

Addressing the Growing Manufacturing Workforce Crisis
As of 2025, the U.S. manufacturing sector faces a pivotal crossroad. Technological innovation is advancing at an unprecedented pace, yet deep-rooted workforce challenges threaten to undermine America’s global competitiveness. Breakthroughs in automation, artificial intelligence, and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) are revolutionizing production but without a highly skilled, future-ready workforce to harness these tools, the full potential of this transformation will remain unrealized.
Manufacturers across the country are confronting mounting pressures:
• Rising labor costs and persistent talent shortages,
• Disruptions in global and domestic supply chains, and
• Rapid shifts in trade policy and reshoring strategies.
The labor market data continues to confirm a widening skills gap. Hundreds of thousands of positions remain unfilled— from CNC machinists and maintenance technicians to quality inspectors and engineers. These shortages represent lost productivity, delayed innovation, and weakened resilience for manufacturers of all sizes.
At the same time, policy changes in trade, tariffs, and reshoring have dramatically reshaped supply chains. While some manufacturers have adapted successfully, many face operational uncertainty, cost increases, and a pressing need to pivot strategies without the workforce to support transformation.
12,893,460
2025 Manufacturing Industry Jobs
Source: Lightcast, July 2025
5,232,133
2025 Manufacturing Industry Hires
Quality Control job postings grew 365% from 2020 to 2024
Workforce readiness is no longer optional; it is a national imperative. America needs a talent pipeline that is agile and aligned with the technologies and realities of modern manufacturing.


1
Executive Summary
The Manufacturing Imperative—Workforce Pipeline Challenge (MI-WPC) is a bold, nationwide initiative led by SME in partnership with 25 community colleges across 17 states. Designed to close the skills gap in manufacturing, MI-WPC is aligning education and industry to create a stronger workforce pipeline to support the growing manufacturing needs.
Now in its second year, the initiative is translating local innovation into national impact, centered around three priority areas:
Increasing Career Awareness
Backed by SME’s marketing expertise and data from the Demography & Engagement (D&E) Study, colleges are launching precision-targeted campaigns aimed at reshaping public perception of modern manufacturing. These strategic efforts are not only generating immediate interest in education and training but also engaging a broad audience including students, parents, career switchers, and those previously disengaged and guiding them toward high-opportunity, living-waged, future-focused career pathways.
2

226,209 individuals were reached through Meta marketing initiatives, increasing career awareness (3 select colleges reporting)
Expanding Faculty and Faculty Capacity
To keep pace with rising employer demand and overcome chronic faculty shortages, colleges are scaling up their instructional capacity. With investments in new training facilities, the expansion of evening and weekend programs, colleges are implementing creative partnerships with retired industry professionals helping to strengthen the pipeline of qualified instructors. Meanwhile, some states are taking bold policy steps such as adjusting compensation structures for example, to attract and retain high-demand technical educators.
3
Deepening Industry Engagement
In partnership with SME and Manufacturing Association Advisory Council (MAAC), colleges are leveraging regional labor market data, employer surveys, and local roundtables to strengthen ties with small- and mid-sized manufacturers. This collaboration is directly informing curriculum updates, ensuring that credentials reflect real-time job demands. Colleges are also collaborating with their local employers to develop earn-and-learn models. This opens the door for more individuals to access career-aligned training without interrupting their livelihoods.
12,914 New Students Enrolled across Programs (Spring data, 23 colleges reporting)
1,169
Earn and Learn Participants (Spring 2025 data, 21 colleges reporting)
As MI-WPC enters the second half of its three-year initiative, this report showcases how innovative, locally driven solutions are tackling some of the nation’s most urgent manufacturing workforce challenges. Together, we are not just preparing the next generation of manufacturing talent, rather, we are boldly empowering individuals, revitalizing communities, and laying the foundation for a workforce that will power the future of American manufacturing.

MI-WPC: Year 2 – From Planning to Action
Entering 2025 with strong momentum, the Manufacturing Imperative—Workforce Pipeline Challenge (MI-WPC) has transitioned from strategic planning to coordinated national action. At the start of the year, MI-WPC finalized and launched a bold strategic roadmap, co-developed with leaders from the President’s Advisory Council (PAC), Champion’s Advisory Council (CAC), and the Manufacturing Association Advisory Council (MAAC). This roadmap is more than a vision; it is a tactical blueprint for measurable progress across 25 colleges in 17 states.
The roadmap targets six high-impact areas central to both industry needs and learner success:
• Strengthening partnerships between colleges and manufacturers
• Aligning education and training with real-time workforce demands
• Expanding career awareness to share the benefits of manufacturing
• Building faculty, facilities, and equipment capacity to meet current and future demand
• Offering flexible scheduling and learning options that fit the lives of working adults and non-traditional students
• Deepening community engagement to build the next generation of talent from the ground up



These principles are shaping every partnership, pilot, and innovation launched this year. SME is accelerating implementation, providing national expertise, investing in proven strategies, and supporting colleges as they deploy bold, community-informed solutions that drive local and regional impact. MI-WPC laying the foundation for a manufacturing workforce that’s prepared, resilient, and ready for the future.



Increasing Career Awareness
Despite significant advancements in the industry, many students still hold outdated understanding of manufacturing viewing it as low-skill, low-wage, and unsafe. These misconceptions continue to discourage younger generations from exploring careers in the field. In reality, modern manufacturing is a dynamic, technology-driven sector offering livingwaged, high-skill jobs that are critical to both the U.S. economy and national security.
To help mitigate this misconception, SME is supporting colleges with targeted marketing campaigns, rooted in data and tailored to each community. Through the Demography and Engagement (D&E) Study, colleges are equipped with tools to identify and engage learners most likely to enroll in manufacturing programs. These campaigns use demographic and behavioral data, personalized outreach, and modern messaging to reshape public perception and connect with students, parents, and career influencers.
Colleges are also testing creative career awareness strategies through high school counselors. For example, College of Lake County hosts K–12 counselors at its Advanced Manufacturing Center to showcase the clean, innovative nature of today’s manufacturing environment. These firsthand experiences help shift perceptions and open new conversations around manufacturing career pathways. These efforts ensure that counselors are equipped with accurate, up-to-date knowledge to guide students toward high-growth opportunities in modern manufacturing.
MI-WPC’s Demography & Engagement Study is scaling to collaborate with all 25 community colleges to increase manufacturing and STEM awareness for all learners.
226,209 Reached Individuals
778
Leads or Interested Individuals
Cost and time are reported as the main barriers to access training and education.
(3 colleges reporting)



Some programs, such as Mechatronics, have seen lower enrollment due to lack of awareness. Greenville Technical College tackled this by launching a focused messaging campaign highlighting the strong job outlook and high wages associated with Mechatronics careers. The result was a measurable increase in both interest and enrollment — proving that the right message, delivered the right way, can drive real outcomes.



Expanding Faculty and Faculty Capacity
Faculty serve as more than instructors; they are mentors, program champions, and vital bridges between educational institutions and industry. Their ability to translate real-world experience into classroom instruction is critical to preparing learners for today’s advanced manufacturing environment. However, across the MI-WPC network, colleges report difficulty attracting and retaining instructors, largely due to wage disparities between industry roles and academic appointments.
In response, colleges are implementing innovative approaches to strengthen faculty pipelines and improve instructional capacity. These include:
• Refining job descriptions to prioritize essential industry experience over formal academic credentials where appropriate,
• Leveraging professional, industry, and alumni networks to identify teaching talent,
• Developing “grow-your-own” pathways, which encourages high-performing graduates to return as instructors after gaining experience in the field, and
• Partnering with large employers to engage retiring or semi-retired professionals interested in transitioning into education.
By rethinking faculty recruitment and embracing cross-sector collaboration, MI-WPC colleges are laying the groundwork for sustainable growth in both program offerings and instructional quality. These efforts are essential to ensure that learners are not only entering high-demand fields but are guided by experienced mentors equipped to help them succeed.

A strong example of this collaboration can be seen in the partnership between St. Louis Community College and Boeing. Through a strategic, yet informal, pipeline of Boeing retirees who transition from the shop floor to the classroom. These experts bring decades of hands-on expertise into the classroom while enriching the learning experience for students.


Deepening Industry Engagement
Strong industry engagement continues to be a critical driver of effective workforce development across the MI-WPC network. Colleges are partnering closely with employers to ensure that training programs reflect the realities of the modern manufacturing sector and remain responsive to its evolving skill demands.
To better engage small and mid-sized manufacturers (SMMs), SME implemented a strategic, multi-pronged approach. This includes leveraging regional labor market data, job postings, and proprietary analytics to identify workforce needs. In addition, SME co-hosted local industry roundtables with the Manufacturing Association Advisory Council (MAAC) to facilitate open dialogue between educators and manufacturers. Employers emphasized the high demand for roles such as CNC operators, machinists, welders, and maintenance technicians. Employers also emphasized the importance of blueprint reading, mechanical aptitude, metrology, and software proficiency, along with soft skills like teamwork, reliability, and adaptability to new technologies.
To deepen industry engagement between the colleges and industry, SME awarded professional memberships to all MI-WPC Champions. These connections to SME’s 115 local chapters help faculty and administrators stay informed on emerging trends, promote continued collaboration with industry, and ensure that education and workforce development efforts remain tightly aligned with real-world needs.


APPENDIX


State Manufacturing Association’s Promising Practices
Manufacture Alabama has developed and incubated a career exploration program titled Girls Learning About Manufacturing (GLAM). GLAM engages girls from 6th-12th grade, through VIP Tours and Summer Day Camps. GLAM Camp, which launched in the Mobile area in partnership with Bishop State Community College, is poised to scale across the state with the goal of engaging more students and additional industry partners and growing the number of women pursuing manufacturing careers.

The Illinois Manufacturers’ Association (IMA) is a key partner in scaling transformative advanced manufacturing pathways across the state. In collaboration with Education Systems Center at NIU, the IMA supports regional teams working to expand high-quality, work-based learning experiences aligned with Illinois’ Manufacturing and Engineering Career Pathway Endorsements. Launched three years ago across eight regions, the initiative has already enrolled more than 1,400 students. By strengthening employer-education partnerships and creating clear, equitable pathways from high school into in-demand careers, this program helps address workforce needs while opening doors to high-wage, high-skill jobs for learners across the state.
The Michigan Manufacturers Association plays a central role in fostering workforce partnerships across local communities statewide. By helping to scale promising practices from smaller regions, the Association supports the growth of Michigan’s manufacturing talent pipeline. Key focus areas include pre-apprenticeship models, K–12 engagement, and outreach to adult learners.
Minnesota Precision Manufacturing Association is furthering career awareness through a statewide marketing awareness campaign. This campaign has tested innovative approaches such as sponsoring a local kids soccer team with Minnesota Manufactured on the front of their jerseys. This strategy includes follow-up emails to the parents on the team and social media posts on the clubs pages explaining the career opportunities in manufacturing guiding them to a career portal.
State Manufacturing Association’s Promising Practices
Missouri Association of Manufacturers (MAM) regularly tours manufacturing facilities all over the state of Missouri with the objective of connecting with manufacturers, understand their operations, learn about their challenges, celebrate their successes and gain insights on their pain points from workforce challenges to gathering innovative promising practices. These gathered challenges and solutions are passed along to advance increased productivity, to share best practices, to connect resources and information, and to support the manufacturing industry. MAM also hosts manufacturers regional roundtables and other events to create a culture of connection and increase communications across the manufacturing industry, which truly strengthens the network.
The North Carolina Manufacturers Alliance has identified a growing communication gap between younger and older generations in the manufacturing workforce—a challenge that can directly impact retention. When younger workers are unclear about advancement opportunities, wage growth, or long-term career pathways, it can lead to disengagement and turnover. To address this, the association is fostering stronger generational understanding by hosting targeted events and industry roundtables, and by collaborating with key partners to promote transparent communication strategies within manufacturing workplaces. These efforts aim to build a more connected, fulfilled, and stable workforce across all age groups.
MACNY, the Manufacturers Association and The Manufacturers Alliance of New York developed apprenticeship and pre-apprenticeship programs to support increasing workforce needs at industrial locations throughout the state. To date they have enrolled 182 in pre-apprenticeship programs and 1,184 in apprenticeship programs. Apprentices can access state funding sources to pay for the Related Training and Instruction.

The Ohio Manufacturers’ Association (OMA) has developed the comprehensive Ohio Manufacturing Competency Model that serves as a unified framework to align education and workforce development with industry needs. Built on foundational manufacturing skills, the model also includes three industry-specific layers: EV, Battery, and EVSE; Aerospace & Defense; and Semiconductor. Developed through extensive employer engagement, including in-person meetings and surveys, this model ensures that training reflects real-world requirements. It is inspired by federal competency frameworks and is increasingly adopted across Ohio, with many schools assessing their curricula against the model and using the results to adapt their programs. As the model evolves, the OMA will continue to update it to stay aligned with the rapid pace of technological change in manufacturing.
APPENDIX
State Manufacturing Association’s Promising Practices
South Carolina Manufacturers Alliance developed an Educator Industry Academy made up consisting of up to 18 educators across the state. The design of this academy is to increase manufacturing career awareness among key student influencers: teachers in the classroom. This year-long academy will introduce math and science teachers, educators, and administrator’s to manufacturing through immersive experiences, industry tours, and handson learning.
Tennessee Association of Manufacturers, in partnership with SCORE and as a subgrantee of a JP Morgan Chase grant, is developing a teacher externship program aimed at increasing classroom-based career awareness in manufacturing. This initiative will immerse educators in real-world manufacturing environments, providing firsthand experience with modern technologies, processes, and workplace expectations. By bringing teachers onto the manufacturing floor, the program equips them to better inform and inspire students about high-tech, high-demand career pathways in the industry.
Dallas County Manufacturers Association is partnering with Dallas College, Garland Chamber of Commerce, Garland ISD and several local industry partners to support the FAME program. This career aligned work-based learning program ensures learners are prepared to successfully enter the workforce, while meeting the local employers needs. This talent pipeline development program establishes a stream of world class maintenance technicians suitable for manufacturing companies and a career path for motivated, STEM-minded high-school and college students who are diligent, motivated and who enjoy working with their hands.

The Virginia Manufacturers Association (VMA) supports manufacturers in establishing and expanding Registered Apprenticeship programs. By offering tailored guidance and helping align training with industry needs, VMA strengthens employer capacity to attract and retain talent. This approach enhances the manufacturing workforce pipeline and serves as a model for scalable, industry-led workforce solutions.
APPENDIX
For-Credit Students Non-Credit Students

Spring 2025: New Students Breakdown
For-Credit Students
Dual Credit Students Non-Credit Students
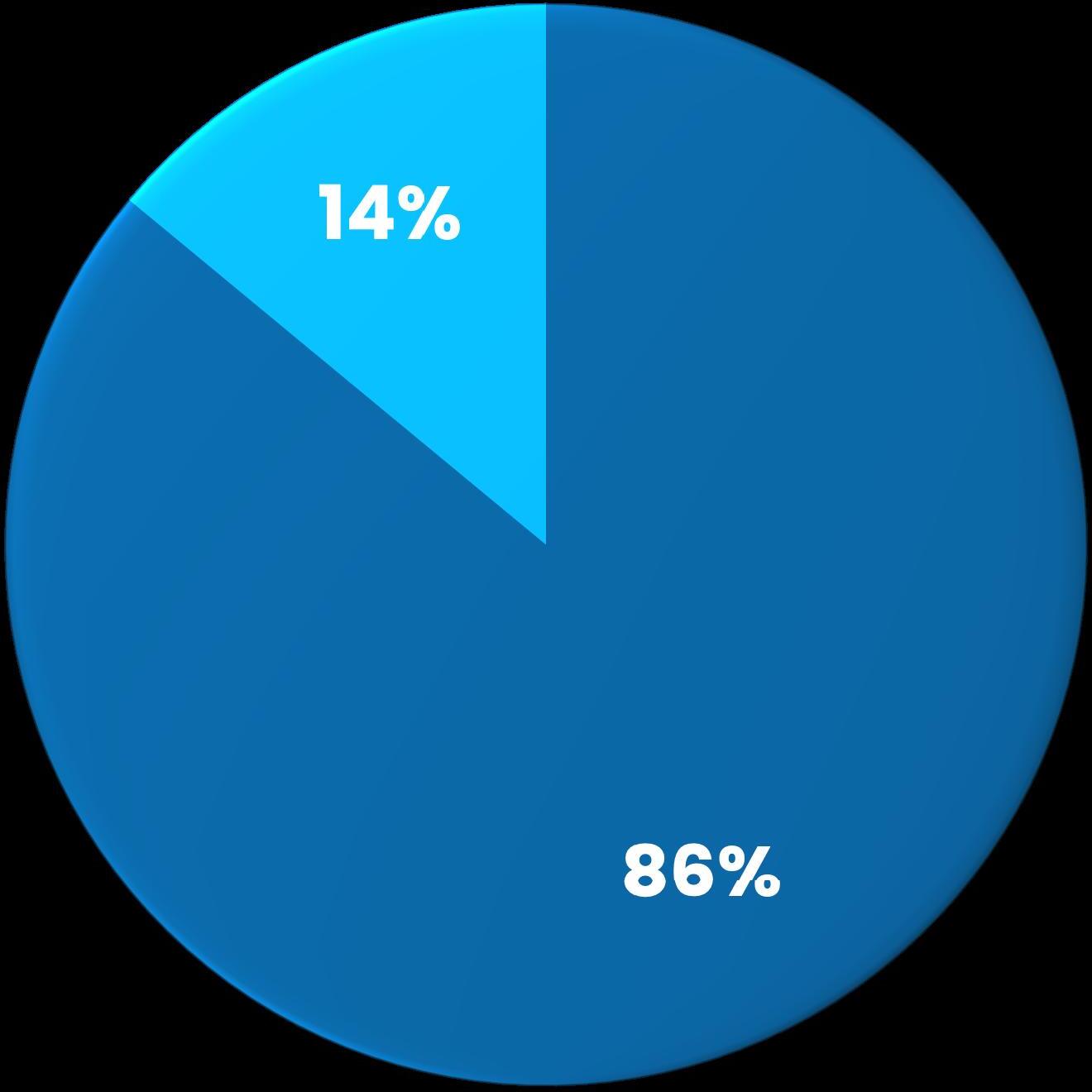
Spring 2025: Non-Traditional Student Breakdown
JII Students
244 or 5,079 or 11,072 or 1,842 or
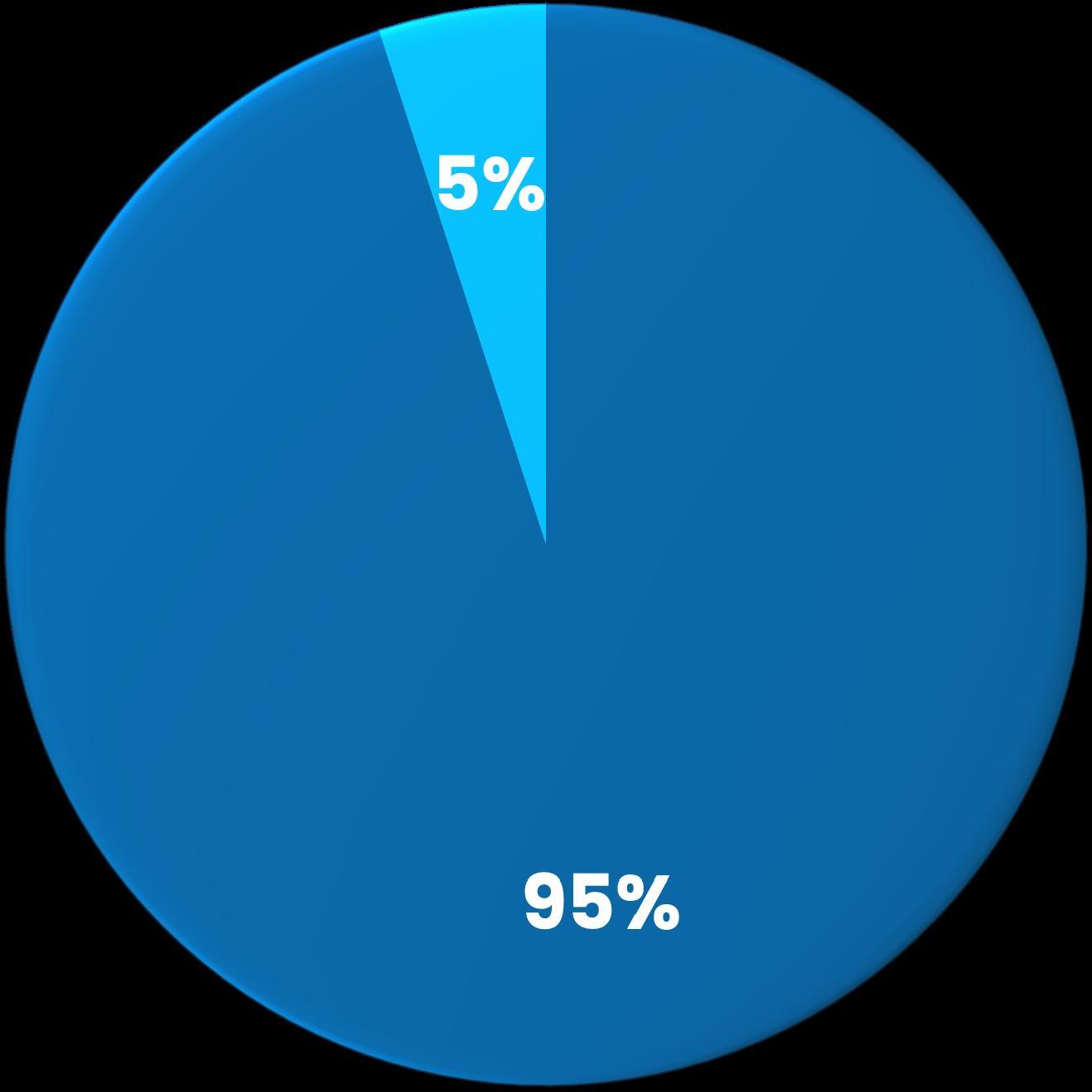
Dual Credit Students JII Students
Industry Credentials Earned
APPENDIX
Earn & Learn Participants
Employer Sponsored Training Participants
Spring 2025: Programmatic Breakdown
Industry Credentials Earned
Earn & Learn Participants
Employer Sponsored Training Particiants

1,169 or 850 or
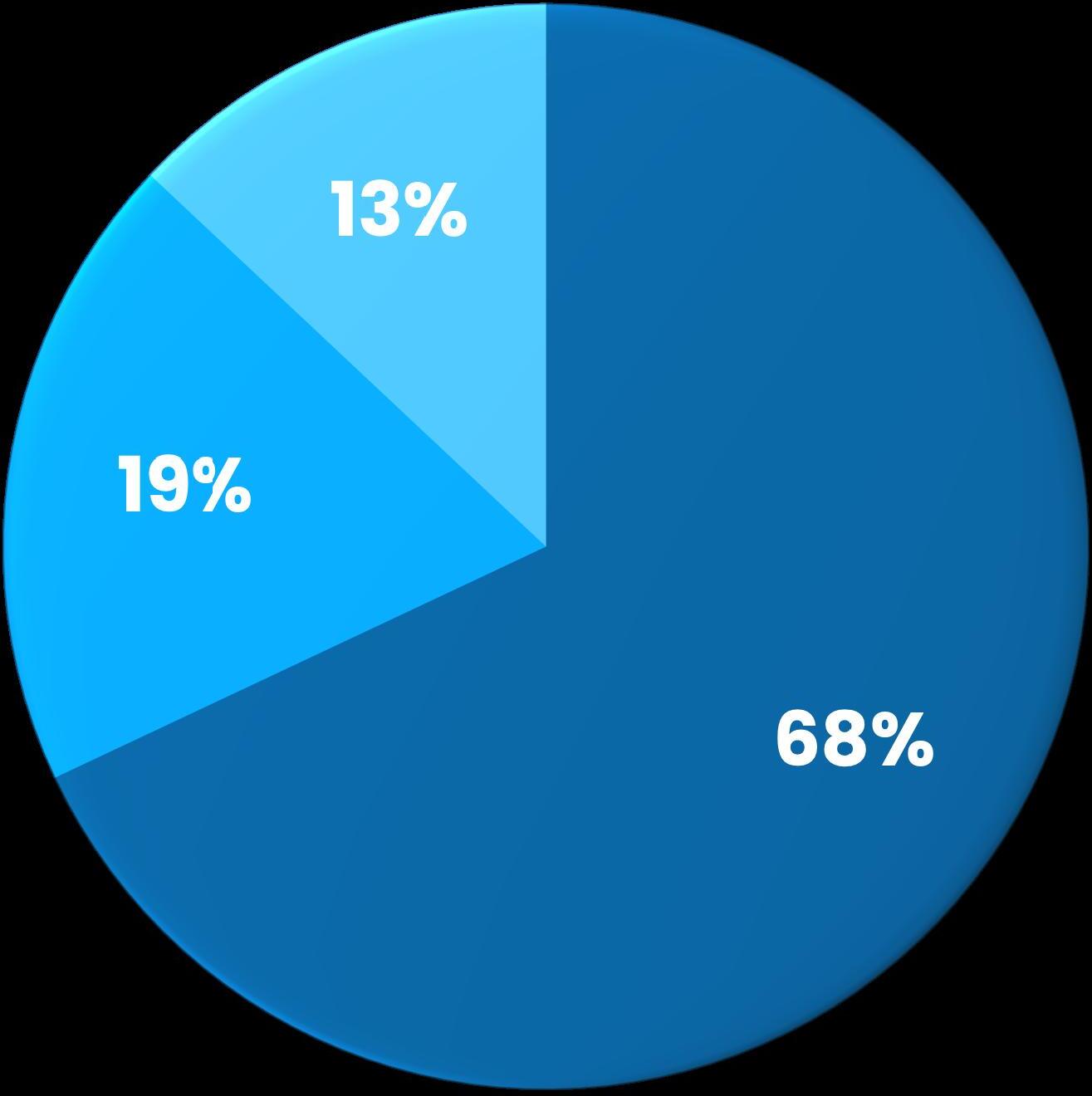
4,388 or
Most of the enrolled students were dual or concurrent enrollment students as compared to a smaller portion of the Justice Involved Individual (JII) population. Many states are investing in dual enrollment support, creating an ease of access to dual enrollment populations while increasing credential attainment across the states. A majority of the students enrolled were in for-credit courses. The for-credit courses typically have access to additional funding sources such as Pell or scholarships.
CONTACT US
Dr. Deb Volzer Vice President of Workforce Development (614) 499-5889, dvolzer@sme.org

Established in 1932 as a nonprofit organization, SME represents the entire North American manufacturing industry, including manufacturers, academia, professionals, students, and the communities in which they operate. Together we share one common belief: Manufacturing holds the key to economic growth and prosperity. SME accelerates new technology adoption and inspires and builds North America’s talent and capabilities to advance manufacturing as a diverse, thriving and valued ecosystem that drives competitiveness, resiliency, and national security. We believe in technology’s power and humanity’s innovation to advance our society and meet many national challenges. We design new ways to understand and solve problems, and our solutions advance the next wave of innovation and growth. Learn more at SME.org.

