More products digital (pdf, epub, mobi) instant download maybe you interests ...

Elements of Ecology 8th Edition Smith Test Bank
https://testbankfan.com/product/elements-of-ecology-8th-editionsmith-test-bank/

Elements of Ecology Canadian 1st Edition Smith Test Bank
https://testbankfan.com/product/elements-of-ecology-canadian-1stedition-smith-test-bank/

Elements of Ecology Canadian 1st Edition Smith Solutions Manual
https://testbankfan.com/product/elements-of-ecology-canadian-1stedition-smith-solutions-manual/

Elements of Physical Chemistry 7th Edition Smith Solutions Manual
https://testbankfan.com/product/elements-of-physicalchemistry-7th-edition-smith-solutions-manual/

Essentials of Ecology 4th Edition Begon Test Bank
https://testbankfan.com/product/essentials-of-ecology-4thedition-begon-test-bank/

Emerys Elements of Medical Genetics 14th Edition Turnpenny Test Bank
https://testbankfan.com/product/emerys-elements-of-medicalgenetics-14th-edition-turnpenny-test-bank/

Ecology The Economy of Nature 7th Edition Ricklefs Test Bank
https://testbankfan.com/product/ecology-the-economy-ofnature-7th-edition-ricklefs-test-bank/

Elements
of
the Nature and Properties of Soils 3rd Edition Brady Test Bank
https://testbankfan.com/product/elements-of-the-nature-andproperties-of-soils-3rd-edition-brady-test-bank/

Essentials of Ecology 7th Edition Miller Solutions
Manual
https://testbankfan.com/product/essentials-of-ecology-7thedition-miller-solutions-manual/
Elements of Ecology, 9e (Smith)
Chapter 8 Properties of Populations
8.1 Short Answer Questions
1) A group of individuals of the same species inhabiting a given area is called a(n) ________.
Answer: population
Topic: Introduction to Chapter 8
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
2) An individual tree or plant produced by sexual reproduction and thus arising from a zygote is a genetic individual, known as a(n) ________.
Answer: genet
Topic: Section 8.1
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
3) The ________ of a population describes its spatial location, the area over which it occurs.
Answer: distribution
Topic: Section 8.2
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
4) As a result of environmental heterogeneity, most populations are divided into smaller populations, referred to as local ________.
Answer: subpopulations
Topic: Section 8.2
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
5) ________ defines the size of a population, the number of individuals in it.
Answer: Abundance
Topic: Section 8.3
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
6) Population ________ is the number of individuals per unit area, or per unit volume.
Answer: density
Topic: Section 8.3
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
7) Because a direct count of all individuals within a population is often impossible, population density is usually estimated by one or more methods of ________.
Answer: sampling
Topic: Section 8.4
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
8) Counting the total number of individuals within a square or rectangle of known area, referred to as a(n) ________, is a sampling method that is commonly used to study plants or other sessile animals.
Answer: quadrat
Topic: Section 8.4
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
9) Populations can be divided into three ecologically important age classes: prereproductive, reproductive, and ________.
Answer: postreproductive
Topic: Section 8.5
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
10) A graph that compares the relative number of individuals within different age groups of a population is called an age ________.
Answer: pyramid
Topic: Section 8.5
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
11) In most mammalian populations, the ________ sex ratio at birth is often weighted toward males.
Answer: secondary
Topic: Section 8.6
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
12) Individuals moving from another location into a subpopulation is referred to as ________.
Answer: immigration
Topic: Section 8.7
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
13) A round-trip movement of an individual from one place to another and back again is called ________.
Answer: migration
Topic: Section 8.7
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
14) The primary factors driving the dynamics of population abundance are the demographic processes of ________ and ________.
Answer: birth; death
Topic: Section 8.8
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
8.2 Multiple-Choice Questions
1) Which of the following is not a feature of a population?
A) size
B) density
C) number of species
D) distribution
Answer: C
Topic: Introduction to Chapter 8
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
2) A module that is produced asexually by an original genetic individual, which may remain physically linked to the parent or may be separate, is referred to as a A) genet.
B) ramet.
C) clone.
D) bud.
Answer: B
Topic: Section 8.1
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
3) Which of the following represents a modular organism?
A) lizard
B) coral
C) dog
D) ant
Answer: B
Topic: Section 8.1
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
4) You see three shoots of a plant with a connected root system. This is an example of A) 3 ramets.
B) 1 ramet.
C) 3 genets.
D) 6 genets.
Answer: A
Topic: Section 8.1
Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis
5) Which of the following is a clonal animal?
A) sheep
B) coral
C) mouse
D) quail
Answer: B
Topic: Section 8.1
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
6) The California newt is found only in California. This is an example of a(n) ________ species.
A) ubiquitous
B) metapopulation
C) endemic
D) invasive
Answer: C
Topic: Section 8.2
Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis
7) If, via global warming, the temperatures increased in Canada, the red maple might be able to extend its ________ to the North.
A) population size
B) migration route
C) age structure
D) geographic range
Answer: D
Topic: Section 8.2
Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis
8) A group of local subpopulations is called a(n)
A) community.
B) species.
C) metapopulation.
D) ecogroup.
Answer: C
Topic: Section 8.2
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
9) The area inhabited by all individuals of a particular species is known as the population's A) geographic range.
B) density.
C) ecosystem.
D) habitat.
Answer: A
Topic: Section 8.2
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
10) A population's density is calculated as the A) area over which the population is distributed.
B) number of individuals within the population.
C) unit of area divided by the number of individuals.
D) number of individuals per unit area.
Answer: D
Topic: Section 8.3
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
11) In populations of animals that defend an area for their own exclusive use or in plants that compete intensively for belowground resources such as water or nutrients, the spatial distribution of individuals is usually
A) homogenous.
B) clumped.
C) random.
D) uniform.
Answer: D
Topic: Section 8.3
Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis
12) An ecologist counts the number of individuals in five samples of equal area for four species of organisms. Which of these counts best represents a clumped population?
A) 23, 21, 25, 22, 18
B) 133, 124, 113, 128, 119
C) 47, 18, 93, 12, 28
D) 12, 13, 12, 13, 11
Answer: C
Topic: Section 8.3
Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis
13) Which of the following best represents a measure of ecological density?
A) number of frogs per meter of pond shoreline
B) number of birds per hectare
C) number of mammals per meter
D) number of fish per volume of ocean
Answer: A
Topic: Section 8.3
Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis
14) Which of the following best describes the distribution of corn in an agricultural field?
A) uniform
B) random
C) clumped
D) ideal
Answer: A
Topic: Section 8.3
Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis

When sampling a species that has clumped distributions, which approach listed below is best?
A) sampling at random locations
B) counting every individual
C) calculating an ecological density
D) assuming a uniform distribution
Answer: D
Topic: Section 8.3
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
16) Which of the following methods would work best to estimate flower species diversity?
A) mark-recapture
B) Lincoln Peterson index
C) quadrats
D) distribution mapping
Answer: C
Topic: Section 8.4
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
17) Calculate the estimated population size, N, given a study that initially marked 100 animals and subsequently captured 50, of which 25 were marked.
A) 25
B) 100
C) 50
D) 200
Answer: D
Topic: Section 8.4
Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis
18) Which of the following sampling techniques represents an index of abundance rather than an estimate of density?
A) number of oak trees within a quadrat
B) number of bear droppings along a trail
C) ratio of marked and unmarked mice in a field
D) number of ducks on a pond
Answer: B
Topic: Section 8.4
Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis
19) The age of a tree is best approximated by
A) estimating tree height.
B) counting tree growth rings.
C) measuring the diameter of a trunk at breast height (dbh).
D) counting the number of leaves.
Answer: B
Topic: Section 8.5
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
20) The demographic age pyramid of a rapidly growing population is
A) wide at the base, narrow at the top.
B) wide at the top, narrow at the bottom.
C) wide at top and bottom, narrow in the middle.
D) similarly wide from top to bottom.
Answer: A
Topic: Section 8.5
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
21) What is one way biologists determine the life stage of birds?
A) counting otoliths
B) plumage
C) examining the gap in wing bones
D) tooth shape
Answer: B
Topic: Section 8.5
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
22) Which of the following countries have an age structure that most resembles a pyramid?
A) United States
B) Japan
C) Egypt
D) none resemble a pyramid
Answer: C
Topic: Section 8.5
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
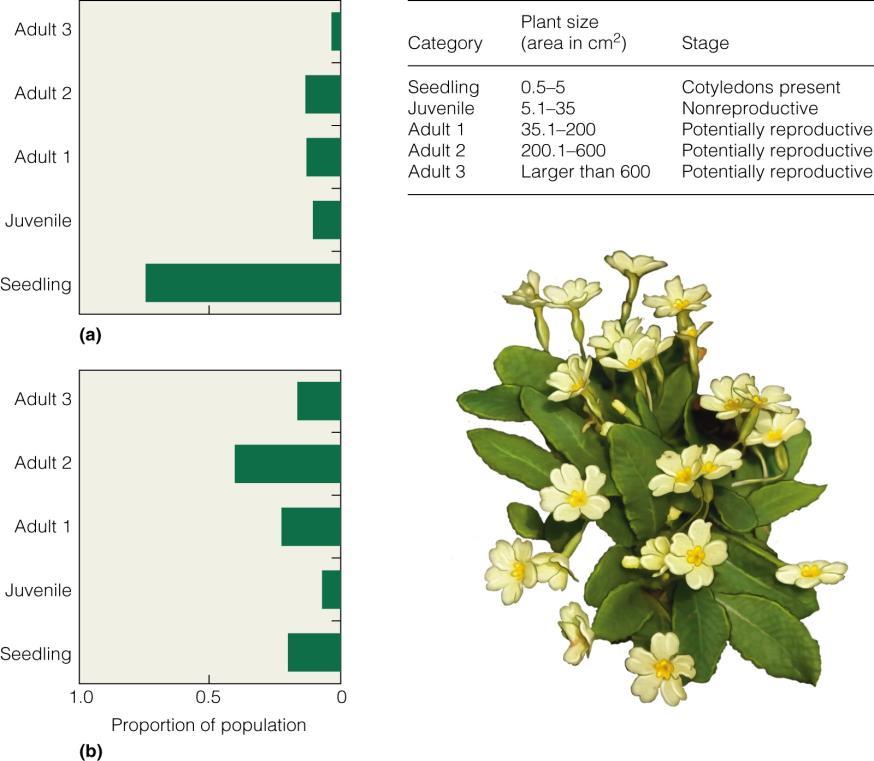
According to the figure, the predominant plant in an open site is roughly ________ cm3 in size.
A) larger than 600
B) 200.1-600
C) 5.1-35
D) 0.5-5
Answer: D
Topic: Section 8.5
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
24) Which of the following is an example of dendrochronology?
A) measuring seedling recruitment
B) counting juveniles in a population
C) measuring finger bone size over time
D) counting tree rings
Answer: D
Topic: Section 8.5
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
25) The sex ratio of human senior citizens (>65 years) is A) skewed toward females.
B) skewed toward males.
C) 1:1.
D) the same as birds'.
Answer: A
Topic: Section 8.6
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
26)
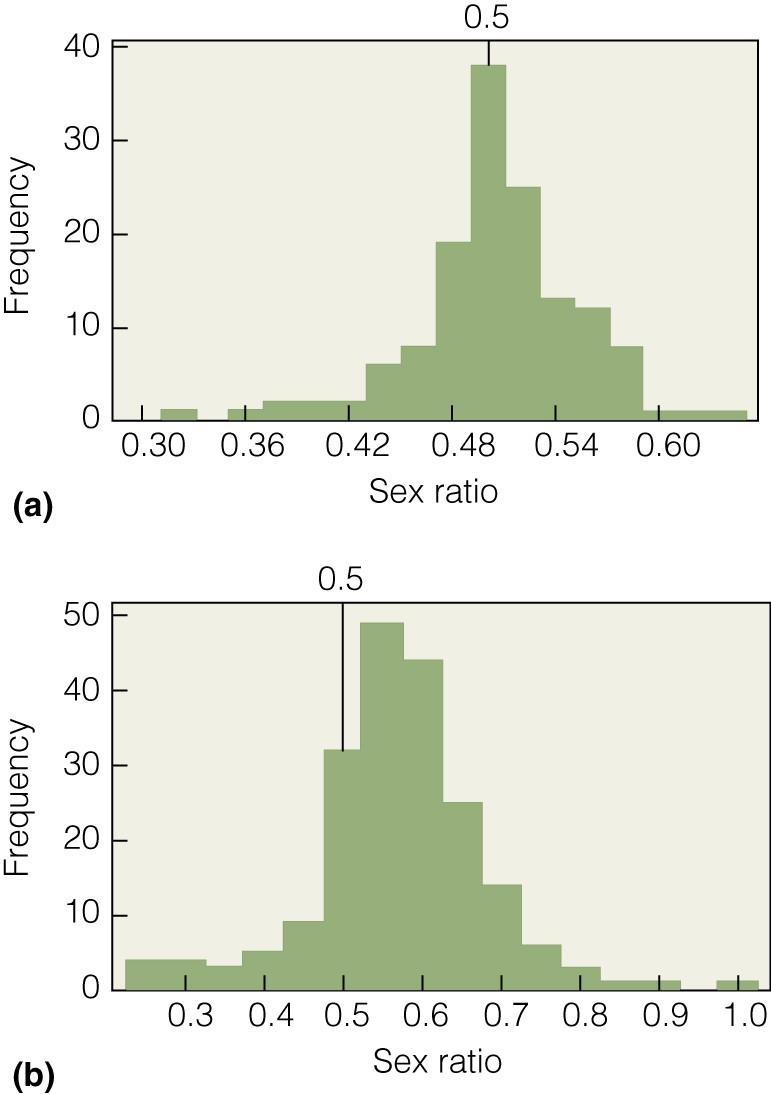
Why might the sex ratio of bird species in the figure change from as they grow from juveniles to adults?
A) Nesting females are vulnerable to predatory attack.
B) Males that are unable to mate die quickly.
C) Females are less able to feed effectively as juveniles.
D) More females are required to sustain the population.
Answer: A
Topic: Section 8.6
Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis
27) The movement of individuals in space is called
A) distribution.
B) migration.
C) dispersal.
D) density.
Answer: C
Topic: Section 8.7
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
28) An ecologist spent a year studying the population dynamics of a species of duck on a lake. At the beginning of the year, there were 86 adults. Of these, 16 adults left the lake, 12 adults arrived on the lake from elsewhere, 76 chicks hatched from eggs, 24 chicks survived to become adults, and 8 adults died. How many individuals emigrated?
A) 8
B) 12
C) 16
D) 24
Answer: C
Topic: Section 8.7
Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis
29) If more individuals move out of a forest than into it every year, the ________ rate is high.
A) immigration
B) fidelity
C) emigration
D) migration
Answer: C
Topic: Section 8.7
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
30) Which of the following is an example of migration?
A) frogs leaving a pond after metamorphosis
B) hawks finding a new territory after maturing
C) seeds dispersing from a tree
D) humpback whales traveling up and down the coast of western United States
Answer: D
Topic: Section 8.7
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
31) Why is Pacific salmon movement into freshwater streams considered migration if the salmon die at the head of the stream and never return to the ocean?
A) It is not considered migration but immigration.
B) Migration is a one-way movement.
C) Because their offspring return to the ocean, the entire population participates in the migratory event via different life stages
D) Most male adult fish survive reproduction and return to the ocean.
Answer: C
Topic: Section 8.7
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
32) How might a species' range be extended?
A) through increased migration rates
B) through increased immigration rates
C) through climate change
D) through decreased reproductive rates
Answer: C
Topic: Section 8.8
Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis
33) Which of the following species' range has extended extensively over the past 100 years?
A) grizzly bear
B) gypsy moth
C) polar bear
D) spotted owl
Answer: B
Topic: Section 8.8
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
34) Which of the following is not an invasive species?
A) cheatgrass
B) purple loosestrife
C) ring-necked duck
D) Asian longhorned beetle
Answer: C
Topic: Ecological Issues & Applications 8: Invasive Species
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
35) Which of the following was propagated and promoted for use by the Soil Conservation Service but is now listed as a Federal Noxious Weed?
A) purple loosestrife
B) Australian paperbark tree
C) kudzu
D) evening primrose
Answer: C
Topic: Ecological Issues & Applications 8: Invasive Species
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
8.3 True/False Questions
1) A genet is produced asexually.
Answer: FALSE
Topic: Section 8.1
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
2) A ramet is genetically identical to its original parent. Answer: TRUE
Topic: Section 8.1
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
3) An individual plant is often more difficult to recognize than an individual animal. Answer: TRUE
Topic: Section 8.1
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
4) The distribution of species is rarely determined by minimum and maximum temperature tolerances.
Answer: FALSE
Topic: Section 8.2
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
5) Most populations are divided into subpopulations. Answer: TRUE
Topic: Section 8.2
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
6) A uniform distribution of individuals within a population occurs if each individual's position is independent of others' positions.
Answer: FALSE
Topic: Section 8.3
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
7) The most common spatial distribution among individuals within a population is clumped. Answer: TRUE
Topic: Section 8.3
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
8) Ecological density is a measure of the number of individuals per unit of available living space. Answer: TRUE
Topic: Section 8.3
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
9) The density of a population is usually measured by counting every individual. Answer: FALSE
Topic: Section 8.4
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
10) A quadrat is usually used to measure density in mobile populations of animals. Answer: FALSE
Topic: Section 8.4
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
11) The age of a fish can be determined by counting the annual rings of otoliths (ear bones). Answer: TRUE
Topic: Section 8.5
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
12) Small trees are often the same age as large individuals in the canopy. Answer: TRUE
Topic: Section 8.5
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
13) The sex ratio in a population is usually fixed and does not vary among age classes. Answer: FALSE
Topic: Section 8.6
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
14) All animals disperse actively, whereas all plants disperse passively. Answer: FALSE
Topic: Section 8.7
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
15) Unlike the one-way movement of an individual in emigration and immigration, migration refers to round-trip movements.
Answer: TRUE
Topic: Section 8.7
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
8.4 Essay Questions
1) Explain how the mode of reproduction can make it difficult to define an individual. Provide some examples of individual and modular organisms.
Topic: Section 8.1
Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis
2) Discuss the three distribution patterns of individuals within a population and explain the conditions that give rise to each pattern.
Topic: Section 8.3
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
3) Discuss three methods of determining density in a species of organisms, and identify the conditions under which each method would be most useful.
Topic: Section 8.4
Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis
4) Describe several approaches used by ecologists to establish age structure for plant and animal populations.
Topic: Section 8.5
Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis
5) Describe several ways that plants disperse.
Topic: Section 8.7
Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension
6) Some animals migrate daily, whereas others migrate seasonally. Give an example of each type of migration pattern and explain the benefit of this pattern to the organisms exhibiting it.
Topic: Section 8.7
Bloom's Taxonomy: Synthesis/Evaluation
7) Given the industrialization of countries across the globe, what might you predict the age structures will look like for countries such as Egypt and India in 100 years? Why might they be different than before?
Topic: Section 8.5
Bloom's Taxonomy: Synthesis/Evaluation
Another random document with no related content on Scribd: