Thesis Masters of Urban and Regional Planning


Capacity
Municipal Limits An approach towards Infrastructural Upgradation
Building for Urban Tourism Development of Ayodhya
-APresentation by: Ar.
Sayan Munshi
MURP, FOAP, AKTU, Lucknow
Introduction
Tourism is an integral pillar of the Make in India program Tourism plays a role of significant economic multiplier in the states which acts as a host As per the Manila Declaration on World Tourism of 1980 recognized its importance as "an activity essential to the life of nations because of its direct effects on the social, cultural, educational, and economic sectors of national societies, and on their international relations ” Tourism boosts the revenue of the economy, creates thousands of jobs, tend to develop the infrastructures of a country, and plants a sense of cultural exchange between foreigners and citizens
Tourism infrastructure is the basis of tourism development and utilization of existing destination resources
Equation for Tourism Potential
σ������ = Y��(Transport) + Y��(SWM) + Y��(Accommodation) ±11.752
Components of Equation
TRANSPORTATION χ1

• No of Trip Generated
• No of Parking at destination
• Mode of transport
• Condition of Road
• No. of Destination per city
• Population (Census)
• Population (Floating)
• Generation of Tourist
SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT χ2
• Collection cycle
• Tourist flow
• Population
• Household size
Tourism Infrastructure
Physical Cultural Service Governance
Tourism Potential
Tourism potential can be defined as “the totality of natural, cultural, historical and socio-economic background for the organization of tourist activity in the particular area
Tourism Super Potential
Tourism Super potential Tts is the Summation of the overall potentiality mapped through the components X1, X2 and X3 in an Region
Critical need of Infrastructure to support Tourism (YTS < 20)
• Preparation of Tourism Master Plan
• Preparation or Modification in CMP
• Setup of Tourism Cell under Local Government
• Empowering Local Government with better structure of SWM
• PPP for Accommodation infrastructure
• Dedicated Transport system to ensure lower congestion and Higher LOS on local road

• Training and employment of Tourism related Tertiary sector workers.
• Participatory approach by Diagnostics, Consultation, and Action plan
• Policy Guidance Document that mobilizes all Municipal policies and Tourism Ecosystem across a broad circuit.
Potential need of Infrastructure to support Tourism (YTS = 20 – 24.89)
• Preparation of Tourism Master Plan
• Preparation or Modification in CMP
• Setup of Tourism Cell under Local Government
• Empowering Local Government with better structure of SWM and Revenue Structure.
• PPP for Accommodation infrastructure and Control over Cost Structure.
• Dedicated Transport system to ensure lower congestion and Higher LOS on local road and Increase share of Public Transportation.
• Training and employment of Tourism related Tertiary sector workers.
• Participatory approach by Diagnostics, Consultation, and Action plan
• Policy Guidance Document that mobilizes all Municipal policies and Tourism Ecosystem across a broad circuit
χ3
• No of Accommodation
• Disposal and treatment
• Waste generation

ACCOMODATION
• Duration of stay
• Category of Hotel
• Parking facility
• No. of Destination per city
• Population floating
• Need of Accommodation
Upgradation of Infrastructure and Governance support Tourism (YTS > 24.89)
• Circuit Definition of Tourism Master Plan
• Circuit planning or Modification in CMP
• Improvisation of Tourism Cell under Local Government
• Empowering Local Government with better structure of SWM and Revenue Structure.
• PPP for Accommodation infrastructure and Control over Cost Structure.

• Dedicated Transport system to ensure lower congestion and Higher LOS on local road and Increase share of Public Transportation and Concentration Towards NMT.
• Action plan incorporated with Master Plan.
• Policy Guidance Document that mobilizes all Municipal policies and Tourism Ecosystem across a broad circuit Upgradation of the Peri Urban Area.
Capacity Building for Urban Tourism Development of Ayodhya Municipal Limits
INTRODUCTION
Introduction to the Thesis, Conceptualization, Tourism Potentiality
LEGENDS SHEET TITLE STUDENT NAME
Ar. Sayan Munshi
IVth Semester, M.Plan FOAP, AKTU, Lucknow, UP
Dr. Subhrajit Banerjee Thesis Guide
SOURCES
Sayan Munshi, SB , IC – 2022 IRJET
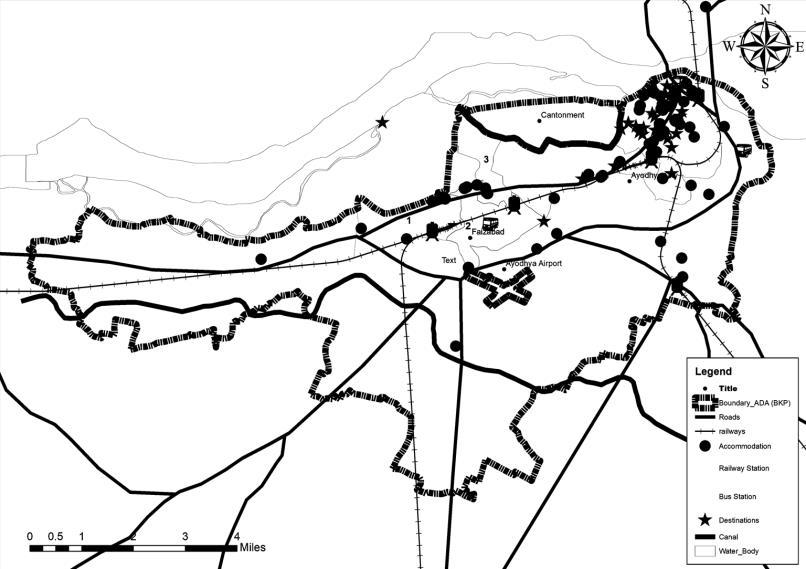
KEY MAP
X X
X
3
2
01
Aim:
To formulate a comprehensive model for capacity building related to tourism infrastructure based on Transportation, SWM and Accommodation Infra.
PHASE 1
• Enumeration of Tourism Specific Infrastructure (determinants)

• Prime Sector of Infrastructure (Determinants)
PHASE 2
Objectives:
1. To identify various tourism-related infrastructure needs in Ayodhya Municipal Limits.
2. To study the impact of determinants of infrastructure by the tourism industry.
3. To suggest a Proposal model to improve the tourism potential of the Municipal Limits by capacity building.
Scope:
• To find and analyze tourism’s effect in Municipal limits of Ayodhya City

• Cultural tourism will be focused
• To find ways to augment the Existing infrastructure and find possible solutions by capacity Building.
• To develop a Proposal Model to upgrade Tourism led Infrastructure.
• Analysis of the Existing
• Infrastructure Including:
• Transportation
• Solid waste management
• Accommodation / Hotel Infrastructure demarcation
METHODOLOGY
Limitations:
• The study will be limited to Urban Area of Ayodhya
• Study would focus on components/determinants of Infrastructure and its upgradation
• The study will be a limited sub-category of Inbound tourists.
• Economic aspects of tourism are not included.
Ranking of the City based on Structural Equation derived in Dissertation
PHASE 3 PHASE 4
• Proposal based on Analysis of the Existing.
• Possible retrofitting and Augmentation to improve ranking.

PHASE 5
Ranking of the City based on Structural Equation derived in Dissertation
LEGENDS SHEET TITLE
THESIS BRIEF
STUDENT NAME
Ar. Sayan Munshi
IVth Semester, M.Plan FOAP, AKTU, Lucknow, UP
Dr. Subhrajit Banerjee Thesis Guide
SOURCES
Capacity Building for Urban Tourism Development of Ayodhya Municipal Limits
KEY MAP
Inference Tourism Infrastructure Physical Cultural Service Governance Analysis URDPFI Guidelines P. Infrastructure Retrofitting Possibility Data Collection Primary Survey Secondary Data Sources
Ranking Through
Gap
Augmentation Possibilities
Infra
Stage 1 : Application of Structural Equation Stage 2 : Application of Structural Equation
MLR
in Tourism Infrastructure
Traffic & Transport Solid Waste Management Accommodation
Ranking Through MLR Validity
02
Aim, Objective, Scope, Limitation, Methodology
AYODHYA, UTTAR PRADESH
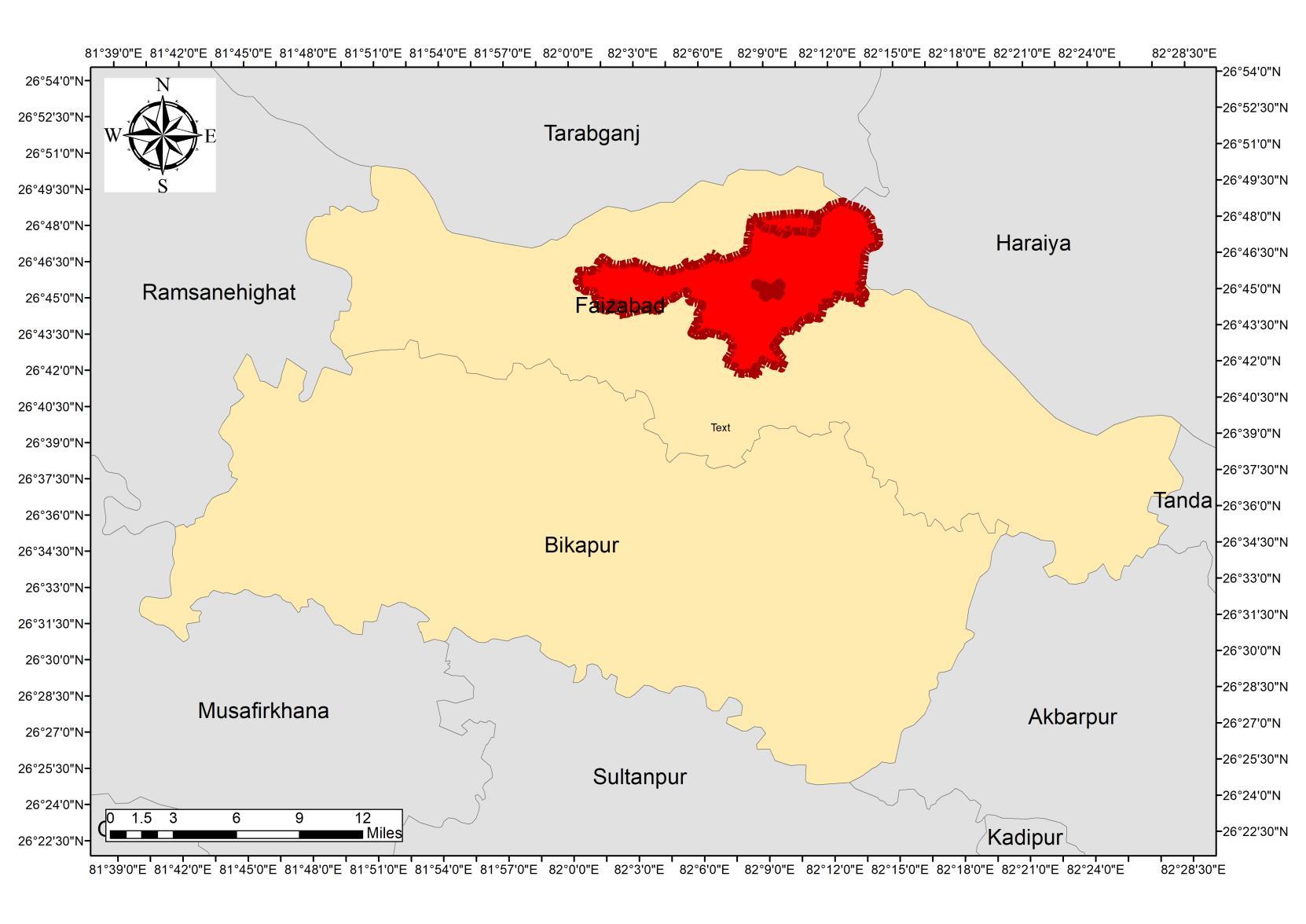
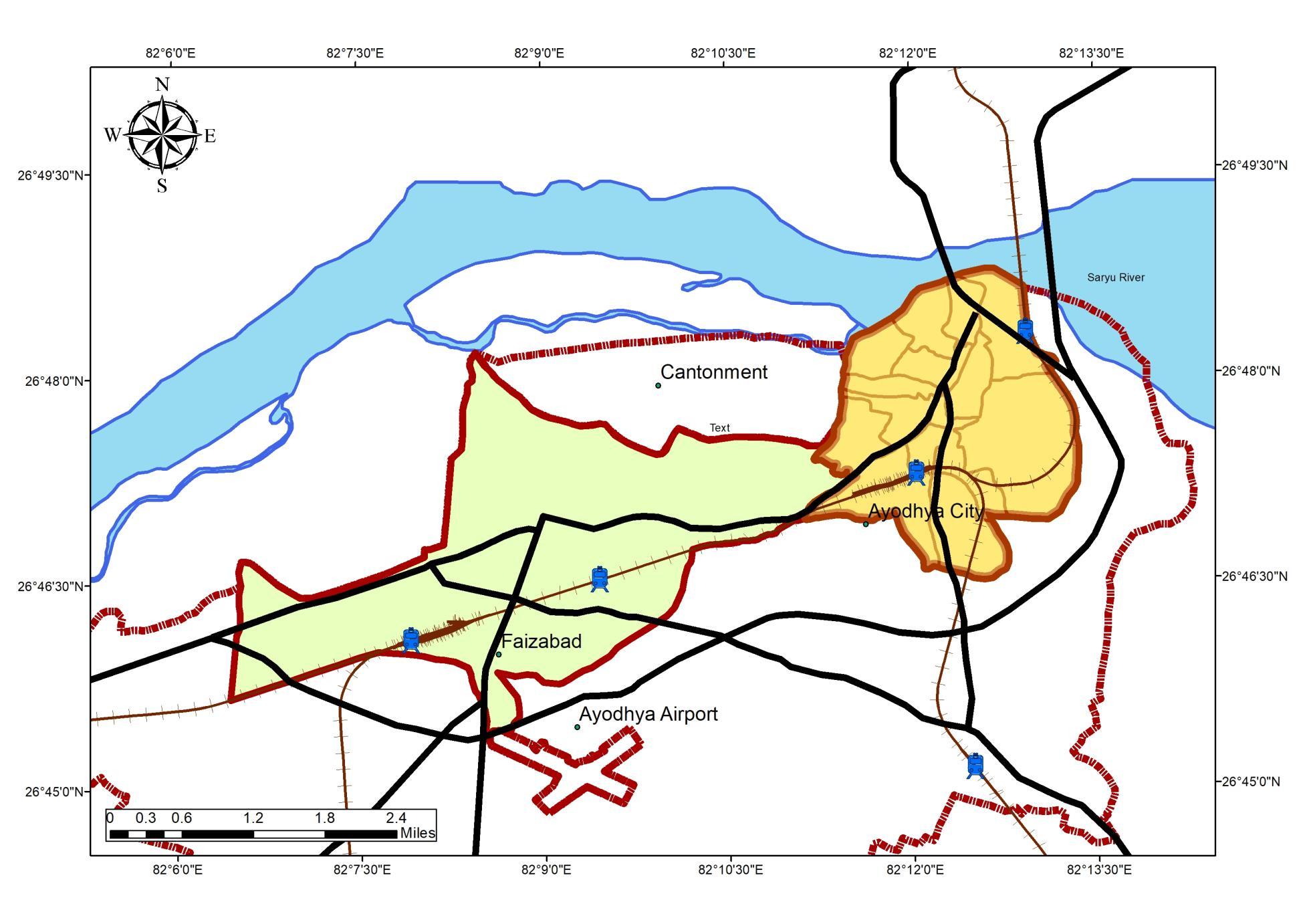
Ayodhya is a city situated on the banks of the holy river Saryu in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh It is the administrative headquarters of Faizabad district and the Faizabad division of Uttar Pradesh, India
Faizabad-Ayodhya Region
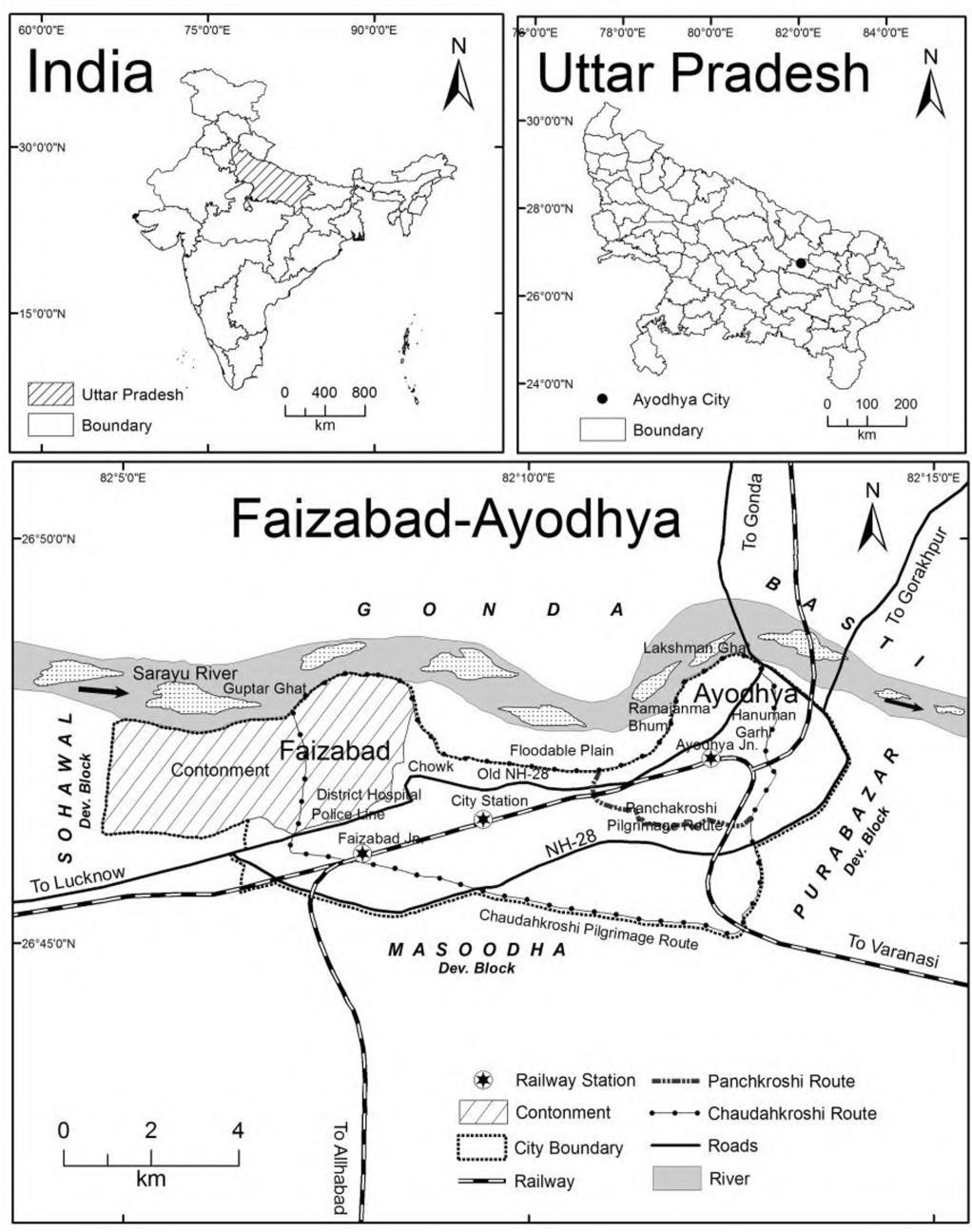
Ghats ofAyodhya
The growth of the city is mostly seen along the roads such as Ayodhya-Azamgarh, Ayodhya -Prayagraj, Ayodhya -Raibareli and AyodhyaLucknow Ayodhya Municipal Corporation is growing at faster rate
Urban Sprawl in 2001 Urban Sprawl in 2011 Urban Sprawl in 2021
Ayodhya master plan is constituted with an area of 388 Sq.Km
• Regulated area of Ayodhya development authority is 133 67 Sq Km
• Planning area considered for the Master plan is 133 67 Sq Km
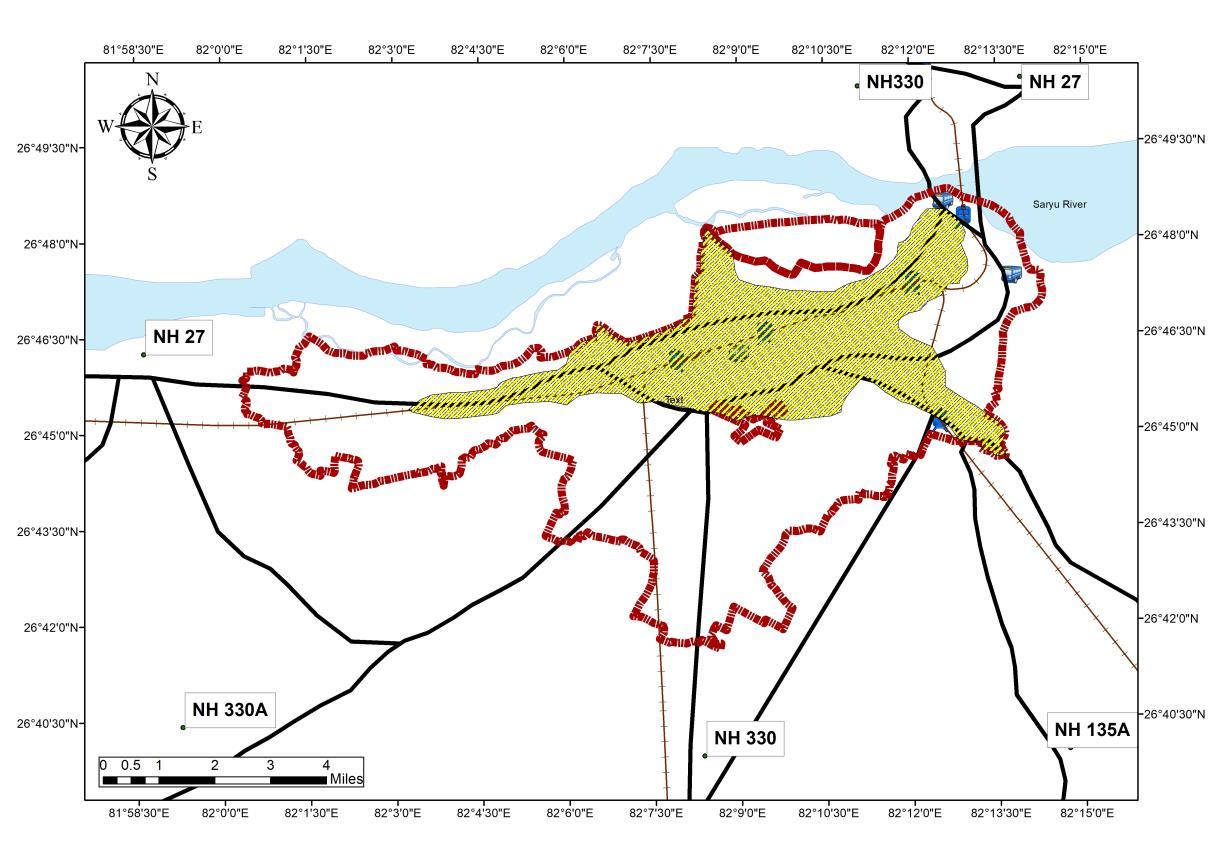
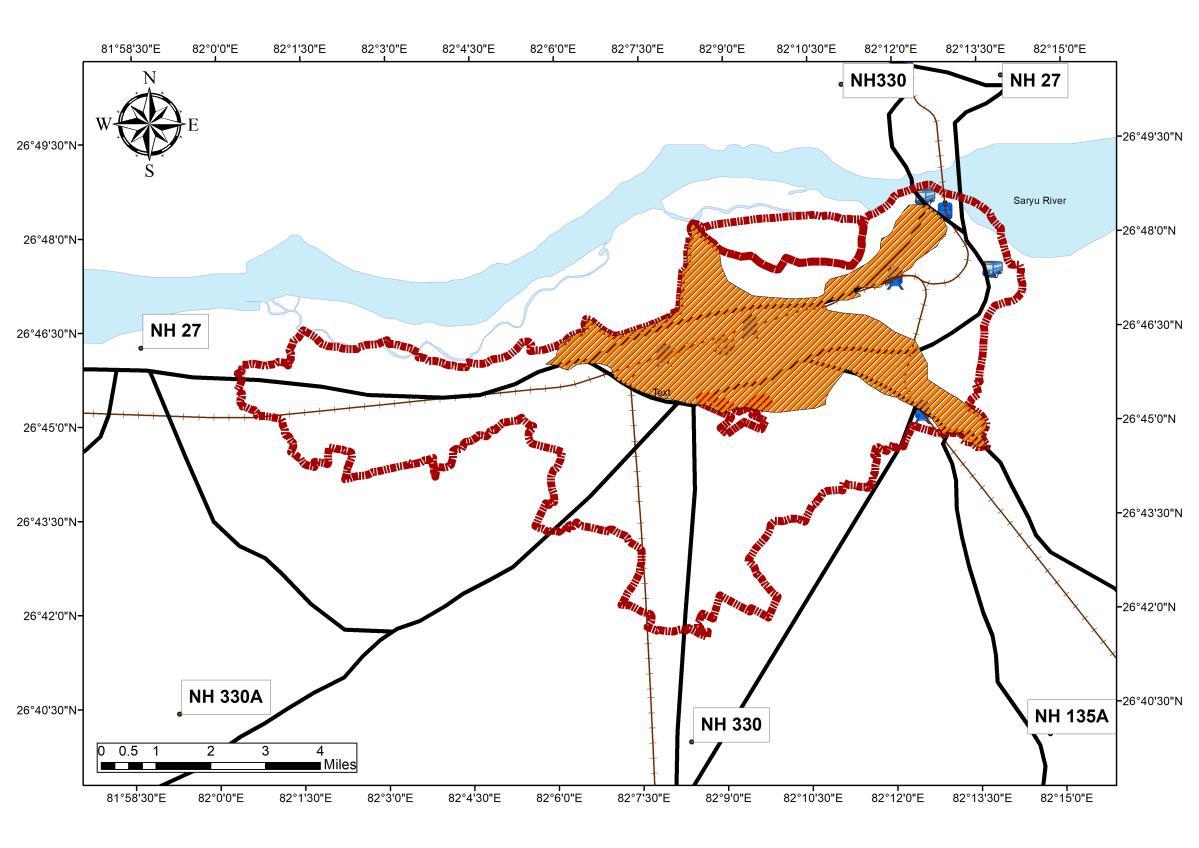
Analysis
Source Author wr tAyodhya Masterplan 2031, Generated Arc Gis 10 7 (April,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)
• The year 2001 shows a trend of the sprawl along NH135A and NH27 connecting Major Cities, thus linear development are observed.
• Following Year 2011 shows an Omni-directional Growth following the pattern of the Sprawls character of the Year 2001
• The Influence of Tourism and industrial growth can be observed in the Urban sprawl character with an increase of municipal area on the SW axis, along NH 330A and NH 330
Decadal Growth and Urban Sprawl
AREA (SQ.KM)

Area (sq Km) Linear (Area (sq Km))
Source: Rana P.B. Singh, BHU, Varanasi (2020)
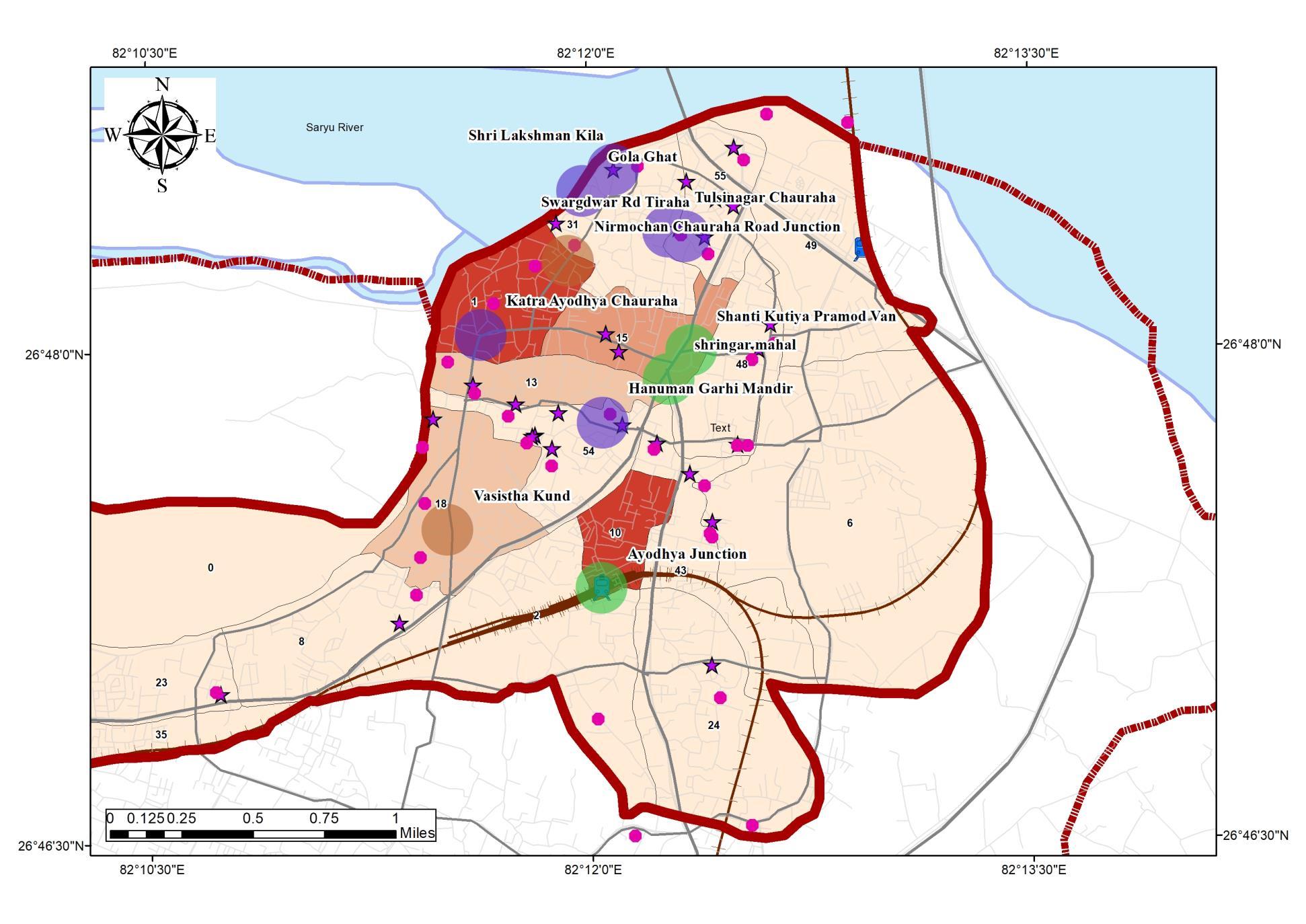
HISTORIC DEVELOPMENT OF AYODHYA CITY
Ayodhya is regarded as one of the seven sacred cities of the Hindus, revered because of its association in the great Indian epic poem Ramayana with the birth of Rama and with the rule of his father, Dasharatha. According to this source, the town was prosperous and well fortified and had a large population
Ayodhya was the early capital of the kingdom of Kosala, with 25 kings in 90 regions in Indian sub continent ranging from UP to Orissa, Ruled by Emperor Pasenadi. 600 – 700 BCE
Faxian (Buddhist monk whose pilgrimage to India initiated SinoIndian relations) Built 100 Monasteries 400 -600 CE
Settlements started to flourish, Market streets emerged along Major Roads (Shravasti-Pratishthana north–south road and the Rajagriha-Varanasi-Shravasti-Taxila east–west road.)
During Gupta period, the recognition of Saketa as legendary city of Ayodhya, the capital of Iskshvanku / Solar dynasty was recognized.
After the Invasions of Gupta Dynasty by Mihirakula Ayodhya lost its position as an important political center. 650–1050 AD
Ayodhya became the capital of the province of Awadh (or "Oudh") within the Delhi sultanate. 1226 BC
Nawabs Built several Structures in Ayodhya, Gulab Bari, Moti Mahal and the tomb of Bahu Begum.
Under Mughal rule, the Babri mosque was constructed in Ayodhya. 1700 - 1850
Historic Settlement Pattern chronology
Source:Author wr Ayodhya Masterplan 2031, Generated Arc Gis 10 7 (April,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)

33
79.8
133.67 AREA IN SQ. KM DECADE
2001 2011 2021 Area (sq Km) 33 79.8 133.67
Source:Author w.r.tAyodhya Masterplan 2031 (April,2022)
Year Area Growth % 2001 33 2011 79.8 141% 2021 133.67 67.5%
Analysis:
• The city experience a growth rate of 67 5% during the Last Decade, which is due to Reverse Migration
URBAN SPRAWL : PRESENT STATUS
Ayodhya Municipal Corporation is growing at a faster rate
• The highways passing through the city is joining Lucknow and Gorakhpur.
• Linear development is taking place towards Lucknow road
• The development at faster rate is observed on Sultanpur road.
• Linear development is also observed on Faizabad to Ambedkar Nagar road On Sultanpur and Raibareli main roads commercial development and interior area is developed for residential use.
• Industrial development is developed on Lucknow road
• Institutional development is developed on Lucknow road, and Ram Manohar university is developed on Sultanpur road. K.S.Sanket Mahavidyalaya and ITI are developed between Ayodhya and Faizabad
• Mix land use is observed towards the National highway and state highway
Building for Urban Tourism Development of Ayodhya Municipal Limits



LEGENDS SHEET TITLE
STUDY AREA
Background, Historic Profile, Decadal Urban Sprawl
STUDENT NAME
Ar. Sayan Munshi
IVth Semester, M.Plan FOAP, AKTU, Lucknow, UP
Dr. Subhrajit Banerjee
Guide
SOURCES
ADA Reports Ayodhya NN Reports MDP Draft 2031 Primary Data Collection ADA Website
Capacity
KEY MAP
Thesis
URBAN SPRAWL IN THE REGION OF AYODHYA STUDY AREA:
03
OVERVIEW
District Overview
Faizabad district, officially Ayodhya district, is one of the 75 districts of Indian state of Uttar Pradesh The district occupies an area of 2,522 square kilometers (974 sq mi),and had a population of 24,70,996 in the 2011 census.
➢ The percentage share of urban population in the district is 13 8% as against 22.3% of the population in urban areas of the state.
➢ Faizabad district has population density of 980 persons per sq.km. which is more than the state average 829 persons per sq. km.
➢ The district has 10 towns out of them 7 are statutory and 3 census towns.
Source: DCHB, Census India 2011 (Available Online)
Faizabad District (OfficiallyAyodhya)
Source:Author wr DCHB 2011, Generated Arc Gis 10 7 (April,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)
Ayodhya City Overview
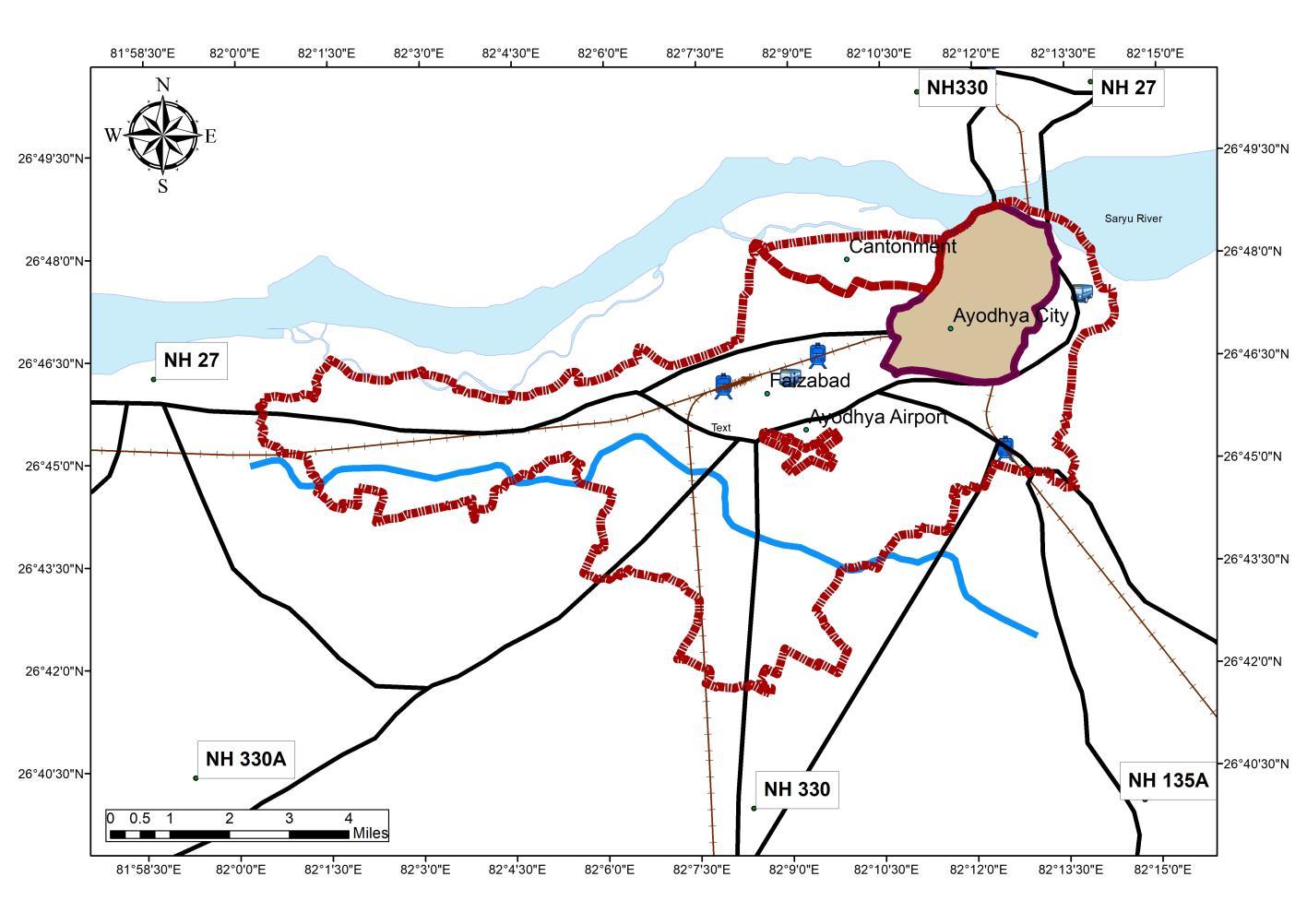
Ayodhya city located in Ayodhya district of eastern Uttar Pradesh is situated on the south bank of the Saryu River The National Highway 27 which connects New Delhi to Nepal passes through the city ofAyodhya
Influence of Tourism
Ayodhya holds significance in History through the mythological character Rama and the Influence of tourism would further increase by the competition of Ram Mandir by the year 2030. As per the Research on the Tourism potential VS Infrastructure it has been found that the City of Ayodhya Lacks in infrastructure potential. An upgraded infrastructure would lead towards a upgraded tourism potential of the region
Population (ADA Urban Area) 2,21,118
Population Density 1056 person/sq km
INTRODUCTION TO STUDY AREA
Source:Author, Generated Arc Gis 10 7 (April,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)
ANALYSIS
Regional Setting

Ayodhya is the headquarters of the Ayodhya district and Ayodhya division. Ayodhya is a market center for the production of the surrounding area, including grain, oilseeds, cotton, and tobacco Ayodhya District is bounded by the following:
• North: Gonda and Basti district
• South: Sultanpur
• West: Barabanki
• East: Ambedkar Nagar
Connectivity
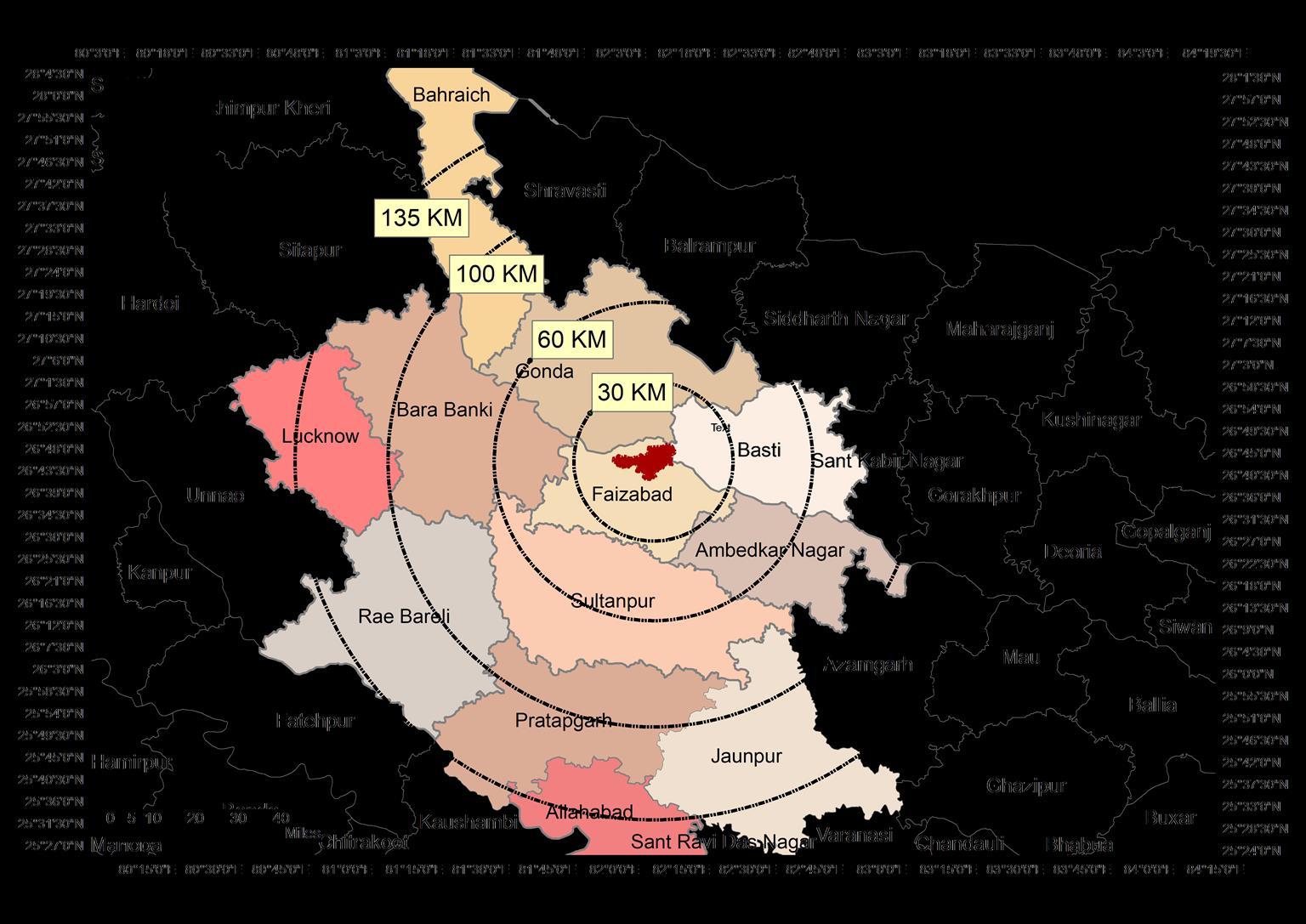
Ayodhya is well-connected to major cities like Lucknow, Kanpur, Gorakhpur and Varanasi
Cities Distance
Lucknow 135 km Varanasi 200 km Prayagraj 134 Km Gorakhpur 134 Km Delhi 636 Km
It has an airport which is now developing as international Airport by acquiring 600 acre of land
LEGENDS
Legend
Legend
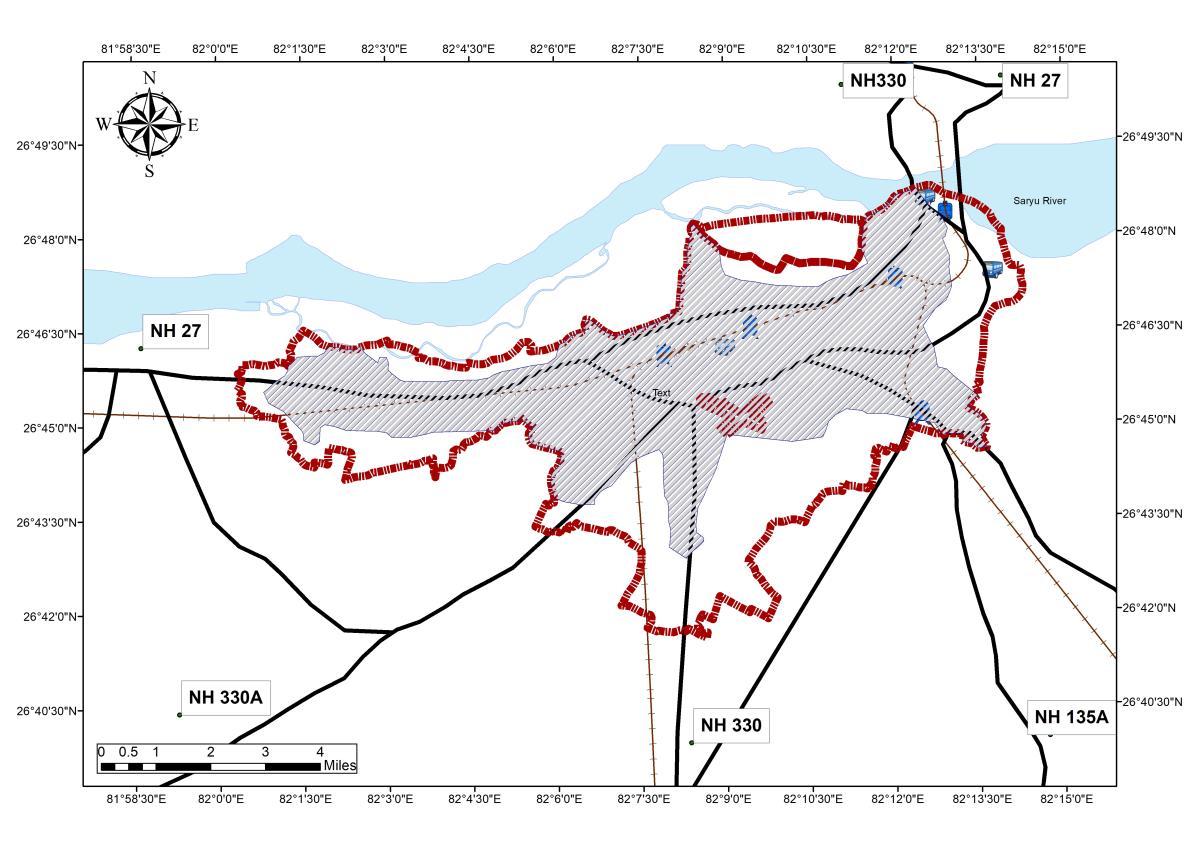
Boundary_ADA(BKP)
Total Registered Vehicle 48338
Source: DCHB, Census India 2011 (Available Online),Ayodhya Master Plan 2031 (Available Online)
LK VA AL AY
35.75 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 0 10 20 30 40 50 60
Ayodhya PlanningArea (APA) Wards Under Study
Assumption for Site Selection: 1. Geography of the destination is to be constant to perform reliability test, in order to reduce errors in analysis.
Market conditions are assumed constant 3. Analysis is to be made on same scale 4. Tourism Typology must be constant
Source:Author wr tAyodhya Masterplan 2031 Generated Arc Gis 10 7 (April,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)

Capacity Building for Urban Tourism Development of Ayodhya Municipal Limits
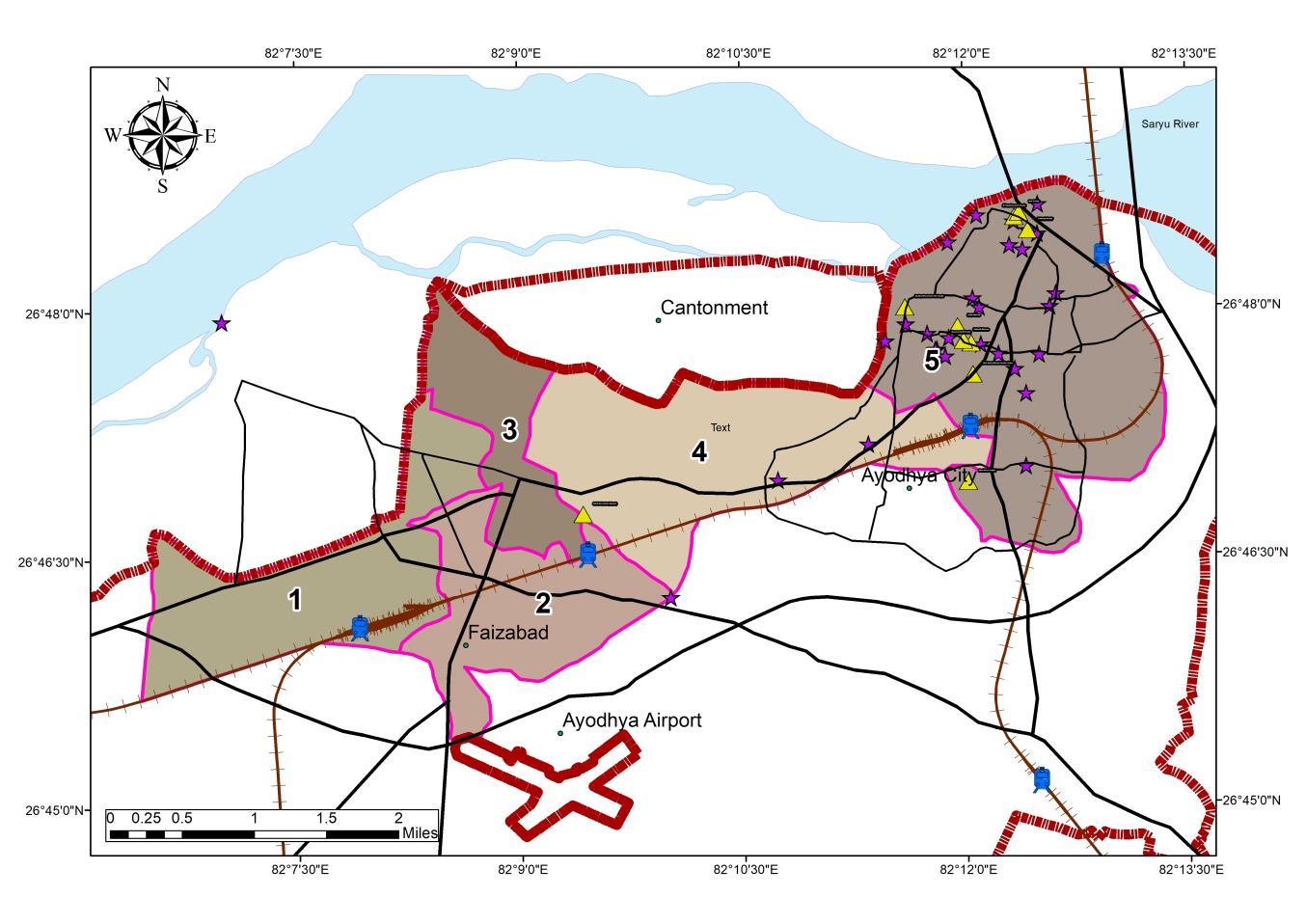
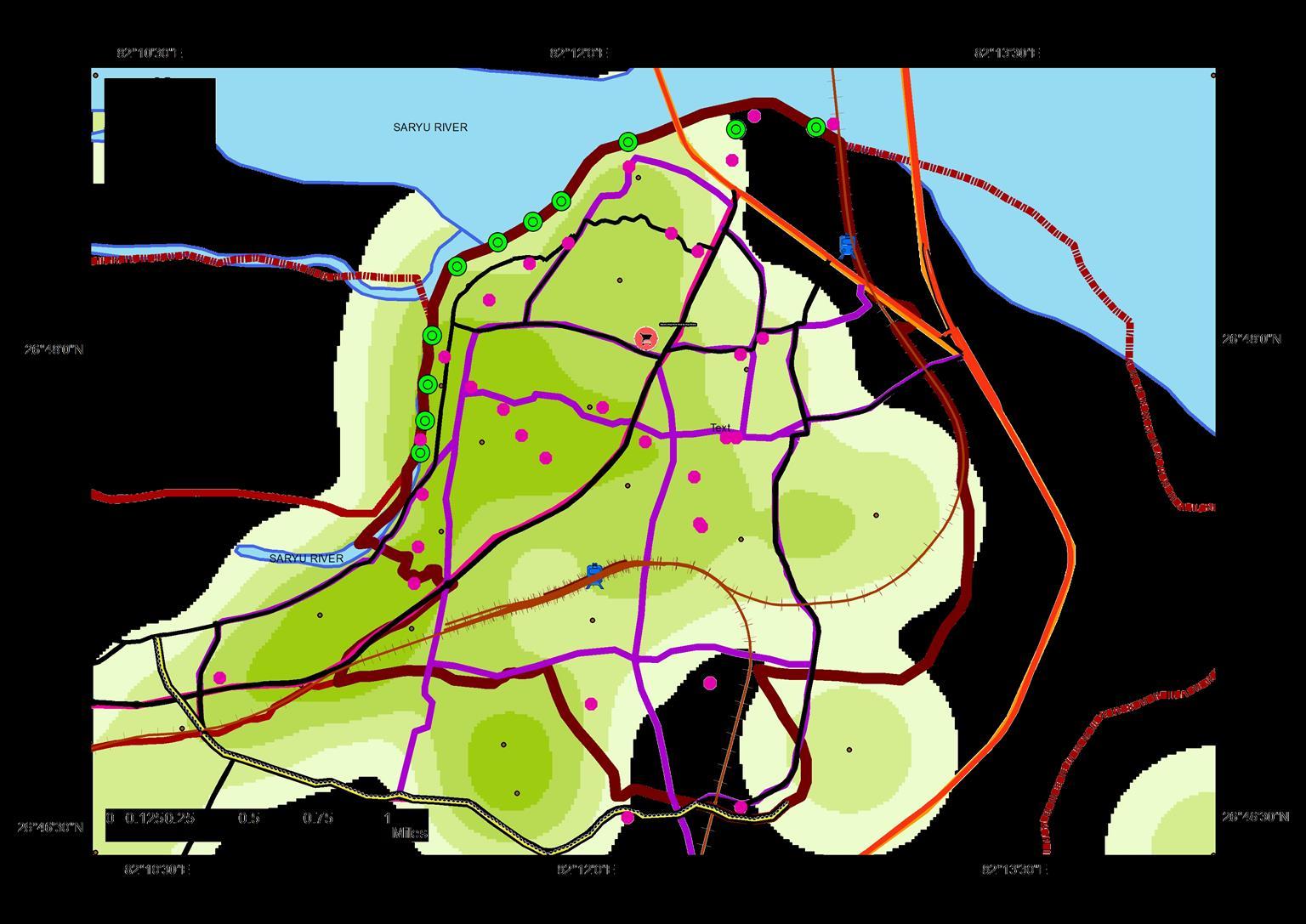
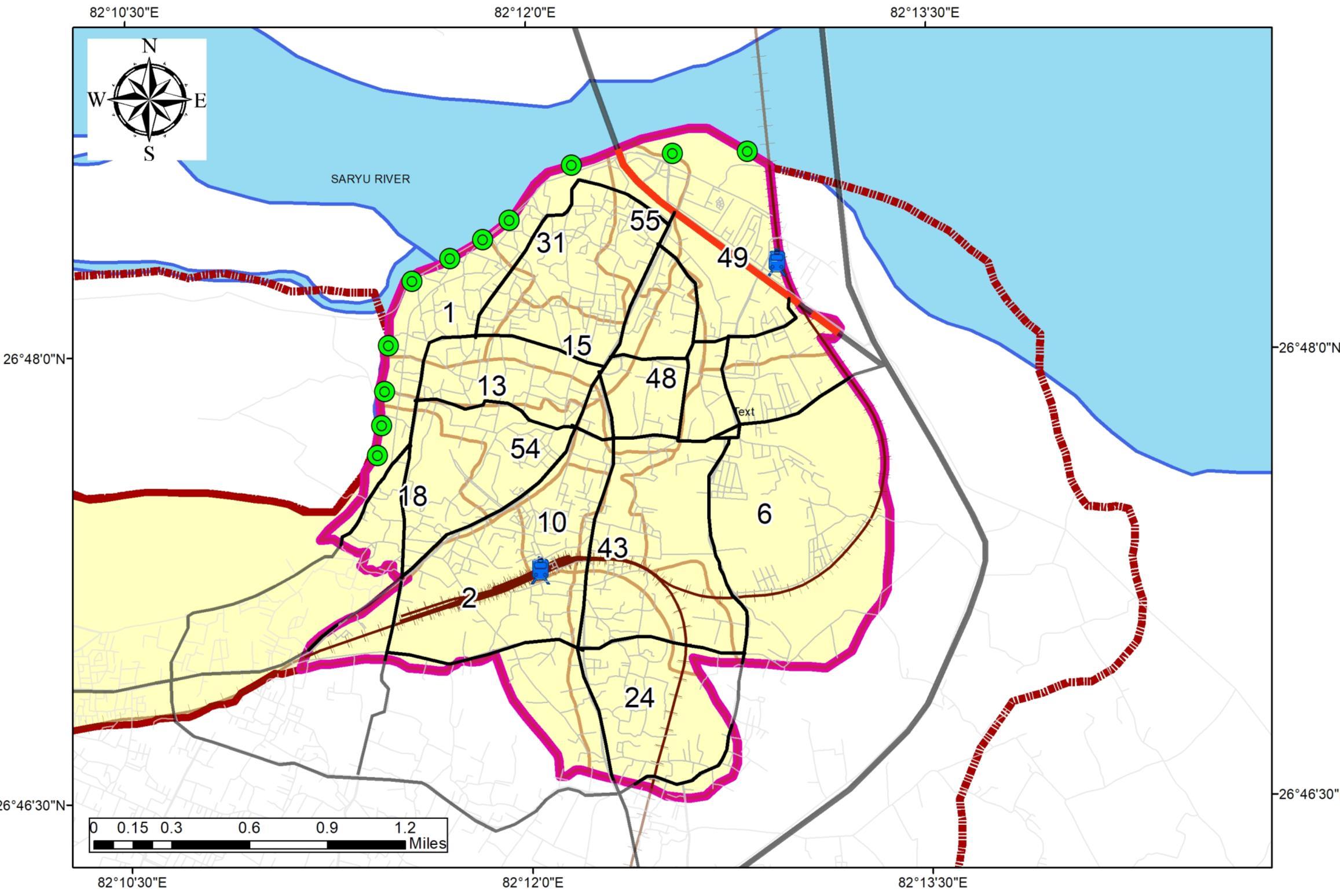
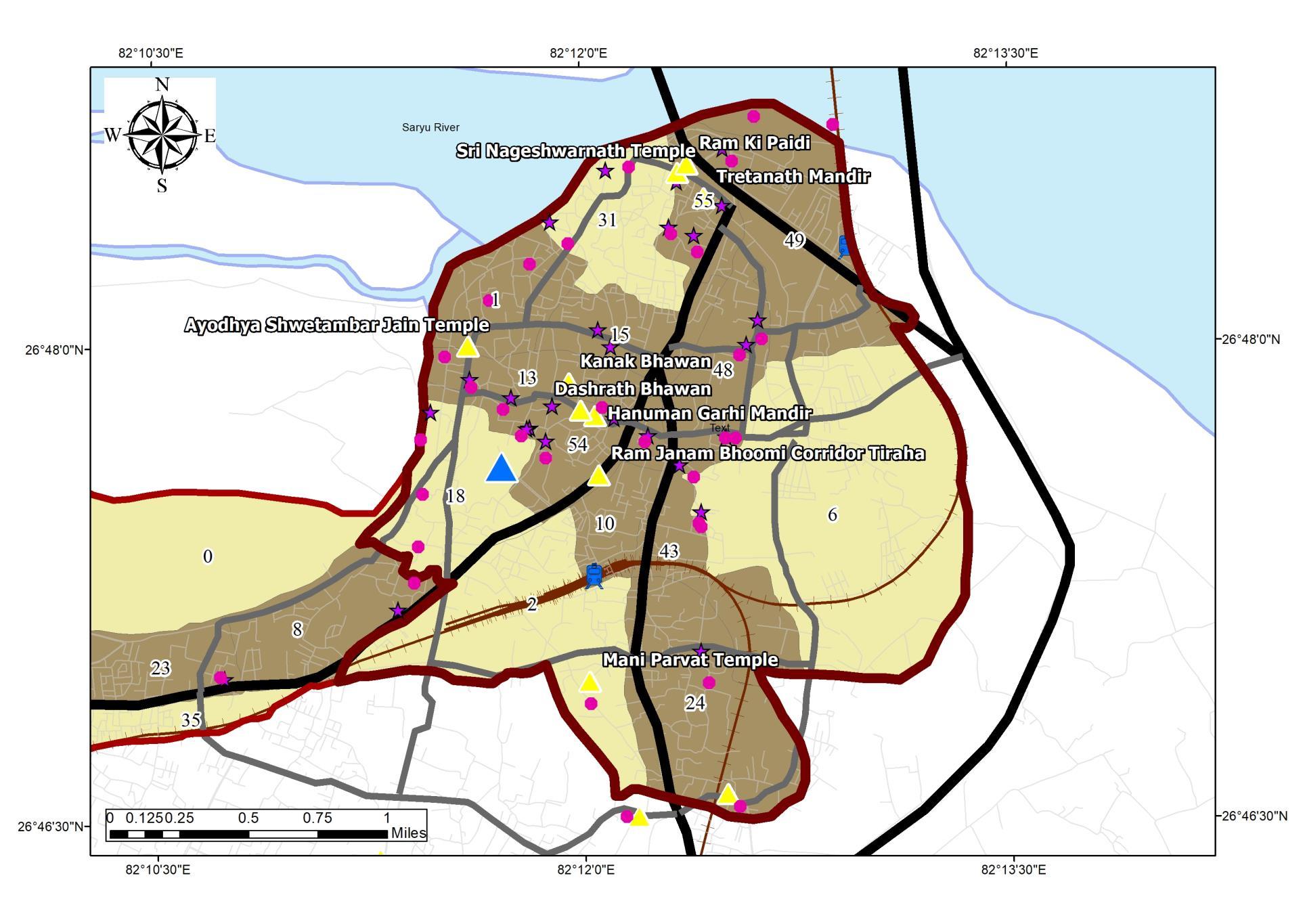
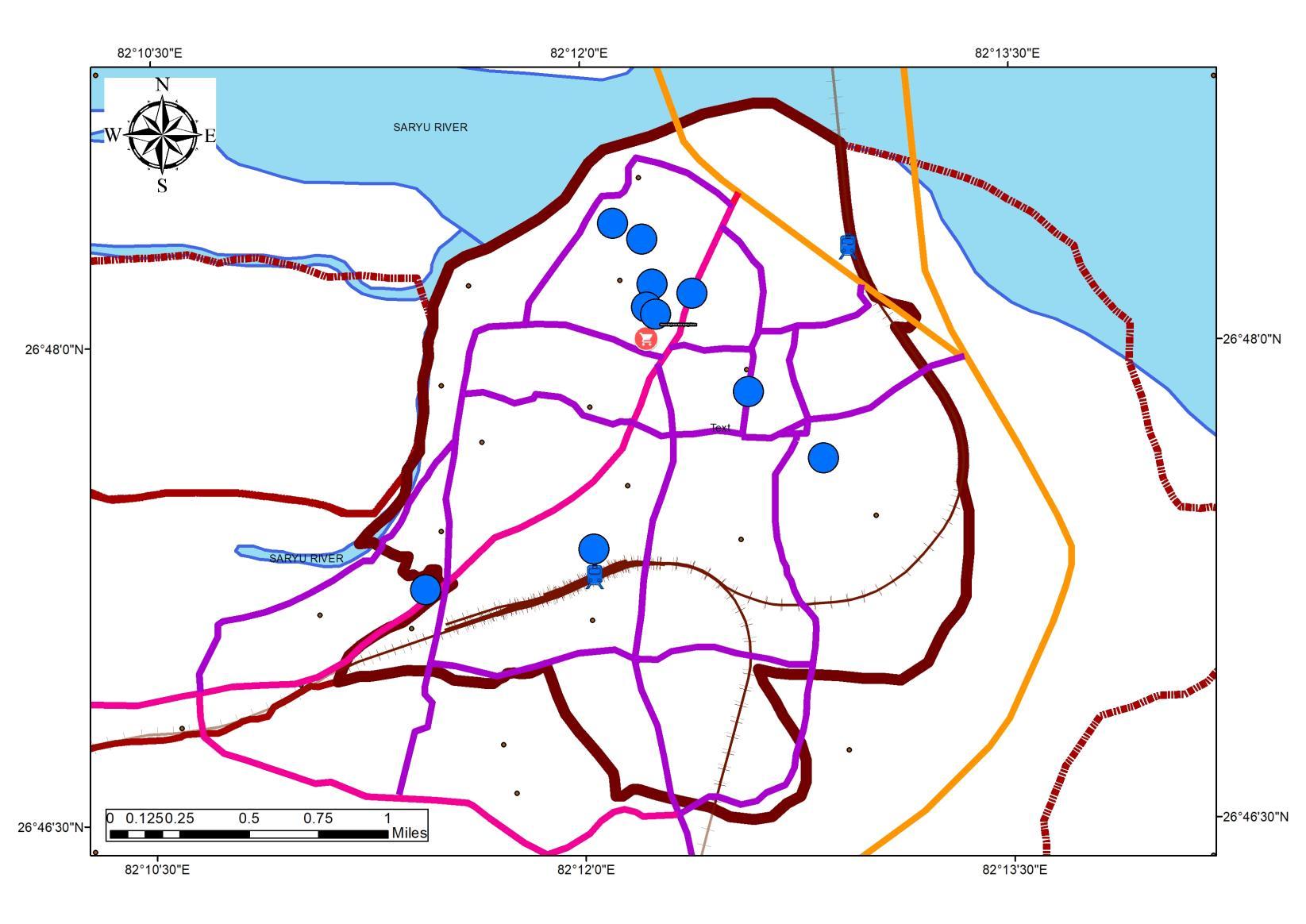
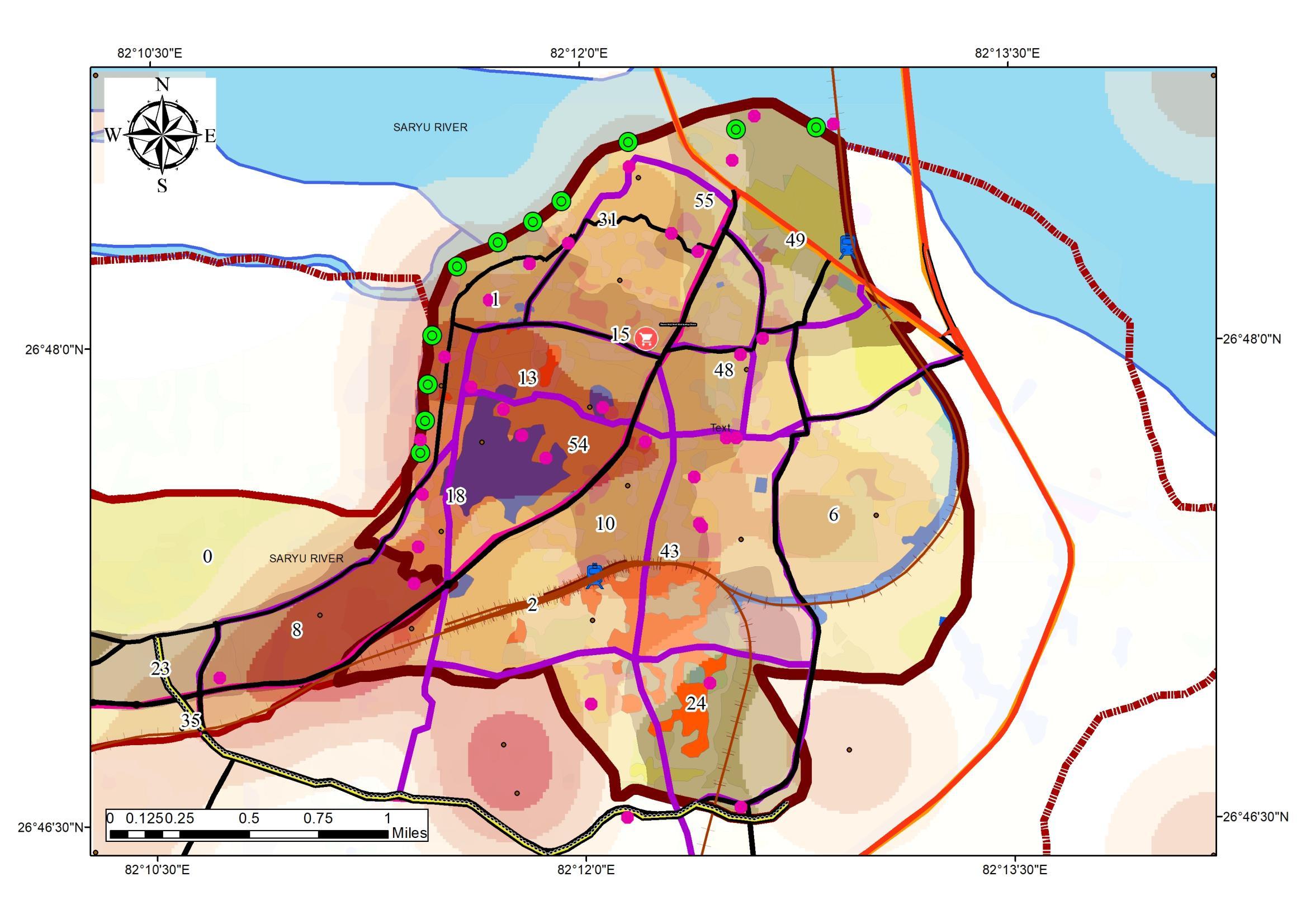
• Study to be Conducted for 14 Wards {1, 2, 6, 8, 10, 15, 18, 24,31, 43, 48, 49, 54, 55}.
• Study Delineation would Include determinants of Transport, SWM and Accommodation
Buffer_30Km
Buffer_60km Buffer_100km Buffer_135Km Regional_buffer <all other values>
Regions
Boundary_ADA(BKP) Buffer_30Km Buffer_60km Buffer_100km Buffer_135Km Regional_buffer <all other values>
NAME_2 Allahabad Ambedkar Nagar Bahraich Bara Banki Basti Faizabad Gonda Jaunpur Lucknow Pratapgarh Rae Bareli Sultanpur
NAME_2 Allahabad Ambedkar Nagar Bahraich Bara Banki Basti Faizabad Gonda Jaunpur Lucknow Pratapgarh Rae Bareli Sultanpur
SHEET TITLE
STUDY AREA
Regional Setting, Tourism Influence and Overview
STUDENT NAME
Ar. Sayan Munshi
IVth Semester, M.Plan FOAP, AKTU, Lucknow, UP
Dr. Subhrajit Banerjee Thesis Guide
SOURCES
ADA Reports
Ayodhya NN Reports
MDP Draft 2031
Primary Data Collection ADA Website
KEY MAP
REGIONAL SETTING
2.
AYODHYA CITY – URBAN AREA
Area 135 Sq. Km + 135 Sq. Km Number of Wards 60 DEMOGRAPHY AND ECONOMIC OVERVIEW
Economic Activity Primary and Tertiary Number of households 10026 HH
Average Household Size 6.0
INFRASTRUCTURE OVERVIEW
Accounting 55%
Transport Roadways, Railways,
Largest Vehicle Share 2- Wheeler (40727)
Total Road Length 228.65 KM Mode of Public
Airways Solid Waste Generation per Day 93.5 Tons D2D Coverage 35 Wards Highest Waste generators Residential and Commercial
04
BASIS OF STUDY AREA SELECTION
WALKABILITY
• Walkability refers to the ability to safely walk to amenities within a reasonable distance, usually defined as a walk of 30 minutes or less
• As per the TOD Standards proposed by DLCA ( under UN-HABITAT), the walkability factor is defined as 1/8 to 1 mile, or 1 6 km (Maximum)

Destination Walkability delineation Map
DEMOGRAPHICAL ANALYSIS
BACKGROUND
• Ayodhya Nagar Palika Parishad (NPP) presently Ayodhya Municipal corporation census data collection started in the Year 1981
• As per the Census 2011, Ayodhya Urban Area of ADA (Ayodhya DevelopmentAuthority)constitutes a population of 2,21,118 Persons
• Presently, the Ayodhya (M Corp) population is 55,890 Persons with anAverage Decadal growth rate of 22 6%
Population Growth Statistics ofAyodhya (M.Corp)
Population
Population Statistics ofAyodhya (M.Corp)
POPULATION OF AYODHYA MUNICIPAL CORPORATION (NPP)
Census Years Population Absolute Growth Growth Rate (%)
1961 83177
1971 102835 19658 23.63 1981 132373 29538 28.72 1991 165079 32706 24.71 2001 194122 29043 17.59
2011 221118 26996 13.91
2021 248706 27588 12.48 2031 276294 27588 11.09
Source:Author w.r.t Census India 1981 – 2011, DCHB
Legend Roads R_type
Population Linear (Population) Expon. (Population)
Source:Author w.r.t Census India 1981 – 2011, DCHB
POPULATION DISTRIBUTION WITHIN AMC
Inference
• The Decadal population of Ayodhya M Corp has increased 3 times the population of the initial Census year 1961 The trend can be observed by the year 1991
• The growth trend shows a range of 13% to 28%, the increase in the resident population is due to the growth in the tourism and industrial sector
INFLUENCE ON THE WARDS
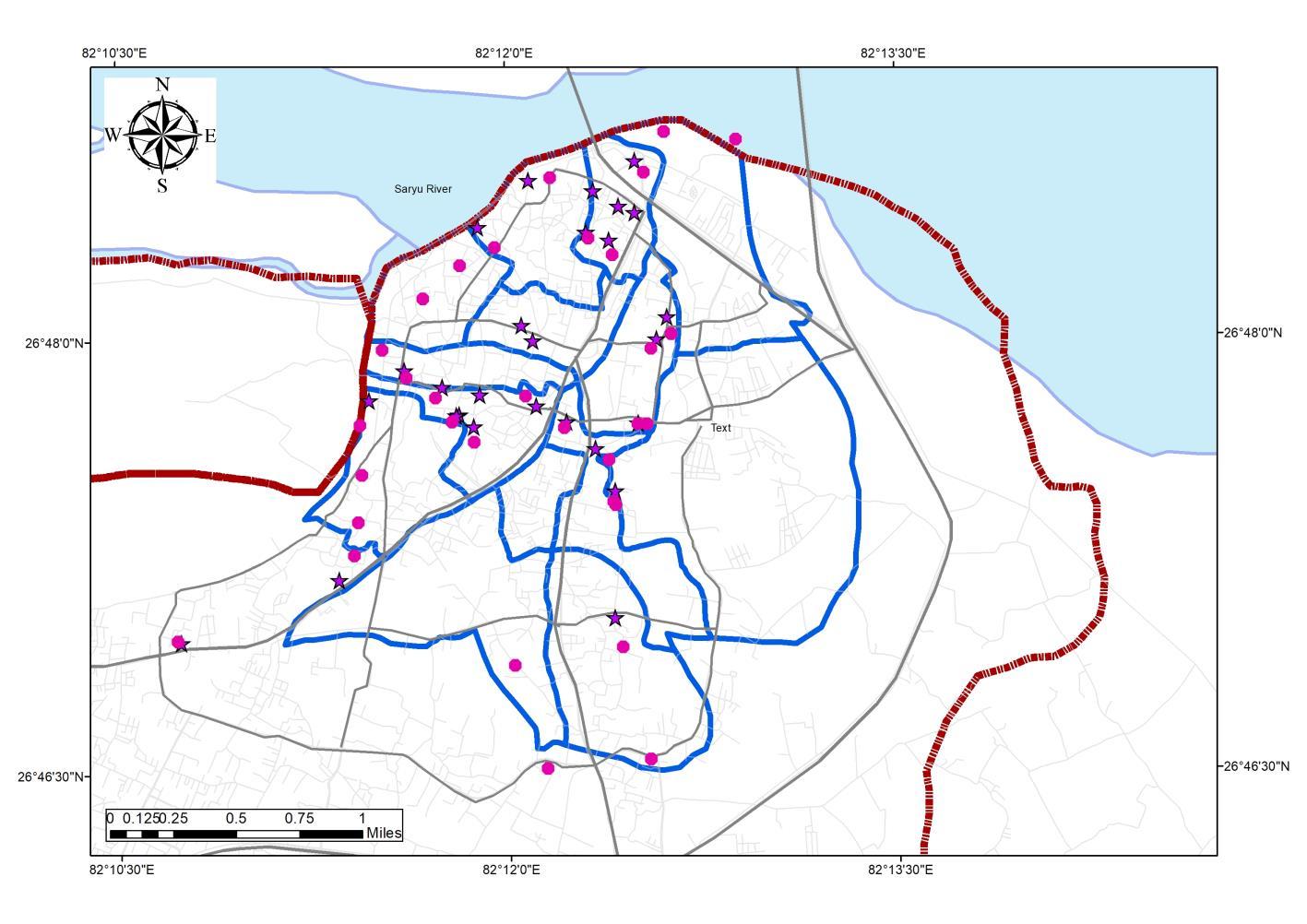
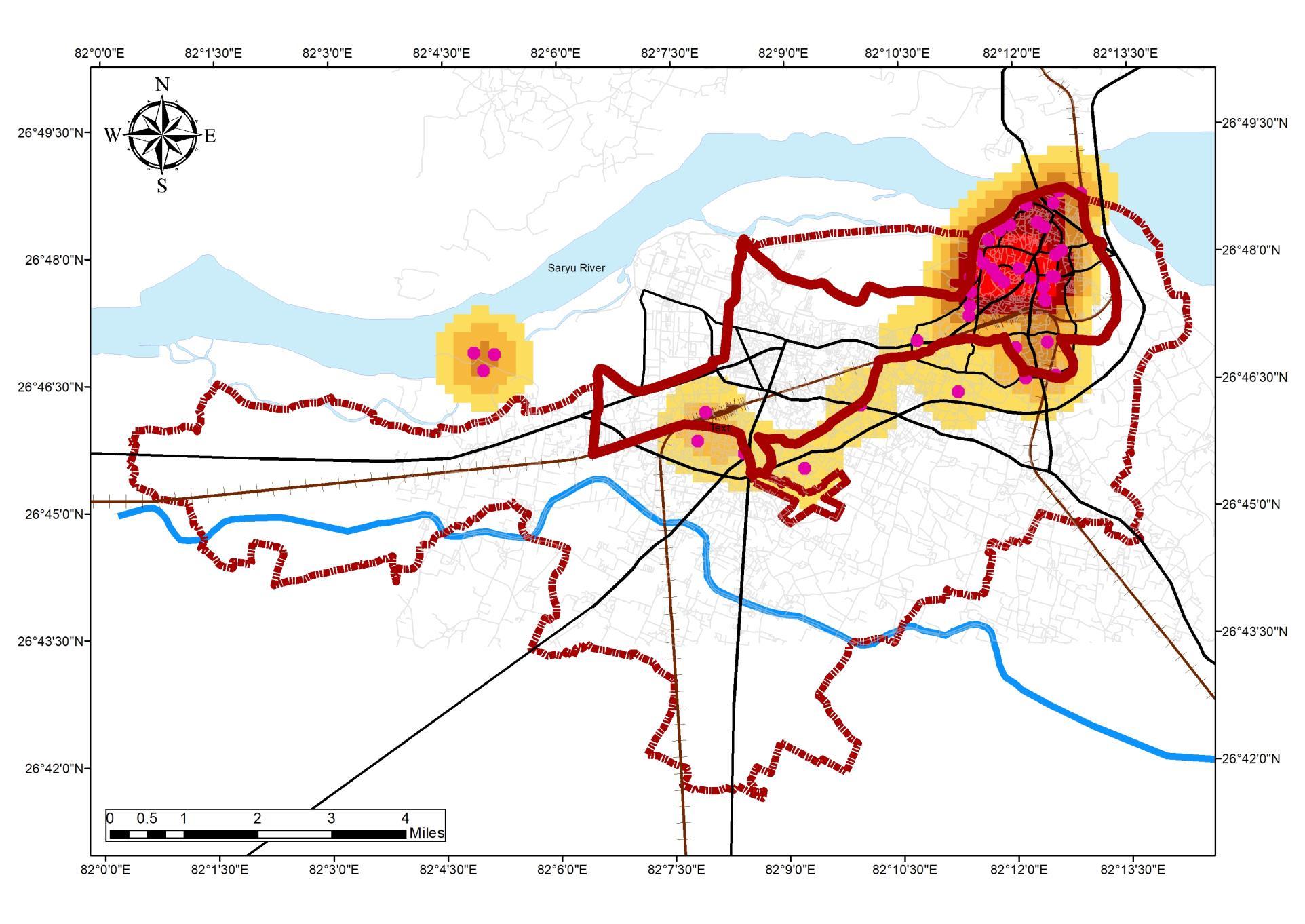
• Ayodhya Municipal corporation region has been divided into 5 Zones under which, Zone 4 and 5 have the largest number of Destinations
• The wards under tourism influx are 1, 2, 6, 8, 10, 15, 18, 24,31, 43, 48, 49, 54, 55
• Wards under Tourism influx account for 30% of Native Population constituting 73326 Persons in the ADA PlanningArea.
• Average population density of the Municipal Area is 142 person per Hectare.
• The trends population shows the concentration in and around the tourism core, the reason can be the increased economic possibilities for the locals and the migratory population
Inference
• Study of the wards in conjuncture to the tourism destination shows the trend of population increase towards the Tourism core showing a concept of multiple Micro CBD formation.
• As tourism is a prime sector of the economy migratory population tends to agglomerate around the center for opportunities
• This also affects the rental properties in the area
Source: Author wr Tourist Destination (MOT InGOV), Generated Arc Gis 10 7 (April,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)
Study to be Conducted for 14 Wards {1, 2, 6, 8, 10, 15, 18, 24,31, 43, 48, 49, 54, 55}.
Capacity Building for Urban Tourism Development of Ayodhya Municipal Limits
05

Legend Roads R_type
LEGENDS
NH Railway Station railways Title TO_1KM_Buffer2 Boundary_ADA(BKP) SymbolID # * 0 ^ _ Destinations
Legend Roads R_type
NH Railway Station railways Title TO_1KM_Buffer2 Boundary_ADA(BKP) SymbolID # 0 ^ _ Destinations
Ayodhya_Ward Ward_pop 0 1 2 2000 2001 5000 5001 10000 10001 12000 12001 20000 Water_Body
NH Railway Station railways Title TO_1KM_Buffer2 Boundary_ADA(BKP) SymbolID # * 0 ^ _ Destinations
Legends Ward Population
Ayodhya_Ward Ward_pop 0 - 1 2 - 2000 2001 - 5000 5001 - 10000 10001 - 12000 12001 - 20000 Water_Body
Ayodhya_Ward Ward_pop 0 - 1 2 - 2000 2001 - 5000 5001 - 10000 10001 12000 12001 20000 Water_Body
SHEET TITLE
STUDY AREA
Tourism Destination, Study Area Selection, Demographical Analysis and Population Distribution
STUDENT NAME
Ar. Sayan Munshi
IVth Semester, M.Plan FOAP, AKTU, Lucknow, UP
Dr. Subhrajit Banerjee Thesis Guide
SOURCES
ADA Reports
Ayodhya NN Reports MDP Draft 2031
Primary Data Collection ADA Website
KEY MAP
TOURISM AND DESTINATION OVERVIEW
132373 165079 194122 221118 248706 276294 0 50000 100000 150000 200000 250000 300000 350000
2011 2021
Census Population Census Years
83177 102835
1961 1971 1981 1991 2001
2031
Source Author wr t Census 2011 SBM and Tourist Destination (MOT InGOV), Generated Arc Gis 10 7 (April,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)
WARD WISE POPULATION DENSITY DISTRIBUTION 0 100 200 300 400 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 33 35 37 39 41 43 45 47 49 51 53 55 57 59 29% 71% Population Under Tourism Not Under Tourism Source:Author w.r.t Census India 1981 – 2011, DCHB Tourism in the Region • Major tourism destinations in the Region • Major Zone of influence: 4,5 • Tourism site distribution Ward No. Ward name N_Des 55 Swarg Dwar 6 56 Fatehganj 6 32 Ram Prasad Bismil 4 44 Mangal Pandey 3 49 Maniram Das Chhawni 3 14 Badi Devkali 2 16 Rath Haweli 2 Swarg Dwar, 6 23% Fatehgan , 6, 23% Ram Prasad Bismil, 4, 15% Mangal Pandey, 3 11% Maniram Das Chhawni, 3, 12% Badi Devkali, 2, 8% Rath Haweli 2, 8% Tourism Destination in Zones Source:Author wr t Tourist Destination (MOT InGOV), Generated Arc Gis 10 7 (April,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)
Tourism develops Association with industries like the Hotel industry, transport, handicraft, and travel agent. Tourism brings in large amounts of earnings into a local economy in the form of payment for goods and services needed for tourists It also creates a platform for employment in the economy’s service sector associated with Tourism
TOURISM POTENTIAL ZONES
MAJOR TOURISTACTIVITY
1. Mokshdayni walk Weave through lanes with traditional akhadas, step into tucked away temples, along serene ghats and unmatched Ayodhya’s monumental and spiritual heritage before joining a motley crowd for the Saryu aarti at sunset The walk is offered as part of a day-trip as well as an overnight stay
2. Parikramas Religious circumambulations are a necessary part of Hindu worship; the devotees of Lord Ram who visit here undertake the parikramas which are as follows:
• Antargrahi Parikrama: Shortest and completed in one day; the devotee is required to take a holy dip in Saryu and walk-through Ram Ghat, Sita Kund, Mani Parvat, Brahma Kund and finally reach Kanak Bhawan
MAJOR ACTIVITYAROUND THE REGION
Source: TripAdvisor Website, Re-generated April 2022
Ayodhya’s Heritage areas with historical and tangible/ intangible cultural values; preserved, conserved, and evolved by social interactions and changing economic factors have given shape to tourism in these cities
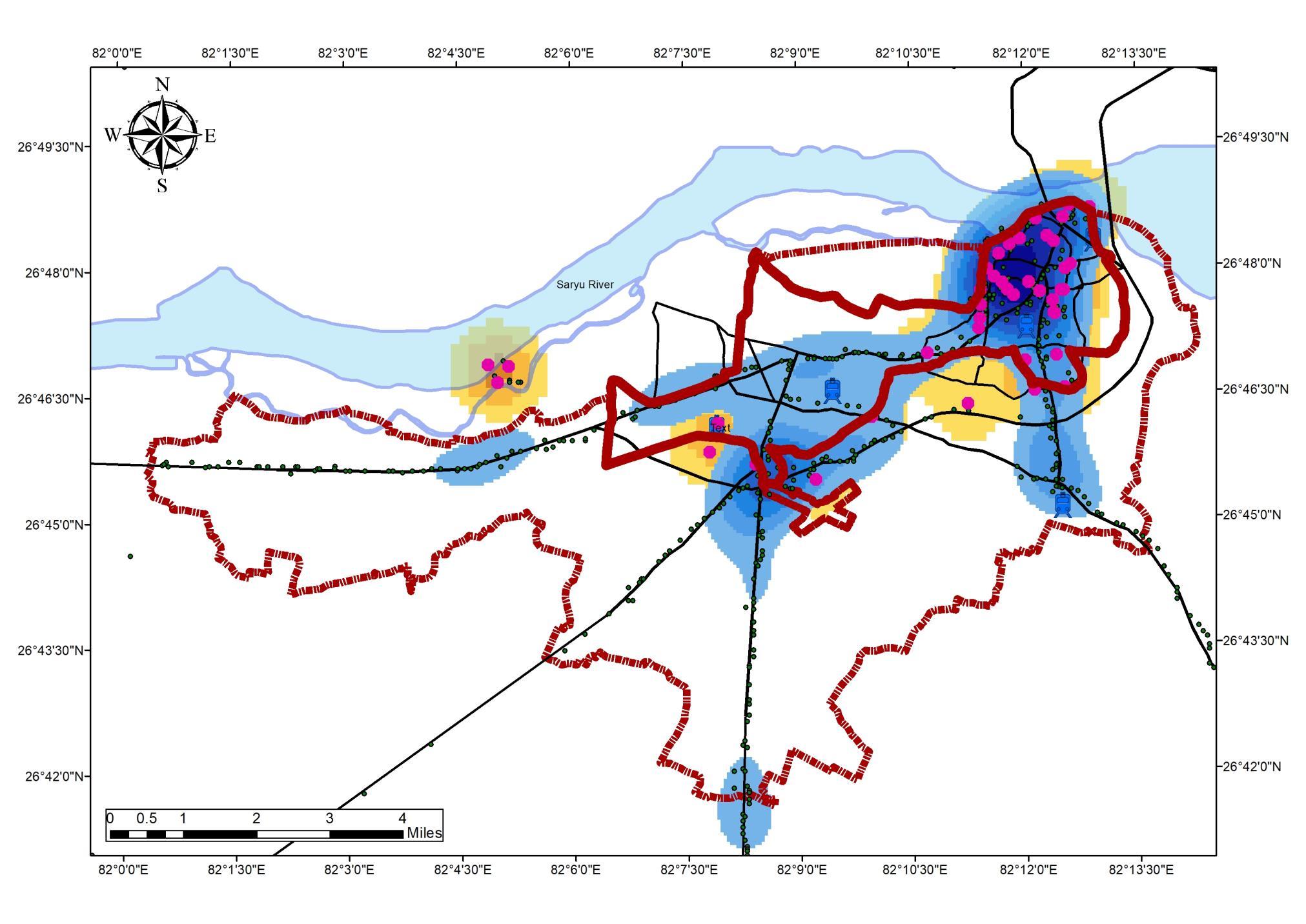
TOURISM INFLUENCE THE REGION INAYODHYA(HOTSPOT MAP)
• Panchkoshi Parikrama: Circuit of 16 km as it means, the circumambulation begins from Chakratirtha and moves to Naya Ghat, Ram Ghat, Saryu Bagh, Holkar-Ka-pura, Dashrath Kund, Jogiana, Ranopali, Jalpa Nala and Mahtabagh
• Chaturdashi Koshi Parikrama: A journey of 45 km, the parikrama is done during the auspicious Akshaya Navami and has to be completed in one day
FAIRS AND FESTIVALS
Ramnavami Mela
Ramnavami Mela in Ayodhya marks the birth anniversary of Lord Rama

• It is usually celebrated in the month of March orApril
• The Ramnavami Mela, Ayodhya is dedicated to Lord Rama Devotees gather in large numbers in the temples of Ayodhya in Uttar Pradesh to celebrate the Ramnavami Mela which is the birth place of Rama
RAMNAVAMI FOOTFALL
Source:Author w.r.t Ayodhya Master plan 2031, Generated Arc Gis 10.7 (April,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)
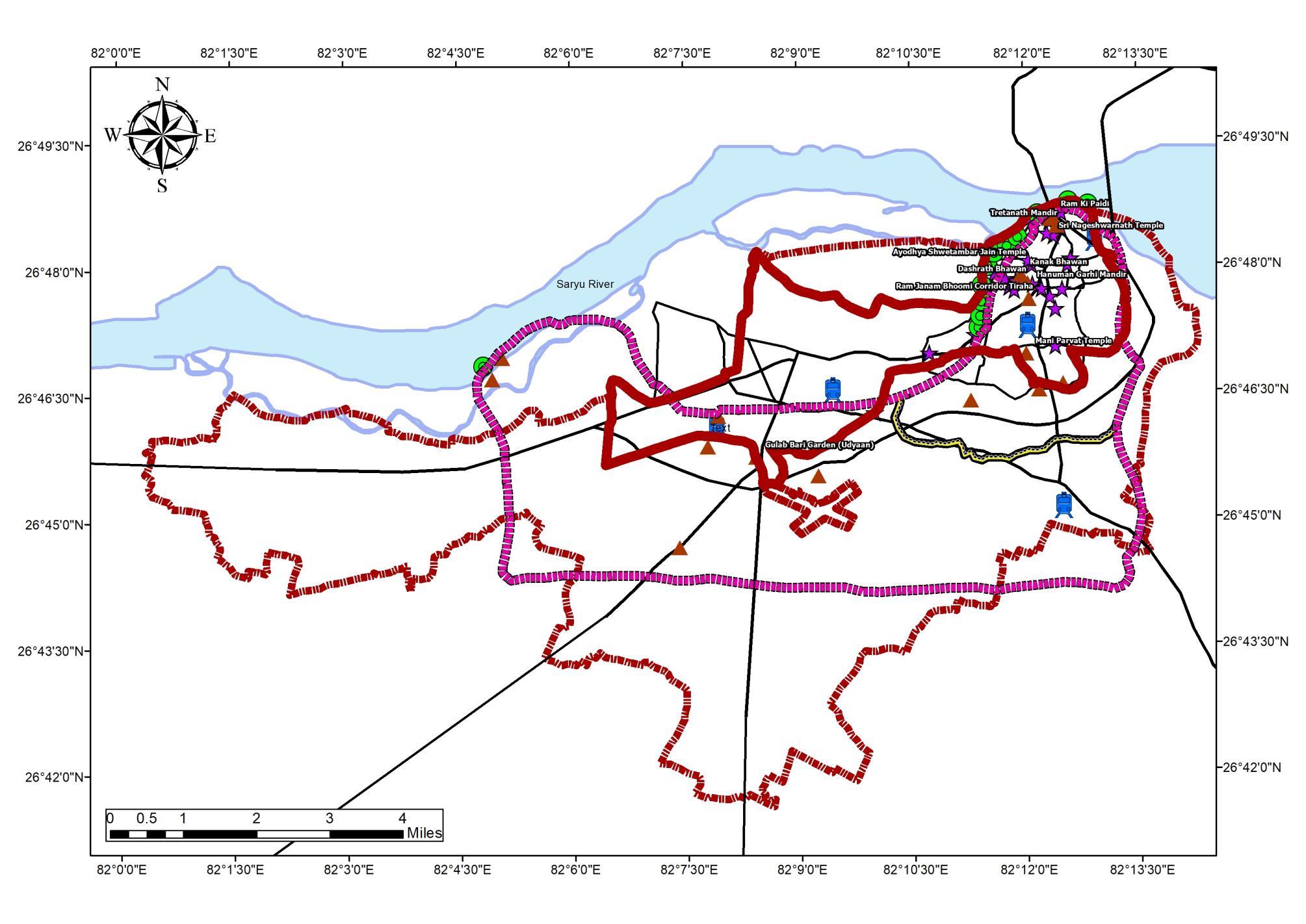
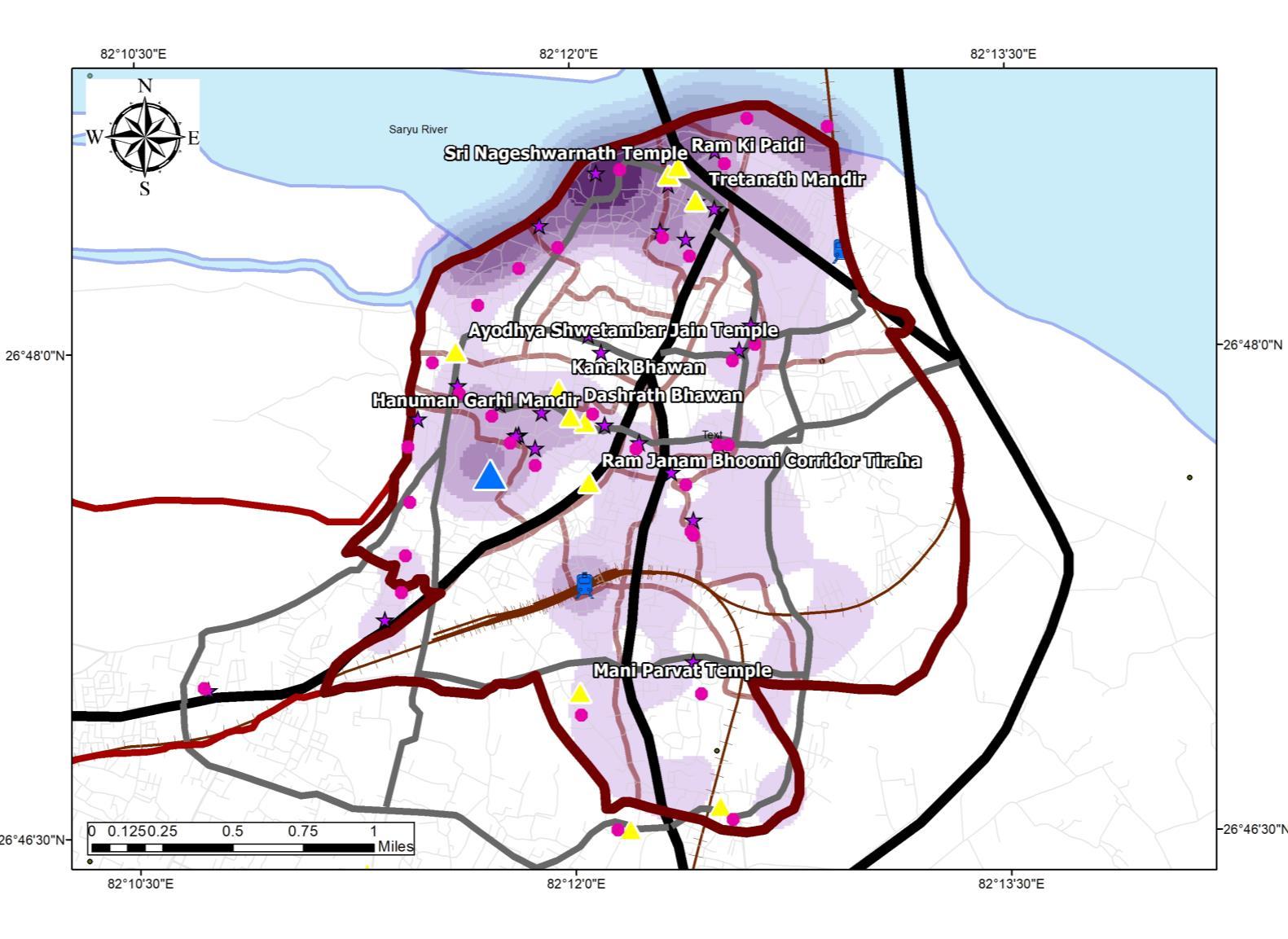
MAJOR TOURIST DESTINATIONS
Ayodhya receives a large number of tourists every year and there are some major attraction points that is the focal point of tourism, they are as follows:

• The Ram Janma-Bhoomi Temple is one of the major attractions of Ayodhya. It is considered to be the birthplace of Lord Ram the 7th incarnation of Lord Vishnu
• Hanuman Garhi is one of the most popular temples in the region Legend has it that Lord Hanuman used to live here to protectAyodhya
• Kanak Bhawan Temple in Ayodhya is dedicated to Lord Ram and his divine consort Goddess Sita

• Mani Parvat is the place where some parts of sanjivni Booti fell off while Lord Hanuman was carrying the huge mountain of Sanjivni Booti to Lanka to save injured Lakshman, brother of Lord Rama.
• Nageshwarnath Temple The temple is dedicated to Lord Shri Nageshwar Nath, the presiding deity ofAyodhya.

• Ram ki Paidi is a series of ghats on the bank of River Saryu

Source:Author
Source:Author w.r.t Ayodhya Master Plan 2031, Generated Arc Gis 10.7 (April,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)

Saryu Aarti Catch this beautiful honoring of the Saryu River at Saryu Ghat Join an increasing footfall of regulars and visitors at the riverside steps while the priests arrive and light brass lamps, often in trying windy moments, as a loudspeaker belt out hymns This is followed by gentle clapping, conch blowing, gong beating, lamp swirling and fervent chanting.
LEGENDS SHEET TITLE STUDENT NAME
Ar. Sayan Munshi
IVth Semester, M.Plan FOAP, AKTU, Lucknow, UP
Dr. Subhrajit Banerjee Thesis Guide
SOURCES

Capacity Building for Urban Tourism Development of Ayodhya Municipal Limits
KEY MAP
Ayodhya’s Ghats Ram Janmabhoomi Hanuman Garhi Temple
1000000 4000000 4800000 0 0 5940000 0 1000000 2000000 3000000 4000000 5000000 6000000 7000000 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2025 Area in Sq. Km Decade
Footfall 2 per. Mov. Avg.
(Footfall)
w.r.t TOI Reports 2017 - 21
Source:Author w.r.t Primary Survey, Generated Arc Gis 10.7 (April,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)
• Ayodhya Ram Navami Mela strikes an average inbound population of 32 Lakh devotees • Major share of the footfall concentrates on the Ram ki Paidi Ghats and
location. •
tourists
load on the existing transportation, solid waste management, and
infrastructure of the region, for
duration
2 months FAIR DURING COVID 19 After 2 Years of Consecutive cancellation, 2022 is witnessing the fair with an administrative setup divided into 9 sectors to manage the traffic and tourists (25 lakh inbound on 3rd April 2022). Legends TOURISM ANALYSIS Tourism Overview and Impact during season ADA Reports Ayodhya NN Reports MDP Draft 2031 Primary Data Collection ADA Website 07 Legend UrbanArea & Destinations Ramnavami_impact Road_Name MajorRoads R_type NH RailwayStation Boundary_ADA Water_Body RamNavamiInboundDensity 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 DestinationDensity 1 2 3 4 5 6 TOURISM ANALYSIS
INBOUND TOURIST FLOW DURING RAM NAVAMI (HOTSPOT MAP)
INFERENCE
the temples in the
Inbound
impose a
Accommodation
a
of
ROLE OF PRIVATE ENTERPRISE IN TOURISM INAYODHYA
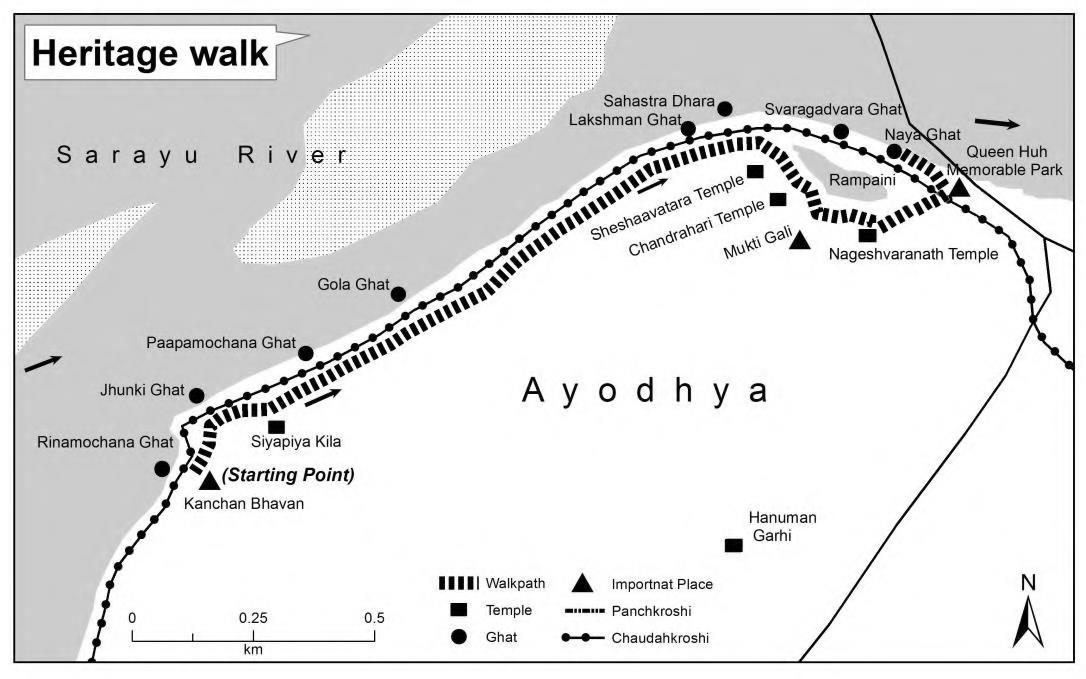
Tornos is a tour and travel company, founded in 1994 in Lucknow The Tornos foundation promoted the Mokshadayini walk, i e ‘Heritage walk to feel salvation’in Ayodhya. Exclusively it is based on the concept of revealing life by the side of the Sarayu River and the attached riverfront ghats (stairways).
MAPOFTHE HERITAGE WALK PROMOTED BY TORNOS
SEASONALVARIATION IN TOURISM
20
10

INSTITUTIONAL SETUP
The main institutional-administrative bodies ofAyodhya:
• Municipality,
• City DevelopmentAuthority,
• Ayodhya Research Institute,
• Indian National Trust forArt, Culture and Heritage,
• Tornos
This fulfills the three dimensions of urban governance, i e political, economic, and institutional, altogether they play important role in making heritage inclusive development policies and programmes as suggested by UNESCO
TOURISTAND FOOTFALL
Seasonal Character
INFERENCE 0
• Based on the observation on the tourist Inflow statistics, a steady increase is been observed from 2001 to 2019, but a decline in growth of inflow can be seen in 2020, the pandemic being a prime reason for revenge tourism
• UP has a large number of religious attractions for Hindus, Islamic, Buddhists, Jain & Christian Ayodhya lies as one of the greatest attractions for the following religious group: ➢ Hinduism ➢ Sikhism ➢ Jainism
Overall Mokshdayni walk Antargrahi Parikrama: Panchkoshi Parikrama Chaturdashi Koshi Saryu Aarti
Ramleela Ramnavami Other Temples
Source:Author w.r.t UPTOURISM STATISTICS 2016-2020
TOURISM INFLUX IN THE STUDYAREAAND LAND RATES
• The season variation in Ayodhya is between the September to April, this time engages the Parikramas as well as major fairs and festivals in the region, which is the prime duration on the year that tend to impose load on the Infrastructure
INFERENCE: LAND RATES

•
• Peri-urban area shows a very low land rate as compared with core area.

As per the URDPFI Guidelines of Sustainable
TOURISM ANALYSIS
•
INFERENCE BASED ON URDPFI
•
•
•
Ar. Sayan Munshi
IVth Semester, M.Plan FOAP, AKTU, Lucknow, UP
Dr. Subhrajit Banerjee Thesis Guide
Capacity Building for Urban Tourism Development of Ayodhya Municipal Limits
KEY MAP
LEGENDS SHEET TITLE STUDENT NAME SOURCES
TOURISM ANALYSIS
Being a part of RAM VAN GAMAN YATRA CIRCUIT and AWADH CIRCUIT Ayodhya city gained its potential in the tourism Destination ranking in the country Ayodhya City marks an Inbound tourists ~70,000 persons/day
Development
Planning
Ayodhya Region Domestic Foreign Total % Growth 2016 21659573 144820 21804393 2017 24597335 179426 24776761 13.6 2018 28296517 207226 28503743 15.0 2019 30253819 202127 30455946 6.8 2020 8778855 10053 8788908 -71.1 2030 33405043 223140 33628182 282.6 21659573 24597335 28296517 30253819 8778855 33405043 144820 179426 207226 202127 10053 223140 0 10000000 20000000 30000000 40000000 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2030 Area in Sq. Km Decade REGION FOOTFALL Domestic Foreign 2 per. Mov. Avg. (Domestic) Expon. (Foreign)
Source: Holy-Heritage City
and
in India (PB SINGH 2020)
variation in tourism can be seen during the following
Source:Author w.r.t UPTOURISM STATISTICS 2016-2020 Source:Author w.r.t UPTOURISM STATISTICS 2016-2020
Seasonal
months:
30 40 50 60
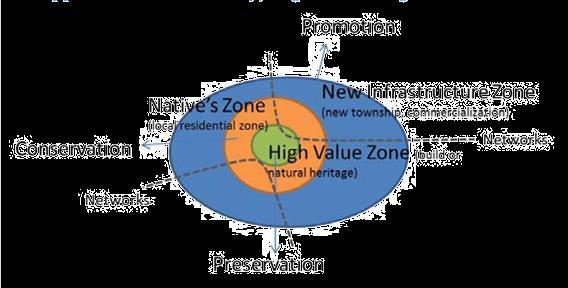
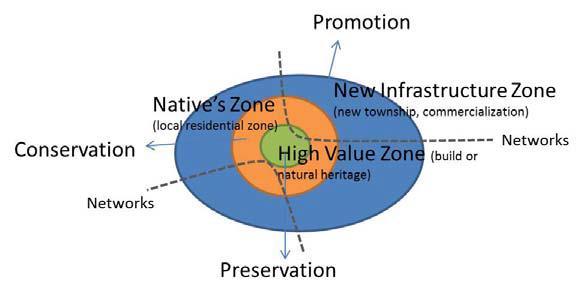
tourism development, norms
define
1. High-Value Zone 2. Native Zone 3. New Infrastructure Zone 4. Networks
suggested by UNESCO
a region into the following zones where the influence can be observed:
OBSERVATIONS PER U.R.D.P.F.I
• Land rates Ranges from as high as 3000/- per sq ft to low as 250/- –350/- per square feet.
Land rates are high along the central spine as well as area near hanuman Garhi and ProposedAyodhya Ram Mandir.
High-Value Zone: Central
Spine and Temple area
Native Zone:
Ghat area, N-E Region in StudyArea
New Infrastructure: Mani Parvat area, and PeriUrban
1. 2. 3. Source:Author w.r.t. Faizabad Circle Rates and Land Brokers (Anonymous Source), Generated Arc Gis 10.7 (May,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)
Network: Central Spine is the Major connection Corridor.
08
Role of Private organization, Seasonal Character and Tourism Influx
ADA Reports Ayodhya NN Reports MDP Draft 2031 Primary Data Collection ADA Website
Road and Transport constitute the main entities of the efficiency of working of any urban area
• Urban transportation aims at supporting transport demands generated by the diversity of urban activities within the city including tourism.
• Tourism certainly requires an integrated development of basic infrastructural components, and transport is one of them
• Transport occupies a key position in the tourism sector and it is an important driver of socio-economic progress
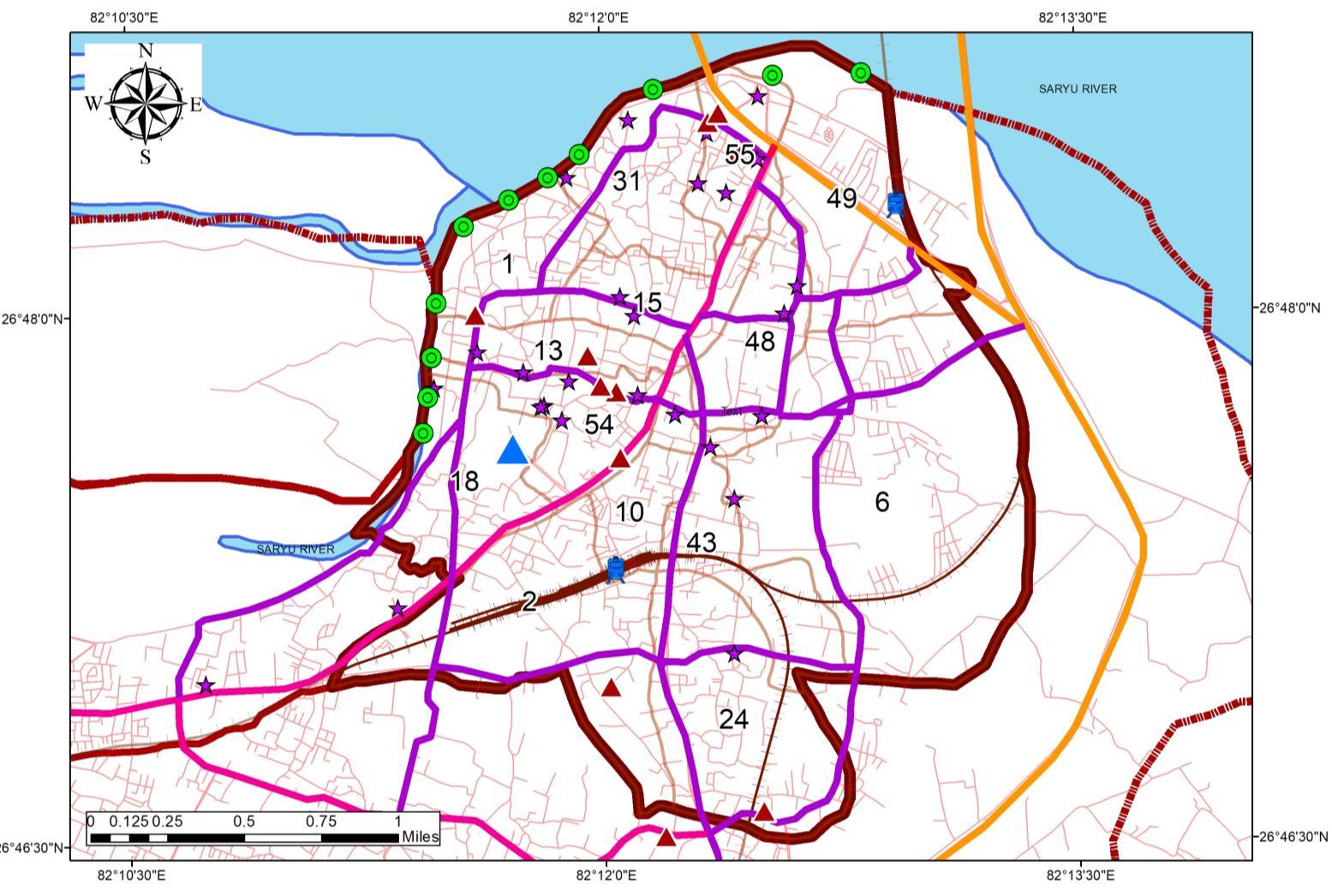
NETWORK DISTRIBUTION MAP
HIERARCHYAND PLANNING OF ROADS IN STUDYAREA
Ayodhya is an important region of historic and cultural importance, the city developed in phases that evolved in due course of time This led to unplanned development and the Organic form of the city evolved This led to:
• Uneven Road width
• Lack of Motorable Roads
• Encroachments
• Congested City core
CONDITION OF ROADS
Most of the road in the Study area is Asphalt, while, some parts of kutcha roads in the periphery region can be observed,
Total Road Length (km) Surfaced (Km) Un-surfaced (Km) 152 km 129.2 22.8
ROAD CONDITION
UnSurfaced Surfaced
INFERENCE
• Due to the Lack of Road Infrastructure, the Major roads are Asphalt, while Gully roads are paved.
• 15% of Unsurfaced roads indicated Kutcha roads in the Study area
DISTRIBUTION OF ROAD AS PER WIDTH
LEGENDS
Source:Author w.r.t. Draft Master PlanAyodhya, Generated Arc Gis 10.7 (May,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)
INFERENCE
• Reduced road width is observed as we move close to the CBD.
• Central Spine of the city is 12m wide, which is a reason of congestion.
• NH27 acts as a outer peripheral road to connect through traffic
Source:Author w.r.t. Draft Master PlanAyodhya, Generated Arc Gis 10.7 (May,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)
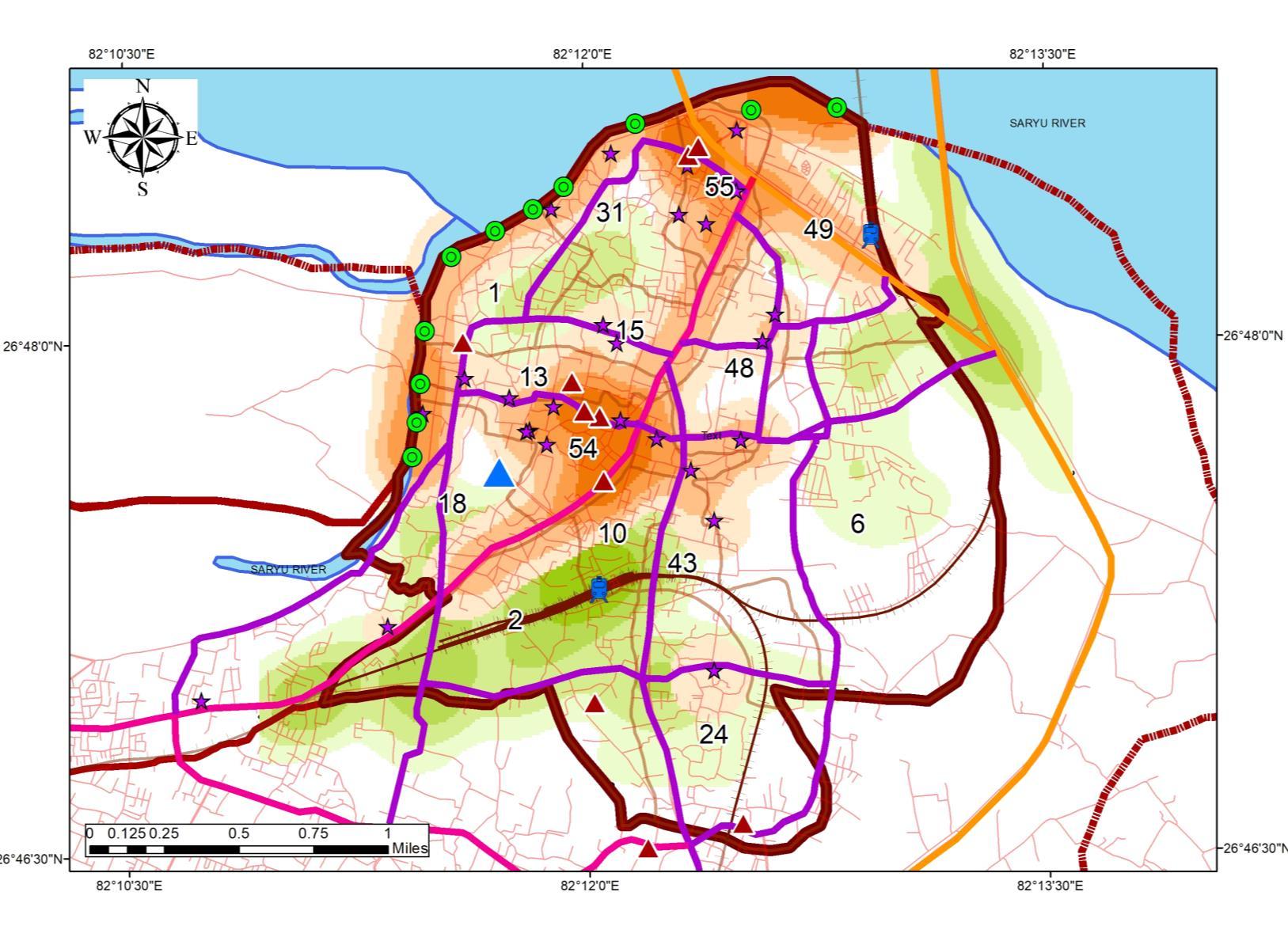
DISTRIBUTION AND CONNECTIVITY

Ayodhya Municipal Corporation area is connected to a number of regions such as Lucknow, Varanasi, and Allahabad through major corridors such as NH30, NH330, and Wide Gauge railway connects to Major Cities
2. Airways:
Ayodhya Airport (Maryada Purushottam Shriram International Airport) is located 8km from the CBD of Study Area Transportation Covers: 1.08 sq km in the StudyArea accounting 11% of the total area
Source:Author w.r.t. Draft Master PlanAyodhya & IRC 69, 1977, Generated Arc Gis 10.7 (May,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)

The Study area experienced about 70,000 tourists a day pre-COVID, an expected rise in tourists would further add to the current situation.
FLOW OFTOURISTS & RESIDENTS VS NARROW ROADS LOAD OFTOURISM ON ROAD
SHEET TITLE
Source:Author w.r.t. Tourism Statistics UP, Generated Arc Gis 10.7 (May,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)
INFERENCE
• The tourism characteristics show the mix between the Locals and the tourists.
• Tourist tend to be spotted more on the central spine
• While, residents or the workforce can be observed on the commuters lines (Such as Railway Stations and Bus stops)
STUDENT NAME
Ar. Sayan Munshi
IVth Semester, M.Plan FOAP, AKTU, Lucknow, UP
Dr. Subhrajit Banerjee Thesis Guide
SOURCES
Capacity Building for Urban Tourism Development of Ayodhya Municipal Limits
KEY MAP
Transportation Character of Study Area: 1. Road: ROAD TYPE Road Length (km) Width (m) Area (Sq. km) Arterial Road 2 40 0.08 Collector Road 3 24 0.072 Local Street 3 12 0.036 Gully Roads 141 6 0.846
:
2. Railway
The study Area consists of 16 km of Wide gauge Railway line with 2 Railway Station.
15% 85%
09
Transport Character, Hierarchy, Distribution, Connectivity and Effect on Tourism Legend ! R
R_type
Collector
Local
roads_Road Local
TYPE Expressway Local
<all
Legend !
#
#
^
0 <all
!
#
#
18 12 9 0 <all
values>
Value 2
TRANSPORTATION ANALYSIS
ADA Reports Ayodhya NN Reports MDP Draft 2031 Primary Data Collection ADA Website TRANSPORTATION
Ghats
Arterial Road
Street
Street
Major Roads
Street Sub-Arterial Road
other values> Railway Station railways railways_Intersect Study Wards Study_Boundary UrbanArea Boundary_ADA Water_Body
Ghats
POI Name
Proposed RamTemple
_ Destinations Major Roads Width__M_ 60 40 32 23 18 12 9
other values> Railway Station railways railways_Intersect Study Wards Study_Boundary UrbanArea Boundary_ADA Water_Body Value 2 3 4 5 5 Value 2 3 4 5 5 pub_Flow Legend
Ghats
POI Name
Proposed RamTemple ^ _ Destinations Major Roads Width__M_ 60 40 32 23
other
Railway Station railways railways_Intersect Study Wards Study_Boundary UrbanArea Boundary_ADA Water_Body Value 2 3 4 5 5
3 4 5 5 pub_Flow Tourist Flow Resident Flow Legends
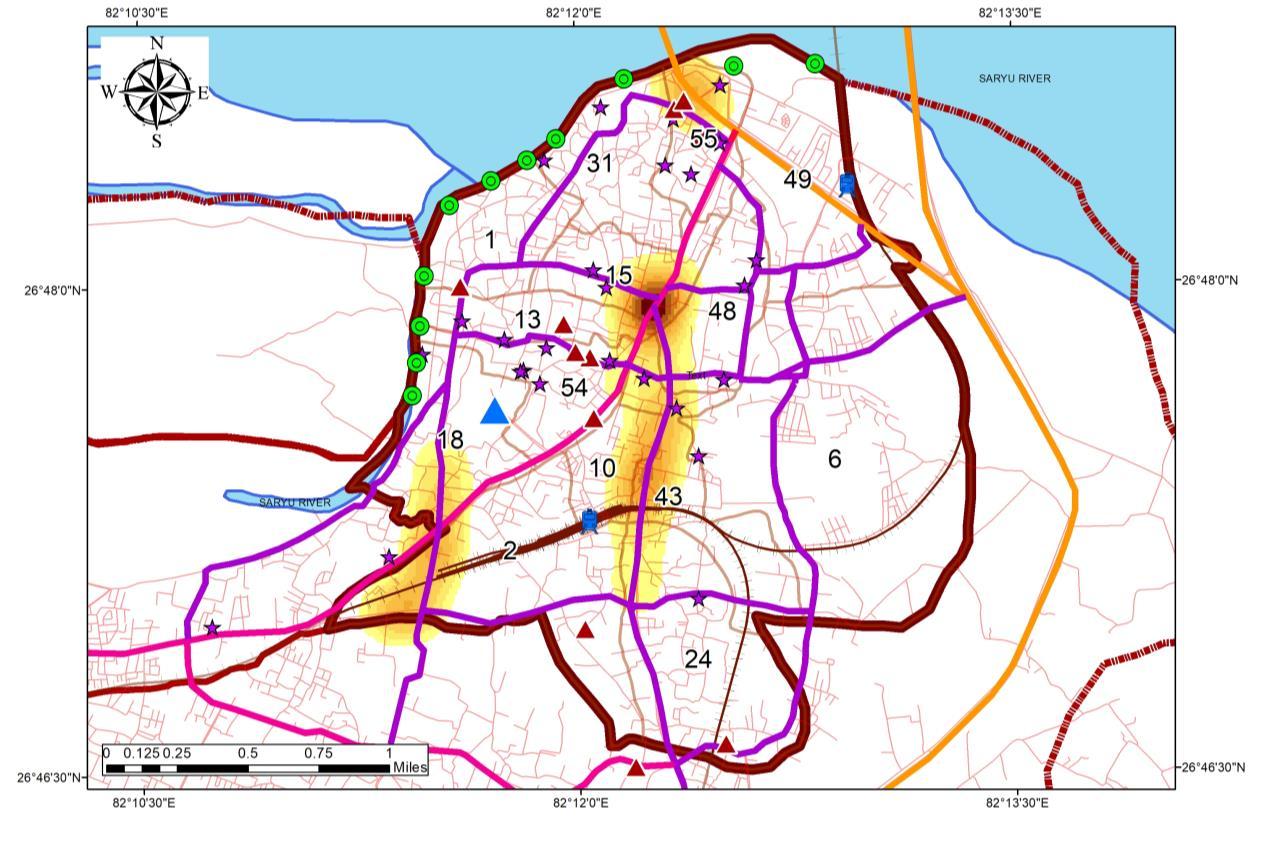
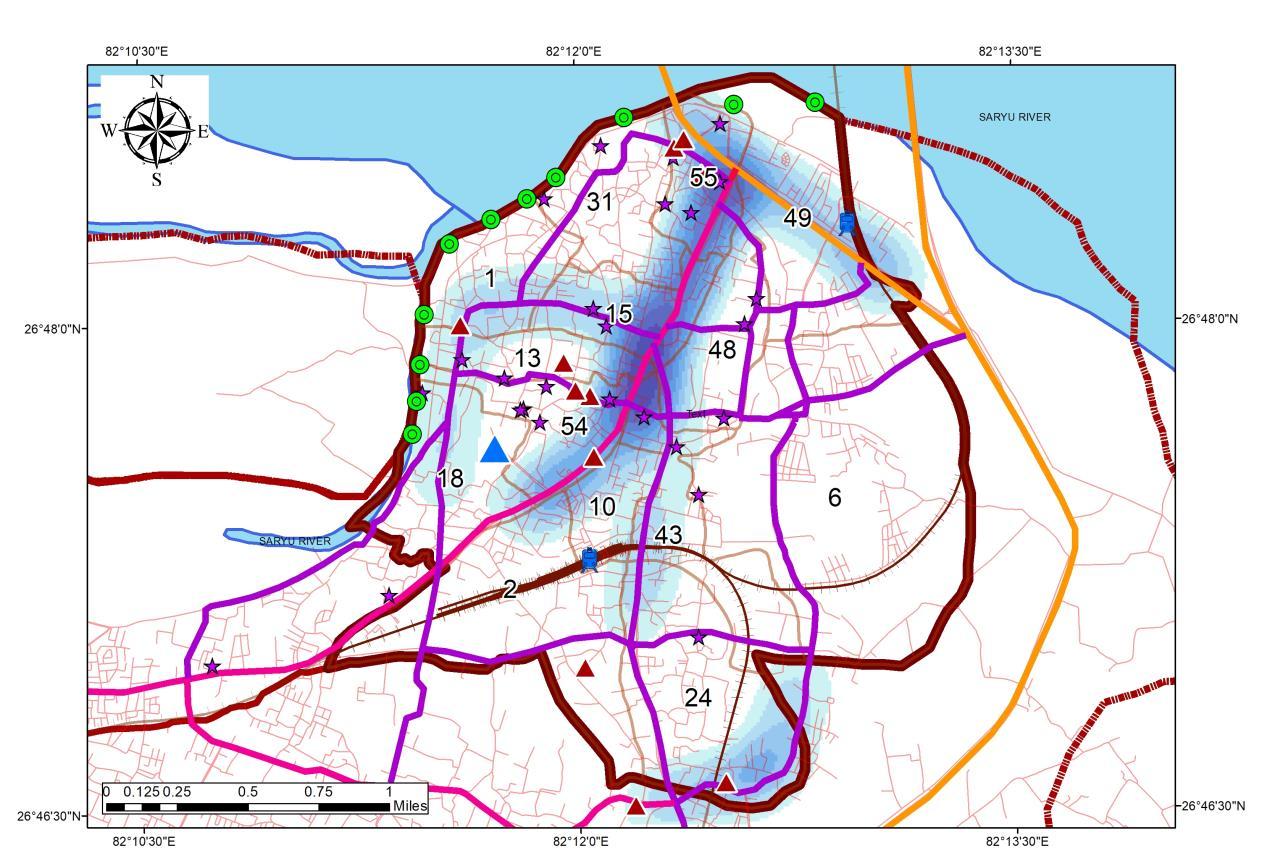
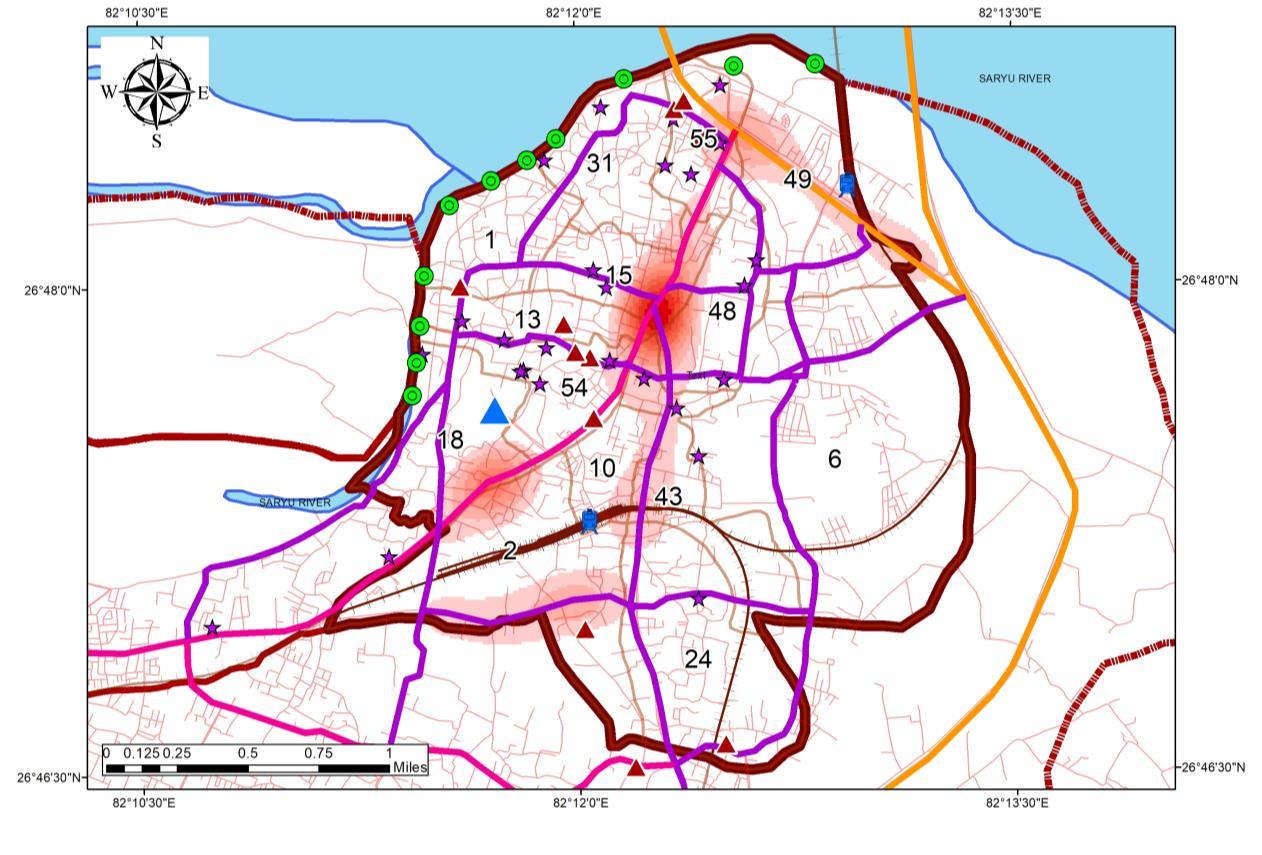
TRANSPORTATION ANALYSIS ANALYSIS OF CONGESTION

CHARACTERISTICS OFVEHICLE OWNERSHIP
Over the Years, Ayodhya shows the variable character of ownership, the analysis is done on the basis of private and commercial owned vehicles
INFERENCE
• 2-Wheeler section shows the maximum growth, which indicated the affordability of road Transport Here, 2 Wheeler is the most convenient mode of transport due to the Narrow ROW of the Existing Road

• For tourism Specific mode, E-Rickshaw dominated the commercial sector over Maxi Cabs and 3-Wheeler by 91% growth between 201619.

• Growth in Private Car ownership shows 80%. Which accounts for 5% of the number of 2-Wheeler.
• Significant modes of tourism Sector can be defined as E-Rickshaw, 3Wheeler, Commercial LMV, and Maxi Cabs.
• Public transport shows significant growth.
INDICATORS FOR TOURISM SPECIFIC TRANSPORTATION
• Precedence over paratransit can be observed
• Lower Growth of Private owned vehicles
• Growth rates of Commercial LMV are less than E-Rickshaw, which proposes greener transportation that is environmentally friendly
• E-Rickshaw on the other hand reduces the Design speed of a road, due to low speed, and increases the chance of congestion.
• E-Rickshaw can easily access Narrow Stretch of Roads.
• Due to public dependency on Para-Transit, it can be an advantage to plan NMT Corridors in Destination regions.

• 30% dependency on Bicycles.
CHARACTERISTICS OFVEHICLE OWNERSHIP
Study of the Congestion includes monitoring at a different time of day. Following time were recorded:
0600 Hours
0600 Hours or 9.00 Am signifies the transition or delivery time for the Accommodations on the destination which ranges from 0400 to 0630 Hours in Ayodhya.
0900 Hours
0900 Hours or 9Am starts the Rush hours and incoming of Workforce.
1030 Hours
1030 Hours signifies the incoming of tourists and marks the start of Congestion
3-Wheeler Passenger 262 401 789 1461
Source:Author w.r.t. RTOAyodhya 2020
PRESENT ROAD CONDITIONS
Source:Author Primary Survey, March 2022
RECORDING AT 0600 HOURS RECORDING AT 1030 HOURS RECORDING AT 1900 HOURS RECORDING AT 0900 HOURS
1930 Hours
7 00 pm Signifies the evening rush hours, which is influenced by tourists as well as residents
INFERENCE
• Congestion characterizes a major role of Para Transit and Low-speed vehicles
• Tourist influences stretch, road width ranges from 9 to 12 m which becomes a major issue in the Study area.
• Rush Hours majorly impacts the Core of the study area.


• Areas under influence is places close to Kanak Bhawan, Hanuman Garhi, Ram Janam Bhoomi, Dashrath Bhawan, Ram ki Paidi
RECORDINGS AT PEAK HOURS
Source:Author w.r.t. OPENSTREETMAP viz,Airbus, Maxar, Landsat, Copernicious Technology Generated Arc Gis 10.7 (May,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)
Ar. Sayan Munshi IVth Semester, M.Plan FOAP, AKTU, Lucknow, UP
Dr. Subhrajit Banerjee Thesis Guide


Capacity
KEY MAP
Building for Urban Tourism Development of Ayodhya Municipal Limits LEGENDS SHEET TITLE STUDENT NAME SOURCES
Types of Vehicles 2016 2017 2018 2019 Bus 107 215 325 418 E-Rickshaw 218 1099 1947 2487 Maxi Cabs 113 255 403 534 motorcycle 28789 65253 104107 144834 Commercial (LMV) 40 100 138 166 Private car 1670 3821 6057 8232
10
ADA Reports Ayodhya NN Reports MDP Draft 2031 Primary Data Collection ADA Website TRANSPORTATION Character of Ownership, Analysis of Congestion
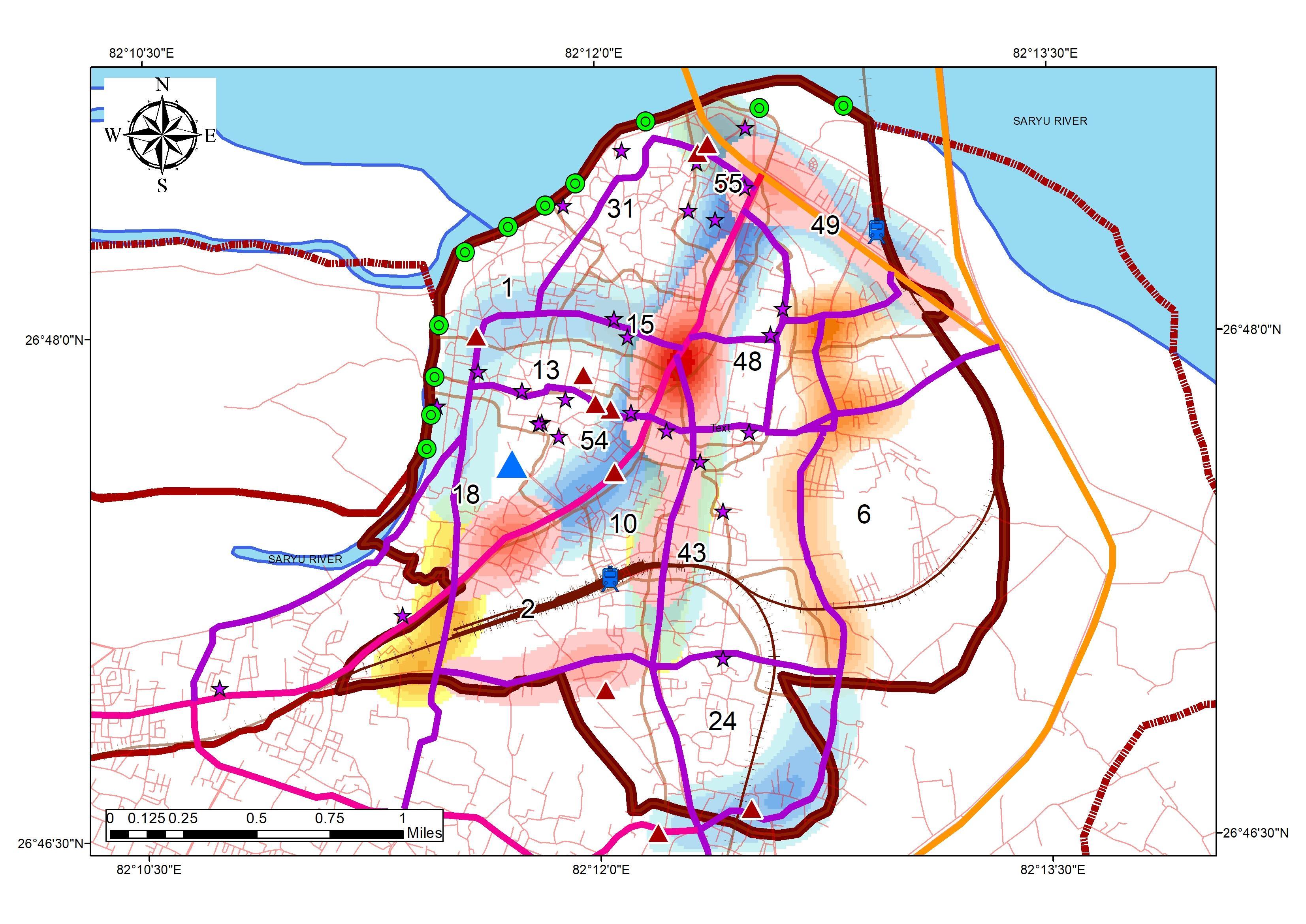
SOLID WASTE






Capacity Building for Urban Tourism Development of Ayodhya Municipal Limits
SHEET TITLE STUDENT NAME SOURCES KEY MAP Ar. Sayan Munshi IVth Semester,
FOAP, AKTU,
UP Dr.
Thesis Guide
Author w.r.t. SWM rules
QUANTUM OF WASTE GENERATION BYTOURISTS
EFFECTS ON THE STUDY AREA Municipal Solid Waste (WSWM) is the trash or garbage that is discarded day to day in a human settlement. As per MSW Rules, 2000
2016 MSW includes commercial and residential waste generated
municipal
areas in
solid or
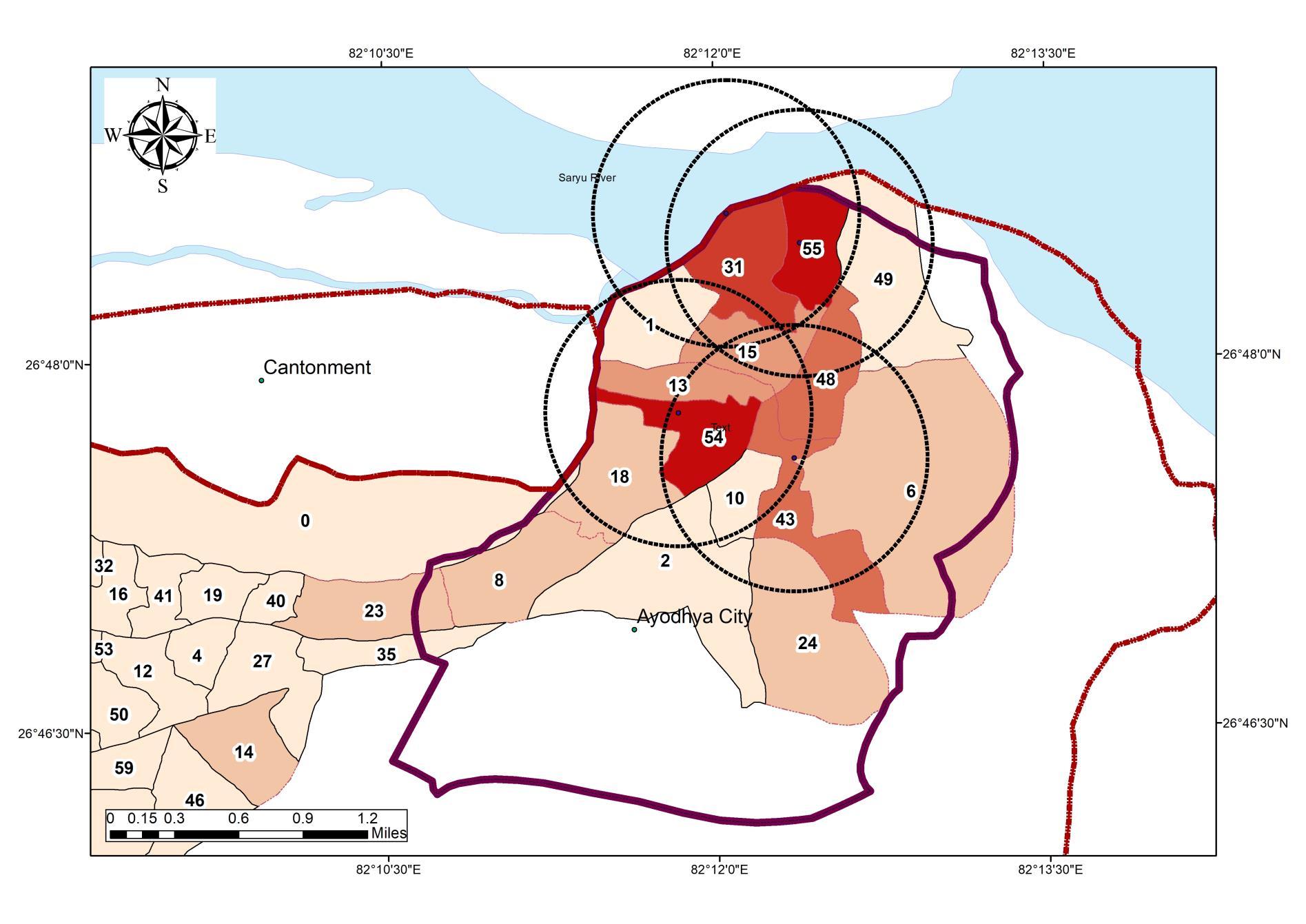
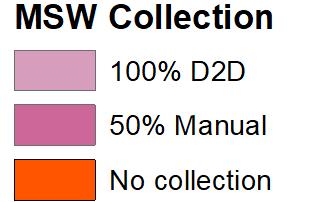
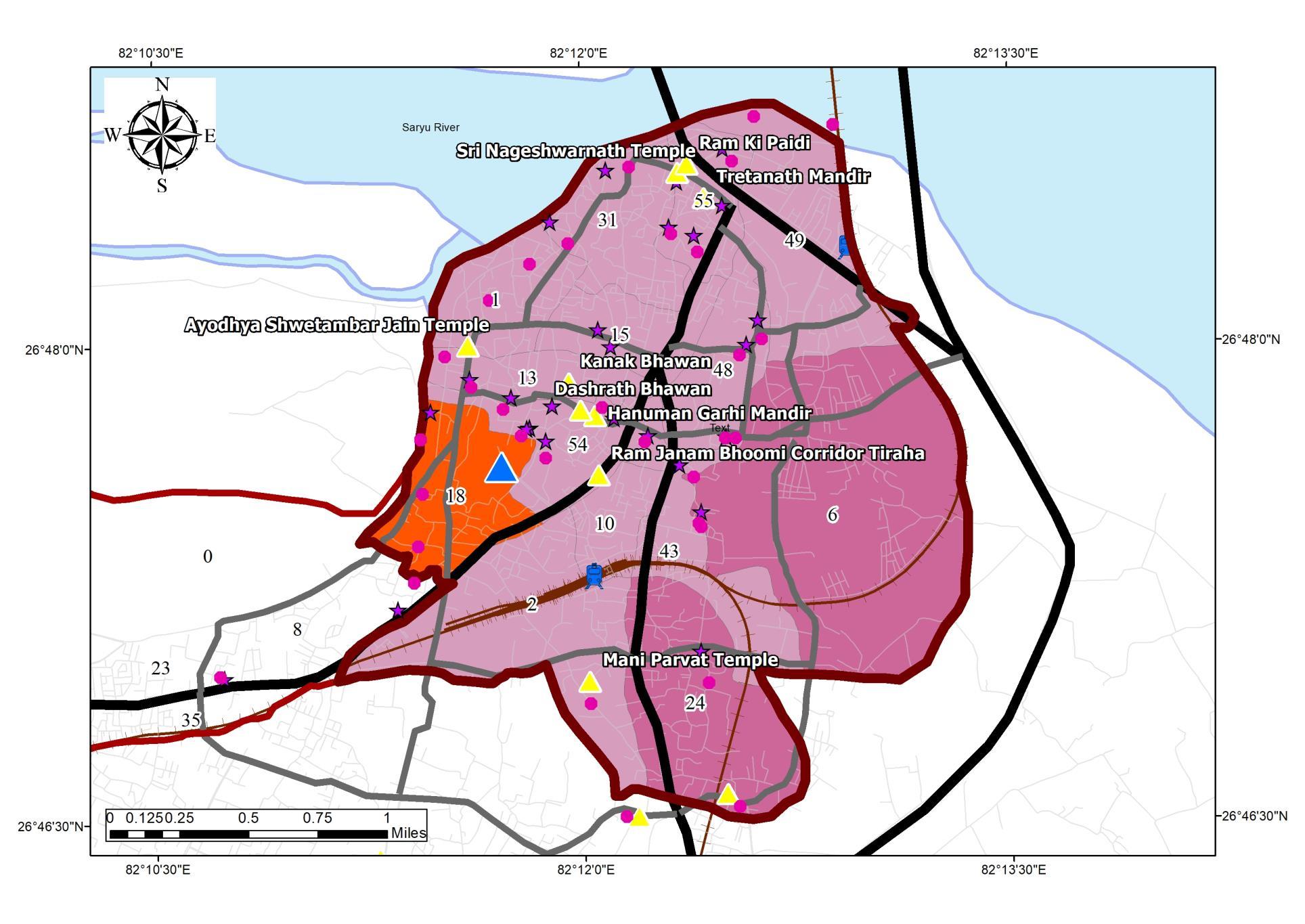
excluding industrial hazardous waste Sl No. Land use type Estimate waste generation 1. Residential refuge 0.3 to 0.6 kg/cap/day 2. Commercial refuge 0.1 to 0.2 kg/cap/day 3. Street sweeping 0.05 to 0.2 kg/cap/day 4. Institutional refuge 0.05 to 0.2 kg/cap/day STANDARD WASTE GENERATION Source:Author w.r.t. SWM rules 2000, India DISTRIBUTION MAPOF SWM IN THE STUDYAREA Source:Author w.r.t. SWM rules 2000, India 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 1 2 6 8 10 15 18 24 31 43 48 49 54 55 WASTE GENERATION WARDS UNDER DIRECT IMPACT OFTOURIST DESTINATION Source:Author w.r.t. SWM rules 2000, India Generation of waste in the Urban Area : 93 Ton per day Generation of waste in Study Area: 33 9 Ton per day Sl No. Land use type Estimate waste generation 1. Residential refuge 238800 2. Commercial refuge 119400 3. Street sweeping 59700 4. Institutional refuge 59700 59.1 33.9 Waste Generation Urban Area Study Area WASTE GENERATION CHARACTERISTICS 1. Study area comprises 34% of the total generated waste 2. Residential population accounts 50% the largest generation in the Urban Area 3. Commercial Areas including the Accommodation Infrastructure accounts 25% of the total generation WASTE GENERATION CHARACTERISTICS Source:Author w.r.t.Ayodhya Master Plan 50% 25% 12% 13% Residential Commercial Street Institutional Waste Generation Sources • Airport Waste Generation 1Ton /day • Tourist Additional Waste Statistics: • Per day Tourist Arrival: 13500 • Average Waste Generation as per IATA: 1 67 Kg/day 93 128 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 MSW Tourist WASTE GENERATION MSW + TOURISM WASTE Source: Author w.r.t. SWM rules 2000, India Waste Generation Comparison • Waste generation exceeds the MSW capacity on Seasons by 30% • Waste generation characteristics Vary from MSW generation rate by 76% on seasons. COLLECTION MECHANISM • Collection Process is done by a Private company “Om Swwatchta Corporation” under Ayodhya Nagar Nigam. • 35 wards out of 60 Wards are under 100% Door to Door Collection (P) • 25 Wards out of 60 Wards are under 50% Manual Collection. (S) DISPOSAL DOOR TO DOOR COLLECTION INAYODHYA Refuge collection D2D Collection COVERAGE MAPFOR COLLECTION Source:Author w.r.t. SWM rules 2000, India Dumpster • Disposal site is allotted at Bikapur with 10052 sq mt within new limit. The project covering the ADA limit is under preparation. 11
LEGENDS
M.Plan
Lucknow,
Subhrajit Banerjee
Source:
2000, India
(HOTSPOT MAP)
&
in
or notified
either
semi-solid form
Solid waste
Transport and
Tourism ADA Reports Ayodhya NN Reports MDP Draft 2031 Primary Data Collection ADA Website Legends SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT ANALYSIS
Management: Collection, Segregation,
Impact of
WASTE GENERATION RELATIONSHIPWITH ECONOMY
ACCOMMODATION
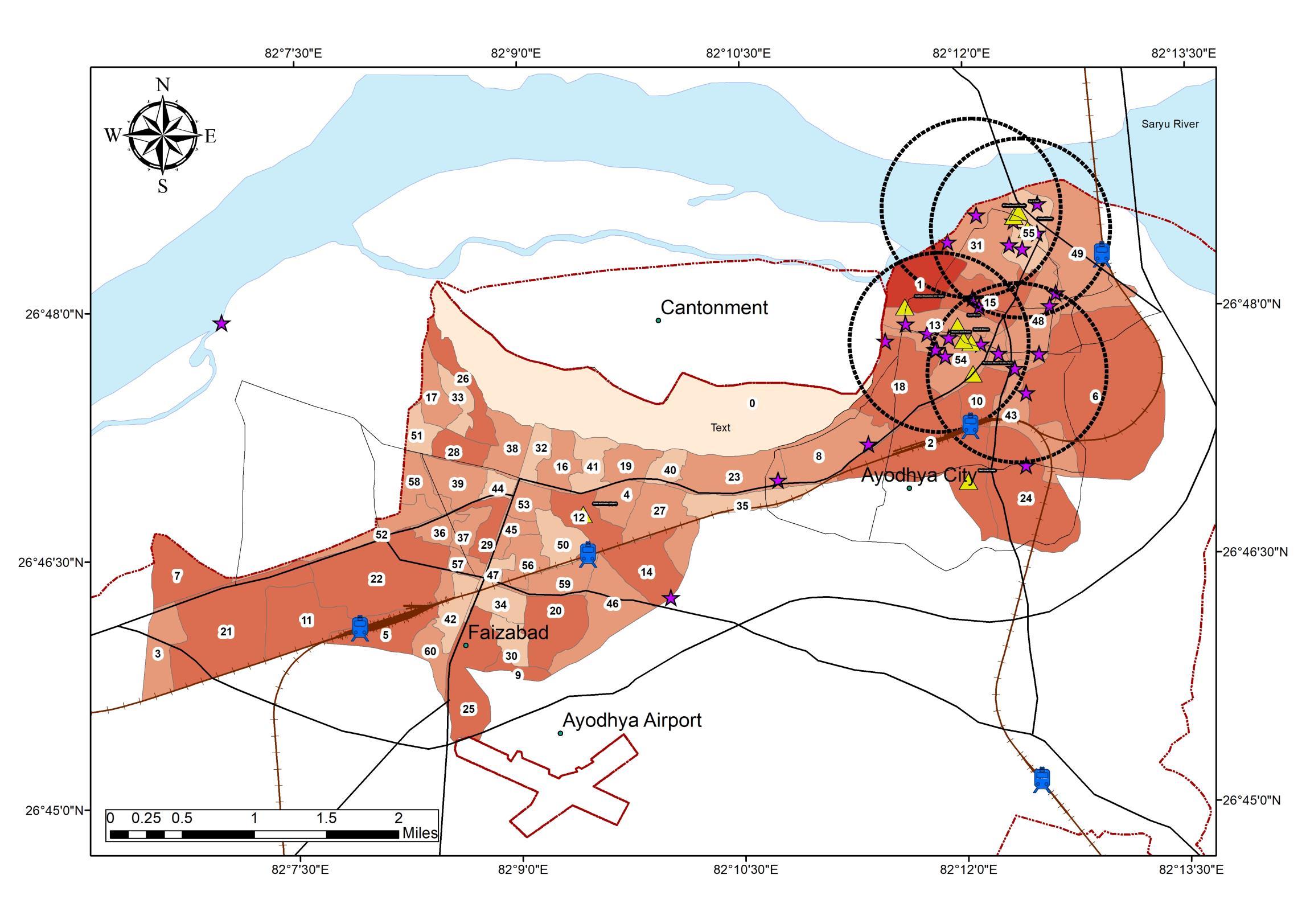
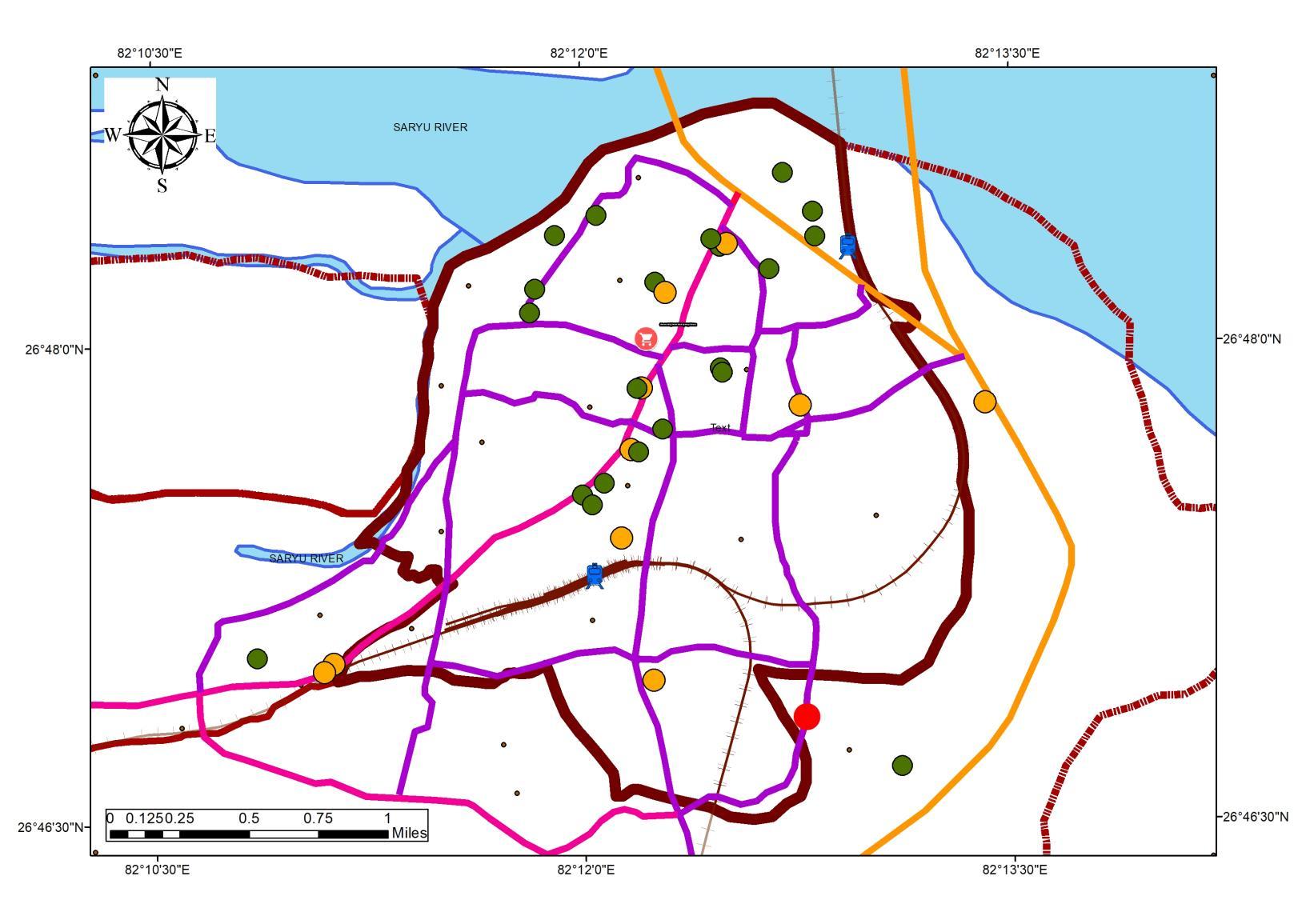
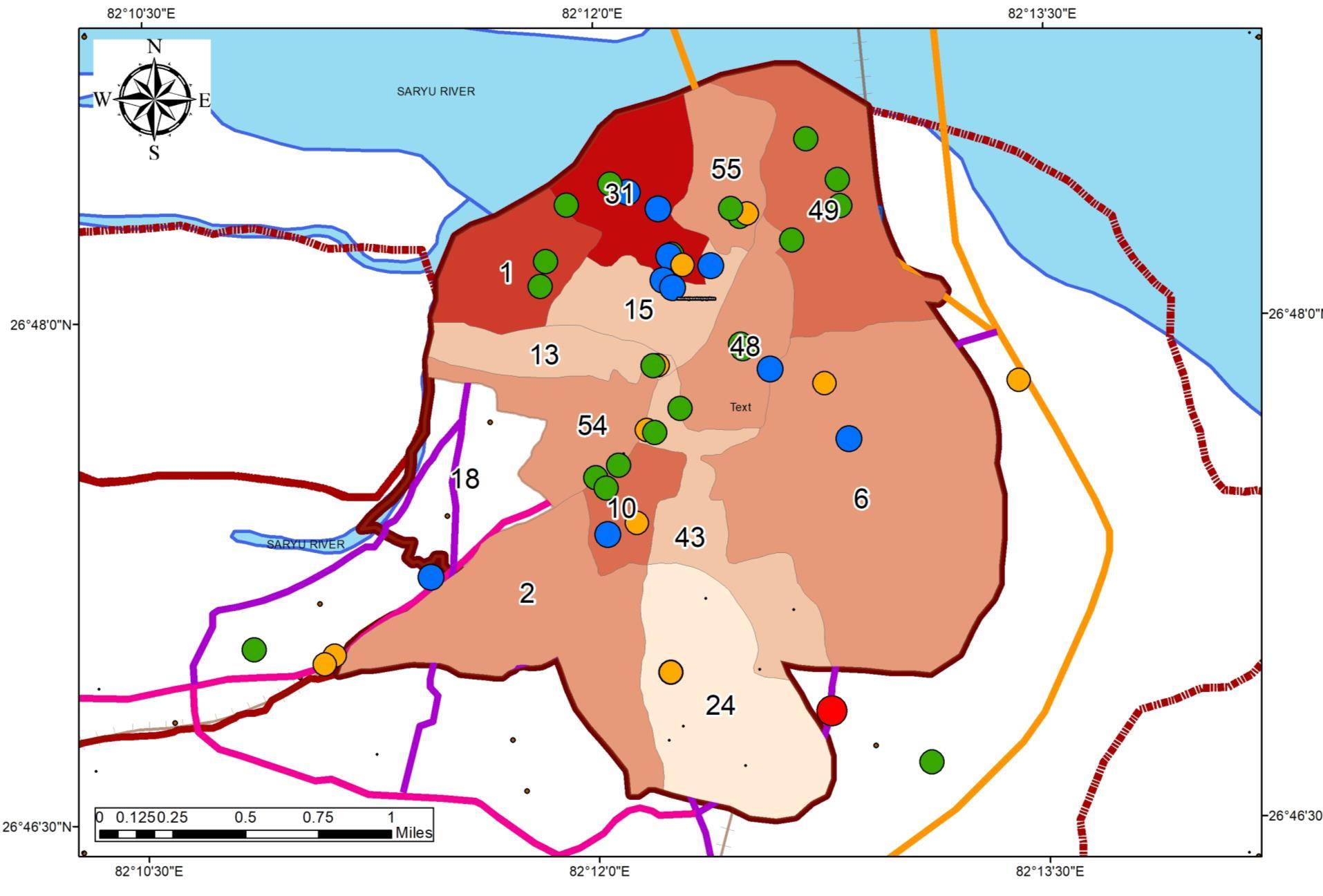
ACCOMMODATION DISTRIBUTION IN THE STUDYAREA
FORMALACCOMMODATION INFORMALACCOMMODATION
Source:Author w.r.t. LAND-RATESAND SWM GENERATION MAP, Generated Arc Gis 10.7 (May,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)
As per WASTE 2.0, the report of World Bank states “Waste generation is expected to grow by 70% by 2050, while world population is expected to grow by less than ½ the rate.
”
ECONOMIC LINKAGES WITH WASTE GENERATION
The lowest income group produces 0.39 kg per capita per day during winter months which is the minimum of MSW generated as compared to the high Income Group with the production of 1 1 kg per capita per day and the middle (0 56 kg per capita per day) income groups in the same season
Source:Author w.r.t DOI 10.1186/s12302-015-0050-9 (Ali Karman)
WASTE GENERATION RELATIONSHIPWITH ECONOMY
• The Super-Imposed maps show a trend of high waste generation in the areas with high land rates, which established the fact of waste generation based on SocioEconomic Group
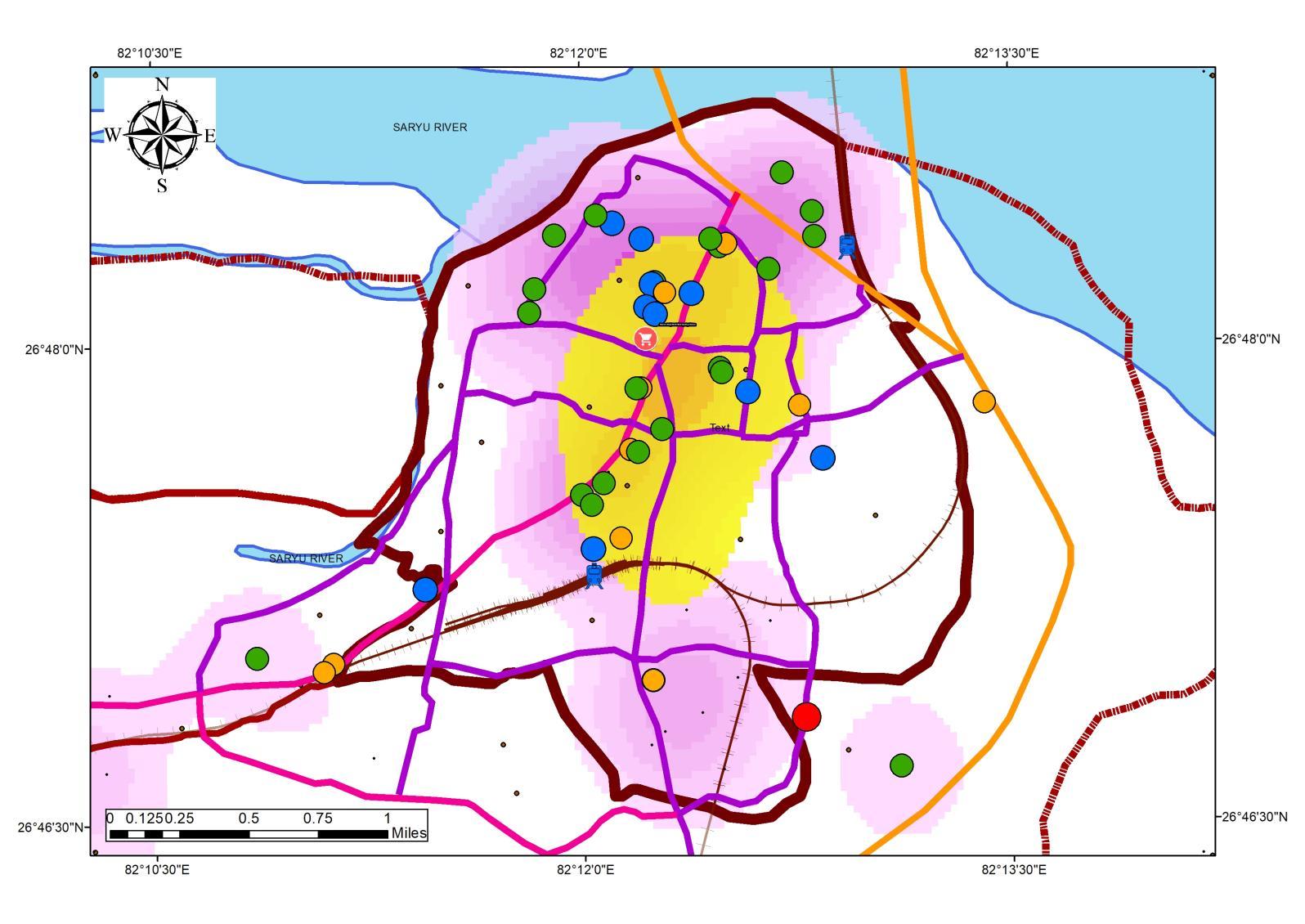
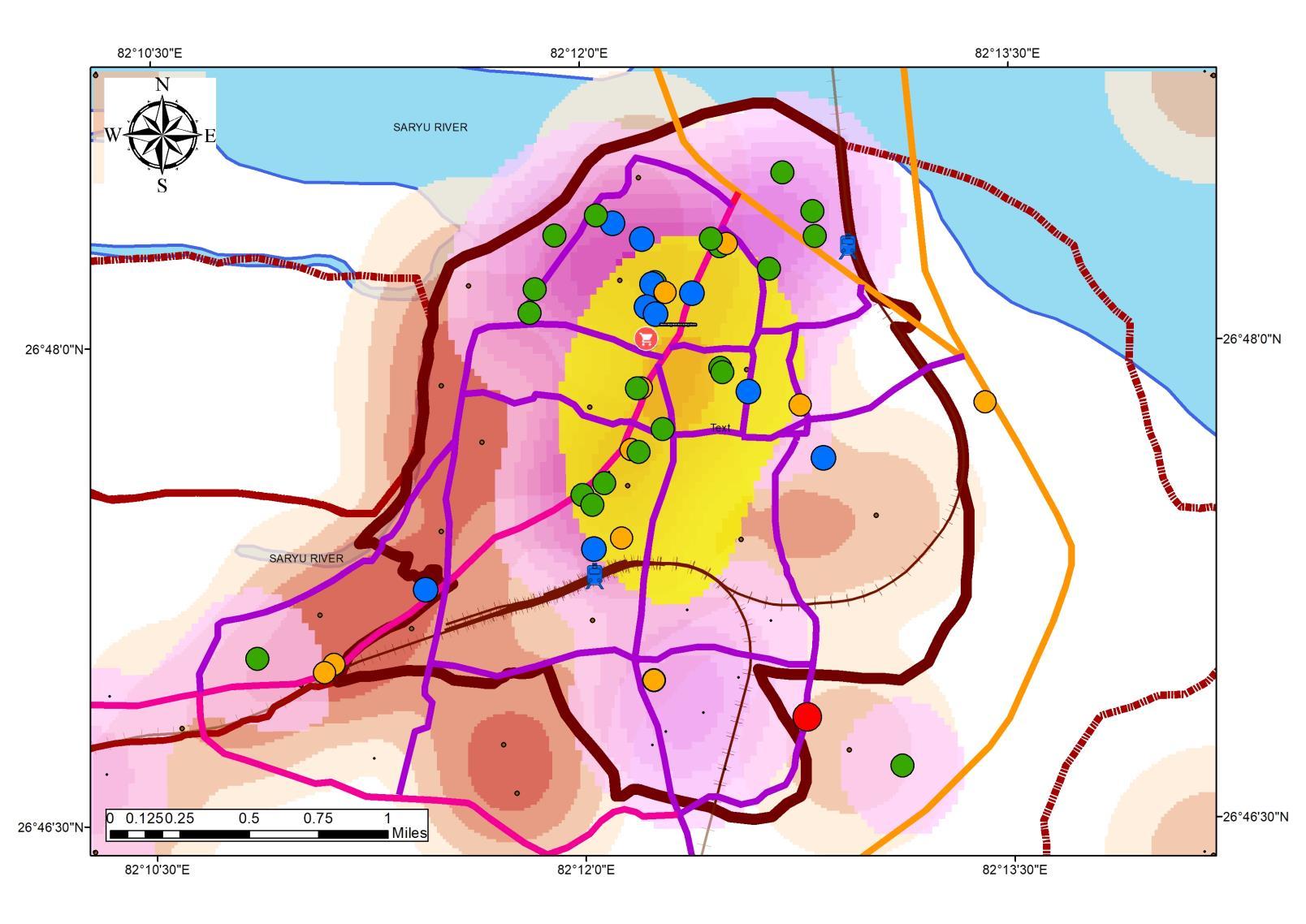
CATALYST OFWASTE GENERATION ALTERATION
• CHANGE IN SOCIO-ECONOMIC STATUS.
• CHANGE IN NUMBER OF GENERATORS (USER)
• CHANGE IN USER VOLUME (0.4 – 1.6 kg/cap/day)
• PEAK SEASON AUGMENTATION.
• SOCIO ECONOMY MIX
ESTABLISHMENT FOR STUDY FOR ACCOMMODATION
• Accommodation includes Hotel, Dharamshala, residence cum Stay facility
• Causes Mix of Socio Economy status, thus changes in waste composition
• Hotel Infrastructure needs proper management of waste as this can be termed waste guzzler during peak season.
Source:Author, Generated Arc Gis 10.7 (May,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)
• At present there are only 17 hotels for accommodation with 592 total rooms and around 70 Dharamshala.
• Around 5500 person Accommodation facilities are available in the Ayodhya city.
INFERENCE
Source:Author, Generated Arc Gis 10.7 (May,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)
• Formal Accommodations are located along the central spine.
• Informal accommodations are distributed through the region, as per the land rates and mixed-use
FORMAL/INFORMALLOCATION LOCATION VS LAND RATES
Source:Author, Generated Arc Gis 10.7 (May,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)

PRESENT SITUATION
As per ADA
• In phase B the development of Hotels and guest houses will be proposed to develop on bye pass road and on the north side after Saryu River it can be located
• In the present scenario, only redevelopment of old Dharamshala and a few guest houses will be possible.
• Accommodation of foreign tourists and domestic tourists, around 25000 rooms will be required of different categories of Hotels
INFERENCE
• Formal Accommodations are located along the central spine.
• Informal accommodations are distributed through the region, as per the land rates and mixed-use
• Spread of Informal Accommodations can be observed towards the lower land rates in peri-urban areas.
• Residential to commercial mixed-use can be observed in the North and central study area.
• Hotel Infrastructure runs in Parallel to Dharmshalas located in the central core.
• Upcoming Informal Hotels are seen near mani parvat area.
LEGENDS SHEET TITLE STUDENT NAME
Ar. Sayan Munshi
IVth Semester, M.Plan FOAP, AKTU, Lucknow, UP
Dr. Subhrajit Banerjee Thesis Guide
SOURCES

Capacity Building for Urban Tourism Development of Ayodhya Municipal Limits
KEY MAP
SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT
12 Legend AgricultureMarket Mandi MajorRoads Width__M_ 60 40
18 12 9 0 Railway
Landrate
!
Water_Body Legend AccommodationType 2STAR ! 3STAR DHARMSHALA INFORMALACCOM. Agriculture
0 Railway
ADA Reports Ayodhya NN Reports MDP Draft 2031 Primary Data Collection ADA Website ACCOMMODATION Waste Generation Character, Accommodation Distribution
Source:Author, Generated Arc Gis 10.7 (May,2022), WGS 1984 (N44)
32 23
Station railways railways_Intersect Study_Boundary UrbanArea
Boundary_ADA
Accommodation
Market Mandi MajorRoads Width__M_ 60 40 32 23 18 12 9
Station railways railways_Intersect Study_Boundary UrbanArea Landrate Boundary_ADA Water_Body
ACCOMMODATION
PRIMARY SURVEY OF HOTELS

DURATION OF STAY

Ayodhya with inbound tourists of 70000 per day, accommodates 5500 persons as per ADA reports.
Distributed among 17 Registered Hotels and 70 Dharmshalas.
Inference
• 46% of the inbound tourist prefers to stay 1 – 2 days.
• While 25-28% of the inbound prefers a stay of 2-8 days.
REACH OFTHEACCOMMODATIONS
Ayodhya with inbound tourists of 70000 per day, Prefers hotels in the range of 1-2 km
Distributed among 17 Registered Hotels and 70 Dharmshalas.
Inference
• With the most hotels located in the core, 48% of the tourists concentrate in the core.
OF STAY
ACCOMMODATIONAND SOLID WASTE GENERATION
is a measure of
the

can
interpreted as the proportion of variance of the outcome
explained by the linear regression model Tolerance is a useful tool for diagnosing multicollinearity, which happens when variables are too closely related. A tolerance of below .40 is cause for concern.
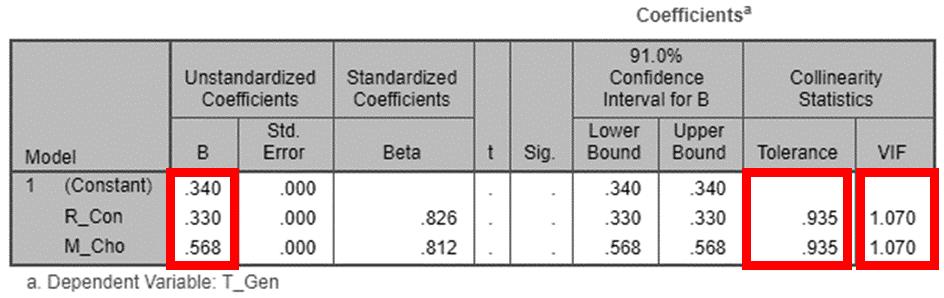
Variance inflation factor (VIF) is a measure of the amount of multicollinearity in a set of multiple regression variables.
Capacity
Building for Urban Tourism Development of Ayodhya Municipal Limits
KEY MAP
LEGENDS SHEET TITLE STUDENT NAME SOURCES
Ar. Sayan Munshi IVth Semester, M.Plan FOAP, AKTU, Lucknow, UP Dr. Subhrajit Banerjee Thesis Guide
46.2 28 25.6
1-2 days 5-8 days 2-5 days Transit Use 8 or more
DURATION
15.4 48.7 17.9 10.3 7.7 Reach of Accommodation <1 KM 1-2 KM 2-4 KM 4-8 KM 8KM >
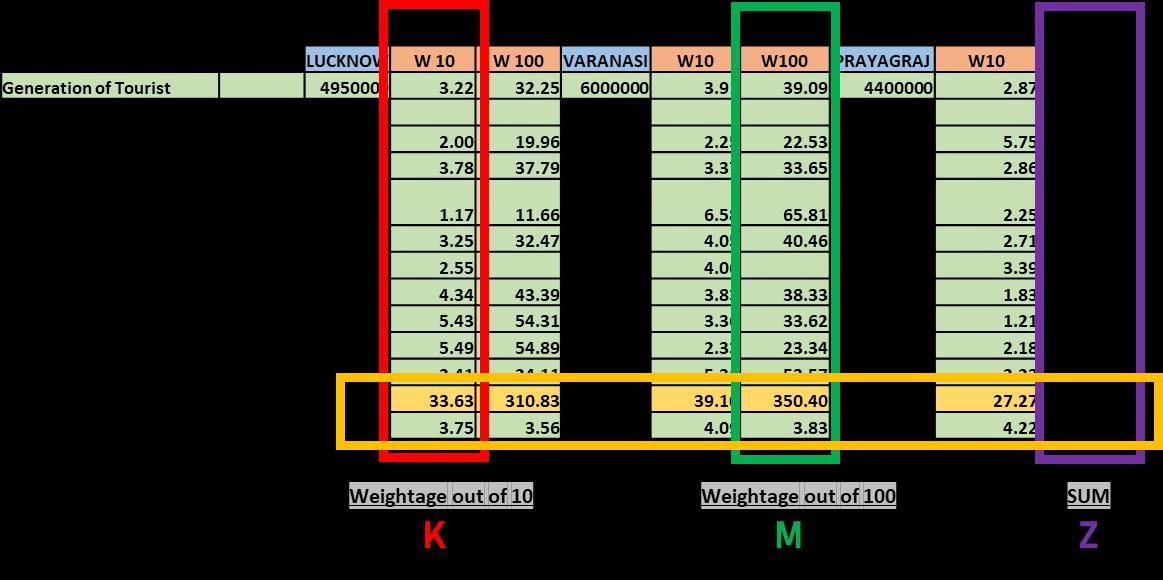
Source:Author, Generated Arc Gis 10.7 (May,2022), WGS 1984 (N44) COMPUTATION BASED ON RESEARCH ON TOURISM POTENTIAL Step 1: Collection of Data in True Value Step 2: Interpretation Sum of weights under each city’s infrastructure provides the ranking criteria Step 3: SPSS Data Assigning as per Weightage LK VA AL AY 35.75 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 ANALYSIS Step 4: Linear Regration with D/I Value and Analysis Type Step 5: Results Step 6: Coefficient
linear regression
R-squared
how well a
model fits
data It
be
Y
YFin=A + B + C σ�� = 0.33 (R_con) + 3.578 (P_Float) - 0.30 (W_Disp) + 2.675 (D_Stay) + 0.239 (N_des) ± 11.752 • Survey duration interval = 4 Months • Transition change form 12 15 to 22 86 ( df = 1 71) • Expected Change after proposal 2.03 (minimum df required) ADA Reports Ayodhya NN Reports MDP Draft 2031 Primary Data Collection ADA Website COMPUTATION Accommodation Analysis, Computation of Tourism Super potentiality 13 Legend Accommodation Type 2 STAR ! 3 STAR DHARMSHALA INFORMALACCOM. Agriculture Market Mandi Major Roads Width__M_ 60 40 32 23 18 12 9 0 Railway Station railways railways_Intersect Study_Boundary Urban Area Landrate Boundary_ADA Water_Body
4 PROPOSALS
ADDRESSING 5 Issues

TOURISM RELATED ASSOCIATED ISSUEAS PER URDPFI
• As per the Tourism Vision 2020, Issues related to tourism are addressed under Section 5, sub section 5, Clause 4 of URDPFI 2014
• Sub Clause: 1 ,2, 6,7, and 9 are focused
1. Influx of the floating population or tourists, 2. Assessment of areas of influence of tourism/ pilgrimage, 3. Pressure on fragile/sensitive tourism zones and on eco‐tourism sites in the tourist circuits,
4. Seasonal variation of the local economic base,
5. Unclear infrastructure estimations & planning estimations for the tourism towns due to fluctuation in the population to be served,
6. Transport planning issues associated with terrain, slopes and undulated systems,

7. Priority for non‐motorized transport and public transport.
8. Conservation and improvement of land profile, areas of scenic value and utilization of site features for strengthening the ambience, 9. Issues in solid waste management especially in religious/pilgrim towns,
10.Street vending activities in the popular religious and tourist sites and measures for their rehabilitation,
11.Lack of documentation of heritage buildings and areas and application of general architectural control in historical areas,
12. Supporting investment in heritage assets and generating returns by ULBs or by private sector,
13.Lack of social guidance in case of exposure to cultural variation, specifically in international tourism destination, et al.
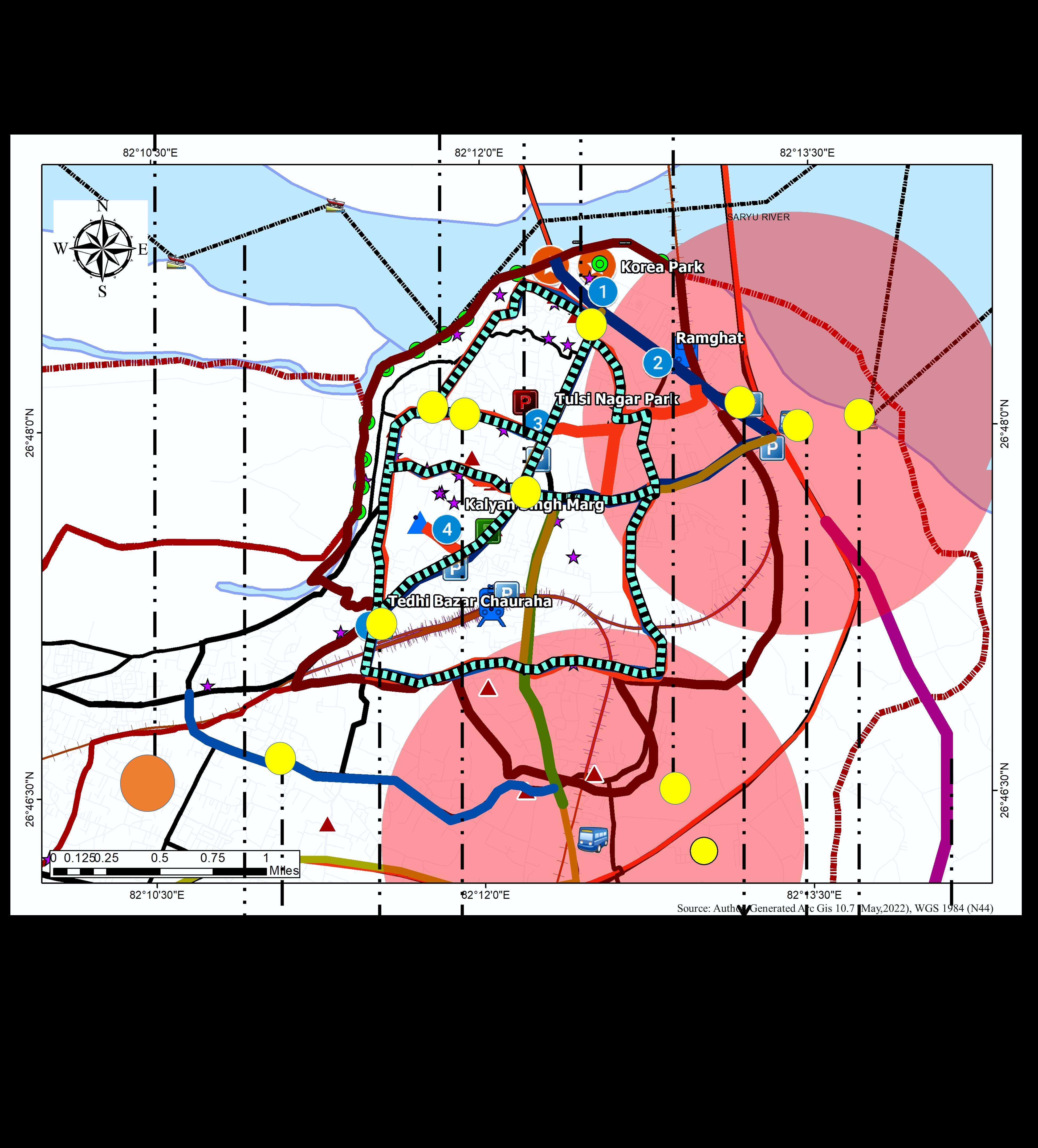
PROPOSAL ON AYODHYA MUNICIPAL AREA (Study area)
1.1 CORE DECONGESTION
Issue Identification:
i. Low Road Width ii. Lower LOS iii. Railway Station and Bus Stand are Located in the Center of the Study area.
iv. Slow-moving vehicles on the central spine v. Encroachment under commercialization vi. High volume of Mix modal transportation vii. Improper design of the intersections viii.On-road Parking due to lack of parking facility ix. Heavy influence of Para Transit on the Major roads
x. Improper connectivity between Transit modes
1.2. CENTRAL SPINE DECONGESTION
Issue Identification:
i. Low Road Width
ii. Slow-moving vehicles on the central spine iii. Encroachment under commercialization iv. Improper design of the intersections v. On-road Parking due to lack of parking facility vi. Heavy influence of Para Transit on the Major roads
2.1. TOURISM-BASED COLLECTION MECHANISM
Issue Identification:
i. Commercial Sector Stands high in waste generation ii. Significant areas under development lie under manual collection (Secondary) iii. Areas under heavy commercialization are under manual collection iv. Lack of Reach due to lower width of Road
2.2. LANDFILL BASED ON WASTE TO ENERGY
Issue Identification: i. Rising quantum of solid waste due to tourism led to a change in composition ii. Ayodhya has no designated Landfill iii. Inorganic Municipal waste requires special treatment of waste disposal unlike organic waste.
Primary Proposals:
i. New Peripheral Bypass Roads
ii. Proposal of Bus Stands on the Junction in conjuncture to Bypass Roads.
iii. Railway and Airport Connectivity with Bypass Road
iv. Mix Modal Control as per axel configuration
v. Proposal of Water Ways (Alternate Route)
Primary Proposals: i. Augmentation of proposed road widening ii. Augmentation in transit modes iii. Improvisation of intersections under study iv. Augmentation of parking issue v. Retrofitting of para transit routes
Primary Proposals: i. Newer Technology in Waste Collection ii. Increase in Reach of Vehicles iii. Upgradation of Collection Vehicles iv. Increase in Door to Door collection
Primary Proposals: i. Waste to energy project aims to convert waste into energy ii. Selection of Site
Source:Author, wrt URDPFI 2014
Ar. Sayan Munshi IVth Semester, M.Plan FOAP, AKTU, Lucknow, UP
Dr. Subhrajit Banerjee Thesis Guide
LEGENDS SHEET TITLE STUDENT NAME SOURCES
Capacity Building for Urban Tourism Development of Ayodhya Municipal Limits
KEY MAP
PROPOSAL HIGHLIGHTS FOR TOURISM INFRASTRUCTURE 1 1
2
Transportation
Management
1
to
1
Core decongestion 1
Central Spine Decongestion 1.
2. Solid Waste
2
Tourism-based Collection Mechanism 2.2. Landfill based on Waste
Energy 3.Accommodation 3
New Infrastructure Zone delineation
ADA
MDP
PROPOSAL 14 σ�� = 0.33 (R_con) + 3.578 (P_Float) - 0.30 (W_Disp) + 2.675 (D_Stay) + 0.239 (N_des) ± 11.752 ��.�� & 1.2 �� ��.��&��.�� ��−�� ��−�� �� �� �� Dependent on Factors Constant based on dependent
Reports Ayodhya NN Reports
Draft 2031 Primary Data Collection ADA Website
It was observed that the Proposals in Ayodhya for the Above case satisfies the structural equation, Hence, the Proposals are proven to be adding Tourism Potential to the region of Ayodhya through Infrastructure Upgradation.
Following Recommendation is Generated for the case:
TSP > 24.89
• Circuit Definition of Tourism Master Plan
• Circuit planning or Modification in CMP

• Improvisation of Tourism Cell under Local Government
• Empowering Local Government with better structure of SWM and Revenue Structure.
• PPP for Accommodation infrastructure and Control over Cost Structure.
• Dedicated Transport system to ensure lower congestion and Higher LOS on local road and Increase share of Public Transportation and Concentration Towards NMT.
• Action plan incorporated with Master Plan.
• Policy Guidance Document that mobilizes all Municipal policies and Tourism Ecosystem across a broad circuit Upgradation of the Peri Urban Area.
• Develop niche Markets and Strengthening assets

• Reinforce Emerging Sector and Digital Enterprises.
• International Promotion.
CONCLUSION
Capacity Building for Urban Tourism Development of Ayodhya Municipal Limits LEGENDS SHEET TITLE STUDENT NAME SOURCES KEY MAP Ar. Sayan Munshi IVth Semester, M.Plan FOAP, AKTU, Lucknow, UP Dr. Subhrajit Banerjee Thesis Guide PROPOSAL ON AYODHYA MUNICIPAL AREA (Study area) ASSESMENT OF STRUCTURAL EQUATION 15 ADA Reports Ayodhya NN Reports MDP Draft 2031 Primary Data Collection ADA Website σ�� = 0.33 (R_con) + 3.578 (P_Float) - 0.30 (W_Disp) + 2.675 (D_Stay) + 0.239 (N_des) ± 11.752 Code Month of Assessment R_Con P_Float W_Disp D_Stay N_Des YTSP A (Existing) December 2021 0.22 7.14 0.64 2.86 2.76 22.86 B (Proposed) June 2022 3.20 12.50 2.1 3.9 2.76 28.98 �������� ���������������� �������� ���� ����.���� �������� �� �������� �� Legend ProposedBusstand RailwayStation ! Ghats # POI Name # ProposedRamTemple ^ _ Destinations 1.6kmbuffer Study_Boundary UrbanArea ProposedWaterWay WaterRoute TYPE Bypass1 Bypass2 Bypass3 Improvement R_type ArterialRoad CollectorStreet LocalStreet roads_RoadLocal <allothervalues> railways railways_Intersect Boundary_ADA Water_Body Legend ProposedBusstand RailwayStation ! R Ghats # POI Name # ProposedRamTemple ^ Destinations 1.6kmbuffer Study_Boundary UrbanArea ProposedWaterWay WaterRoute TYPE Bypass1 Bypass2
Improvement R_type ArterialRoad CollectorStreet Local
<all
values>
Bypass3
Street roads_RoadLocal
other
railways railways_Intersect Boundary_ADA Water_Body
Upgradation of Infrastructure and Governance support Tourism










































































