1) By studying thecorresponding table, thecorrectorder of theelements (Z, Y and X) in order of density (Ch 1)
Ion symbol Electronic strcture
X+2 (Ar),3d2
Y+3 (Ar),3d4
Z+3 (Ar),3d5
2) Which of the following does not occur whensiderite andlimonite areroasted? (Ch 1)
a) Red ore, easily reduced is produced
b) The iron percentage in theore increases
c) Impurities areoxidized into solid substances
d) Theore is dried from moisture
3) Three transition elements (Z, Yand X) arelocated at theendof the 3d series and form the compounds ZB2, YB2, XB2 , if (X) is the largest in atomic number, the correct order of their ions according to the magnetic moment ----- (Ch 1)
a) Z+2 > Y+2 > X+2
c) Z+2 > X+2 > Y+2
4) Thecorrect orderto obtain iron (II) sulphidefromsideriteis (Ch 1)
a) reduction / oxidation/heating / reactionwithsulphur
b) heating / oxidation/reduction / reactionwithsulphur
c)Reaction with sulphur /oxidation/reduction/heating
d) Reaction with sulphur /heating /reduction/oxidation
5- From the following diagram:-
-Theproduct(C)is (Ch 1) a) FeCl2 b) FeCl3 c) Fe2(SO4)3 d) FeSO4
6) From the following diagram:-
-Thecompounds (A),(B)and (C)are (Ch 1) Choice A
7) Element (X) is used as a catalystinthe industrialpreparationof ammonia gas by the HaberBosch method, and element (Y) is used in the manufacture of car tires and printing inks.
- When the two elements are chemically combined, the alloy is (Ch 1) a)duralumin b) stainlesssteel c) cementite d) steeliron Explanation:
8) Silver cation is precipitated with each of the following except (Ch 2) a) HCl (aq) b) Na2S(aq) c) NaI (aq) d) NaNO3 (aq)
9) Thegas thatdecolorizes theacidifiedpotassium permanganate is (Ch 2) a) CO2 gas and actsas an oxidizing agent b) SO2 gas acts as areducing agent c) SO3 gas acts as anoxidizing agent d) H2Sgas acts as areducing agent
10) A solution of salt (X) is divided into two parts:
-Silver nitrate solutionwas added to thefirst part, forminga whiteprecipitatethat turns violet when exposed to light
- Tothe secondpart,anammonium carbonatesolution was added,forminga white precipitate that dissolves in water containing CO2. -Then the salt (X) is (Ch 2) a) calcium phosphate b) lead iodide c)calcium iodide d) calcium chloride
11) A mixtureof 4grams ofcalciumhydroxideand calcium chloride,required 100 mlof 0.5M HCl acid to titrated.
-Thepercentage of the basein the sampleis equals------ (Ca=40, 16, H=1) (Ch 2) a)
12) Fromthefollowing diagram:
Black precipitate (��)������������������ ← X (��) yellow precipitate soluble in ammonia solution -Then the compounds(X), (Y) and (Z) are (Ch 2) Choices X Y Z
a Cu3(PO4)2 AgNO3 H2S b AgNO3 Cu3(PO4)2 NH4OH
c H2S Na2SO4 CuS d CuS NH4OH HCl
13) 200ml of 2M nitricacid added to300mlof 3M of another sample of the same acid . Then the concentration of the produced solution equal (Ch 2) a) 6.2M b) 1.3M c) 2.6M d) 3.1M
14) When a brown iodine solution is added to Salt (A), the brown color of iodine disappears and when dilute sulphuricacid is added toanother quantityof thesame Salt (A) solution, a white precipitate is formed.
-So the salt (A) is (Ch 2)
a) potassium sulphate
c) copper (II) sulphide
b) lead (II) thiosulphate
d) sodium nitrite
15) Inthe reaction: N2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2NO (g), ∆H= (+)
-Whichof the following factors increases the concentrationofthe products? (Ch 2)
a) Lowering thetemperature
c) Adding anamount of oxygen tothereaction
b) Increasing thepressure
d) Increasing thevolume of the vessel
16) What is thepH value of the solutionresultingfrommixing40ml of 0.1M HCl with 10ml of 0.45 M NaOH? (Ch 2)
a) 6 b) 8 c) 12 d) 10
17) In the reaction: N2O4 (g) ⇌ 2NO2(g) (Colorless) (Reddishbrown)
-Whenaddingexcessofthecolorless gas (Ch 3)
a) thecolor increasesand the Kcvalue remain constant
b) the color increasesand the Kcvalue increases
c) the color decreases and the Kcvalue remain constant
d) the color decreases and the Kcvalue decreases
18) If you knowthatthe solubility of silver chloridesalt in a saturated 0.1L solution is 2.56 X10-6 , then the mass of silver chloride in the solution is: (AgCl = 143.5g/mol) (Ch 3)
a) 0.023g b) 0.0115g
19) Inthe correspondingequilibriumsystem: MgCO3(S) +117.3KJ =MgO(S) +CO2(g)
-Thevalueof theequilibrium constantof this system increaseswhen (Ch 3) a) adding morecarbon dioxide b) raisingthe temperature c) decreasing theamount of carbon dioxide d) lowering thetemperature
20) Which of the following systems is irreversible? (Ch 3)
a) N2O4(g) =NO2(g) (Closed vessel)
b) AgBr(s) =Ag+ (aq) + Br(aq) (saturated solution)
c) HCOOH(aq) +H2O(l) =HCOO(aq) + H3O(aq)
d) Mg(s) +H2SO4(aq) =MgSO4(aq) + H2(g)
21) Inthefollowing equilibrium system
CH3COOH (l) +H2O (l)=CH3COO(aq) +H3O+ (aq) ,(kc= 1.4x10-6)
-When dropsofHNO3 areaddedto thereaction, theKa value foraceticacid becomes (Ch 3)
a) 1.4x10-6 b) 2.3x10-4 c) 0.99x10-6 d) 2.3 x 10-7
22) An electrochemical cell has a reduction potential of it electrodes:
Mg+2 + 2e→ Mg , E= -2.87 V Cu+2 + 2e→ Cu , E= +0.34 V
-Which of the following is true?
a) Thereaction isspontaneous and the emf =+2.72 V
b) Spontaneous reaction and e.m.f.=+3.21V
c)Thereaction is non-spontaneous and the e.m.f.=-2.72V
d)Non-spontaneousreaction and emf =-3.21V
(Ch 4)
23) Themass of sulfuric acid in (380 cm3)of the electrolyte of afullycharged lead- acid battery is (Ch 4) a)340g b) 494g
c) 425g d) 325g
24) Theamount of electricity required toevolve355gm ofchlorinebyelectrolysis of molten NaCl compound is (Cl=35.5) (Ch 4)
a) 9.25x104 c b) 9.65 x105 c c) 9.65 x106 c d) 4.83 x 105 c
25) The quantityof electricity required toconvert 1 mol of MnO- to 1 molof Mn+2 is (Ch 4) a) 96500 c b) 3x96500c c) 5x96500 c d) 7x96500c
26) Whichofthe followingdiagrams showsthechangein themass ofa pieceof iron to be plated when an electric current is passed through an aqueous solution of gold chloride III using a pure gold anode? (Ch 4)











27) The standardreduction potential of X, Y, and Z are as in the table: (Ch 4) Element
-Whichofthe followingplating causes thefastestcorrosionofthecoatedmetal when scratched?
a) Platingelement ZwithelementY
c)PlatingelementY withelementZ
b) PlatingelementY withelementX
d)PlatingElementX withElementZ
28) Thefollowing reactions occur at the electrodes of a galvaniccell: (Ch 4) A → A+2 + 2e= +1.4v B + 2e→ B-2 = +0.8 v
-Theelectricalpotentialrequired to convert this celltoelectrolyticcellintoan electrolytic cell equals: a) 8 V
29) When a stripofthe zincis placed inasilver nitrate solution, the followingreaction occurs: Zn(s) + 2AgNO3 → Zn(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
-Whichofthe followingcorrectly describeswhathappened? (Ch 4)
a) Oxidationof zincandreductionof silverions
b) Reductionof the zincandreductionofsilver ions
c)Oxidationofzincandoxidationof silver
d)Reductionofzincandoxidationof silver
30) Whatis the product of halogenation of halothane with onemole of bromine? (Ch 5)
a)1, 2-dibromo-2,2,2-trifluoro-1-chloroethane
b) 1,1-dibromo-1-chloro-2,2,2-trifluoro ethane
c)1,2-dibromo-1,2-difluoroethane
d)1,1, 1- trifluoro-2-chloro-1,2-bromoethane
31) When adding2 moles ofhydrogen and then 1moleof chlorinerespectivelyto one mole of the compound CH2=CH-C≡CH, we get (Ch 5)
a) 1,1-dichlorobutane
c) 1, 3-dichlorobutane
b) 1,2-dichlorobutane
d)2, 3-dichlorobutane
32) Whichofthe followingprocess is suitableto obtain3-methyl-sulfonic-benzene acid from benzene? (Ch 5)
a) Alkylation t followed by sulfonation
c) Halogenation followed by sulfonation
b) Sulfonation followed by alkylation
d)Sulfonation followed by halogenation
33) Whichofthe followingcompounds isproduced fromoxidationofthe Corresponding compound? CH3 - CH (CH3) -CH (CH3) –CHO (Ch 5)
a) 2,3-dimethyl propanoic acid
c) 2,2-dimethyl Butanoic acid
b) 2,3-dimethylButanoic acid
d)3,3-dimethylButanoic acid
34) Thearomaticcompoundwiththe molecular formula C7H8 canbeobtained by which of the following process? (Ch 5)
a) Catalyticreforming of normal hexane
b) Dry distillation ofethyl benzoate
c) Catalytic reforming of normal heptane
d) Dry distillation ofmethyl benzoate
35) Whenthe simplestbranched alkynecombineswithethylgroup,the nameof the compound becomes (Ch 5)
a)3-Methyl-1-hexyne
c)1-methyl-1-hexyne
b) 2-methyl-1-pentyne
d) 3-methyl-1-pentyne
36) Four organiccompounds (A, B, C and D) (Ch 5)
-CompoundA reactswith sodium carbonateandsodium hydroxide
-Compound B reacts with sodium and does not react with NaOH
-Compound C oxidizes to A
-CompoundDreactswithNaOH anddoesnot reactwith HCl So the four compounds are Choices A
a acid alcohol aldehyde phenol
b aldehyde phenol acid alcohol
c phenol acid ether ketone
d acid ketone phenol ether
37) Alkalinehydrolysis of theisomerof ethylpentanoate produces (Ch 5) a) sodium ethanoate b) butanol c) sodium pentanoate d) ethanol
38) Which of the followingprocesses canbeused toobtainthe simplest aromatic hydrocarbon from an aromatic compound with the formula CnHnO3? (Ch 5)
a) Oxidation by hydrogen peroxide oxidation
c) Reduced by 3 moles of zinc
b) Reducedby 2 moles of zinc
d)Oxidation by potassium permanganate
39) Thecorrect IUPACnameof a compound2-bromo-5-ethyl-4-hexene is - (Ch 5)
a)2-Bromo-5-ethyl-4-pentene
c) 6-bromo-3-methyl-3-heptene
b) 6-bromo-2-ethyl-2-hexene
d)2-bromo-5-methyl-4-heptene
40) Which of the following compounds gives CH3 – CBr2 – CH3 ? (Ch 5)
a) Mole of bromineto propene
c) Mole of bromine to propyne
b) HBr to propene
d) Mole of HBr to 2-bromopropene
41) Thecatalytichydrationof ethyne produces compound (A),whichis oxidized to compound (B) , and the compound (B) is reduced in the presence of CuCrO4 to compound (C) - So thecompounds (A) ,(C) respectively are---- (Ch 5)
a) propanal and ethanol
c) ethanal and ethanol
b) ethanoicacid and ethanal
d)propanol and ethanoic acid
42) Upon hydrolysis of primary alkyl halide, compound (A) is formed And byhydrolysisof secondaryalkylhalides,compound(B) isformed
-Sothe compounds (A) and (B) are---- (Ch 5)
a) A: 2-butanol , B: isobutylalcohol
b) A: 1-butanol , B:2-methyl-2-butanol
c)A : 2-methyl-2-propanol, B : 1-butanol
d) A : 2-methyl-1-propanol, B : 2-butanol
43) Whichofthe followingcompounds isproduced fromnitrationofthe corresponding compound? (Ch 5)
a) Ortho-NitroCarboxylbenzene
b) Meta-nitro benzaldehyde
c) Meta-nitro carboxyl benzene
d)Para-nitro benzanal
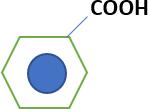
44- You have the following compounds: (X) Has a higher boiling point than the corresponding hydrocarbon (Y) Used in the preparationof a compound used in the treatment of heart disease (Z) Is a starting materialfor the preparationof Marookh oil. The compounds (X, Y, and Z) are: (Ch 5)
Choices X Y Z
a Methyl acetate Copper oxide Ethanol
b Benzoic acid Anhydrous copper sulphate Toluene
c Formic acid Terephthalic acid Benzene
d Ethanoic acid glycerol Salicylic acid
45)Inthe next reaction:H2O(V) + CO(g) ⇌ H2(g) +CO2(g) +heat (Ch 3)
Explain the effect ofthe following factors:
1- Usingthe catalyst onthe carbon dioxideconcentration
2- Increasingthe pressureon the concentration ofcarbonmonoxide
3- Increasingthetemperature onthevalueoftheequilibrium constant
4- The effectof adding a mixtureof (2moles of hydrogen gas and3 moles of carbon monoxide gas)
Factor
Effect
1. Catalyst No change in CO₂ concentration
2. Increase in pressure No change in CO concentration
3. Increase in temperature (exothermic reaction) Decrease in equilibrium constant (K)
4. Add 2 mol H₂ + 3 mol CO Shift to the right
46) (A, B, C, D) four functional groups forfour organic compounds: (Ch 5)
a) Whatis the nameof group (D),and whatis the reason behindthis name?
b) To convert a compound belongto groupD into a compound containing group A,a processis required?
c) Comparingcompounds from group(A)tocompounds fromgroup (B),which hasa higher boiling point?
d) Write thefunctionalgroup ofthe compound resultingfromthe reaction ofa group(A) compound with a group (D) compound?
Given Functional Groups:
Question
a) Name of Group D
b) Conversion process
c) Higher boiling point
Answer
Carboxylic acid – because it contains both a carbonyl and hydroxyl group on the same carbon
Reduction (e.g., with LiAlH₄)
Alcohols (Group A) due to hydrogen bonding
d) Functional group formed (A + D) Ester group (–COO–)