Shenzhen Urban Village
<Connect to the Infinite Boarder of Urbanism>
 RMIT 2022 Sem 2 Major Project Qingrui Luo
RMIT 2022 Sem 2 Major Project Qingrui Luo

<Connect to the Infinite Boarder of Urbanism>
 RMIT 2022 Sem 2 Major Project Qingrui Luo
RMIT 2022 Sem 2 Major Project Qingrui Luo
Shenzhen urban village is a social and historical consequence of urbanization, they still have the format of rural villages, but they bear the population of metropolis. This clash resulted in an interesting potential that people can stay connected in the modern city.
Since SEZ established, Chinese government took the farmland, and developed the urban land with a consistent guideline, but the ownership of farmer’s housing land still retained to villagers. The parallel development of self-organized village and government-controlled urban leads to the strange condition of Shenzhen urban village which brings vitality. It also plays a role of social affordable housing for the low-income people in the wider area which relieves the population pressure brought by migrations.

Shenzhen, also historically known as Sham Chun, is a major sub-provincial city and one of the special economic zones of China. The city is located on the east bank of the Pearl River estuary on the central coast of southern province of Guangdong, bordering Hong Kong to the south, Dongguan to the north, and Huizhou to the northeast. With a population of 17.56 million as of 2020, Shenzhen is the fourth most populous city proper in China. Shenzhen is a global center in technology, research, manufacturing, business and economics, finance, tourism and transportation, and the Port of Shenzhen is the world's fourth busiest container port.
So far, there is about a total of 1,900 urban villages, distributed throughout Shenzhen, including the central city. Urban village and Shenzhen have co-existed.


1. Collective land
2. Collective economy (contracted farming and private poultry)
3. Rural traditional culture and social network
4. Villagers committee
1. Collective land (semiprivate)
2. Collective economy (collective rental) and private economy (private rental)
3. Mixed culture and traditional social norms
4. Urban self-organized grassroots unit
1. Stated-owned land
2. Stated economy and Market economy
3. Civil culture and urbanism
4. Community committee
1. Is a relationship between original villagers and tenants (the majority of the floating population)
2. Is the local community with deep social relationship networks
3. Has a socioeconomic system that adapts to the market demand
The village's joint-stock company manages the whole village, has overall responsibility for the community life, forms an infrastructure and maintenance system which serves the original villagers and tenants.
≠1. Is the shanty area that completely selfbuilt and occupied publiic land
2. Is relatively transient, random, and change location with the government's continuous demolition
1. Is built by the villagers spontaneously, it is people oriented which depends on the demands of living.
2. Keep the original format of rural village, eg. road network, lot sizes, urban form.
1. Is the way of living or characteristics of lifestyle of people living in urban areas.
2. Has a set of regulations and plans drawn before the development of city.
Shenzhen urban village is not only for housing, but also taking the commercial responsibility.
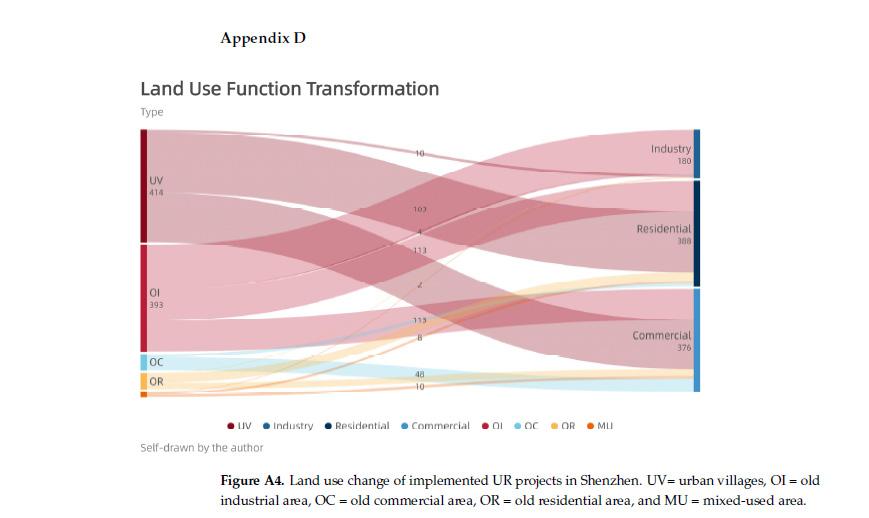
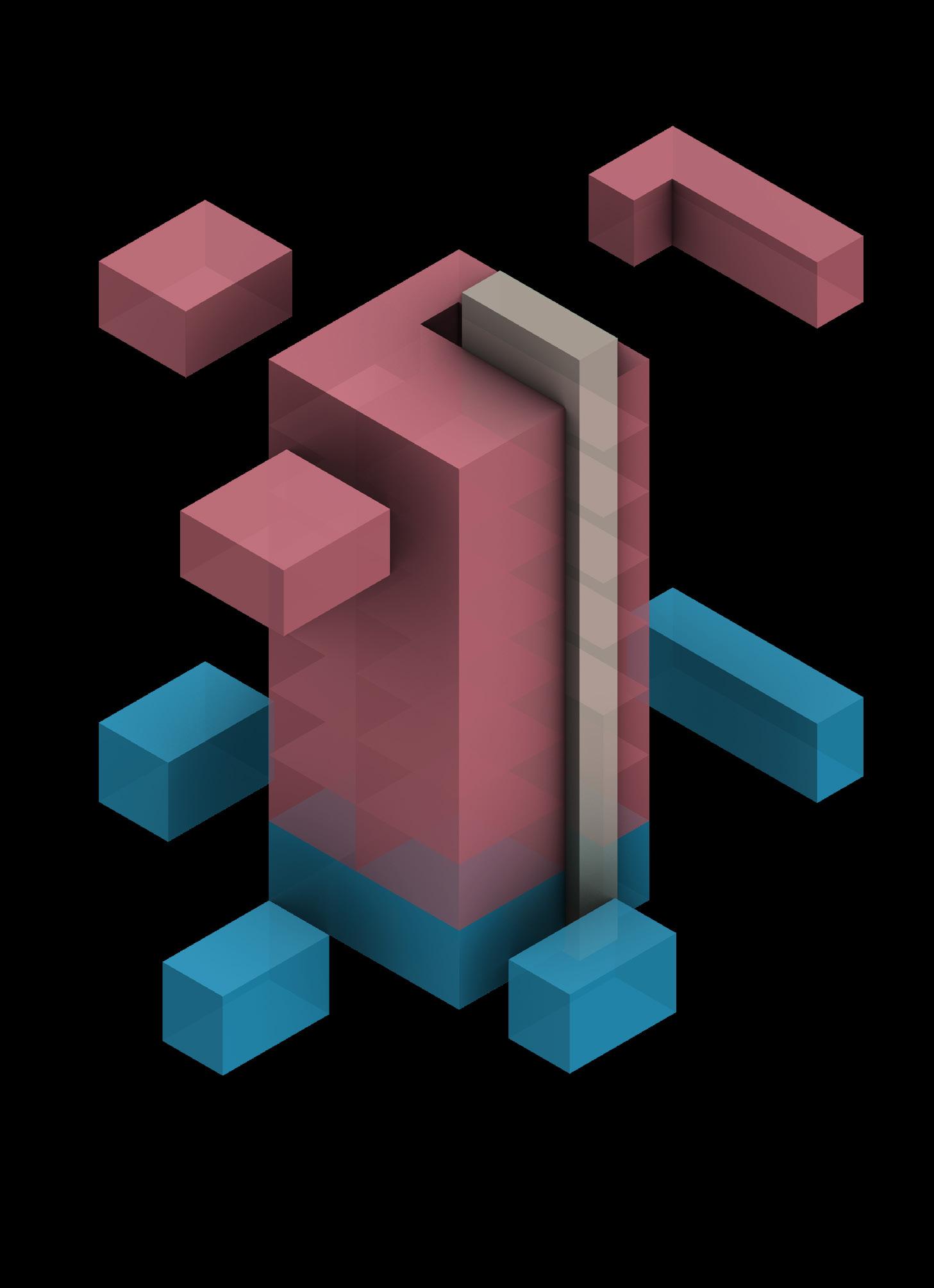
Analyzing and extracting the features from the existing urban village typology in Shenzhen, to set up a series of rules and regulations from the unconscious bottom-up results. Gangsha Village is an example that I picked up which located in the central Shenzhen.
Located in the southeast of the central district, Gangsha is the only urban village in the central district of Futian, Shenzhen, and an important part of the central axis of Shenzhen.

On 150,000 square meters of land, there are 590 houses, most of which are handshaking buildings owned by villagers. There are 900 permanent residents in 486 households, with a temporary population of 67,000.
The site cover area of one residential building unit must be smaller than 10m*10m, and the building has to be less than 10 stories.
- To make sure the ratio between residence and service programs keeping a balance, and still maintaining a surplus functional area to serve the whole city.
<= 10 stories
Residential buildings located heart of commercial, retail service facilities (amenities define the boundary of residential area).
Street scale:
Residential buildings located in the heart of commercial, retail service facilities which are normally adjacent to the primary street (amenities define the boundary of residential area).
Urban village scale: The urban village located in the heart of neighbourhood district.
Street scale: Residential buildings located in the heart of commercial, retail service facilities (amenities define the boundary of residential area).
Urban village scale: The urban village located in the heart of neighbourhood district.
- An express station has to be next to the retail supermarket and they share the same building plot.
- There must be an average of one logistics station per 70 households.
An express station has to be next to the retail supermarket and they share the same building plot.
- There is must be an informal area in front of the shops and it has to be extended to the laneway by steps (stages).






- More than 50% shops on the ground floor should act as a mix of the informal area and formal retail.
Informal area is an unplanned stage spaces that using for commercial and social activities throughout the day.
- There is must be an informal area in front of the shops and it has to be extended to the laneway by steps (stages).



- More than 50% shops on the ground floor should act as a mix of the informal area and formal retail.
Informal area is an unplanned stage spaces that using for commercial and social activities throughout the day.
- Buildings on the primary street must have retail on the ground floor, an informal gardens on the rooftop, a window sill with a suspended extension, and connected by a public access.


- The ratio between open space and floor area should not be less than 1:10.

The ratio between open space and building site cover area should not be less than 1/100.
Rule 1:
The site cover area of one residential building unit must be smaller than 10m*10m, and the building has to be less than 8 stories.
Rule 2:
There must be an average of one logistics station per 70 households.
Rule 3:
More than 50% shops on the ground floor should act as a mix of the informal area and formal retail.
Rule 4: Commercial and retail programs are normally adjacent to the primary street.
Rule 5:
The ratio between open space and floor area should not be less than 1:10.
Residential Shops Stairs
Residential Shops Stairs



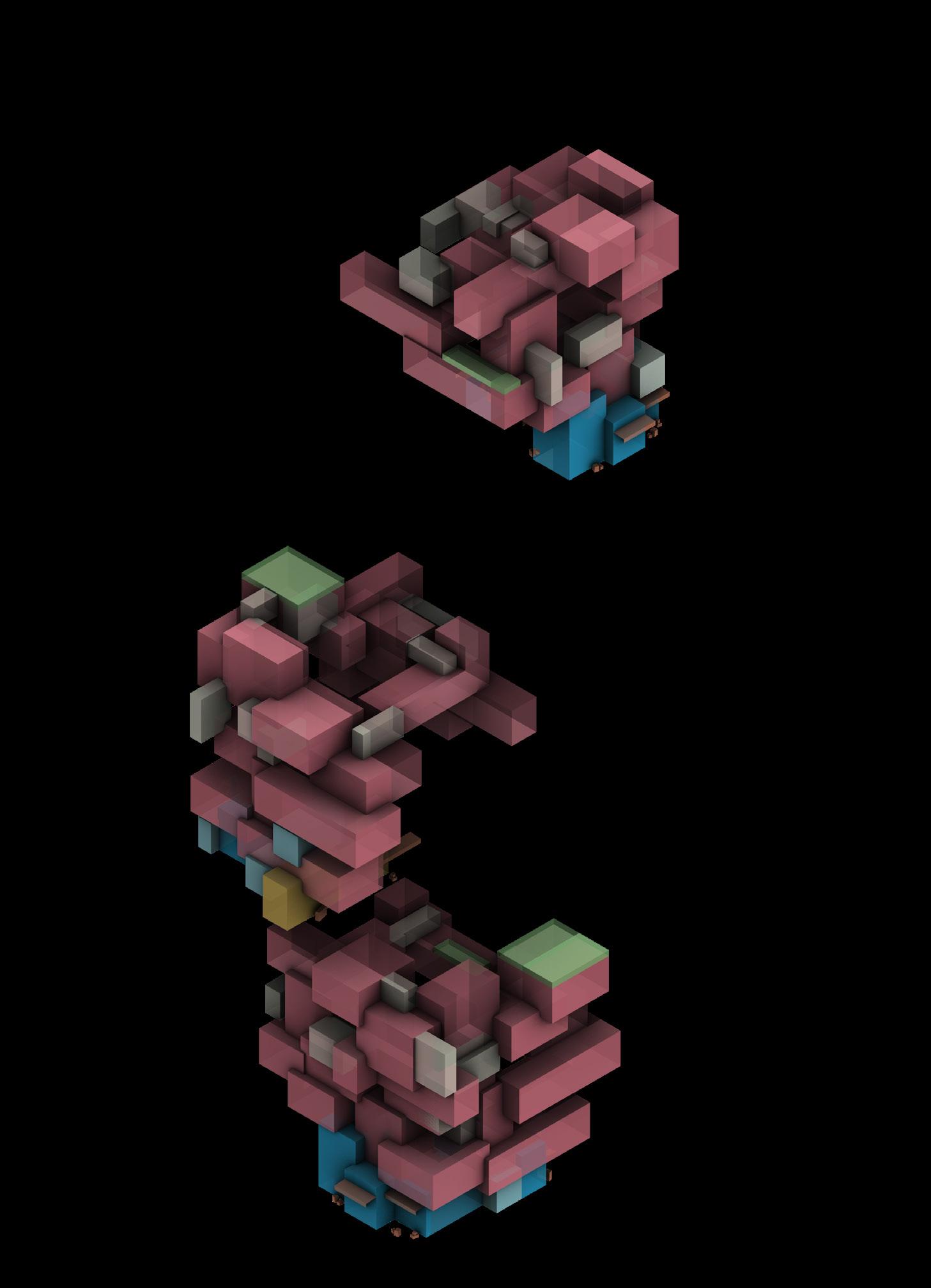
Rule 1: The site cover area of one residential building unit must be smaller than 10m*10m, and the building has to be less than 8 stories.
Rule 2: There must be an average of one logistics station per 70 households.
Rule 3:
An express station has to be next to the retail supermarket and they share the same building plot.
Rule 4: There is must be an informal area in front of the shops and it has to be extended to the laneway by steps (stages).
Rule 5: Residential buildings located in the heart of commercial, retail service facilities (amenities define the boundary of residential area).
Rule 6:
Buildings on the primary street must have retail on the ground floor, an informal gardens on the rooftop, a window sill with a suspended extension, and connected by a public access.















