Porte-folio
Computational Urban Design
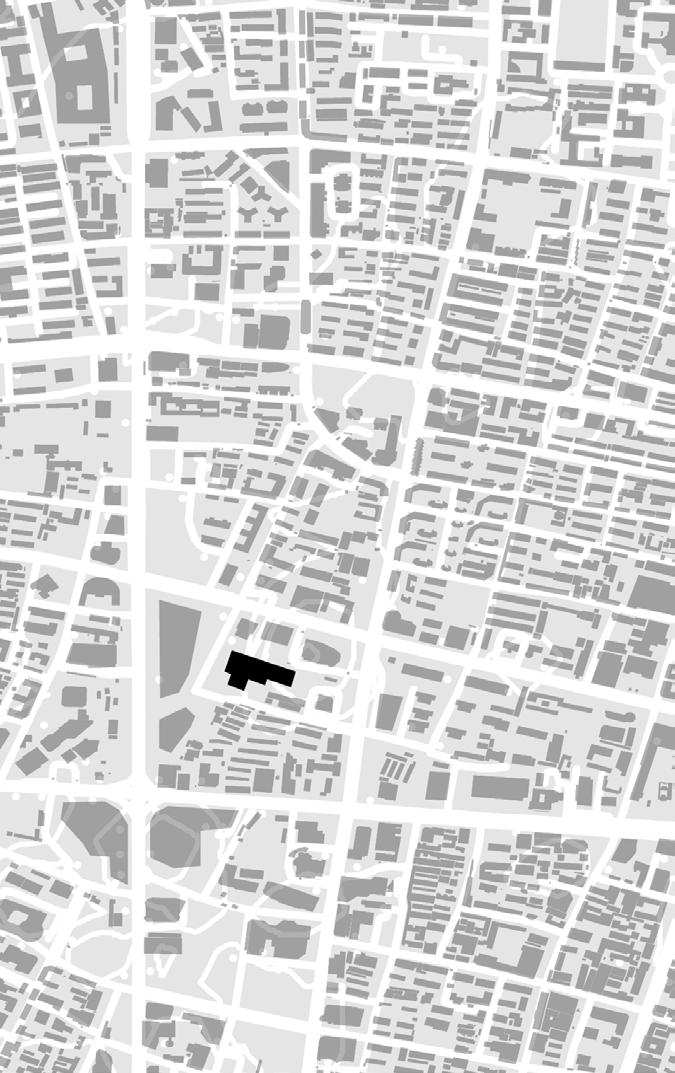
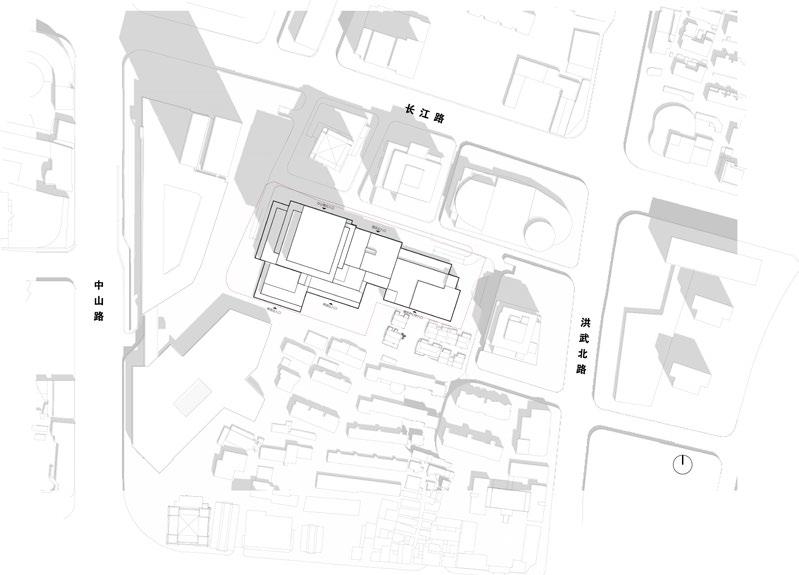
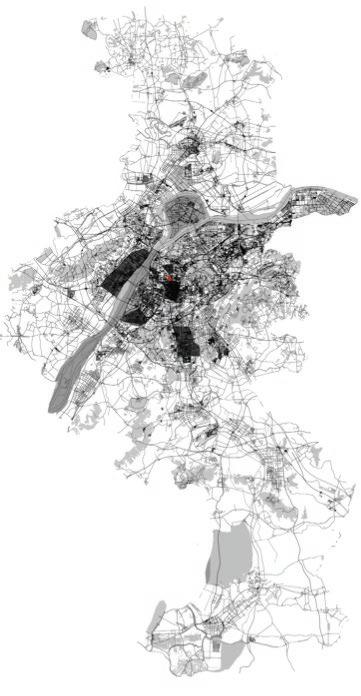
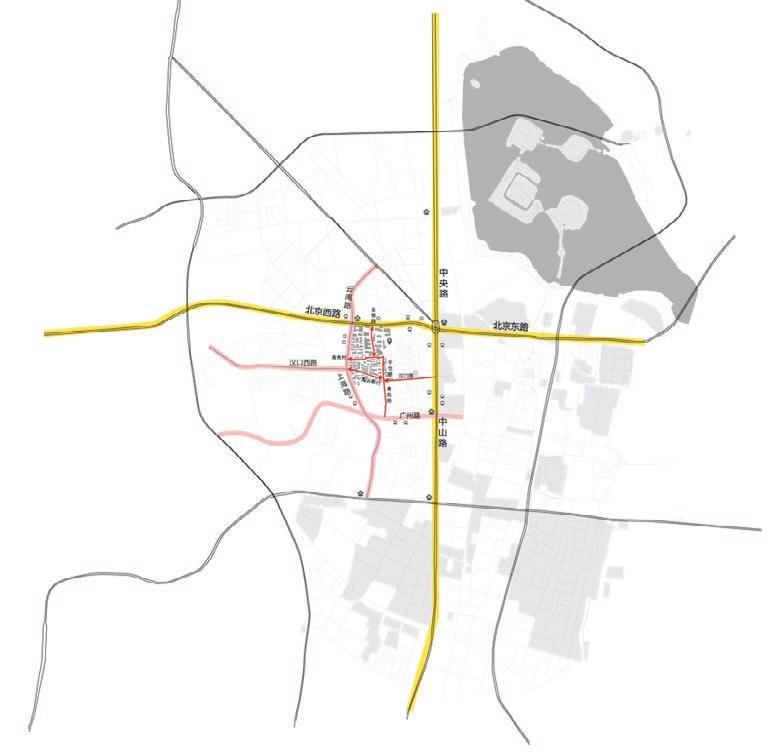
The information provided pertains to the Gulou campus area of Nanjing University in downtown Nanjing. The main phase of construction occurred in the 1980s and 1990s with the intention of utilising educational and research resources to develop “NJU’s Alley” and promote industrial growth. However, concerns have arisen regarding traffic congestion in the existing neighbourhood and inefficient use of space.
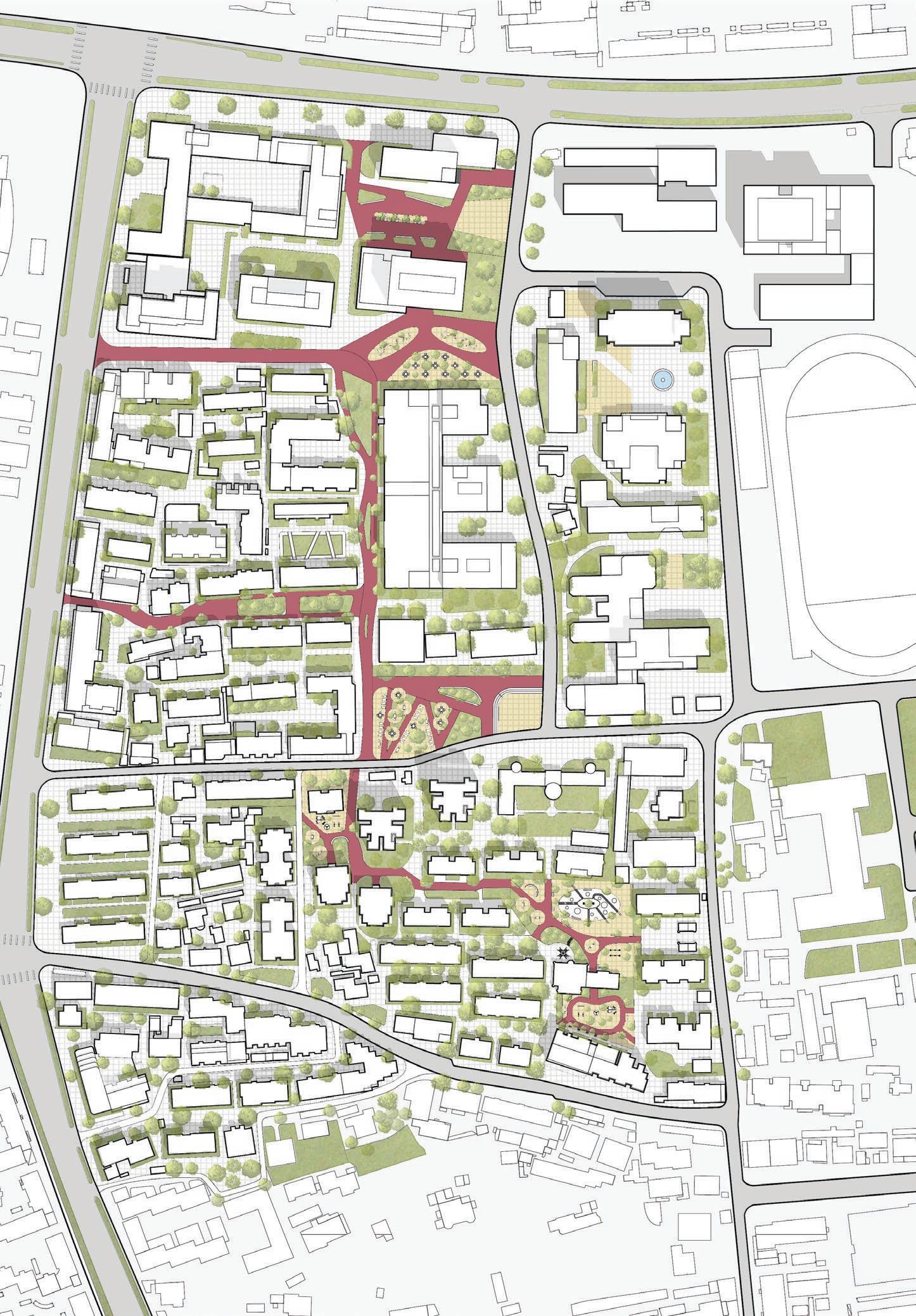
To address these issues, a project has been initiated to explore possibilities for new public spaces while preserving the architectural context of the old town. This involves reconfiguring the spatial organisation of the territory by creating activity and transport zones that break away from the original structure. The ultimate goal is to revitalise the area, making it more appealling to younger generations and fostering a sense of community.
Instructor: Tong, Zi-Yu
Architectural Design Studio VII Fall Semester, UG4

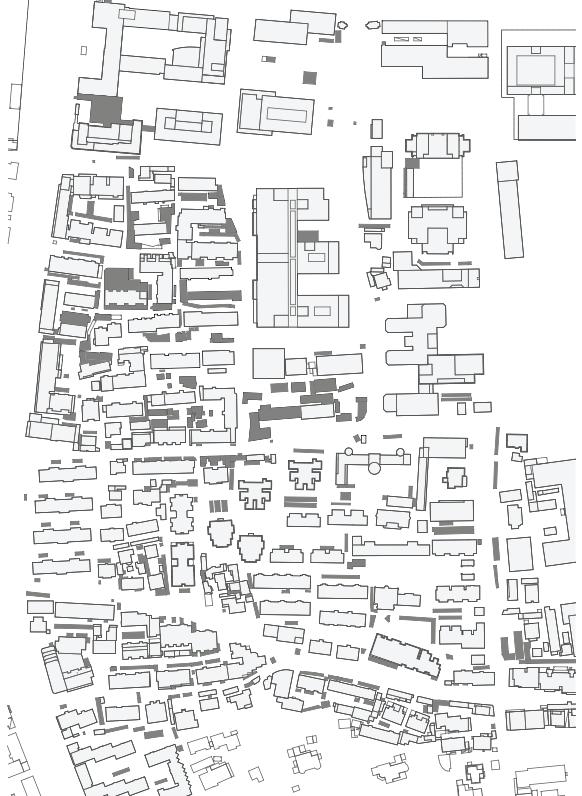
1st Phase : Research
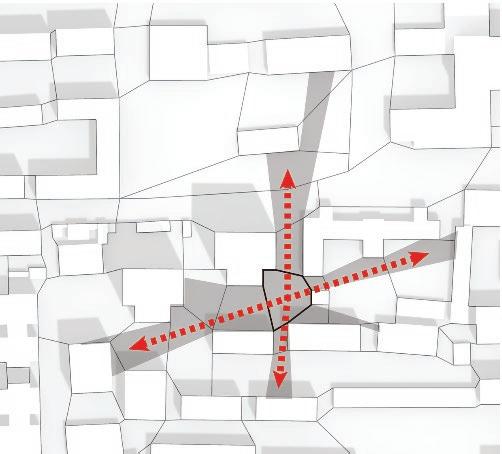
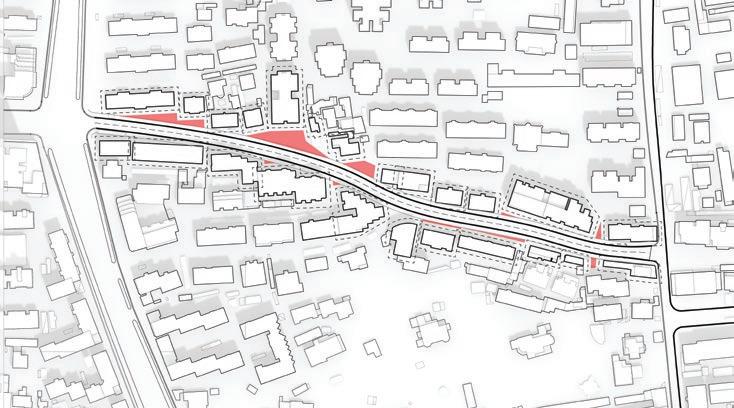
Mixture of pedestrians and vehicles
Narrow lanes restrict space and visibility
A lack of greenery makes for an unsatisfactory visual experience

Low efficiency in the use of empty space due to insufficient integration of functionalities
2nd Phase : Strategy
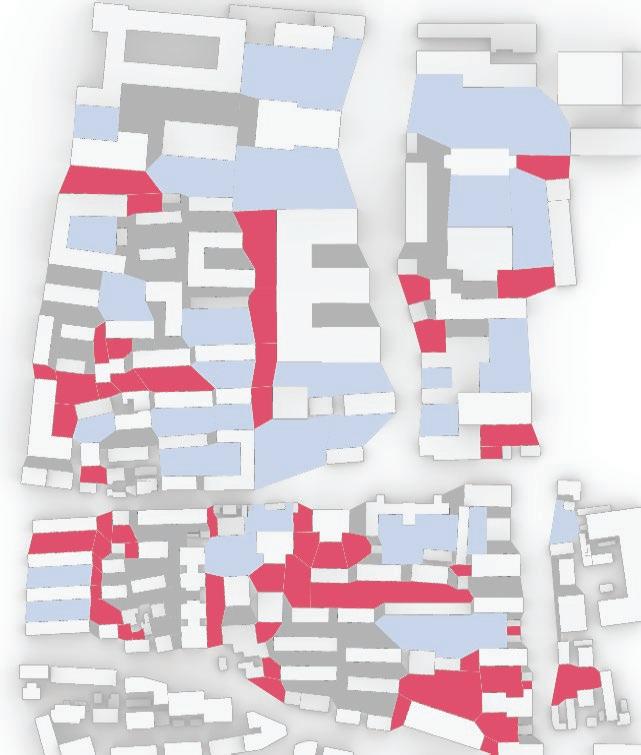
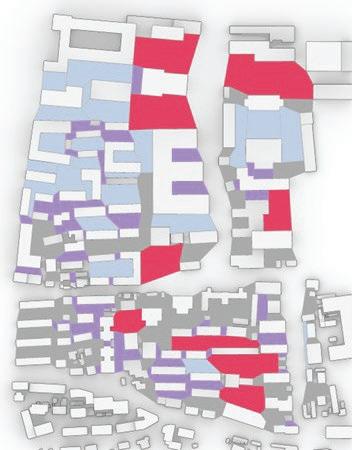
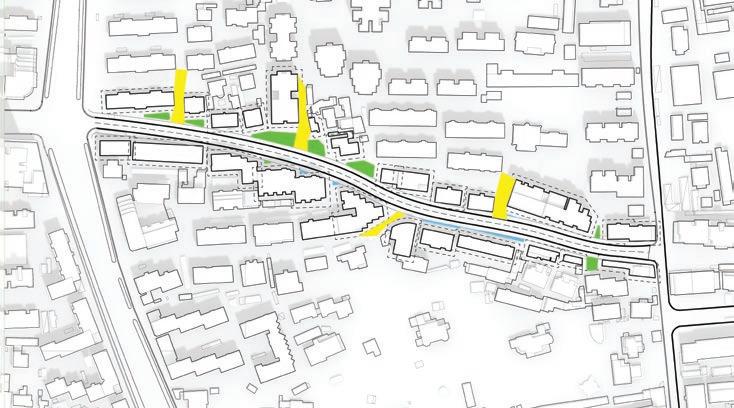
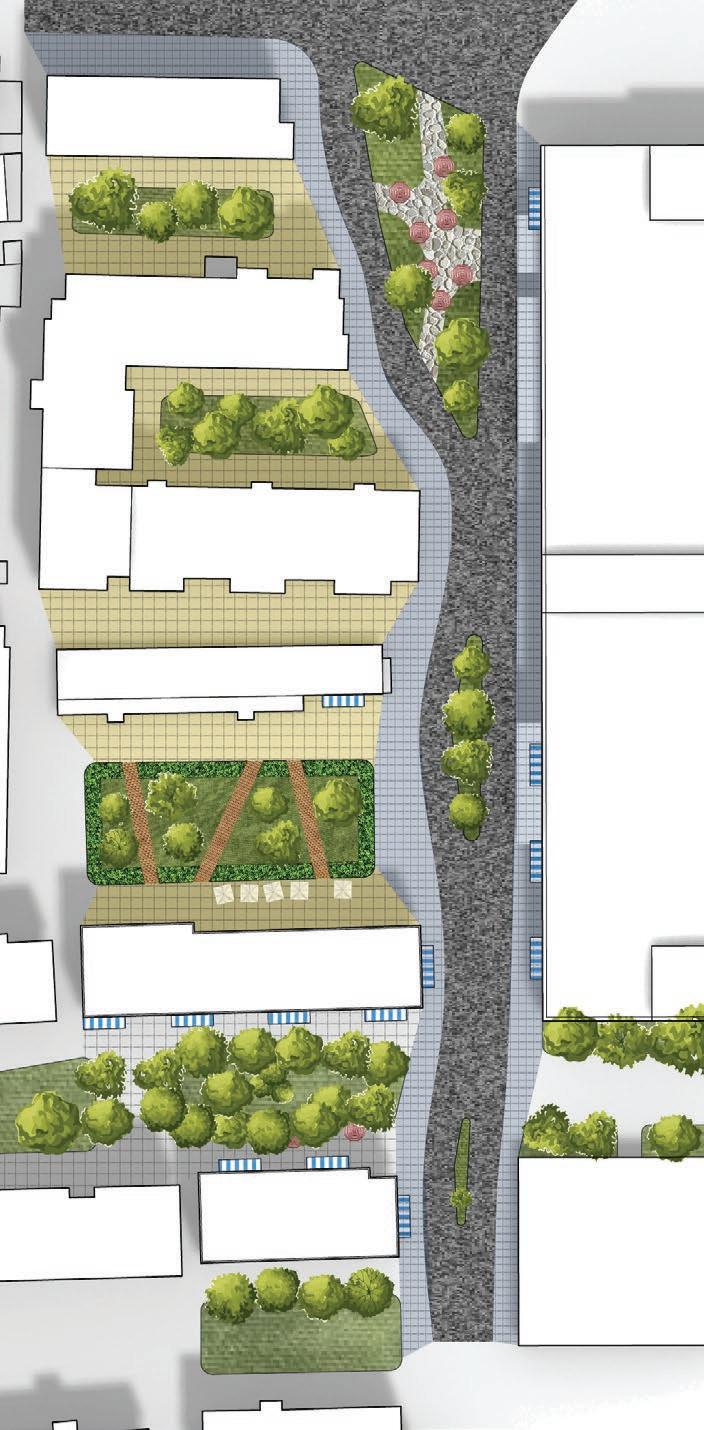
To improve the analysis of the area, it may be beneficial to evaluate the potential demolition of smaller or illegally constructed buildings. After the demolition process, it could be wise to simplify the design of any remaining structures to achieve the most favorable results. These efforts could ultimately lead to the optimal use of the area.
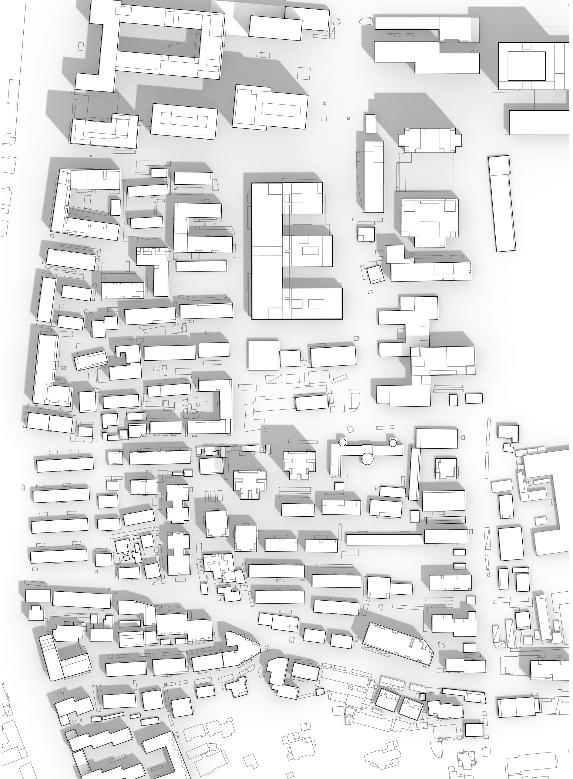
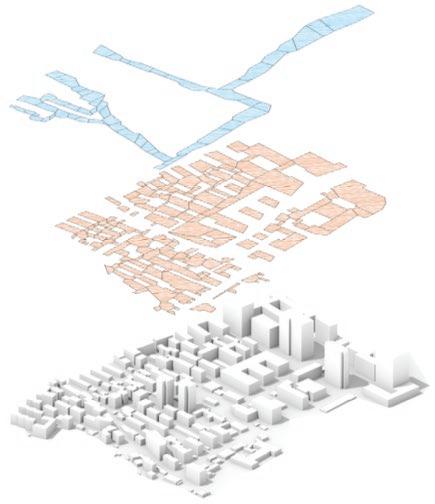
of building contours Segments of existing street and remaining spaces
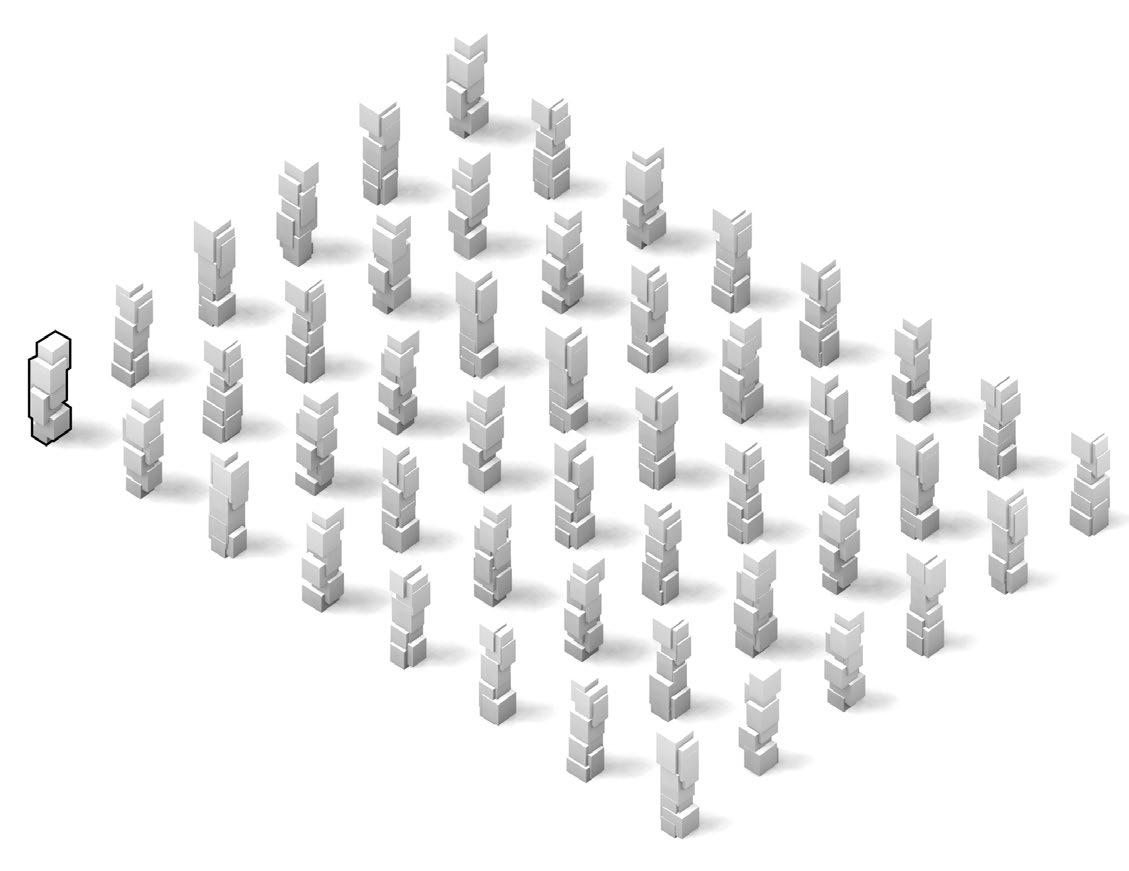
3rd Phase : Algorithmic Method
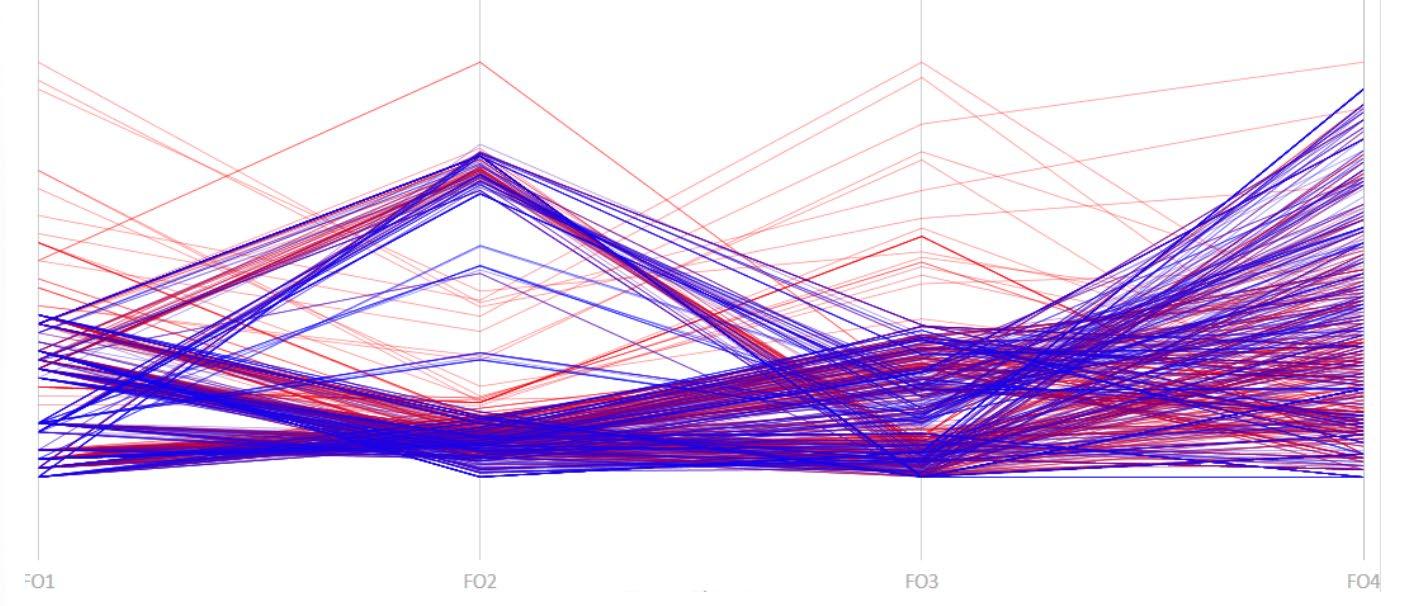
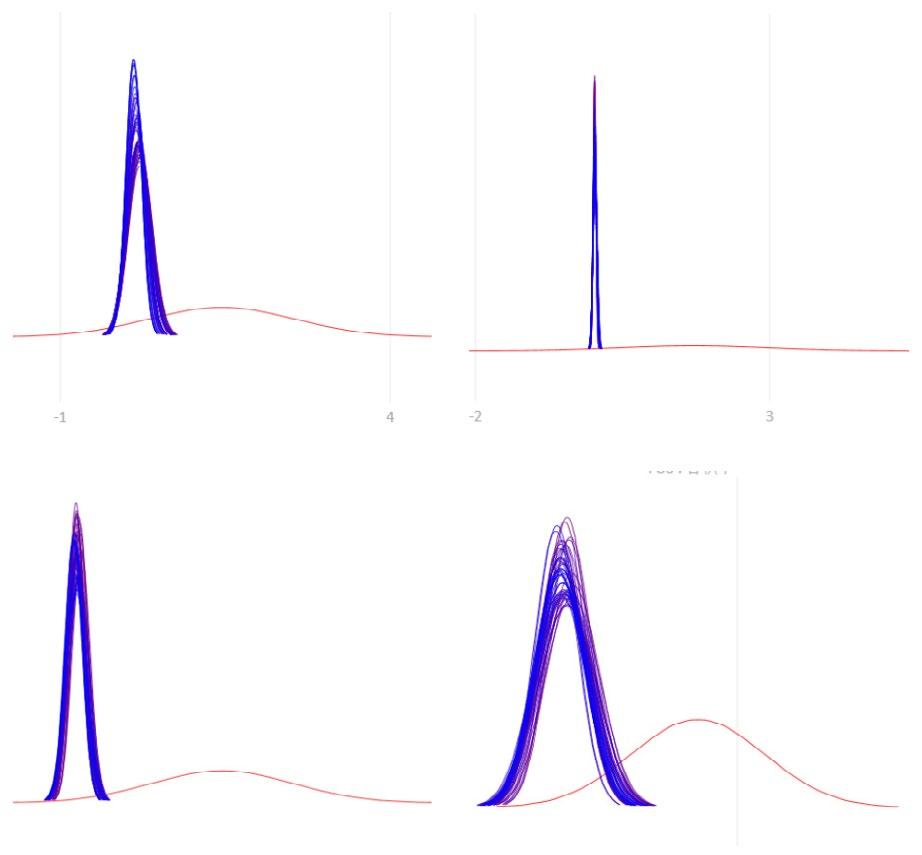
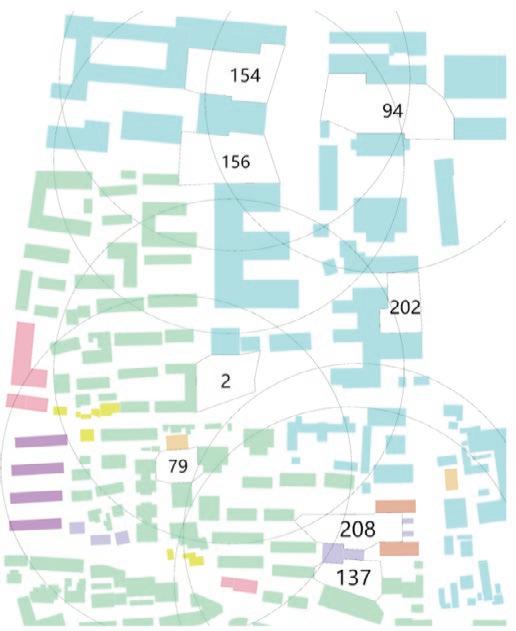
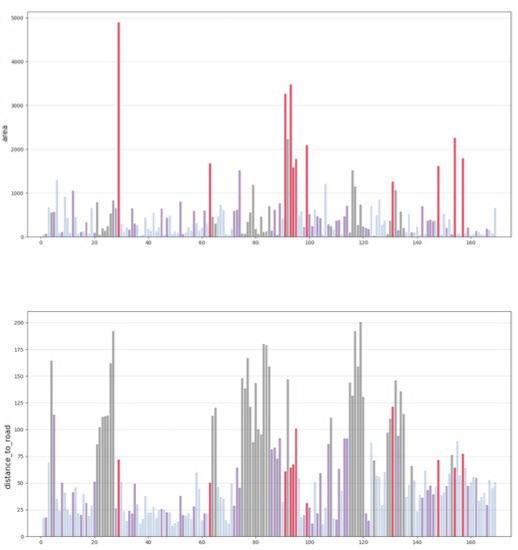
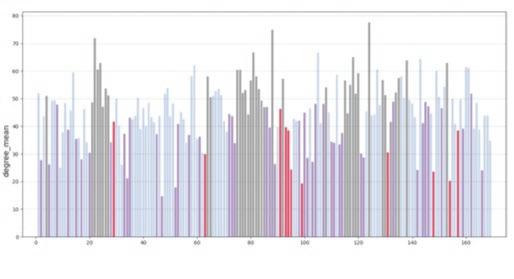
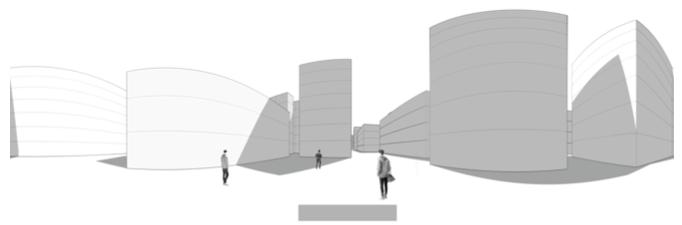
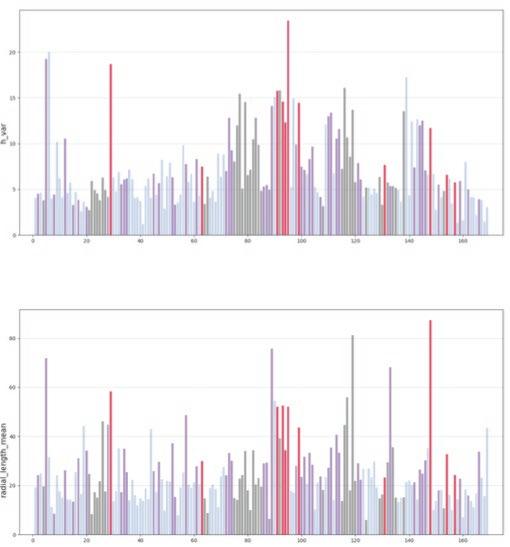
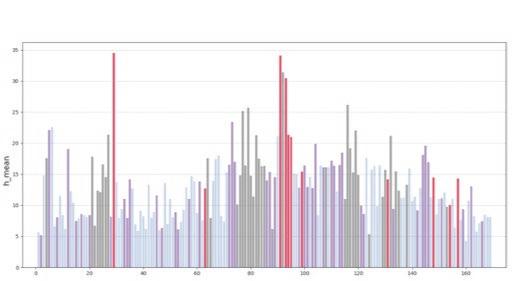
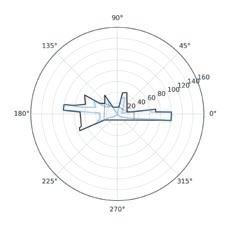
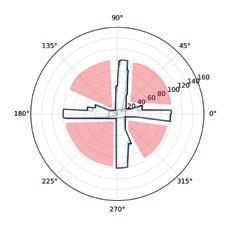
The fundamental aspect of this technique involves implementing the k-means machine learning algorithm to cluster the space and deduce the visual elements present. As a result, suitable options can then be chosen from the clustered space and incorporated into the space choices by utilizing a panoramic image.
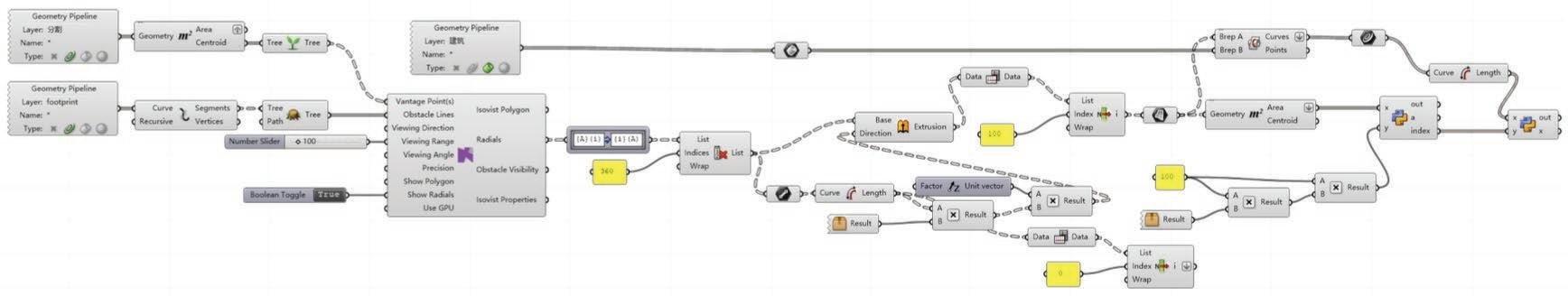
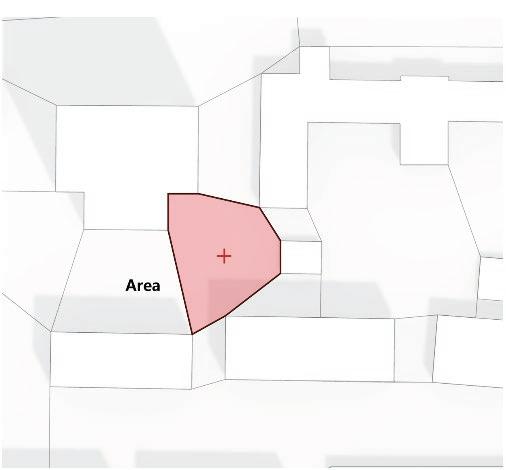
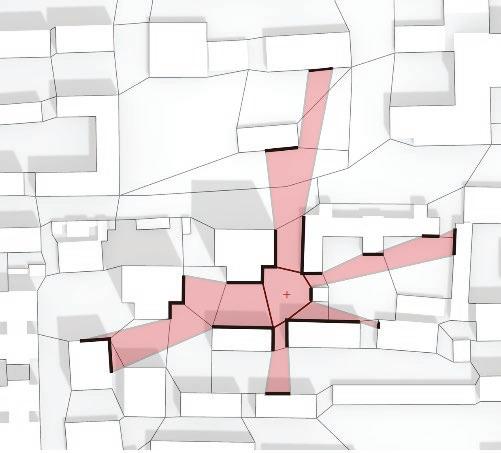
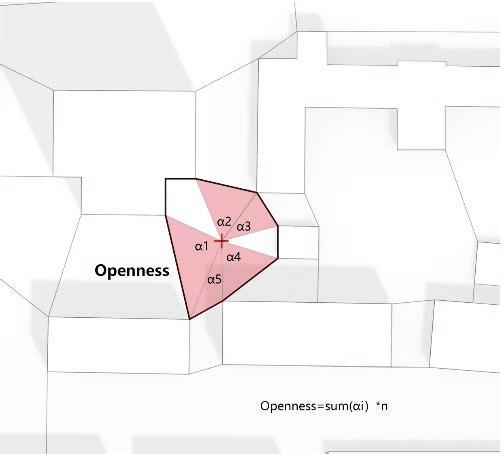
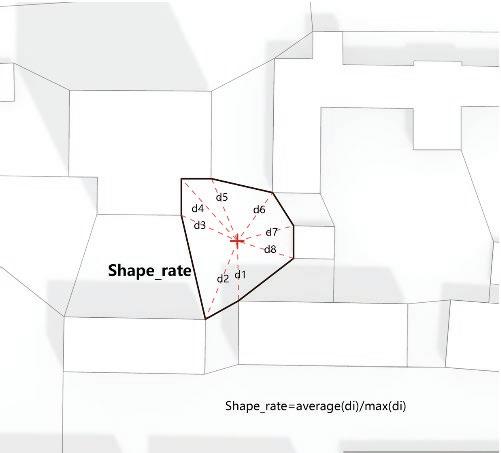
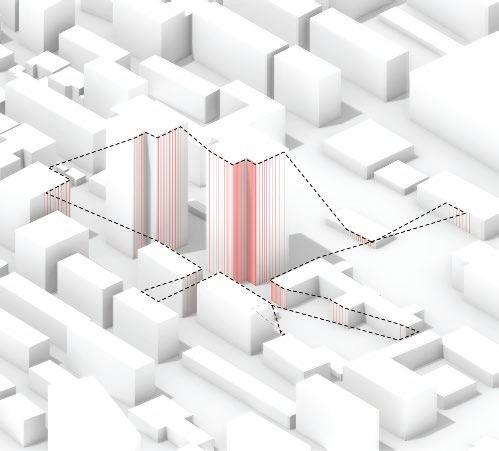
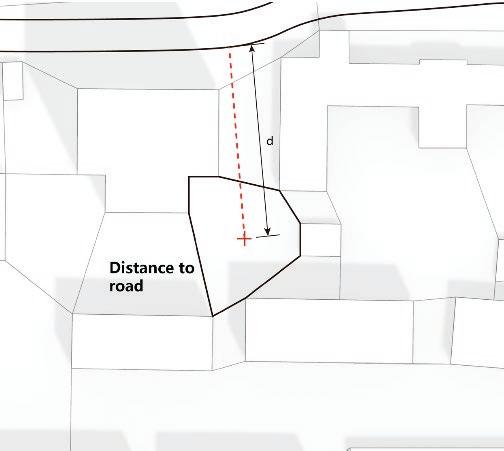
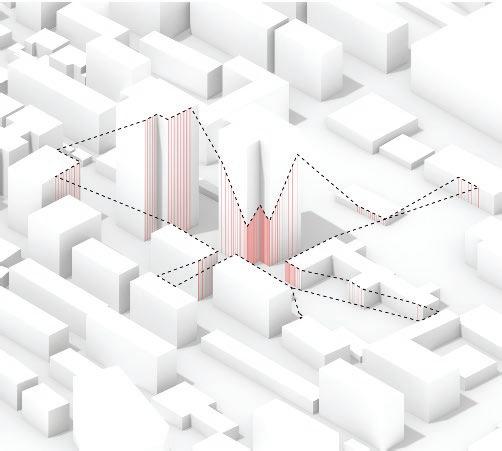
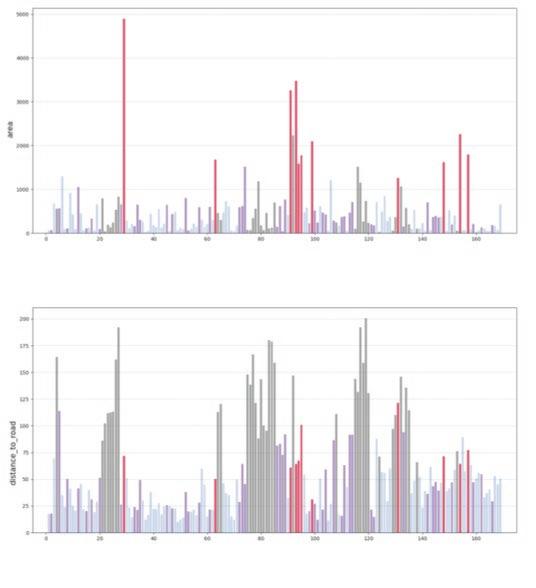
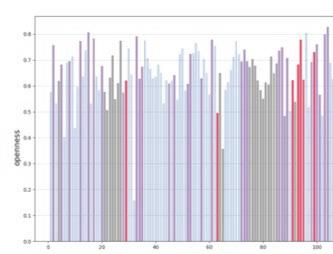
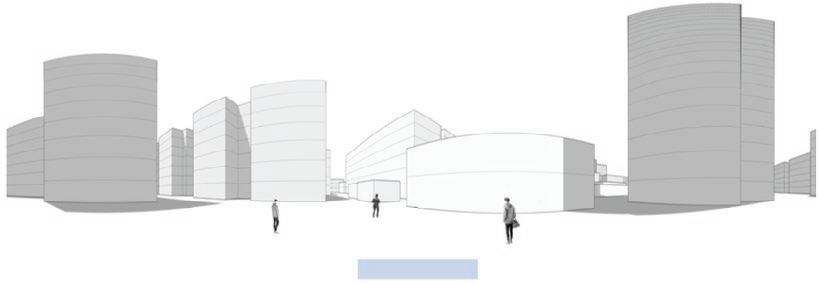
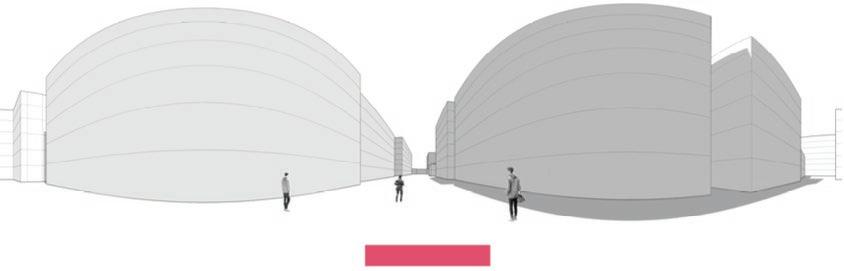
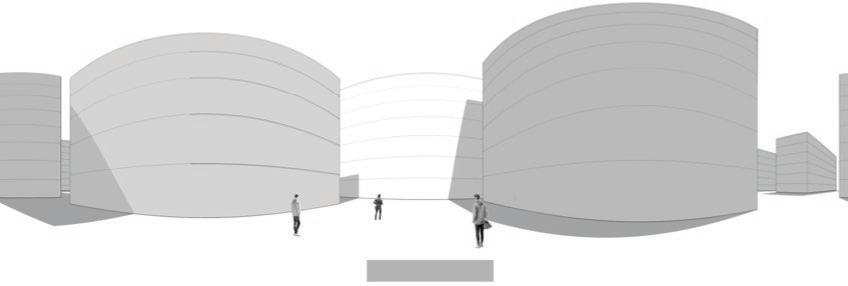
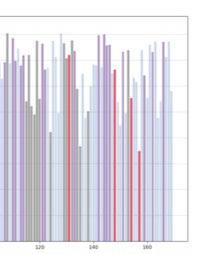
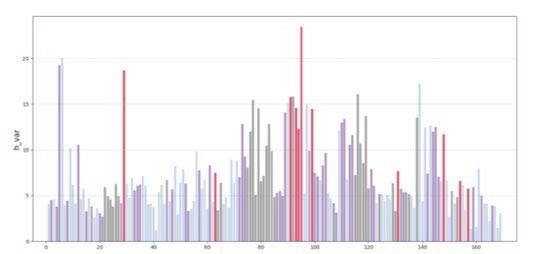
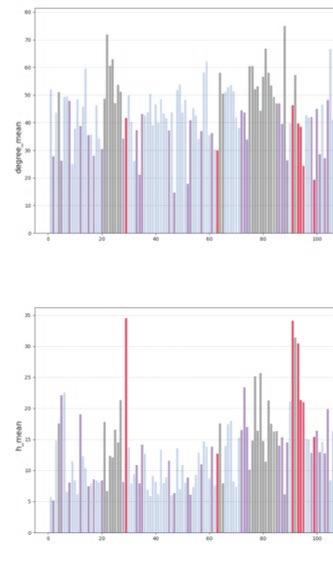
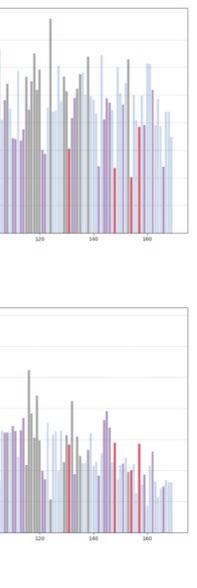
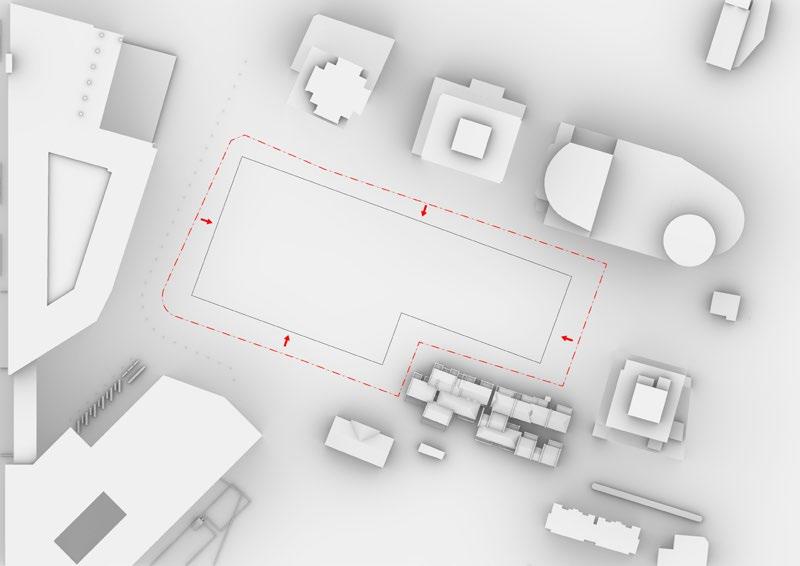
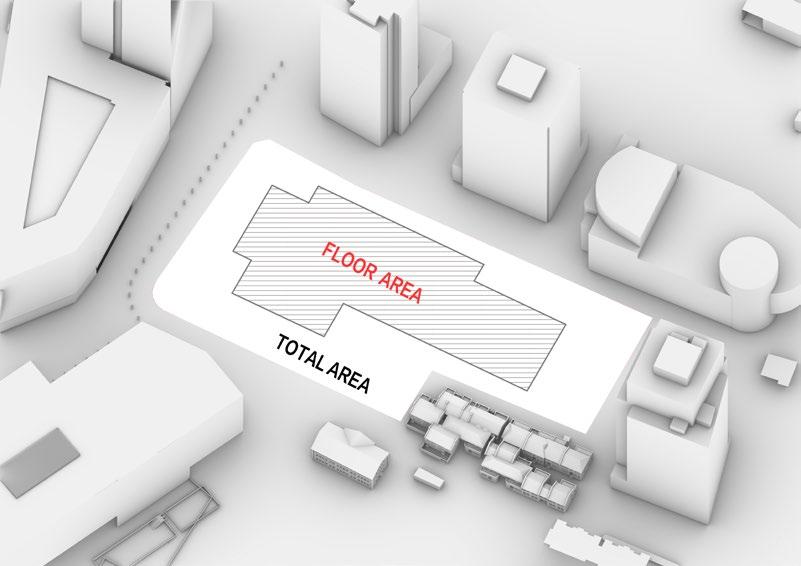
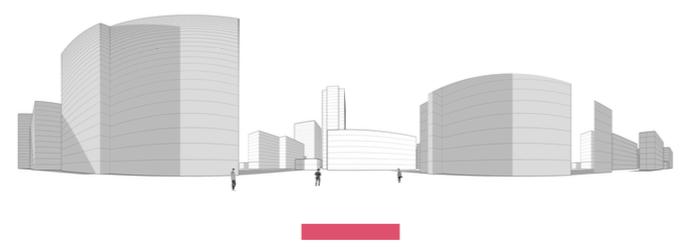
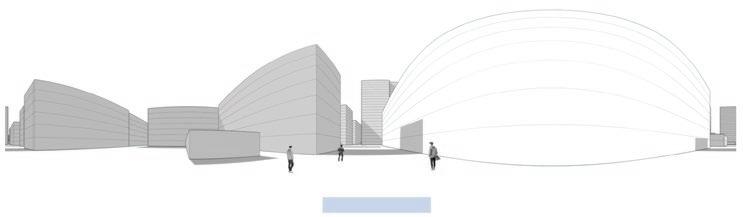
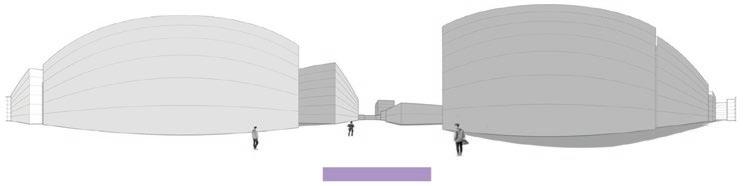
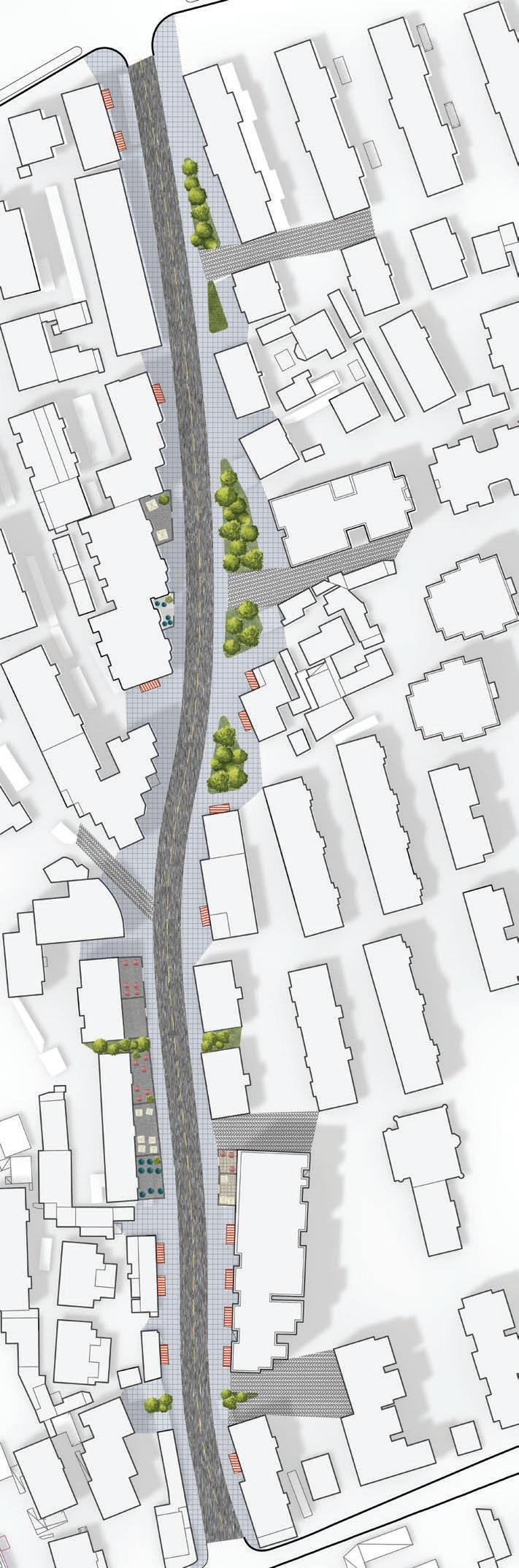
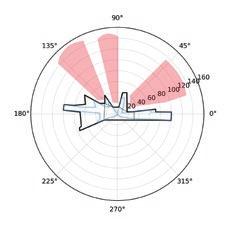
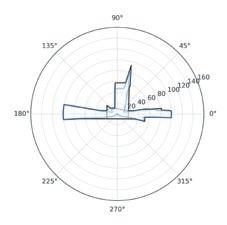
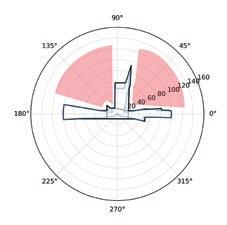
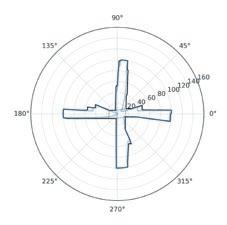
Following this, We began designing plazas that were determined based on cluster analysis. To create a pavement strategy that simulates pedestrian movement, We utilised Grasshopper to develop a programme that aligns with our vision. As a result, We have documented the outcome of each plaza in the figures specified alongside the corresponding plan.
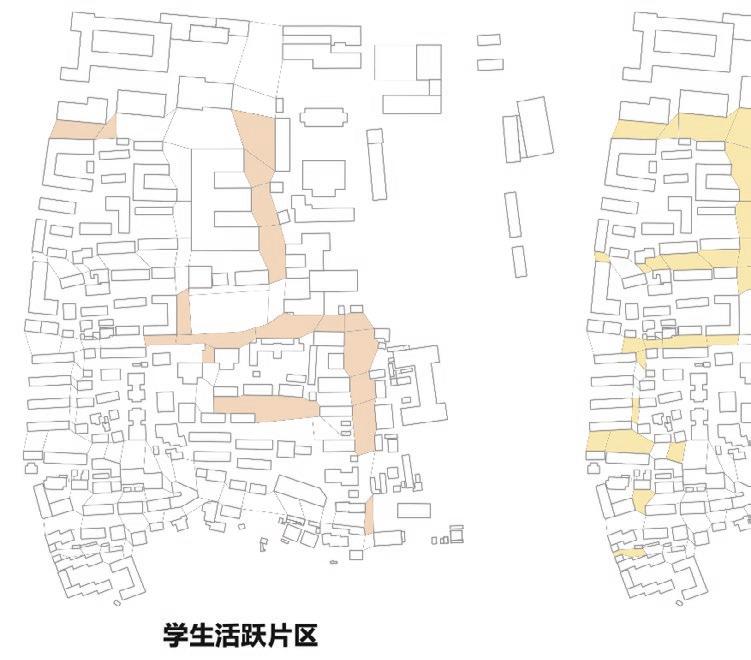
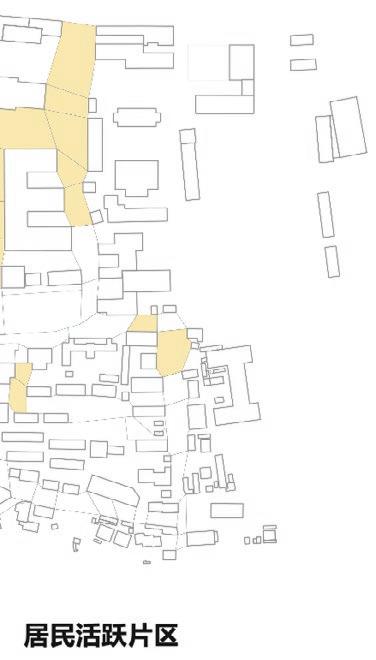
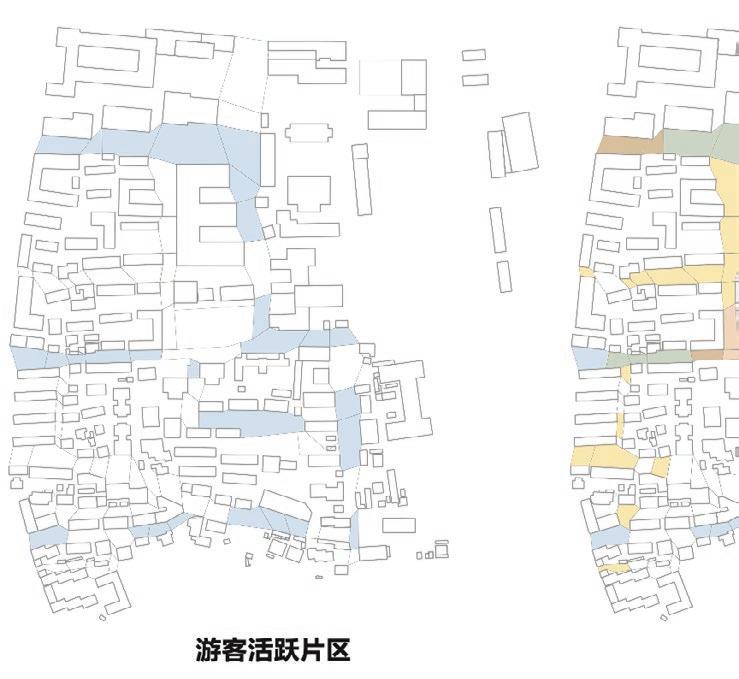
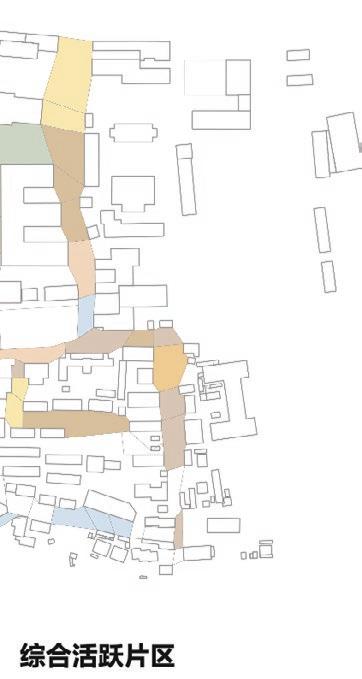
2nd Cluster
4th Phase : Design








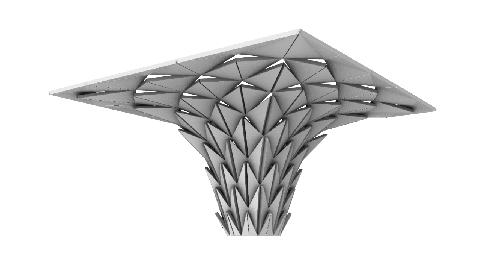
Algorithmic Skyscraper
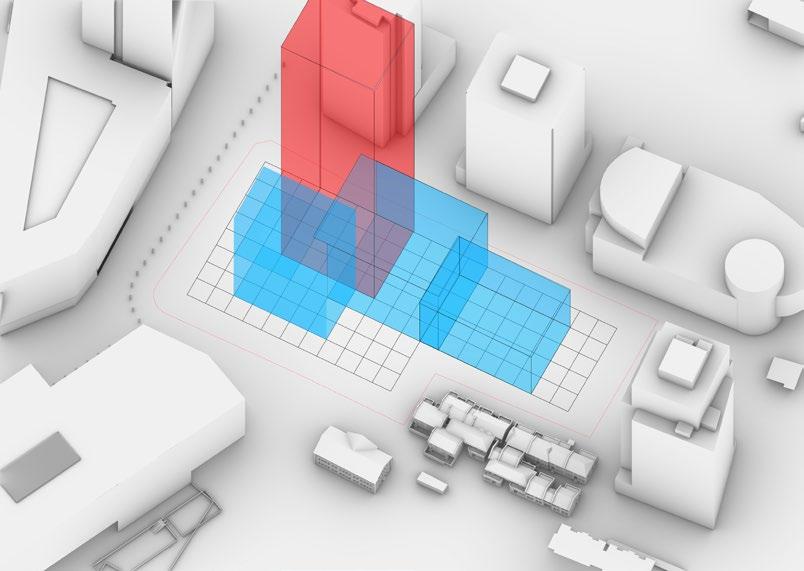
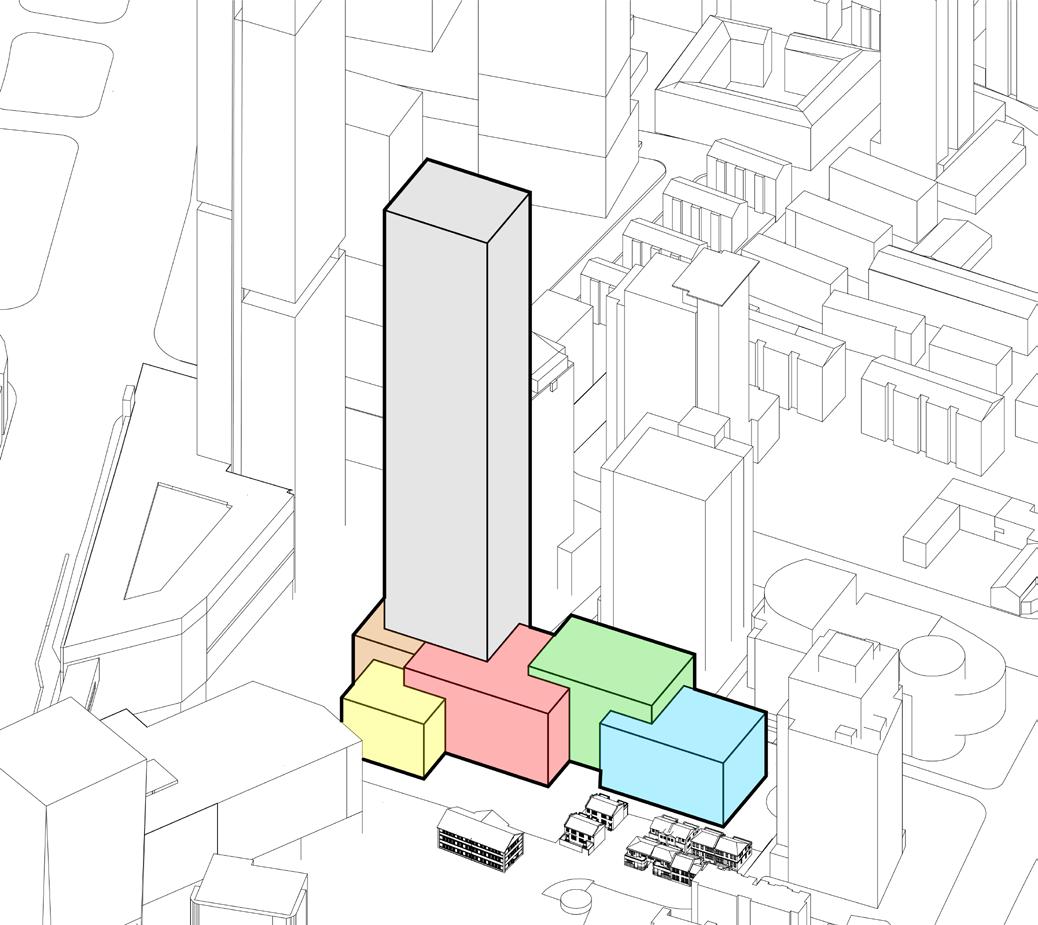
The design site is located in the northeast corner of Xinjiekou, Nanjing, Jiangsu Province. There is less high-rise building capacity in this area, and a high-rise building of over 200 m is proposed.
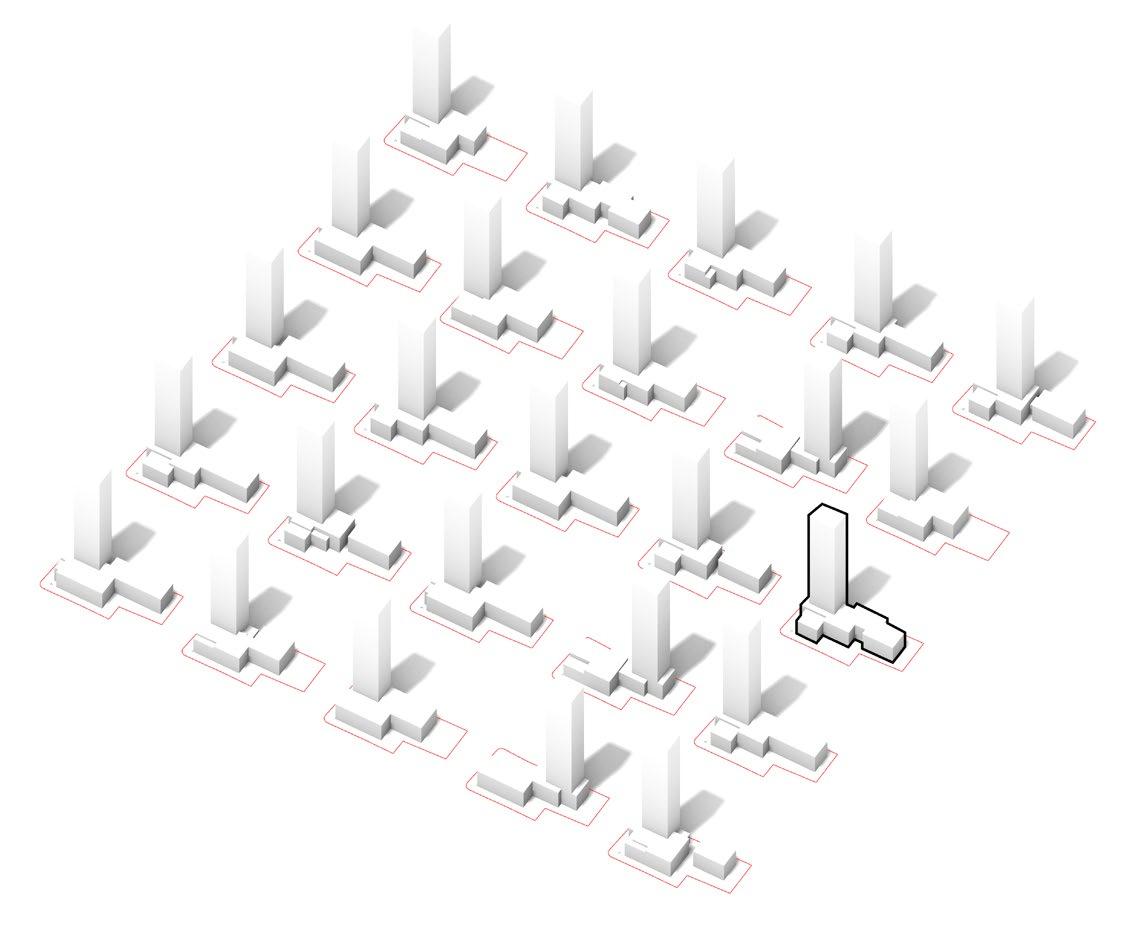
At the beginning of the design, due to the complexity of the site environment, the team proposed to use computer-aided analysis of the impact of the building form on the surrounding environment to derive the design concept. The building was divided into two parts, the podium and the tower, and the main parts of the study were the selection of the location of the tower, the morphology of the podium and the morphology of the tower.
The programme aims to form a functional commercial office space nested across the staggered blocks, with the podium and towers organised in a formal manner.This façade is implemented in the organisation of the podium and tower. The size and location of the blocks are introduced iteratively using a genetic algorithm.
Instructor : Tong, Zi-Yu
Architectural Design Studio VIII Fall Semester, UG4