SYNTHIFY July








05 08 12 16 19
WATER RESOURCE MANAGEMENT AND WATER POLLUTION
- YEWON PARK
THE IMPACT OF MICROPLASTICS ON MARINE ECOSYSTEMS AND HUMAN HEALTH
- WOOJIN CHUNG
THE DARKNESS OF THE BRIGHTNESS
- TAKATO IKEDA
CCUS TECHNOLOGY, THE KEY TO NET-ZERO EMISSIONS
- SEOYOON WON
CLIMATE JUSTICE
- RHIANNA KIM
ADVANCES IN RENEWABLE ENERGY
- JOSEPH LIM
TWO DIFFERENT TYPES OF SOLAR ENERGY
- HOSUNG BAE
THE SDGS: A PATHWAY TO A BETTER FUTURE - HARSHITA YANGALASETTY
THE GREEN DILEMMA: NAVIGATING GOLF'S ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT
- ETHAN KIM
CLEAN AIR, CLEAR FUTURE: COMBATING POLLUTION WITH ADVANCED TECHNOLOGIES
26 29 32 35
- AUDREY CHOI 23

EXISTING METHODS AND WAYS TO IMPROVE


Water resource management involves the planning, development, and oversight processes for both the sustainable quantity and quality of water The management process aims for efficient usage to prevent pollution, and is a complex task that utilizes water in a variety of aspects. Therefore, as water resource management plays an important role in protecting our surroundings, it is essential to understand the correlation between water pollution and the overall ecosystem Without proper management, water resources can become depleted and the environment can suffer serious damage.

Currently, there are many ways to manage water resources. One of them is recycling greywater. Gray water refers to sewage generated in showers and washing, which can be recycled to water plants or used in toilets Another is “measurement and management ” This is to measure and control the amount of water used based on it Moreover , “water-saving landscaping and irrigation” is a technology that reduces water consumption while supplying the right amount of water to plants This technology can contribute to the reuse of cultured water used in the laboratory and to save water resources Finally, there are also ways to increase energy efficiency and reduce water use by optimizing cooling towers, which are structures that remove heat from water by evaporative cooling.
There are also various ways to prevent water pollution First of all, it is very important not to drain certain products, such as chemicals, medications, and oils, into the sink or toilet.Reducing the use of plastic in everyday life also helps to reduce water pollution, as plastics can release harmful chemicals into the water and contribute to the buildup of non-biodegradable waste, which disrupts aquatic ecosystems and endangers marine life In addition, spill prevention measures can prevent fertilizers or chemicals from flowing into the groundwater and air separation, which is a method of removing pollutants from the water using air. Other methods such as precipitation, ion exchange, reverse osmosis, and agglomeration are used as well

In order to improve water resource management, considering sustainable development is essential. The environmental benefits and economic balance must be considered together, and institutional tools can be utilized for this. It will be very important to come up with a legal and regulatory framework, and to reduce resource waste by appropriately setting water prices Encouraging water conservation through incentives can also be done, which potentially can strengthen water resource management worldwide through international cooperation.
To improve water pollution, source prevention is the most effective. One should thoroughly manage the disposal of chemicals and cleaners used at home, and make sure not to throw drugs into the toilet or sink Just like water resource management, it is also necessary to strengthen these management measures through institutional tools

To sum up, water resource management and water pollution prevention are essential to protect our health and the environment. Improvements in water resource management will contribute to sustainable development and economic balance, and clean water should be passed down to the next generation through water pollution prevention These efforts must be recognized and practiced by all of us for the future, and I think the result of those efforts will be a benefit that everyone can enjoy

ECOSYSTEMS ECOSYSTEMS ECOSYSTEMS
Marine debris, also known as “ ocean ' s nightmare,” is called sea trash in short It includes a broad range of synthetic waste buried in oceans, seas, and other large bodies of water Among them, in particular, microplastics are the most harmful component. According to a report from Kyushu University in 2021, it is said that approximately 24 trillion pieces of microplastics are under the world's oceans Microplastics–with their underlying risks like contamination and health problems–are ingested by diverse marine organisms, redounding such results of physical harm, chemical contamination, and disruptions in growth and reproduction. Eventually, such risks can ascend to the very summit of the food chain, affecting human health as well. The part of which microplastics take part is escalating in marine environments and thus is an urgent need to address this issue The following parts of this article will discuss how to mitigate such marine pollution caused by the presence of microplastics.

The “ ocean nightmare” can be divided into two groups: primary microplastics and secondary microplastics. Primary microplastics are intentionally made small in size, such as the microbeads used in personal care products like exfoliating scrubs or industrial abrasive materials Conversely, secondary microplastics result from the degradation of bigger plastic objects through natural processes like weathering and environmental decay. It could be noted from this that most of the environmental particles are of man-made origin, such as the use of personal care products by humans, any industrial process or method that does not adhere to regulations governing their disposal Once these particles go into marine environments, they pose a significant threat to marine life. Severe consequences may arise after marine organisms ingest microplastic particles, including blockage of digestive tract, chemical pollution and accumulation of toxic substances leading to bioaccumulation in body tissues A report from Fauna and Flora reveals that 100000 marine mammals are killed annually by plastics This is also evident on a much broader scale within marine ecosystems where species’ food chains become disrupted, biodiversity loss occurs and habitat destruction becomes extreme.
We can no longer sit back and leave this problem to develop. The microplastic crisis in oceans needs some solutions that can effectively reduce the pollution caused by microplastics. Regulation on the production and disposal of plastics is the cause of the plastic waste management problems at the international and national levels Scientific and technological progress is needed for the development of alternatives to plastic and recycling methods. Besides, a comprehensive approach to notify the public on the presence of microplastics is important, in order to prevent people from utilizing plastics In brief, it is crucial to execute all kinds of actions to mitigate the impacts of microplastics on marine species and human beings who are also exposed to the ocean ’ s biggest menace

Termed “ ocean ' s nightmare,” microplastics come with grave concerns and a surging existence They have redounded into several environmental crises that involve marine ecosystems and human health. Microplastic contamination of our oceans is estimated at 24 trillion pieces, with serious impacts of such pollutants on marine life. More essential actions are hence highly required to attenuate these consequences This may involve legislation on plastic production, developing technologies for recycling, and even the invention of new applications for sustainable products Raising people's awareness and the consequent actions are also very important with regard to the reduction in the use of plastics and increasing the intake of eco-friendly products. Gaining insight into its impacts and proactive solution-finding is really possible to help safeguard marine ecosystems and our health Let’s take up the challenge to the world and set a foundation for a much healthier planet for future generations to come.


TAKATO IKEDA TAKATO IKEDA
UNDERSTANDING THE DANGER OF LIGHT POLLUTION OF LIGHT POLLUTION
UNDERSTANDING THE DANGER

Imagine a night where the natural rhythm of our bodies is disturbed by the light, animals become lost, and the stars are hidden from our view This is just like a scene from a dystopian novel. However, light pollution is making this scenario a reality. According to the United Nations (UN) environment programme (Law and Environment Assistance Platform), light pollution refers to artificial light that alters the natural patterns of brightness in the ecosystems The effects of light pollution on the environment, health, and astronomy are so significant that immediate action is required to address them

There are several categories that light pollution can be separated into Each has a different effect on the environment and public health. Firstly, “skyglow” is the brightening of the night sky over urban areas, diminishing our ability to see stars and other celestial bodies Not only is this aesthetically displeasing, but also it limits the access of the universe and makes astronomical research more difficult Furthermore, excessive brightness causes “glare”, which impairs vision and reduces visibility, also making driving dangerous In fact, it has a detrimental impact on both people and animals. Lastly, when undesirable light leaks into naturally dark spaces where it is not essential, it is referred to as “light trespass ” An example of this would be streetlights beaming through bedroom windows, disturbing our sleep. In metropolitan environments, a clutter bright, disorienting, and overwhelming clusters of light sources causes visual disarray and may be a factor in mishaps and confusion


Light pollution has a significant negative influence on the environment. Artificial light causes nocturnal creatures to behave differently, which can cause confusion and have negative effects Sea turtles, for example, frequently confuse man-made lights for the moon, guiding their hatchlings away from the ocean and toward hazardous urban areas. Additionally, owls also find that light pollution interferes with their ability to hunt as they mainly forage at night Light pollution causes navigational problems for migratory birds, which can result in lethal disorientation. In addition, light pollution messes up the predator-prey equilibrium:because they are at a disadvantage when hunting in the dark, some prey species overpopulate, while predator numbers drop. The ecosystem as a whole is impacted by this imbalance, which changes plant growth patterns and biodiversity

Furthermore, light pollution has a major negative impact on human health as well A long-term exhaustion and a lower quality of life can be caused from excessive exposure to artificial light. In addition, it can also cause insomnia and circadian cycle disruptions Moreover, extended nighttime exposure to artificial light has been found to be associated with an increased risk of diabetes, obesity, and several cancer disease. A possible explanation for these health problems is the inhibition of melatonin production, a hormone that is controlled by exposure to light Disrupted sleep patterns can also exacerbate mental health disorders like anxiety and depression and lower overall mental well-being since they put stress on the body
Considering these consequences, light pollution requires a diversified approach to be addressed. Light pollution can be considerably decreased by putting improved lighting practices into place, such as employing energy-efficient bulbs and shielded fixtures that direct light downward. Governments may play a significant role in reducing light pollution by establishing rules and guidelines. It is imperative to have policies that restrict the use of excessive lighting and promote the adoption of more advanced lighting technology. Public awareness campaigns and education about the risks posed by light pollution can influence public opinion and encourage support for initiatives aimed at reducing light pollution.

THE FUNCTIONING AND FUTURE SIGNIFICANCE OF CCUS TECHNOLOGY
SEOYOON WON

Extreme wildfires, hurricanes, droughts, and ocean changes. Why are these strange events happening on our Earth? Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the culprit With people burning more fossil fuels for energy, global CO2 emissions have increased by more than 60 percent since 1990 For a sustainable future, the entire world is proceeding toward “net-zero”, a state in which the emissions of greenhouse gases are counterbalanced by removing carbon from the atmosphere Recently, CCUS technology has been brought to the social spotlight as an innovative method to remove CO2 emissions
CCUS, which stands for Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage, refers to a technology that captures CO2 emissions and either recycles it to useful forms or stores it deep underground permanently.

In this process, capturing CO2 emissions is the most significant part. Mainly from power plants, natural gas processing facilities, or other industrial processes, there are three methods to capture CO2 emissions: pre-combustion, post-combustion, or oxyfuel combustion During the precombustion, CO2 is removed before the burning of fossil fuels. On the contrary, post-combustion separates CO2 from exhaust gas streams emitted during the process of combustion In oxyfuel combustion, pure oxygen is used for combustion instead of air, producing pure CO2. The captured carbon is then transported to the point of usage or storage

Carbon can be transformed into mainly three categories: fuels, chemicals, and materials By reacting with hydrogen from water electrolysis, the captured carbon can be made into CCU fuels. Also, it can be used as a feedstock to produce chemical products such as plastics, polymers, or pharmaceuticals, or transformed into a state that can be used as a building material, such as calcium-carbonate (CaCO3), through carbonation
Alternatively, the captured carbon may be kept under deep geological formations or minerals. For geological storage, CO2 is converted into a state known as ‘supercritical CO2’, which behaves like a liquid and is injected into sedimentary rocks. In mineral storage, CO2 goes through a process called mineral carbonation, reacting with iron, magnesium, and calcium minerals to form stable carbonates. Since these minerals are naturally occurring and abundant, the re-release of CO2 into the atmosphere never happens.

concern is its high cost due to energy-intensive facilities. Besides, several risks, such as CO2 leakages from storage sites, exist around the technological process But fortunately, experts expect that the cost will fall when the market expands and the key technologies develop further. Moreover, government regulation and management strategies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency’s carbon sequestration rule, are being placed to minimize the possibility of safety problems.
The International Energy Agency suggests that CCUS will account for 15 percent of the total amount of reduced greenhouse gas emissions in the near future In this crucial period of transition to net-zero emissions, the role of CCUS will expand to almost every part of the energy production system The mission for now is to accelerate research and development, until the widespread implementation of CCUS technology.
RHIANNA KIM

As a child, you are most likely to have fun memories of running around in parks, having picnics in the shade below tall trees or even simply strolling by streets full of bushes and flowers. However, in communities of low socioeconomic standings, these natural, green regions are rare sights As a matter of fact, residents are surrounded by industrial pollution, debris from extreme weather conditions, and the deteriorating state of climate change has been making these communities more vulnerable
According to NASA Science, climate change is defined as the “long-term change in the average weather patterns”, with iits key indicators being increased frequency of extreme weather events like wildfires and droughts. Unfortunately, climate change does not impact all regions equally. Despite the statistic that “the richest 1% of the global population is responsible for more carbon emissions than the poorest 66%” as stated by the Guardian, these marginalized communities are bearing the extreme consequences of climate change This is the core of climate justice, which recognizes the unfair extent of the effects of climate change on marginalized communities.
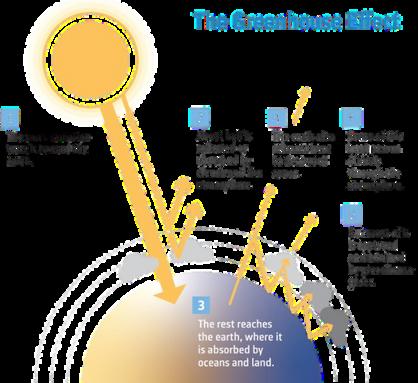
A key contributor to climate change is known as ‘The Greenhouse Effect’ The greenhouse effect is a process where ‘greenhouse gasses ’ , which consist of carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and water vapor, trap the sun ’ s heat in the earth’s atmosphere. Many human activities including the burning of fossil fuels, food production, power generation and use of transportation increase the amount of greenhouse gasses being released into the atmosphere which inevitably results in an increased amount of trapped heat and consequently, a rise in the global surface temperature. Scientists have discovered that the temperature of the Earth’s surface has been increasing by 0 06º Celsius per decade since the 1850s In fact, last year (2023) has been recorded as the warmest year since the beginning of global records which could ultimately lead to rising sea levels, loss of species and a spike in natural weather events. Unfortunately this spawns greater, long-term consequences, in particular, reduced food supply, and greater health risks.
But, how exactly do these impacts of climate change differ in regions of different economic statuses?

Although both rich and marginalized communities are unable to completely insulate themselves from the impacts of climate change in the long-run, wealthier communities are exposed to more resources to adapt to changes
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has stated that wealth plays a pivotal role in the ability for communities to respond to extreme weather conditions and natural events caused by climate change Wealthier communities have a proportionately larger amount of disposable income that could be spent on protective measures for their households and invest in new technology like renewable energy and smart systems to maintain their living standards However, the disparate reality is that wealthy individuals are key stakeholders contributing to global carbon emissions from investing in manufacturing industries and other sources that are pollution-causing
In contrast, marginalized communities, who in fact are the least responsible for climate change, suffer the most from the severe consequences. A report by the United States Environmental Protection Agency has discovered that the key threats to marginalized communities are various illnesses ranging from respiratory to water-related, and impacts in food systems. One of the most prevalent impacts are respiratory diseases Research has proven that climate change causes an increase in outdoor air pollution which, according to Cancer Research UK, is a mixture of miniscule particles and substances in the air that have negative impacts on health When humans breathe in this polluted air, the tiny particles enter the lining of the lungs and may begin to build up.
This ultimately leads to damage of DNA in cells and causes mutations leading to cancer Socially vulnerable individuals have higher risks of developing such illnesses due to the lack of quality healthcare and greater exposure to factory pollution

Luckily, many countries are beginning to acknowledge the severity of the burden on marginalized communities and are taking action For instance, the United States’ Federal Government has implemented an initiative called “Justice40” with the goal of proceeding 40% of Federal investments to underprivileged communities that are bearing the burden of climate change. It has been officially stated by The White House that the Federal investments include clean energy, affordable and sustainable housing, and the development of clean water and wastewater infrastructure By utilizing a new technological device called the Climate and Economic Justice Screening Tool (CEJST), which is an “interactive mapping tool to identify communities that are overburdened by pollution”, Federal Agencies are aiming to identify disadvantaged regions and direct resources to these communities to aid in alleviating these climate burdens
Alongside the growing consequences of climate change becoming more obvious and individuals are increasingly suffering, nations are beginning to implement initiatives as such to reach the goals of Climate Justice As BBC has stated, “When we reach a point when every human being lives with a life of dignity, then we would have achieved climate justice”.

Especially in a rapidly developing society like ours, the need to switch from fossil fuels to renewable energy is imperative This change is motivated by environmental worries and worldwide climate objectives, including, but not limited to, climate change. This article discusses recent advancements in renewable energy technologies, evaluates their impact, and identifies possible research directions.
Since the development of solar technology, solar energy has been a popular topic of discussion In fact, solar panels, a device that directly converts sunlight into electricity by using photovoltaic cells, are reaching conversion efficiencies exceeding 25%. In other words, it can effectively use a quarter of the sunlight it absorbs as clean and renewable energy.
The increased efficiency of solar panels has driven down the cost of solar power, making it largely accessible to a wide range of people, thus successfully implanting the hope of completely getting rid of unrenewable energies. Being the most abundant of all energy sources, solar energy is developed by many large corporations such as Vestas, NextEra energy, Sunrun, and more
Since its invention in 1887 by American scientist Charles F Bush, wind turbines have seen massive advancements in both models and efficiency. Research done by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) shows that “technology innovations making their way into commercial markets today and in coming years could unlock 80% more economically viable wind energy capacity within the contiguous United States ” This has been the trend not only in the US, but in countries such as Germany, the UK, and China. Scientists predict that future enhancements to our pre-existing technologies and innovations may effectively augment our ability to harness wind energy further, contributing toward the clean energy goals

The focus of recent developments has been on hydrokinetic energy technologies, technologies utilizing the energy created by the movement of a body of water, with innovative techniques to lessen and possibly mitigate environmental impacts such as pollution. An example is the hydraulic turbine: using the energy of flowing water in bodies of water, it successfully converts those energies into mechanical energy - energy that can be used.

Innovations consist of improved biofuels derived from algae and waste; enhanced techniques for converting biomass such as gasification, the process of converting solid and liquid waste into usable energy; and pyrolysis, the heating of an organic material in the absence of oxygen
Although the rapid boom of advancements in the scientific fields may seem comprising, we must not forget the continuously deteriorating condition of the Earth’s climate, in which the temperature is expected to rise by 1 5 degrees Celsius by the end of 2050





Nowadays, global warming is an issue we should treat with gravity: Earth became about 1.36℃ warmer in 2023 than in the late 19th-century (1850-1900) pre industrial average, according to NASA 1 36℃ might look like a trivial figure, but it is not actually Due to this subtle rise in temperature, sea levels are rising, more droughts and hurricanes are taking place, and many species are being lost. The best way to mitigate this problem is to produce less carbon dioxide (CO₂) by using renewable energy. There are many types of renewable energy such as wind energy, biomass energy, tidal energy, and solar energy. Solar energy uses the sun as a source to generate electricity However, not all solar energy is the same There are two different types of solar energy: solar thermal energy and solar photovoltaic energy.
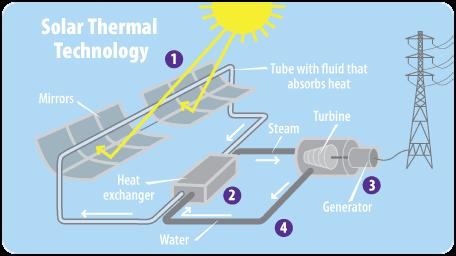
As its name suggests, solar thermal energy uses the sun ' s thermal heat to produce electrical energy To reach a high temperature, the solar thermal system uses a reflector and a mirror to concentrate light on a receiver Then the heat-transfer fluid is heated and circulated in the receiver to produce steam. Finally, the steam rotates the turbine and the turbine’s mechanical energy turns into electrical energy This is the main principle of solar thermal energy. Since the process of turning thermal energy into electricity is complicated, there are many instances where solar thermal systems are used in heating systems Moreover, solar thermal systems are less frequently used compared to solar photovoltaic systems because of their lower energy turning efficiency
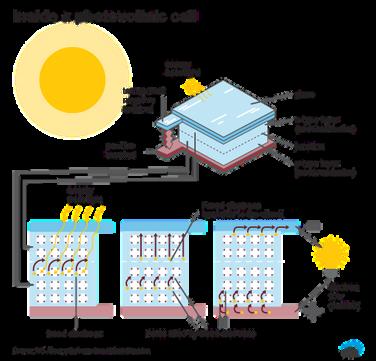
In contrast, solar photovoltaic energy converts sunlight directly into electricity. The basic concept behind this is as follows. PhotoVoltaic(PV) cells, the basic component of solar photovoltaic systems, are made of semiconductors. Some photons from the sunlight are absorbed by the semiconductor material and dislodge electrons from the material’s atom A special manufacturing of semiconductor makes the front surface of it more receptive to electrons, and this creates an electric potential difference Due to this potential difference, electrons flow when the conductors are connected to an electric circuit such as batteries. The photovoltaic cells’ life span is quite long, more than 20 years, and the whole system can be operated and maintained automatically.
One flaw in the solar photovoltaic system is that the amount of sunshine each day affects the amount of electrical energy generated, and the initial cost invested is high. Nonetheless, due to its relatively high efficiency, Solar PV alone accounted for 4 5% of total global energy generation in 2023, according to IEA
In summary, there are two ways in which we can produce electrical energy using the sun as a source Solar thermal energy utilizes the sun ' s thermal energy to produce electricity or to heat water or houses In comparison, solar photovoltaic energy turns sunlight into electricity using PhotoVoltaic(PV) cells These renewable energy technologies are constantly being improved Nevertheless, only about 9% of the total electricity was generated from renewable sources in Korea. Global cooperation and coordination in terms of technology and reforming domestic policy to fast-track renewable energy projects should take place concurrently in order to increase the usage of renewable energy Then someday, we might be able to stop global warming or even reverse the effects of it.
YANGALASETTY

Imagine a world where no person is poor, no person is hungry, and all persons have clean water, healthcare, and education This is the dream behind the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDG). These 17 goals, set in 2015 with a target to achieve them by 2030, bring us together to perform actions needed to solve problems such as poverty, inequality, climate change and the need for peace and justice.
The Sustainable Development Goals are a global plan to end poverty, protect the planet and ensure all humans enjoy peace and prosperity by 2030. These set goals form challenges toward poverty, hunger, inequality, climate change and degradation in the environment with promotion of peace and justice to make this world a fair place
Poverty and hunger are two closely intertwined challenges that the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) aim to address through their targets of 'No Poverty' and 'Zero Hunger ' These problems become interlinked because access to basic needs such as food, clean water, health facilities, and education can help get out of the trap of poverty When people's basic needs can be met, they are healthy and can be productive, sustain themselves, and their families All this would change thousands of lives and offer millions an opportunity to live better and more secure lives.

Of major consideration in the SDGs is sustainability This involves the use of clean energy, reducing waste, and acting on climate change. The goal pitch is harvesting economic growth against environmental protection and that ensures that no one is left behind in progress. Renewable energy and the promotion of sustainable practices reduce pollution and secure a healthy future for the planet. In its place, responsible consumption and production would ensure prudent use of resources coupled with reduced wastages that help protect the environment

The second priority in requirements for sustainable development is peaceful, inclusive societies. SDGs underline respect for human rights, access to fair justice, and the building of efficient institutions that protect these principles Greater unity and cooperation could be achieved by reducing inequality within and between countries through inculcating a sense of common purpose and mutual respect If people feel they are being fairly treated and enjoying equal opportunities, the urge to work together in the pursuit of common goals will be heightened, breaking barriers that often lead to conflict In addition, it is the case that equitable societies will be more resilient to withstand and address challenges with much strength; such societies have trust and collaboration as the basis for progress. Equally necessary are the partnerships between governmental circles, businesses, and civil society That would not only speed up progress but include all people without exception.
The SDGs are a pathway to overcome the stiff challenges of our times These goals, however, cannot be attained by any one country or institution acting in isolation. On the contrary, realization calls for responsible governance, responsive businesses, and active citizenship It is the choices we make today that will have an impact on generations tomorrow; therefore, we should strive with resolute effort toward the achievement of these goals Thus may we strive towards a better world for all human beings
FROM COURSE CREATION TO MAINTENANCE: UNDERSTANDING THE HIDDEN COSTS AND EMBRACING SUSTAINABLE SOLUTIONS

Golf, a widely played sport throughout the whole world, is originated from the east coast of Scotland Initially played by simply hitting small pebbles on sand with a bent stick, nowadays its form has been transformed, resembling nothing like what it was before. Along with the extreme growth of the sport, the environmental harm caused by golf courses–often overlooked or unacknowledged by golf players–has been rising as a significant concern Destruction of ecosystems, carbon emission due to machinery usage, and excessive water usage are the most prominent issues regarding the land usage for golf
Due to the massive scale of a golf course, impacting surrounding habitats, food sources, and shelters for organisms in a wide range of areas, an entire ecosystem is often wiped out Even in cases where a part of the ecosystem may remain untouched, a once uniform ecosystem gets divided into smaller fragments, causing detrimental harm to the environment Considering the fact that there are approximately 16000 golf courses only in the United States, the predicted number of damaged ecosystems is inconceivable . Moreover, Ecosystems nearby golf courses are also indirectly harmed The shifting movements of living creatures and unprecedented human invasion not only negatively impacts the initial ecosystem where the golf course is built, but also the surrounding natural areas As such, the destruction of an ecosystem ensues additional harm like a domino collapsing in sequence.


g g g g go g ga share a common factor: carbon emissions The enormous amount of machinery operated during these processes has been an inevitable issue ;not to mention the emissions derived from creating such massive courses In fact, golf ranks 4th among sports producing the most carbon emission, with an average value of 565 5 kg emitted every day for playing and training. This is also affected by golfers traveling to golf courses which are located far away from each other. Unlike other field sports such as soccer or football, each golf course has its own unique structure, tempting golfers to travel to specific courses in order to experience their distinct features.

Lastly, water usage committed in the maintenance of golf courses also serves as a crucial factor For instance, golf courses in Utah use 9 million gallons of water per day solely on maintenance Such an enormous amount of water is necessary for golf courses because of their dependency on grass condition Especially in the area referred to as the “putting green, ” even the smallest bumps and imperfections require intense care. To ensure careful management of the grass, such seemingly excessive water usage is required
In conclusion, while golf stems from an extremely unique and distinct history, its environmental harm currently poses significant challenges that cannot be overlooked To support a healthier environment, all golfers (and non-golfers) should be aware of and support environmentally friendly initiatives
CUTTING-EDGE SOLUTIONS FOR REDUCING AIR POLLUTION AND PROTECTING PUBLIC HEALTH

Air pollution is one of the most detrimental environmental challenges today, affecting both the environment and human health A report by the American Lung Association states that 2024 has had the most hazardous air quality days in 25 years Typically, an air quality index (AQI) value of over 300 is considered hazardous Reducing air pollution is crucial as it reduces chances of lung cancer, heart disease, stroke, and respiratory diseases, including asthma Air pollution control technologies typically aim to target pollutants emitted by factories, industries, and vehicles. There are different types of these technologies, and each technology plays a significant role in reducing environmental pollution.

Electrostatic precipitators are used mostly in the air purifier industry, as they are effective at purifying industrial pollutants. Consisting of wires and collection plates, electrostatic precipitators use electrostatic force to grab dust and other particles. Sometimes, they are also used in power plants to remove fine particles such as dust and smoke from exhaust gases In short, electrostatic precipitators are highly efficient, and are able to remove 99% of particulate matter

Electrostatic precipitators are used mostly in the air purifier industry, as they are effective at purifying industrial pollutants Consisting of wires and collection plates, electrostatic precipitators use electrostatic force to grab dust and other particles Sometimes, they are also used in power plants to remove fine particles such as dust and smoke from exhaust gases In short, electrostatic precipitators are highly efficient, and are able to remove 99% of particulate matter.

Baghouse dust collectors, to put it simply, are fabric filters They capture particulate matter in the surface of the fabricand keep dust particles from being released into the atmosphere. These bags are cleaned to remove the accumulated dust, which can then be disposed of or recycled. This type of technology is commonly used in cement manufacturing or power generation industries.
Scrubbers are another type of air pollution control technology. There are wet scrubbers and dry scrubbers, each designed for specific types of gases or particles Wet scrubbers wash particulates out of polluted airstreams, particularly controlling sulfur dioxide and chlorine They remove harmful substances and neutralize acidic compounds, functions that make them a type of versatile technology for air pollution reduction

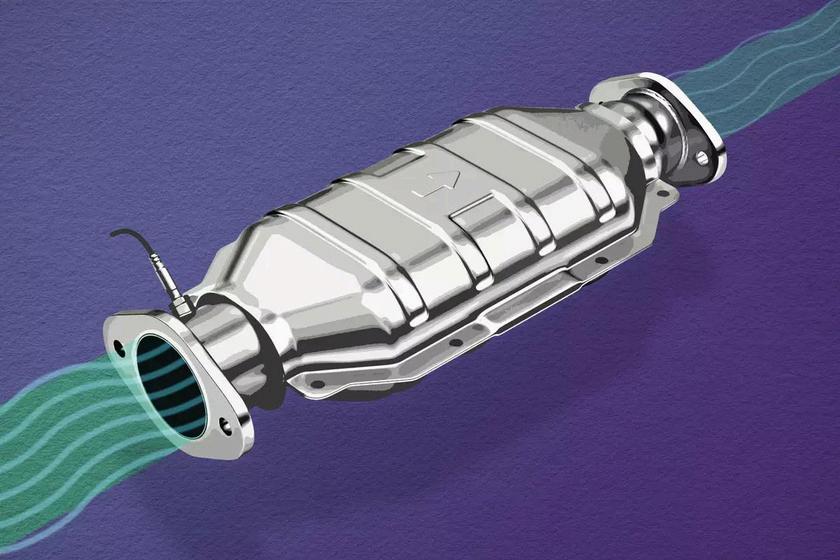
Finally, catalytic converters are critical for reducing air pollution from vehicles They convert pollutants into harmless nitrogen, water vapor, or carbon dioxide with the use of catalytic reactions Interestingly, catalytic converters are mandatory in many countries in order to meet emission standards
All in all, air pollution remains one of the most pressing environmental issues of our time. The significant increase in hazardous air quality index (AQI) days underscores the urgency of addressing this problem. Air pollution control technologies, such as electrostatic precipitators, catalytic oxidizers, scrubbers, baghouse dust collectors, and catalytic converters, play vital roles in mitigating the harmful effects of pollution They reduce the emission of harmful pollutants and consequently improve human health As we move forward, it is crucial to continue investing in and improving these technologies By doing so, we can ensure a healthier environment and a brighter future
WATERRESOURCEMANAGEMENTANDWATERPOLLUTION-YEWONPARK
Denchak,Melissa“WaterPollution:EverythingYouNeedtoKnow”WaterPollutionDefinition-Types,Causes,Effects,11Jan2023,wwwnrdcorg/stories/waterpollution-everything-you-need-know#whatis
“WaterQualityandWastewater:UN-Water”UN,wwwunwaterorg/water-facts/water-quality-and-wastewaterAccessed6Aug2024
Sensorex“9EffectiveWaterPollutionSolutionstoProtectOurEnvironment”SensorexLiquidAnalysisTechnology,23Sept2022,sensorexcom/effective-water-pollutionsolutions-to-protect-our-environment/?srsltidAfmBOopfMo8puPpFaze7SnSueP6-AX4BG7HBewezH22cmkSsiD72zOP. Office,USGovernmentAccountability“WaterQualityandProtection”USGAO,wwwgaogov/water-quality-and-protectionAccessed6Aug2024
Impulse,Solar“SolutionstoWaterPollution”HowtoImproveWaterQuality?,SolarImpulseFoundation,solarimpulsecom/water-pollution-solutionsAccessed6Aug 2024
THEIMPACTOFMICROPLASTICSONMARINEECOSYSTEMSANDHUMANHEALTH-WOOJIN CHUNG
“Twenty-FourTrillionPiecesofMicroplasticsintheOceanandCounting”ScienceDaily,ScienceDaily,27Oct2021, wwwsciencedailycom/releases/2021/10/211027122120htm
“HowDoesPlasticPollutionAffectMarineLife?”Fauna&Flora,21Mar2024,wwwfauna-floraorg/explained/how-does-plastic-pollution-affect-marine-life/ THEDARKNESSOFTHEBRIGHTNESS-TAKATOIKEDA
“InformationaboutSeaTurtles:ThreatsfromArtificialLighting”SeaTurtleConservancy,conserveturtlesorg/information-sea-turtles-threats-artificial-lighting/Accessed3 Aug2024
“LightPollution”Education,educationnationalgeographicorg/resource/light-pollution/Accessed3Aug2024
“LightPollution.”LightPollution|UNEPLawandEnvironmentAssistancePlatform,leap.unep.org/en/knowledge/glossary/light-pollution.Accessed3Aug.2024.
Staff“LightPollutionAffectsHumanHealth”DarkSkyInternational,darkskyorg/resources/what-is-light-pollution/effects/human-health/Accessed3Aug2024
“WhatIsLightPollution?”DarkSkyInternational,darkskyorg/resources/what-is-light-pollution/Accessed3Aug2024
“CarbonCapture,UtilisationandStorage-EnergySystem”IEA,wwwieaorg/energy-system/carbon-capture-utilisation-and-storageAccessed3Aug2024
“CCU:WhatIsCarbonCaptureandUtilisation:CO₂valueEurope”CO2ValueEurope,6Feb2024,co2valueeu/what-is-ccu/ “CCUSinCleanEnergyTransitions–Analysis”IEA,Sept2020,wwwieaorg/reports/ccus-in-clean-energy-transitions EPA,EnvironmentalProtectionAgency, www.epa.gov/ghgreporting/subpart-rr-geologic-sequestration-carbon-dioxide.Accessed12Aug.2024.
Khan,Usman,etal“AssessingAbsorption-BasedCO2Capture:ResearchProgressandTechno-EconomicAssessmentOverview”ScienceDirect,Elsevier,Sept2023, wwwsciencedirectcom/science/article/pii/S2772656823000295
Levin,Kelly,etal“WhatDoes‘Net-ZeroEmissions’Mean?8CommonQuestions,Answered”WorldResourcesInstitute,20Mar2023,wwwwriorg/insights/net-zeroghg-emissions-questions-answered
Roberts,Alice“WhyandHowIsCarbonDioxideTransported?”DraxGlobal,29Apr2022,wwwdraxcom/carbon-capture/why-and-how-is-carbon-dioxide-transported/ Tiseo,Ian“GlobalCO2EmissionsbyYear1940-2023”Statista,13June2024,wwwstatistacom/statistics/276629/global-co2-emissions/ “UnderstandingCarbonCaptureandStorage”BritishGeologicalSurvey,16Nov2022,wwwbgsacuk/discovering-geology/climate-change/carbon-capture-and-storage/ “WhatIsCarbonCapture,UsageandStorage(CCUS)andWhatRoleCanItPlayinTacklingClimateChange?”GranthamResearchInstituteonClimateChangeandthe Environment,13Mar2023,wwwlseacuk/granthaminstitute/explainers/what-is-carbon-capture-and-storage-and-what-role-can-it-play-in-tackling-climate-change/
ClimateChange:GlobalTemperature(2024,January18)NOAAClimategovhttps://wwwclimategov/news-features/understanding-climate/climate-change-globaltemperature
WhatIsClimateChange?-NASAScience(2022,June15)Nasagovhttps://sciencenasagov/climate-change/what-is-climate-change/ Climatechange:thescience(2023)NIWAhttps://niwaconz/climate-change-information-climate-solvers/climate-change-science Whatisthegreenhouseeffect?-NASAScience(2014,September18)Nasagovhttps://sciencenasagov/climate-change/faq/what-is-the-greenhouse-effect/ Nations,U(2023)CausesandEffectsofClimateChange|UnitedNationsUnitedNations;UnitedNationshttps://wwwunorg/en/climatechange/science/causes-effectsclimate-change#::textAs%20greenhouse%20gas%20emissions%20blanket,the%20usual%20balance%20of%20nature ClimateChange2022:Impacts,AdaptationandVulnerability(2022)Ipccch;IPCChttps://wwwipccch/report/ar6/wg2/ ClimateChangeandtheHealthofSociallyVulnerablePeople|USEPA(2022,March21)USEPAhttps://wwwepagov/climateimpacts/climate-change-and-healthsocially-vulnerablepeople#::textIn%20both%20urban%20and%20rural%20low%2Dincome%20areas%2C%20water%20resources,vulnerable%20to%20water%20quality%20issues Howcanairpollutioncausecancer?(2019,July12)CancerResearchUK;CRUKhttps://wwwcancerresearchukorg/about-cancer/causes-of-cancer/air-pollution-radongas-and-cancer/how-can-air-pollution-cause-cancer#::text=Because%20air%20pollution%20contains%20a,which%20can%20lead%20to%20cancer Justice40Initiative|EnvironmentalJustice|TheWhiteHouse(2024,February28)TheWhiteHouse;TheWhiteHouse https://wwwwhitehousegov/environmentaljustice/justice40/
ADVANCESINRENEWABLEENERGY-JOSEPHLIM
Lai,Olivia“ExaminingtheProsandConsofHydroelectricEnergy”EarthOrg,12January2023,https://earthorg/pros-and-cons-of-hydroelectric-energy/Accessed8 August2024
Laurie,Carol,etal“TechnologyAdvancementsCouldUnlock80%MoreWindEnergyPotentialDuringThisDecade”NREL,22September2023, https://wwwnrelgov/news/program/2023/technology-advancements-could-unlock-80-more-wind-energy-potential-during-this-decadehtmlAccessed3August2024 Lozanova,Sarah“7NewSolarPanelTechnologyTrendsShapingtheFutureofEnergy”GreenLancer,12June2024,https://wwwgreenlancercom/post/solar-paneltechnology-trends.Accessed3August2024.
“NATIONALWINDMILLDAY-May10,2025”NationalToday,https://nationaltodaycom/national-windmill-day/Accessed8August2024
“Solarpanel”Wikipedia,https://enwikipediaorg/wiki/SolarpanelAccessed8August2024
TWODIFFERENTTYPESOFSOLARENERGY-HOSUNGBAE
NASA(nd)Effects-NASAscienceNASAhttps://sciencenasagov/climate-change/effects/ NASA(2024,February7)GlobalsurfacetemperatureNASAhttps://climatenasagov/vital-signs/global-temperature/? intent=121#::text=Overall%2C%20Earth%20was%20about%20245,change%20in%20global%20surface%20temperatures
USEnergyInformationAdministration-EIA-independentstatisticsandanalysisSolarthermalpowerplants-USEnergyInformationAdministration(EIA)(nd) https://wwweiagov/energyexplained/solar/solar-thermal-power-plantsphp USEnergyInformationAdministration-EIA-independentstatisticsandanalysisPhotovoltaicsandelectricity-USEnergyInformationAdministration(EIA)(nd) https://eiagov/energyexplained/solar/photovoltaics-and-electricityphp Iea(nd)SolarIEAhttps://wwwieaorg/energy-system/renewables/solar-pv
UnitedNations(nd)Fivewaystojump-starttheRenewableEnergyTransitionNowUnitedNationshttps://wwwunorg/en/climatechange/raisingambition/renewable-energy-transition
THESDGS:APATHWAYTOABETTERFUTURE-HARSHITAYANGALASETTY
UnitedNations(nd)**SustainableDevelopmentGoals**UnitedNationsRetrievedfrom[https://wwwunorg/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/] (https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/)
UnitedNationsDevelopmentProgramme(nd)**WhataretheSustainableDevelopmentGoals?**UNDPRetrievedfrom[https://wwwundporg/sustainabledevelopment-goals](https://wwwundporg/sustainable-development-goals)
UnitedNations(nd)**Goal1:EndPovertyinAllItsFormsEverywhere**UnitedNationsRetrievedfrom[https://wwwunorg/sustainabledevelopment/poverty/] (https://wwwunorg/sustainabledevelopment/poverty/)
UnitedNations(nd)**Goal13:ClimateAction**UnitedNationsRetrievedfrom[https://wwwunorg/sustainabledevelopment/climate-change/] (https://wwwunorg/sustainabledevelopment/climate-change/)
THEGREENDILEMMA:NAVIGATINGGOLF'SENVIRONMENTALIMPACT-ETHANKIM
"CO2andGolf:WhatIstheFootprint?"GolfSustainable,https://golfsustainablecom/en/co2-and-golf-what-is-the-footprint/Accessed3Aug2024
"Eco-FriendlyGolfCourses"Today'sGolfer,https://wwwtodays-golfercom/courses/best/eco-friendly-golf-courses/Accessed3Aug2024
"Hole-in-One:TheHistoryofGolf"HistoricUK,https://wwwhistoric-ukcom/HistoryUK/HistoryofScotland/The-History-of-Golf/Accessed3Aug2024
"GolfSlang"GolfDrives,https://wwwgolf-drivescom/guides/golf-slang/Accessed3Aug2024
"SixWaysGolfCoursesHurttheEnvironment"Causes,https://wwwcausescom/articles/54567-six-ways-golf-courses-hurt-environmentAccessed3Aug2024
CLEANAIR,CLEARFUTURE:COMBATINGPOLLUTIONWITHADVANCEDTECHNOLOGIESAUDREYCHOI
“Ambient(Outdoor)AirPollution”WorldHealthOrganization,WorldHealthOrganization,wwwwhoint/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ambient-(outdoor)-air-qualityand-healthAccessed5Aug2024
AmericanLungAssociation“2024‘stateoftheAir’ReportRevealsMost‘Hazardous’AirQualityDaysin25Years”AmericanLungAssociation, www.lung.org/media/press-releases/sota-2024.Accessed5Aug.2024.
Phillips,Jodie“InnovativeTechnologiesforAirPollutionReduction:What’sontheHorizon?”SustainableLiving,19Sept2023, wwwenvironmentalconsortiumorg/innovative-technologies-for-airpollution-reduction-whats-on-the-horizon/
Publication: Synthify
Editor: Hajin Ra, Jinsun Yoo, Eunha Jeon, Philip Jeon, Haelim Hahn, Jiyeon Park, Gabeen Ko, Ayeon Cho, Rachel Cho, Dominic Hahm, Colin Chung, Jason Hwang, Jian Hong, David Jin
Writer: Yewon Park, Woojin Chung, Takato Ikeda, Seoyoon Won, Rhianna Kim, Joseph Lim, Hosung Bae, Harshita Yangalasetty, Ethan Kim, Audrey Choi
“The environment is where we all meet; where we all have a mutual interest; it is the one thing all of us share.”
-Lady Bird Johnson