3 minute read
RURAL HOUSING 02
Sustainable village resolution, creating harmony between man & nature.
Studio VIII I 2015 Group project
Advertisement
Responsibility: Site survey, formulation of design and preparation of drawing, model making etc
Supervisor : Dr. Shayer Gofur, Asst. Prof. Mohammad Tahajibul Hossain, Lec. Nusrat Ishtiaque Jahan
Site : Hobuarchala, Gosaibari, Gazipur
Site Area : 43 Acres
Sal forest is a forest type dominated by a single plant species, commonly known as Sal tree (Shorea robusta). It belongs to the category ‘Tropical Moist Decidious Forest’. Continuous unplanned deforestation for human need, as well as spread of scattered settlement through the area has been detrimental to the forest ecology just within last 100 years. Where the forest occupies most of the land is now squeezing drastically.
The Prime objective of the project was to save the forest land, proposing a compact rural settlement which will coexist with the forest and maintain harmony and bio-diversity. The another objective was to study the common rural settlement pattern of Bangladesh, and see how ideas of ‘Compact township’ can provide better opportunities and create a more sustainable future for a agricultural economy oriented country which is suffering to accommodate its huge population.
Design decissions were made with precision to ensure that the proposing settlement pattern do not compromise with the essence of rural life, but promotes opportunity for future development.
‘Compact Township’ is a highly notable idea from Economist Professor Salim Rashid. The idea is basically a futuristic planning approach of rural settlements, where a number of ‘settlement units’ will be formed with basic facilities along with housing. They will replace the existing scattered rural homestead, and preserve valuable cultivable land and will be flood resilient.
The design idea is highly inspired from the compact township theory, applying the concept in ethnic rural village, Hobuarchala, Gosaibari to preseve the cultivable land along with Sal forest land around.
The site is part of the famous Madhupur tract. This valuable Sal forest is getting captured by unscattered settlements and illegal encroachments. Now only 600 sq km of the forest is left alone, whereas it was double in size just 100 years before spreading from northern bengal to comilla. This continuous deforestation has serious enviromental threats. The under ground water level and bio-diversity is decreasing day by day.
The enormous expansion of Dhaka City is the most conspious features of Madhupur Track/ Sal forest. The growth of the city has given birth to numerous small urban areas, in nearest future which will be absorbed into the expanding city.

Baid use: low land, paddy field
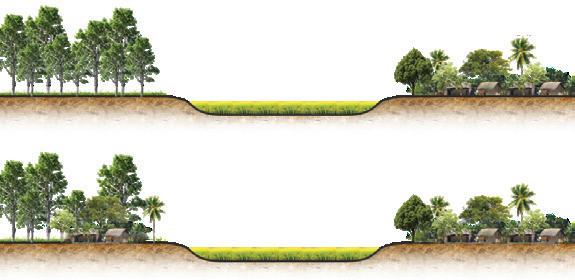
Chala use: high land, settlement, forest
Scattered settlements causing severe harm to the forest. One of them is excessive road infrustructure demand between built structures to connect those villages that set apart from each other.
Individual identity
providing each family with an separate homestead unit and yard, to uphold their age-old culture and social identity. Thus preserving their traditional rural living pattern.
Key design features
Low rise settlements and use of local material
The village deep into the forest is designed with careful use of local materials, to inspire local/community construction.
Inspiring community activity and courtyards
Court-yards are a typical characteristic of rural houses in Bengal, for their micro-climatic benefit. Also these shared yards inspire community gathering and community activities
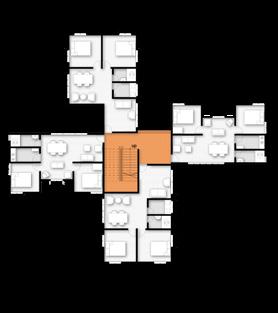
Dwelling unit types
The invaluable forest
The scattered housing pattern is replaced with more compact and sustainable form of settlement, preserving forest land and in a way people can live alongside the forest bio-diversity , even with future extension
Dwelling Type 01 user group: farmer economic class: agriculture dependent economy area: 1800 sqft (for two family unit) facilities: 1 nos living room store room kitchen kitchen garden (back yard) toilet shared yard (front yard) scale: 2 storey mass

Dwelling Type 02 user group: non agricultural farm economic class: higher economic capability area: 650 sq ft facility: 2 nos bed room dinning space living room kitchen toilet veranda scale: 2 storey mass
Dwelling Type 03 user group: non agricultural farmily economic class: lower economic capability area: 540 sq ft/ 580 sq ft facility: 2 nos bed room dinning space living room kitchen toilet scale: 4 storey mass
Dwelling type 02 user group: non agricultural family economic class: higher economic capability
Dwelling type 03 user group: non agricultural family economic class: lower economic capability
High school user group: local community children economic class: govt. school
Community hall user group: local community
Mosque user group: local community
Community bazar user group: local community
Central pond user group: local community
Mondir user group: farmer community
Dwelling type 01 user group: farmer economic class: agriculture dependent economy
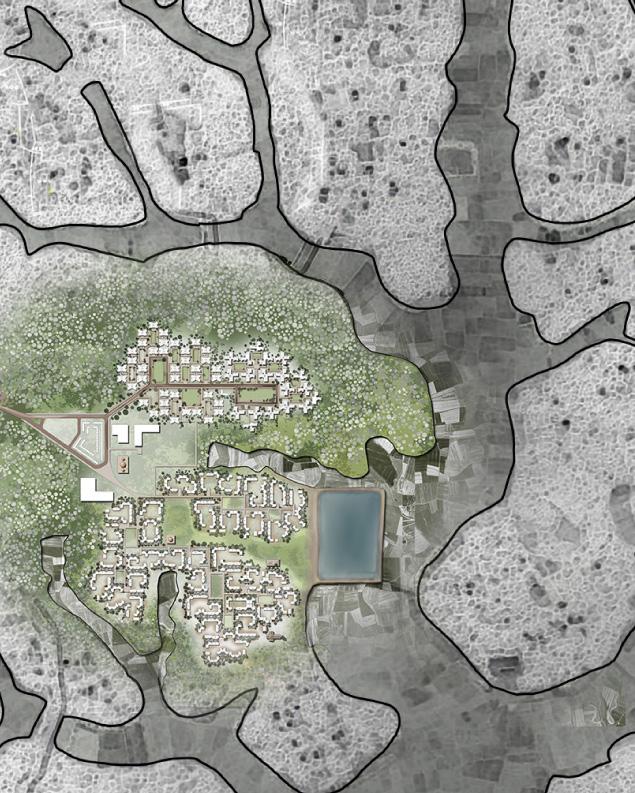
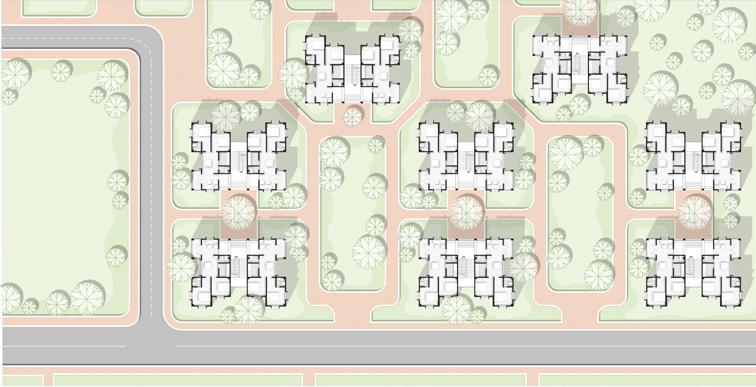
Master Plan
15
0 45 105 m
Cluster for dwelling type 01
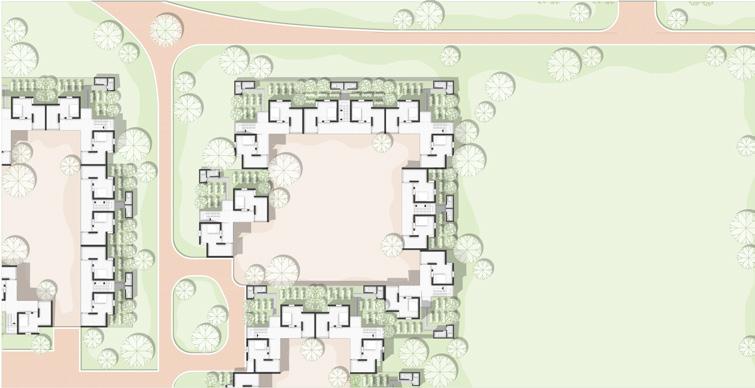
Expandable housing unit
A low cost sustainable solution for families (farmer), using local materials inspiring local construction tecnique. These expandable dwelling unit has carefully designed to serve future expansion providing direct ground level contact for individual.

Visual of Type 01 Cluster Court









