy Birthday’ in the following designs.


a The Middle and Center alignment options serve the same purpose.
b The To Front option is different from the Forward option.
c The To Back option places an element immediately behind the other element.
d You can change the order in which the elements are layered.
Tick () the correct option.
The Align to Page feature helps you to:
a Make elements invisible.
c Align the elements on page.
Have you ever seen a flipbook?
b Create complex designs.
d Change the colour of the element.
It is a small book with a series of images at various positions on separate pages. When you quickly flip through such a book, it creates the illusion of movement of the objects drawn on the pages.
The cartoon movies that you watch are created in a similar fashion. Many images are drawn and flipped through at a fast pace so that the characters seem to be moving. This is what we call animation.
Animation is a method in which figures or objects are manipulated to appear as moving images


“Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs”, released in 1937, is Disney’s first full-length animated movie!
After creating a design in Canva, you can make it look interactive by adding animations. Canva has many useful tools using which you can create interesting animations. Let us learn how to use them.
Page animations decide how your page will enter the screen.
Follow the given steps to add page animation:
1. Select the page. (Make sure the whole page is selected, not a single element.)

2. Click the Animate option on the top bar. A sidebar with the tab Page Animations opens showing a list of animations.
3. Place the mouse cursor over the effects to see what they look like on your page.
4. Click the Play button, at the top right-hand side of your screen to observe the effect of the animation.
You can animate specific texts and elements present on a page in the same way as you can animate the entire page.
Follow the given steps to add element animation:
1. Click the text/element you want to animate.
2. Select the Element Animation tab from the sidebar and apply the desired animation effect to your element.
Applying transparency means making the elements look see-through. In Canva, all elements are fully visible by default. This means that Transparency is set to 100.
To apply transparency:
1. Select an element from your design, for example, the mobile.
2. Click the Transparency icon from the options bar above the design area. The Transparency slider appears.

3. Move the slider to the left to decrease the transparency of the element and to the right to increase it.
4. Observe the effect on the element’s transparency.

Did You Know?
The Transparency slider goes from 0% (fully transparent — invisible) to 100% (fully opaque — fully visible). Move the slider left toward 0 to make the element more see-through; move it right toward 100 to make it more solid.

Suppose you like the style of an element or a page, such as font, colour, effects, or transparency. You can apply the same styles to other elements or pages as well.
To copy and apply a style, follow the given steps:
1. Let’s say, you like the mobile for its transparency and want to copy the same to another element.
2. Right-click the mobile. A context menu appears.
3. Click the Copy style option. The style is copied.
4. Click the element where you want to apply the copied style. For example, click the image of the laptop.
The laptop becomes transparent with the same transparency value, just like the mobile.

Locking an object makes sure that the object remains at its place while you work on the other parts of the design. You can either lock an individual element or the entire page.
To lock the entire page:
1. Select the thumbnail of the page from the bottom and click on the More option (three dots).
2. A context menu will appear. Select the Lock page option to lock the page.

How can the Lock feature be helpful when you are creating a project?

To lock the specific elements, right-click the element and select the Lock option from the context menu. The element is locked. Note that another Lock symbol appears near the locked element.
To unlock the element, click the Lock symbol again.



Fill in the blanks.

Wonder how animation works practically? Scan this QR code.
a Page Animation decides how the will enter the screen.
b To see how your animation looks on an element, you use the button.
c The feature is used to copy the style of an element to another.
Match the following:
When you want to make sure that the object remains on its place.
When you want to make the elements look see-through
When you want to have the same style as the current element


Canva is a free graphic design platform that is used to create various visual contents, such as graphics, presentations, posters, social media graphics, flyers, and more.
Canva has a wide variety of design templates and tools to choose from for your projects.
Canva offers colourful images, stickers, icons, and shapes as elements that you can easily add to the designs to make them more engaging.
You can also add text to your design using the Text option from the sidebar. You can choose various options for fonts, sizes, and types.
When you add new elements in Canva, they are placed on top of the ones you have already added, creating layers of elements.
You can use the Position option to adjust the layering, alignment, and size of elements.
You can make your designs look interactive by adding animations.
You can use the Copy Style option to copy the style of one element and apply it to other elements.
You can use the Lock option to lock specific elements or the entire page to prevent accidental changes while
of your design.
A. Fill in the blanks.
Hints Create a design Transparency Position shapes visuals
Canva is a popular online tool used for creating various types of
To create a design in Canva, you need to click the button.
Elements in Canva include graphics, stickers, icons, and
The option in Canva allows you to control the arrangement of various elements in your design. means making the elements look see-through.
B. Tick () the correct option.
What can layers in Canva NOT be compared to?
a Transparent sheets kept on top of each other b Jigsaw puzzle
c Layers of paint d Images put on top of each other
In Canva, all elements are fully visible by default. This means that the Transparency setting is at what value?
a 0 b 50
c 100 d 75
Which tab helps you set the background image for your card in Canva?
a Text b Apps
c Draw d Background
What does adjusting transparency in Canva do?
a Changes the font size of the element b Rotates the element
c Makes a layer see-through d Duplicates the element
How does the Copy Style feature in Canva help your design?
a It changes the animation effects.
c It duplicates the entire design.
C. Who am I?
I make layers see-through, creating visual effects and overlays.
I can save a lot of time when you want to use the same element multiple times in a project.
I prevent unwanted changes in the project.
b It applies the same style from one element to another.
d It adds comments to the design.

I help you position the element at the top, middle, or centre of the design area. I am used to turn elements around by a desired angle.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
Canva is difficult to use and requires professional design skills.
The Layers tab in Canva helps order the elements like a stack.
Locking objects in Canva prevents any changes to that element.
The element will not be visible if the transparency value is 100.
The Forward option brings the layer to the top of the stack.
E. Answer the following questions.
What is the purpose of the Position option in Canva?
Explain the difference between the Forward/Backward and To Front/To Back arrangement options.
you use the Lock option for an object in Canva?
F. Apply your learning.
Aleena is making a poster for Diwali. She placed various elements in her design. Which Canva feature can she use to put the elements exactly in the centre?
Archita made a crossword puzzle for her classmates, using Canva. However, she made some adjustments to the project, causing the crossword to become nearly invisible. What do you think she must have done?
Maya is creating a design with lots of elements. She wants some objects to be in front while others hide behind them. Which Canva feature can she use to control the layers and make her design look like a playful scene?
Imagine you are a young chef who wants to share your favourite recipes. You have designed a digital recipe card using Canva. You have created multiple layers of elements in the recipe card. The text of the recipe card is hidden behind the images. What might be the problem?
Rani created a card for her friend’s birthday. She was showing it to her younger brother Anuj. Anuj was very curious and deleted the text in the card by mistake. How could have Rani prevented this mistake?

Generating Images Using AI Tools in Canva
Objective: To explore and use the AI tools available in Canva.
Activity: Use the AI tools in Canva to design an image.
Solution: Follow the given steps:
1 Open www.canva.com. You will see the homepage as shown below.
2 Click on the Canva AI option.
3 You will see various options such as ‘Design for me,’ ‘Create an image,’ ‘Draft a doc,’ and more.
4 Select any of these options and write a simple prompt for Canva to perform the desired task for you.
5 Here, the option Create an image is selected. Type a simple prompt for Canva to generate artwork.
Example prompts:
• “A rainbow castle in the clouds.”
• “A robot watering flowers in a garden.”
• Animate
Ideas with Canva
6 Canva AI will show you multiple images based on your prompt.
7 Choose an image you like and edit them in the Canva editor as per your choice. You can also include the changes you want directly in the prompt, as shown.

8 Save your final design or share it with your classmates.





We live in a world filled with data. Think about all the things you do in a day—sending text messages, watching videos online, playing games, or even searching for something on the internet. Each of these activities generates data. Now, imagine the amount of data created by everyone in the world doing these activities every single day. That is what we call big data.
Big data refers to extremely large sets of data that can be analysed to reveal patterns, trends, and associations, especially relating to human behaviour and interactions.






Big data is not just about having a lot of data. It is about how we handle and use this data to make decisions. There are six main characteristics of big data, often called the six Vs:
1. Volume: This means the amount of data. For example, all the photos, videos, and messages that are sent on social media every minute. That is a huge volume of data.
2. Velocity: This refers to the speed at which data is generated and processed. For example, every second, thousands of tweets are posted on Twitter. The faster we can process this data, the more quickly we can react to trends.
3. Variety: This means different types of data. Data comes in many forms, like text, images, videos, and even sounds. For example, a video of a cute cat is different from a text message about dinner plans, yet both are valuable data.
4. Veracity: This refers to the quality or accuracy of the data. It is important to ensure that the data we use is reliable and trustworthy. For example, data collected from a broken sensor might not be accurate.
5. Value: This means the usefulness of the data. Not all data is equally valuable. For example, data about what people buy online can help companies decide what products to stock.
6. Visualisation: Visualisation is often considered as the sixth V of big data. Visualisation is crucial in big data because it allows complex data to be presented in a more understandable and accessible way. By using graphs, charts, and other visual tools, we can interpret and analyse large datasets more effectively, helping to uncover trends, patterns, and insights that might not be immediately apparent from raw data alone.
Let us take the example of Smart City and how we can apply the concept of 6 Vs to it.
Volume: A smart city generates enormous amounts of data from various sources, such as traffic sensors, surveillance cameras, social media, weather stations, and public transportation systems. For instance,

thousands of cameras and sensors installed across a city can generate terabytes of data daily, providing insights into traffic patterns, crime rates, and environmental conditions.
Velocity: In a smart city, data needs to be processed in real-time to be effective. For instance, traffic management systems rely on real-time data from traffic lights, road sensors, and GPS devices in vehicles to manage congestion and reroute traffic efficiently. This real-time processing helps reduce traffic jams and improve commute times.
Variety: A smart city collects a wide variety of data from different sources. Structured data might include numerical data from utility usage, semi-structured data might involve XML files from sensors, and unstructured data might consist of social media posts, video feeds, and images. For instance, data from social media can help city officials gauge public sentiment and respond to concerns more effectively.

































Veracity: In a smart city, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data is crucial. For example, data from weather sensors must be accurate to predict weather conditions effectively and prepare for natural disasters. Similarly, accurate data from health sensors can help monitor the spread of diseases and manage public health resources efficiently.
Value: The goal of collecting and analysing big data in a smart city is to derive valuable insights that improve urban life. For instance, analysing data from energy consumption can lead to more efficient energy use and cost savings for residents. Data from public transportation can be used to optimise routes and schedules, making commuting more convenient for citizens.
Visualisation: At the end, presenting this data through visualisations, such as interactive maps and dashboards, helps decision-makers and citizens understand and utilise the information effectively.
Match the characteristic of big data with its description.
Column A
Volume
Velocity
Variety
Veracity
Value
Visualisation
Column B
The speed at which data is generated and processed
The accuracy and reliability of the data
Presenting data in an understandable and accessible way using visual tools
The amount of data generated
Different types of data, such as text, images, videos, and sounds
The usefulness of data for making decisions
To work with big data, first we collect data from many sources; then we clean and analyse it to find useful patterns. Let us learn how to do it.
Big data is collected from various sources. Here are some common ones:
1. Social media: Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram generate tonnes of data through posts, likes, comments, and shares.

2. Sensors: Devices like weather stations, GPS systems, and even smart home devices collect data continuously. For example, a fitness tracker records your steps, heart rate, and sleep patterns.
3. Transactions: Every time you buy something online or use a credit card, data is collected about what you bought, where you bought it, and how much you spent.
4. Websites: Websites collect data on what pages you visit, how long you stay on them, and what you click.

5. Surveys and forms: When you fill out a survey or form, you provide data that can be analysed to understand trends and preferences.
Collecting big data is just the first step. To make sense of it, we need to analyse and interpret it. Here are some ways this is done:
1. Data Mining: This is the process of discovering patterns and relationships in large sets of data. For example, a grocery store might use data mining to find out which products are often bought together.


2. Machine Learning: This involves teaching computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions. For example, a machine learning algorithm might learn to recognise spam emails based on patterns it finds in previous emails.
3. Data Visualisation: This means creating visual representations of data, like graphs and charts, to make it easier to understand. For example, a line graph might show how sales have increased over time.
4. Statistical Analysis: This involves using statistics to analyse data and make conclusions. For example, calculating the average score of a class in a test to understand overall performance.
Consider a weather app. It collects data from weather stations and satellites, and then uses data visualisation to show you a map with the current weather conditions. It also uses machine learning to predict the weather for the next few days based on patterns in the data.
Big data is used in many different fields. Here are some examples:
1. Healthcare: Big data plays a crucial role in healthcare. It helps doctors predict disease outbreaks, understand patient symptoms, and improve treatments. For example, during flu season, hospitals can use big data to prepare for more patients.
2. Transportation: Big data helps cities manage traffic flow, reduce accidents, and improve public transport. For instance, by analysing traffic data, cities can change traffic light timings to reduce congestion.
3. Shopping: Big data helps stores understand what products are popular, manage inventory, and personalise shopping experiences. For example, an online store might suggest items you might like based on your previous purchases.
4. Finance: Big data enhances risk management and fraud detection by analysing market trends and transaction patterns in real-time, preventing potential risks and fraudulent activities. It also provides valuable customer insights, allowing banks to offer personalised services and improve customer satisfaction.
5. Retail: In retail, big data enables personalised marketing and targeted campaigns by analysing customer behaviour and purchase history. It optimises inventory management by predicting product demand and allows for dynamic price adjustments based on market trends and customer preferences.
6. Entertainment: Big data helps streaming services recommend films and shows and helps video game developers understand player behaviour to improve games.
7. Education: Big data can help teachers understand how students learn best and create personalised learning plans. For example, educational apps can track how students interact with content and provide feedback to teachers.
8. Environment: Big data aids climate change analysis by processing large volumes of environmental data, helping understand climate patterns and develop mitigation strategies. It also supports wildlife conservation through data from sensors and tracking devices and facilitates real-time pollution monitoring to maintain air and water quality.

Big data continues to grow and evolve, and it will play an even bigger role in the future. Here are some ways it might affect our lives:
1. The future of big data is set to revolutionise how we collect, analyse, and utilise information, driven by several key trends. Data generation will surge due to the rapid growth of IoT devices, social media, and sensors, providing vast amounts of information for analysis. For example, smart home devices will continuously generate data on energy usage, contributing to more efficient home management.
2. Integration with advanced analytics and AI will enable predictions that are more accurate and automate decision-making, such as using machine learning to forecast market trends.
3. Real-time processing will enhance decision-making speed and efficiency, as seen in fraud detection that identify suspicious transactions instantly.
4. Edge computing will reduce latency by processing data closer to its source, crucial for applications like autonomous vehicles that require immediate data analysis.
5. Enhanced data security and privacy measures will be essential, with advanced encryption protecting sensitive information like personal health records.
6. Greater interoperability between platforms will facilitate seamless data integration, for instance, combining data from various healthcare systems to improve patient care.
7. Ethical and responsible data use will gain prominence, ensuring fairness and privacy in analytics.
8. Industry-specific applications will drive innovation, such as using big data in agriculture for precision farming and crop management.
9. Big data will also aid sustainability efforts by analysing environmental data to develop strategies for reducing carbon footprints.
10. Collaboration between humans and machines will enhance decision-making, such as AI-assisted tools providing insights that improve business strategies.

Big data could help create ‘smart cities’ where self-driving cars communicate with traffic lights to reduce congestion and accidents. These cities will use real-time data from various sources to improve everything from public transportation to energy consumption.

Let us perform the following activity to understand how AI learns from data.
Objective: The Impact Filter experiment has a huge data base of images of various species. While performing this experiment, one can experience how rising temperatures affect the survival of various species and how it would affect our daily lives.
Follow the given steps to learn how this application works.
1. Visit the link: https://artsexperiments.withgoogle.com/impactfilter/
2. The following screen appears.
3. Click on the CLICK TO START button.
4. You will be redirected to a tutorial. If you wish to take the tutorial, then follow the steps. Otherwise, you can exit it.
5. Now, from the top bar, select any of the various categories of species, such as insects, birds, reptiles and amphibians, and so on. Let us click on the INSECT category.

6. Another web page with the option of insects will appear. Click on any of them, for example, BUMBLEBEE
7. A web page opens, showing the percentage of bumblebee that will disappear at the current temperature of the Earth, which is already increased by 1.2 °C.
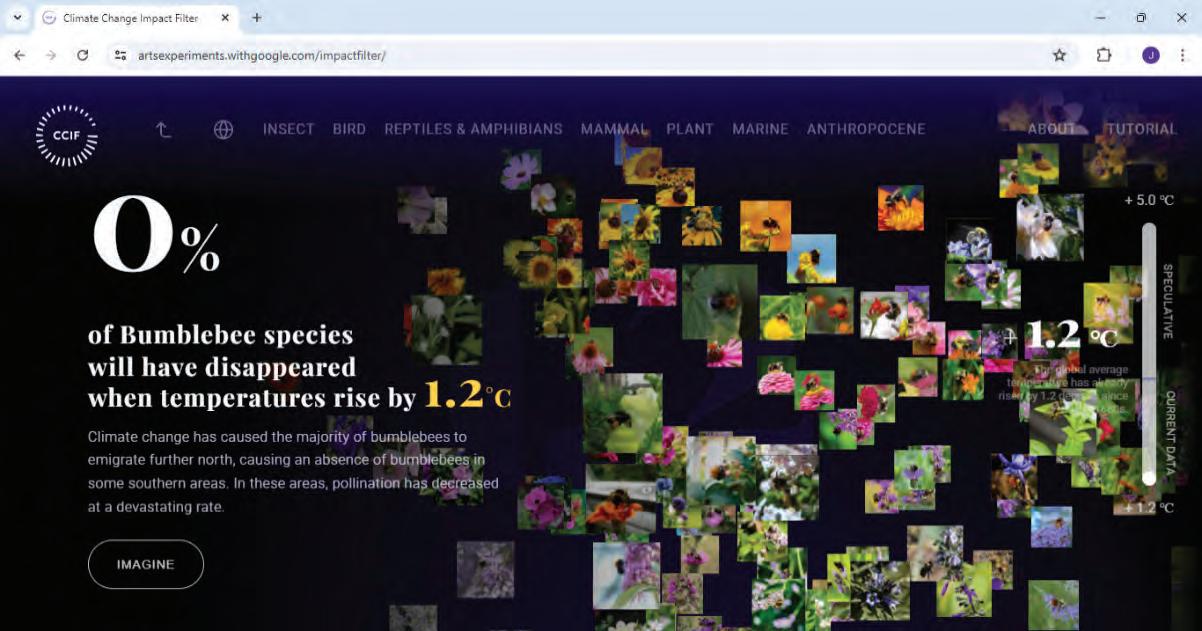
8. Look at the bar on the right side displaying the temperature. It can be used to increase or decrease the temperature by moving the slider upwards or downwards.
9. You can observe the impact of rising temperatures on the population of bumblebees as you increase the temperature.
10. You can try the same with the other species as well, and understand the impact of rising global temperature on these species.




Create a table to analyse the performance of your classmates in a weekly test. Record the values in the given table and complete it. A sample entry has been done for you. After that, answer the following questions.
1 What is the average test score in the class? 2 Is there a noticeable difference in test scores between students with high and low attendance? 3 How does class participation relate to homework completion rates? 4 What recommendations can you make to improve class performance based on the data?

1 Big data refers to extremely large sets of data that can be analysed to reveal patterns, trends, and associations.
2 The amount of data generated, such as photos, videos, and messages.
3 The speed at which data is generated and processed, like the rapid posting of tweets.
4 The different types of data include text, images, videos, and sounds.
5 The quality and accuracy of data, ensuring reliability and trustworthiness.
6 The usefulness of data, determining how valuable it is for making decisions.
7 Presenting complex data in a more understandable and accessible way using graphs, charts, and other visual tools.
8 Big data is used in various fields like healthcare, transportation, shopping, finance, retail, entertainment, education, and the environment.
A. Fill in the blanks.
Hints volume patterns visualisation variety velocity
1 Big data refers to extremely large sets of data that can be analysed to reveal
2 The of data means the amount of data generated.
3 refers to the speed at which data is generated and processed.
4 Different types of data are referred to as .
5 is crucial for presenting complex data in a more understandable way.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 Big data can reveal patterns, trends, and:
a Numbers b Associations
c Colors d Shapes
2 The of big data involves ensuring the data is reliable.
a Volume b Veracity
c Variety d Visualisation
3 An example of the of data is the rapid posting of tweets.
a Velocity b Value
c Visualisation d Variety
4 Data that includes text, images, and videos is an example of:
a Volume b Veracity
c Variety d Velocity
5 Presenting data using graphs and charts is an example of:
a Volume b Visualisation
c Velocity d Veracity
C. Who am I?
1 I am the characteristic of big data that ensures the accuracy and reliability of data.
2 I refer to the speed at which data is generated and processed.
3 I represent the usefulness of data for making decisions.
4 I involve presenting complex data in an understandable way.
5 I refer to the amount of data generated.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1 Big data only includes text data.
2 Volume refers to the speed at which data is generated.
3 Visualisation helps in making complex data more understandable.
4 Value determines the usefulness of data.
5 Veracity refers to the variety of data types.
E. Answer the following questions.
1 What is big data?
2 Explain the concept of volume in big data.

4 What are the ways through which you can collect big data?
5 Give an example of how big data is used in healthcare.
F. Apply your learning.
1 Riya is analysing traffic data in a smart city. Explain how volume, velocity, and variety play a role in her analysis.
2 Arjun is managing a public transportation system. Discuss the importance of veracity and value in his work.
3 Priya is working in retail. Describe how visualisation can help her business.
4 Kabir is studying the future trends of big data. How might these trends affect his daily life?
5 Ananya is reflecting on how big data is collected. Give an example from her life where big data might be collected and used.

Have you ever wondered how your phone unlocks itself with your face or fingerprint, and how some apps suggest words while you type, or recommend TV shows that you might like? All of this is possible because of Machine Learning (ML). Let us learn more about machine learning in this chapter.
Machine Learning (ML) is a branch of Artificial Intelligence that teaches computers to find patterns in data so they can make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed for each case. It allows systems to improve their performance over time as they are exposed to more data. ML is used in many everyday applications, such as voice assistants, recommendation systems, and fraud detection.


To better understand how machines learn, let us take an example of fruits. Let us take an apple and a banana. How do we differentiate between them? When we look at an apple, we know it is spherical in shape and red in colour. However, when we look at a banana, we see that it is curved in shape and yellow in colour.
Just as we can differentiate the two fruits by looking at their shapes and colours, computers too can differentiate them from the data we provide, such as images of apples and bananas. We show the computer a lot of images of each fruit. The computer identifies the patterns. It appears that all the images of apples follow a certain pattern (in terms of colour and shape), whereas the images of bananas follow a different pattern. We call these images of apples and bananas as training data, as we use these images to train the computer to learn about the patterns of the fruits.
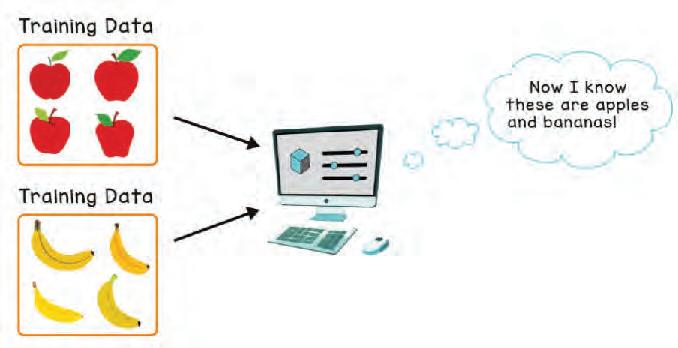
Training Data
Now I know these are apples and bananas!
Training Data
Once the computer has learnt to identify and understand the pattern, we use test data, which is any new image of an apple or a banana, and give it to the computer to identify the image based on its learning.
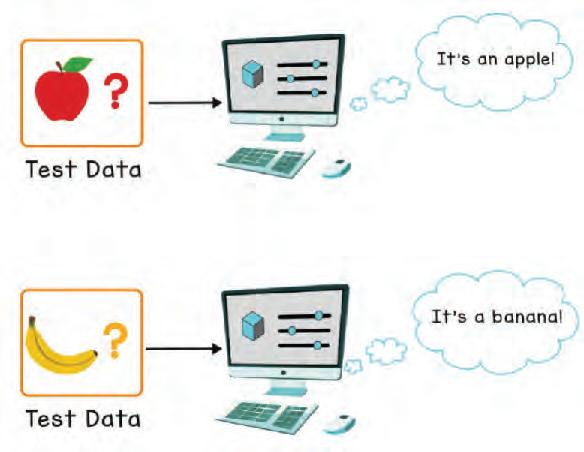
It’s an apple!
Test Data
It’s a banana!
Test Data
Machine learning involves showing a large volume of data to a machine so that it can learn and make predictions, find patterns, or classify data. The three types of machine learning are supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning.
Supervised learning is a machine learning method that uses well-labelled datasets to train algorithms to predict outcomes and recognise patterns.
In supervised machine learning, we know the data really well. We provide this known data to the machine learning model, which then learns from the data. Here, the model refers to the algorithms or programs, which can be trained to give intelligent outputs and solve our problem statement. Once the model learns the relationship between the input and output data, it becomes capable of classifying new and unseen datasets, as well as predicting outcomes.
The identification of apples and bananas as different fruits is a great example of supervised learning.
Since we knew the data really well, i.e., apples are spherical and red, while bananas are curved and yellow, we ‘feed’ this data to the computer by providing a large number of images of both apples and bananas. This is then reasoned into the statements, “Given an image of an apple, we know it as an apple”, and “Given an image of a banana, we know it as a banana”.
Thus, the computer learns this information, and applies it on new images, thereby starting to make predictions.

Its an apple!

These are apples.
As the name suggests, unsupervised learning is a machine learning technique in which models are not supervised using datasets. In unsupervised machine learning, machines do not know any patterns in the data. Instead, the model itself finds hidden patterns and insights from the given data.
Imagine showing a computer various picture of fruits—apples, bananas, and grapes. We do not tell the computer anything about these images, including which one belongs to which fruit. We simply display all the images on the computer. The computer automatically finds a pattern in these images.
For example, it understands that all the apple images have similar properties, like red colour and spherical shape. All the bananas have similar properties, like yellow colour and curved shape. Similarly, all the grapes have similar properties, like green colour and small and round shape.
Hence, it creates clusters (groups) and separates these images into three different groups.
Now, every time you give a new image of apple, banana, or grapes, the computer can ‘separate’ them into one of these three groups. This is an example of unsupervised learning.
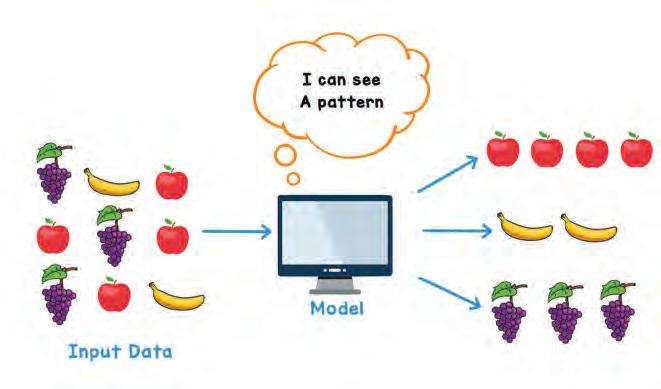
I can see a pattern.
Reinforcement learning is a type of machine learning where an agent learns to take actions in an environment to maximise a cumulative reward. The agent learns through trial and error, receiving rewards for good actions and penalties for bad ones. In our fruit recognition problem, the computer learns to recognise fruits by identifying images. When the computer correctly identifies a fruit, it receives a reward. However, if it guesses incorrectly, there is no reward. With each attempt and its corresponding feedback, the computer becomes ‘smarter’. It starts recognising the key features that distinguish different fruits. For example, it learnt that apples are red and spherical, while bananas are curved and yellow. This process helps it understand which actions, like identifying specific features, are effective and which can be ignored.
The learning and accuracy of the machine learning model are dependent on various factors, like:

• Quantity of Data: The more images of apples and bananas we feed to the computer, the better it will learn from this data and predict more accurately.
• Quality of Data: Depending on how good the images of apples and bananas are, the accuracy of the model will vary.
Let us do the following experiment using the application Teachable Machine to understand how machine learning works.
Objective: Teachable Machine is a web-based tool that makes the creation of machine learning models fast, easy, and accessible to everyone. It helps train a computer to recognise images, sounds, and poses. Follow the given steps to explore how this application works.
1. Visit this link: https://teachablemachine.withgoogle.com/
2. The following window opens. Click on the Get Started button.

3. You will be directed to a web page, as shown. From the window that appears, you can use any of the following options to teach your machines:
• Images: To teach a model to classify images using files on your system or your webcam.
• Sounds: To teach a model to classify audio by recording short sound samples.
• Poses: To teach a model to classify body positions or poses using image files on your system or striking poses in your webcam.
4. Let us create a pose project. For this, click on the Pose Project option.
5. Collect images of random people’s sitting and standing poses, as shown. Here is the training data, in the form of images of standing and sitting poses, for your reference.













Machine learning can help predict earthquakes. By analysing seismic data, these algorithms can find patterns that might indicate an impending earthquake, providing early warnings and potentially saving lives.
6. Click on the Upload button to upload the images related to these poses.
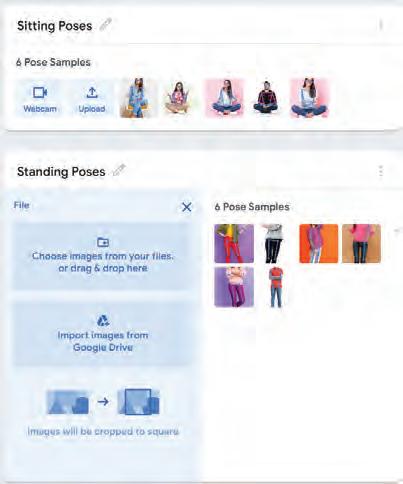
7. The results of any machine learning model depend on the examples or the sample data you give it. So, if it’s not working as you had intended, then add more samples in the training data that was provided to your computer.
8. After uploading the training data, click on the Train Model button.
9. Now, test your machine learning model by posing in front of the webcam and see what Output (standing or sitting pose) it displays in the Preview window.
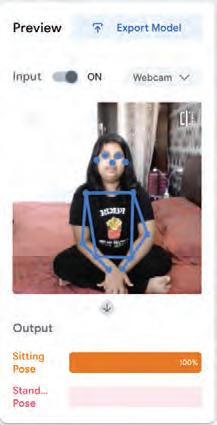



Match the following.
Column A
Supervised Learning
Unsupervised Learning
Reinforcement Learning
Classification Problem
Clustering Problem
Column B
Trial and error learning
Predict outcomes from labelled data
Finding hidden patterns
Separating data into clusters
Identifying images of apples and bananas
From self-driving cars to personalised recommendations, machine learning is transforming our daily lives. Here are some exciting applications of this technology.
Recommendation Systems: Imagine that you have been watching a lot of videos on YouTube that are on computer programming. The machine-learning algorithms on YouTube track your choices. By analysing this data, they can recommend programming videos that align with your interests.

Language Translation: Google Translate, a translation app, uses machine learning to understand and translate text instantly, enabling us to communicate in different languages. It learns from millions of translated texts to understand the patterns and meanings in different languages.
Customer Service Chatbots: Have you ever wondered how the chatbots seem to get smarter with every new conversation? It is because of machine learning. By analysing the questions that the customers ask, these chatbots learn to provide increasingly helpful and accurate answers.


Image Recognition: Applications like Snapchat or Instagram can add fun effects to your photos by analysing your facial features using machine-learning algorithms. A machine learning application looks at your face in the camera and figures out where your eyes, nose, and mouth are. Then, it puts the filter on the right spot to make it look like it is part of your face. For instance, Snapchat might overlay a dog’s nose and ears on your face or add funky glasses.
Self-driving Cars: Self-driving cars use both computer vision (to see the road, pedestrians, vehicles, etc.) and machine learning (to make decisions). A self-driving car learns from all the different situations it encounters on the road, like slowing down on detecting pedestrians, stopping at a red light, or navigating around other vehicles.


Banking: Machine learning makes banking safer, more personalised, and easier for everyone. It helps banks detect unusual activity that may be fraudulent. It also helps banks decide who can get loans by looking at their borrowing history and their likelihood of repaying them. Also, there are chatbots on banking apps that provide customer support by answering questions effectively.
Weather Prediction: Machine learning helps predict the weather by analysing historical weather data, like temperature, precipitation, wind, etc., to find patterns. It makes use of these patterns to make better guesses about what’s going to happen next.

Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning in which a machine is trained with vast amounts of data which help it to train itself around that data. Some practical applications of deep learning includes virtual assistants, computer vision for driverless cars, detection of money laundering, face recognition, and many more. It is an AI function that mimics the working of the human brain in processing data and uses it in detecting objects, recognising speech, translating languages, and making decisions.
Deep learning is the most advanced form of artificial intelligence. Then there is machine learning, which is intermediately intelligent, and artificial intelligence which covers all the concepts and algorithms that, in some way or other, mimic human intelligence.





Unscramble the given words from 1 to 6. Then, form the term given afterwards by picking up the numbered letters from the unscrambled words.
1 Machine Learning (ML) is a branch of AI where the machine makes predictions and decisions based on the data that we provide it.
2 In supervised ML, we give data to the machine on which it is already trained, and it learns from that data.
3 In unsupervised ML, we do not give any data that has patterns in it. Instead, the machine adapts itself to find the hidden patterns and insights from the given data.
4 In reinforcement learning, machines learn from the feedback on the predictions they make. They are rewarded for correct guesses. They learn about the nature of actions that are necessary or unnecessary.
5 Machine learning algorithms learn from your past choices or preferences and make recommendations for films, songs, articles, etc., tailored to your interests.
6 Google Translate, a translation app, makes use of machine learning to understand and translate texts instantly.
7 Machine learning helps chatbots function more efficiently by making them learn from the different types of questions customers ask and get better at giving helpful answers.
8 Self-driving cars use both computer vision (to see the road, pedestrians, vehicles, etc.) and machine learning to make decisions.
9 Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning where a machine is trained with vast amounts of data which then help it to train itself around the data. It is the most advanced form of AI.
A. Fill in the blanks.
Hints Google Translate test data supervised chatbot Machine Learning
1 is a branch of AI that uses large amounts of data to make predictions.
2 makes use of machine learning to help us communicate in different languages.
3 A interacts with you online to answer your queries or assist during online shopping.
4 In machine learning, we know the data really well.
5 Once the computer learns, we use or any new image, and the computer can identify these new images based on its learning.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 In learning, a computer gets feedback on whether it is right or wrong.
a Reinforcement
c Unsupervised
2 How does machine learning helps in banking?
a It helps banks detect unusual activity.
b Supervised
d Superlative
b It helps banks decide who can get loans by looking at borrowing history.
c It provides customer support on banking apps.
d All of these.
3 Machine learning involves feeding a large volume of to a machine so that it can make predictions.
a Outputs
c Noise
4 Which among the following is the most advanced form of AI?
a Supervised Machine Learning
c Deep Learning
b Data
d Algorithms
b Machine Learning
d Unsupervised Machine Learning

5 In learning, the model can classify new datasets and predict outcomes after learning the relationship between input and output data.
a Supervised b Unsupervised
c Reinforcement d None of these
C. Write T for True and F for False.
1 Deep learning is a subset of machine learning.
2 Machine learning does not have the capability to predict the weather.
3 A self-driving car uses both computer vision and machine learning.
4 The accuracy of the machine learning model depends only on the quality of the data.
5 YouTube is an example of a recommendation system.
D. Answer the following questions.
1 Define machine learning.
2 Differentiate between supervised and unsupervised machine learning.
3 Explain any three applications of machine learning.
4 What is deep learning?
5 Differentiate between training data and test data.
1 When Neelam first heard about self-driving cars, she was curious about how she would manage to navigate on the road. Explain to Neelam how self-driving cars achieve this.
2 Yashika visits Germany, but she cannot speak German. You have suggested using Google Translate to communicate effectively there. Explain to her how the app can help her communicate with ease.
3 Avartika and her grandmother like adding filters to the pictures they click using Snapchat. Curious, Avartika’s grandmother asks her how these filters work. What should Avartika tell her grandmother?
4 Avni’s grandfather has found weather prediction apps on his phone. He is curious to know how those apps predict the weather. Explain the process to him.


We use language every day to talk, write, and share our thoughts. But for a long time, computers could only understand numbers, not words. Today, technology has made it possible for machines to understand human language too. This is where Natural Language Processing (NLP) comes in.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a part of Artificial Intelligence that helps computers understand and use human language.
It allows machines to read, listen, and even reply to us in a meaningful way. You see NLP when your phone suggests words while typing or corrects your spelling. It also works in voice assistants like Siri or Alexa, which can answer your questions. NLP is the reason why we can “talk” to machines in our own language.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) has several key applications across different domains. Here are some of the common applications:
Language Translation: NLP is used extensively in translation applications like Google Translate and Microsoft Translator, where it processes and translates text from one language to another, preserving context and meaning.





Sentiment Analysis: NLP can study text to find out if people are happy, sad, or angry. This is used on social media posts, product reviews, and surveys to understand what people feel. Companies use this to make their products better and keep customers happy.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Chatbots and virtual assistants are computer programs that can talk with people using text or voice.
Chatbots usually appear in chat windows on websites or apps. They answer questions, give information, and are widely used in customer service to handle queries quickly.
Virtual assistants, like Siri or Alexa, are used more for personal tasks. They listen to voice commands and help with things like setting reminders, playing music, or searching for information.
Both are powered by Natural Language Processing (NLP), which allows them to understand and respond in a human-like way.


Text Summarisation: NLP is used to generate concise summaries of long documents, articles, and reports by extracting key points. This helps users quickly grasp important information without reading the entire text.
Speech Recognition: NLP can change spoken words into written text. This is used in voice assistants like Siri, in apps that write down what people say, and in tools that help people with disabilities.
Autocomplete and Spell Check: NLP is used in search engines, messaging apps, and word processors to suggest words, correct spelling mistakes, and improve typing efficiency. NLP gives us predictive text, which suggests the next word while typing.
This feature makes writing messages quicker and easier.

Did You Know?
NLP techniques are used in automated content generation, where AI systems can write articles, summaries, and even poetry by analysing patterns in large datasets of text.
Match the following.
Column A
Language Translation
Chatbots
Virtual assistants
Text summarisation
Speech recognition
Autocomplete
Which app can identify and provide information about objects and landmarks using your camera?

Column B
Suggesting words
Giving a short version of a long text
Changing text from one language to another
Answering questions in chat form
Helping users through voice commands like Siri or Alexa
Converting spoken words into text
MIT App Inventor is an online platform for creating apps for mobile phones and tablets. It is a very easy and simple platform to learn app creation and coding. This platform focuses on making everyone, especially young children, create their own apps. No coding skill is required to build your own app using MIT App Inventor. Apps are software programs that can be downloaded and installed on electronic devices.

MIT App Inventor was initially developed by Google and later released as an open-source project.
MIT app inventor can be accessed from the link: https://appinventor.mit.edu/
Here, you will learn the easy steps to create a mobile app to recognise the user’s speech. The components used for the application will be as follows:
1. A button to display ‘Start Speech Recognition’.
2. A label to show ‘Recognised text’.
3. Another label to display the recognised speech.
Set Up MIT App Inventor
1. Go to the MIT App Inventor website (https://appinventor.mit.edu/).
2. Log in with your Google account. If you do not have one, ask your teacher or parents to help you create one.

3. From the Palette on the left side, drag a Button component into the viewer.
4. Set the Text property of the button to “SpeechRecognition”.
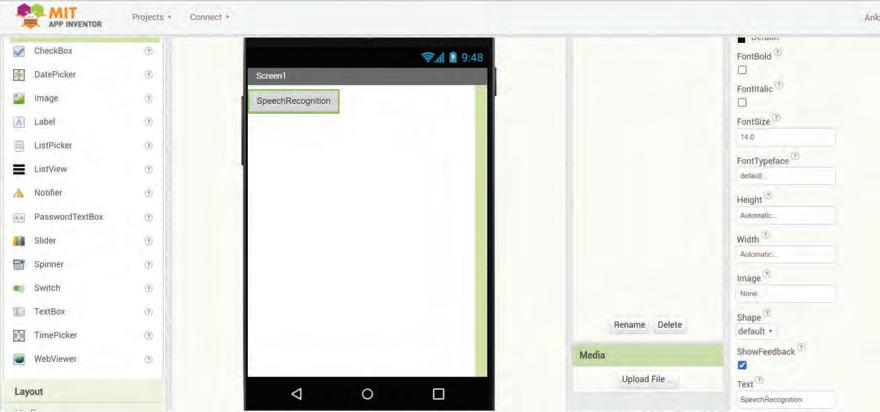
5. Drag a Label component onto the viewer.
6. Set the Text property of the Label component to “Recognised Text” and the FontSize property to 18.
7. Drag another Label component onto the viewer. This label will display the recognised speech.
8. Set the Text property to blank “ “ and the FontSize property to 18.
9. Rename this label to “RecognisedText”.
10. Now, from the Palette under the Media section, drag a SpeechRecognizer component into the viewer. This will appear in the “Non-visible components” area.
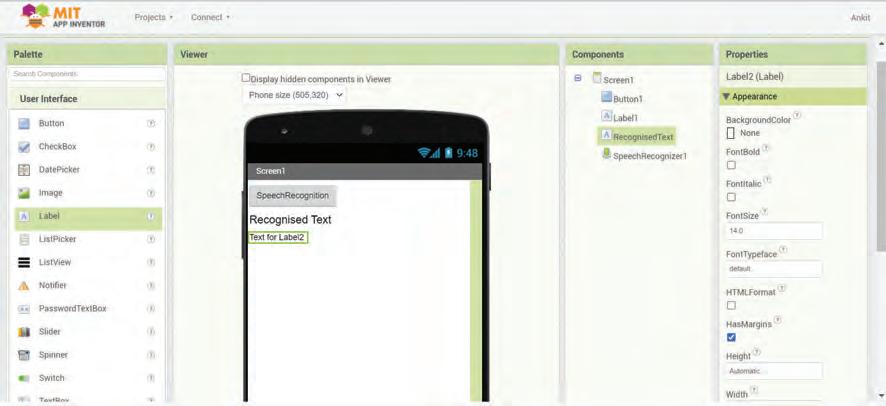
1. Click on the Blocks button in the top right.
2. Find the Button1 block under Screen1 and drag out the when Button1.Click block.
3. Inside this block, add the call SpeechRecognizer1.GetText block from the blocks drawer of the SpeechRecognizer1 component.

4. From the SpeechRecognizer1 blocks drawer, drag out the when SpeechRecognizer1. AfterGettingText block.
5. Inside this block, drag the set RecognisedText.Text to block.
6. Attach the get result block from the SpeechRecognizer1.AfterGettingText block.
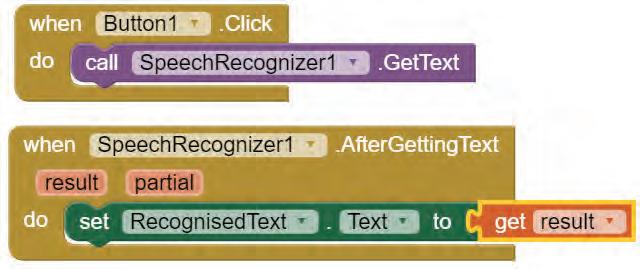
Testing Your App:
1. To connect to the companion, click on the Connect drop-down and select AI Companion
2. A Connect to Companion window will open with a six-character code.
3. You can either scan the QR code or fill in this six-character code on the mobile phone app.
4. The app will now open on your mobile.
5. Click on the button that you have created, “Start Speech Recognition” button, and speak into the microphone.
6. The app will display the recognised text.
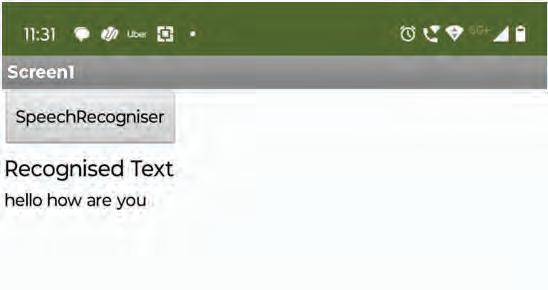

A. Fill in the blanks.
Hints
Google Translate Numbers NLP Apps Alexa
1 is a part of Artificial Intelligence that helps computers understand and use human language.
2 For a long time, computers could only understand , not words.
3 Siri and are examples of virtual assistants.
4 are software programs that can be downloaded and installed on electronic devices.
5 NLP is used in translation applications like
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 NLP mainly helps computers to understand which of the following?
a Music
c Human language
2 Why is NLP considered important for humans?
a It lets us talk to machines
c It paints pictures
3 Predictive text is useful because it .
a Makes typing faster
c Translates pictures
4 Which among the following is not an application of NLP?
a Spell Check
c Playing Cricket
5 In which area are chatbots most commonly used?
a Sports
c Gardening
b Numbers
d Weather
b It helps play sports
d It builds houses
b Plays music
d Deletes text
b Autocomplete
d Language Translation
b Cooking
d Customer service
C. Write T for True and F for False.
1 MIT App Inventor is an online platform for creating apps for mobile phones and tablets.
2 Sentiment analysis checks the mood of text.
3 Speech recognition helps turn text into speech.
4 NLP is only used in games and entertainment.
5 NLP is used in word processors to suggest words and correct spelling mistakes.
D. Answer the following questions.
1 What is NLP?
2 Give two examples of NLP applications you use in daily life.
3 What is the role of sentiment analysis?
4 How does predictive text make typing easier?
5 What is a virtual assistant? Give two examples.
E. Apply your learning.
1 Meena speaks to her phone and it writes down her words in a note. Which NLP technique is this?
2 Lovey wants to open her restaurant, for which she needs to create an app that can understand the language of foreign customers as well. Which platform can she use to create this app?

3 Arjun wants to quickly read the main points of a 10-page article. Which NLP feature can help him?
4 Riya is typing a message and her phone suggests the next word. Which NLP feature is at work?
5 Kabir checks product reviews online to see if most people are happy with a new mobile. Which NLP technique helps find this?
A. Fill in the blanks.
1 The octal number system has a base of
2 An attempt to trick a user to get his or her personal information through fake emails is called .
3 devices are used to give instructions to the computer.
4 The function in Google Sheets counts the number of cells that contain numbers.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 scanners use flat glass surfaces to scan objects, such as documents, photographs, and artwork.
a Flatbed
c Sheetfed scanners
b Handheld
d Drum scanners
2 A is a type of computer virus that infects executable.
a Boot sector virus
c Macro virus
b Program file virus
d Network virus
3 Which of the following functions returns remainder when the dividend is divided by the divisor?
a Max
c Min
C. Write T for True and F for False.
b Mod
d Average
1 The hexadecimal number system uses numbers from 0-9 and letters from A-F.
2 There is no harm in sharing our address with strangers online.
3 Incognito mode lets you browse the internet without leaving behind a trace of your activity.
4 A projector is an output device that projects images on a small screen.

D. Answer the following questions.
1 Define a number system.
2 What is a light pen?
3 What do you mean by Trojan horse?
4 Define the following functions used in Google Sheets:
E. Apply your learning.
1 Sheena is trying to decipher a number written in a series of 0s and 1s. She does not know how to convert the number to a decimal number. Help her convert the number.
2 Ravi wants to watch high-definition movies and store large video files on a durable, portable, and high-capacity disc. Name the type of disc he should use.
3 Shalini wants to check today ’s date and time using a function in Google Sheets. Which function is suitable for this?
A. Fill in the blanks.
1 listen to voice commands and help with things like setting reminders, playing music, or searching for information.
2 is a process that makes sure the data is correct, whole, and the same as long as it exists in the database.
3 an object makes sure that the object remains on its place while you work on the other parts of the design.
4 is a branch of AI that makes machines learn from large amounts of data.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 makes the computers understand the human language in text and spoken form.
a Machine Learning b Computer Vision
c NLP d Big data
2 occurs when we have multiple copies of the same data.
a Data redundancy b Data Security
c Database
d DBMS
3 refers to the quality or accuracy of the data.
a Value
c Volume
C. Write T for True and F for False.
1 A layer can be considered as a transparent sheet.
b Velocity
d Veracity
2 A database is a collection of information stored electronically in a computer system.
3 Unsupervised learning uses labelled data to train algorithms to predict outcomes and recognise patterns.
4 The backward option brings the layer to the bottom of the stack.

D. Answer the following questions.
1 What is SQL?
2 What do you mean by duplicating a layer?
3 What is a chatbot?
4 Write the syntax of the create table command with the primary key.
E. Apply your learning.
1 Pranjal is organising a survey and wants to visualise how many participants selected each option in a questionnaire. Which feature can she use to accomplish this?
2 Tanay wants to know about big data. Help him by explaining a real-life example of big data.
3 Palak is teaching her little brother, and she is explaining to him the concept of machine learning. However, she forgets to tell him about applications of machine learning. Help her by mentioning two applications of it.
Tekie.AI is a pioneering Computer Science series that places Artificial Intelligence at its core, helping learners understand how AI is transforming everyday life. Compliant with NEP 2020, it blends core computer science knowledge with real-world AI applications, building skills, curiosity, and confidence for an AI-driven future. Through the thrilling adventures of Mel and Conji from the world of Avora, the series makes complex ideas engaging and relatable. More than just a book, Tekie.AI is a pathway to the future, connecting classroom learning with the technologies shaping tomorrow’s world.

• AI Connect: Linking core computer concepts with cutting-edge AI applications
• AI Activities: Engaging exercises to explore and apply AI concepts in practical ways
• Experiential Learning: Hands-on exposure through digital experiences
• In-built Triggers: Stimulating prompts and questions for classroom interaction and critical thinking
• Assessments: Tools to evaluate understanding of concepts and application of skills
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to provide technology-enabled learning programs. We believe that pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 15,000+ schools across India, Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
ISBN 978-93-89789-99-7

