TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE


SEM-VIII
2BL10AT007 SHANTA PATIL, 2BL19AT024
BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture
HIREMANI SAMEERSAB,

Exesting condition
Issues
Proposals
VAJRAHANUMAN RAILWAY CROSSING
Exesting condition
Issues
Proposals
GOL-GUMBAZ RAIL OVER BRIDGE
Exesting condition
Issues
Proposals
SHAHAPUR GATE
Exesting condition
Issues
Proposals
BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE INTRODUCTION 05-07 08-13 14-18 19-23 24-26 MANGOLI GATE
03
BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE
Bijapur, officially known as Vijayapura, is the district headquarters of Bijapur District of Karnataka state. The district is bounded by Solapur district on the North and Sangali on the North-West, Belgaum district on the West, Bagalkot on the South, Gulbarga on the East and by Raichur on the South-East.
The city was established in the 10th-11th centuries by the Kalyani Chalukyas and was known as Vijayapura (City of victory). The city was passed to Yadavas after Chalukya’s demise. Bijapur came under Muslim influence, first under Allaudin Khalji, the Sultan of Delhi, towards the end of the 13th century, and then under the Bahamani kings of Bidar in 1347.
TRANSPORTATION OF BIJAPUR:

Roadways Roadways: geographically & strategically well connected through major cities by four lane NH-13(Solapur–Mangalore) (now NH50), NH-218 (Hubli–Humnabad) and other state highways. The main stand in Bijapur is near the southwestern side of the citadel, near the city center. Bus services to Badami, Belgaum, Almatti, Gulbarga, Bidar, Hubli and Solapur are frequent. Bijapur is geographically & strategically well connected through major cities by four lane NH 13(Solapur–Mangalore) (now NH50), NH-218 (Hubli–Humnabad) and other state highways. Bijapur is a big road transport hub and its state run bus transport division has 6 depots/units and comes under Kalyana Karnataka Road Transport Corporation (KKRTC) headquartered at Gulbarga. The division plys many premium multi-axle coaches, sleeper coach, sitting push back coach with AC and Non AC with makers like Volvo, Mercedes Benz, Isuzu Tata Motors, Ashok Leyland, Mitsubishi etc. services to Bangalore, Mumbai, Pune, Hyderabad, Mangalore, Mysore, Hubli, Belgaum and other major cities.
Railways Bijapur is well connected by rail with Bangalore and other major cities of India (Mumbai, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad, Hubli and Solapur). It has its own railhead that is located just 2 km (1.2 mi) from the main town.
Bijapur railway station is connected by a broad-gauge railway (Gadag–Hotgi railway line) to Hotgi Junction near Solapur railway station and Kurduvadi railway station on Central Railway towards the north and to Bagalkote and Gadag junction on South Western Railway towards the south. Bijapur is connected with direct trains to Solapur, Bagalkote, Gadag, Dharwad, Ballari, Yeswanthpur (Bangalore), Hubli, Mumbai, Hyderabad and Ahmedabad. Bijapur comes under Hubli division of South Western Railway (SWR)
Air Transport
The nearest airport is at Gulbarga (152 km). Many airlines connect Bijapur to the rest of India via this airport. A greenfield airport which can accommodate ATR 72 & Airbus 320 (expansion afterwards) is currently being built by Karnataka government. Land has already been acquired. Bijapur Airport will be built by the Karnataka State Industrial and Infrastructure Development Corporation (KSIIDC) at a cost of Rs 220 crore. The project site is located 15 km from the city on 727-acre (2.94 km2) of land in Madhubavi villages. The construction has strarted and airport is expected to be ready by August 2023
SHAHAPUR GATE: problem due to immediate curve and improper road attempt to solve the traffic conjuction is been done indone in the report
RAILWAY STSTION FLY-OVER: immediate turn need to be taken towards the vijayapur railway station hence it is the accident prone zone. the major connectivity road to railway station is via bypass and station road causing traffic conjuction

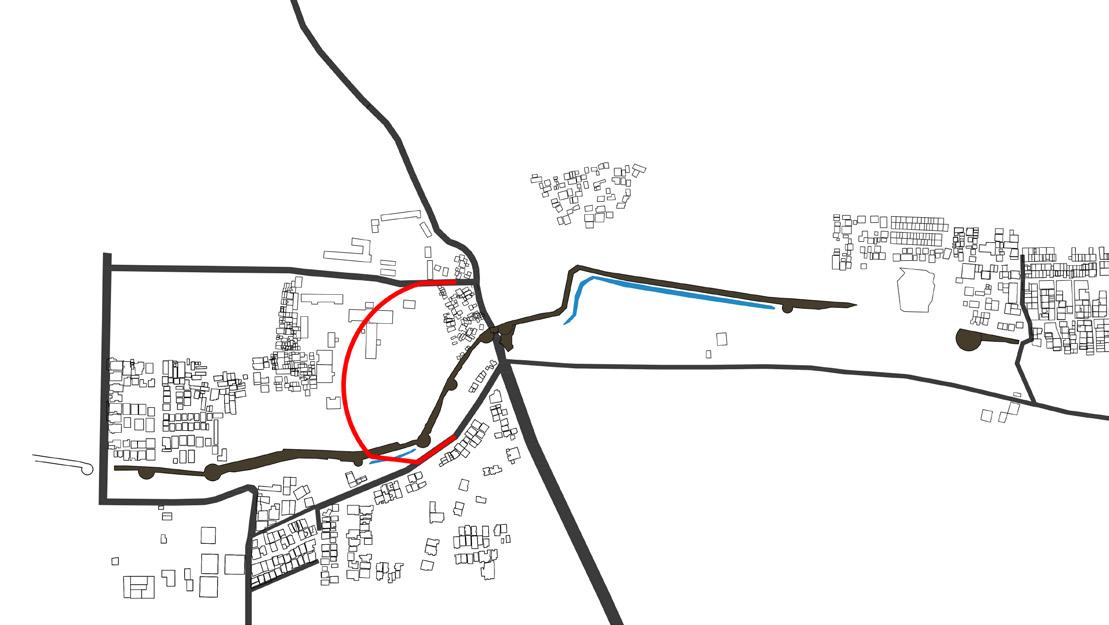
MANGOLI GATE: Mangoli road which is 18m 2way road with the divider Problem: outer side of mangoli gate it creates a bottle neck road and left side of the road leads to kastur colony which creats traffic congestion


VAJRAHANUMAN GATE: since the railway gate is closed every 15m min which leads to traffic congection on all the 5 roads

ABOUT CITY
BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE 05
TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRINFRASTRUCTURE
Infrastructure for traffic control and road safety are essential elements of urban planning and transportation systems. They seek to prevent accidents and congestion while ensuring the swift and safe passage of vehicles, pedestrians, and cyclists. Here are some essential components of the infrastructure for traffic control and road safety:
Traffic Signals and Signs: Traffic signals control the flow of traffic at intersections, while signs inform drivers and pedestrians of critical information including speed limits, lane designations, and directions.
Road Markings: Visible and unambiguous road markings, such as lane lines, crosswalks, and stop lines, enable pedestrians and drivers navigate the road, increasing safety and minimising confusion.
Pedestrian Crossings: Designated pedestrian crossings, such as zebra crossings, signalized crosswalks, and pedestrian islands, enhance safety and encourage walking. These areas may include additional safety features like countdown timers and audible signals for visually impaired individuals.
Speed Calming Measures: Speed bumps, speed humps, rumble strips, and raised intersections are examples of physical interventions used to slow down vehicles and promote compliance with speed limits in residential areas and near schools.
Roundabouts: Roundabouts help manage traffic flow at intersections and reduce the severity of accidents by eliminating head-on and high-speed collisions. They can improve traffic efficiency and safety compared to traditional signal-controlled intersections.
Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS): ITS incorporates technology and communication systems to enhance traffic management. This may include traffic surveillance cameras, dynamic message signs, adaptive traffic signal systems, and real-time traveler information to inform drivers about road conditions, accidents, and congestion.

Traffic Enforcement: Strict traffic enforcement through the deployment of police officers, speed cameras, and red-light cameras helps deter violations and improves compliance with traffic rules.
Public Awareness and Education: Road safety campaigns, driver education programs, and public awareness initiatives play a vital role in promoting responsible behavior among road users and reducing accidents. These are just some examples of traffic management and road safety infrastructure. The specific measures implemented may vary depending on the local context, traffic patterns, and infrastructure requirements. Effective traffic management and road safety infrastructure require a comprehensive approach that combines engineering, enforcement, education, and evaluation.
(SOURCE: CHATGPT)
VIJAYAPURA CIRCULATION PATTERN
BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE
06



BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE 07
Image source: google earth
VAJRAHANUMAN RAILWAY CROSSING
COURT CROSS
MANGOLI GATE
WAY TO PDJ SCHOOL
BUS STAND
BASWESHWAR CIRCLE
AMBEDKAR CIRCLE
APMC ROAD
SHAHAPUR GATE
MAHATMA GANDI CIRCLE
MINAKSHI CHOWK
SHIVAJI CIRCLE
WATER TANK ROAD
SATELLITE BUS STAND
GOLGUMBAZ RAILWAT OVERHEAD BRIDGE

BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE 08
ISSUES
Formation of bottleneck road on the outer side of the fort wall is the main reason for traffic congestion East side of the mangoli gate is the ancient Hanuman temple and west side is the bastion Road that passes through mangoli gate is very narrow i.e, 3m which is the main reason for the formation of bottleneck road

BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE 09
two arch entrance gates- mangoli gate and entrance to hanuman temple
formation of bottle neck
entrance gate and bastion along both side
entrance from inner side of fort wall




BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE 10
flyover over fort wall from inner to outer fort wall connects to mangoli road
RTO RTO RTO
2 way roads above fort wall
MANGOLI ROAD MANGOLI ROAD
2 roads from mangoli road to rto and mangoli road to keerti nagar respectively


fly over from mangoli road to keerti nagar

BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE 11 RTO RTO RTO
MANGOLI ROAD
MANGOLI ROAD
MANGOLI ROAD




BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE 12
flyover over fort wall from inner to outer fort wall and connecting to keerti nagar
flyover over fort wall from inner fort wall to mubarak masjid road MANGOLI ROAD MANGOLI ROAD
traffic
on either side of the gate should be properly mentainef
BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE 13
siglels
1 way road from outer side of mangoli gate to inner side of gate and people going towards bagalkot road can be connected through keerti nagar road

BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G.
of
TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD
INFRASTRUCTURE 14
Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department
architecture
SAFETY
ISSUES
In A Day 47 Train Passes By This Track. At Every 15 Minutes A Train Passes. So We Face A Lot Of Traffic Issues. As It Has 5 Road Which Connects To It. The Gate Is Supposed To Be Closed By Govt. But Due To The Location Of The Flyover, It Is Very Difficult For People To Access It Easily. Due To The Condition Of The Road, The Flyover Is Not Constructed In This Area As The Space Is Very Narrow. As This Area Has A Hanuman Temple, It Is a Very Busy Road On Saturday.

BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE
IBrahimpur railway station road connecting to ibrahimpur railway over bridge
road leading to flyover connects bagalkot road
15
vajrahanuman temple road
A flyover is provided for easy flow of the vehicles near the railway gate and seperate road is provided form jamkhandi road connecting to Highway(bypass)

A flyover is provided for easy flow of the vehicles near the railway gate and people who want to access to the secondary roads a seperate flyover is provided near the scholarline road to connect to chandpur road

BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE 16
BAGALKOT ROAD
RAILWAY TRACK
RAILWAY TRACK
BAGALKOT ROAD


BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE 17
A flyover is provided to reduce the number of traffic caused due to railway
A huge flyover is provided to directly connect to the highway bridge people coming from Bagalkot road
RAILWAY TRACK
RAILWAY TRACK
BAGALKOT ROAD
BAGALKOT ROAD

BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE 18
Railway track is been diverted outskirt the city as it creates huge traffic near the vajrahanuman gate.

BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE

BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College
of
TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE 19
of Engineering and Technology, Department
architecture
ISSUES
6m wide road leading to the vijayapura railway station there is a dargah on the main road next to the police station next to the flyover is a police station
Unorganised settlements alomg the fort wall

BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC
MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE
road below flyover leading to railway station condition of moat
20
station road station over bridge
A road is provided below the flyover for the people to directly connect to the main road, for people coming from railway station

A service road is been provided from the SINDAGI road to directly connect to the railway station road rather then waiting at the junction for the turn.

TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE 21
SINDAGI ROAD
SINDAGI ROAD
A flyover is provided for the people coming from the railway station road to connect to the SINDAGI road and a service road is provided below the flyover to connect to the ghandi chowk road

A flyover is provided to connect to the SINDAGI road and service road is provided next to SINDAGI road to connect to the station road

BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE 22
SINDAGI ROAD
SINDAGI ROAD
A service road is been provided from the SINDAGI road to directly connect to the railway station road rather then waiting at the junction for the turn.

A road is provided below the flyover for the people to directly connect to the ghandi chowk road and flyover is provided to connect to the SINDAGI road A road is provided below the flyover for the people to directly connect to the ghandi chowk

BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE 23
SINDAGI ROAD
SINDAGI ROAD

BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE

BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College
and
of
TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD
INFRASTRUCTURE 24
of Engineering
Technology, Department
architecture
SAFETY
two gates are present at shahapur gate located in such a way that gate 1 is not visible from gate 2 and vice versa
ISSUES
major traffic is caused in the gate due to the presence of 2 gates, curve in the gate is a major issue

BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE 25
moat converted into garbage dump road adjacent to the fort wall
temple present at the entrance
BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture
26 40 41
TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE
OPTION 1- traffic siglels on either side of the gate
OPTION 2- overhead bridge from inner fort wall to shivaji road
SHIVAJI ROAD
BLDEAs V. P. Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology, Department of architecture TRAFIC MANAGEMENT AND ROAD SAFETY INFRASTRUCTURE













































