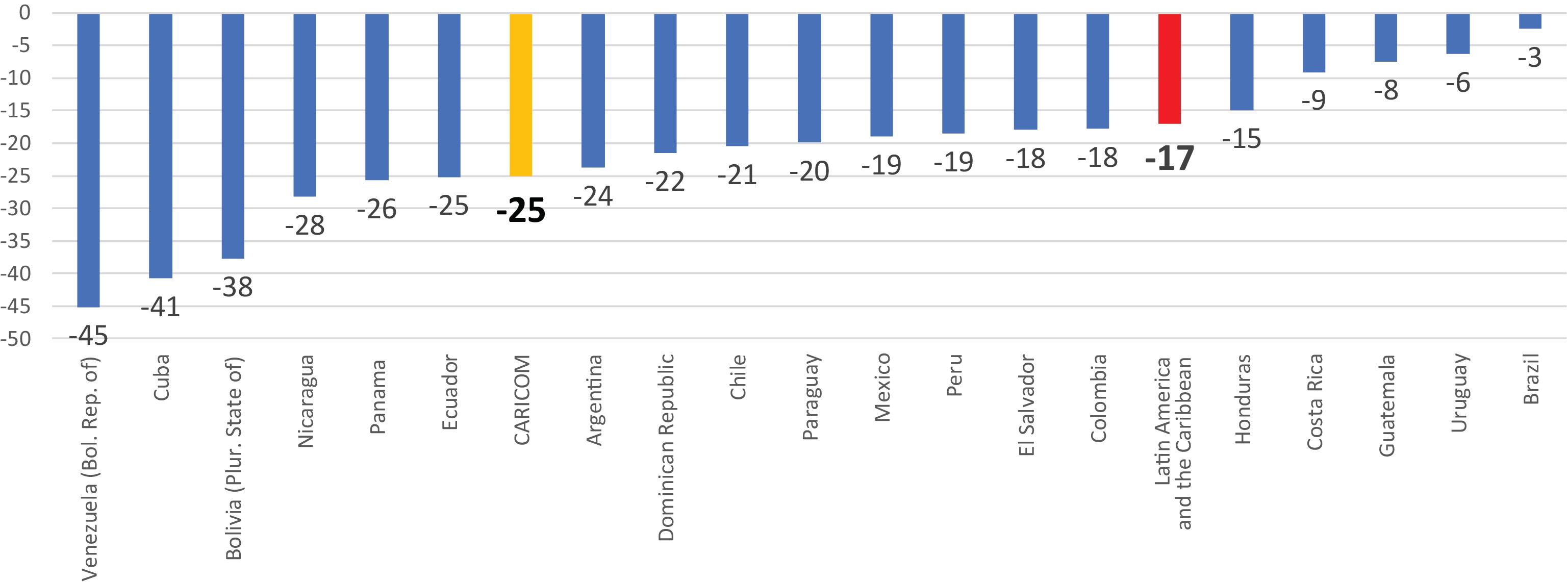
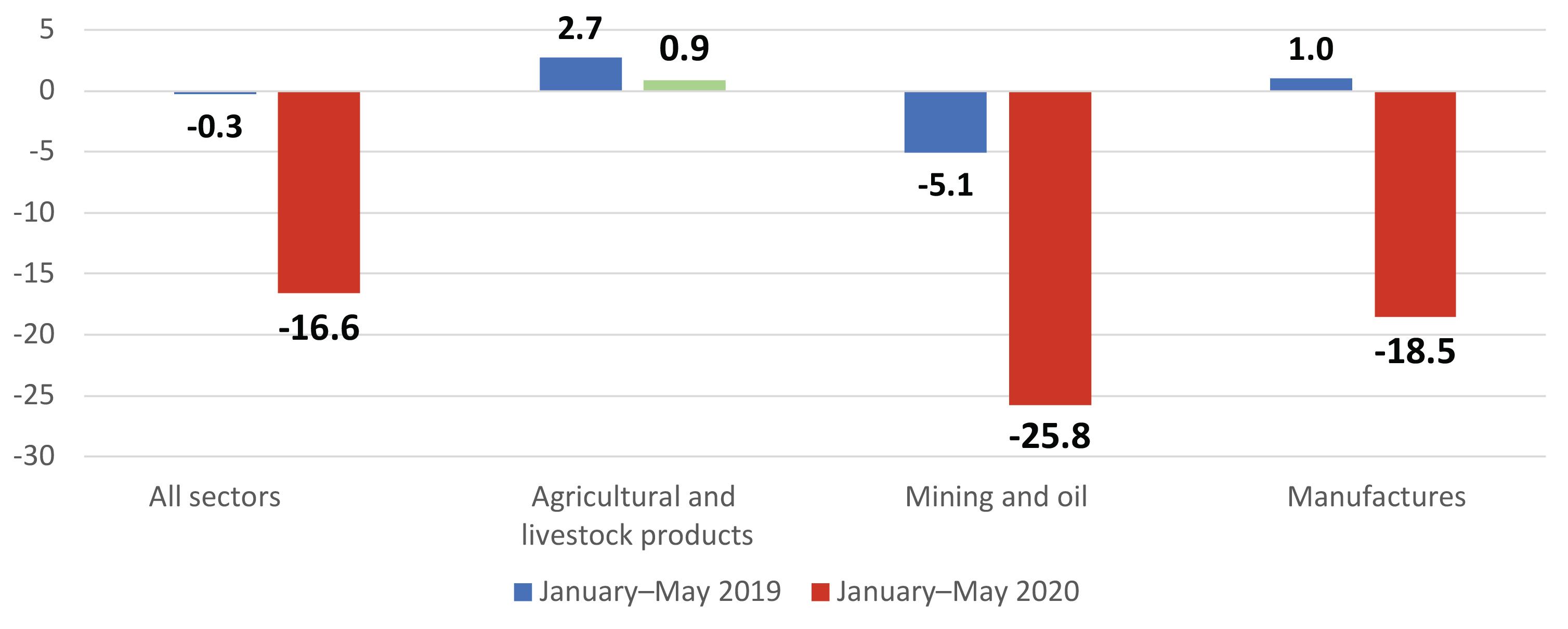
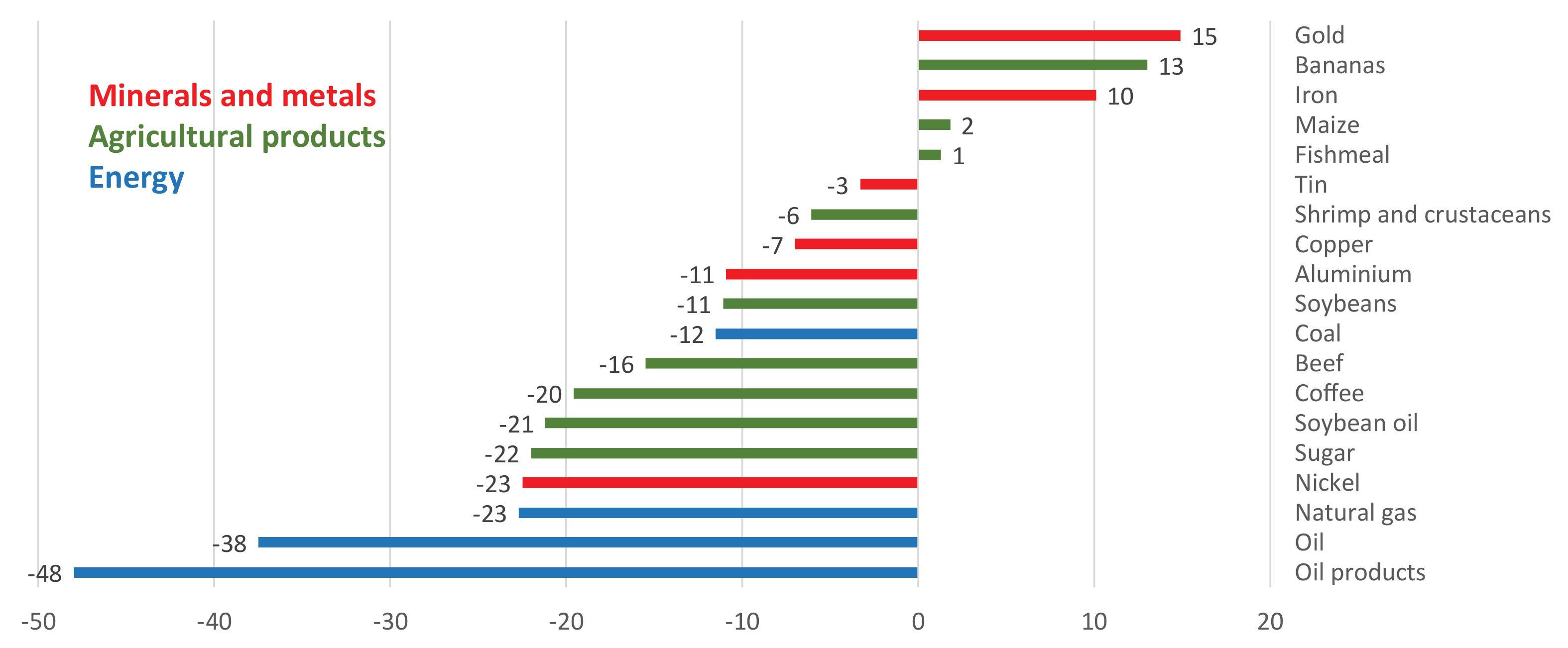
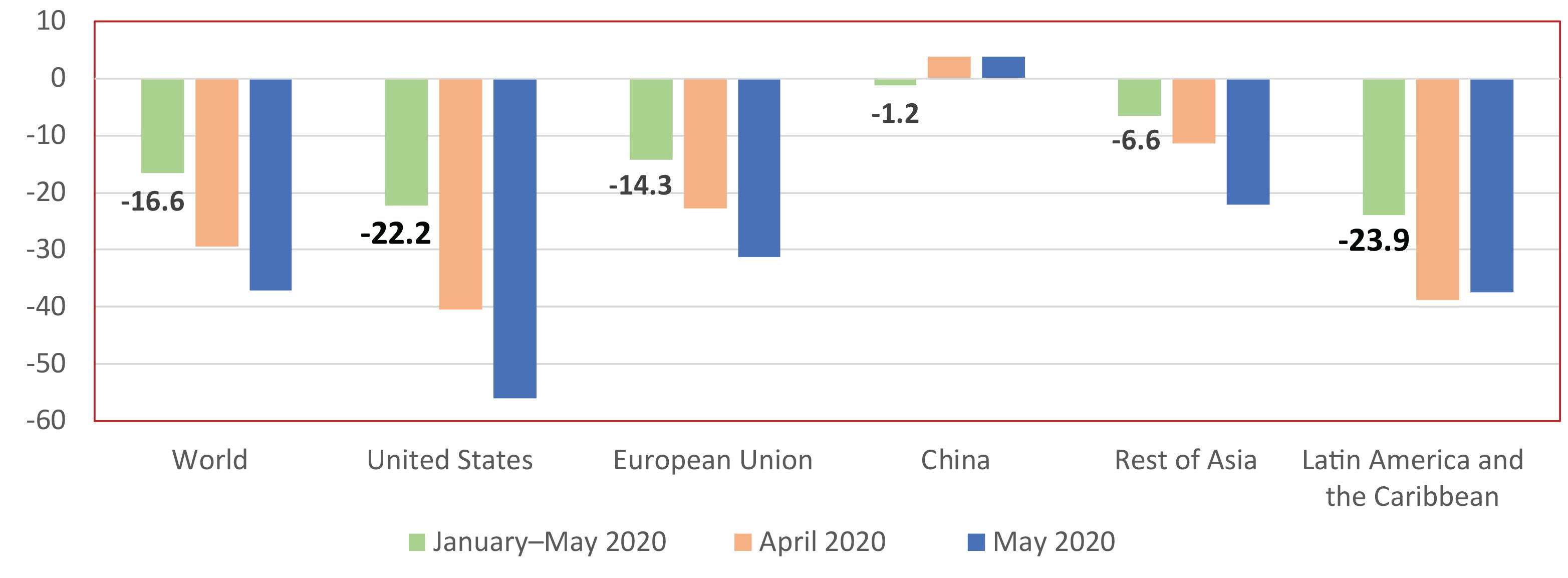
In the post-pandemic era, production and trade are likely to become more regionalized o Reinforcement of two trends that were already taking shape: • Less interdependence in production, trade and technology between the United States and Europe, on one hand, and between the United States and China, on the other. • Trade that is less open, more influenced by geopolitical and national security considerations, with more frequent disputes and a weakened World Trade Organization (WTO). o Outcome: a more regionalized world economy. o Greater pressure for more autonomy in production: reshoring, nearshoring. o Several mega deals are moving in this direction: • USMCA in North America, the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) in the Asia-Pacific region and the Agreement Establishing the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) o By contrast, regional integration in Latin America and the Caribbean remains fragmented and the weight of intraregional trade has decreased from 21% in 2008 to less than 13% in 2020. The effects of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic on international trade and logistics Alicia Bárcena
The effects of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic on international trade and logistics

Issuu converts static files into: digital portfolios, online yearbooks, online catalogs, digital photo albums and more. Sign up and create your flipbook.