What is Nuclear Medicine?
Nuclear medicine is a form of sensitive imaging that uses minimal amount of radioactive material to diagnose and treat diseases such as cancers, h e a r t d i s e a s e s , g a s t r o i n t e s t i n a l , b r a i n a n d e n d o c r i n e ( t h y r o i d , p a r a t h y r o i d ) d i s o r d e r s . These tests can detect diseases at very early stage before it can be seen on any other imaging methods.
Diagnosis
D e p e n d i n g o n t h e t y p e o f n u c l e a r t e s t , t h e r a d i o t r a c e r i s e i t h e r i n j e c t e d , s w a l l o w e d o r inhaled as a gas which eventually collects and a c c u m u l a t e s i n t h e o r g a n o r a r e a o f t h e b o d y being imaged.
Treatment
N u c l e a r m e d i c i n e a l s o o ff e r s a w i d e r a n g e o f t h e r a p e u t i c p r o c e d u r e s l i k e r a d i o a c t i v e i o d i n e ( I - 1 3 1 ) t h e r a p y t o t r e a t t h y r o i d c a n c e r a n d benign thyroid diseases. Nuclear medicine also offers treatment for bone pains from the spread o f c a n c e r, t h i c k e n i n g o f b l o o d , a n d t u m o u r s o r i g i n a t i n g f r o m t h e e n d o c r i n e a n d n e r v o u s system.
W h a t a r e s o m e c o m m o n u s e s o f t h e procedure?
R a d i o a c t i v e m a t e r i a l s a r e u s e d i n i m a g i n g p r o c e d u r e s t o v i s u a l i s e t h e s t r u c t u r e a n d f u n c t i o n o f d i ff e r e n t o r g a n s i n t h e b o d y. T h i s procedure can be used to diagnose and stage
cancers and see the response to therapy. It can a l s o i d e n t i f y a n d l o c a t e o t h e r a b n o r m a l i t i e s o r disorders of various organs
Nuclear medicine therapies:
• R a d i o a c t i v e i o d i n e ( I - 1 3 1 ) t o t r e a t o v e r a c t i v e t h y r o i d g l a n d ( h y p e rthyroidism) and thyroid cancer.
• Radioactive materials to treat pain from spread of tumour to the bones.
How can I prepare for the procedure?
P r e p a r a t i o n f o r d i ff e r e n t s c a n s v a r i e s f r o m f a s t i n g f o r s o m e h o u r s , d i s c o n t i n u i n g d i ff e r e n t medications, avoiding beverages and is based on the scan that you will undergo. Physician can a s k a b o u t a n y m e d i c a t i o n t h a t y o u a r e t a k i n g and advise discontinuing it The doctor will also ask about any allergy that you might have. All women should always inform their physician if there is any possibility that they are pregnant or i f t h e y a r e b r e a s t f e e d i n g . I f r e q u i r e d , a p r e g n a n c y t e s t w i l l b e p e r f o r m e d b e f o r e t h e procedure.
How does the procedure work?
With ordinary x-ray examinations, an image is made by passing x-rays through the body from an outside source. In contrast, nuclear medicine procedures use a radioactive material called a r a d i o - p h a r m a c e u t i c a l o r r a d i o t r a c e r, w h i c h i s injected into your blood, swallowed or inhaled. T h i s r a d i o a c t i v e m a t e r i a l a c c u m u l a t e s i n t h e o r g a n o r a r e a o f y o u r b o d y b e i n g e x a m i n e d , w h e r e i t g i v e s o ff g a m m a r a y s . A g a m m a
c a m e r a , P E T s c a n n e r o r p r o b e d e t e c t s t h i s r a d i a t i o n a n d w i t h t h e h e l p o f a c o m p u t e r creates pictures
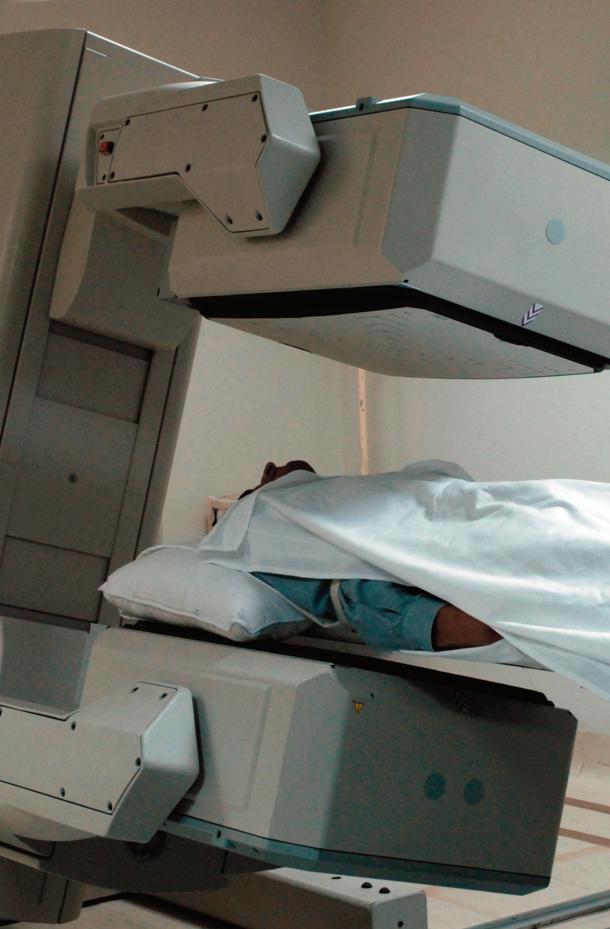
How is the procedure performed?
Nuclear medicine imaging is usually performed on an outpatient basis, but can be performed on hospitalised patients.
You will be positioned on an examination table. If necessary, a nurse or technologist will insert an intravenous line into a vein in your hand or arm.
I t c a n t a k e a n y w h e r e f r o m s e v e r a l s e c o n d s t o several days for the radiotracer to travel through your body and accumulate in the organ or area being studied. As a result, imaging may be done immediately, a few hours later, or even several d a y s a f t e r y o u h a v e r e c e i v e d t h e r a d i o a c t i v e material.
W h i l e t h e c a m e r a i s t a k i n g p i c t u r e s , y o u w i l l n e e d t o r e m a i n s t i l l f o r b r i e f p e r i o d s o f t i m e I n s o m e c a s e s , t h e c a m e r a m a y m o v e v e r y c l o s e t o y o u r b o d y. T h i s i s n e c e s s a r y t o o b t a i n t h e b e s t q u a l i t y i m a g e s . I f y o u a r e a f r a i d o f c l o s e d
p l a c e s , y o u s h o u l d i n f o r m t h e s t a ff .
Young children may require gentle wrapping or s e d a t i o n t o h e l p t h e m h o l d s t i l l . I f y o u r d o c t o r feels sedation is needed for your child, you will receive specific instructions regarding when and i f y o u c a n f e e d y o u r c h i l d o n t h e d a y o f t h e
exam A doctors’ team will be available during t h e e x a m t o e n s u r e y o u r c h i l d ' s s a f e t y w h i l e under the effects of sedation.
When the examination is completed, you may be asked to wait until the technologist checks the images in case additional images are needed O c c a s i o n a l l y, m o r e i m a g e s a r e o b t a i n e d f o r c l a r i f i c a t i o n o r b e t t e r v i s u a l i s a t i o n o f c e r t a i n a r e a s o r s t r u c t u r e s . T h e n e e d f o r a d d i t i o n a l images does not necessarily mean there was a p r o b l e m w i t h t h e e x a m o r t h a t s o m e t h i n g abnormal was found, and should not be a cause of concern for you.
I f y o u h a d a n i n t r a v e n o u s l i n e i n s e r t e d f o r t h e procedure, it will usually be removed unless you are scheduled for an additional procedure that same day requires an intravenous line.
During radioactive iodine (I-131) therapy, which i s m o s t o f t e n a n o u t p a t i e n t p r o c e d u r e , t h e radioactive iodine is swallowed, either in capsule o r l i q u i d f o r m . P a t i e n t s r e c e i v i n g h i g h d o s e r a d i o a c t i v e i o d i n e a r e a d m i t t e d , a s p e r i n t e r n a t i o n a l r e c o m m e n d a t i o n t i l l r a d i a t i o n exposure is within accepted limits.
W h a t w i l l I e x p e r i e n c e d u r i n g a n d a f t e r the procedure?
Most nuclear medicine procedures are painless a n d a r e r a r e l y a s s o c i a t e d w i t h s i g n i f i c a n t discomfort or side effects.
When the radiotracer is given intravenously, you w i l l f e e l a s l i g h t p i n p r i c k w h e n t h e n e e d l e i s inserted into your vein.
When swallowed, the radiotracer has little or no t a s t e . W h e n i n h a l e d , y o u s h o u l d f e e l n o
d i ff e r e n t l y t h a n w h e n b r e a t h i n g r o o m a i r o r holding your breath.
W i t h s o m e p r o c e d u r e s , a c a t h e t e r m a y b e p l a c e d i n t o y o u r b l a d d e r, w h i c h m a y c a u s e temporary discomfort.
Unless your physician tells you otherwise, you m a y r e s u m e y o u r n o r m a l a c t i v i t i e s a f t e r y o u r nuclear scan. If any special instructions are necessary, you will be informed by a technologist, nurse or physician before you leave the Nuclear Medicine department.

It may also pass out of your body through your urine or stool during the first few hours or days following the test. You should also drink plenty of water to help flush the radioactive material out of your body, need to flush two times well after passing urine or stools.
Who interprets the results and how do I get them?
N u c l e a r M e d i c i n e P h y s i c i a n s a d m i n i s t e r radionuclide therapies and interpret the images. Registered hospital patients will get their reports from the medical record department in Services Building. The outside referred patients will get their reports the next day from the reception of nuclear medicine
Is the scan dangerous?
N u c l e a r m e d i c i n e t e s t s a r e v e r y s a f e b e c a u s e v e r y s m a l l a m o u n t o f r a d i o a c t i v e m a t e r i a l i s used.
What happens afterwards?
Yo u c a n g o h o m e a s s o o n a s t h e s c a n i s c o m p l e t e d . Yo u n e e d t o f o l l o w t h e d o c t o r ’s instructions after the scan.
What if I cannot keep my appointment?
Yo u s h o u l d c o n t a c t t h e N u c l e a r M e d i c i n e d e p a r t m e n t a s s o o n a s p o s s i b l e o n t h e telephone numbers given below. The staff in the Nuclear Medicine Department will be happy to answer any questions you may have.
Where can you get help?
If you have any queries or problems related to your procedure, please contact the Nuclear Medicine Department at +92 42 3590 5000 Ext 4192 or 4193.
