User Story and Acceptance Criteria: Description and Recommendation
BA’s scope of work includes developing documentation of different levels: from business (high) level to software details of the development level. At the beginning of the new project development or separate epic task of the current project is comfortable and informative enough to apply such instruments as a user story and acceptance criteria. These short but informative ‘guides’ help to understand the main aim of the client`s requirements and true scenarios of their implementation. User story is a minimal unit of finite goal but not some variant of a possible scenario. A User story is a description of the functionality of the software in a simple, general description, written from the point of view of the end-user or customer. User Stories mostly used in flexible methodologies like Agile is.
User Story: Structure and Principals

The basic formula of the user story consists of the next coherent steps: “User-Action-Aim”.
Let`s discuss some examples.
Thus, User stories are:
independent (no connection with other actors or actions)
valuable (the aim of the action should be useful)
small (deep description takes away attention to unimportant details)
testable (QA will able to test)
estimable (capable of being estimated).
Acceptance Criteria: Results Testing Process
It`s important to understand the appropriate result of the implementation of user stories. In this case, BA describes acceptance criteria for each user story — what should be done(system response).
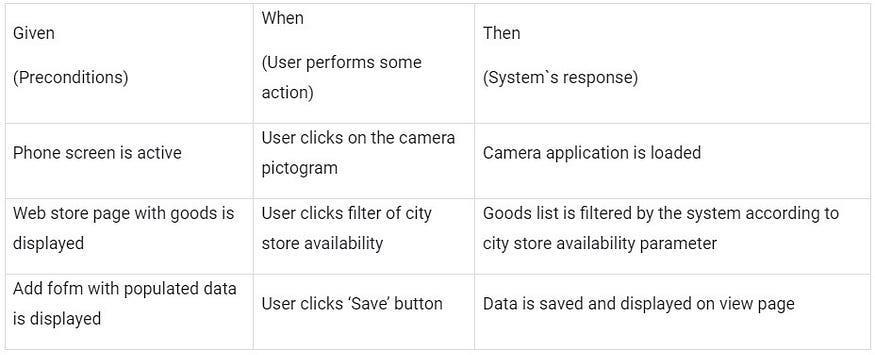
The basic formula of acceptance criteria includes steps: “Given-WhenThen”
Some examples of earlier described user stories.

Read also: What ‘Scope Creep’ is and How to Escape It

Acceptance criteria should be:
cleared (the result should be understood both by users and developers)
binary (there should be only two possible results: success or deny)
confirmable (user (client) can easily read, understand and test them)
fully described (response of the system should be similar to the description of the functional requirements)
Cons and Pros
Discussing positive points we can admit:
easy to describe
easy to understand
easy to manage
doesn`t need special options to detect
focused on business or functional value
involves all components of the functional system
At the same time, we have to attribute to the disadvantages next details:
too small description can bring to misunderstanding
demands well-experienced team developers in the domain area
no specific details
needs additional visualization
User story and acceptance criteria give the basic description of the client`s functional requirements. It`s a rather simple and easy for understandable method. At the same time, as it is a high level of description, the IT team should be experienced enough in the domain of the project to estimate requirements correctly. These instruments
don’t focus on details but on main functional results. After a basic main scenario is confirmed, BA continues work with UI, UX, and various details functional requirements.
Software Development Hub provides services for development mobile applications, web apps and software for various fields. Competent implementation of client’s ideas is possible due to expertise of technical specialists, whose work is coordinated by an experienced project manager.
