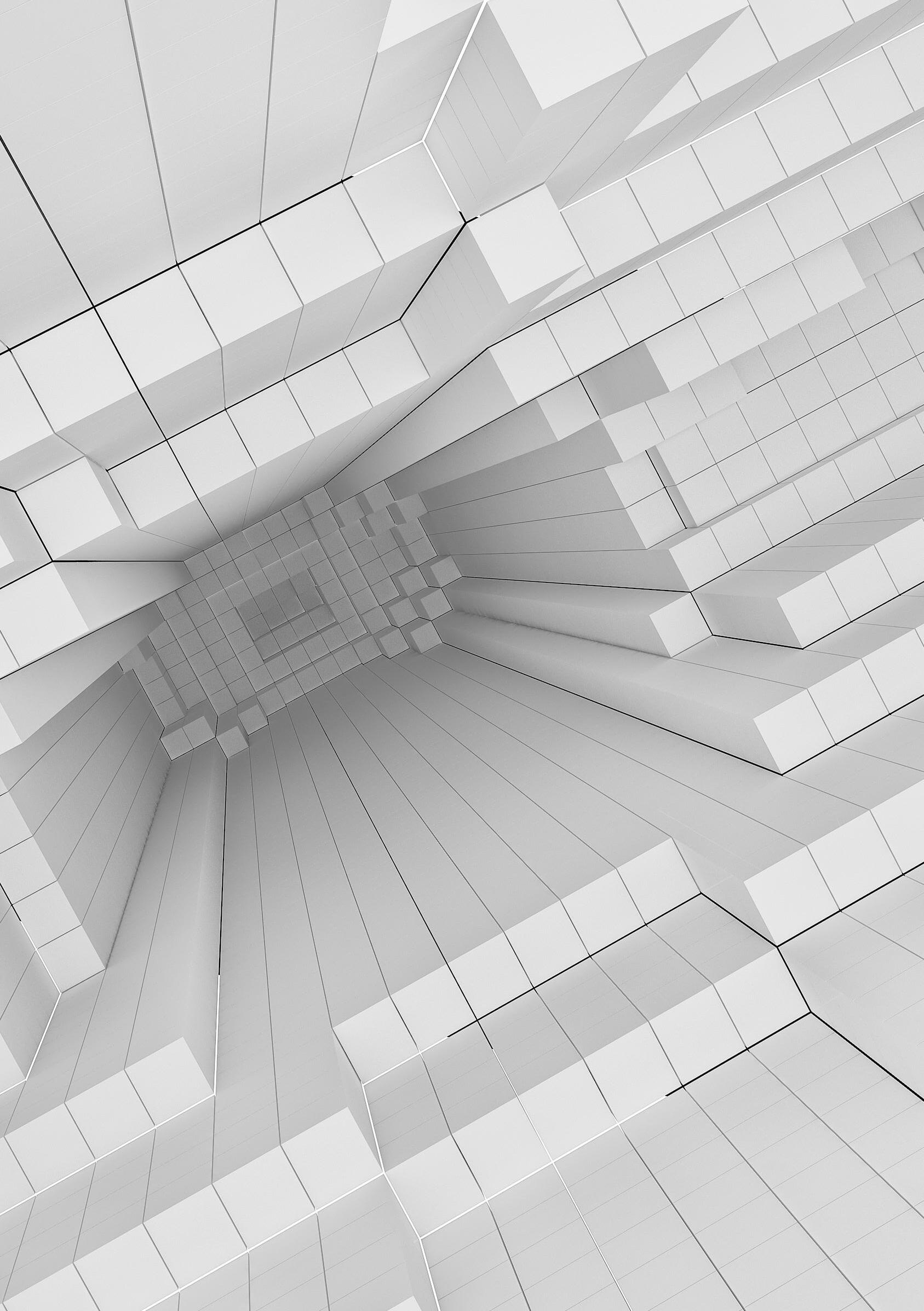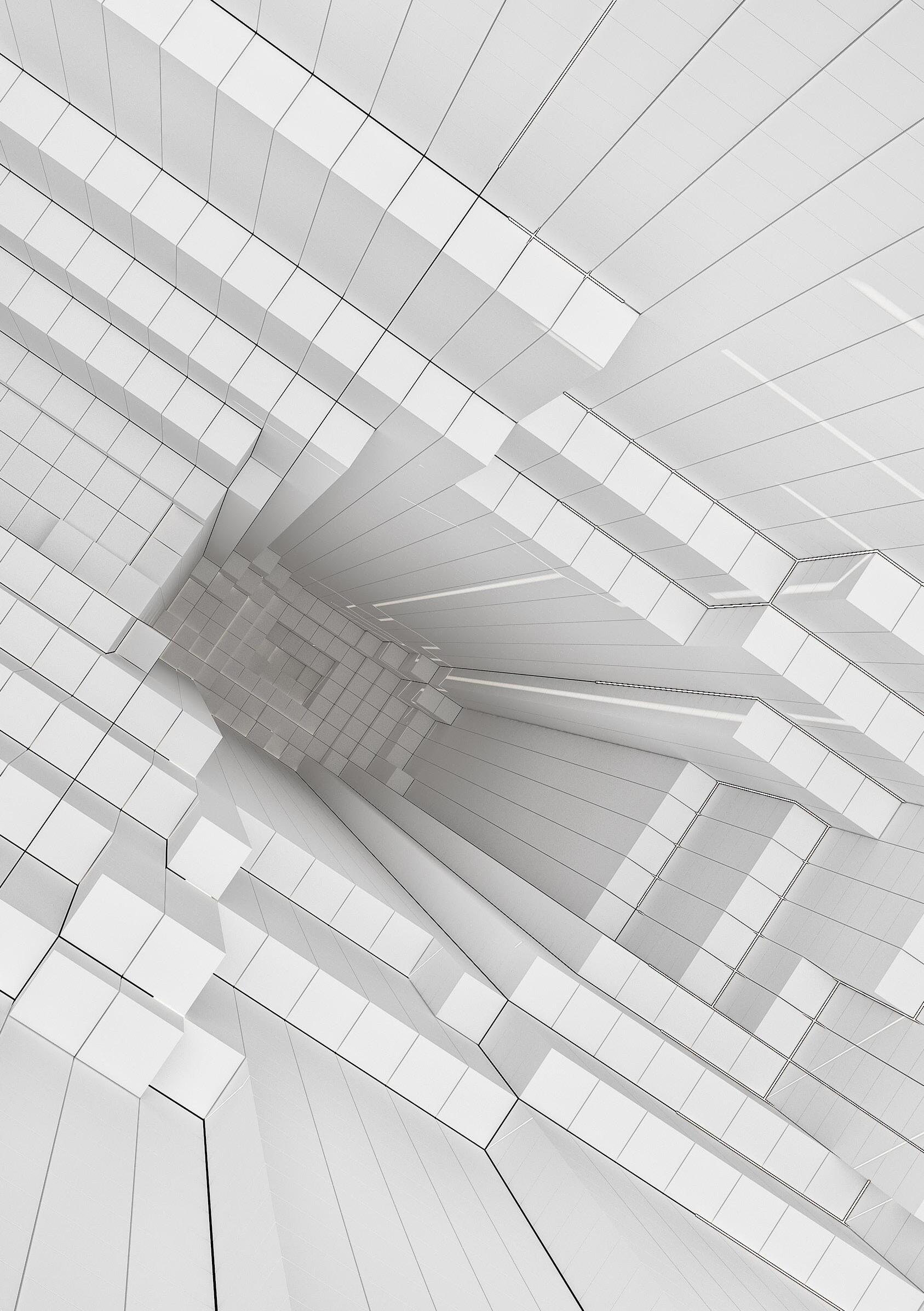









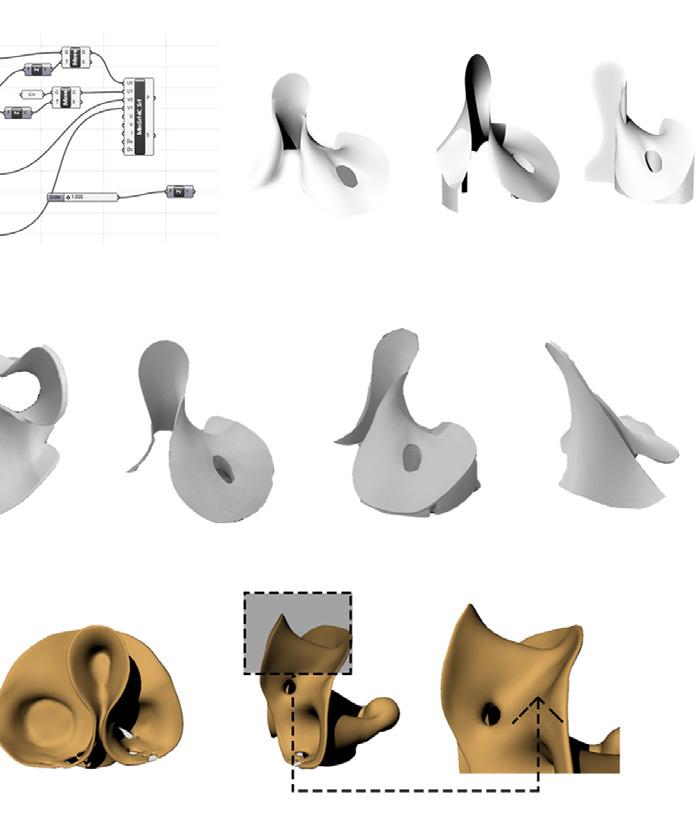
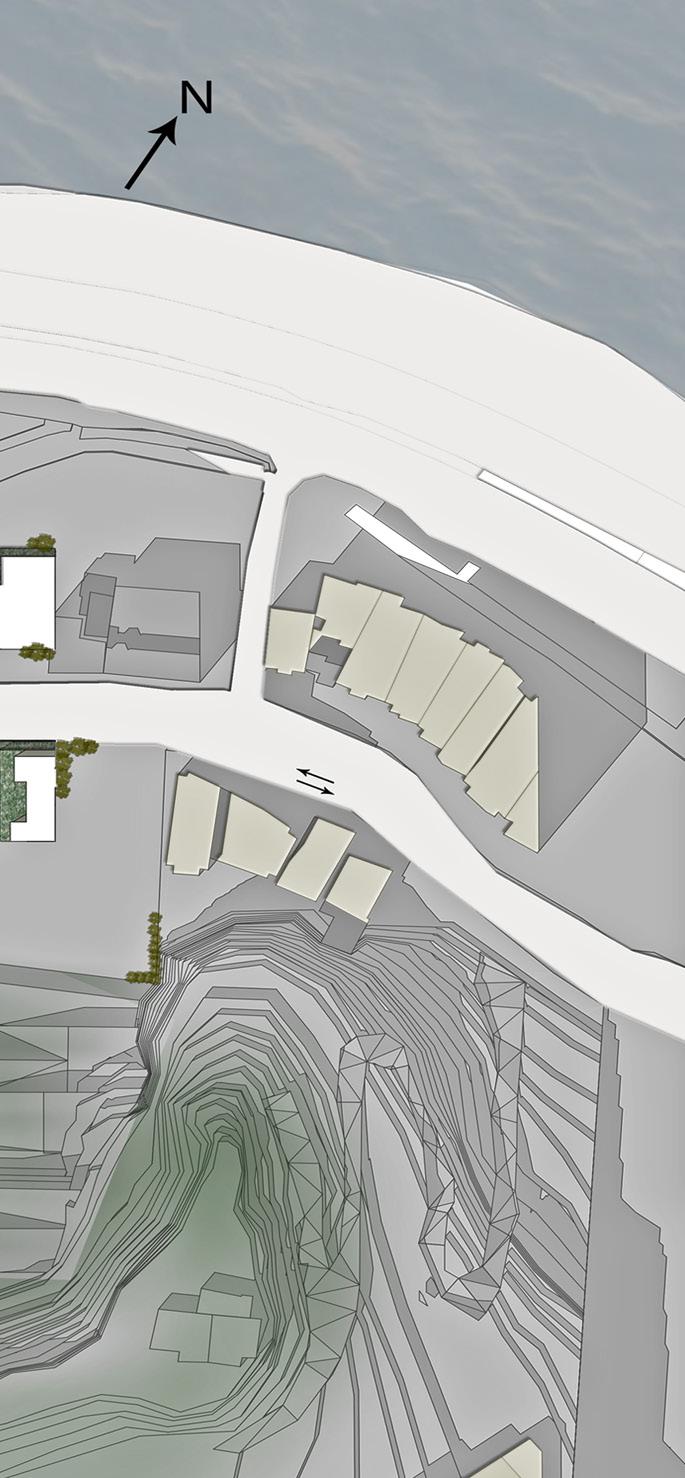
Visibility model develeoped for architectural geometries.Works with multiple observation points and defined obstacles.The outcomes comes from the voxeled geometry interaction.





Defining visible areas in architectural space have been introduced by Benedikt in his “To Take a Hold in Space” article. He defines visible areas with isovist methodology. “An isovist is the set of all points visible from a given vantage point in space and with respect to an environment” (Benedikt, 1979). Studies involved with isovist, quantifies the areas as either visible or invisible. Defined methodology usually includes a vantage point in an environment (that were usually convex spaces) and some obstacles that blocks the view. “Using the visibility graph, we can extend both isovist and current graphbased analyses of architectural space to form a new methodology for the investigation of configurational relationships” (Turner et al., 2001).

Voxel Model
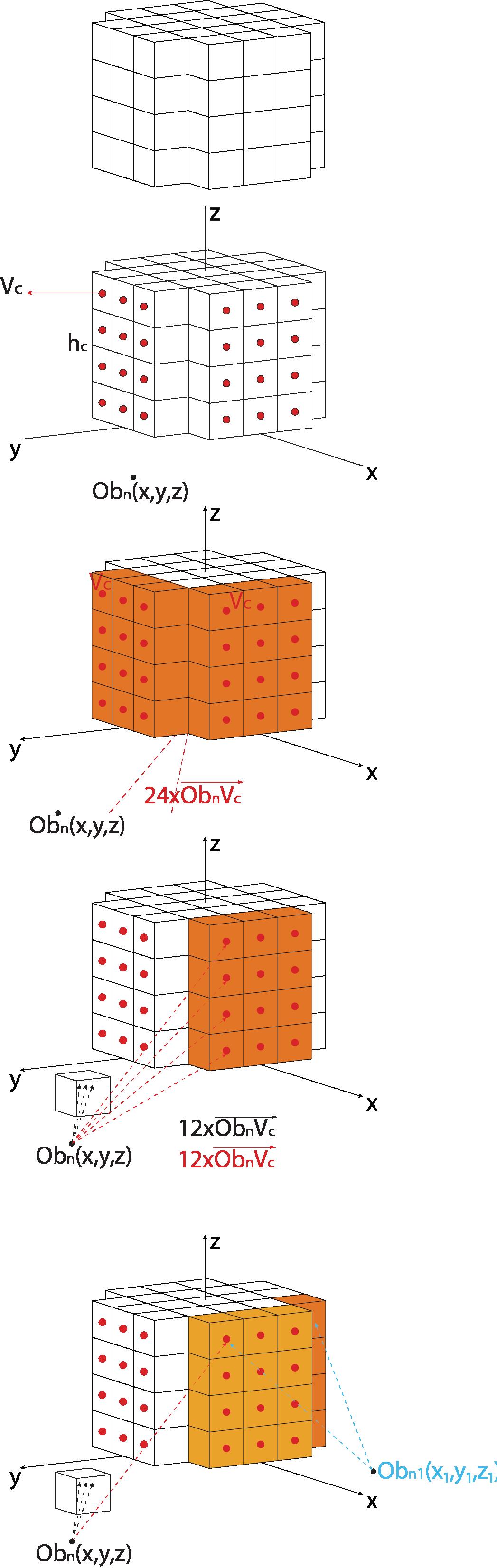
Center points of the tested geometry and the observer
Interacted voxels with the observer
Blocked interaction by the obstacles
Multiple observers and obstacle around the tested geometry
The visual extend of geometries need to be found. For this purpose, geometries, then the obstacles and finally the location of those observers have been identified.
The complexity of the models and MoV adeptness on those models have been also practiced in this phase. Boolean operations on focal geometries create concave and convex spaces on the geometry. These spaces are hard to represent in digital fields therefore they were required time consuming operations to create FoV (Field of Vision) areas on them. The visibility range is the area that stays in the largest angle of observer’s viewing angle.
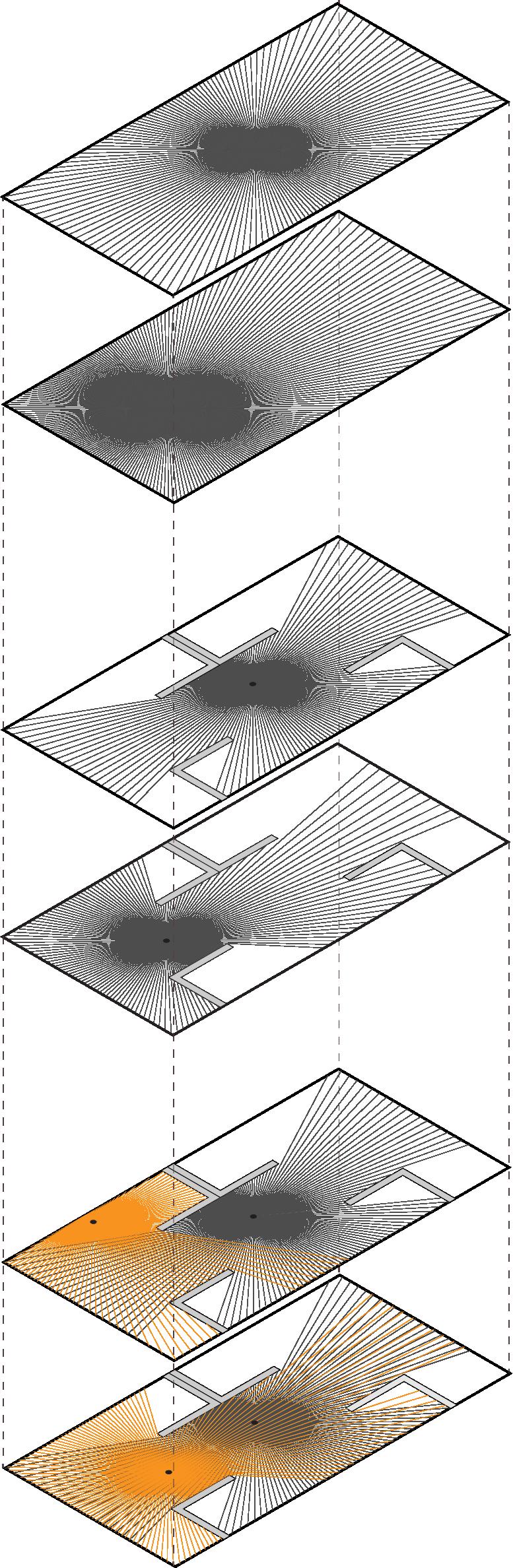
It is important to remember the vector lines that we draw to the voxeled geometry are linear therefore the impact of obstacles on the geometry is calculated above and beneath that vector lines, not the exact shape of that obstacle.
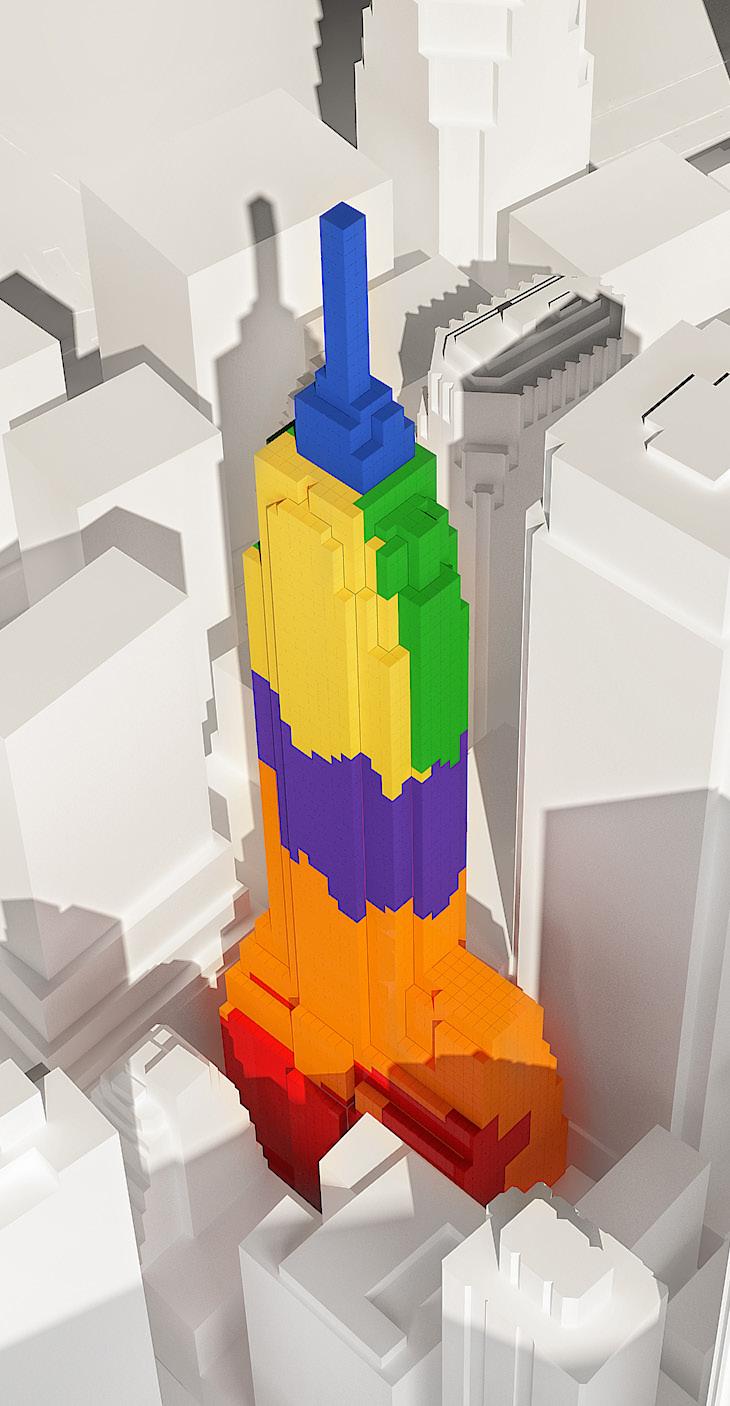

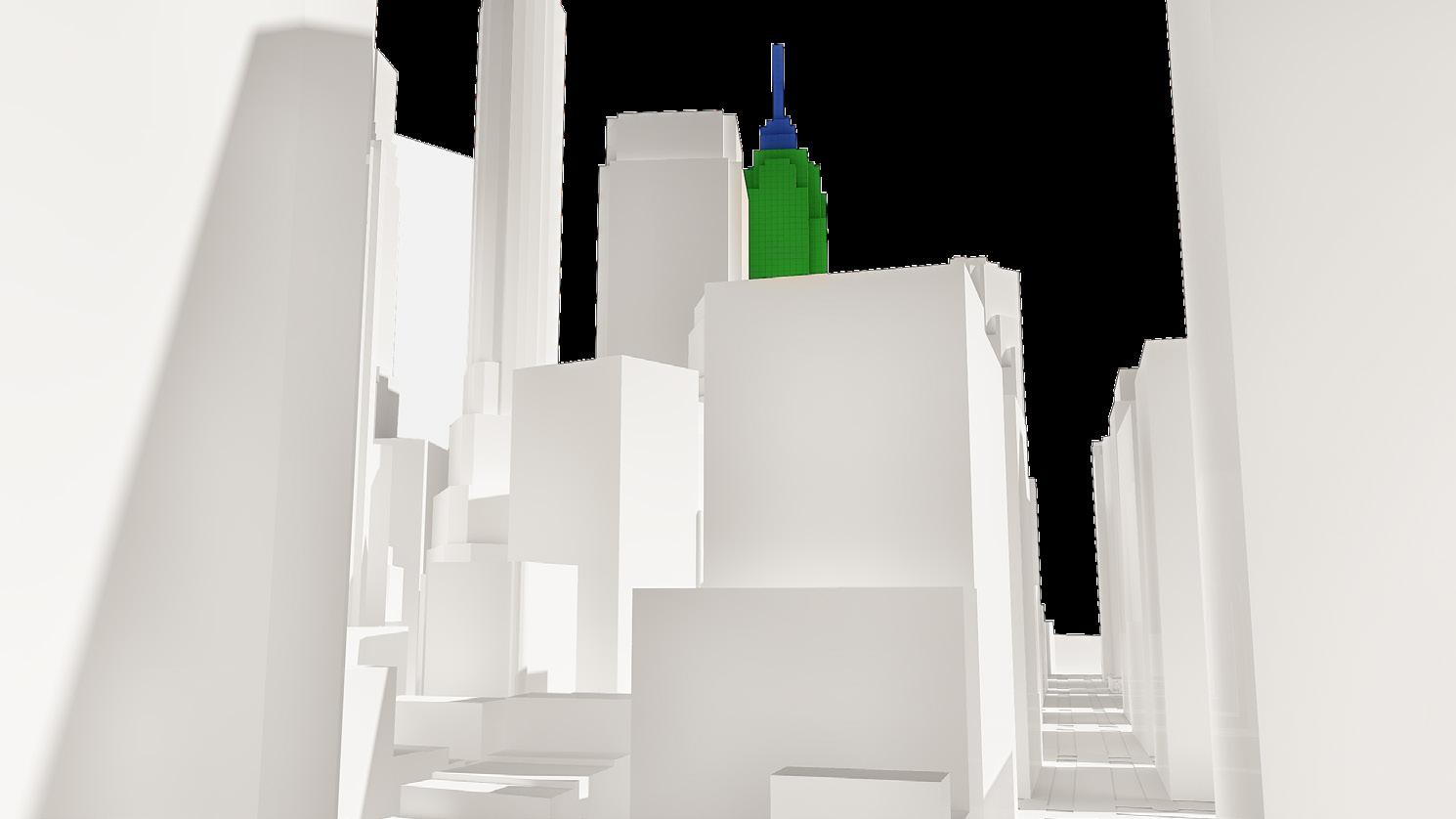

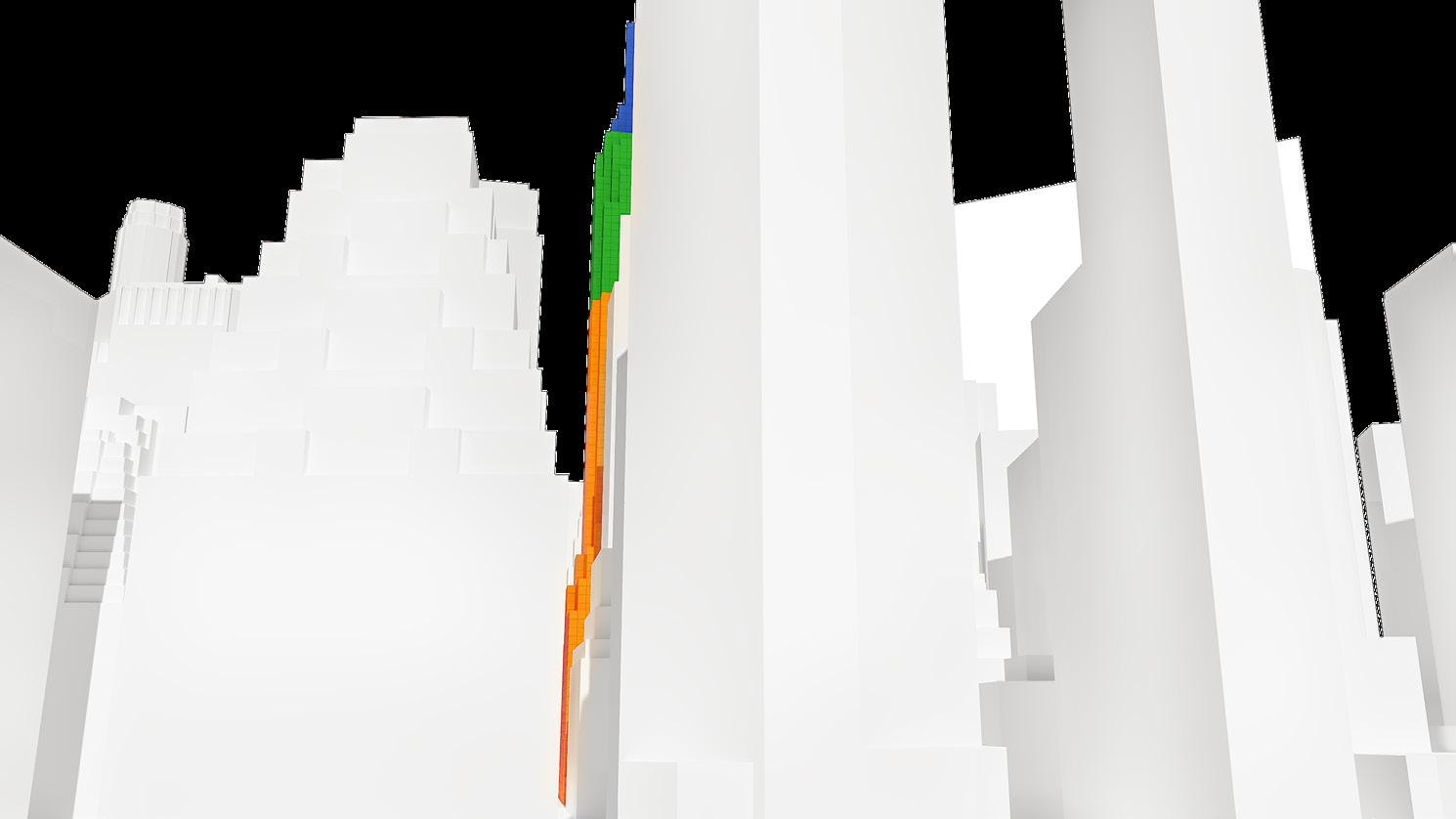


Theresults of the MOV operated with the observer points placed at the same heights at various observation points are as in the images. 4 different observation points, together with the defined obstacles, were looked at the focal point modeled by the voxel modeling method. The color of each voxel has taken on different colors depending on the number of observers interacting with it.



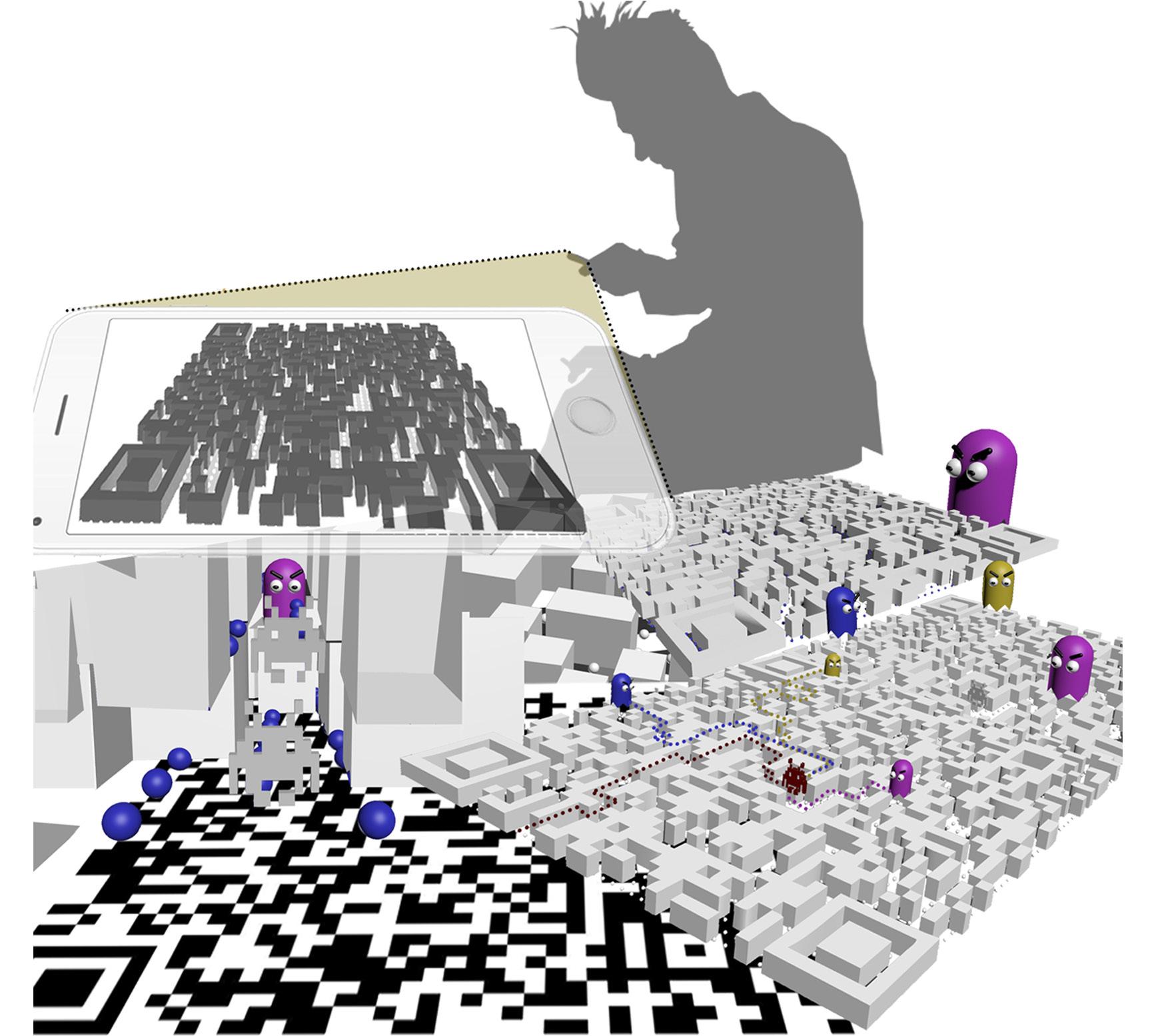
The proposed study aims to prepare an interface that brings two dimensional objects to the third dimension and to create an interactive video gaming area in this interface. The proposed gaming environment is the world of Pac-Man, which was produced in 1980 and still has its original ego even though it has undergone many changes til today. This environment designed by using Unity and Vuforia programs and the characters developed in 3D studio max. There are three main stages of the proposed study, first stage is to prepare the two dimensional world, second stage is bringing them into the third dimension and then making the placement layouts and the last stage is to relocate them into the Augmented Reality world. At the end of the study, the process and the outputs are evaluated.
First of all, the gaming environment contains twodimensional maze area which is based on a QR code. Secondly, there are some PacDots and fruits which need to be collected during the game and finally there are main characters Pac-Man (player himself) and ghosts that player needs to avoid during the play. Those elements appear when the player scans the QR code on their screens. If the player manages to reach those fruits, a visual button appears on the screen and player has a chance to click on it and see the entire environment above.
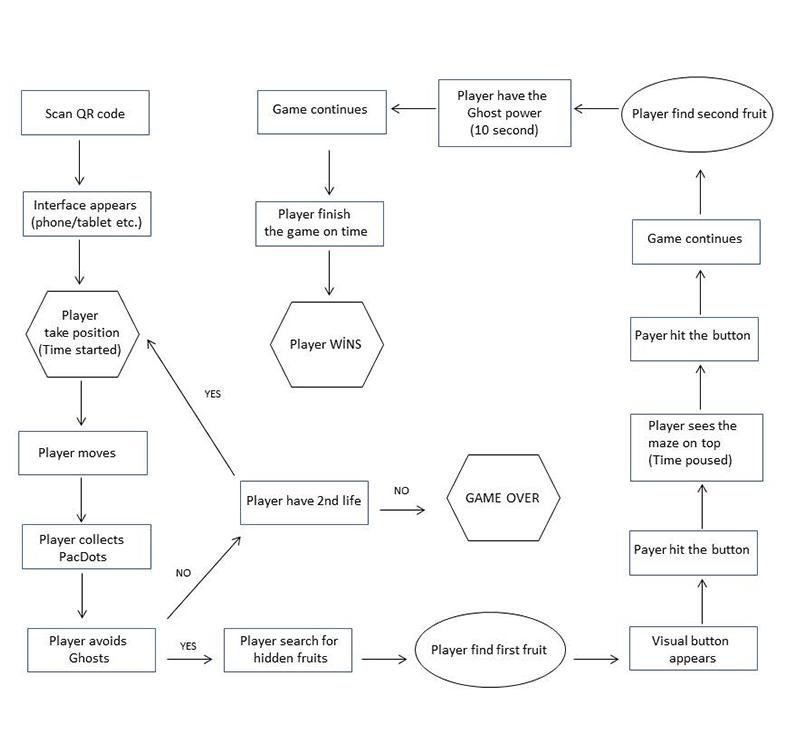



The study keeps the original logic of Pac-Man. The aim of the game collects all the PacDots in a certain period of time. In this case, it would be one hundred and eighty seconds. So, there is a main character that needs to be played by the player himself. When the game starts after scanning the QR code, player starts to move by the help of the screen while the player moving he needs to collect the PacDots but also he needs to avoid from ghosts. Every player has two lifes during the game. If a player catched by the ghost, his first life ends and the other one begins at the same point where he left. There are some hidden fruits in the game, they are randomly appears every time the game starts. If the player finds them, he gets some spatial powers. One of them creates a visual button and if the player pushes it, he has a chance to see whole maze on top. The other fruit gives the chance that flows through walls like the ghosts. At the end, if the player manages to collect all the PacDots on time, the game is over and player wins.
2018-2019 Fall Term Project
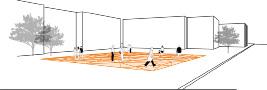
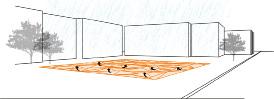
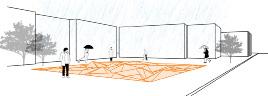
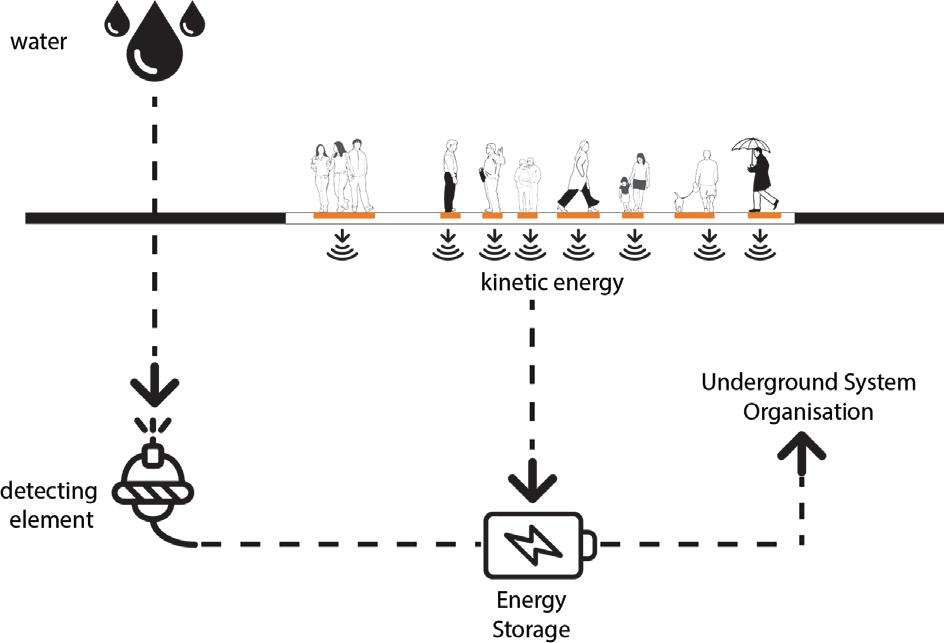
Thestarting point of the study was the concept of Allometry - the proportional change that comes with growth - as the evolution of the geometry of an architectural element over time. As an architectural element, a digital model was created in which the ground surface is actuated by water, an environmental input, and changes its shape. It is aimed that this kinetic floor will create a new geometry with the energy it receives from the movement of the users and thus become an urban installation.
It has been tried to create an urban center of attention by attracting the users’ attention with a floor design other than the usual ground texture in daily life.

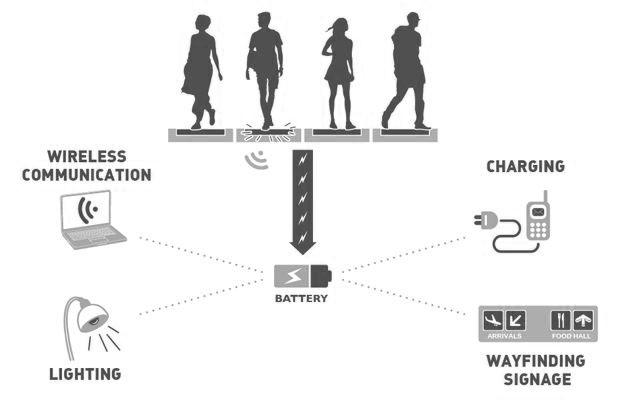
The droplets coming to the surface by rain water or any water source are detected by the sensors. Sensors trigger the action of the mechanism beneath the surfaces. It is aimed to convert the kinetic energy accumulated by human movements during the day into electrical energy and use it for the mechanism that activates the system.
The water-activated mechanism enables the surfaces to move in the ‘z’ axis and creates an unfamiliarthreedimensional floor. This kinetic ground turns into both an installation and a landscape element for the city.

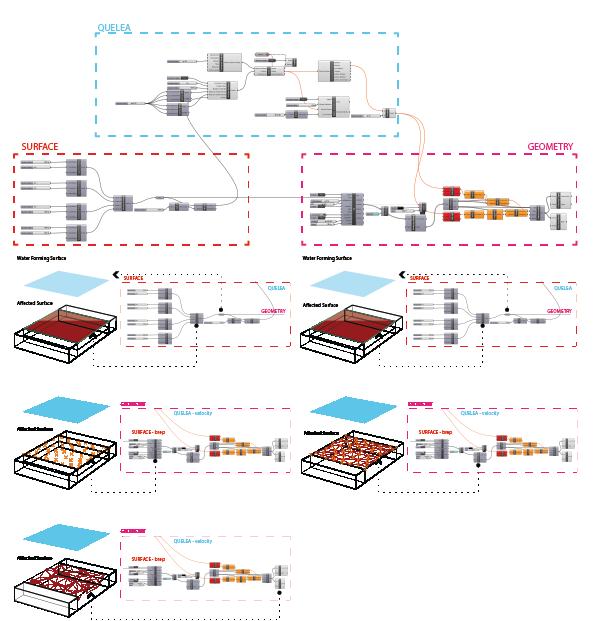
hopper3D add-on, and it was aimed to synchronize with the geometry model with a timer. The velocity value formed in Quelea activates the triangles that form the main character of the geometry.

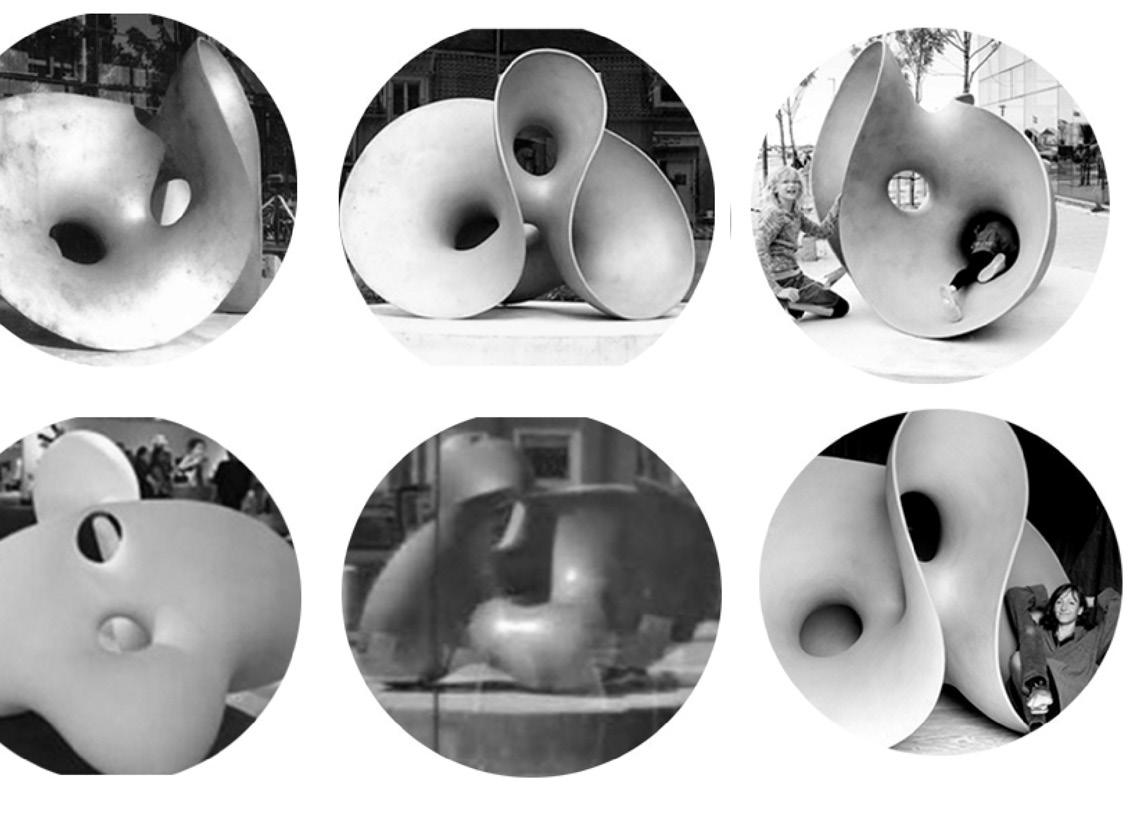
The physical model is made and exhibited in order to better understand the movement mechanism of the floor system.



Theproposed study includes the production of a pattern followed by the analysis of this pattern with computational thinking method; and using the analysis results as input data for the computational systems process. While using the obtained result in computational systems, some of the data are presumed as variable values and some are presumed as constant values. The pattern generated at the beginning is intuitively generated, and the final results include a conscious decision process to determine whether a data should be used as constant or variable. The aim of the study was to obtain the geometry which can be most efficient for the production of architectural acoustic panel by manipulating the parameters of the image in the framework of the proposed structure. The process of architectural acoustics panel production consists of two stages. The first stage is to generate the pattern with computational systems and the second stage includes the computation of acoustic values of 3-dimensional physical reality from a 2-dimensional pattern, followed by the re-production of an efficient acoustic panel with the combination of the obtained

data and the data from Odeon architectural space second stage of production of acoustic panels, the details were considered, and the proposal was application. At the end of the study, the process


space acoustic analysis program. In the the material and material combination was concluded with a study on the process and the outputs were evaluated.

undergraduate













extracurricular activities