How does a septic tank work, why does it clog and what vegetation you can grow near it
A septic tank is an underground wastewater treatment system commonly found in areas where sewage treatment plants are not available. It's a large, watertight container that's designed to collect and treat sewage from households or businesses.
How does a septic tank work?
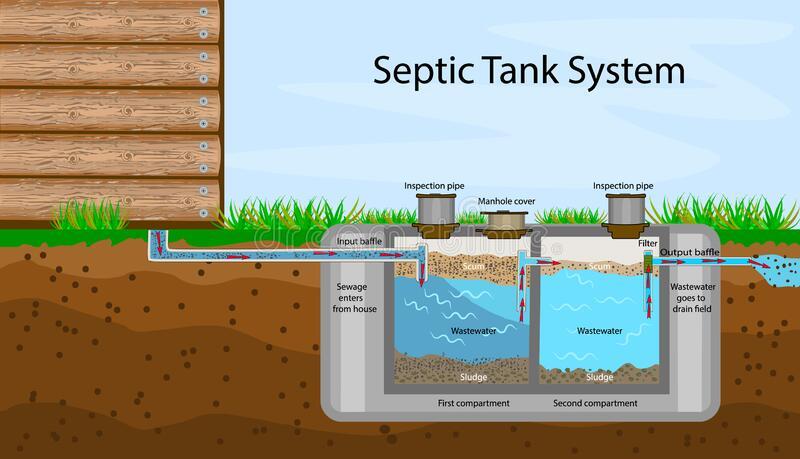
Septic tanks function by separating solids from liquids. Wastewater flows into the tank through a pipe, and the solids settle to the bottom, while the liquids rise to the top. Modern septic tanks often contain two chambers that are divided by a wall with openings located midway between the tank's top and bottom. The clear liquid, also known as effluent, then exits the tank through another pipe and is dispersed into the soil through a drain field or leach field.
Septic drain fields are comprised of trenches that hold perforated pipes and a porous substance, such as gravel. This layer is then topped off with soil, serving as a barrier to prevent animals from coming into contact with the wastewater. The perforated pipes disperse the wastewater into the gravel, which works to further eliminate impurities and contaminants. As a result of this process, the treated water is reintroduced into the environment through the plant roots and via evaporation.
(Diagram of a septic tank system)Bacteria and other microorganisms present in the tank break down the solids over time, turning them into sludge. This sludge will eventually need to be pumped out and disposed of properly to avoid clogging the tank and causing costly damage to the system.
How to check if a septic tank is full?
It's essential to check your septic tank regularly to prevent it from overflowing, which can lead to environmental contamination, health hazards, and costly repairs. Here are some signs that indicate your septic tank is full:
1. Slow drains and toilets: If you notice that your sinks, showers, and toilets are draining slowly, it could indicate that your septic tank is full.
2. Foul odors: If you smell sewage odors coming from your drains, yard, or septic tank, it's a sign that something is wrong. It could be due to a full tank, clogged pipes, or a damaged septic system.
3. Wet spots or lush vegetation: If you see wet spots or areas of lush vegetation in your yard, it could be a sign of a leaking septic tank.
4. Backup: If sewage backs up into your house, it's a clear indication that your septic tank is full and needs immediate attention.
If you notice any of these signs, it's crucial to have your septic tank inspected. It's important to exercise caution when it comes to old septic tanks. As purchasing a home represents a significant investment, a home inspection is typically conducted prior to closing the deal. Similarly, septic systems are expensive and warrant thorough inspection, either by yourself or a professional, in order to fully understand their condition. If your home is on the older side, it may feature a septic tank constructed from steel or wood. In such cases, replacement is likely necessary. Septic tanks made from steel will inevitably rust over time, rendering them unusable and necessitating replacement. Likewise, wooden septic tanks are prone to rotting and deterioration, and will likewise require replacement. Nowadays, septic tanks are generally made from more durable and efficient materials such as concrete, fiberglass, or polyethylene.
Concrete septic tanks
Concrete septic tanks are the most common type of septic tank. They are durable, longlasting, and can withstand the weight of heavy vehicles and equipment. They are also resistant to fire, rodents, and insects.
Concrete septic tanks come in various sizes, ranging from 500 to 2,000 gallons or more, depending on the size of your household or business.
Concrete septic tanks possess significant weight even when empty, ensuring that they won't shift or float in the ground over time, as can happen with plastic tanks. Due to their robust construction, concrete tanks are highly recommended for large households, as they can be created in almost any size. However, larger concrete tanks are proportionately more substantial, requiring more extensive equipment such as cranes for installation. In comparison, a plastic tank of the same size is considerably lighter. Also
if not properly built concrete septic tanks can crack or deteriorate over time due to age, ground movement, or exposure to harsh chemicals.
One of the most significant benefits of concrete tanks is that they are permitted in all states. In contrast, plastic and fiberglass tanks are not legal in certain regions.
Fiberglass septic tanks
Fiberglass septic tanks are often preferred over concrete tanks in areas where delivery trucks may not be able to access easily due to their lighter weight. Additionally, if a fiberglass tank has a thick coating of resin, it can be more durable than concrete tanks. This is because the thick resin coating is resistant to degradation from the gases produced by the waste.
To determine the appropriate size of fiberglass septic tank for your needs, it is important to review local regulations on the matter and consider the number of bathrooms in your home. Typically, a 1000-gallon tank will suffice for a two-bedroom home, while a 1500gallon tank is suitable for a house with three or four bedrooms.
What causes septic tank backups?
Septic tanks are designed to store waste while bacteria and enzymes digest it, breaking it down into a liquid that can be dispersed through leaching fields. As long as the tank is functioning properly, and the bacteria and enzymes are doing their job, everything should run smoothly. However, household cleaning products like anti-bacterial soap, bleach, scented soaps, laundry detergent, and other cleaners are designed to kill bacteria and germs, which can upset the natural environment of the bacteria in the septic system over time. This slows digestion and causes waste to back up not only in the tank, but also in the pipes of the home, resulting in unpleasant odors and wet spots. While it's not reasonable to stop using cleaning products altogether, septic system owners can be mindful of their behavior and give their systems a boost with a bacteria and enzyme treatment and regular maintenance. The cost of these small tablets that dissolves all clogs and solid waist from the septic tanks with a potent eco-friendly drain cleaner bacteria created especially for septic tank owners, is far less expensive than regular pumping and replacement of the entire system. The tablets digests the toughest clogs and odor-causing organic matter, reducing also the risk of pipe corrosion or damaged seals, which can be very costly.
Safe Plants to Grow Over Septic Tanks and Drain Fields
Instead of being overly cautious and avoiding planting anything around your septic system due to concerns about root damage, it is important to follow some best practices for landscaping in this area. Growing the right type of vegetation can actually be beneficial, as it helps prevent erosion and absorbs excess moisture from the drain field. Grasses, including ornamental grasses, and small, non-woody ground covers are good choices because they have shallow root systems that are less likely to invade and damage the septic system. If you want to plant trees and shrubs, it's best to choose shallow-rooted varieties like dogwoods, Japanese maples, Eastern redbuds, and cherry trees. When choosing plants, consider factors such as sunlight and soil conditions. Perennials like bee balm, hollyhocks, and wild violets that can tolerate wet and salty soil are a good option for areas around septic systems.
Unsafe Plants to Grow Over Septic Systems and Drain Fields
It is recommended to avoid planting large, fast-growing trees with aggressive root systems over your septic system as they can cause damage by invading the pipes of the septic tank drain field. Trees and shrubs with root systems that aggressively seek out sources of water should also be avoided. Some common trees and shrubs that fall under this category include Pussy willows, Japanese willows, Weeping willows, Aspen trees, Lombardy poplars, Birch trees, Beech trees, Elm trees, most Maple trees other than the Japanese maple, American sweet gum trees, and Ash trees, among others. It is not safe to grow food crops over the septic field due to the risk of bacteria in the area. Even if problematic plants are not grown directly over the septic system, the roots of large, mature trees nearby can still pose a risk. It is recommended to maintain a distance between trees and the septic drain field, with the general rule being that a tree should be at least as many feet away from the drain field as it is tall. Alternatively, root barriers can be installed to prevent tree roots from invading the septic drain field.
In conclusion, septic tanks play a vital role in managing wastewater in areas where there are no sewage treatment plants. It's essential to understand how they work, how to check if they're full, and how to maintain them properly.
Regular inexpensive maintenance of your septic tank as described before can help prevent costly repairs and environmental contamination. If you're considering your septic tank needs servicing check the tablets here to start declogging it.
