Test Bank for Chemistry in Context 6th Edition by American Chemical Society ACS ISBN 0077221346
9780077221348
Full download link at:
https://testbankpack.com/p/test-bank-for-chemistry-in-context-6thedition-by-american-chemical-society-acs-isbn-00772213469780077221348/
Chapter 4: Energy, Chemistry, and Society
Student: ______________________________________________________________________
1. Based on this pie chart, what percentage of the USA's total energy needs come from fossil fuels? A. 40% B. 61% C. 63%
D. 84%

2. A calorie is defined as exactly 4.184 J. Therefore 1.000 Cal is exactly
A. 41.84 J.
B. 418.4 J.
C. 1000 J.
D. 4184 J.
3. The heat of combustion of ethane, C2H6, is 1560 kJ/mol. What is the heat of combustion of ethane, in kJ per gram?
A. 51.9 kJ/g
B. 195 kJ/g
C. 4.69 104 kJ/g
D. 9.39 1026 kJ/g
4. The heat of combustion of methane, CH4, is 50.1 kJ/g. How much heat would be generated if 1.00 mol of methane undergoes complete combustion?
A. 0.32 kJ
B. 3.12 kJ
C. 601 kJ
D. 804 kJ
5. The energy that flows from a warmer body to a colder body is called
A. heat.
B. temperature.
C. potential.
D. work.
6. The property of matter that determines the direction of heat flow is the
A. mass.
B. temperature.
C. volume.
D. density.
7. The energy equivalent of a certain cheeseburger is approximately 525 Cal. Since 1 Cal is 4.184 kJ this corresponds to
A. 1.25 kJ.
B. 125 kJ.
C. 220 kJ.
D. 2200 kJ.
8. The energy stored in the chemical bonds of fossil fuels is a form of ______ energy.
A. electrical
B. mechanical
C. potential
D. kinetic
9. The energy of motion is called _________ energy.
A. electrical
B. mechanical
C. potential
D. kinetic
10. The first law of thermodynamics states that
A. energy is the capacity to do work.
B. doing work is defined as causing movement against a resisting force.
C. heat flows from a warmer body to a cooler body.
D. energy is neither created nor destroyed.
11. The conclusion that it is impossible to completely convert heat into work without making other changes in the universe is
A. based on erroneous observations.
B. the concept that increasing entropy characterizes all changes in the universe.
C. another way of stating that all energy is either thermal energy or heat.
D. the second law of thermodynamics.
12. In an exothermic chemical reaction
A. the mass of the products is greater than the mass of the reactants.
B. the mass of the products is less than the mass of the reactants.
C. heat is released as the reaction proceeds.
D. heat is absorbed as the reaction proceeds.
13. Based on this reaction and its energy profile,
the reaction
A. is exothermic.
B. is endothermic.
C. has a high activation energy.
D. violates the first law of thermodynamics.
14. A chemical reaction accompanied by a release of energy is called a/an ______ reaction.

A. endothermic
B. catalyzed
C. exothermic
D. fast
15. The energy needed to initiate a chemical reaction is called the
A. heat of combustion.
B. bond energy.
C. activation energy.
D. renewable energy.
16. Any chemical or physical change that absorbs energy
A. has high activation energy.
B. is an endothermic process.
C. is an exothermic process.
D. is a catalyzed process.
17. In a typical power plant, the combustion of a fuel is used to boil water. The steam then causes a turbine to spin. At this stage, the potential energy of the fuel has been transformed into _________ energy of the spinning turbine.
A. kinetic
B. mechanical
C. electrical
D. potential
18. How is heat energy used to generate electricity in a modern power plant?
A. Heat warms wires causing electrons to move through them more rapidly.
B. Heat boils water to make steam, which drives a turbine.
C. Heat warms the fins on a turbine, causing them to spin.
D. Heat generates strong magnetic fields through which the wires of a turbine move.
19. Assume that an extremely inefficient electrical utility company delivers electrical energy to your home from a natural gas-burning power plant with an overall efficiency of only 21% and your furnace is 100% efficient in converting electrical energy into heat energy. What mass of natural gas must be burned by the power plant if heating your home requires 3.5 107 kJ? The heat of combustion of natural gas is 50.1 kJ/g.
A. 1.5 105 g
B. 3.3 106 g
C. 3.7 108 g
D. 8.4 109 g
20. The degree of randomness in position or energy is called the
A. entropy.
B. activation energy.
C. heat of combustion.
D. potential energy.
21. In which example is the entropy of the initial state greater than the entropy of the final state?
A. A building collapses during an earthquake.
B. A lump of sugar dissolves in a cup of warm water.
C. Liquid water freezes into ice.
D. Liquid water evaporates.
22. In which example is the entropy of the initial state lower than the entropy of the final state?
A. A pot of water boils to produce water vapor at 100C.
B. Librarians put library books back onto the shelves at the end of the day.
C. A raw egg heated at 100C in boiling water becomes hard boiled.
D. Soldiers are called to attention when the general enters the room.
23. Which is a correct statement of the second law of thermodynamics?
A. In any natural process, the entropy of the universe must increase.
B. Nature allows the conversion of potential energy into kinetic energy, but not vice versa.
C. Heat is the only form of energy that can be converted into work with 100% efficiency.
D. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change form.
24. Combustion is a chemical process in which a fuel combines with______ to release energy and form products.
A. nitrogen
B. oxygen
C. methane
D. hydrogen
25. Which common process on earth is endothermic?
A. the production of oxygen by photosynthesis
B. ozone decomposing into O2 in the upper atmosphere
C. water freezing to form ice at 0C
D. the reaction of wood with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, water, and ash
26. The heat energy released or absorbed by a chemical reaction is generally determined by the difference between the energy that
A. must be put in to break the bonds in the reactants and the energy that must be put in to make the bonds in the products.
B. must be put in to break the bonds in the reactants and the energy that is released upon making the bonds in the products.
C. is released upon breaking the bonds in the reactants and the energy that must be put in to make the bonds in the products.
D. is released upon breaking the bonds in the reactants and the energy that is released upon making the bonds in the products.

27. Use the equation to help you calculate the heat of combustion of ethylene, C2H4. The bond energies are: C H 416 kJ/mol; C C 356 kJ/mol; C C 598 kJ/mol; O O 498 kJ/mol; C O 803 kJ/mol; H O 467 kJ/mol.
The heat of combustion of ethylene is
A. +220 kJ/mol.
B. +1216 kJ/mol.
C. -754 kJ/mol.
D. -1324 kJ/mol.
28. The following molecules contain only single bonds.
NH3(g) + 3F2(g) NF3(g) + 3 HF(g)
The bond energies are: N H 391 kJ/mol; F F 158 kJ/mol; N F 272 kJ/mol; H F 566 kJ/mol. Which is the heat evolved or absorbed per mole of NH3 that reacts with F2?
A. +289 kJ/mol
B. +867 kJ/mol
C. -289kJ/mol
D. -867 kJ/mol
29. Consider the following equation that describes the complete combustion of propane, C3H8
The bond energies are: C H 416 kJ/mol; C C 356 kJ/mol; O O 498 kJ/mol; C O 803 kJ/mol; H O 467 kJ/mol. Which is the total amount of energy required to break all of the bonds in propane?
A. 712 kJ/mol
B. 3328 kJ/mol
C. 4040 kJ/mol
D. 4396 kJ/mol
30. Consider the following equation that describes the complete combustion of propane, C3H8


The bond energies are: C H 416 kJ/mol; C C 356 kJ/mol; O O 498 kJ/mol; C O 803 kJ/mol; H O 467 kJ/mol. Which is the amount of energy gained on making all the bonds in carbon dioxide and water according to the equation?
A. -1270 kJ/mol
B. -2540 kJ/mol
C. -4277 kJ/mol
D. -8554 kJ/mol
31. Consider the following equation that describes the complete combustion of propane.

The bond energies are: C H 416 kJ/mol; C C 356 kJ/mol; O O 498 kJ/mol;
C O 803 kJ/mol; H O 467 kJ/mol. Which is the net energy released on complete combustion of propane?
A. -1668 kJ/mol
B. -2024 kJ/mol
C. -4277 kJ/mol
D. -8554 kJ/mol
32. Which is a fossil fuel?
A. wood
B. uranium
C. ethanol
D. natural gas
33. According to the figure below,

the total energy consumption of North America is now matched by
A. the Pacific Asian countries.
B. Europe.
C. the Middle East and Africa.
D. South and Central America.
34. According to the figure below,
the total energy consumption during the period 1990 to 2000 decreased in which area?

A. North America
B. Europe
C. former Soviet Union
D. Middle East and Africa
35. According to the graph below,
the major source of energy in the United States during the years 1900 to 1950 was

A. coal.
B. wood.
C. natural gas.
D. petroleum.
36. In the year 2000, which two energy sources contributed almost equally to our total energy usage?
A. coal and natural gas
B. petroleum and natural gas
C. petroleum and nuclear electric power
D. coal and nuclear electric power
37. Which factor did not play a major role in the formation of fossil fuels from plant matter?

A. high temperatures
B. high pressures
C. an absence of O2
D. an abundance of sunlight
38. Soft lignite (brown coal) is the lowest grade of coal. Since it has undergone the least change since burial, its chemical composition and hence its heat of combustion is most similar to that of
A. natural gas.
B. petroleum.
C. water.
D. wood.
39. According to current estimates, the fuel in greatest abundance on earth is
A. coal.
B. natural gas.
C. petroleum.
D. uranium.
40. Which is an advantage of using coal over petroleum as a source of energy in the United States?
A. As a solid, coal is easier to transport than a liquid such as petroleum.
B. Carbon makes up a smaller proportion of coal than it does of petroleum.
C. Coal reserves in the United States are far greater than petroleum reserves.
D. Coal is the source of many more different fuels with a wide range of properties than is petroleum.
41. In the petroleum industry, what does a refinery do?
A. It separates crude oil into fractions consisting of compounds with similar boiling points.
B. It separates crude oil from the coal with which it is almost always found.
C. It mixes natural gas or coal with crude oil in order to remove the impurities from the crude oil.
D. It produces the machinery by which crude oil is removed from the ground.
42. Which is not a known advantage of natural gas over other fossil fuels?
A. It burns more completely than other fossil fuels.
B. It burns more cleanly than other fossil fuels.
C. It is far more abundant than any other fossil fuel.
D. Sulfur dioxide is rarely produced by burning natural gas.
43. According to the graph below,
the domestic production of petroleum has steadily decreased since

A. 1950.
B. 1960.
C. 1975.
D. 1985.
44. According to the graph below, the net import of petroleum drastically decreased during the years

A. 1970 to 1977.
B. 1973 to 1975.
C. 1977 to 1982.
D. 1985 to 1990.
45. Petroleum (crude oil) is a complex mixture of thousands of substances, the majority of which are
A. carbohydrates.
B. hydrocarbons.
C. natural gases.
D. proteins.
46. The process by which a solution is heated to its boiling point and the vapors are condensed and collected is known as
A. combustion.
B. cracking.
C. crystallization.
D. distillation.
47. Which is produced in the greatest amount from a barrel of petroleum?
A. asphalt and road oil
B. gasoline
C. home heating oil
D. lubricants and waxes
48. During petroleum refining, catalysts play an extremely important role during the
A. cracking and reforming processes.
B. environmental cleanup of oil wells.
C. extraction of the oil from the earth.
D. physical separation of the various components of the petroleum.
49. The diagram below shows a simplified version of a fractionating column used in the petroleum industry.
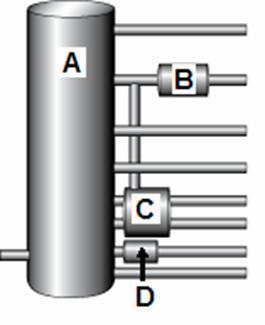
The compounds with the lowest boiling points are condensed at position

50. The diagram below shows a simplified version of a fractionating column used in the petroleum industry.
The position marked ___ corresponds to the cracker where large molecules are broken into smaller molecules.
51. The diagram below shows a simplified version of a fractionating column used in the petroleum industry.

The compounds that are obtained at position D are

A. asphalt.
B. gasoline.
C. jet fuel.
D. refinery gases.
52. Cracking is
A. the breaking of larger molecules into smaller ones.
B. the combination of small molecules to form larger molecules.
C. any reaction that is accompanied by the release of heat.
D. any reaction that is accompanied by the absorption of heat.
53. Compounds with the same molecular formulas but different molecular structures are called
A. isotopes.
B. isomers.
C. isobars.
D. allotropes.
54. Consider these three compounds.
Which are isomers?
A. I and II only
B. II and III only
C. I and III only
D. I, II, and III
55. Consider these three compounds.
Which are isomers?
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II, and III
56. In a refinery, the components of petroleum are separated by
A. combustion reactions.
B. crystallization.
C. fractional distillation.
D. isomerization.

57. A gasoline's octane rating is a measure of the
A. gasoline's resistance to causing knocking in a vehicle's engine.
B. pollutants produced by burning the gasoline in a vehicle's engine.
C. energy content of the gasoline.
D. purity of the gasoline.
58. The burning characteristics of a gasoline can be improved by converting the octane it contains into isooctane. This conversion requires the use of expensive catalysts such as
A. biological enzymes.
B. gold and titanium.
C. platinum and palladium.
D. ultraviolet radiation.
59. A gasoline's octane rating is determined by
A. comparing its burning properties to those of pure isooctane, which has an octane rating of 100.
B. comparing its burning properties to those of natural gas, which produces far fewer pollutants than gasoline normally does.
C. comparing the deposits left on the engine cylinders by burning gasoline to the deposits left by burning diesel fuel.
D. comparing the acceleration of a vehicle when burning gasoline to its acceleration when burning pure ethanol.
60. Oxygenated gasolines are blends of petroleum-derived compounds with oxygen-containing compounds. Which of the following oxygenated compounds has been discontinued in some states because of potential health risks?
A. ethanol
B. methanol
C. MTBE
D. methane
61. Alternative energy sources are currently being researched in effort to replace our dependence on fossil fuels. Which is not a current research effort in this regard?
A. obtaining alternative fuels from renewable sources such as garbage
B. reintroducing the use of tetraethyl lead to increase the octane rating of gasoline
C. converting coal into gaseous and liquid fuels similar to petroleum products
D. increasing the use of farm product biomass, such as corn, to produce ethanol.
62. The general term for plant matter such as trees, grasses, agricultural crops, or other biological material is
A. biomass.
B. cornstarch.
C. diesel.
D. fossil fuel.
63. Which of these statements about biodiesel is not true?
A. Biodiesel is made from renewable resources such as vegetable oils and animal fats.
B. Biodiesel is non-toxic and biodegradable.
C. Biodiesel can be used in diesel engines without major modifications.
D. Biodiesel has been withdrawn from several states due to health concerns.
64. Consider this graph that shows the fuel economies for U.S. cars and light vehicles.
During which years did the fuel economies of U.S. cars and light trucks increase dramatically?

A. 1977 to 1979
B. 1975 to 1986
C. 1986 to 1995
D. 1995 to 2005
65. Which is not true about energy conservation within the United States?
A. Over the past two decades, industrial production has increased substantially, whereas the associated energy consumption has gone down.
B. Reusing aluminum saves approximately 70% of the energy required to extract equivalent amounts of aluminum from its ore.
C. Because of conservation efforts and lighter automobiles, gasoline consumption in the United States declined by 50% between the mid-1970s and the early 1990s.
D. By following strict conservation efforts, the United States could eliminate its dependence on imported fossil fuels within a decade.
66. Calculate the amount of energy that may be saved by replacing a 75 watt incandescent light bulb with an 18 watt fluorescent bulb during the 1500 hour life of the incandescent bulb. One watt is the equivalent of one joule of energy used per second.
A. 8.55 104 J
B. 5.13 106 J
C. 3.08 108 J
D. 1.84 1010 J
67. Advertising claims sometimes state that adding something mechanical to a car's engine will allow it to recover 100% of the energy that comes from burning gasoline. You should be skeptical of such claims because they violate the
A. first law of thermodynamics.
B. second law of thermodynamics.
C. law of conservation of matter.
D. activation energy requirements of all chemical reactions.
68. Over the very long run, the energy source that has the greatest potential to meet humanity's needs is
A. coal.
B. hydropower.
C. renewable biomass.
D. solar (the sun).
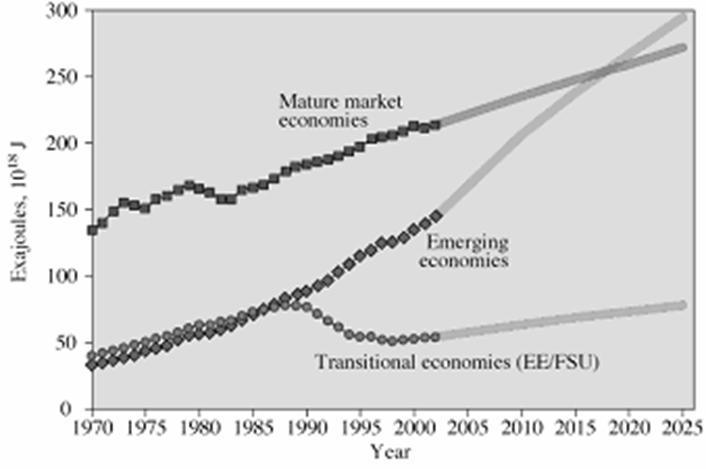
69. Based on this graph, which group of economies is predicted to have the largest energy consumption in 2010?
A. mature market economies
B. emerging economies
C. transitional economies
D. impossible to say