

BEKÆMP INFLAMMATIONEN IKKE BIOMARKØREN
Den eosinofile celle er en vigtig biomarkør for type 2-inflammation - men ikke årsagen1
MÅSKE ER DET
TYPE 2-
INFLAMMATION
SOM ER ÅRSAG TIL KOL HOS
DIN PATIENT1,2
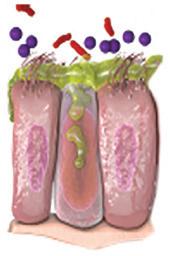
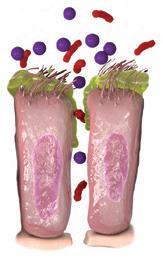
KOL patienter med type 2-inflammation kan have øget risiko for eksacerbationer2 32 % ØGET RISIKO FOR

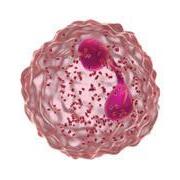
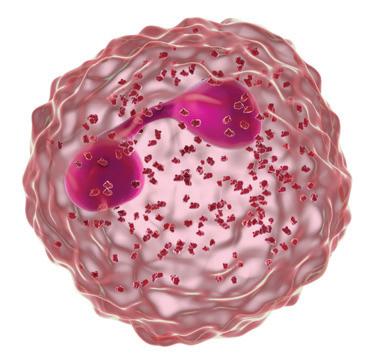
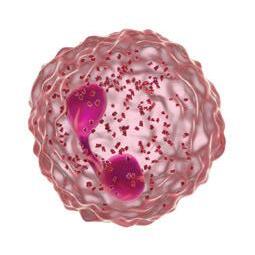
Forhøjede eosinofile celler er et tegn på type 2-inflammation1 GOLD rapporten fra 2025 anerkender forhøjede blod-eosinofile celler, som en klinisk anvendelig biomarkør til identifikation af KOL hos patienter med type 2-inflammation 1
KONTROLLER RUTINEMÆSSIGT BLOD-EOS NIVEAUET HOS DINE PATIENTER MED KOL1
a Resultater fra en observationsbaseret analyse af 1553 patienter med GOLD spirometriklasse 2-4 KOL til vurdering af forholdet mellem blodets eosinofiltal og risikoen for KOL-eksacerbationer2 b Stratificeret analyse bekræftede, at den øgede risiko for eksacerbationer var drevet af patienter med en historik med hyppige eksacerbationer, defineret som ≥2 eksacerbationer pr. år.2
DER DRIVER
SYGDOMSAKTIVITETEN
IL-4 og IL-13 er vigtige og centrale spillere i aktivering af type 2-inflammation3
IL-4 IL-13
IL-4 og IL-13 fremmer aktivering og rekruttering af type 2-inflammatoriske celler, herunder eosinofiler, til lungerne, hvilket kan bidrage til airway remodellering og destruktion af lungeparaenkymet ved KOL4-13

IL-4, IL-13, og IL-5 har forskellige roller i type 2-inflammation4,6,13-23
Virus, bakterier, mikrobiom, røg/ forurenende stoffer, oxidativt stress
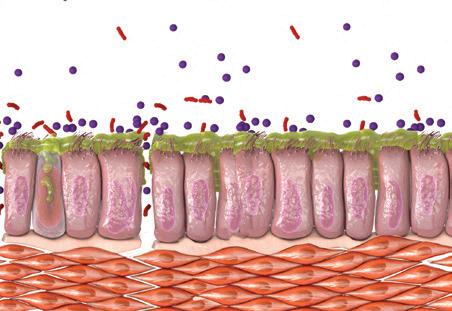
LUFTVEJSEPITEL
Alarminer: IL-25, IL-33, TSLP
ILC2 celler

Bægercellehyperplasi og mucusproduktion
Positiv feedback loop



Luftvejs-remodellering og fibrose
Parenkymal destruktion
Barrier disruption
Th0-celle differentierer til Th2-celle
Eosinofil differentiering i knoglemarven
Eosinofil Eosinofil trafficking til væv
FOR AT HÅNDTERE ÅRSAGEN TIL TYPE 2-
INFLAMMATIONEN, ER DET VIGTIGT AT ADRESSERE DE UNDERLIGGENDE MEKANISMER
IL-4
IL-5
IL-13
IL-13
IL-4

Referencer: 1. Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (2025 report). Accessed [July 30, 2025]. https://goldcopd.org/2025-gold-report/ 2. Yun JH, Lamb A, Chase R, et al; COPDGene and ECLIPSE Investigators. Blood eosinophil count thresholds and exacerbations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141(6):2037-2047.e10. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2018.04.010 3. Garudadri S, Woodruff PG. Targeting chronic obstructive pulmonary disease phenotypes, endotypes, and biomarkers. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018;15(suppl 4):S234-S238. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.201808-533MG 4. Gandhi NA, Bennett BL, Graham NMH, Pirozzi G, Stahl N, Yancopoulos GD. Targeting key proximal drivers of type 2 inflammation in disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016;15(1):35-50. doi:10.1038/nrd4624 5. Rosenberg HF, Phipps S, Foster PS. Eosinophil trafficking in allergy and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007;119(6):1303-1310. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2007.03.048 6. Doyle AD, Mukherjee M, LeSuer WE, et al. Eosinophil-derived IL-13 promotes emphysema. Eur Respir J. 2019;53(5):1801291. doi:10.1183/13993003.01291-2018 7. Barnes PJ. Inflammatory mechanisms in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;138(1):16-27. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2016.05.011 8. Defrance T, Carayon P, Billian G, et al. Interleukin 13 is a B cell stimulating factor. J Exp Med. 1994;179(1):135-143. doi:10.1084/jem.179.1.135 9. Yanagihara Y, Ikizawa K, Kajiwara K, Koshio T, Basaki Y, Akiyama K. Functional significance of IL-4 receptor on B cells in IL-4–induced human IgE production. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995;96(6 pt 2):1145-1151. doi:10.1016/ s0091-6749(95)70199-0 10. Gandhi NA, Pirozzi G, Graham NMH. Commonality of the IL-4/IL-13 pathway in atopic diseases. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2017;13(5):425-437. doi:10.1080/1744666X.2017.1298443 11. Kaur D, Hollins F, Woodman L, et al. Mast cells express IL-13Rα1: IL-13 promotes human lung mast cell proliferation and FcεRI expression. Allergy. 2006;61(9):1047-1053. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2006.01139.x 12. Zheng T, Zhu Z, Wang Z, et al. Inducible targeting of IL-13 to the adult lung causes matrix metalloproteinase– and cathepsin-dependent emphysema. J Clin Invest. 2000;106(9):10811093. doi:10.1172/JCI10458 13. Saatian B, Rezaee F, Desando S, et al. Interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 cause barrier dysfunction in human airway epithelial cells. Tissue Barriers. 2013;1(2):e24333. doi:10.4161/tisb.24333 14. Oishi K, Matsunaga K, Shirai T, Hirai K, Gon Y. Role of type2 inflammatory biomarkers in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Clin Med. 2020;9(8):2670. doi:10.3390/jcm9082670 15. Yousuf A, Ibrahim W, Greening NJ, Brightling CE. T2 biologics for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7(5):1406-1416. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2019.01.036 16. Aghapour M, Raee P, Moghaddam SJ, Hiemstra PS, Heijink IH. Airway epithelial barrier dysfunction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: role of cigarette smoke exposure. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018;58(2):157-169. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2017-0200TR 17. Alevy YG, Patel AC, Romero AG, et al. IL-13–induced airway mucus production is attenuated by MAPK13 inhibition. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(12):4555-4568. doi:10.1172/JCI64896 18. Cooper PR, Poll CT, Barnes PJ, Sturton RG. Involvement of IL-13 in tobacco smoke–induced changes in the structure and function of rat intrapulmonary airways. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2010;43(2):220-226. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2009-0117OC 19. Arora S, Dev K, Agarwal B, Das P, Syed MA. Macrophages: their role, activation, and polarization in pulmonary diseases. Immunobiology. 2018;223(4-5):383-396. doi:10.1016/j.imbio.2017.11.001 20. He S, Xie L, Lu J, Sun S. Characteristics and potential role of M2 macrophages in COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017;12:3029-3039. doi:10.2147/COPD.S147144 21. Wang Z, Bafadhel M, Haldar K, et al. Lung microbiome dynamics in COPD exacerbations. Eur Respir J. 2016;47(4):1082-1092. doi:10.1183/13993003.01406-2015 22. Linden D, Guo-Parke H, Coyle PV, et al. Respiratory viral infection: a potential “missing link” in the pathogenesis of COPD. Eur Respir Rev. 2019;28(151):180063. doi:10.1183/16000617.0063-2018 23. Wang X, Xu C, Ji J, et al. IL-4/IL-13 upregulates Sonic hedgehog expression to induce allergic airway epithelial remodeling. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020;318(5):L888-L899. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00186.2019
