

Acknowledgements
Academic Authors: Muskan Panjwani, Anna Danchenko
Creative Directors: Alena Sizintseva
Book Production: Natalia Karabanova, Anastasia Voitovich
All products and brand names used in this book are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
© Uolo EdTech Private Limited First edition 2026
This book is sold subject to the condition that it shall not by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, resold, hired out, or otherwise circulated without the publisher’s prior written consent in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published and without a similar condition including this condition being imposed on the subsequent purchaser and without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the abovementioned publisher of this book.
Book Title: DinoLab Math Smartbook 6
ISBN: 978-93-89789-84-3
Published by: Uolo EdTech Private Limited
Corporate Office Address: 91Springboard, 3rd Floor 145, Sector 44, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
CIN: U74999DL2020PTC360472
Printed by: Printpro Solutions
All suggested use of the internet should be under adult supervision.
How to get access to DinoLab
Get access to animated interactive courses, Marathons, Olympiads and much more — all in the Uolo Learn app!
1. Download the "Uolo Learn" app from Google Play (Android) or App Store (iPhone).
2. In the app, click scanner to scan the QR code below.
Class:
Name:
School:
3. Follow the instructions in the app to access the content.
Welcome to DinoLab!
DinoLab is an AI-powered self-learning platform that helps children learn Mathematics and other subjects step by step, at their own pace. Students can practise and revise every topic digitally and through printed smartbooks.
The DinoLab Mathematics Smartbook is a companion to the digital course. Each exercise has a QR code linking to the Uolo Learn app for continued practice.
Using AI, DinoLab creates a personalised learning path: it explains the concept, gives guided practice and adapts if mistakes occur — helping students gain clear understanding.
Digital content is presented as interactive flashcards with 50,000+ gamified exercises and animations, making learning engaging and enjoyable.
DinoLab works in Uolo apps and on multiple devices
To use DinoLab on the web, Smartboards and in computer labs, your school will receive special access for each student and teacher.
Uolo Mobile App SmartboardComputer Lab Smartbooks Tablet and Laptop SMART
How to Use the DinoLab Solution
Once the Uolo Learn app is installed and you are logged in, you can access DinoLab. Our Mathematics course is designed with interactive exercises that help children cover the school syllabus step by step, at their own pace.
1 2 3
Compete and win in Marathons!
• Solve problems and earn points
• Check the leaderboards of your class, school and all of India
• Get achievement certificates
1 3 In this Smartbook, you will find QR codes placed next to the exercises. Simply use the QR scanner inside the app to access the interactive content. QR codes in the smartbook
2
Open the Uolo Learn app.
1. LARGE NUMBERS AND OPERATIONS
UNDERSTANDING LARGE NUMBERS
1. Join each digit of the following number to its correct place.






2. Read each number name. Write it using numerals.
Three hundred fifty-six =
Eight thousand twenty-five = Fourteen thousand one = 356
Nine hundred six = Four hundred eighty-two = Three thousand twelve =
3. Write the expanded form.
300 + 50 + 6 356 = 4871 = 1,00,001 =
ESTIMATING LARGE NUMBERS
4. Round each number to the given place.
5. Check each pair. Which one shows the correct rounding to the nearest hundred? Tick ( ) it.
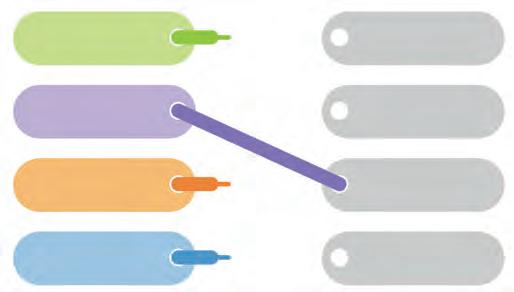
6. Join each number to its possible rounded value.


7. Round the population of each city to the given values. Complete the table.
Population Rounded to the nearest hundreds Rounded to the nearest thousands
8. Read what the lady wants. Join the correct piece of cheese to her cart.
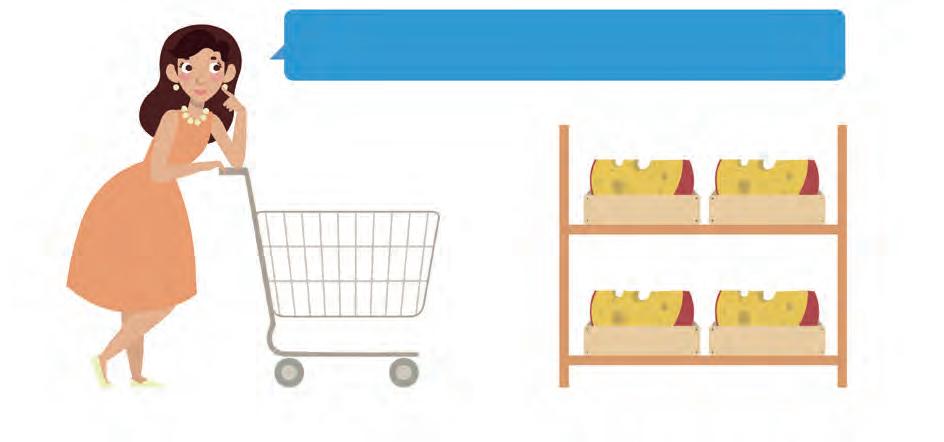
I need approximately two hundred grams of cheese.
I need approximately four hundred grams of cheese.
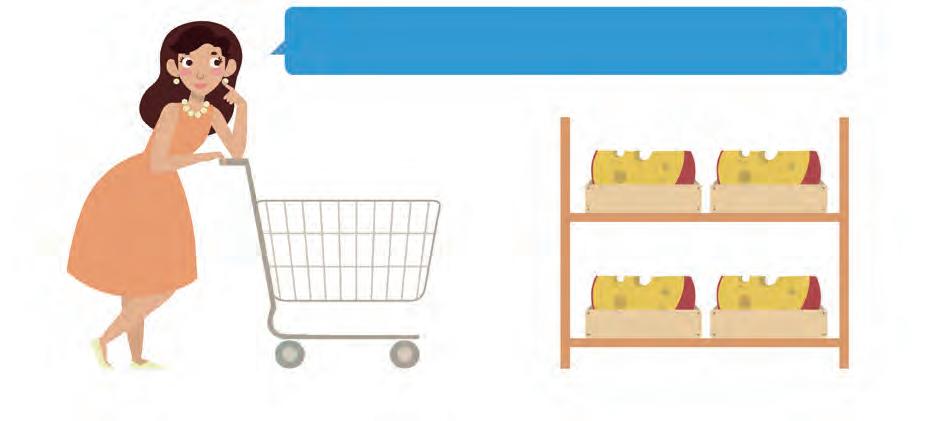
I need approximately three hundred grams of cheese.

9. Puneet and Lalit rounded some numbers to the nearest thousands. Read what they wrote. Circle who is correct.
Mount Everest is about 8,000 m high.
Mount Everest is about 9,000 m high.
The area of this island is approximately 9,000 km².
The area of this island is approximately 10,000 km².
Puneet
Puneet
Lalit
Lalit
Mount Everest is 8,848 high.
The area of this island is 9,250 km².
+ 10 =
+ 10 =
+ 10 =
+ 30 =
+
+ 30 =
OPERATIONS ON LARGE NUMBERS
10. Solve. Write the answers in the boxes.
− 60 =
−
=
−
=
−
−
−
11. Help the mouse reach the cheese! Trace the path. Start at 200. Add 10 each time to find the next step.
12. Help the mouse reach the cheese! Trace the path. Start at 506. Add 10 each time to find the next step.
13. Help the mouse reach the cheese! Trace the path. Start at 733. Add 10 each time to find the next step.
14. Add. Write the answers in the blanks. Show your work.
47,383 + 8,274 = 38,927 + 1,839 =
37,452 + 3,874 = 82,654 + 1,281 =
5,00,091 + 377 = 17,499 + 8,346 =
85,167 + 1,098 = 17,776 + 2,771 =
15. The horse needs to jump! Look at each number line and find how wide is the gap. Write the answer in the given space.




16. Help the spider complete its web. Fill in the missing numbers in the empty circles.
17. Subtract. Write the answers in the blanks. Show your work.
47,383 − 8,274 = 38,927 − 1,839 =
37,452 − 3,874 = 82,654 − 1,281 =
5,00,091 − 377 = 17,499 − 8,346 =
85,167 − 1,098 = 17,776 − 2,771 =
18. Fill in the boxes.
Let’s learn to double a number! First split the number in tens and ones.
Then double both numbers.
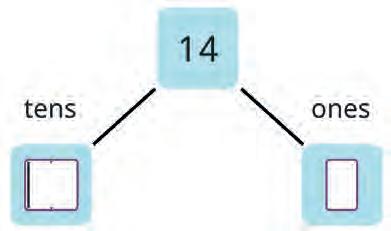

Change the tens to ones.
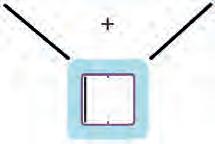
Then add both numbers.
Now double 32 in the same way.
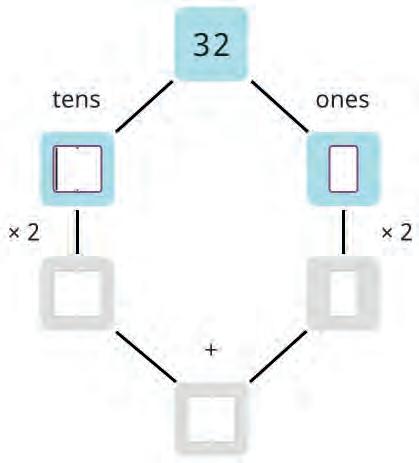
19. Help the hedgehog get the mushroom. Start at the first number. Solve and write the answer in the box. Continue till you reach the mushroom.
20. Solve. Write the answers in the boxes.
× 75 =
21. Solve. Write the answers in the blanks.
× 24 =
56 × 478 =
22. Solve. Write the answers in the blanks.
× 63 =
÷ 19 = 396 × 27 =
÷ 16 =
÷ 27 = 238 × 71 =
÷ 12 =
÷ 20 =
23. Simplify the given expressions. Write your answers in the blanks. Show your work.
100 – (50 – 38) – (25 + 13) = 50
1) 50 – 38 = 12 2) 25 + 13 = 38
3) 100 – 12 = 88 4) 88 – 38 = 50
(49 +11 – 16) – (92 – 76) =
(51 – 17) + (85 – 46) + (43 – 24) =
(29 + 64 – 72) – (35 + 35 – 49) =
24. Simplify the given expressions. Write your answers in the blanks. Show your work.
27 + (9 × 6 – 25) + 72 ÷ 8 =
100 – (63 + 27 – 58) ÷ 4 =
(31 – 30) × (63 ÷ 7 + 64 ÷ 8) =
(63 – 23) × 2 – (45 + 45) ÷ 30 – (72 + 28) ÷ 10 =
25. A humming bird beats its wings 80 times per second. How many times will it beat its wings in three hours?
26. A squirrel eats 950 nuts during winter. How many nuts will four squirrels eat in three winters?
27. Fifteen sacks of flour weigh 2040 kg in total. What is the weight of one sack?
28. A book has 57 pages with 23 lines on each page. Each line has 9 words. Find the total number of words in the book.
29. A shop sold 15 kg of bananas on Monday. On Tuesday, it sold three times as much as it sold on Monday. On Wednesday, it sold 12 kg less than on Tuesday. How many kilograms of bananas were sold in total?
2. PATTERNS IN WHOLE NUMBERS
WHOLE NUMBERS AND NATURAL NUMBERS
1. Look at each number line. Fill in the blank spaces with the correct numbers.
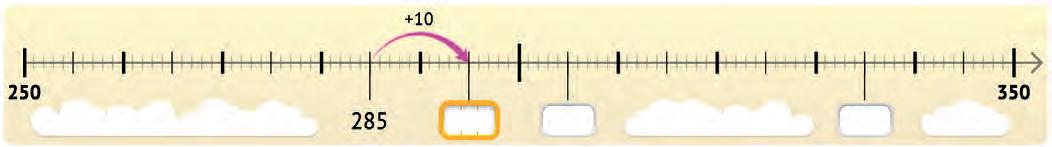
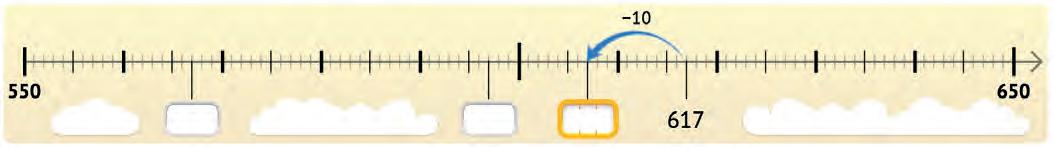
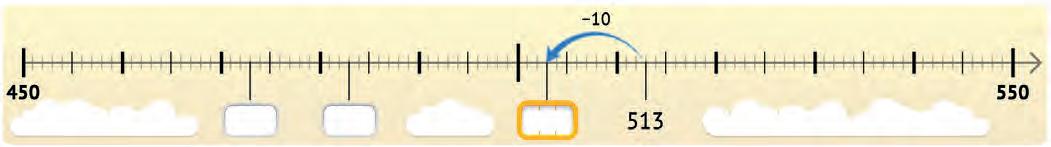
2. Look at each pair of numbers. Write how far apart they are on the number line.
a) 4 and 9?
Answer d) 0 and 14?
Answer
b) 15 and 29?
Answer e) 13 and 21?
Answer
c) 2 and 13?
Answer f) 4 and 43?
Answer
3. Look at each number line. Write the missing numbers in the blanks.
4. Fill in the blanks.
Answer a) 5 × 13 = 13 × b) 382 × = 382 c) 21 × (51 + ) = 21 × 51 + 21 × 42 d) ÷ 312 = 0 e) (31 × 24) × 3 = 31 × ( × 3) f ) 0 × 2829 = g) × 8472 + × 3717 = 2025 × ( + )h) 1 × = 831
5. How many whole numbers are there between 21 and 49?
PATTERNS
6. Find each pattern. Use it to write the next number.
2, 8, 32, 128, 14, 28, 56, 112, 5, 15, 45, 135, 5, 20, 80, 3, 9, 27, 81, 4, 12, 36, 108
2, 4, 12, 48, 1, 5, 10, 16, 23, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13,
7. Find the pattern in each column. Use it to complete the table.
8. Find the pattern in each column. Use it to complete the table.
3. PLAYING WITH NUMBERS: FACTORS
AND MULTIPLES
REVIEWING FACTORS AND MULTIPLES
1. Find two factors of each number given below. Write your answers in the blanks.
a) 14: ;
c) 36: ;
b) 19: ;
d) 67: ;
2. Find two multiples of each number given below. Write your answers in the blanks.
a) 18: ;
c) 71: ;
b) 43: ;
d) 103: ;
3. Look at each number. Write all its factors. Then write any three multiples of that number.
Factors: 46
Multiples: Factors: 32
Multiples: Factors: 25
Multiples: Factors: 56
Multiples:
TYPES OF NUMBERS
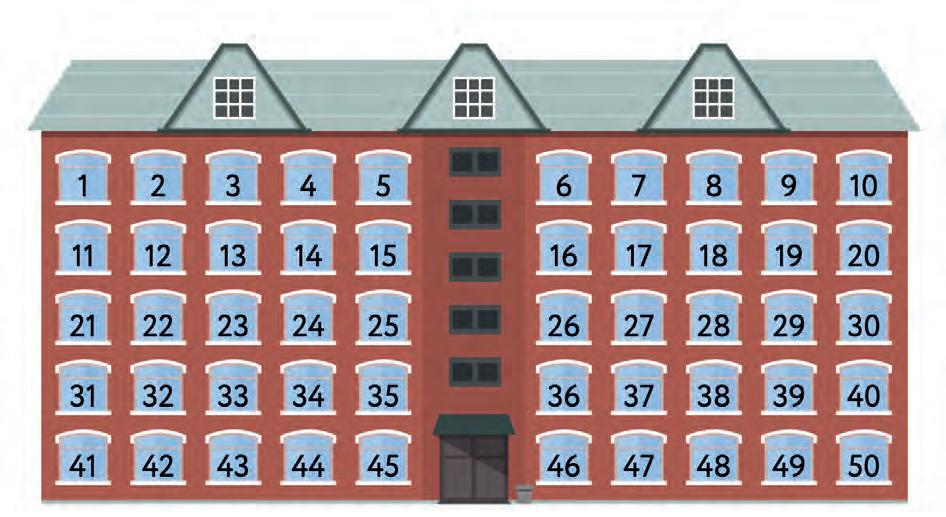
4. Look at the picture below. Is the number of students even or odd? Try to answer without actually counting.

Answer:
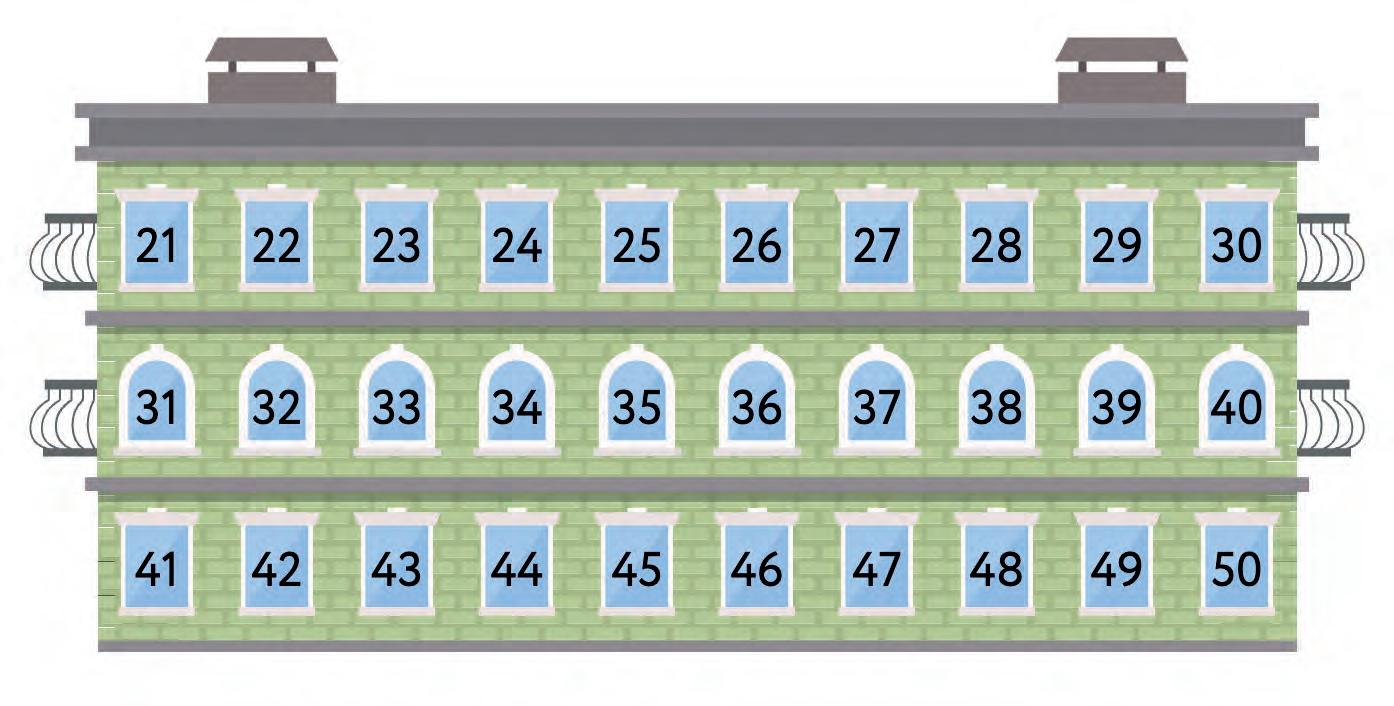
5. Look at the picture below. Is the number of fish even or odd? Try to answer without actually counting.

Answer:
6. Sort the numbers into even and odd. Write your answers in the blanks.
73, 14, 42, 85, 2, 51, 102, 52, 37, 1, 88, 8, 67, 31
Odd numbers:
Even numbers:
7. Will each answer be odd or even? Tick the correct word.
a) even number + even number = __________ number
b) even number + odd number = __________ number
c) odd number + odd number = __________ number
d) even number × odd number = __________ number
e) even number × even number = __________ number
f) odd number × odd number = __________ number
8. Write three factors of 14 other than 14 itself.
Now look at the factors above and answer these questions. Tick the correct option.
a. The sum of the factor of 14 = 14.
b. 14 is a perfect number.
9. Which of the following numbers are perfect squares? Circle them. Cross out the others.
10. How many factors does a prime number have? Tick the correct answer.
11. Look at each number. Is it prime or composite? Write your answer.
17 = 1 × 17 — prime number
12. Look at the given numbers. Find the numbers that are divisible by 10. Circle them.
13. Read each of the statements. Is it true or false? Tick your answer.
1) If a number ends in 0, it is divisible by 8.
True False
2) If a number ends in 0, it is divisible by 10.
True False
3) If a number ends in 3, it is not divisible by 10.
True False
14. Look at the given numbers. Find the numbers that are divisible by 5. Circle them.

15. Read each of the statements. Is it true or false? Tick your answer.
1) If a number ends with 0, then it is divisible by 5.
True False
2) If a number ends with 5, then it is always divisible by 3.
True False
3) If a number ends with 3, then it is not divisible by 5.
True False
16. Look at the given numbers. Find the numbers that are divisible by 2. Circle them.
17. Read each of the statements. Is it true or false? Tick your answer.
1) If a number ends in an odd digit, it is not divisible by 2.
True False
2) If a number ends in an even digit, it is always divisible by 8.
True False
3) If a number ends with 5, it is not divisible by 2.
True False
18. Complete each sentence. Tick the correct answer.
1) To check if a number is divisible by 10, check whether___ is 0. its last digit the sum of its digits
2) To check if a number is divisible by 3, check whether ___ is divisible by 3. its last digit the sum of its digits
3) To check if a number is divisible by 2, check whether ___ is even. its last digit the sum of its digits
4) To check if a number is divisible by 9, check whether ___ is divisible by 9. its last digit the sum of its digits
5) To check if a number is divisible by 5, check whether ___ is 0 or 5. its last digit the sum of its digits
19. Make 4 different numbers that are divisible by 3 as well as 5. Use some or all of the given digits.
20. Make 4 different numbers that are divisible by 3 but not by 9. Use some or all of the given digits.
21. Make 4 different even numbers that are divisible by 3. Use some or all of the given digits.
22. Look at each number. Check its divisibility. Write it in the correct column.
12, 18, 27, 10, 25, 35, 20, 30, 50, 4, 8, 14, 9, 36, 45 Divisible by 10Divisible by 5Divisible by 2Divisible by 3Divisible by 9
23. Find the sum and the difference of each pair of numbers. Check if each one is divisible by the given divisor. Write Yes or No.
DivisorIs Sum divisible? Is Difference divisible?
24. Pick the correct numbers from the list and write them in the circles. Remember, the arrow shows is divisible by.
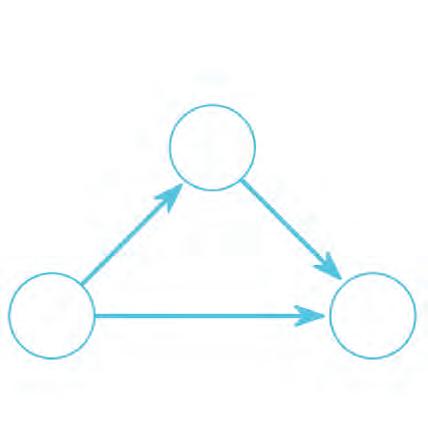
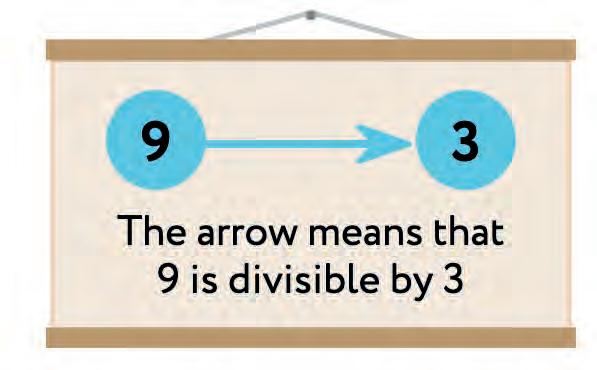
The arrow shows that 9 is divisible by 3.
25. Write all the factors of the numbers given below. Use the hints shown.
Factors of 8125
Hint: 8125 = 25 × 25 × 13
Factors of 6220
Hint: 6220 = 20 × 311
26. In a game, each team must have the same number of boys and the same number of girls. Read each question and tick the correct answer.
1) Can 12 boys and 10 girls be divided into 2 equal teams?
Yes, each team will have boys and girls.
No
2) Can 22 boys and 12 girls be divided into 3 equal teams?
Yes, each team will have boys and girls.
No
27. Write the missing factors of 12 and 8. Circle the pairs of common factors. Then complete the sentence.

The highest common factor of 12 and 8 is .
28. Write the missing factors of 6 and 10. Circle the pairs of common factors. Then complete the sentence.

The highest common factor of 6 and 10 is .
29. Write the missing factors of 15 and 16. Circle the pairs of common factors. Then complete the sentence.

The highest common factor of 15 and 16 is .
30. Write the missing multiples of 4 and 6. Circle the pairs of common multiples. Then complete the sentence.

The lowest common multiple of 4 and 6 is .
31. Write the missing multiples of 3 and 2. Circle the pairs of common multiples. Then complete the sentence.

The lowest common multiple of 3 and 2 is .
32. Write the missing multiples of 5 and 3. Circle the pairs of common multiples. Then complete the sentence.

The lowest common multiple of 5 and 3 is .
WORKING WITH LCM AND HCF
33. What does LCM stand for? Tick the correct answer.
Lowest Common Metre
Lowest Common Multiple
Largest Common Multiple
Longest Common Multiple
34. What does HCF stand for? Tick the correct answer.
Highest Common Function
Highest Common Factor
Highest Common Figure
Highest Common Fraction
35. Read what Dino says! Use it to find whether the given statements are true or false. Tick the correct answer.

a) 9 and 4 are co-prime numbers.b) 7 and 14 are co-prime numbers.
36. Look at each pair of numbers. Tick the pair if the two numbers in it are co-primes. Show your work.
a) 13 and 24
d) 27 and 58
b) 35 and 49
e) 32 and 33
c) 56 and 39 f) 46 and 69
a) 13 = 1 × 1324 = 1 × 2 × 3 × 4 × 6 × 8 × 12 × 24HCF (13, 24) = 1
37. Find the HCF of the numbers in each pair. Write your answers in the blanks.
a) HCF ( 5; 9 ) =
b) HCF ( 6; 12 ) =
c) HCF ( 5; 10 ) =
d) HCF ( 14; 21 ) =
e) HCF ( 35; 63 ) =
38. Find the LCM of the numbers in each pair. Write your answers in the blanks.
a) LCM ( 8; 4 ) =
b) LCM ( 9; 3 ) =
c) LCM ( 6; 5 ) =
d) LCM ( 11; 10 ) =
e) LCM ( 18; 9 ) =
4. LINES, ANGLES AND SHAPES
RAYS, LINES AND LINE SEGMENTS
1. Look at the given picture. Choose the correct words and fill in the blanks.




2. Look at the lines drawn in each image. Then choose the correct word and complete the sentence.


All the lines in this image are lines.
The shortest path between the ship and the island is a straight straight curved curved
line.
3. Look at each figure. Then choose the correct word and complete the sentence.
This is a . It has a starting point but has no end point. line segment ray line segment ray
This is a . It has two end points.
4. Look at the following image. How many different line segments are in it? Write your answer in the blank.
Answer:
5. Look at the following image. How many different rays are in it? Write your answer in the blank.
Answer:
6. Read the ways to name a line. Then tick the correct names of the line shown.

A line is denoted by one lowercase (small) English letter. Also, a line segment can be named using two points that lie on it.
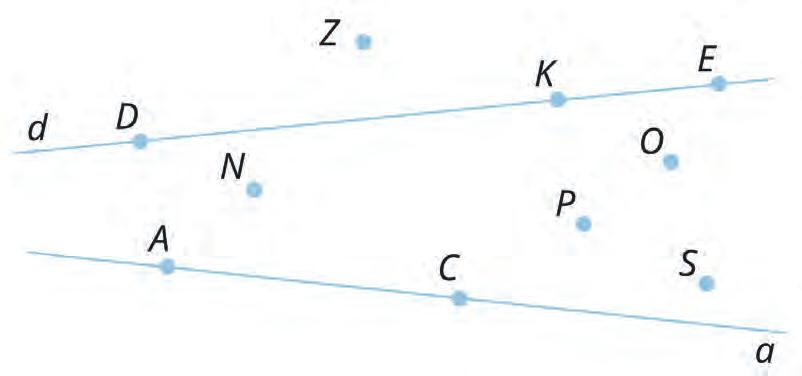
7. Look at the points shown. Circle all the points that lie on line d.
8. Try to draw straight lines that pass through the point A. Then answer the question given below.
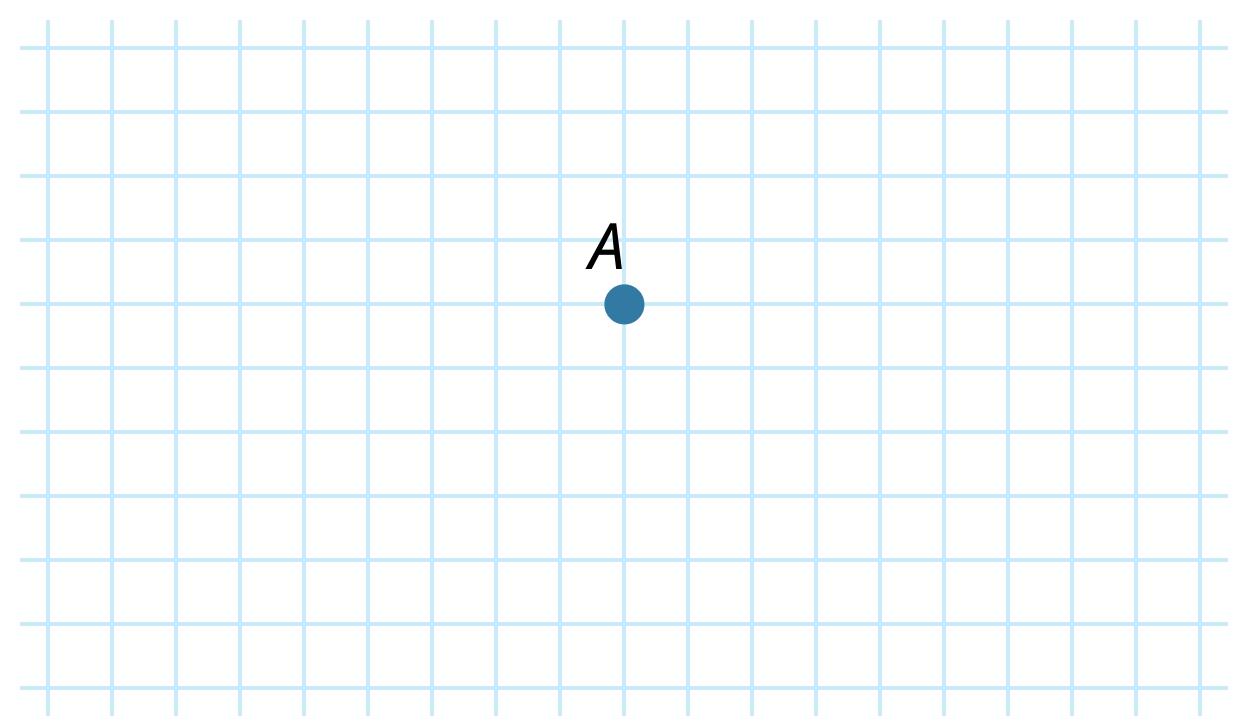
How many straight lines can pass through a point? Tick the correct option.
As many lines as needed
Only one line
Only five lines
9. Try to draw straight lines that pass through both points A and B. Then answer the question given below.
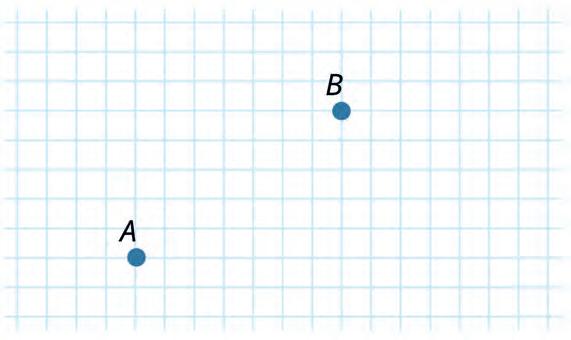
How many straight lines can pass through two given points? Tick the correct option.
As many lines as needed
Only one line
Only five lines
10. Read each of the following questions. Tick the correct answer.
How many different straight lines can be drawn through one point?
Only oneAs many as needed
How many different curved lines can be drawn through one point? Only one
How many different curved lines can be drawn through two points? Only one
How many different straight lines can be drawn through two points? Only one
As many as needed
As many as needed
As many as needed
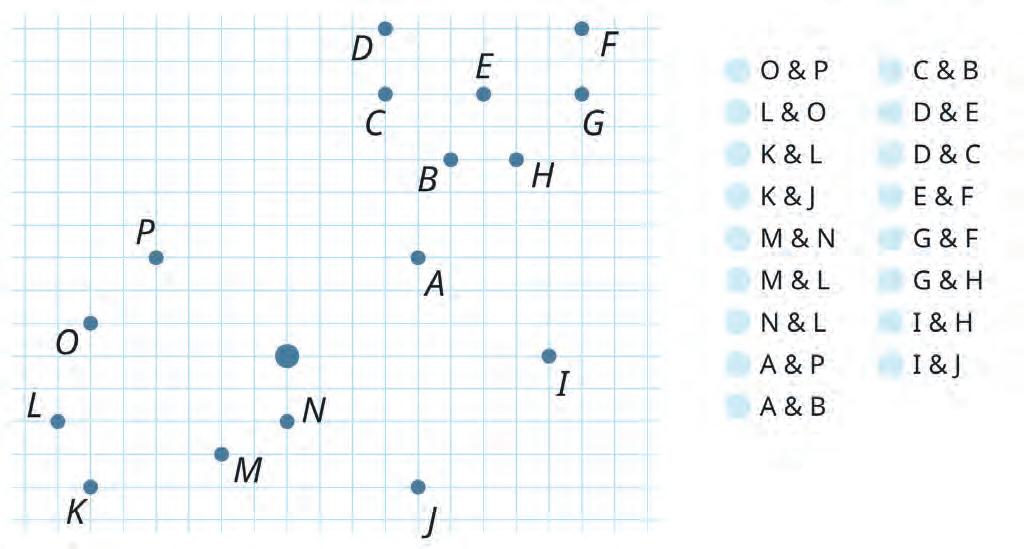
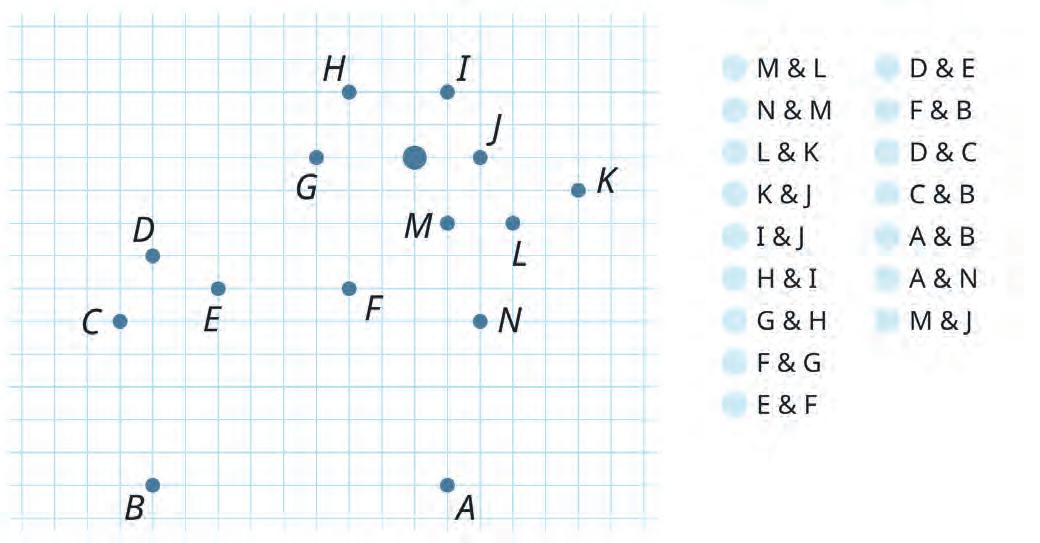
11. Read the names of the points in each pair. Then join them.
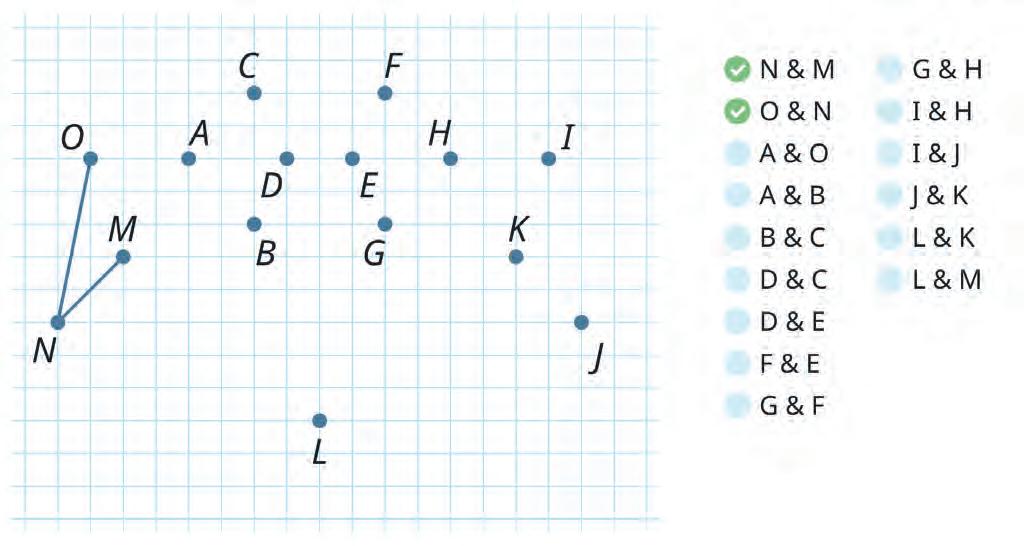
12. Read the names of the points in each pair. Then join them.
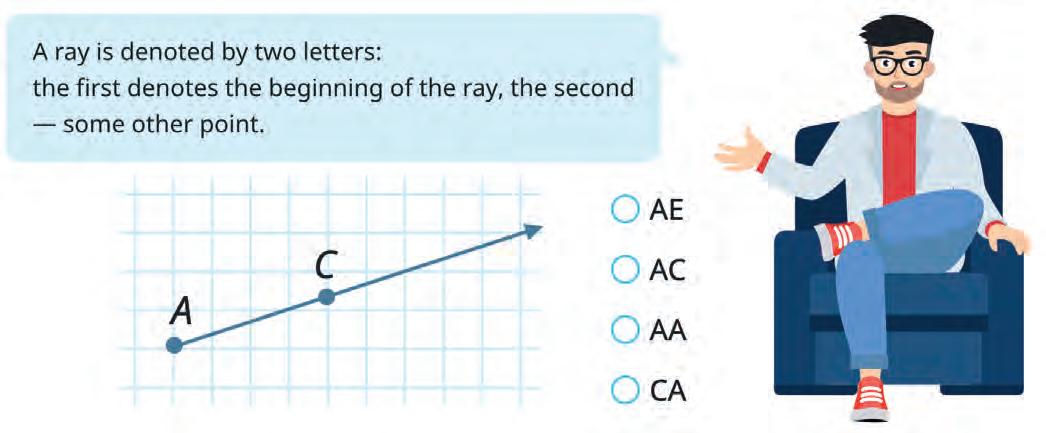
13. Read how a ray is named. Then tick the correct name of the ray shown.
A ray is named using two letters. The first letter is the starting point. The second letter is any other point on the ray.
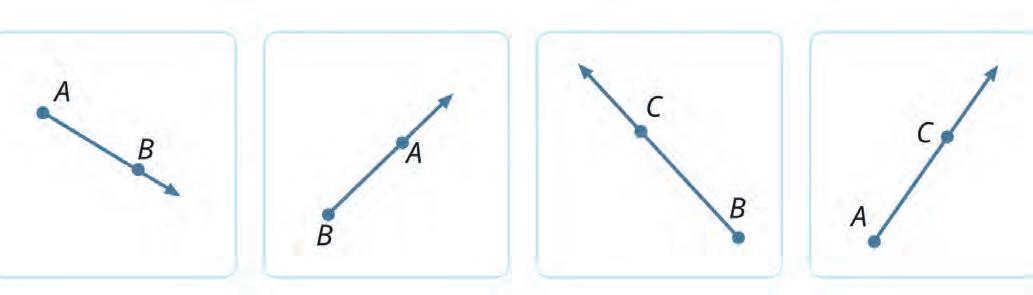
14. Which of these images show ray AB and ray BC? Tick them.
ANGLES
15. Draw two rays that start from point A. Look at the shape formed. Then choose the correct words and complete the sentence.
An angle is formed when rays have the same initial . two three point direction
16. Read how an angle is named. Then, in each row, tick the image that shows the given angle.

a) Angle PQR
An angle is denoted by three letters. The middle letter represents the vertex. The other two letters represent points on each ray of the angle.
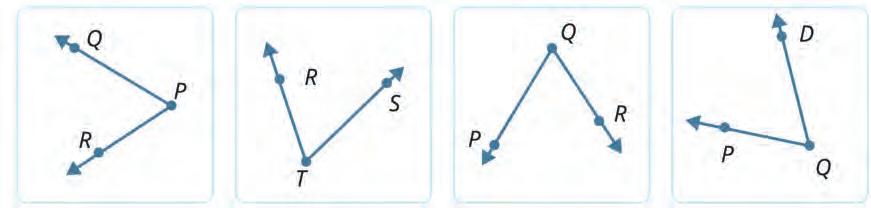
b) Angle ABC
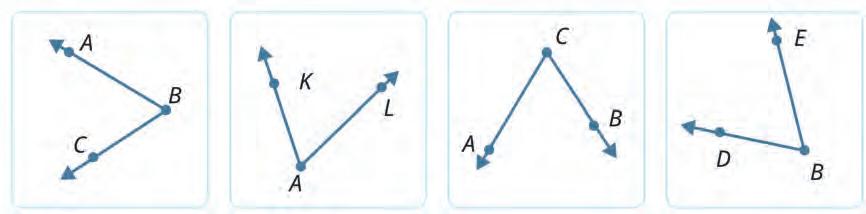
17. Look at the given angle. Then choose the correct words and complete the given sentences.
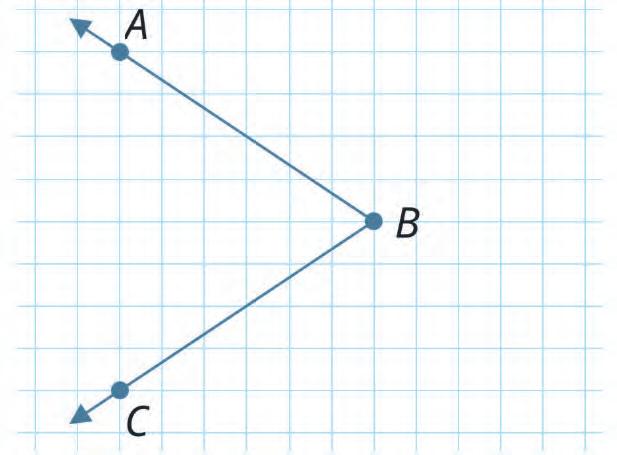
In the angle ABC:
• the ray BA is .
• the ray BC is .
• the point B is . a vertex
an angle an arm an arm
18. Look at the given image. Then choose the correct words and complete the given sentence.
Two rays and start from the point B. So, is an angle.
19. Look at the image. Find all the straight angles and right angles in it. Write their names.
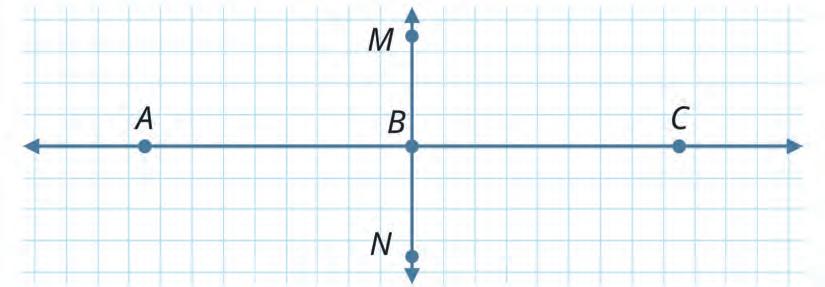
Straight angles: Right angles:
UNDERSTANDING POLYGONS
20. Tick the figure that has 4 vertices and 4 sides.

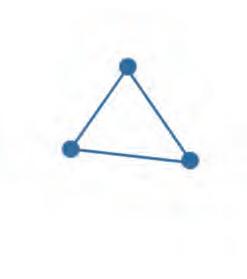
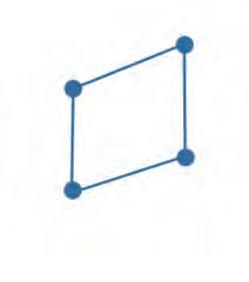
21. Tick the figure that has 5 vertices and 5 sides.
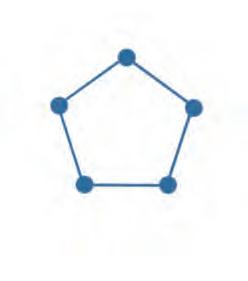
22. Tick the figure that has 3 vertices and 3 sides.
23. Look at each of the following shapes. How many vertices and sides does it have? Write your answers in the blanks.
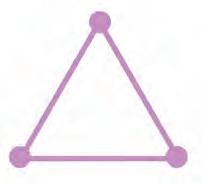
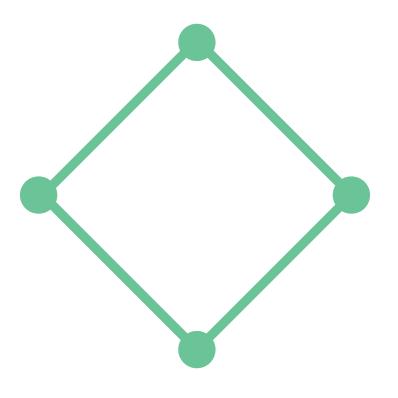
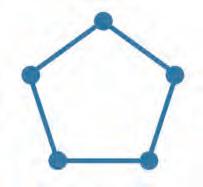
vertices vertices vertices sides sides sides
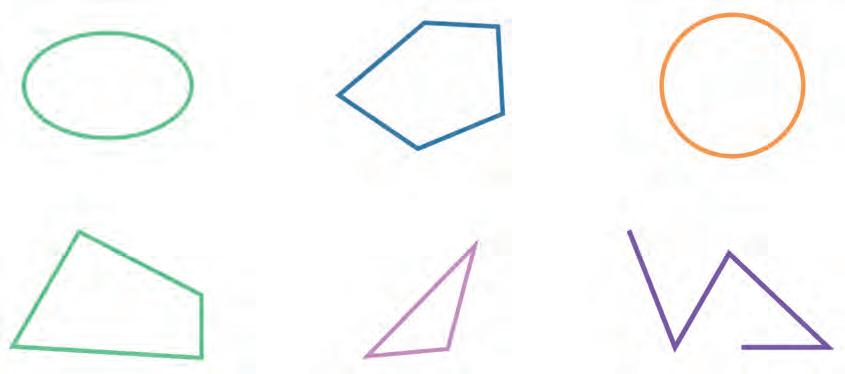
24. Which of these shapes are polygons? Tick them.
25. In the following grid, draw a simple polygonal chain on the left. Then draw a closed polygonal chain on the right. Mark all vertices with red dots and all segments with blue lines.
26. Look at each shape. Tick its name.

27. Each of the following sentences is incomplete. Choose the right words and complete it.
If __________ of the angles of a triangle is _________, then it is called a right-angled triangle.
If __________ of the angles of a triangle is _________, then it is called an obtuse-angled triangle.
If __________ of the angles of a triangle are _________, then it is called an acute-angled triangle.
28. Each of the following sentences is incomplete. Choose the right words and complete it.
If _________ sides of a triangle are _________, then it is called an isosceles triangle.
If _________ sides of a triangle are _________, then it is called an equilateral triangle.
all all one two obtuse equal a right-angle acute one
29. Kavita and Kamal each made a statement about the triangle shown. Look at the triangle and find out who is correct. Tick the correct answer.
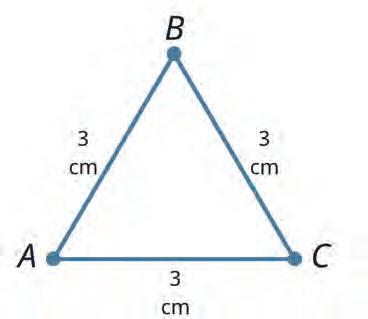

This is an equilateral triangle, since all sides are equal.
It is an isosceles triangle, as it has two equal sides.
is correct. Kavita is correct. Both are correct.

30. Look at each of the triangles. Find how long its sides are. Then choose the correct words and write the names of its sides.
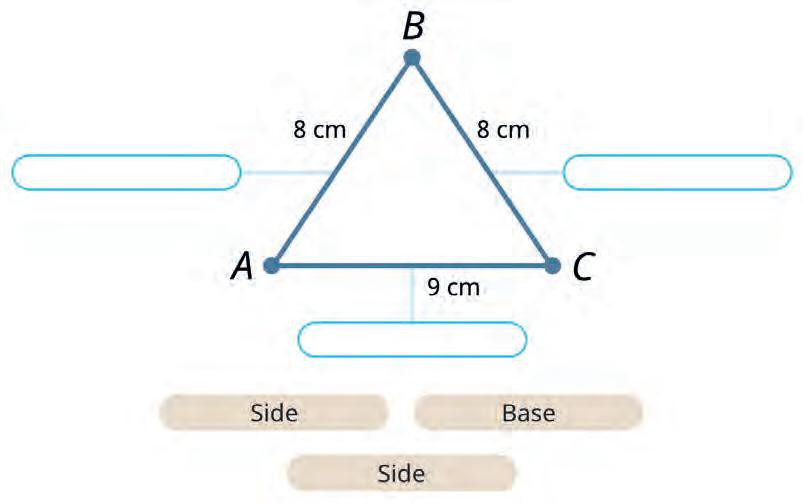
Kamal
Kamal
Kavita
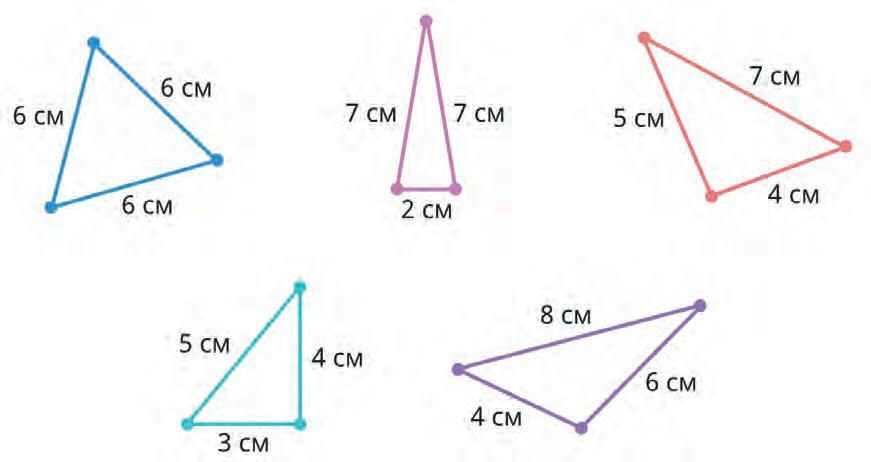
31. Which of these triangles are isosceles? Tick them.
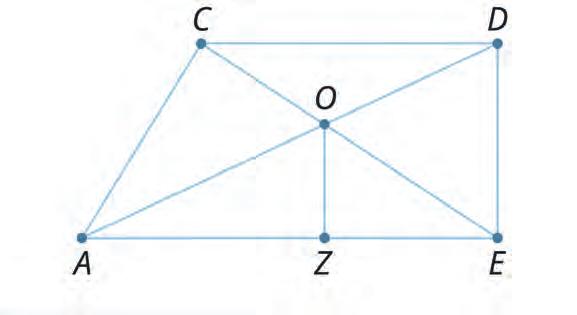
32. Read the names of the triangles given on the right. Spot them in the image. If they are obtuseangled, tick them.

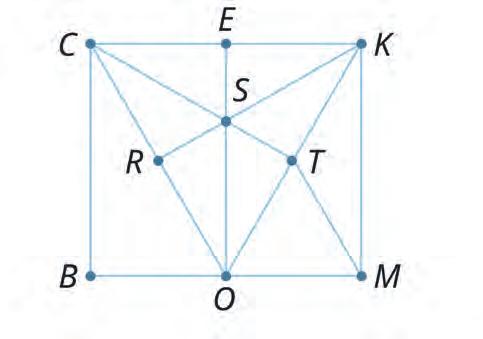
33. Read the names of the triangles given on the right. Spot them in the image. If they are rightangled, tick them.

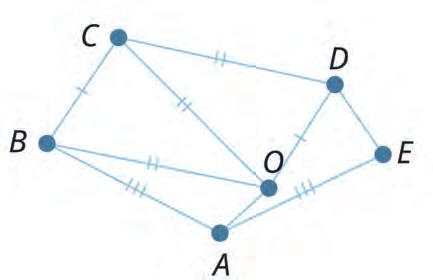
34. Read how to mark the equal sides in a shape. Then tick the pairs in which both sides are equal.



35. Dima and Rohan each made a statement about the shape shown. Look at the shape and find out who is correct. Tick the correct answer.
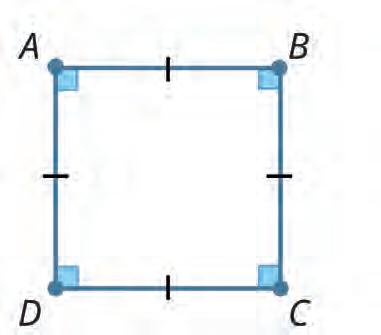
This is a square, since all angles are right-angled.
This is a square, since all angles are right angles and all sides are equal.
36. Which of these shapes are rectangles? Tick them. Dima is correct. Rohan is correct. Both are correct.
Dima
Rohan
UNDERSTANDING CIRCLES
37. Draw two curves of each type.
Simple curve
Non-simple Curve
Open Curve
Closed Curve
38. The radii of some circles are given below. Construct these circles using a compass.
radius = 1 cm
radius = 2 cm
radius = 15 mm
radius = 25 mm
39. Join each part of the circle to its name.
40. Choose the correct words and complete the following sentences.
1) A means half of a circle.
2) circles are circles that share the same but have different .
Concentric semicircle centre radii
41. The diameters of some circles are given below. Construct these circles using a compass.
diameter = 2 cm
diameter = 4 cm
diameter = 30 mm
diameter = 50 mm
Vertices
5. 3-D SHAPES
UNDERSTANDING 3-D SHAPES
1. Complete the table.
2. Fill in the blanks.
1) A square pyramid has edges and vertices.
2) A rectangular pyramid has 5 and 8 .
3) A pentagonal pyramid has faces and edges.
4) A hexagonal pyramid has 7 and vertices.
3. Which of the following nets will make a cube when folded? Circle them.
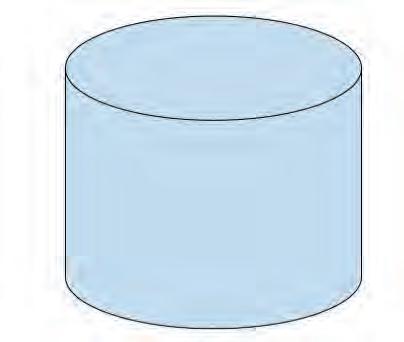
4. A cylinder is shown below. Draw its net.
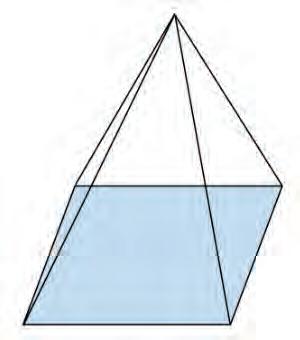
5. A square pyramid is shown below. Draw its net.
6. INTEGERS
UNDERSTANDING INTEGERS
1. Look at each thermometer. What temperature does it show? Tick the correct answer.



2. It was –5°C in the morning, and it was 20°C warmer in the evening. What was the temperature in the evening?
Answer:
3. It was 0 °C in the morning, and it was 5 °C colder in the evening. What was the temperature in the evening?
Answer:
4. Read the message. How many coins will be left after the payment? Tick the answer.
Your balance: 125 coins. Payment due: 75 coins.
Dino Telecom



Your balance: 14 coins. Payment due: 24 coins.
Dino Telecom

5. Read the message. How many coins will be left after the payment? Tick the answer.

Your balance: 150 coins. Payment due: 150 coins.
Dino Telecom

Your balance: 7 coins. Payment due: 18 coins.
Dino Telecom


Your balance: 130 coins. Payment due: 40 coins.
Dino Telecom


c)
6. Look at each number line. What number does the point show? Write it in the box.
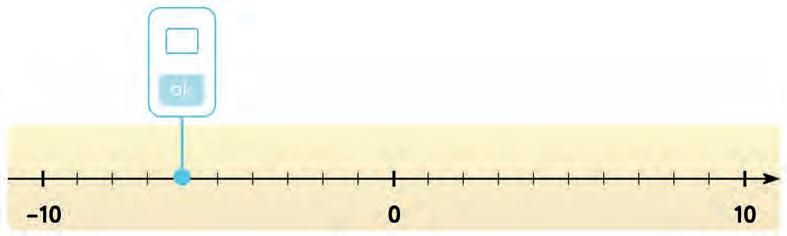
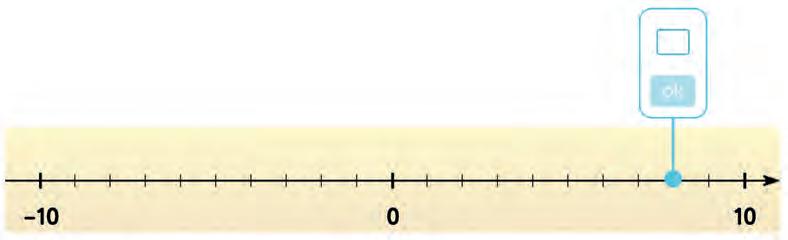
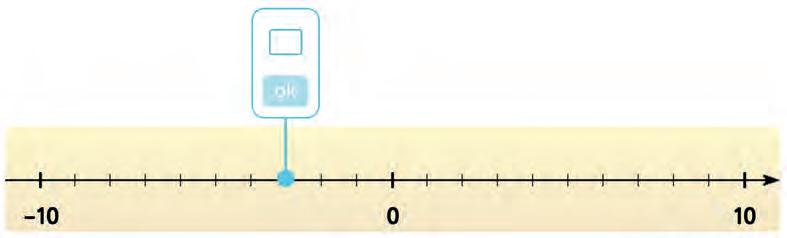
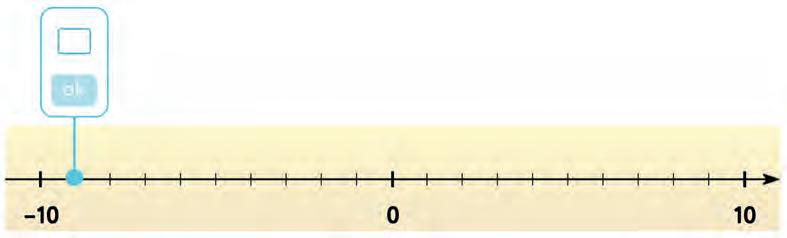
7. Look at each thermometer. What temperature (in °C) does it show? Tick the correct answer.
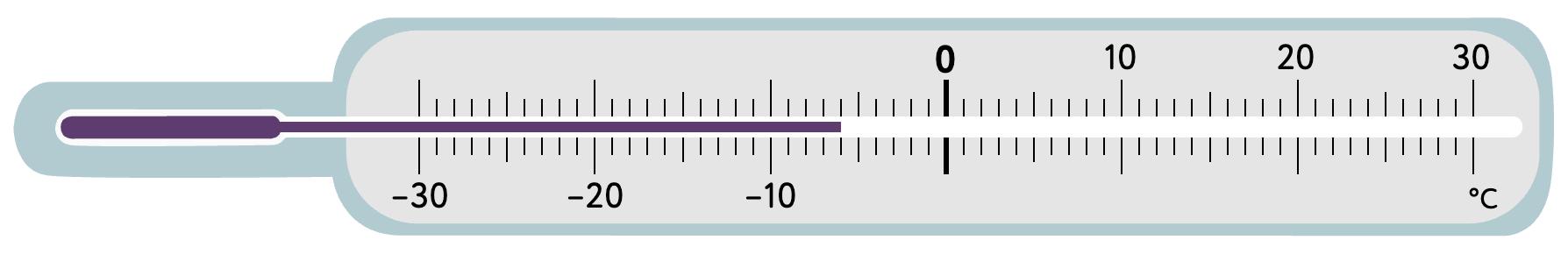
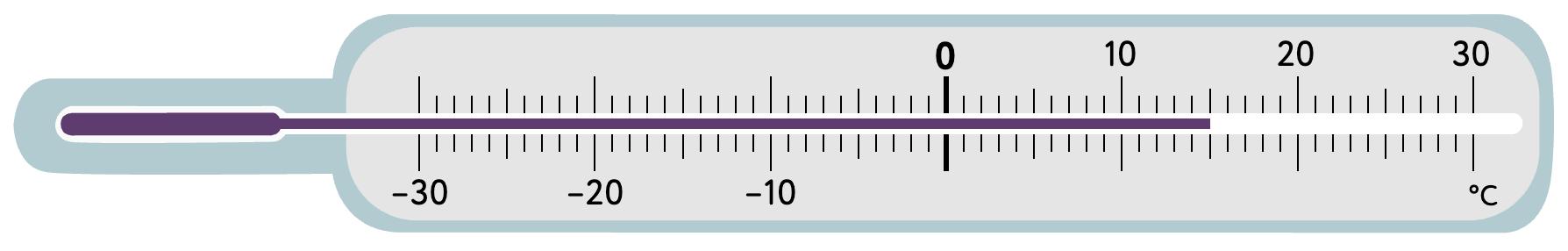
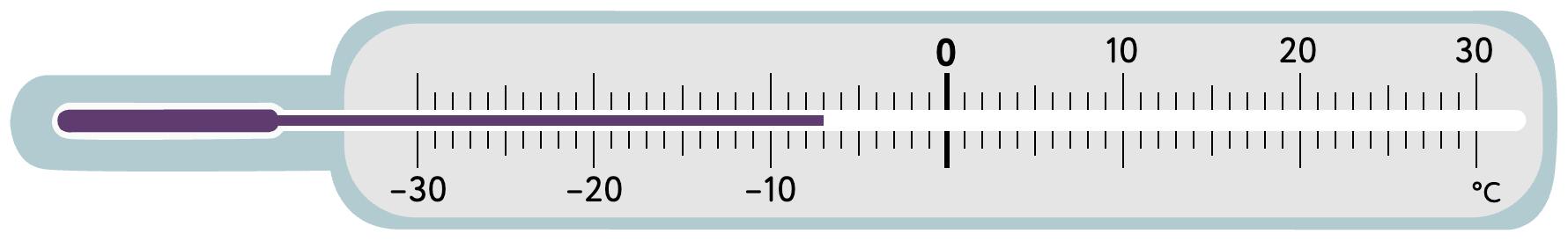
8. Look at the number on each big bean. Circle the small bean that shows its opposite number.
9. Look at each pair of acorns. Find the pairs that show opposite numbers. Tick them.
10. Look at each number. Is it positive or negative? Join it to the correct shelf.
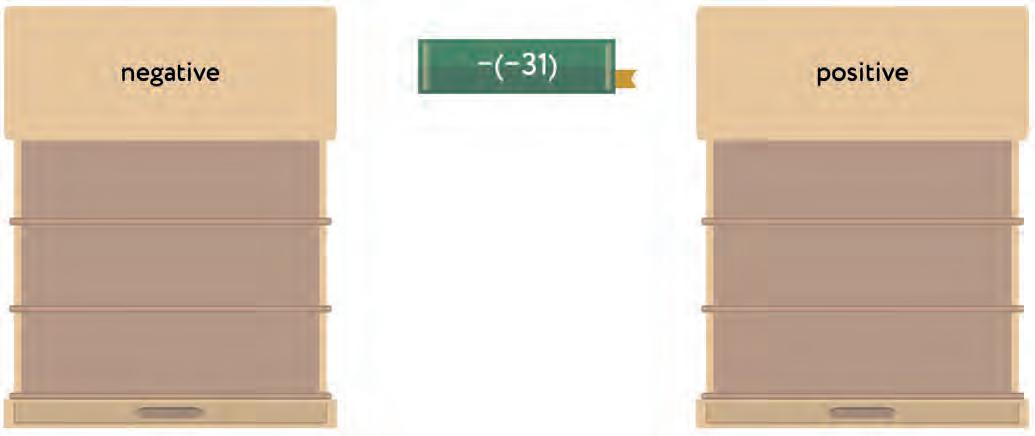


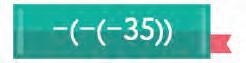

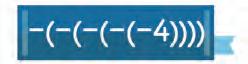
11. Fill in the blanks.
a) A number is negative if the number of negative signs before it is (odd/even).
b) A number is positive if the number of negative signs before it is (odd/even).
12. Simplify each of the following. Write your answers in the blanks.
a) –(–(–3)) = b) –(–12) = c) –4 = d) –(–8) =
e) –(–(–(–6))) = f) –(–(–(–(–2)))) =
13. Choose the correct words and complete the given statement.
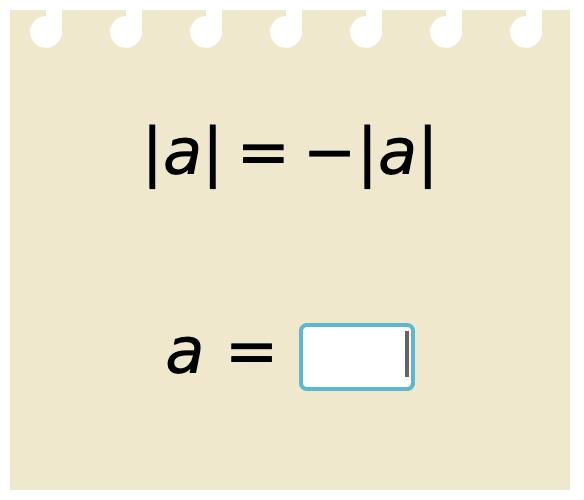
The absolute value of an integer y is on the number line.
the distance between 0 and 1
the distance between 0 and y
the distance between 1 and y
14. Find the absolute value of each of the following.
a) |9| = b) |–5| = c) |0| = d) |13| = e) |–9| = f) |8| =
15. Look at the numbers on the beans. Choose the correct words and complete the statement.
The numbers on the beans show a pair of numbers.
16. Read each statement. Then find the integers that match it. Write your answers in the boxes.


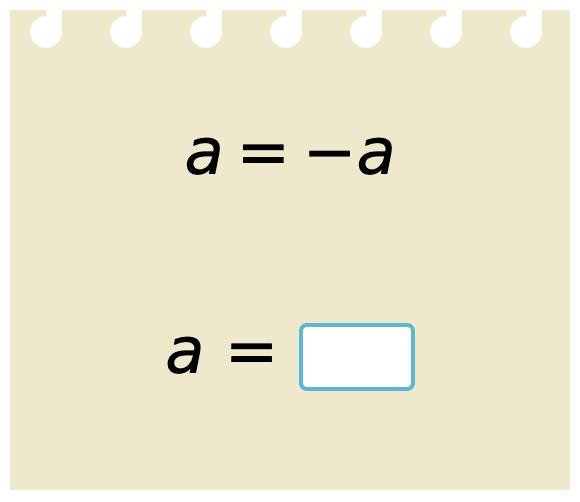
17. Solve. –a is positive number.
÷ |–2| =
– |20| =
=
– |–8| =
– |122| = 17 + 4 = 21
=
18. Look at the orange dots. They show places above and below sea level. Match each dot to its distance from sea level.

19. Look at the orange dots. They show places above and below sea level. Match each dot to its distance from sea level.

20. First, mark the numbers in each pair on the number line. Then compare them. Write <, = or > in the blank.
21. See how the integer a compares with other integers. Write the value of a in each box.


22. Read the following statements. Are they true or false? Write your answers in the blanks.
A positive integer is always larger than a negative integer. A negative integer is always larger than zero. a) –7 –|–7| d) –|–3| 2 g) 0 |–9|
23. Look at the numbers or absolute values in each pair. Compare them. Write <, = or > in each circle.
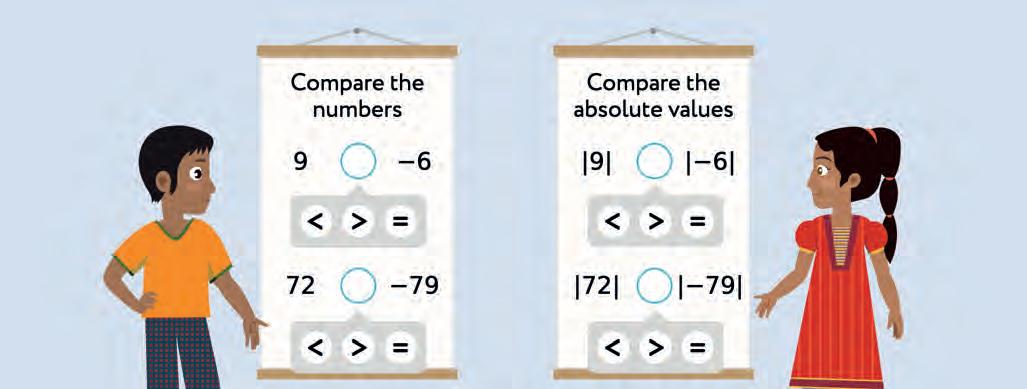
24. Compare the values in each pair. Write <, = or > in each blank.
a)
OPERATIONS ON INTEGERS
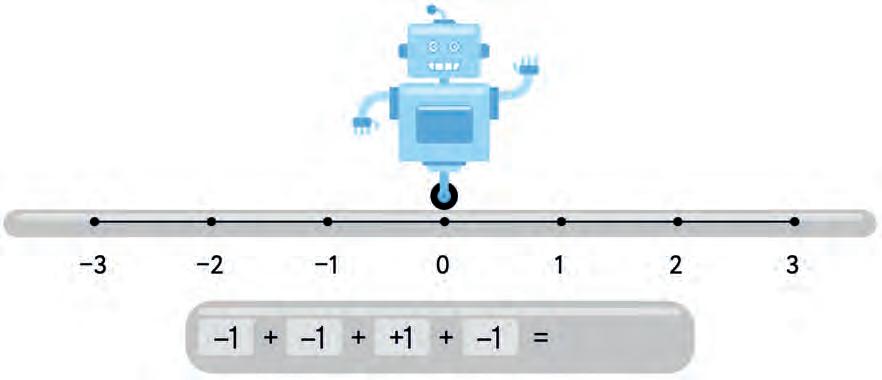
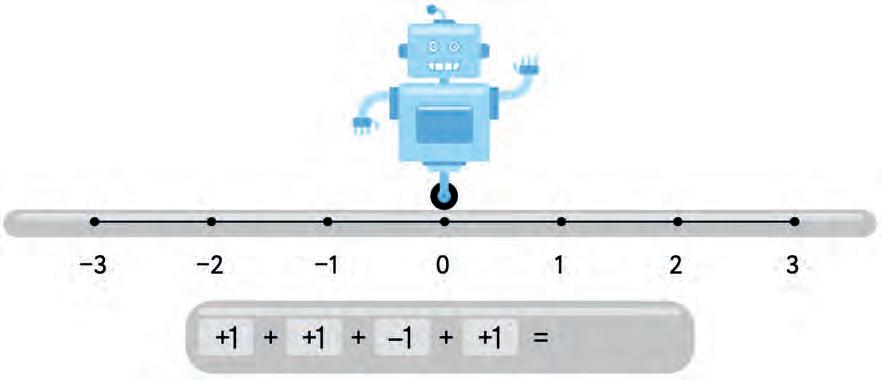
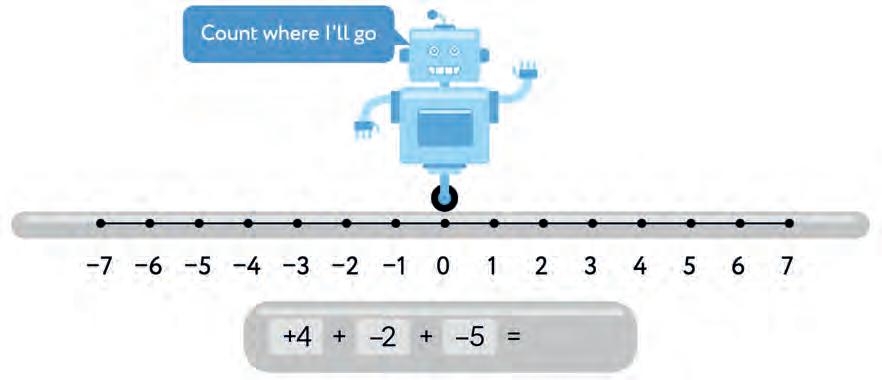
25. The robot starts at 0. Move it left to add a negative integer. Move it right to add a positive integer. Where does it finally land? Write your answer.
b)
c)
26. Use the number line to add the given integers. Write your answers in the boxes.
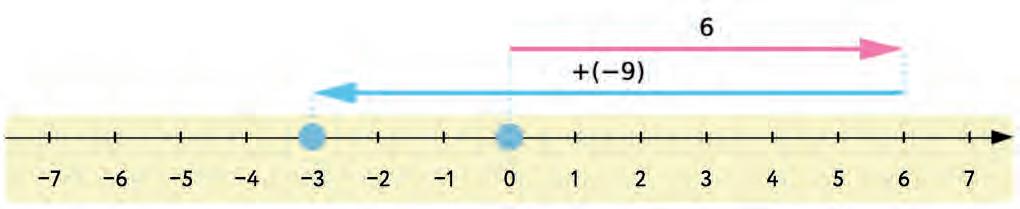
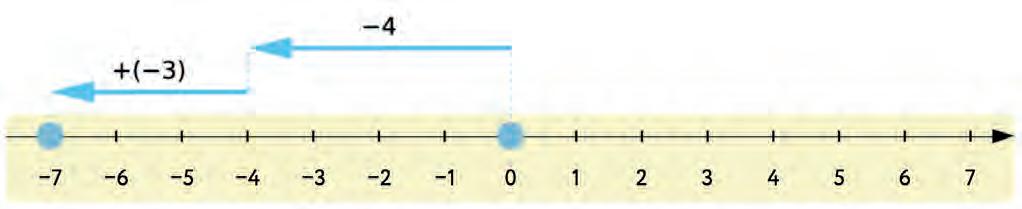
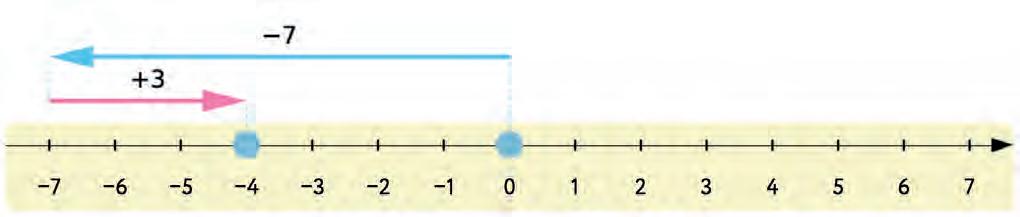
27. Choose the correct words and complete the following sentences.
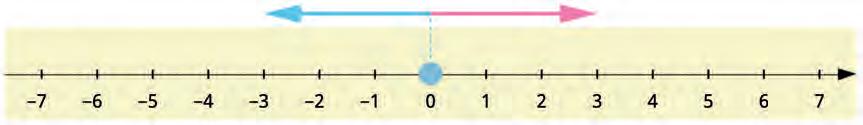
a) To add a positive integer x to y on the number line, start at y and move x steps to the_____________ (left/right).
b) To add a negative integer x to y on the number line, start at y and move x steps to the______________ (left/right).
28. As a part of her exercise, Mary ran 4 stairs up and then 8 stairs down. What is Mary’s position from the starting stair? Choose the correct word and complete the sentence.
Mary is _________( above/below) the starting stair.
Which of these will you use to find how many stairs below she is? Tick the correct answer.
29. Peter takes out ₹20 from his wallet and then puts back ₹14. Does Peter have more or less money in his wallet now? Choose the correct word and complete the sentence.
Peter has ______ money in his wallet now. (more / less)
Which of these will you use to find how much less money Peter has? Tick the correct answer. (–20) + 14 20 + 14
30. Make a rule. Look at each example. Then complete the sentence by choosing the correct option.
a) 5 + (–3) = 2
I add a positive integer and a negative integer. If , the sum will be positive. their absolute values are equal the negative integer has the larger absolute value the positive integer has the larger absolute value
b) –4 + (–2) = –6
I add two negative integers. Their sum is . always positive always negative always zero
c) 3 + (–9) = –6
I add a positive and a negative integer. If , the sum will be negative. the absolute values of integers are equal the negative integer has the larger absolute value the positive integer has the larger absolute value
31. Look at each pair of numbers. Is the sum negative, zero or positive? Tick your answer.
24 + 47
–49 + 14
–5 + 5 –29 + 18
–3 + 25
15 + (–22)
4 + (–4)
–43 + (–5)
32 + (–9)
84 + 26
–74 + 21
32. Write the missing numbers.
27 + = 27
–9 + = 4
16 + = 12
33. Solve.
a) –24 + 12 =
d) 61 + (–17) =
g) 93 + 34 =
j) –76 + (–43) =
m) 50 + (–51) = + (–8) = 17 –12 + 3 = –10 + 5 =
b) –82 + 32 =
e) –52 + 52 =
h) 51 + 72 =
–5 + (–7) = + 19 = 12
c) 45 + (–11) = f ) 73 + (–73) = i) -28 + (–34) =
l) 82 + (–49) =
k) 63 + (–23) = n) 39 + (–46) = + 14 = 0
34. Look at the positions of the arrows on the number line. Find the sum they show. Tick the correct options.
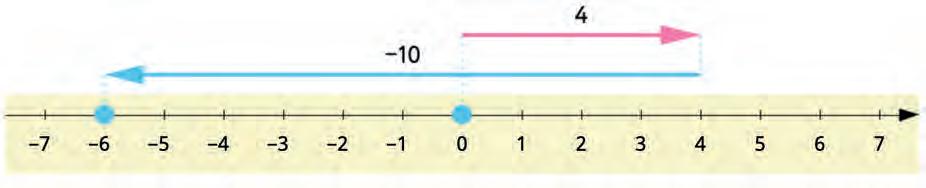
–4 – 10 4 + 10 4 + (–10) 4 – 10
35. Make a rule. Tick the right answer.
To subtract integer b from integer a, add to a. opposite of a b opposite of b 0
Which of these formulas show the above rule. Tick the correct option.
– b = a + (–b)
– b = –a + b
+ b = a – b
36. Join each operation on the left to the matching operation on the right.

37. Read how to subtract –1 from an integer. Then fill in the blanks.
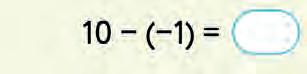
38. Choose the correct words and fill in the blanks.
a) If you add a negative integer x to an integer y, the value of y becomes __________ (larger / smaller).
b) If you subtract a negative integer x from an integer y, the value of y becomes __________ (larger / smaller).
39. Solve.
a) 33 – (–2) =
c) 24 + (–5) = b) 21 – (–4) = d) 31 + (–2) =
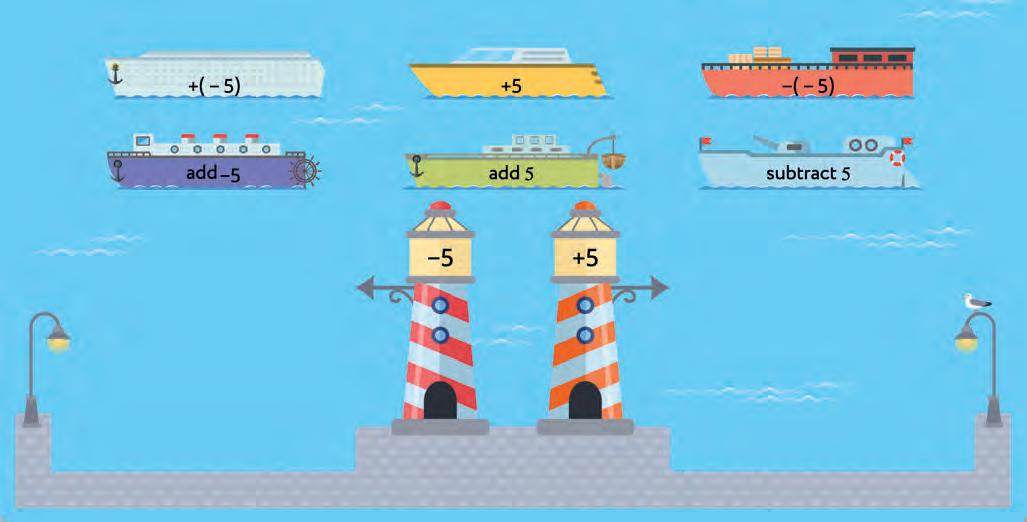
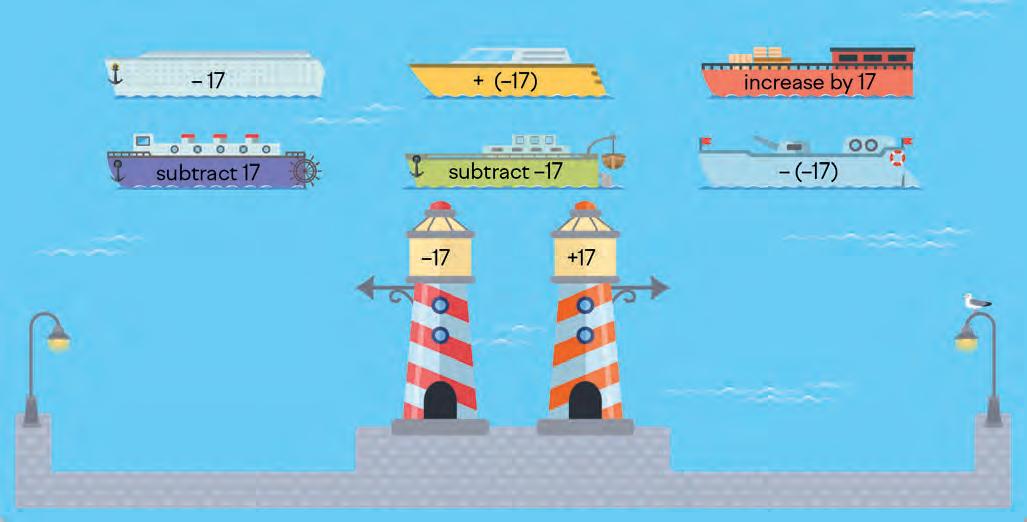
40. Look at the operations and numbers on the ships and lighthouses. Decide which bay each ship should go to. Join each ship to the correct bay.
41. Look at each problem. Will the answer be negative, zero, or positive? Tick your answer.
–40 + 4
–24 + 24
–18 + (–18)
–45 – 26
–13 + 15
–31 – (–12)
–21 – (–26)
43 + (–5) 57 – (–68)
82 + (–91)
+ (–13)
23 – = 23
–7 – = 3
18 – = 6
42. Write the missing numbers. 43. Solve.
a) –2 – (–3) =
–2 + 3 = 1
b) –4 – (–4) =
c) –7 – (–13) =
d) 0 – (–15) =
e) 3– (–11) =
f) 5 – 82 =
g) –24 – 26 =
– (–3) = 19 –12 – 9 = –12 – 8 = – 16 = 0
–2 – (–7) = – 14 = 19
h) 74 – (–34) =
i) 48 – (–24) =
j) 63 – 24 =
k) 13 – (–29) =
l) 14 – 17 =
m) 78 – 89 =
n) –19 – (–75) =
44. Look at the number line. Write the distance between the two marked points in the box.
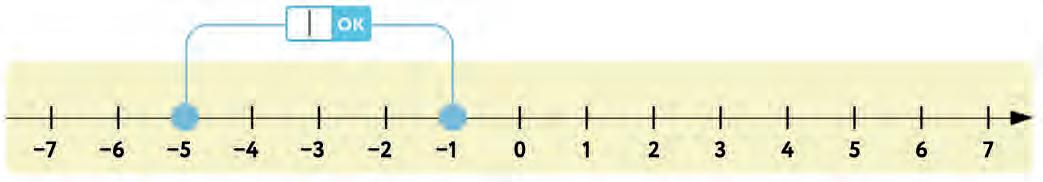
Now use the distance you found to solve each sum. Write your answer in the box.
–(–1)| =
–(–5)| =
45. Look at the number line. Write the distance between the two marked points in the box. –5 –(–1) = –1 –(–5) =
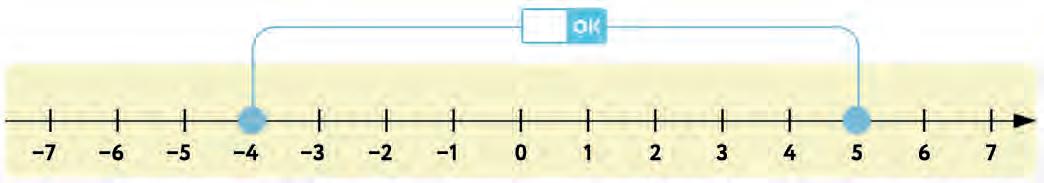
Now use the distance you found to solve each sum. Write your answer in the box.
–5 =
–(–4) =
–5| =
46. Find the number line that shows two integers x and y such that x > y. Tick it.


Now use the correct number line above, and fill in the blanks with <, = or >.
47. Find the number line that shows two integers c and d such that c < d. Tick it.


Now use the correct number line above, and fill in the blanks with <, = or >.
48. Choose the correct word and complete the following sentence.
The distance between two points is always taken as __________ (negative / positive).
49. You want to find the distance between two integers a and b on a number line. However, you do not know which one is larger. Which of these will you find to get the correct distance? Tick the right answer.
50. The different values of the integers m and k are given. Use them to complete the table.
7. FRACTIONS
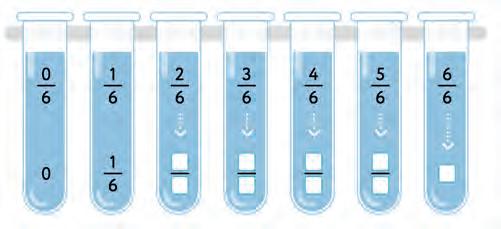
1. Shade the circles to show 2 .
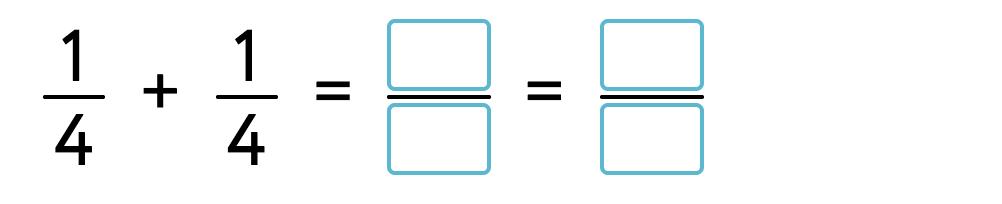
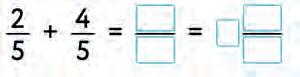
2. Shade the circles to show 1 .
REVIEWING FRACTIONS 1 6 4 6
3. Join each coloured part of the fraction to its correct name or type.
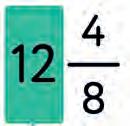
mixed fraction fraction part numerator whole part fraction bar denominator a) b) c) d) f) e)
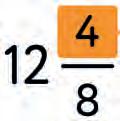

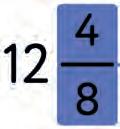
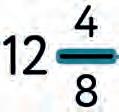
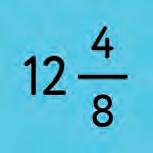
4. Look at each fraction. How do you read it? Choose the correct words and fill in the blanks.
3 4 4 1 2 1
5. Look at the points marked on the number line. What mixed fraction do they show? Write your answers in the boxes.
6. Look at each fraction. Join it to its correct type.








7. Convert the mixed fraction to an improper fraction. Complete the steps and the formula. Fill in the blanks using the words and numbers given on the right.
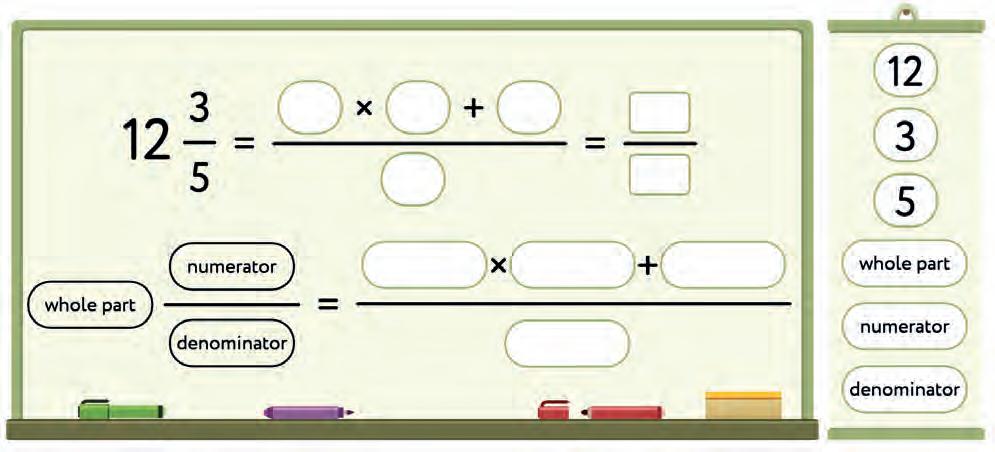
8. Change each mixed fraction to an improper fraction. Write the answers in the blanks.
9. Convert the improper fraction to a mixed fraction. Complete the steps. Fill in the blanks using the words given at the bottom.
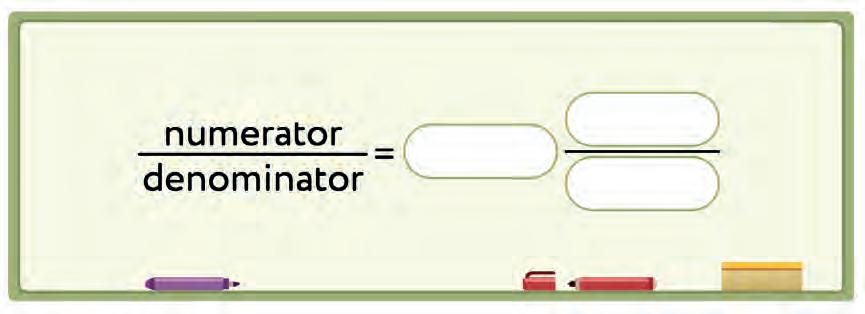
quotient denominator remainder numerator
10. Change each improper fraction to a mixed fraction or a whole number. Write the answers in the blanks.
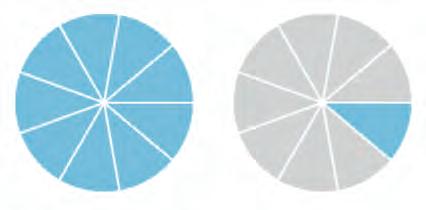
11. Look at each group of shaded circles. Write the mixed fraction and the improper fraction it shows. Fill in all the blanks.
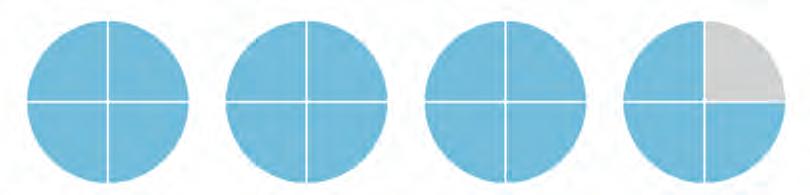
Mixed fraction
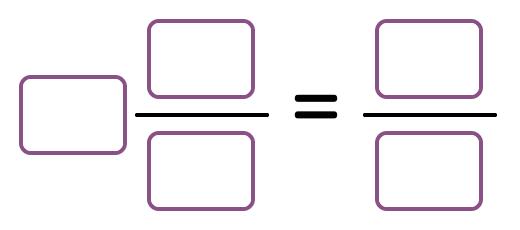
Improper fraction
Mixed fraction
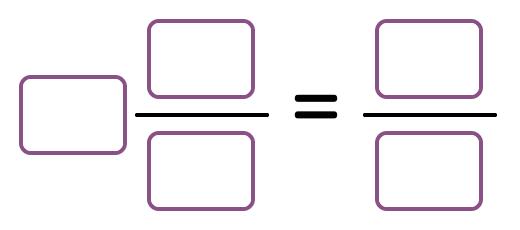
Improper fraction
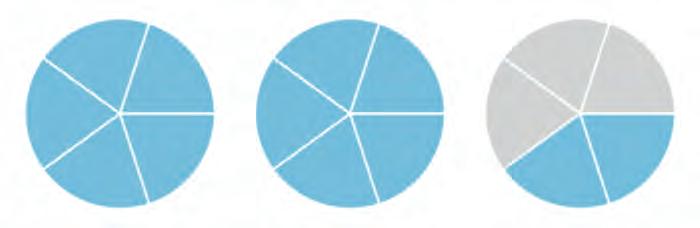
Mixed fraction
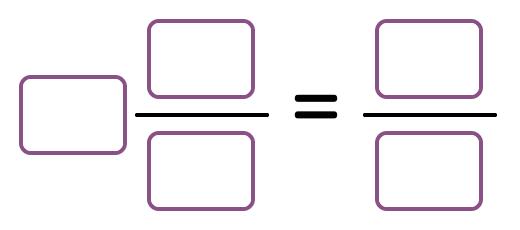
Improper fraction
12. Write each mixed fraction as an improper fraction. Write each improper fraction as a mixed fraction.
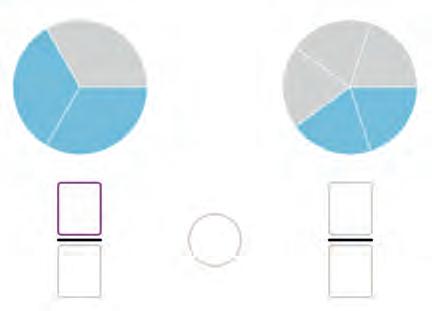
13. Complete the fractions for each pair of shaded circles. Then compare them. Write the numbers in the boxes and write <, =, or > in the circles.
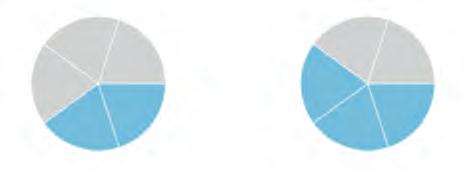

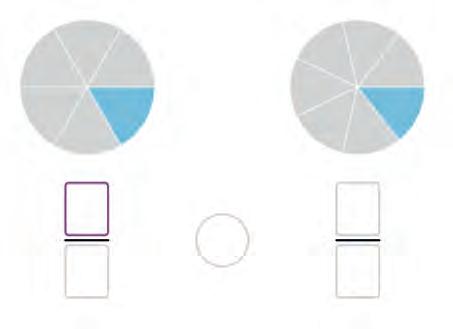
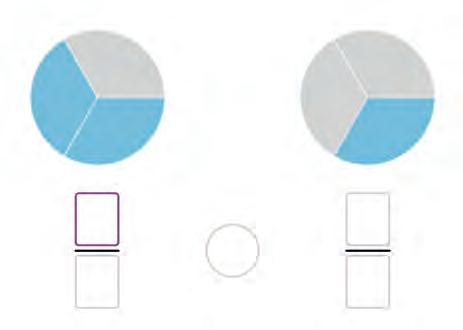
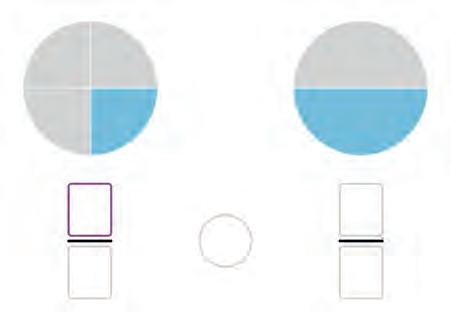
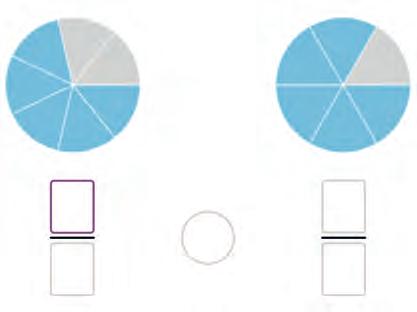
14. Look at the fractions and the shaded parts they show. Arrange them from the smallest to the largest. Fill in the blanks.
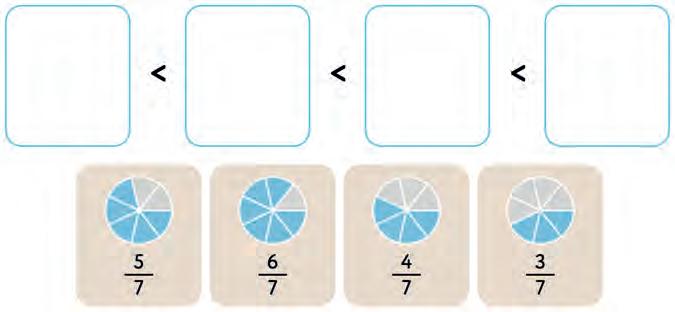
These fractions have the same denominators.
Now choose the correct word and complete the following.
Among the fractions having the same denominator, the larger the numerator, the (larger / smaller) the fraction.
15. Look at the fractions and the shaded parts they show. Arrange them from the smallest to the largest. Fill in the blanks.
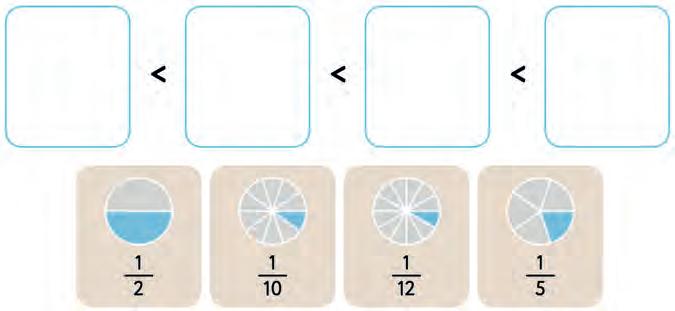
These fractions have the same denominators.
Now choose the correct word and complete the following.
Among the fractions having the same numerator, the larger the denominator, the (larger / smaller) the fraction.
16. Compare the fractions.
17. Find each pair of fractions on the number line. Then compare them. Write the correct symbol in the circle.
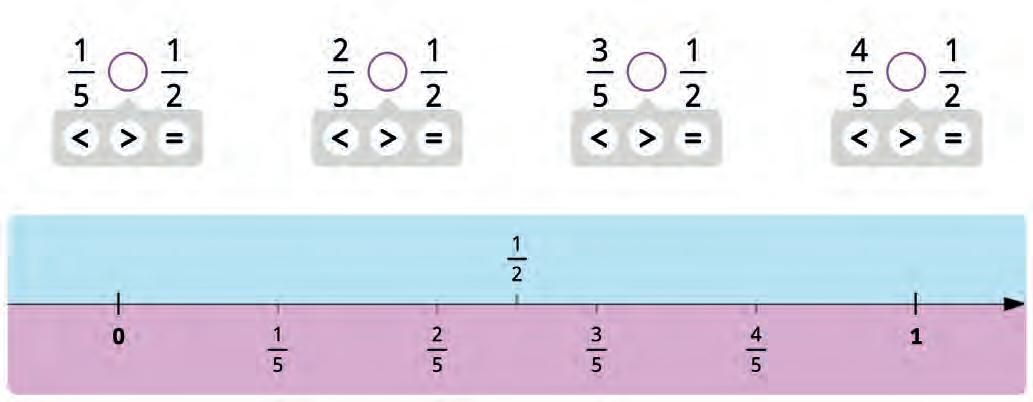
18. Find each pair of fractions on the number line. Then compare them. Write the correct symbol in the circle.
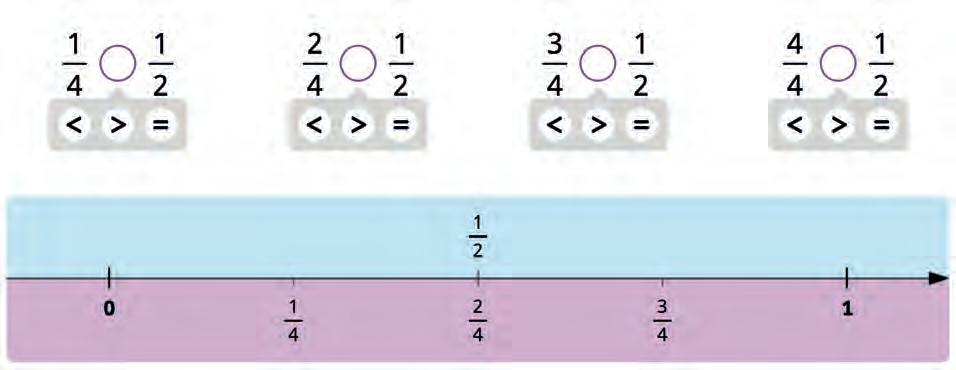
19. Compare and with . Then compare them with each other.
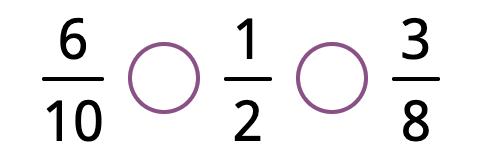
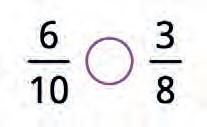
20. Each fraction lies between two whole numbers. Find them and write them in the boxes.
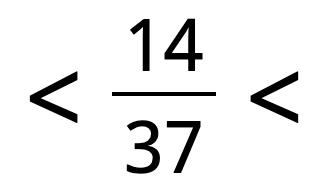
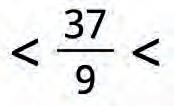
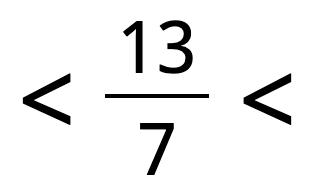
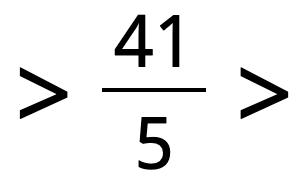
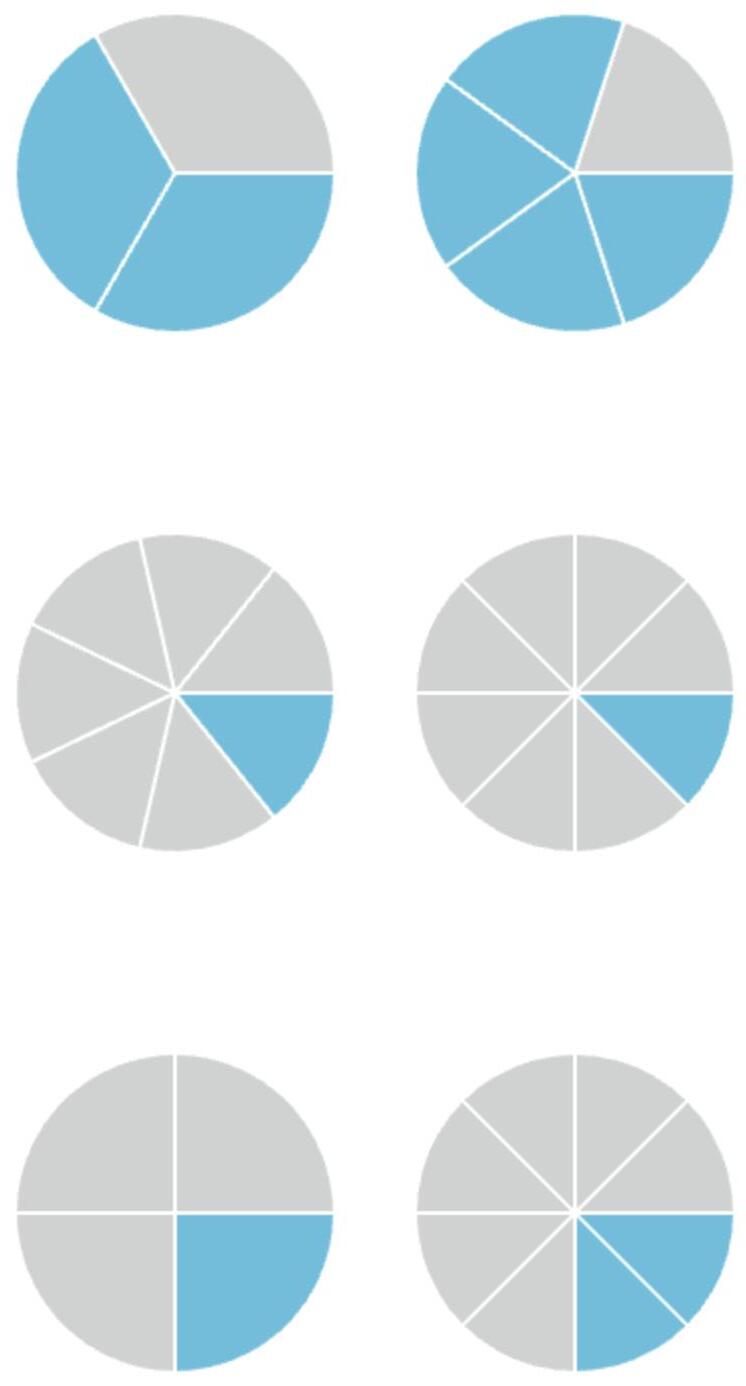
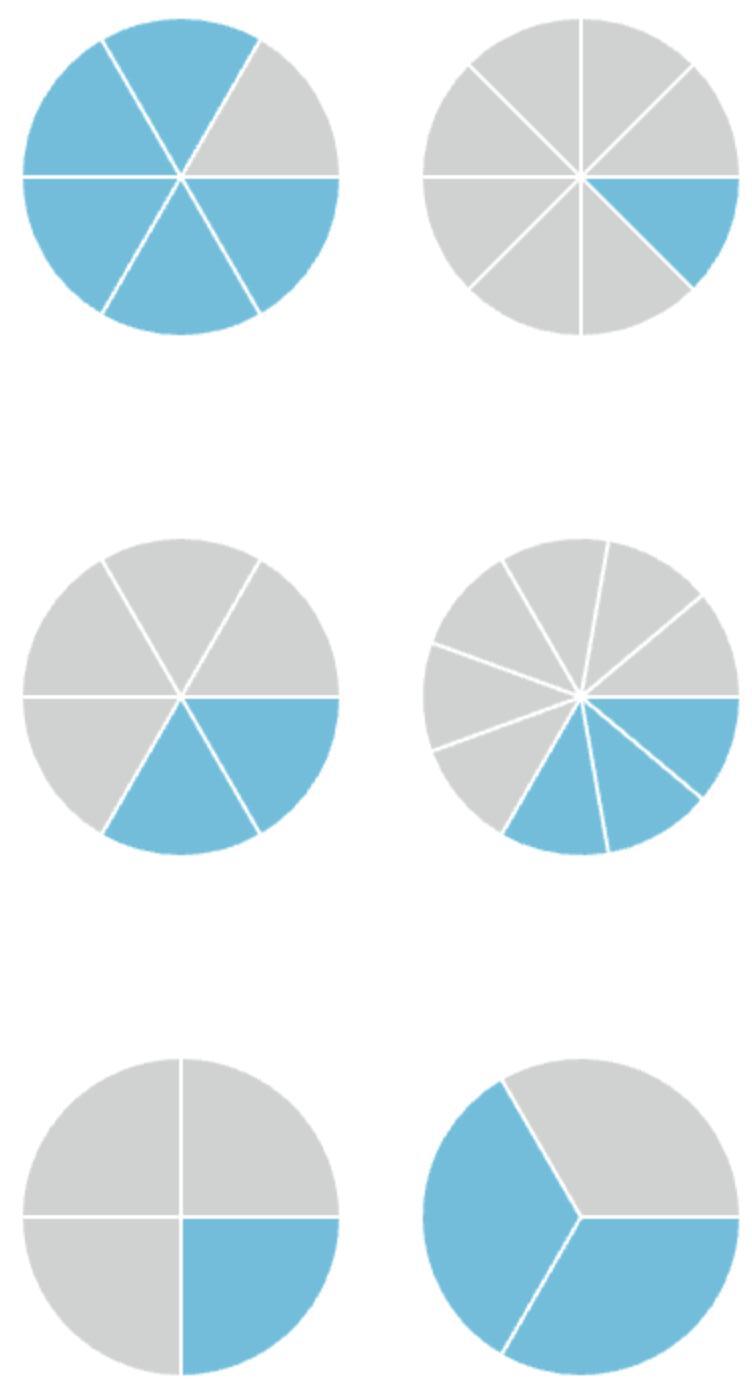
21. Look at the pairs of circles. Tick the pairs where the shaded parts are equal.
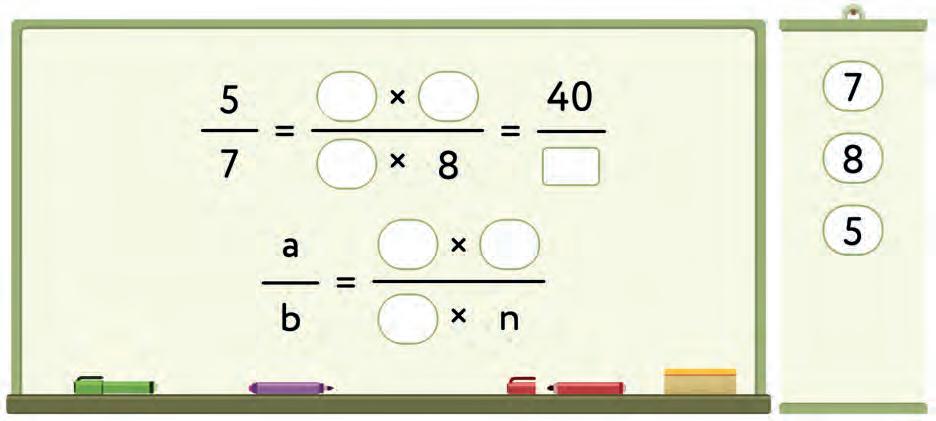
22. Rewrite as an equivalent fraction with numerator 40. Use this to complete the rule for finding equivalent fractions. Fill in the blanks. 5 7
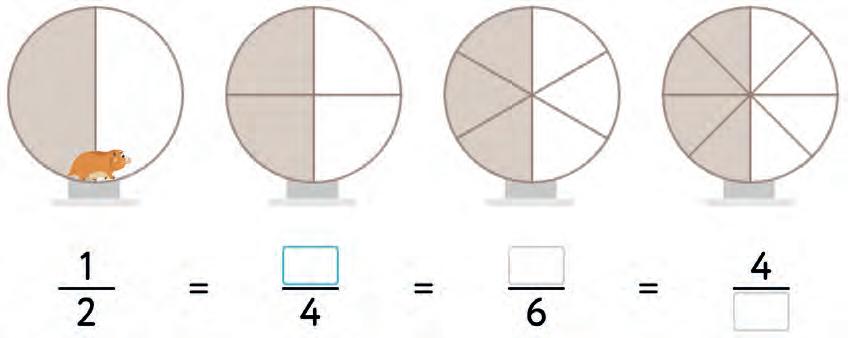
23. Express the shaded part of each circle as different equivalent fractions. Write the correct numerator or denominator in the boxes.
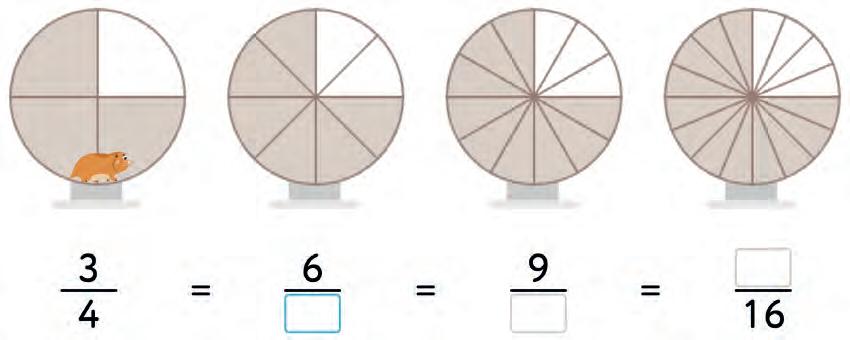
24. Express each fraction as equivalent fractions. Write the correct numerator or denominator in each box.
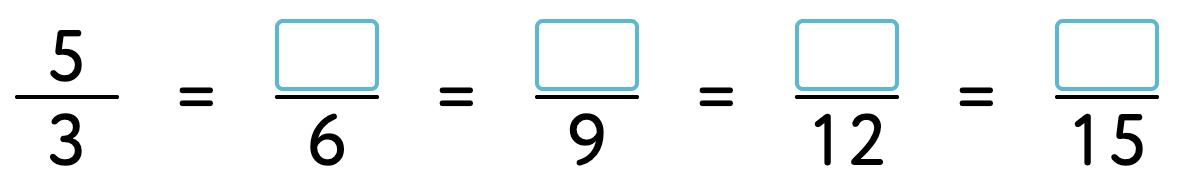
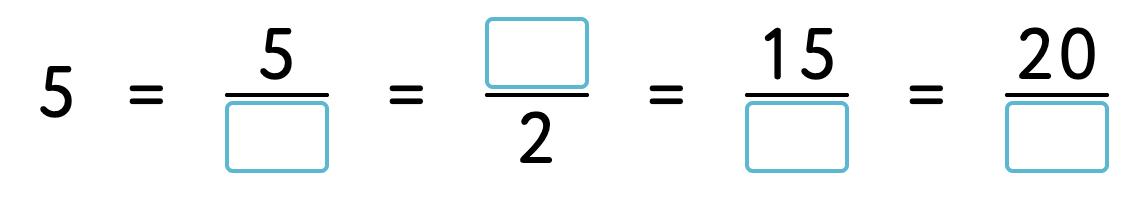
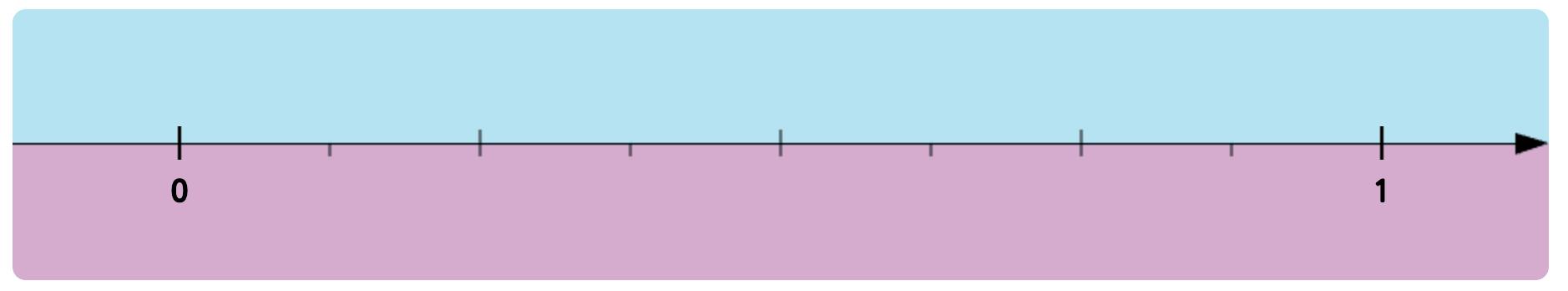
25. Mark the fractions in each pair on the number line. Then compare them. Write <, = or > in the circles.





26. Simplify each fraction. Write correct numbers in the blanks.
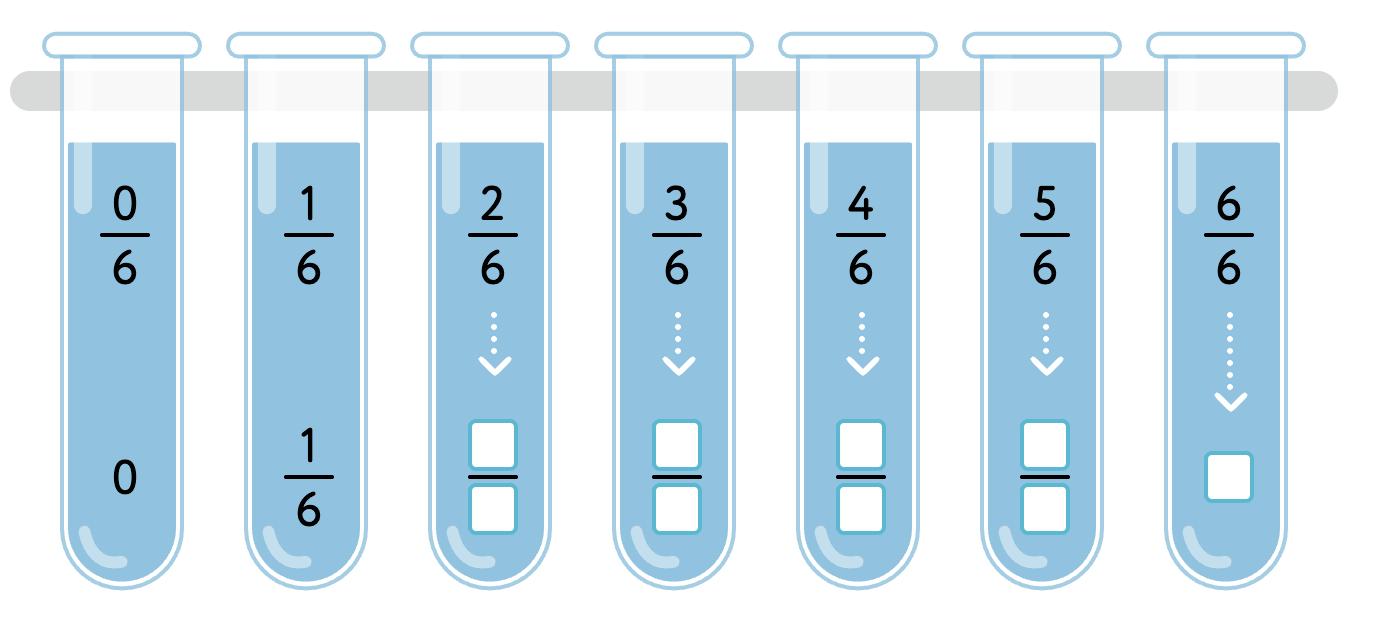
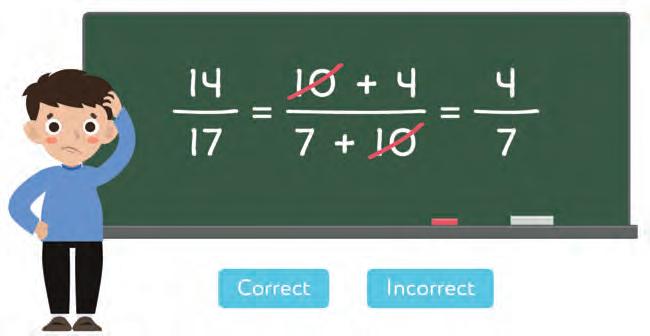
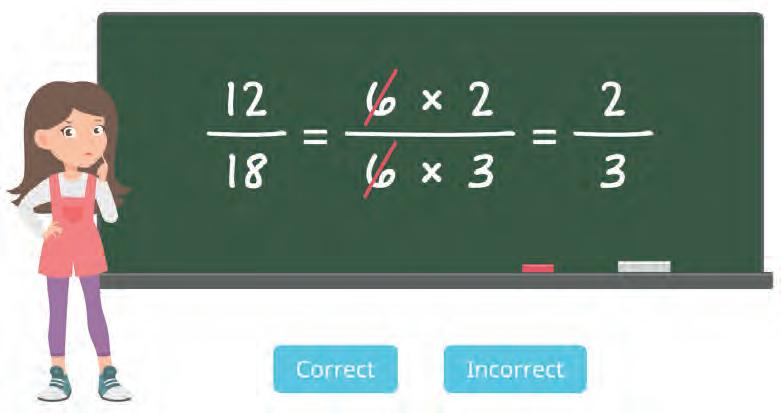
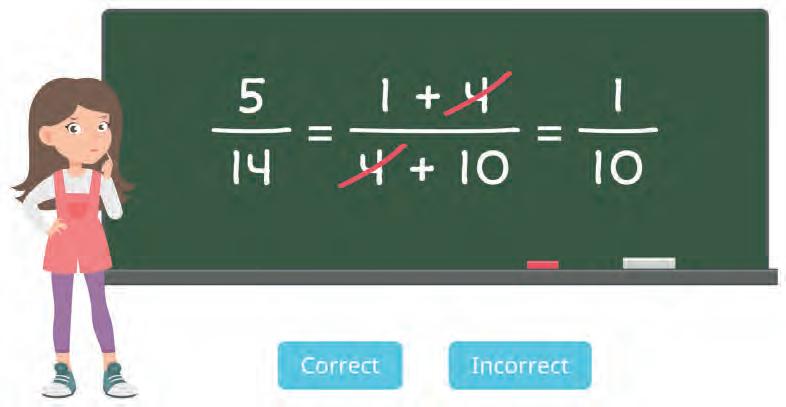
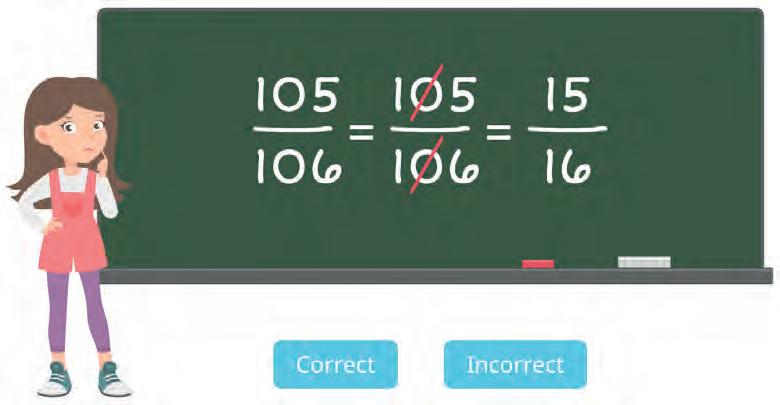
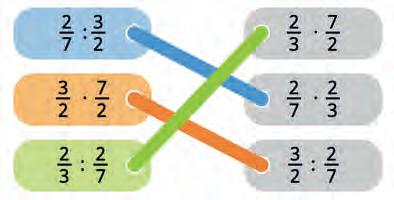
27. Gagan simplified some fractions as shown. Are his solutions correct? Tick your answers.

Yes No

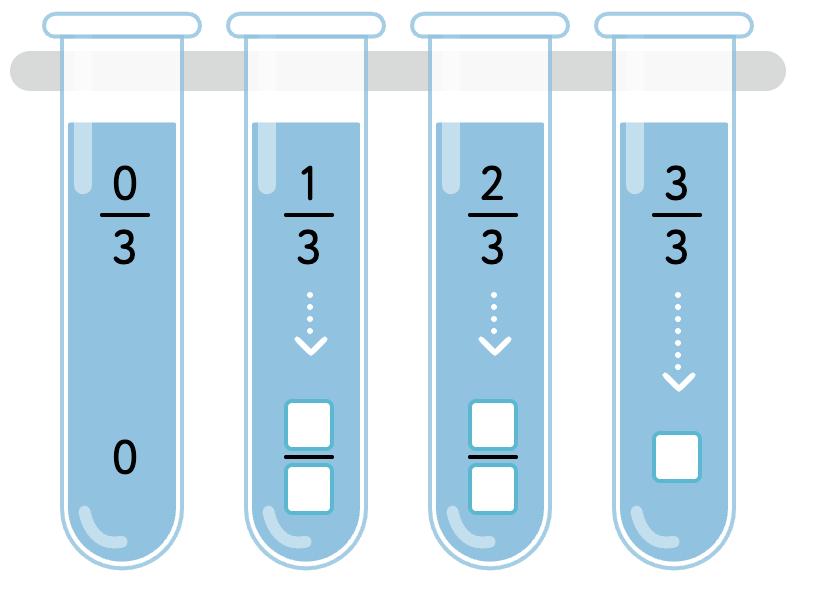
28. Simplify the fractions.
OPERATIONS ON FRACTIONS
29. Look at the amount of lemonade in each jar. Fill in the boxes.
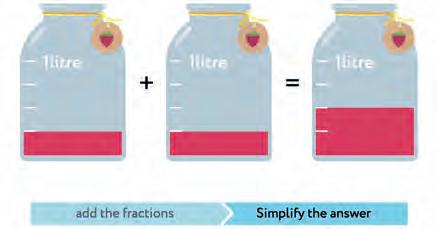
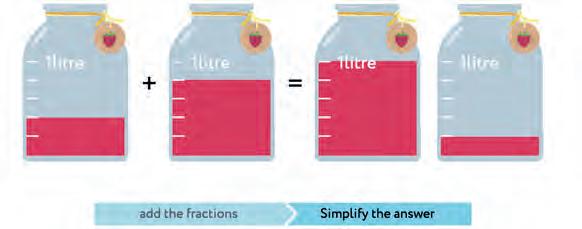
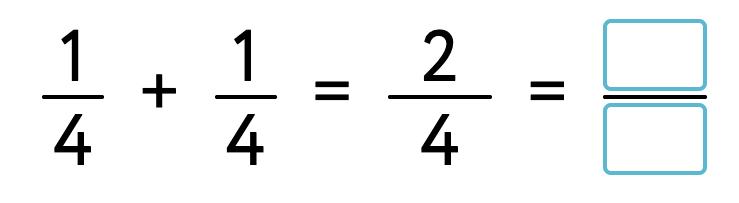
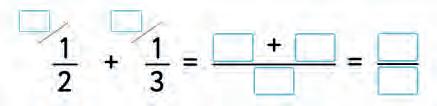
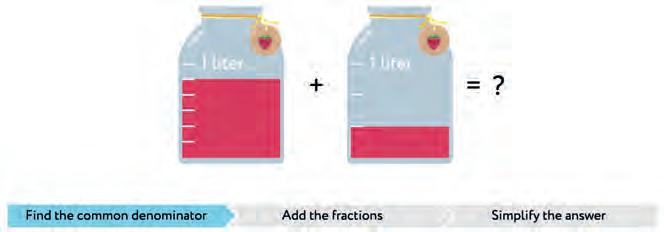
a)
b) c) d)
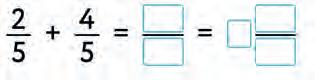
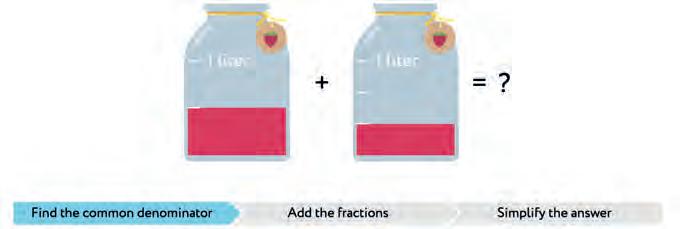
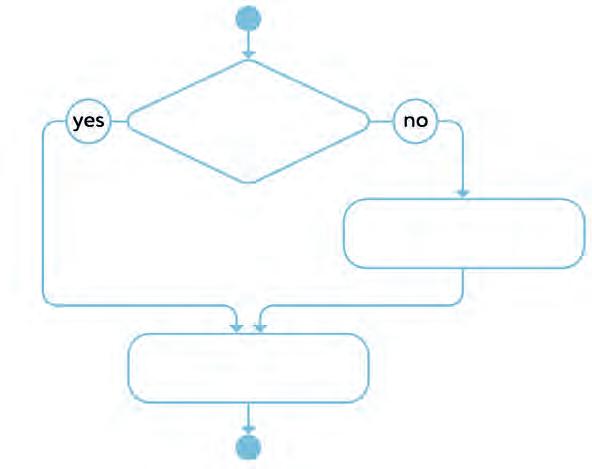
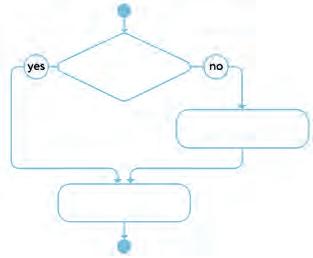
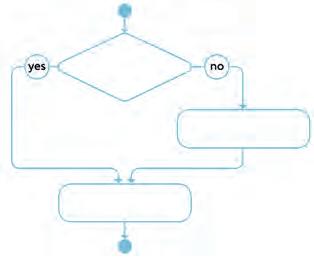
30. Make rules to add and subtract fractions. Join each step to the correct part of the flow chart.
Find the common denominator.
Add the fractions. Are the denominators the same?
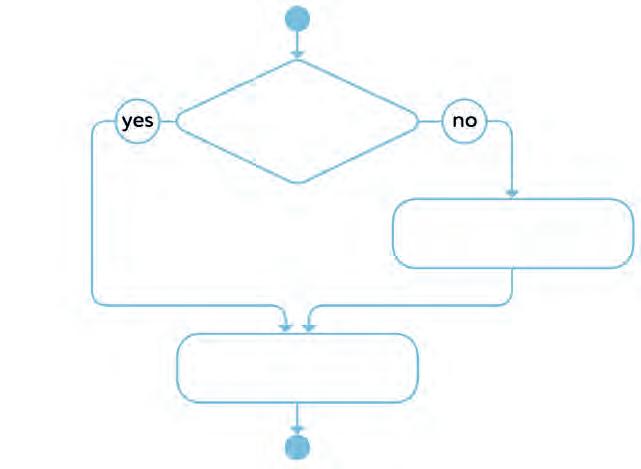
Find the common denominator.
Subtract the fractions. Are the denominators the same?
Subtract the fractions
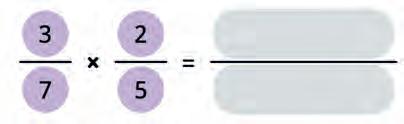
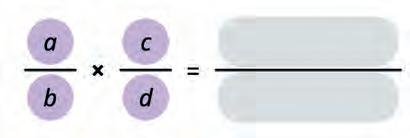
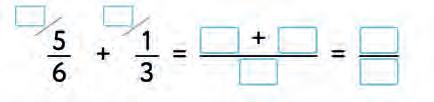
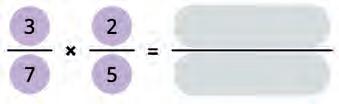
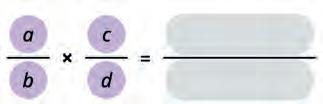
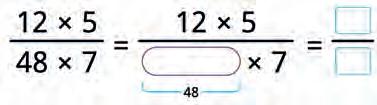
32. Multiply the given fractions. Use this to complete the rule for finding the product of two fractions. Fill in the blanks.
33. Choose the correct numbers and fill in the blanks.
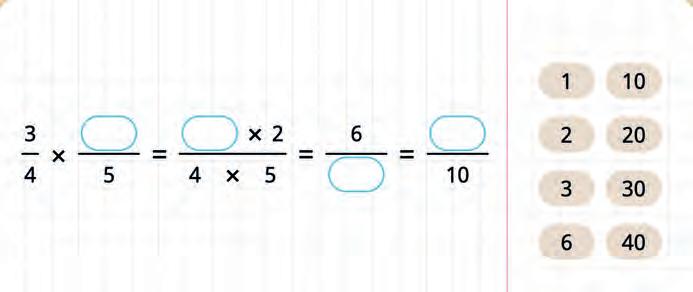
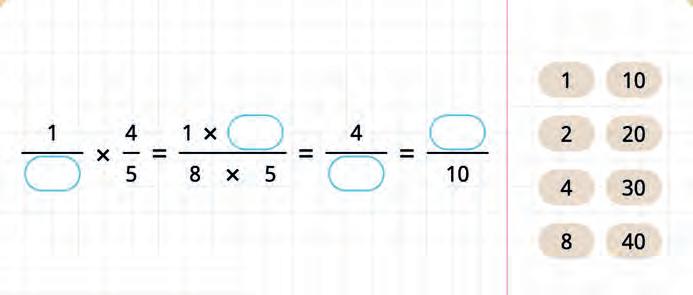
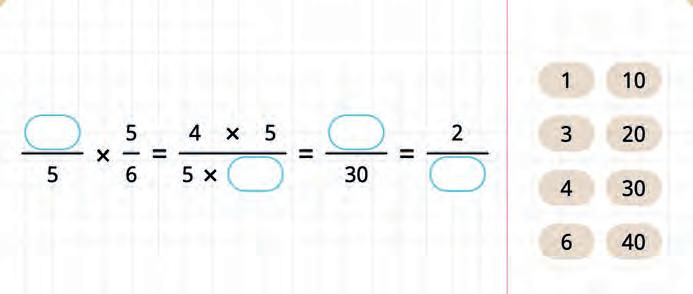
Method 1:
34. Find the product of the given fractions in two ways. Show your work.
Multiply first, then simplify.
8 × 7 × 2
7 × 3 × 8 = =
Method 2:
Cancel common factors between numerators and denominators first. Then multiply.
8 × 7 × 2
7 × 3 × 8 = =
35. Simplify. Fill in the blanks.
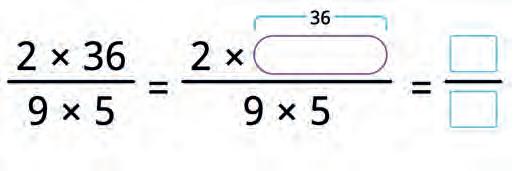
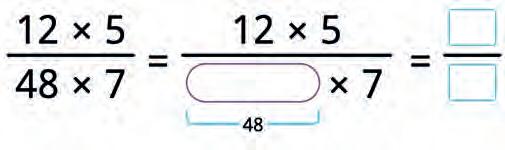
36. Ira simplified some fractions as shown. Are her solutions correct or incorrect? Tick your answers.
37. Fill in the blanks.
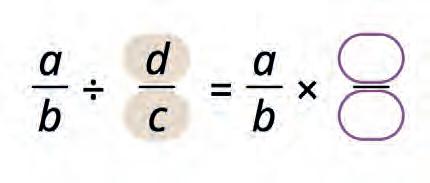
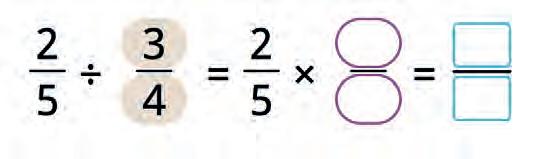
38. Join each sum on the left with its equivalent sum on the right.
39. Match the pairs of reciprocal numbers.
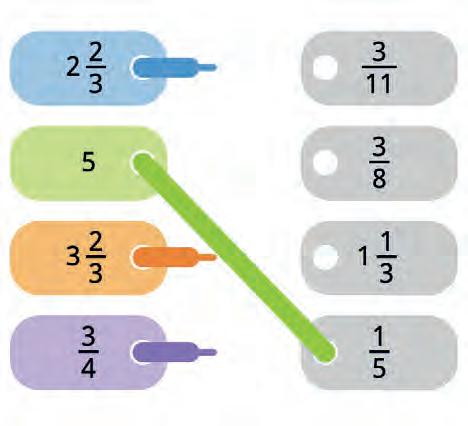
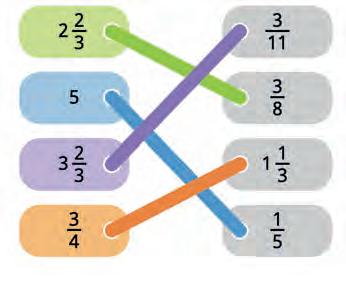
41. Misha goes to football practice for 1 3 4 hours every day. How many hours does Misha spend at football practice in 3 days?
42. Shweta paints 1 2 3 metres of fence in one hour. How many metres of fence will she be able to paint in 1 1 2 hours?
43. Rita wants to make rolls. She has 2 1 2 cups of rice. One roll needs 1 4 cup of rice. How many rolls can she make?
44. Grandmother made 4 2 4 litres of soup. If each dinosaur eats 2 1 4 litres, how many dinosaurs can she feed?
8. DECIMALS
UNDERSTANDING DECIMALS
1. Look at each bottle. How much water does it have? Fill in the blanks.
a) Write answer as a simple fraction. a) b) c) b) Write answer as a decimal.
2. Look at each thermometer. What temperature does it show? Write your answers in the blanks.
3. Look at the given ruler and the pencil. What is the length of the pencil? Write your answer as a decimal in the box.
4. Look at the shaded part of each square. Show this shaded part as a fraction and as a decimal number. Fill in the blanks.
5. Complete the table.
3 tenths
3 hundredths
3 thousandths
3 ten thousandths
3 hundred thousandths
6. Read each number written in words. Write it as a decimal number.
five and seven hundred seventy four thousandths
two hundred and thirty four and nineteen hundredths
eighty four and sixty five thousandths
eleven hundredths
twelve and twelve thousandths
7. Look at the digits in the decimal number. Choose and write the place each digit is in.
8. Join each number to its equivalent value.
9. Complete the table. Express each fraction as a fraction with the given denominator. Then write it as a decimal number.
10. Compare the numbers. Write <, = or > in the blanks.
11. In each of the following, three decimal numbers are written in order. Write the missing digit so that the order is maintained.
12. Convert each decimal number to a fraction with a suitable denominator. Then compare it with the fraction in the last column.
OPERATIONS ON DECIMALS
13. Fill in the blanks.
14. John added two numbers as shown. Is his answer correct or incorrect? Tick your answer.
2,543 5,329 + 7,862 6,375 2,068 + 8,443
CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect 11
15. Choose the correct option and complete the given sentence.
Attaching zeros of a decimal number doesn’t change its value. after the tenths place in the middle in the end
16. John subtracted two numbers as shown. Is his answer correct or incorrect? Tick your answer.
7,861 5,328 –2,543 8,443 2,068 6,375 Correct Incorrect CorrectIncorrect –
17. Which of these numbers are the same as 4.2? Tick them.
4.2000.424.204.02
18. Fill in the blanks.
19. Look at each problem on the left. Join it to the correct answer.
20. Solve. Show your work. Write the answers in the blanks.
49.266 + 14.42 =
6.6226 + 55.14 =
23.51 + 562.57 =
344.15 + 13.24 =
– 24.718 = 771.31 – 456.2 = 64.11 – 23.741 = 512.1 – 24.541 =
21. Gagan multiplied two numbers as shown. Is his answer correct or incorrect? Tick your answer.
CorrectIncorrect
1.627 0.4 × 0.6508 0.128 8 10.24 1.236 0.7 8.652
CorrectIncorrect × ×
CorrectIncorrect
22. Fill in the blanks. Write the decimal point in the correct circle.
× 4 =
23. Solve.
× 3 =
× 2 =
× 4 =
24. Solve.
× 100 =
× 100 =
÷ 100 = 4.12 × 2 =
× 10 =
÷ 10 =
÷ 1000 =
× 2 =
25. Choose the correct options and complete the given sentences.
a) If 9 tenths is divided by 3 then you will get
b) If 5 hundredths is divided by 5 then you will get
c) If 3 thousandths is divided by 3 then you will get . . .
26. To solve the following expression, you need to change its divisor to a whole number. How will you do it? Fill in the blanks.
We need to move the decimal points in the dividend and the divisor to the right by places.
27. Solve.
28. Solve the problems. Show your work. Write the answers in the boxes.
645 × 6.4 =
0.0998 × 9.4 =
0.25 × 756 =
0.034 × 48 = 9 ÷ 0.12 = 900 ÷ 12 = 315 ÷ 7.2 = 153 ÷ 2.4 =
0.6912 ÷ 0.432 =
9. DATA HANDLING
1. Read the data given in the table. Use it to answer the following questions. Fill in the blanks.
The table shows the weights and heights of savanna animals.
1) What is the weight of an elephant? _______ kg.
2) Which animal is 140 cm tall? ______
3) Find the animal with the smallest height. Its height ______ cm.
2. Read the data given in the table. Use it to answer the following question. Fill in the blank.
The table shows how many students of the 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th grade visited the school library this week. How many students of the 4th grade visited the library on the 4th day?
The answer: students.
Animal
3. Read the data given in the table. Use it to answer the following question. Fill in the blank.
The table shows how many flowers of each type were planted in the park. If 100 more tulips are planted, how many tulips will be in the park?
The answer: tulips.
4. Read the data given in the table. Use it to answer the following question. Fill in the blank.
The table shows how many hours of each subject per year are taught in grades 1–4. How many hours of Art are taught in Grade 5, if it is half of the hours taught in Grade 4?
The answer: hrs.
5. Look at the data about Anusha’s height. Mark her height at 5 years and complete the graph. Then find the difference between the greatest and the smallest height.
Anusha’s height:
At 4 years: 1 m
At 5 years: 1.1 m
At 6 years: 1.15 m
At 7 years: 1.2 m
At 8 years: 1.25 m
6. Look at the population data below. Mark all the points and complete the graph.
City population:
2011: 4.9 million people
2012: 4.95 million people
2013: 5.05 million people
2014: 5.1 million people
2015: 5.2 million people
7. Look at the rainfall data below. Mark all the points and complete the graph.
May: 60 mm
June: 50 mm
July: 95 mm
August: 85 mm
September: 55 mm
8. Look at the data in the table. Mark all the points and complete the graph.
9. Use the graph to answer the question.
The graph shows how the price of sandals changed over several months. How much did sandals cost in September?
The answer: rupees
10. Use the graphs to answer the questions.
a) The graph shows approximately how the Earth’s population changed in the second half of the 20th century. How many million people lived on Earth in 1970?
The answer:
b) The graph shows how many countries participated in the Winter Olympics in different years. In what year did 82 countries participate?
The answer:
a) The graph shows how the area of the Aral Sea changed due to the negative impact of human activities. What is the smallest area of the Aral Sea shown on the graph?
The answer:
b) The graph shows how the temperature changes in the Sahara Desert during the day. At what time is the air temperature the lowest?
The answer:
c) The graph shows how the helicopter’s altitude changed during the flight. How many minutes after the flight began did the helicopter reach the highest altitude?
The answer:
12. Look at the graph. It shows at what temperature water boils at different altitudes above sea level. Read each statement. Is it true or false? Tick your answer.
a) At an altitude of 3,000 m, the water boils at a temperature of 80 °C.
b) The lowest boiling point is at an altitude of 9,000 m.
c) At an altitude of 1,000 m and 5,000 m, water boils at the same temperature.
13. Look at the table. It shows how many paper snowflakes the girls made on Day 1. On Day 2, each girl made twice as many snowflakes as on Day 1. Complete the table.
14. The graph shows how the temperature in the Sahara Desert changes during the day. Write all the hours when the temperature is below 34 °C.
15. The graph shows how the population of Bhopal changed in recent years. How much did the population of Bhopal decrease from 2007 to 2015? Tick the correct answer.
16. The chart shows the length (in metres) of different sports areas. What is the length of the basketball court?
DATA H ANDLIN G 10. MENSURATION
UNDERSTANDING PERIMETER
1. Look at the measurements of each shape. Then answer the questions that follow. Fill in the blanks.
a) The perimeter of the triangle is
b) The perimeter of the quadrilateral is
с) The perimeter of the pentagon is cm. cm. cm.
Answer:
2. The first side of a triangle is 2 cm. The second side is 3 cm. The third side is 2 cm longer than the first side. Find the perimeter.
Answer:
3. The first side of a triangle is 6 cm. The second side is 5 cm. The third side is 2 cm smaller than the second side. Find the perimeter.
UNDERSTANDING AREA
4. Look at the measurements of each shape. Then answer the questions that follow. Fill in the blanks.
a) The perimeter of the square is
The area of the square is
b) The perimeter of the rectangle is
The area of the rectangle is cm. cm. cm2. cm2.
5. The rectangle and square shown below have the same perimeter. Use it to solve the following questions. Fill in the blanks.
1) The perimeter of the square is
2) Hence, the perimeter of the rectangle is
4) Area of the square is
3) Find the lengths of the unknown sides of the rectangle. cm. cm. cm2. cm2. + 5 ++ 5 = 24. So, the side of the rectangle is cm.
5) Area of the rectangle is
6. Complete the formulas for finding the perimeter and area of a rectangle. Next, use these formulas to find the perimeter and area of the rectangle shown below. Write your answer in the boxes.
1) Perimeter = AB +
2) Area = AB ×
PERIMETER AND AREA PROBLEMS
7. Find the perimeter of the shape shown. Write your answer in the blank.
8. Find the perimeter and area of the shape shown. Write your answers in the blanks.
9. What is the area of shaded rectangle? Write your answer in the box.
DATA H ANDLIN G 11. INTRODUCTION TO ALGEBRA
ALGEBRA AND PATTERNS
1. Which symbols represent mathematical operations? Tick the correct options.
2. Read each statement. Then tick the option that represents it.
a) The sum of one hundred five and three hundred sixty.
b) The difference between one hundred seven and eighty-five.
c) The product of one hundred forty-five and sixty-eight.
d) The quotient of three hundred five and twenty-three.
3. Join each verbal expression with its correct numerical form.
Sum of four and two
Difference of four and two
Product of four and two
Divide four by two
4. Read each statement. Then write the mathematical expression for it.
a) Sachet won 14 games. Then he won 6 games in each of 12 rounds. How many games did he win in total?
b) Sachet won x games. Then he won 11 games in each of 6 rounds. How many games did he win in total?
d) Aadhan bought p buckets of popcorn which cost ₹140 each and one can of soda which cost ₹x. He paid ₹b in total. How much did the soda cost? 14 + 6 × 12
c) Aadhan bought 7 buckets of popcorn which cost ₹150 each and one can of soda. He paid ₹1,300 in total. How much did the soda cost?
ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS AND EQUATIONS
5. Read what an algebraic expression is. Use it to identify which of the given expressions are algebraic expressions. Tick the correct options.
Numerical expressions that have letters are called algebraic expressions. These letters are usually taken from English alphabet. Letters generally represent unknown quantities called variables.
75 + a + 43
34 + n $
6 – – 7
765 × 765 – n765
6. Join each verbal expression with its correct numerical form.
Sum of seventy five and n
Quotient of x and seventy five
Difference of forty three and n
Product of x and forty three
x ÷ 75
43 – n
75 + n x × 43
7. Join each verbal expression with its correct numerical form.
Product of x and twenty five
Difference of eighty four and n
Quotient of x and eighty four
Sum of twenty five and n
8. Look at each algebraic expression. Evaluate it for the given values of the variables.
a) 42 ÷ a + 12 b) 32 ÷ (a – 10)
For a = 1
For a = –6
For a = 42
For a = 42
For a = 8
For a = 18
9. Read the given scenario. Then answer the questions based on it. Tick the correct options.
A game console costs ₹x, and a game costs ₹y.
What does the expression 2x + y represent?
Cost of 2 game consoles and 1 game
Cost of 2 games and 1 console
What does the equation 2x = y mean?
The cost of 2 consoles equals the cost of 1 game
The cost of 1 console equals the cost of 2 games The difference between the cost of two game consoles and the cost of a game
The cost of 2 games equals the cost of 2 consoles
10. Look at the length of each side of the given triangle. Its perimeter is represented by the variable P. Complete the formula for P.
11. Look at the length of each side of the given triangle. Its perimeter is represented by the variable P. Complete the formula for P. Simplify your answer.
12. Solve the given equations. Show your work.
a) 14 + x = 48
b) 59 – x = 38
d) 6x = 108
g) 5x + 3 = 128
j) 9x + 12x – 5 = 79
e) x ÷ 13 = 15
h) 178 – 3x = 142 k) 23x – 12x + 10 = 32 c) x – 34 = 27
) 196 ÷ x = 14 i) 19x – 13 = 6 l) 16x – x = 150
12. INTRODUCTION TO RATIO AND PROPORTION
DATA H ANDLIN G
UNDERSTANDING RATIO
1. Answer each question. Tick the correct option.
a) There is one big fish for every four small fish. What is the ratio of big fish to small fish?
b) There are three small fish for every one big fish. What is the ratio of small fish to big fish?
2. Count the number of monkeys and bananas in each image. Tick the correct statement.
There are 4 bananas per monkey.
The ratio of the number of monkeys to the number of bananas is 1 : 2.
The ratio of the number of monkeys to the number of bananas is 2 : 1.
There are eight bananas per monkey.
The ratio of the number of bananas to the number of monkeys is 4 : 1.
The number of monkeys is four times the number of bananas.
The ratio of the number of monkeys to the number of bananas is 3 : 2.
The ratio of the number of monkeys to the number of bananas is 2 : 5.
There are three bananas per monkey.
3. Colour each flag. Use blue and pink in the given ratios.
a) blue : pink = 1 : 1
b) blue : pink = 5 : 3
c) blue : pink = 1 : 3
d) blue : pink = 5 : 1
4. Read each statement. Then tick the images that show the correct ratio.
a) The ratio of donuts to cupcakes is four to one.
b) The ratio of purses to coins is 1 : 3.
c) The ratio of tomatoes to plates is 2 : 1.
: : :
5. Look at each image. Find the ratio of rabbits to carrots. Write your answer in simplest form.
6. Solve.
a) For stairs, the ratio of height to length should be 1 : 2. If the height of a step is 150 mm, find its length. Write your answer in the box.
Answer:
b) The ratio of width to length for Dino’s photos is 3 : 4. What is the length of a photo that is 9 cm wide? Write your answer in the box.
Answer:
UNDERSTANDING PROPORTION
7. Look at the blue building and the orange building. Count the floors in each. Find the ratio of floors in the blue building to floors in the orange building. Fill in the blanks.
8. There are 2.5 times as many orange juice glasses as apple juice glasses on the table. Circle the image showing this ratio. What is another way to write this ratio? Tick the correct option.
9. There are 3.5 times as many carrots as brinjals. Circle the image showing this ratio. What is another way to write this ratio? Fill in the blanks.
10. The number of balloons is 1/4 of the number of cacti. Circle the image showing this ratio. What is another way to write this ratio? Tick the correct option.
11. Look at how a ratio is expressed. Use it to complete the given sentence. Tick the correct option.
UNITARY METHOD
12. Solve the problem using unitary method. Show your work. Write the answer in the box.
Amrit picked 40 bananas in 20 minutes. How many bananas did he pick in 3 minutes?
Answer: bananas.
DATA H ANDLIN G 13. SYMMETRY
LINES OF SYMMETRY
1. Look at the shapes. Write whether each one is symmetrical or asymmetrical.
2. Draw the lines of symmetry for each shape. Write how many lines of symmetry each shape has.
a) Number of lines of symmetry:
b) Number of lines of symmetry:
c) Number of lines of symmetry:
d) Number of lines of symmetry:
REFLECTION AND ROTATIONAL SYMMETRY
3. Look at the images in each pair. Tick the pairs that show the first image correctly reflected along the given mirror line.
4. Each image is reflected along the given mirror line. Draw its reflection.
14. CONSTRUCTION OF LINE SEGMENTS AND ANGLES
DATA H ANDLIN G
CONSTRUCTION OF LINE SEGMENTS
1. Use a ruler to draw line segments of the given lengths.
Perimeter =
Area =
2. Construct a rectangle ABCD of length 6 cm and width 2 cm. Use a ruler and a protractor. Find its perimeter and area. Write your answers in the boxes.
a) 7.3 cm
2.9 cm
5.5 cm
3. Construct a copy of each of the following line segments.
A C B D
4. Take OP = 1.7 cm and KM = 2.9 cm. Use these to find the lengths of the following line segments. Then construct those line segments.
a) CM = 4KM – 2OP = 4 × 2.9 – 2 × 1.7 =
b) LH = 2OP + KM
c) DG = 3 × (OP+KM) – 4KM
CONSTRUCTION OF ANGLES
5. Construct a perpendicular to line segment AB passing through point F. Use a ruler and a compass.
6. Construct a perpendicular to KM passing through point L. Use a ruler and a compass.
a) 128°
7. Construct the angle bisectors of ABC and POQ.
8. Draw the angles having the given measures. Construct their angle bisectors.
b) 90°
a) 30°
9. Draw angles having the given measures. Use only a ruler and a compass.
b) 60°
c) 90°
d) 120°
ANSWERS
1. Large Numbers and Operations
1. 2 — ten thousands, 3 — thousands, 1 — hundreds, 6 — tens, 9 — ones
2. 1st column: 8025 14,001 2nd column: 906 482 3012
3. 1st column: 4000 + 800 + 70 + 1; 10,000 + 300 + 80 + 2 2nd column: 1,00,000 + 1;
4. 1st column: 2160 2160 2150 2nd column: 4500 4600 4500 3rd column: 4000 5000 5000
5. 5482 � 5500 8256 � 830 3078 � 3080
6. 1st column: 6687 — 6700; 687 — 690; 6187 — 6000; 68,187 — 70,000 2nd column: 4612 — 4600; 46,612 — 47,000; 41,266 — 40,000; 46,118 — 46,120
Bhiwandi: 7,11,300 — 7,11,000
Noida: 6,42,400 — 6,42,000
Asansol: 5,64,500 — 5,64,000
Kurnool: 4,30,200 — 4,30,000
Dhule: 3,76,100 — 3,76,000
Purnia: 2,80,500 — 2,81,000
8. a) 193 g; b) 368 g; c) 285 g
9. a) Lalit; b) Puneet
10. 1st column: 579 618 404 619 232 197 2nd column: 691 831 204 816 110 866
—
—
—
—
7. Chandigarh: 9,60,800 — 9,61,000 Moradabad: 8,89,800 — 8,90,000 (pages 1–7)
14. 1st column: 55,657 41,326
5,00,468 86,265
2nd column: 40,766 83,935 25,845 20,547
15. 70 m; 40 m; 120 m; 50 m
16. 1st spider: 208 — 215; 284 — 291; 163 — 170
2nd spider: 130 — 125; 167 — 162; 206 — 201; 118 — 113
17. 1st column: 39,109 33,578 4,99,714 84,069
2nd column: 37,088 81,373 9153 15,005 18.
19. 5040 — 1260 — 420 — 60 — 10 — 5
20. 1st column: 36 84 88 160
2nd column: 312 301 17 21
3rd column: 18 19 16 14
21. 1st column: 7052 7106 68,400 10,824
2nd column: 13,728 15,639 10,808 1338
3rd column: 25 16 253 39
22. 1st column: 26,768 49,203
10,692 16,898
2nd column: 15 439 503 56
3rd column: 18 26 27 91
23. 28; 92; 0 24. 65; 92; 17; 67
25. 8,64,000 times 26. 11,400 nuts
27. 136 kg 28. 11,799 29. 93 kg
2. Patterns in Whole Numbers (pages 8–23)
1. 1st line: 295; 305; 335
2nd line: 607; 597; 567
3rd line: 503; 483; 473
2. a) 5 b) 14 c) 11 d) 14 e) 8 f) 39
3. a) 100; 250 b) 15; 20; 35 c) 500; 1500; 3000
4. a) 5 b) 1 c) 42 d) 0 e) 24 f) 0 g) 2025 2025 8472 3717 h) 831
5. 27
6. 1st column: 512; 405; 243; 240; 36
2nd column: 224; 320; 324; 31; 21
7. 1st column: 16 256 1024
2nd column: 25 125 625
3rd column: 100 1000 1,00,000
3. Playing with Numbers: Factors and Multiples
1. a) 7; 2 b) 1; 19 c)* 12; 3 d) 1; 67
2*. a) 18; 36 b) 43; 86 c) 71; 142 d)103; 206
3. 1st column: F. 1 2 23 46
M. 46 92 138
2nd column: F. 1 2 4 8 16 32
M. 32 64 96
3rd column: F. 1 5 25
M. 25 50 75
4th column: F. 1 2 4 7 8 14 28 56
M. 56 112 168
4. Odd 5. Odd
*: possible answer.
6. Odd: 73; 85; 51; 37; 1; 67; 31
Even: 14; 42; 2; 102; 52; 88; 8
7. even + even even + odd odd + odd even * odd even * even odd* odd
8. 1 — 2 — 7; No; No
9. a) No b) Yes c) No d) No e) No f) Yes
10. only 2
11. a) prime b) prime c) composite d) prime e) composite f) composite
12. 10; 20; 30; 40; 50
13. 1) False 2) True 3) True
14. 5; 10; 15; 20; 25; 30; 35; 40; 45; 50
15. 1) True 2) False 3) True
16. 22; 24; 26; 28; 30; 32; 34; 36; 38; 40; 42; 44; 46; 48; 50
17. 1) True 2) False 3) True
18. 1) its last digit; 2) the sum of its digits; 3) its last digit; 4) the sum of its digits; 5) its last digit even odd even even even odd
(pages 9–33)
19*. 240 420 480 840
20*. 12 21 102 120 201 210
21*. 24 42 54 552
sample answers.
25. Factors of 8125: 1 8125 25 5 13 125 325 1625 625 65 Factors of 6220: 1 6220 20 311 2 3110 10 622 4 1555 5 1244
26. 1. 6 boys, 5 girls 2. No
27. 12: 3 12 8: 2
The highest common factor of 12 and 8 is 4.
28. 6: 2 3 10: 5
The highest common factor of 6 and 10 is 2.
29. 15: 3 16: 4 16
The highest common factor of 15 and 16 is 1.
30. 4: 12 20 6: 12 24
The lowest common multiple of 4 and 6 is 12.
31. 3: 6 9 2: 4 12
The lowest common multiple of 3 and 2 is 6.
32. 5: 5 20 3: 3 9
The lowest common multiple of 5 and 3 is 15.
33. LCM — Lowest Common Multiple.
34. HCF — Highest Common Factor.
35. a) True; b) False.
36. c) 56 and 39; d) 27 and 58 e) 32 and 33
37. a) 1 b) 6 c) 5 d) 7 e) 7
38. a) 8 b) 9 c) 30 d) 110 e) 18
4. Lines, Angles and Shapes
1. point; curved; straight
2. curved; straight
3. ray; line segment
4. 6 5. 4 6. a; CD 7. D; K; E
8. As many lines as needed
9. Only one line
10. As many as needed; As many as needed; As many as needed; Only one 11.
13. АС 14.
15. two; point
16. a) b)
17. BA is an arm. BC is an arm. B is a vertex.
18. BA; BC; ABC
19. Straight angles: ABC or CBA; NBM or MBN
Right angles: NBC or CBN; MBC or CBM; ABM or MBA; ABN or NBA
23. 3, 3; 4, 4; 5, 5 24. 25.
26. Pentagon; Hexagon; Quadrilateral
(pages 40–54)
27. 1) one, right-angle 2) one, obtuse 3) all, acute
28. 1) two, equal 2) all, equal
29. Both are correct.
30. a) AB, BC: side AC: base b) FD, DE: side FE: base
31.
40. 1) Semicircle 2) Concentric, centre, radius
32. ACD; COD 33. SEK; CBO
34. CO and CD; AB and AE
35. Both are correct. 36.
5. 3-D Shapes
Faces
Vertices (pages 55–67)
2. 1) 8; 5 2) faces; edges 3) 6; 10 4) faces; 7 3. a; b; c; e; f; h
6. Integers
1. a) 11 ̊C b) –18 ̊C c) 26 ̊C
2. 15 ̊C 3. –5 ̊C 4. a) 50 b) –10
5. a) 0 b) –11 c) 90
6. a) –6 b) 8 c) –3 d) –9
7. a) negative six b) fifteen
c) negative seven
8. –4; 112
9. a) (9, –9) b) (4, –4)
10. 1st column: –32 –(–(–35))
–(–(–(–(–4))))
2nd column: –(–31) 12
–(–(–(–12)))
11. a) odd b) even
12. a) –3 b) 12 c) –4
d) 8 e) 6 f) –2
13. the distance between 0 and a
14. a) 9 b) 5 c) 0 d) 13 e) 9 f) 8
15. opposite
16. Possible answers: a) a = –5 b) 0
c) a = 5; b = –5 d) 0
17. 1st column: 50; 110; –42; 4; 0
2nd column: 21; 5; 34; 23; 15; –7
20. –3 < 2; 0 < 4; –4 < 0
–4–3 24 0
18, 19
21. a) –6 b) 0 22. 1) True 2) False
23. 1st column: 9 > –6 72 > –79
2nd column: |9| > |–6| |72| < |–79|
24. a) –7= –|–7| b) –(–7) > –7
c) –|7| < |–7| d) –|–3| > 2
e) 3 > –2 f) |–3| > |–2|
g) 0 < |–9| h) –(–5) =|–5| i) |4| > 0
25. a) –2 b) 2 c) -3 26. a) –3 b) –7 c) –4
27. a) right b) left 28. below; 4 + (–8)
29. less; (–20) + 14
30. a) the positive number has the larger absolute value b) always negative
c) the negative number has the larger absolute value
(pages 68–83)
24 + 47
–49 + 14
–5 + 5
–29 + 18
–3 + 25
15 + (–22)
4 + (–4)
–43 + (–5)
32 + (–9)
84 + 26
–74 + 21
32. 1st column: 0; 13; (–4)
2nd column: 25; –9; –5
3rd column: –14; –12; –7
33. a) –12 b) –50 c) 34 d) 44 e) 0
f) 0 g) 127 h) 123 i) –62 j) –119 k) 40 l) 33 m) –1 n) –7
34. 4 – 10; 4 + (–10)
35. opposite of b; a – b = a + (–b)
36. add –5 — subtract 5 multiply by 10 — multiply by 2... subtract 10 — add –10 add 3 and then add 2 — add 5
37. 10 + 1 = 11
38. a) smaller b) larger
39. a) 35 b) 25 c) 19 d) 29
40. a) b) 41.
–40 + 4 –24 + 24 –18 + (–18) –45 – 26 –13 + 15 –31 – (–12) –21 – (–26)
+ (–5)
– (–68)
+ (–91)
+ (–13)
42. 1st column: 0; (–10); 12
2nd column: 16; –21; –20
3rd column: 16; 5; 33
43. a) 1 b) 0 c) 6 d) 15 e) 14 f) –77 g) –50 h) 108 i) 72 j) 39 k) 42 l) –3 m) –11 n) 56
44. 4 1st column: –4; 4 2nd column: 4; 4
45. 9 1st column: –9; 9 2nd column: 9; 9
46. x – y > 0; y – x < 0; |x – y| > 0; |y – x| > 0
48. positive 49. |a – b| 50.
6. Proper fractions:
Improper fractions: Mixed fractions:
7. Fractions
3. a) whole part b) numerator c) denominator d) fraction part e) fraction bar f) mixed fraction
4. a) four whole three fourths. b) one whole one half
numerator denominator remainder denominator = quotient


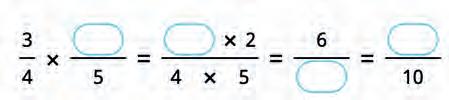
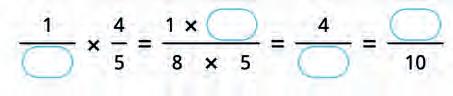
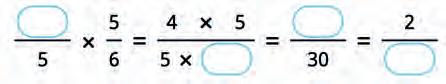
36. a) Correct; b) Incorrect; c) Incorrect.
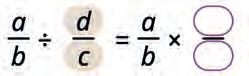
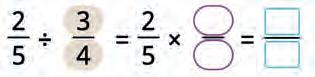
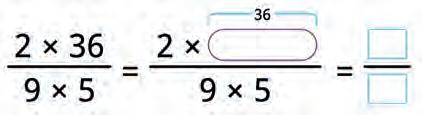
3 hundred thousandths five and seven hundred seventy four thousandths
two hundred and thirty four and nineteen hundredths eighty four and sixty five thousandths eleven hundredths
10. 1) 1.463 < 2.456 2) 2.76 > 2.2933
3) 401.34 > 41.34 4) 528.2 > 52.82
5) 49.1 > 49.01
11. 1) 0.726 < 0.734 < 0.738
2) 9.21 > 9.14 > 9.11
3) 83.39 < 83.41 < 83.42
4) 57.2 < 57.3 < 57.4 5) 82.406 < 82.506 < 82.606
12.
0.46 = 46 100 = 23 50
0.76 = 76 100 = 19 25
0.8 = 8 10 = 4 5
0.256 = 256 1000 = 32 125
13. a) b)
c) d) c) d) a) b)
14. a) Incorrect b) Correct
15. to the end
16. a) Incorrect b) Correct
17. 4.200 and 4.20 18.
19.
20. Column 1: 63.686; 61.7626; 586.08; 357.39
Column 2: 26.702; 315.11; 40.369; 487.559
21. a) Correct b) Incorrect c) Incorrect
22. a) b)
23. 1st line: 8.08; 9.99; 4.2 2nd line: 8.24; 6.82; 4.14
24. 1st column: 3137.1; 52510; 4243 2nd column: 921.52; 0.004781; 2.385
25. a) 3 tenths b) 1 hundredth c) 1 thousandth
26. 2
9. Data Handling
1. 1) 7,000 2) zebra 3) 70
13
320
17
difference — 0.25 cm
10. Mensuration
6. 1) Perimeter = AB + BC + CD + DA = 8 + 11 + 8 + 11 = 38 cm
2) Area = AB × BC = 8 × 11 = 88 cm²
7. Perimeter = 30 m
8. Perimeter = 62 m Area = 165.5 m²
9. 12 m²
11. Introduction to Algebra
1.
2. a) 105 + 360 b) 107 – 85
c) 145 × 68 d) 305 ÷ 23
3.
of four and two
of four and two
of four and two
four by two
4. b) x + 11 × 6 c) 1,300 – (7 × 150)
d) b – (p × 140)
5. Yes: 75 + a + 43 765×765 – n⁷⁶⁵
No: 6 – – 7 34+n$
6.
Sum of seventy five and n
Quotient of x and seventy five
Difference of forty three and n
7.
Product of x and twenty five
Difference of eighty four and n
Quotient of x and eighty four
Sum of twenty five and n
Product of x and forty three (pages 144–154)
8. a) 54, 5, 13 b) 1, –16, 4
9. 1st column: Cost of 2 game consoles and 1 game.
2nd column: The cost of 2 consoles equals the cost of 1 game.
10. P=3a
11. P = 3 × side = 3 × 3b = 9b
12. a) x = 34 b) x = 21 c) x = 61
d) x = 18 e) x = 195 f) x = 14
g) x = 25 h) x = 12 i) x = 1 j) x = 4 k) x = 2 l) x= 10
12. Introduction to Ratio and Proportion
1. a) 1 : 4 b) 3 : 1
2. a) The ratio of the number of monkeys to the number of bananas is 1 : 2.
b) The ratio of the number of bananas to the number of monkeys is 4 : 1.
c) The ratio of the number of monkeys to the number of bananas is 2 : 5.
3. a) b)
c) d)
5. a) 1 : 4 b) 2 : 3 c) 1 : 1
6. a) 300 mm b) 12 cm 7. 6 : 3 = = 2
:
13. Symmetry
1. a) symmetrical b) asymmetrical c) symmetrical d) asymmetrical
2. a) 2 b) 1 c) 0 d) many lines of symmetry
14. Construction of Line Segments and Angles
1. a) 7.3 cm b) 2.9 cm c) 5.5 cm
2. Perimeter = 16 cm Area = 12 cm²
6
3. a) b)
4. a) CM = 8.2 cm b) LH = 6.3 cm c) DG = 2.2 cm
5.
6. C L D


